Analogies between Density Functional Theory Response Kernels and Derivatives of Thermodynamic State Functions
GEERLINGS Paul,DE PROFT Frank,FIAS Stijn
General Chemistry(ALGC),Free University Brussels(VUB),Pleinlaan 2,1050 Brussel,Belgium.
1 Introduction
Within thecontext of Conceptual Density Functional Theory(CDFT,sometimes also referred to as chemical reactivity DFT)1–7,the quantifi cation of various previously well known chemical concepts,which lacked a strong formal basis,has become possible.This is done through so-called response functions of the energy functional E[N,v]where N is the number of electrons of the system and v is the external potential acting on the electrons.Since chemical reactions can be thought of as perturbations in the number of electrons and/or the external potential of a system,it should in theory be possible to study the reactivity of a system through the investigation of the response of its energy.Rather than studying the response of the energy in its entirety,we can look at the functional Taylor expansion of the energy and identify the(mixed)functional derivatives of E with respect to N and v(r),(δn+mE/?Nnδvm),as response functions or reactivity indices.The two fi rst order derivatives,the electronic density ρ(r)and theelectronic chemical potentialμ,havebeen studied intensively as well as two of the second order derivatives,the chemical hardnessand the Fukuifunction f(r)3.
The third one,the linear response kernel,χ(r,r′),is well known in theoretical physics and in the chemical physics literature,however essentially in its frequency dependent form χ(r,r′,ω).In time dependent DFT8its use is ubiquitous as its poles correspond to the system’s excitation energies9.Until recently its frequency independent or static analogue,though initiated already for example in Parr and Yang’s book10,received little attention as compared to other conceptual DFT based reactivity descriptors.Recent studies by the present authors provided computational and interpretational strategies for its study and revealed the rich chemical information hidden in this six-variable kernel11–21,up to its connection with the conductance properties of molecular electronic devices22.
It is well known that diあerent ensemble representations can be used in density-functional theory.The most common,based on the E[N,v]functional,istheso called canonical ensembleof thetotal energy E asafunction of thetotal number of electrons,N,and theexternal potential,v:

Legendre transformations can be used to fi nd other ensemble representations for the ground state23.This yields the grand canonical,isomorphic and grand isomorphic ensembles,for which the respective Legendre transformations are:
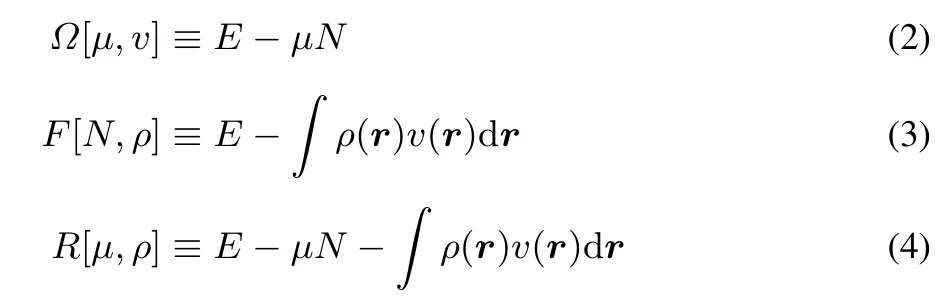
In each of these representations a non-local second order derivative or kernel can be defined,namely the linear response function(for E),the softness kernel(for?)and the hardness kernel(for F).
Looking at the literature some kernels received more attention than others.As stated above,the linear response kernel,although already discussed by Parr and Berkowitz24in thelateeightiesremained somewhat unexplored except in more formal works mainly by Senet,Ayers and Liu25–28until the recent studies mentioned above.The softness kernel was introduced by Berkowitz and Parr24and its relationship with the local softness s(r)proposed by Yang and Parr29was discussed.This integrated form of the softness kernel gained widespread use in the literature,e.g.in applying the HSAB principle at local level30–32.Though,the kernel’s properties,and its ab initio evaluation have been discussed only rarely,an example being some recent work on its ab initio evaluation by some of the present authors33and its role in the quantitative testing,at molecular level,of Kohn’s nearsightedness of electronic matter principle34–36.The hardness kernel on the other hand received much more attention often in view of the non-univocal defi nition of its local counterpart,the local hardness,at fi rst sight the natural companion of the local softness24.A complete bibliography on this issue is beyond the scope of this paper,but for early work we refer to Ghosh et al.37–39,Harbola40,Langenaeker,Torrent-Sucarrat and some of the present authors41–43;for an intermediate status report to Chattaraj’s 2003 critical account44and for very recent work to Polanco-Ramirez,containing references to the very recent literature45.The R kernel received very little attention except in the study by Liu and Parr46,the reason becoming obvious later on in this paper.
The large majority of these studies on the kernels mentioned above,as natural in the context of conceptual or chemical reactivity DFT,concentrated on the role of the kernels on describing chemical reactivity.In the present paper a diあerent aspect of these kernels is highlighted based on the analogy of these functionals with thermodynamic state functions and their properties.The apparent parallelism between classical thermodynamics and DFT has already been addressed in the eighties by Nalewajski and Parr by reformulating the basic variational problem of DFT in terms of various Legendre transformed representations23.
In the present paper which is partly of a perspective-type we thought to be interesting for this Special Issue,we elaborate further on these analogies starting from the convexity/concavity properties of the DFT functionals with respect toρ and v,where the E =E(v)case goes back to Lieb47,Eschrig48,with recent work by Helgaker et al.49and our group21connecting it with the properties of the associated kernels(Note that the convexity of the E=E(N)functional and itspiecewiselinearity havealready been deeply analysed in the seminal contribution by Perdew,Parr,Levy and Balduz50.A companion paper51will be devoted to the more purely mathematical properties of the kernels.Note that we will not concentrate on thermodynamic transcriptions of DFT leading to local thermodynamics(see Ghosh,Parr,Nagy et al.52–55,...)but that westick to theoriginal functionalsof DFT(E and its Legendre transforms-vide infra).
