聚乙二醇-四氧化三鐵納米粒子復(fù)合材料的結(jié)構(gòu)、物理性質(zhì)及應(yīng)用
夏 娟 宋樂新,,* 黨 政 邵志成
(1中國科學(xué)技術(shù)大學(xué)材料科學(xué)與工程系,中國科學(xué)院能量轉(zhuǎn)換材料重點實驗室,合肥230026;2中國科學(xué)技術(shù)大學(xué)化學(xué)系,合肥230026)
1 Introduction
Polymer materials,for their low price and good plasticity,were widely applied in many fields,such as conductive films,optical films,biosensors.1-3However,poor thermal stability,low heat transfer capability,and poor mechanical properties often limit their applications.Extensive studies have been carried out on polymer/inorganic particle composites in order to overcome these constraints.4-7It was found that the incorporation of inorganic particles as filler into a polymer as carrier resulted in significant improvement in physical properties of polymers,such as controlled electrical resistivity,better stiffness,enhanced strength,and improved thermal stability.5-9Various polymer/inorganic composites have been considered to be more promising materials due to a unique combination of desirable organic and inorganic characteristics.8-10For example,graphite or metal powders and thermoplastic polymers such as polyethylene glycol(PEG),or thermosetting polymers such as epoxy resin,can be blended to achieve specific properties,e.g.,anti-static interference,lump absorbent,magnetic activity,and corrosion-resistant character.11-13
Nanometer-scale inorganic particles occupy a larger surface area and consequently lead to an increased fraction of polymer chains interacting with the inorganic particles.14,15Fe3O4nanoparticles may be a good filler for its magnetic properties which have many applications in science and engineering.16,17Although there were many attempts in the past to prepare and characterize polymers/Fe3O4composites,18there were a few reports on the combination between nano-sized Fe3O4particles and a polymer.19PEG,a semicrystalline thermoplastic polymer,is soluble in both aqueous and organic solvents,and has been extensively studied both experimentally and theoretically.20-23
In this paper,PEG was used as a carrier polymer and Fe3O4nanoparticles were used as a filler to combine the two kinds of materials by adjusting their initial amounts,and to produce a series of useful composites.Initially,Fe3O4nanoparticles(diameter<40 nm)with a unique octadecahedral structure were synthesized in the presence of β-cyclodextrin(CD)24,25and characterized.Subsequently,a series of composites consisting of different amounts of Fe3O4nanoparticles embedded in a PEG matrix were prepared.Finally,the physical properties of the composites,including crystallization behaviors,thermal parameters,magnetic properties,and microwave absorption capabilities,were examined by various techniques.
The experiments give interesting and sometimes surprising results.For example,the crystallization degree,phase transition temperature,and degradation process of PEG can be mediated by the presence of Fe3O4nanoparticles.All these results point to the possibility of modification of physical properties of PEG.And the modification can be controlled by varying the relative amount of Fe3O4nanoparticles.We believe that this work may be of interest to researchers interested in the development of polymer/inorganic nanoparticle composite materials.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Ferrous chloride tetrahydrate(FeCl2·4H2O)and ferric chloride hexahydrate(FeCl3·6H2O)were the products of the Shanghai Jinshan Chemical Plant.β-CD was obtained from Shanghai Chemical Reagent Company and recrystallized twice from deionized water.PEG(Mn6000)was purchased from Shanghai Jingchun Chemical Reagent Factory.Crystal violet(CV)was from Aladdin Chemistry Co.Ltd.Rhodamine 6G(R6G)was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.All other reagents are of analytical-reagent grade,unless stated otherwise.
2.2 Preparation of Fe3O4nanoparticles
Fe3O4nanoparticles were prepared by the aqueous co-precipitation(see Eq.(1))of soluble FeC12·4H2O and FeCl3·6H2O with addition of β-CD.26
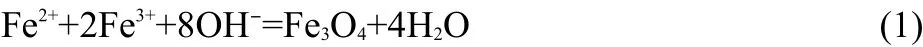
Initially,6 mmol(1.194 g)FeCl2·4H2O and 9 mmol(2.434 g)FeCl3·6H2O were dissolved in 100 mL aqueous solution of β-CD(1 mmol,1.135 g).Subsequently under vigorous stirring,aqueous ammonia(0.3 mol·L-1)was added to adjust the pH to 10.0.The reaction mixture was kept reacting in water bath at room temperature for 30 min under vigorous stirring.An insoluble black material was precipitated and separated via centrifugation.Then,the crystals of product were washed with distilled water until the pH value was lowered to 7.0.Finally,the crystals were collected and dried in a vacuum desiccator over phosphorus pentoxide.
2.3 Preparation of a group of composites of PEG with Fe3O4nanoparticles
All four composites were produced by blending the Fe3O4nanoparticles with an aqueous solution(50 mL)of PEG(1.0 g).The mixtures were dispersed by ultrasonication for 30 min,and stirred for 1 h at 333 K.Then,the formation of colloid solutions was observed.After the water was removed from the colloid solutions by rotary evaporation below 300 K,the crude products were dried under vacuum(76 Pa)at 333 K.The asobtained PEG/Fe3O4composite materials containing 1,10,50,and 200 mg of Fe3O4nanoparticles were marked as CM-1(colourless),CM-2(light grey),CM-3(yellow),and CM-4(brown),respectively.