We fi rst restate the formal analogy between the diあerent DFT functionals and the thermodynamic functions,analyzing the type and combinations of variables,using the Legendre transform approach(Section 2.1).In Section 2.2 we consider the positive and negative semidefi niteness of the kernels starting from the convexity/concavity property of the functionals.In Section 2.3 we concentrate on the analogies between thestability analysisof thermodynamic functions56–58and the convexity/concavity analysis of the DFT functionals and the repercussions on the relationship between thermodynamical derivatives and DFT reactivity descriptors,placing the Berkowitz Parr relationship in abroader context and highlighting in the Grand Canonical Ensemble an inequality involving global softness,local softnessand the softness kernel which can be seen as an analogue between a thermodynamic inequality involving the Gibbsfreeenergy derivatives.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 The different ensemble representations and the analogy with thermodynamics:thermodynamic potentials and DFT functionals
Starting fromthecanonical ensembleof thetotal energy E as a function of thetotal number of electrons,N,and theexternal potential,v,

Legendre transformations can be used to fi nd other ensemble representationsfor theground state,namely thegrand canonical,isomorphic and grand isomorphic ensembles,with the defining equation(see for example reference56)
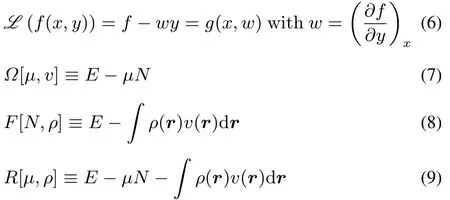
The Legendre transformation connects two ways of specifying the same physics,via functions of two related(“conjugate”)variables.In this case the conjugate pairs of variables are the number of electrons N and the chemical potentialμ,on onehand and theexternal potential v(r)and the electron densityρ(r)on the other hand.The analogy with classical thermodynamics is apparent,where,at constant particle number,the Legendre transformations are used to convert between the internal energy U(as a function of the entropy S and the volume V),Helmholtz free energy F,enthalpy H,and Gibbs free energy G state functions of the system:
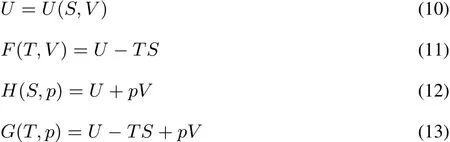
Here,the two conjugate pairs of variables are pressure p and volume V on one hand,and temperature T and entropy S on the other hand.S and V are so-called extensive variables,while p and T are intensive.One of the statefunctions(U)thus depends on two extensive variables,two(F and H)depend on both an intensive and extensive variable and one(G)depends on two intensive variables.The Legendre transformations,as written above,can be seen as the gradual replacement of extensivevariablesby intensiveones.Pleasenotethat all of the above mentioned thermodynamic functions are also depending on thenumber of particles N;ashowever itsdependenceisnot considered explicitly in the remaining text(N is kept constant)wewill not denoteit explicitly in order to simplify thenotation.Nalewajski and Parr23extended the notion of “extensive”variables to the microscopic world as“properties additive with respect to any partitioning of the electronic densityρ(r)=ρA(r)+ ρB(r)”.v(r)and μ are clearly not additive with respect to such partitioning of the density and are intensive as opposed toρ(r)and N which are clearly extensive,the former by defi nition,the latter as can be seen by integrating the defi ning equation ofρ(r)to N = NA+NB.These observations will be of importance when discussing concavity and convexity of the functionals and their repercussion on the response functions.Note that in DFT besides intensive and extensive variables one also distinguishes between global and local quantities1,3varying from point to point(local)or not(global);global and local softness(S and s(r))are typical examples(vide infra).In the variablesmentioned above there is no one-to-one correspondence between intensive/extensive character on onehand and local/global on theother hand.N for exampleisextensiveand global,ρisextensivebut local.
In thecontext of density functional theory,theappearanceof the four Legendre transformations is thus analogous to the thermodynamicscase,beit,(1)that oneworkswith functionals instead of functions,(2)that one now “starts” from a functional,E,with one intensive and oneextensive variable(v and N)instead of U(S,V)containing two extensive variables and(3)that the third functional,F being nothing else than the Hohenberg-Kohn functional,actually only depends on the density,ρ(r):the expected dependency on N drops since ρ(r)obviously also determines N.It would be interesting to investigate in more detail if there is not an inherent diきculty in using the Legendre Transform procedure at zero temperature,(see59,footnote 85).Note that also in this case two functionals(E and R)are dependent on one extensive and one intensive variable/function(as in the thermodynamic case)and one is dependent on two intensive variables(?),in analogy with G in thermodynamics.
2.2 Convexity/concavity of the functionals and positive/negative semidefi niteness of the kernels
Each diあerent functional,corresponding to a diあerent representation,gives rise to one non-local second order response function,a kernel,in v orρ.Explicitly written,they are
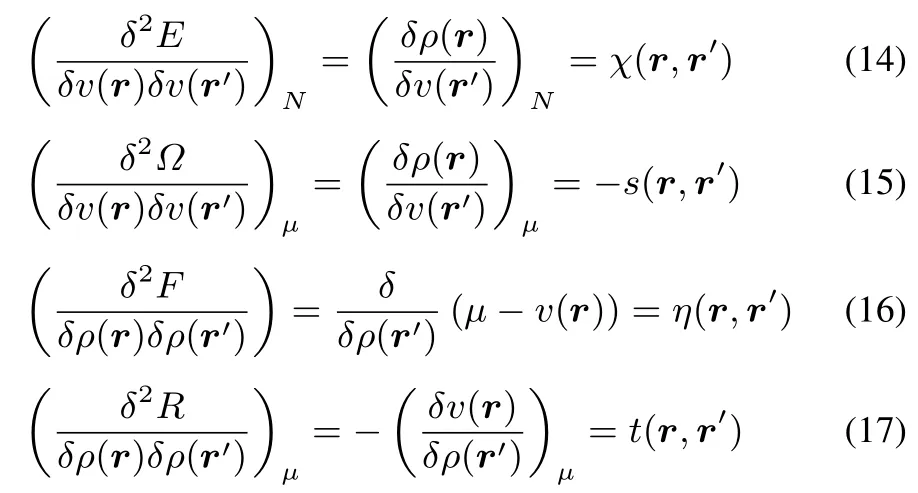
where we recognise the linear response function χ(r,r′),the softnessand hardnesskernels s(r,r′)and η(r,r′)whereasthe fi nal kernel t(r,r′)has not been given a particular name,for reasonsthatwillbecomeobviouslater.Allkernelsaresymmetric in r and r′.Note that in the hardness kernel no constraints are imposed when performing the functional diあerentiation in view of the absence of the expected explicit N dependence discussed before.Note also the ? sign in front of s(r,r′).The analogy between χ(r,r′)and s(r,r′)is striking:they both involve the functional derivative ofρ(r)with respect to v(r′),however with a diあerent constraint:constant N for χ and constant μ for s.The importance of this diあerence has already been stressed in early work by Berkowitz and Parr24,its repercussions when quantifying Kohn’s nearsightedness of electronic matter principle34,35havebeenatstakeinrecentwork by someof thepresent authors36.
We now investigate the positive or negative semidefi niteness of the kernels,as resulting from the convexity/concavity of the functionals.
Using a functional Taylor series of the electronic energy E for which the initial(or unperturbed)external potential v(r)is perturbed by w(r),the next expression,up to second order is obtained:
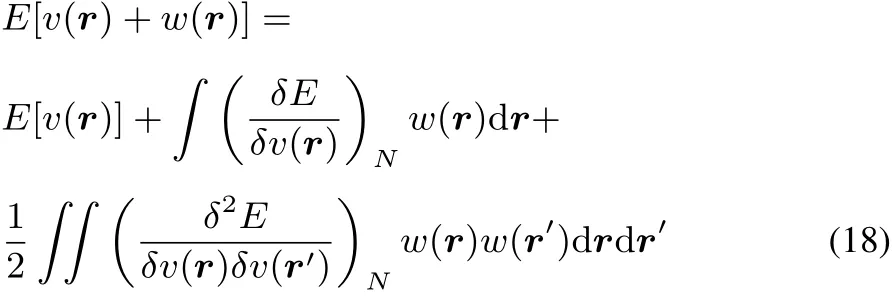
It is well established that E[v]functional is concave,following Jensen’s inequality(see for example Lieb47,Eschrig48,Helgaker et al.49):
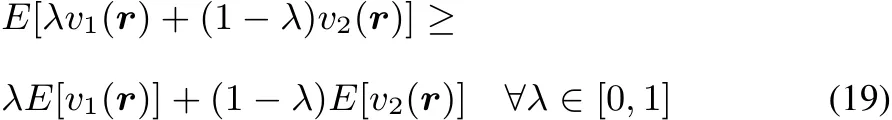
This concavity implies the linear response to be negative semidefi nite:
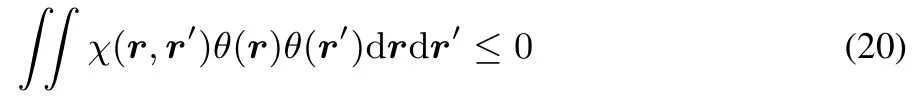
for any continuous functionθ.This can be seen from:
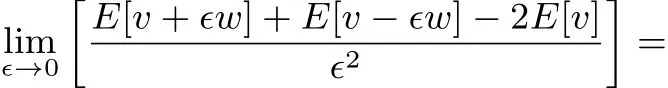
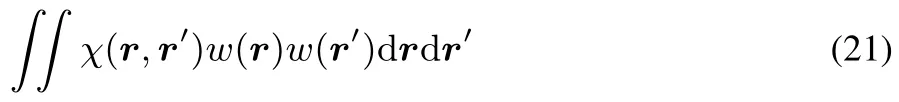
and by recognizing that 19 implies that
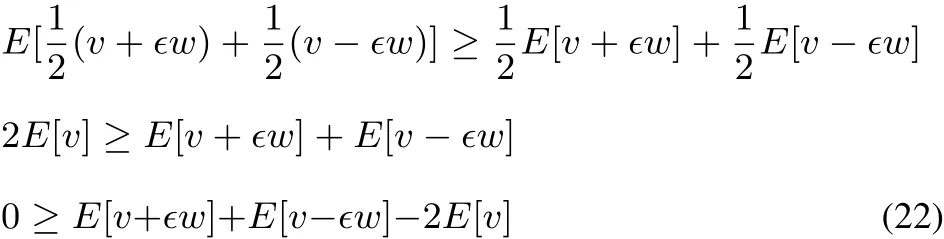
Passing now to the grand canonical ensemble,similar to the convexity of the E[v]functional,it can be shown that?[v]=E[v]? μN isconcave(for acompleteproof,see51):
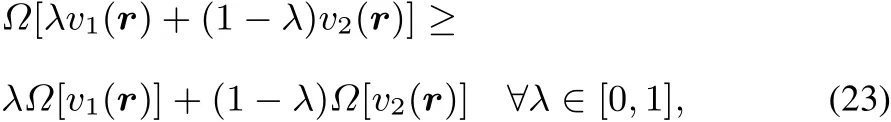
From thisconcavity it followsagain that
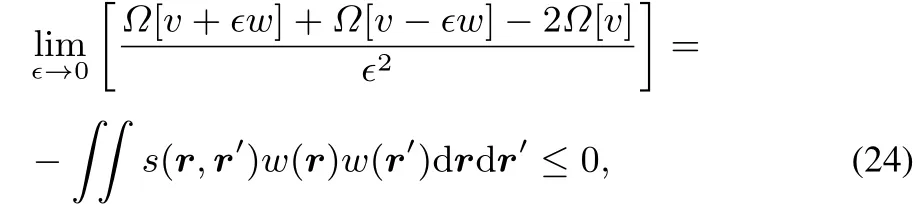
implying that the softness kernel s(r,r′)is positive semidefi nite.This positive semidefi niteness is also evident when using the Berkowitz-Parr relation for s(r,r′):
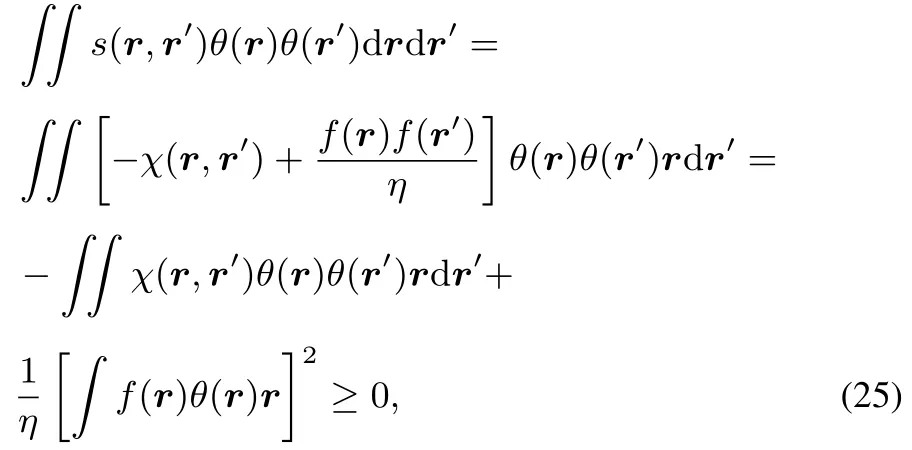
since the hardness,ηis positive.