2.4 Instruments and methods
X-ray diffraction(XRD)patterns of the samples were recorded in a Philips X?Pert Pro X-ray diffractometer(Philips,Netherlands).All the samples were irradiated with monochromatized Cu Kαradiation(λ=0.154178 nm).A continuous scan rate of 5(°)·min-1from 5°to 80°of 2θ was used for all samples.Tube voltage and current were 40 kV and 40 mA,respectively.
Crystal morphologies of the samples were observed using a Supra 40 field emission scanning electron microscope(FE-SEM)(JEOL-2010,Japan)operated at 5 kV.Transmission electron microscope(TEM)and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy(HRTEM)images were obtained with a JEOL-2010(Japan)microscope using an accelerating voltage of 200 kV.
Differential thermogravimetric(DTG)and thermogravimetric analyses(TGA)analyses were obtained on a Shimadzu TGA-50 thermogravimetric analyzer(Japan)at a heating rate of 10.0 K·min-1under a nitrogen atmosphere with a gas flow of 25 mL·min-1.All solid samples were ground to fine powder by mortar and pestle and dried under the same conditions before analysis.The mass of the samples analyzed was all in the range of about 5 to 7 mg.
Differential scanning calorimetry(DSC)measurements were conducted on a DSCQ2000(TA company,United States)with a constant heating and cooling rate of 10.0 K·min-1during three cycles under a nitrogen atmosphere using a gas flow of 100 mL·min-1.
Gas chromatography time-of-flightmass spectrometry(GC-TOF-MS)experiments were performed on a Micromass GCT-MS spectrometer with a controlled heating device(MS company,England).The heating program of the samples was the same as that reported for the previous study.27
Field-dependent magnetization measurements were made with a Quantum Design Magnetic Property Measurement System(United States)equipped with a superconducting quantum interference device(SQUID)using a vibrating sample magnetometer at 300 K.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS)was done at Photoemission Station of National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory of Hefei with a VG Scienta R3000 electron energy analyzer,using Al Kαradiation(1486.6 eV)in ultra-high vacuum(2.00×10-9Pa)at room temperature.The energy resolution of the instrument is 0.16 eV.The C 1s peak(284.8 eV)was used as the internal standard for binding-energy calibration.
The microwave absorption properties of the composites were characterized by an Agilent-8722ES Vector Network Analyzer(VNA,United States)in the range of 7.5 to 12.5 GHz.The analyzer was calibrated before use,and the composites were laminated to films with 1 mm thickness.The electromagnetic wave propagated perpendicular to the surface of the films when these films were placed between the two ports of the waveguide,and the waveguide-fed rectangular aperture was sealed.
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering(SERS)measurements of the Fe3O4nanoparticles,CM-1,and CM-4 were performed using a LABRAM-HR Confocal Laser Micro Raman spectrometer(JY company,France)operated with a 514.5 nm laser excitation in the range of 100-2000 cm-1and laser power of 2.5 mW at the sample for an exposure time of 10 s at room temperature,with a resolution of 0.6 cm-1.R6G and CV were used as probe molecules.The Fe3O4nanoparticles,CM-1,and CM-4 were dispersed on a silica substrate(1 cm×1 cm)after suspended in alcohol.Then,the R6G and CV probe solutions(20 μL,10-3mol·L-1)were dropped onto a freshly prepared silica substrate.The spectra have been background corrected and normalized for comparison.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization of Fe3O4nanoparticles
Fig.1A presents the XRD pattern of the Fe3O4nanoparticles obtained.The position of the Bragg peaks is in accordance with the JCPDS card(65-3107)for crystalline Fe3O4.28The diffraction peaks at 2θ values of 30.6°,35.9°,43.5°,54.1°,57.6°,and 63.2°,with the corresponding(hkl)planes of(220),(311),(400),(422),(511),and(440)respectively,are the characteristic features of the Fe3O4material with a cubic spinel structure.29

Fig.1 XRD pattern(A),SEM image(B),TEM image(C),and HRTEM image(D)of the Fe3O4nanoparticles
As seen from Fig.1A,only the cubic symmetry phase of Fe3O4is observed,and there is no other phase such as ferric hydroxide,γ-or α-ferric oxide.The FE-SEM and TEM images in Fig.1B and 1C,respectively,show relatively uniform particles with a diameter of less than 40 nm.The HRTEM image in Fig.1D reveals that the Fe3O4nanoparticles look like an octadecahedral nanobox structure with corners truncated:eight identical isosceles triangular surfaces,eight identical isosceles trapezoid surfaces,and two square base surfaces.Moreover,all the four sides of the polyhedral nanobox correspond to the<110> zone axis of the cubic spinel structure.The formation of such a special nanostructure of Fe3O4particles is positive and significant for the development of inorganic nanomaterials.Undoubtedly,the addition of β-CD plays an important part in the regulation of the shape of Fe3O4particles,because without it,no regular nanoparticles could be obtained under such mild experimental conditions.30,31We propose that the β-CD may act as a chelating agent for the iron salts and/or a protective agent in the prevention of aggregation of core particles.32,33
The field-dependence of magnetization in Fig.2(left)displays that the Fe3O4nanomaterial presents a soft ferromagnetism behavior with a small hysteresis loop in the magnetic field(1 kOe).The saturation magnetization(Ms)at an applied field of 4.37 kOe at 300 K is about 13.41 emu·g-1,which is much smaller than those reported previously.34-37One reason is due to the formation of a regular polyhedral structure(see Fig.1C)of the Fe3O4nanomaterial since shape anisotropy can play a crucial role in decreasing Ms,38,39The other reason may be due to the very fast nucleation and growth kinetics of Fe3O4nanoparticles.40
3.2 Crystallization behaviors of the composites
The colloid solutions of PEG containing different concentrations of the Fe3O4nanoparticles are displayed in Fig.3.Obviously for the four composites,except for CM-4,there is no sediment in suspension or at the bottom.The formation of colloids is attributed to both the small size of the nanoparticles and the surface effect of PEG chains.A control experiment shows that no colloid is formed in the presence of the commercial Fe3O4(see Fig.3A)under the same conditions as the CM-4.We consider that the generation of such colloids is a distinctive feature of the interaction between insoluble inorganic nanoparticles and soluble polymers.It may be helpful for understanding the formation of the composites.
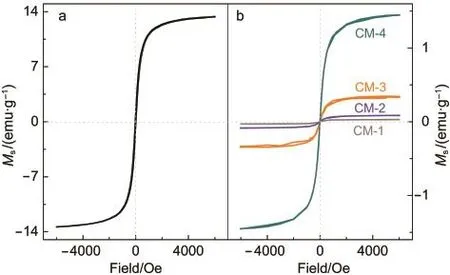
Fig.2 Field dependences of magnetizations of the Fe3O4 nanomaterial(a)and its composites(b)

Fig.3 Photographs of the PEG solutions containing commercial Fe3O4(200 mg)and CM-1,CM-2,CM-3,and CM-4
Further,with the increase of the content of Fe3O4nanoparticles,the solutions gradually deepen in color and become opaque.Also,the solution colors,except CM-4,are stable for weeks in air(see Fig.3B)and accord with the color of the composite materials obtained.This change in color probably is a result of the interaction between the metallic ions(Fe2+and Fe3+)and the oxygen atoms of PEG chains,41,42which was induced by a sufficient dispersion of Fe3O4nanoparticles at PEG surfaces.
After water was removed from the colloids,we obtained the composites.Their surface morphologies are depicted in Fig.4.The CM-1 containing the lowest amount of Fe3O4nanoparticles has a smooth sheet structure with a thickness of about 200 nm,similar to the commercially pure PEG.43However,with the increase of the Fe3O4content,as seen in the figure,the surfaces of the composites become rougher and rougher.This provides experimental evidence for the shape-dependence of the PEG composites on the amount of Fe3O4nanoparticles.
XRD patterns of the composites are indicated in Fig.4.It is apparent that the crystallization behavior of all the four composites was mainly dominated by the crystal growth process of PEG since several main diffraction peaks at 19.2°,23.2°,26.6°,and 36.1°belong to PEG.No signals due to Fe3O4are observed in CM-1,CM-2,and CM-3,but in CM-4,the peaks of Fe3O4at 30.5°and 35.9°occur(labeled by asterisks).The observations give us an impression that a lower amount of Fe3O4nanoparticles can be more effectively dispersed in the crystallization process of PEG.
3.3 Thermal parameters of the composites
Here,in order to investigate how the amount of Fe3O4nanoparticles influences thermal properties of PEG,we performed two independent measurements:DSC and DTG.
Fig.5 displays a comparison of the phase transition properties between PEG and itscomposites.There are two interesting phenomena.First,the higher the amount of added Fe3O4(from CM-1 to CM-3),the lower the melting point of PEG(indicated by the dashed arrow).Second,as the amount of Fe3O4increases further,the melting point of PEG rises slightly(indicated by the solid arrow).Table 1 lists the data of the phase transition points(melting temperatures,Tm).These data provide strong evidence that the melting process of PEG is not only mediated by the presence of Fe3O4nanoparticles,but also directly related to the added amount of Fe3O4.Importantly,this was also supported by the addition of a very little amount of Fe3O4nanoparticles.This result provides an important clue to the possible significance of inorganic oxide nanoparticles in modifying the thermal behavior of polymers.
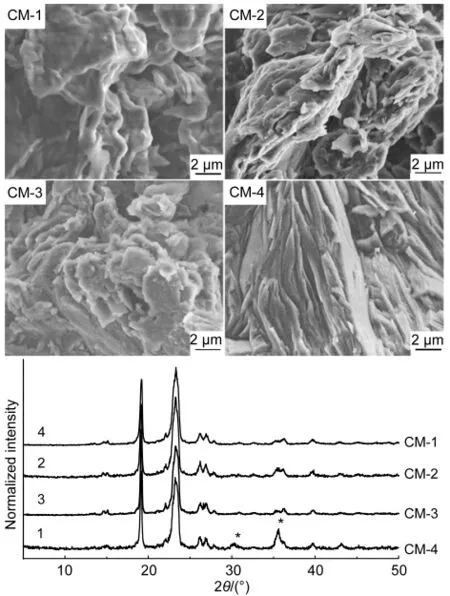
Fig.4 FE-SEM images(upper)and XRD patterns(lower)of CM-1,CM-2,CM-3,and CM-4

Fig.5 DSC curves of PEG and its composites
The degree of crystallinity(Xc)of PEG was determined based on Eq.(2),in which ΔHmand ΔHm?(see Table 1)are the melting enthalpy obtained from DSC curve and the melting enthalpy of fully crystallized PEG(ΔHm?,196.0 J·g-1).44The data of Xcare summarized in Table 1.We can see that the crystallinity of PEG is lowered upon compositing with Fe3O4nanoparticles,and becomes lower and lower with increasing Fe3O4with the exception of CM-4.The difference in Xcmay be an impor-tant reason for the different Tmvalues.