In the isomorphic ensemble we remind that the Hohenberg-Kohn functional,F,actually only depends on the density,ρ(r),since thisobviously also determines N.Keeping,however,the spirit of the Legendre transformation of E[N,v(r)]to F[N,ρ(r)]in mind,it is tempting to look at variations inρwhile fixing the number of electrons.
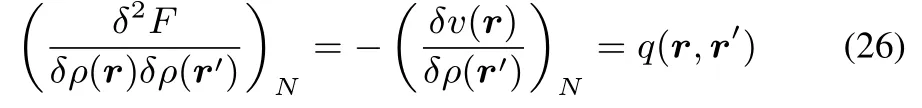
This kernel q(r,r′),which can be viewed as a special case of the hardness kernel under constant N variations ofρ,and has the interesting corollary of being the inverse of the linear response kernel:
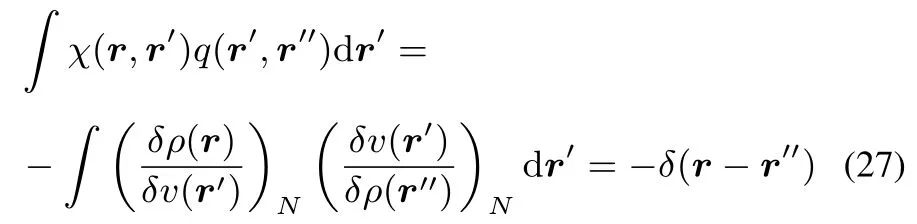
In what follows,we will restrict however our discussion to the “classical”hardness kernel,defined in Eq.(17)without constraint.We now consider the convexity of F[ρ(r)]concentrating on the case of v-representable densities,at stake in the type of studies in conceptual DFT(for a more detailed discussion,see Eschrig48,Lieb47,Ayers60).Its convexity follows from the variational principle.Indeed,ifρ0and ρ1are pure state v-representable densities and if we suppose that the convex sum ρλ= λρ0+(1? λ)ρ1also belongsto thedomain of pure state v-representable densities,then due to the variational principle F[ρλ] ≤ λF[ρ0]+(1 ? λ)F[ρ1],or in other words F isaconvex functional(see51for moredetails).
From thisconvexity it followsthat
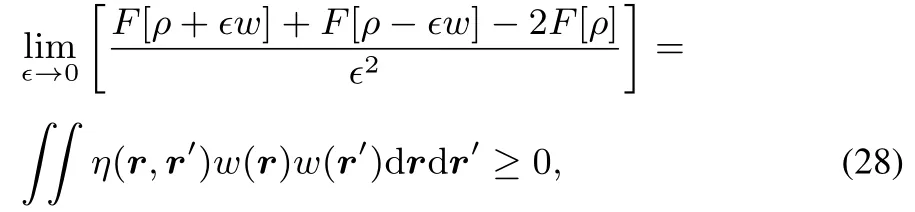
implying that the hardness kernel η(r,r′)is positive semidefi nite.
Finally,we consider the grand isomorphic ensemble.Discussions/use of this functional are less prominent in the literature despite the analysis made already in literature46by Parr and Liu.As its convexity/concavity inρhas not been discussed explicitly at that place we show below that R is convex inρ.
Indeed R(ρ)can be written for a given μ as

Suppose we define,just as in the F case,the density
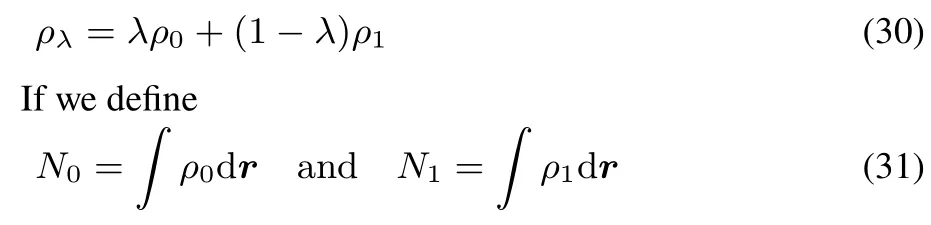
we now prove that
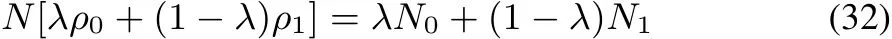
Indeed
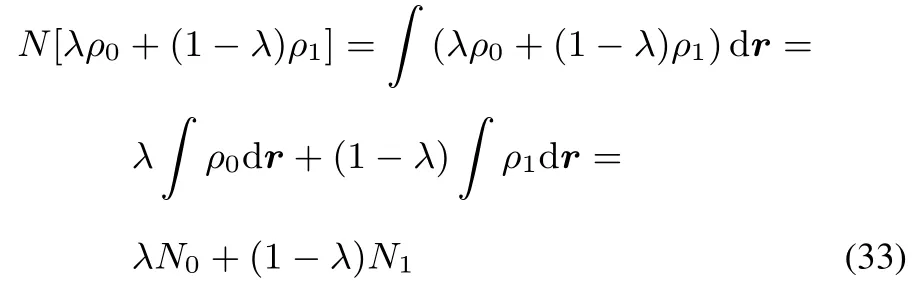
As F[ρ]wasconvex,thisresult yieldsa convex R[ρ].On this basis the corresponding functional derivativeis positivesemidefi nite.