Table 1 Thermal parameters and crystallization behavior of PEG and its composites

TGA curves of the as-obtained PEG/Fe3O4composite materials in Fig.6A indicated that no weight loss was observed below 450 K.Therefore,we can evaluate the relative content of Fe3O4in the materials based on the initial mass of reactants.In the light of calculations,the mass fractions of Fe3O4in CM-1,CM-2,CM-3 and CM-4 were 0.099%,0.99%,4.76%,and 16.67%,respectively.Fig.6B shows the degradation processes of PEG in a free state and in thecomposites.There is only one peak at 671.7 K(Td)corresponding to the degradation process of free PEG.However,in the cases of the composites(CM-1 to CM-3),the peak appears at a higher temperature.Further,as indicated by the arrow,Tdincreases with the content increase of Fe3O4.This finding demonstrates that the composited PEGs have a higher thermal stability than free PEG,dependent on Fe3O4contents.More interestingly,these features are not present in the case of CM-4.The PEG in the composite exhibits a completely different degradation route composed of two degradation stages:one centered at approximately 574.2 K and the other at 658.5 K,both of which are lower than the Tdvalue of free PEG.It suggests that the excess addition of the Fe3O4nanomaterial causes a decrease in thermal stability of PEG.This,together with the DSC results,shows the significant difference between the composite and the other three composites,giving the importance of the content of inorganic oxide nanoparticles in mediating the degradation process of a polymer.
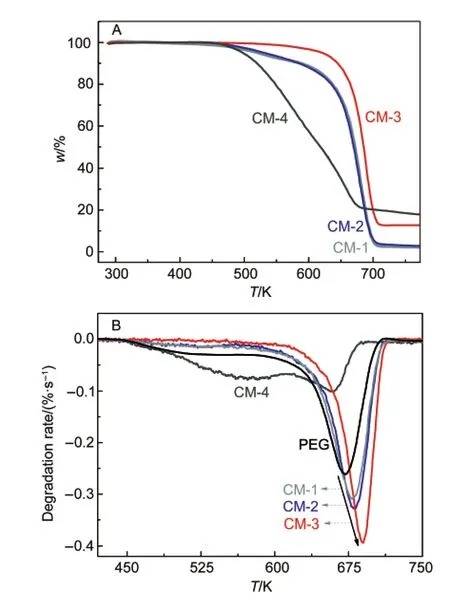
Fig.6 TGAprofiles of the four composites(A)and DTG profiles of PEG and its composites(B)
To further explore whether the Fe3O4nanomaterial is involved in the regulation of thermal degradation products of PEG,we performed GC-TOF-MS experiments.Fig.7 shows total ion current(TIC)curves of PEG and CM-3.Free PEG has a strong release peak at 26.3 min,three moderate peaks at 32.1,35.6,and 42.4 min,and a weak peak at 10.3 min.42However,the PEG in the CM-3 presents different profiles:two strong peaks at 25.6 and 31.6 min,and two weak peaks at 17.6 and 35.8 min.
This difference in TIC profiles,including the number,position,and intensity of peaks(see the arrows in the figure),is a reflection of the effect of Fe3O4nanoparticles on the rupture of PEG chains.Such an effect can be easily seen in mass spectra.Fig.8 indicates the relative abundances(RA)of degradation products of PEG and CM-3 at the maximum degradation rates.Our results show two interesting phenomena including:(1)the presence of Fe3O4nanoparticles leads to the occurrence of more small fragments(indicated by the circle)with m/z lower than 46,e.g.,CHO+(29.002),C2H3O+(43.018),and C2H5O+(45.033).The situation is very similar to that found in the binary system of Fe nanoparticles and PEG;43(2)RA values of several main fragments:C4H9O+(73.058),C4H8O2+(88.051),C4H9O2+(89.060),C6H13O3+(133.086),C8H17O4+(177.114)decrease largely(indicated by the arrow),which is different from the effect of Fe nanoparticles.27These results imply that the degradation process of PEG can be mediated by Fe-based nanomaterials,and different Fe-based nanomaterials have different mediating effects.
3.4 Magnetic properties and electronic structures of the composites

Fig.8 Mass spectra of PEG at 26.3 min and CM-3 at 25.6 min
Magnetic properties of the composites at room temperature are shown in Fig.2.Like the Fe3O4nanomaterial,the Fe3O4components in the composites display soft ferromagnetism with a small hysteresis loop in a low magnetic field(1 kOe).We noticed that the values of Msupon compositing are lower than the pure nanomaterial.45For example,the Msvalue(1.46 emu·g-1)of the Fe3O4component in CM-4 is less than one ninth of that of the Fe3O4nanomaterial(13.41 emu·g-1).In particular,the Fe3O4components in CM-1,CM-2,and CM-3 have a much lower Msvalue(<0.50 emu·g-1).
In order to explain the difference in magnetizations,we have made XPS measurements.Fig.9 indicates the binding energies of Fe 2p3/2and O 1s at 710.4 and 532.2 eV,respectively,46,47in the Fe3O4nanomaterial.However,the core levels of Fe 2p3/2and O 1s are located at lower energies upon compositing with PEG.For example,the binding energies of Fe 2p3/2and O 1s are 709.8 and 531.0 eV in CM-2.The large difference in the energy of O 1s(see the arrow)may be due to the contribution of the oxygen atoms in PEG.
It is worth stressing that with increasing the content of PEG in the composites,the binding energy of Fe 2p3/2increases(indicated by the arrow)while the binding energy of O 1s decreases slightly(indicated by the arrow).The observation points to the electronic shift from iron to oxygen,and supports the hypothesis that the interaction between the oxygen atoms of PEG and Fe3O4nanoparticles decreases the electronic density of the iron.This is likely to be a reason for the lower Msvalues of the Fe3O4components in the composites.

Fig.9 XPS spectra of(A)Fe 2p3/2and(B)O 1s in the Fe3O4nanomaterial and its composites
3.5 Microwave absorption capabilities of the composites
The microwave absorption properties of the films of PEG and its composites were characterized in a frequency range of 7.5-12.5 GHz at room temperature.Before use,the films were laminated to be small pieces with 1 mm thickness and 1 cm diameter.Fig.10 shows the insertion loss and return loss of the films.It is clear that all the films show a very high return loss of at least 7.5 dB and a rather low insertion loss of at most 3.0 dB.In particular,the films present a series of strong signals at the microwave frequency range.For example,the maximum peak values at 8.0,8.2,and 10.2 GHz are all higher than 30 dB.These results mean that the films obtained here may have considerable potential in applications as microwave absorption materials.48
Further,we observed several interesting features from this figure.(1)Two new return loss peaks(indicated by asterisks)appear in the range of 8-9 GHz in the cases of composite films.(2)The shift in position of the return loss peaks from the PEG film to the composite films can be easily seen.(3)The profiles of the return loss peaks of the composite films differ from one another in particular at lower frequencies.These findings reveal that the microwave absorption capability of PEG is affected by the incorporation of Fe3O4nanoparticles,and can be further tuned by the amount of Fe3O4nanoparticles added.
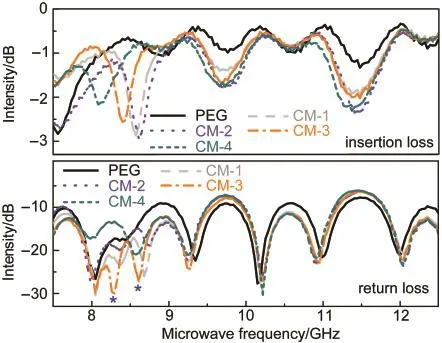
Fig.10 Microwave absorption properties of the films of PEG and its composites
Now,let us make detailed discussion on the relation between the microwave absorption abilities of the composite materials and the contents of Fe3O4.On the one hand,in the frequency range of 9-12 GHz,the insertion losses of the composite materials are much higher than that of pure PEG film,but the content of Fe3O4only makes a small contribution to the improvement of the return loss of PEG film.On the other hand,the microwave absorption abilities of the composite materials including insertion losses and return losses are much higher than that of pure PEG film in the frequency range of 7.5-9.0 GHz,and the return losses are highly associated with the content of Fe3O4.There are two significant aspects to these results.(1)Although no large changes were observed in the insertion losses and return losses of CM-1,CM-2,and CM-3,the three composites exhibit higher microwave absorption abilities than CM-4;(2)With the increase of the content of Fe3O4,the return loss of CM-3 is higher than those of CM-1 and CM-2.These observations indicate that in this frequency range,a moderate content of Fe3O4is advantageous to improve the microwave absorption ability of PEG film.On the contrary,a very high content of Fe3O4will lead to a decrease in the microwave absorption ability.One probable reason is that the microwave absorption abilities of the films may relate to the dispersion level of Fe3O4particles in the films.
3.6 SERS of the composites
Raman spectra from R6G and CV on the pure Fe3O4nanoparticles,CM-1 and CM-4 materials deposited onto a silica substrate are shown in Fig.11.No Raman signal from R6G and CV on a silica glass substrate could be observed(curve a),and both of them in the presence of the Fe3O4nanoparticles(curve b)and CM-1(curve c)deposited on a silica glass substrate exhibit rather weak Raman signals:R6G at 612,773,1361,1513 cm-1and CV at 914,1177,1366,1620 cm-1.49However,in the case of CM-4,there is a large enhancement of the Raman intensity of the signals.For example,the intensity of the strongest peak of R6G at 1361 cm-1and CV at 1620 cm-1are about 5.2 and 4.5 times larger than those in case of CM-1.The result reveals that the SERS enhancement of the PEG composites for the organic dyes is associated with the amount of Fe3O4nanoparticles in the composites.