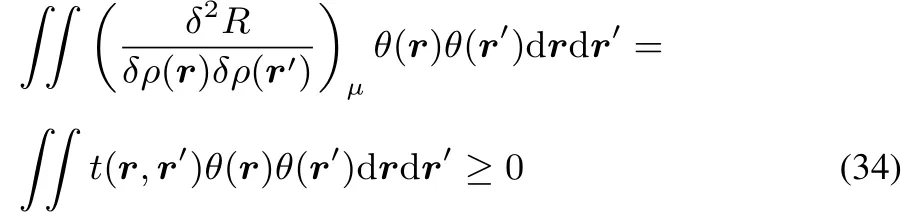
In fact this could be expected by the mere fact that t(r,r′)turns out to be equal to the hardness kernel(cf.reference46).Indeed starting from

onehas
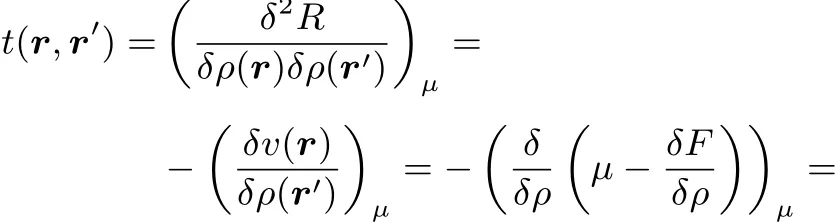
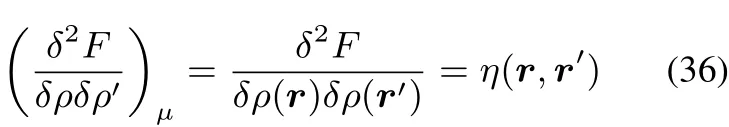
2.3 The analogy with thermodynamic functions
As stated above,when looking at the second order derivatives of the four functionals with respect to the global variables N andμ,only the derivatives of E and? have any signifi cance.(?2F/?2N)ρhas no signifi cance,since the number of electrons can not change when keeping the density fi xed,as is also the reason why(?2R/?2μ)ρ= ?(?N/?μ)ρ=0(see also46).The global hardness(?2E/?2N)v= η is alwayspositive,while(?2?/?2μ)v,equaling minustheglobal softness is always negative.As discussed above,both the derivativeswith respect to v(r)arenegative semidefi nite(with(δ2?/δv(r)δv(r′))μ= ?s(r,r′)and the softness kernel thus being positive definite)and the hardness kernel corresponding to both the second functional derivative with respect toρof F(without constraint)and R(withμ-constraint)is positive semi defi nite.Summarizing,second order(functional)derivatives with respect to extensive variables(N andρ)are positive or positive semi definite,while derivatives with respect to intensive variables(μand v)are negative or negative semi defi nite.This behavior of DFT functionals completely parallels the second derivative behavior of the functionsin macroscopic thermodynamics56assummarized in Table 1,where the sign alternation when passing from extensive to intensive quantities is clear.Thermodynamical potentials and DFT functionals are convex in extensive variables and concave in intensive variables.
In macroscopic thermodynamics second derivatives of state functions play an important role in stability analysis(see e.g.56–58for an extensive treatment).Take for example the entropy,S written as S=S(U,V)where the number of particles is kept constant,the quantity for which the basic extremum principle of thermodynamics can be formulated,namely that for S=S(U,V)d S=0 and d2S≤0 at equilibrium.Thestability condition can then bewritten as56
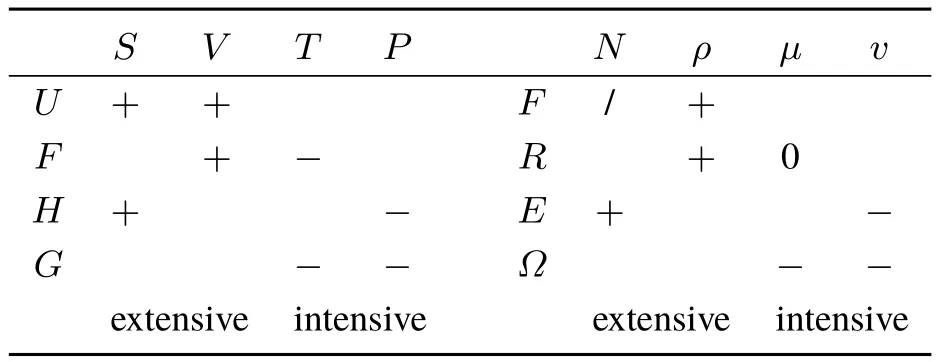
Table1 Analogy between thesign of thesecond order derivatives of thethermodynamic functions and thoseof the DFT functionals(positiveor negativesemidefi nitenessin thecaseof functional derivatives).
SUU(ΔU)2+2SUV(ΔU)(ΔV)+SVV(ΔV)2≤ 0(37)with obvious notations for the second order derivatives SUU,SUVand SVV.Multiplying by SUU(which is negative in view of the maximum entropy postulate)and adding and subtracting S2UV(ΔV)2,one obtains
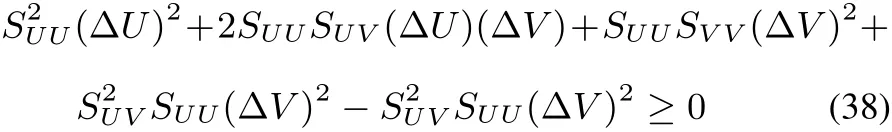
which,after rearrangement of the terms,becomes,
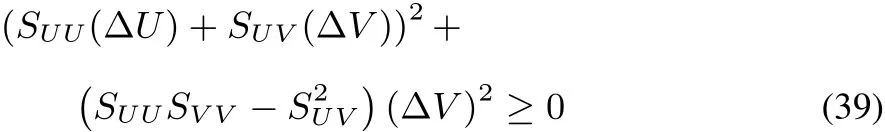
leading to the condition that

Together with thefactthat SUUand SVVarenegative56,this condition of stability expresses the concavity of S(U,V)in all directions.This third condition yields additional conditions for physical quantities that should be obeyed57,58,on top of those for SUUand SVV
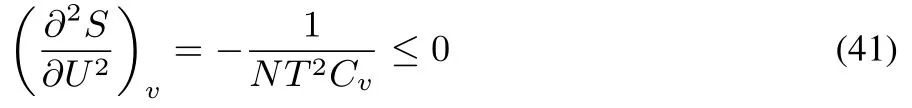
expressing that the molecular heat capacity Cvshould be positive in a stable system.The stability conditions are thus identical to the conditions of convexity/concavity and as the latter have been formulated above for the DFT functionals in the diあerent ensembles,it is tempting to see how these conditions,supplemented with the third condition equivalent to asking concavity/convexity in all directions,could be extended to DFT and which conditions can be derived from it at the electronic structurelevel,taking again into account thedivision of variables into intensive and extensive ones as in thermodynamics.