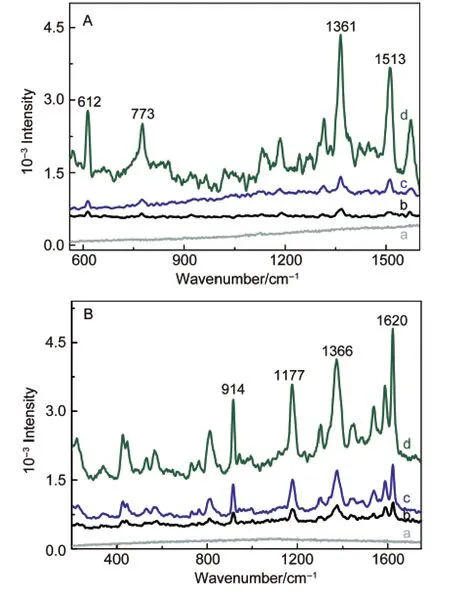
Fig.11 SERS spectra of(A)R6G and(B)CV on a silica substrate(a),the Fe3O4nanoparticles(b),CM-1(c),and CM-4(d)
It is reported that the enhancement of localized electromagnetic field incident on an adsorbed organic molecule is an important factor for SERS effects.50Here,we suggest that the molecule-ion interaction between the Fe3O4nanoparticles and PEG molecules may be a factor contributing to the enhanced localized electromagnetic field.Our data indicate that such an enhancement would jump to a higher level,while more Fe3O4nanoparticles were accommodated near PEG chains leading to an increase in the density of shell-localized charge.
4 Conclusions
In the study,a Fe3O4nanomaterial with a highly symmetric octadecahedral nanobox structure was constructed by a facile,one-step and low temperature water bath method.The material exhibited a soft ferromagnetism behavior with a much lower saturation magnetization than those reported previously.Several composite materials of PEG with the nanomaterial in different initial mass ratios were prepared and characterized by various techniques.The composite materials presented several features of interest.First,the melting process of PEG can,to a certain extent,be tuned by the amount of the Fe3O4nanomaterial added.Also,the PEGs in the composites showed lower melting enthalpies and degrees of crystallinity,but higher degradation temperatures in comparison with free PEG.In particular,the thermal degradation pattern and degradation products of PEG were largely affected by the presence of Fe3O4nanoparticles.Further,although the Fe3O4components in the composite materials indicated a similar soft ferromagnetism response,they had a much lower saturation magnetization than the Fe3O4nanomaterial.This is possibly due to the electronic shift from iron of Fe3O4nanoparticles to oxygen atoms of PEG.More importantly,the composite films displayed very low insertion losses and quite high return losses,suggesting that they could have a potential use in microwave absorption applications.Finally,our data showed that the CM-4 composite material exhibits a relatively large enhancement in SERS for organic dyes,demonstrating that the composite ratio between an inorganic oxide and a polymer is a key parameter,which can make a dominant contribution to the SERS efficiency.We consider that this work may be a contribution to future studies about the design and construction of polymer/inorganic oxide nanoparticle composites.
(1) (a)Fu,M.X.;Chen,F.F.;Zhang,J.X.;Shi,G.Q.J.Mater.Chem.2002,12,2331.doi:10.1039/b201405j(b)Liang,G.J.;Zhong,Z.C.;Xu,J.;Zhang,Z.C.;Chen,M.H.;Li,Z.F.;He,P.;Hou,Q.F.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2012,28,2852.[梁桂杰,鐘志成,許 杰,張增常,陳美華,李在房,和 平,候秋飛.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報,2012,28,2852.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201210091
(2) (a)Liu,M.;Guo,X.F.;Wang,J.M.;Jiang,L.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2012,28,2931.[劉 萌,郭向飛,王景明,江 雷.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報,2012,28,2931.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201209262(b)Darmanin,T.;Guittard,F.;Amigoni,S.;Noblin,X.;Kofman,R.;Celestini,F.Soft Matter 2011,7,1053.
(3) Zhang,R.X.;Gao,B.J.;Wei,X.P.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2012,28,223.[張瑞霞,高保嬌,位霄鵬.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報,2012,28,223.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201111171
(4)Zhang,H.Y.;Qi,R.R.;Tong,M.K.;Su,Y.Z.;Huang,M.J.Appl.Polym.Sci.2012,125,1152.doi:10.1002/app.v125.2
(5) (a)Frickel,N.;Greenbaum,A.G.;Gottlieb,M.;Schmidt,A.M.J.Phys.Chem.C 2011,115,10946.doi:10.1021/jp111348e(b)Liu,J.;Chen,G.M.;Yang,J.P.Polymer 2008,48,3923.
(6) (a)Chen,W.;Qu,B.J.J.Mater.Chem.2004,14,1705.doi:10.1039/b401790k(b)Ghassemzadeh,L.;Pace,G.;DiNoto,V.;Muller,K.Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.2011,13,9327.
(7) Zhang,J.F.;Sun,X.Z.Biomacromolecules 2004,5,1446.doi:10.1021/bm0400022
(8) (a)Song,H.M.;Kim,Y.J.;Park,J.H.J.Phys.Chem.C 2008,112,5397.doi:10.1021/jp709721g(b)Song,L.X.;Du,F.Y.;Yang,J.;Dang,Z.;Yang,J.;Shao,Z.C.Soft Matter 2011,7,6671.
(9) (a)Song,L.X.;Wang,M.;Pan,S.Z.;Yang,J.;Chen,J.;Yang,J.J.Mater.Chem.2011,21,7982.doi:10.1039/c1jm10252d(b)Wang,M.;Song,L.X.;Dang,Z.;Zhu,L.H.;Yang,J.Chem.Lett.2011,40,478.
(10) (a)Babinec,S.J.;Mussell,R.D.;Lundgard,R.L.;Cieslinski,R.Adv.Mater.2000,12,1823.(b)Yang,J.;Song,L.X.;Guo,X.Q.;Yang,J.;Chen,J.Chin.J.Inorg.Chem.2011,27,2013.[楊 軍,宋樂新,郭雪晴,楊 晶,陳 杰.無機化學(xué)學(xué)報,2011,27,2013.]
(11)Zhang,L.;Zhu,J.Q.;Zhou,W.B.;Wang,J.;Wang,Y.Energy 2012,39,294.doi:10.1016/j.energy.2012.01.011
(12) Sakai,T.;Mukawa,T.;Tsuchiya,K.;Sakai,H.;Abe,M.J.Nanosci.Nanotechnol.2009,9,461.doi:10.1166/jnn.2009.J058
(13) Kuzhir,P.;Paddubskaya,A.;Bychanok,D.;Nemilentsau,A.;Shuba,M.;Plusch,A.;Maksimenko,S.;Bellucci,S.;Coderoni,L.;Micciulla,F.;Sacco,I.;Rinaldi,G.;Macutkevic,J.;Seliuta,D.;Valusis,G.;Banys,J.Thin Solid Films 2011,519,4114.doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2011.01.198
(14) Peng,F.B.;Lu,L.Y.;Sun,H.L.;Wang,Y.Q.;Liu,J.Q.;Jiang,Z.Y.Chem.Mater.2005,17,6790.doi:10.1021/cm051890q
(15) (a)Triebel,C.;Vasylyev,S.;Damm,C.;Stara,H.;Ozpinar,C.;Hausmann,S.;Peukert,W.;Munstedt,H.J.Mater.Chem.2011,21,4377.doi:10.1039/c0jm03487h(b)Schubert,U.Chem.Mater.2001,13,3487.
(16) (a)Zeng,L.Y.;Ren,W.Z.;Zheng,J.J.;Cui,P.;Wu,A.G.Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.2012,14,2631.doi:10.1039/c2cp23196d(b)Chen,P.J.;Hu,S.H.;Hsiao,C.S.;Chen,Y.Y.;Liu,D.M.;Chen,S.Y.J.Mater.Chem.2011,21,2535.
(17) (a)Chen,Z.L.;Li,J.;Zhang,X.;Wu,Z.N.;Zhang,H.;Sun,H.Z.;Yang,B.Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.2012,14,6119.(b)Hong,Z.Q.;Li,J.X.;Zhang,F.;Zhou,L.H.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2013,29,590.[洪周琴,李金霞,張 芳,周麗繪.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報,2013,29,590.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201212123
(18) (a)Liu,B.;Zhang,W.;Yang,F.K.;Feng,H.L.;Yang,X.L.J.Phys.Chem.C 2011,115,15875.doi:10.1021/jp204976y(b)Jiang,W.;Li,F.S.;Chen,L.Y.;Yang,Y.;Chu,J.J.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2005,21,182.[姜 煒,李鳳生,陳令允,楊 毅,楚建軍.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報,2005,21,182.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB20050214
(19) (a)Yang,T.I.;Brown,R.N.C.;Kempel,L.C.;Kofinas,P.J.Magn.Magn.Mater.2008,320,2714.doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.06.008(b)Gas,J.;Poddar,P.;Almand,J.;Srinath,S.;Srikanth,H.Adv.Funct.Mater.2006,16,71.
(20)French,A.C.;Thompson,A.L.;Davis,B.G.Angew.Chem.Int.Edit.2009,48,1248.doi:10.1002/anie.200804623
(21)Obermeier,B.;Wurm,F.;Mangold,C.;Frey,H.Angew.Chem.Int.Edit.2011,50,7988.doi:10.1002/anie.v50.35
(22)Ohki,T.;Harada,M.;Okada,T.J.Phys.Chem.B 2007,111,7245.
(23) (a)Wei,D.;Ge,L.L.;Guo,R.J.Phys.Chem.B 2010,114,3472.doi:10.1021/jp910315e(b)Pan,S.Z.;Song,L.X.,Bai,L.;Wang,M.;Zhu,L.H.;Chen,J.Curr.Org.Chem.2011,15,862.
(24)(a)Yang,Y.;Zhang,Y.M.;Chen,Y.;Zhao,D.;Chen,J.T.;Liu,Y.Chem.-Eur.J.2012,18,4208.doi:10.1002/chem.v18.14(b)Cai,W.S.;Xia,B.Y.;Shao,X.G.;Maigret,B.;Pan,Z.X.Chem.Phys.Lett.2000,319,708.(c)Shao,Z.C.;Song,L.X.;Teng,Y.;Dang,Z.;Xia,J.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2013,29,460.[邵志成,宋樂新,滕 越,黨 政,夏 娟.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報,2013,29,460.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201301071
(25) (a)Song,L.X.;Yang,J.;Bai,L.;Du,F.Y.;Chen,J.;Wang,M.Inorg.Chem.2011,50,1682.doi:10.1021/ic1021609(b)Song,L.X.;Chen,J.;Zhu,L.H.;Xia,J.;Yang,J.Inorg.Chem.2011,50,7988.