The analogy to S(U,V)is,however,diきcult to draw,as no DFTfunctional isdepending on two extensivevariables.Taking the opposite situation of a thermodynamic function and DFT functional depending on two intensive variables,the analogy between G(T,p)and ?[μ,v(r)]can be drawn.
G is concave in p and T(this can be traced back to the maximum entropy postulate,its equivalence to the minimum energy(U)principle,and the properties of the Legendre transformations of transforming U into G).The Legendre transformations replace the two extensive variables S and V by their conjugates T and p,turning the convex behavior into a concave one.Concavity along all directions implies
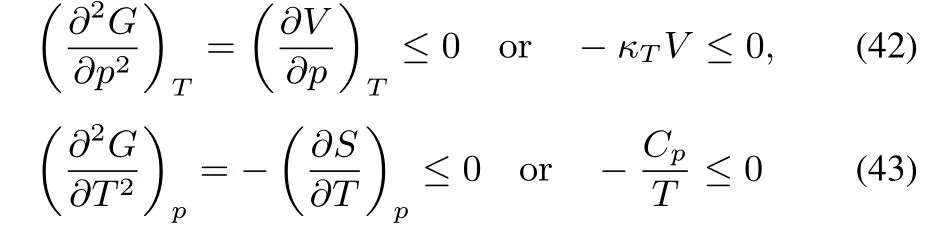
and
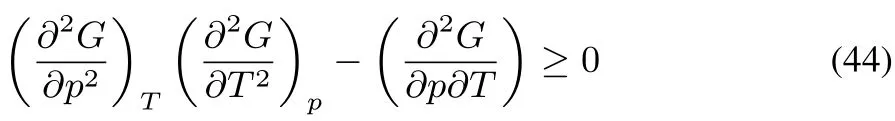
The fi rst two conditions express that the isothermal compressibilityand the heat capacity at constant pressure Cpshould be positive.The third condition yields the inequality

as= αV,whereα is the coeきcient of thermal expansion
Thisis the same inequality derived by Rice,Ross and Berry for the U(S,V)stability58.
Let us now look at the analogy of G(T,p)with ?[μ,v(r)],which isknown to yield=?S3,or minusthe global softness,which is always negative,showing the concavity of?inμ.As shown above? is also concave in v(r)with associated thepositivesemidefi nite softnesskernel(s(r,r′)=The third condition imposing concavity in all directions can be derived from the second(functional)diあerential asfollows.
The condition for concavity in all directions for?can be written as follows,extending Callen’s56approach for the S(U,V)function to the?functional,leading to single or doublefunctional derivativesinstead of partial derivatives.
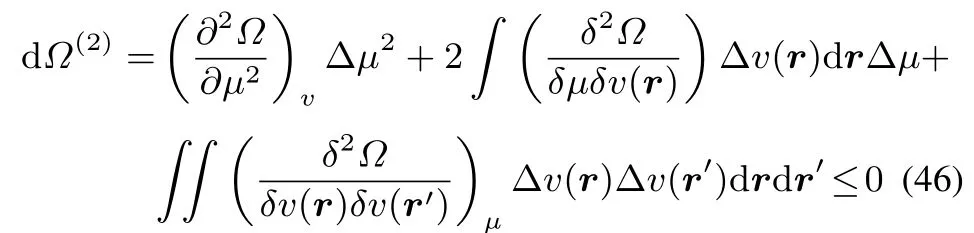
By multiplying withminus the softness,?S)and adding and subtractingv,which is negative(as it isΔv(r′)d r′the following inequality arises:
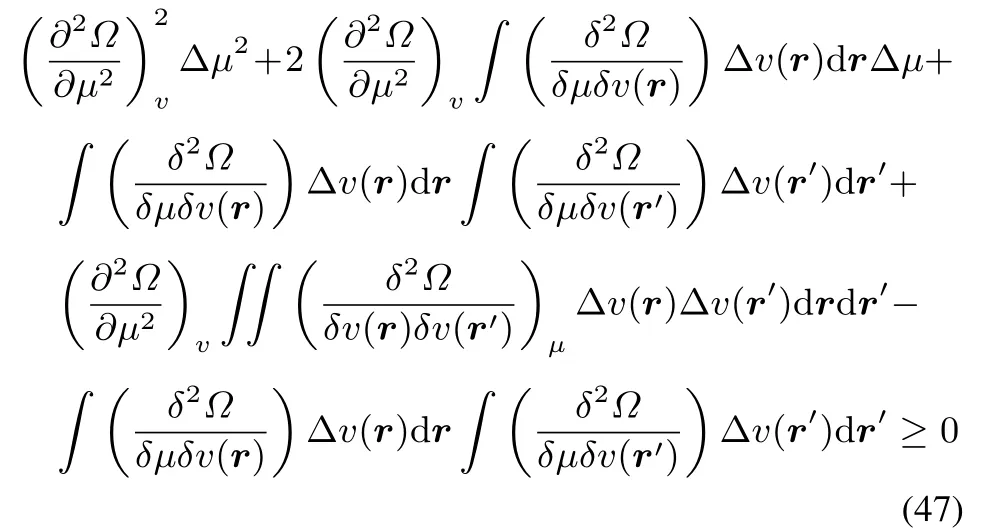
Collecting thefirst threetermsand thelast two,oneobtains
As the fi rst term is larger than or equal to zero,the condition onthesecond termto belarger than or equal tozero,for arbitrary ΔμandΔv(r)becomes
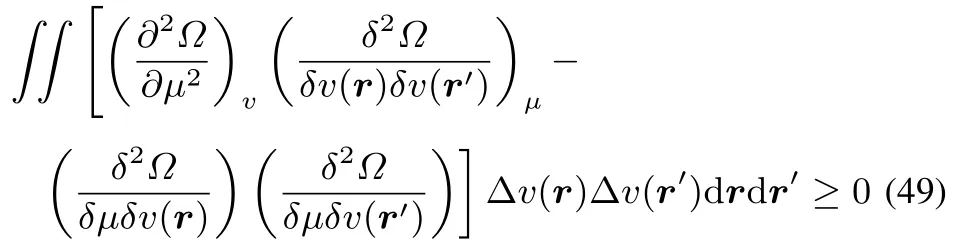
which,by filling inthedefi nitionsof theglobal softness S,local softness s(r)and softnesskernel s(r,r′)becomes
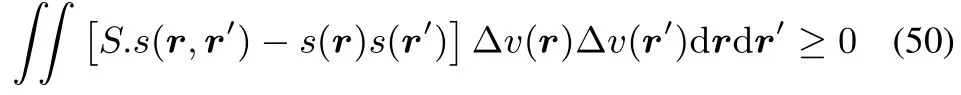
which is the extra condition for concavity of?in all directions combining global and local softness and the softness kernel in a single inequality.
Taking the particular choice of a dirac delta function,Δv(r)= δ(r? r1)andΔv(r′)= δ(r′? r1),asΔv(r)is arbitrary,one obtains
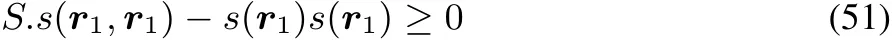
or

Thisinequality showsthat the third condition implies that all diagonal elements of the softness kernel should be positive,as opposed to the linear response function,where they are negative20,21.Remark that thistype of inequality isalso unique as in only one of the four diあerent representations the third condition is at stake and that on top of that the passage from non-local to local and global quantity corresponds in this case to simple integration which is not the case in the other representations.The formal analogy with the F=F(N,ρ)case is left out of consideration in view of the above discussed peculiaritieswith theρdependenceof N.
Eq.(52)puts a restriction on the relative values of the softness descriptors S,s(r)and s(r,r)and is an analogue to the thermodynamic expression involvingκ,α and Cp.This result is compatible with the famous Berkowitz-Parr formula24,relating theρversus v functional derivative for two diあerent constraints(constant N,leading to χ and constantμ,leading to the softness kernel)
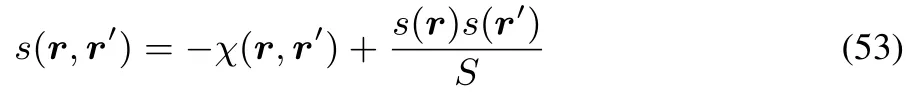
and our fi nding thatχ(r,r)≤ 021,converting(53)in the r=r′caseto an inequality
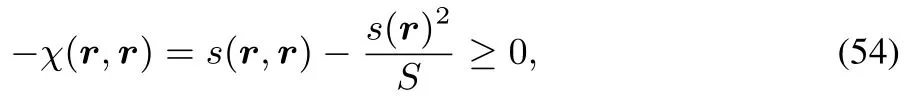
retrieving our conclusionsabove.
Two of the other DFT functionals,E=E[N,v]and R=R[μ,ρ]combinean extensiveand an intensivevariableand thus have both a positive and a negative second order(functional)derivative(Table 1)but no third condition for concavity and convexity in all directions:For E the well-known result for the convexity of E(N)yieldsa positive hardness

whereas the linear response function is negative semidefi nite as already mentioned above
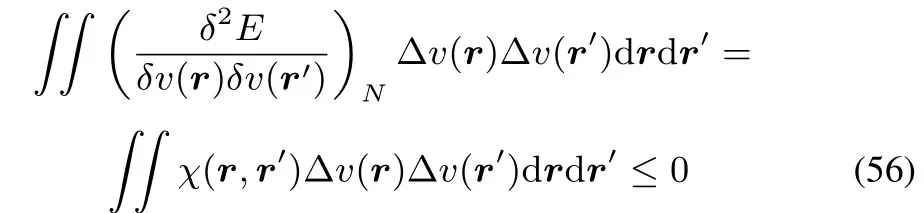
For R,onegets
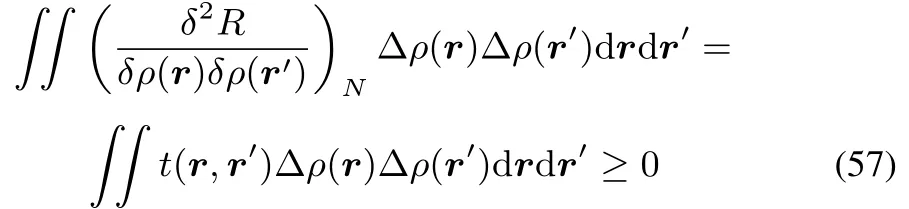
Theconditionon R withrespecttoμhasnophysicalmeaning,sinceit would requireachangein thenumber of electrons N at constant densityρ,which isobviously impossible:

Due to the mixed behaviour of these functionals,depending on both an extensive and an intensive variable,this situation is analogues to the thermodynamic potentials H and F.The fourth DFT functional F=F[ρ]can not be considered in a similar way since it is only dependent on one variable,ρ.It should be noticed that in this paper zero temperature DFT was at stake.It would be nice in the future to explore the analogies between the more realistic fi nite temperature dependent DFT,which recently gained much interest also in the context of conceptual DFT(see for example references61,62),and its thermodynamic counterparts.
Finally note that in thermodynamics a second Legendre transform series of quantities was defi ned,now starting from the entropy, leading to four entropy dimensioned thermodynamic functions:the Massieu function(s)useful in the theory of irreversible thermodynamics and statistical thermodynamics56.It would be tempting to see,if starting from theconvexity/concavity properties of thesefunctionsand an appropriately defined DFT analogue of the entropy,supplementary conditions on the electronic structure properties of atomic or molecular systems could be derived.
3 Conclusions
In this study the convexity/concavity of the functionals E,?,F and R of thefour diあerent ensemblerepresentationsused in(conceptual)density functional theory is scrutinized and connected with the positive/negative semidefiniteness of the associated kernels.A comparison with the four energy dimensioned thermodynamical state-functions U,F,H,G,just as the DFT functionals interrelated by Legendre transformations,along the lines set out by Nalewajski and Parr shows that stability conditions in Thermodynamics are similar in structure to convexity/concavity conditions for DFT functionals.In the case of functionals which are twice convex or twice concave in their variables,the condition for concavity/convexity in all directions yields a inequality involving the three second order(functional)derivatives of the functional considered.In case of?(the only functional obeying both the aforementioned conditions and the condition of non-interdependency of its variables),an inequality involving global softness,local softness and the softness kernel then results,which is shown to be compatible with the Berkowitz-Parr relationship.It might betempting to extend this study to fi nite temperature DFT and to see if analogous relationships might be put forward for DFT functionals which are the analogues of the entropy dimensioned thermodynamic functions as the Massieu function,demanding an entropy analogue in DFT.
(1)Parr,R.G.;Yang,W.Ann.Rev.Phys.Chem.1995,46,701.doi:10.1146/annurev.pc.46.100195.003413
(2)Chermette,H.J.Comput.Chem.1999,20,129.doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(19990115)20:1<129::AIDJCC13>3.0.CO;2-A
(3)Geerlings,P.;De Proft,F.;Langenaeker,W.Chem.Rev.2003,103,1793.doi:10.1021/cr990029p
(4)De Proft,F.;Geerlings,P.Chem.Rev.2001,101,1451.doi:10.1021/cr9903205
(5)Ayers,P.W.;Anderson,J.S.M.;Bartolotti,L.J.Int.J.Quantum Chem.2005,101,520.doi:10.1002/qua.20307
(6)Gazquez,J.L.J.Mex.Chem.Soc.2008,52,3.
(7)Liu,S.B.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2009,25,590.doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB20090332
(8)Gross,E.K.U.;Kohn,W.Phys.Rev.Lett.1985,55,2850.doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.55.2850
(9)Casida,M.E.Recent Advancesin Density Functional Methods;Chong,D.P.Ed.;World Scientifi c Pub.Co.Inc.:Singapore,1995;p.155.
(10)Parr,R.G.;Yang,W.Density-Functional Theory of Atomsand Molecules;Oxford University Press:New York,NY,USA,1989.
(11)Ayers,P.W.;De Proft,F.;Borgoo,A.;Geerlings,P.J.Chem.Phys.2007,126,224107.doi:10.1063/1.2736697
(12)Sablon,N.;De Proft,F.;Geerlings,P.J.Phys.Chem.Lett.2010,1,1228.doi:10.1021/jz1002132
(13)Sablon,N.;De Proft,F.;Ayers,P.W.;Geerlings,P.J.Chem.Theory Comput.2010,6,3671.doi:10.1021/ct1004577
(14)Fias,S.;Boisdenghien,Z.;Stuyver,T.;Audiあred,M.;Merino,G.;Geerlings,P.;De Proft,F.J.Phys.Chem.A 2013,117,3556.doi:10.1021/jp401760j
(15)Fias,S.;Geerlings,P.;Ayers,P.;De Proft,F.Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.2013,15,2882.doi:10.1039/c2cp43612d
(16)Boisdenghien,Z.;Van Alsenoy,C.;De Proft,F.;Geerlings,P.J.Chem.Theory Comp.2013,9,1007.doi:10.1021/ct300861r
(17)Yang,W.;Cohen,A.J.;De Proft,F.;Geerlings,P.J.Chem.Phys.2012,136,144110.doi:10.1063/1.3701562
(18)Boisenghien,Z.;Fias,S.;Van Alsenoy,C.;De Proft,F.;Geerlings,P.Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.2014,16,14614.doi:10.1039/c4cp01331j
(19)Fias,S.;Boisdenghien,Z.;De Proft,F.;Geerlings,P.J.Chem.Phys.2014,141,184107.doi:10.1063/1.4900513
(20)Geerlings,P.;Fias,S.;Boisdenghien,Z.;De Proft,F.Chem.Soc.Rev.2014,43,4989.doi:10.1039/c3cs60456j
(21)Geerlings,P.;Boisdenghien,Z.;De Proft,F.;Fias,S.Theor.Chem.Acc.2016,135,213.doi:10.1007/s00214-016-1967-9
(22)Stuyver,T.;Fias,S.;De Proft,F.;Fowler,P.;Geerlings,P.J.Chem.Phys.2015,142,094103.doi:10.1063/1.4913415
(23)Nalewajski,R.F.;Parr,R.G.J.Chem.Phys.1982,77,399.doi:10.1063/1.443620
(24)Berkowitz,M.;Parr,R.G.J.Chem.Phys.1988,88,2554.doi:10.1063/1.454034
(25)Senet,P.J.Chem.Phys.1996,105,6471.doi:10.1063/1.472498
(26)Ayers,P.W.;Parr,R.G.J.Am.Chem.Soc.2001,123,2007.doi:10.1021/ja002966g
(27)Ayers,P.W.Theor.Chem.Acc.2001,106,271.doi:10.1007/PL00012385
(28)Liu,S.;Li,T.;Ayers,P.W.J.Chem.Phys.2009,131,114106.doi:10.1063/1.3231687
(29)Yang,W.;Parr,R.Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA 1985,82,6723.doi:10.1073/pnas.82.20.6723
(30)Mendez,F.;Gazquez,J.L.J.Am.Chem.Soc.1994,116,9298.doi:10.1021/ja00099a055
(31)Damoun,S.;Van de Woude,G.;Mendez,F.;Geerlings,P.J.Phys.Chem.1997,101,886.doi:10.1021/jp9611840
(32)Geerlings,P.;De