(26)(a)Cruz,L.A.C.;Perez,C.A.M.;Romero,H.A.M.;Casillas,P.E.G.J.Alloy.Compd.2008,466,330.doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.11.081(b)Xu,P.;Song,L.X.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2008,24,2214.[徐 鵬,宋樂新.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報,2008,24,2214.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB20081212(c)Xu,P.;Song,L.X.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2008,24,729.[徐 鵬,宋樂新.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報,2008,24,729.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB20080433
(27) (a)Song,L.X.;Xu,P.J.Phys.Chem.A 2008,112,11341.doi:10.1021/jp806026q(b)Dang,Z.;Song,L.X.;Yang,J.;Chen,J.;Teng,Y.Dalton Trans.2012,41,3006.(c)Du,F.Y.;Song,L.X.;Wang,M.;Pan,S.Z.;Zhu,L.H.;Yang,J.Soft Matter 2011,7,9078.
(28)Yu,X.G.;Shan,Y.;Du,B.;Chen,K.Z.CrystEngComm 2011,13,1525.doi:10.1039/c0ce00280a
(29) Jiao,F.;Jumas,J.C.;Womes,M.;Chadwick,A.V.;Harrison,A.;Bruce,P.G.J.Am.Chem.Soc.2006,128,12905.doi:10.1021/ja063662i
(30)Wang,B.;Zhang,F.;Qiu,J.H.;Zhang,X.H.;Chen,H.;Du,Y.;Xu,P.Acta Chim.Sin.2009,67,1211.[王 冰,張 鋒,邱建華,張雪洪,陳 洪,杜 毅,許 平.化學(xué)學(xué)報,2009,67,1211.]
(31)Wang,H.B.;Liu,Z.L.;Lu,Q.H.;Peng,L.;Yao,K.L.Chin.J.Inorg.Chem.2004,20,1279.[汪漢斌,劉祖黎,盧強華,彭 麗,姚凱倫.無機化學(xué)學(xué)報,2004,20,1279.]
(32) Hapiot,F.;Bricout,H.;Tilloy,S.;Monflier,E.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.2012,1571.
(33) Jean-Marie,A.;Griboval-Constant,A.;Khodakov,A.Y.;Monflier,E.;Diehl,F.Chem.Commun.2011,47,10767.doi:10.1039/c1cc13800f
(34)Yang,X.W.;Jiang,W.;Liu,L.;Chen,B.H.;Wu,S.X.;Sun,D.P.;Li,F.S.J.Magn.Magn.Mater.2012,324,2249.doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.02.111
(35)Yang,C.;Wu,J.J.;Hou,Y.L.Chem.Commun.2011,47,5130.doi:10.1039/c0cc05862a
(36)Wu,H.X.;Gao,G.;Zhou,X.J.;Zhang,Y.;Guo,S.W.CrystEngComm 2012,14,499.doi:10.1039/c1ce05724c
(37)Wang,L.X.;Li,J.C.;Jiang,Q.;Zhao,L.J.Dalton Trans.2012,41,4544.doi:10.1039/c2dt11827k
(38)Wang,J.;Chen,Q.;Zeng,C.;Hou,B.Adv.Mater.2004,16,137.
(39) Zhang,D.;Zhang,X.;Ni,X.;Song,J.;Zheng,H.Cryst.Growth Des.2007,7,2117.doi:10.1021/cg060395j
(40) Li,Z.;Sun,Q.;Gao,M.Y.Angew.Chem.Int.Edit.2005,44,123.
(41)Yiapanis,G.;Henry,D.J.;Maclaughlin,S.;Evans,E.;Yarovsky,I.Langmuir 2012,28,17263.doi:10.1021/la3023375
(42) Huang,C.L.;Jiao,L.;Zeng,J.B.;Zhang,M.;Xiao,L.P.;Yang,K.K.;Wang,Y.Z.Polymer 2012,53,3780.doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2012.06.027
(43) Pan,S.Z.;Song,L.X.;Chen,J.;Du,F.Y.;Yang,J.;Xia,J.Dalton Trans.2011,40,10117.doi:10.1039/c1dt11090j
(44)Wunderlich,B.Thermal Analysis;Academic Press:Los Angeles,1990.
(45) Zhou,J.P.;He,H.C.;Shi,Z.;Nan,C.W.Appl.Phys.Lett.2006,88,013111.doi:10.1063/1.2162262
(46)Grosvenor,A.P.;Kobe,B.A.;Biesinger,M.C.;McIntyre,N.S.Surf.Interface Anal.2004,36,1564.
(47)Yang,C.Q.;Wang,G.;Lu,Z.Y.;Sun,J.;Zhuang,J.Q.;Yang,W.S.J.Mater.Chem.2005,15,4252.doi:10.1039/b505018a
(48)Zhang,Z.Y.;Liu,X.X.;Wang,X.J.;Wu,Y.P.;Liu,Y.J.Magn.Magn.Mater.2012,324,2177.doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.02.107
(49)(a)Chen,L.M.;Liu,Y.N.CrystEngComm 2011,13,6481.doi:10.1039/c1ce05557g(b)Doherty,M.D.;Murphy,A.;Mcphillips,J.;Pollard,R.J.;Dawson,P.J.Phys.Chem.C 2010,114,19913.
(50) (a)Jena,B.K.;Raj,C.R.Chem.Mater.2008,20,3546.doi:10.1021/cm7019608(b)Haynes,C.L.;McFarland,A.D.;Van Duyne,R.P.Anal.Chem.2005,77,338.

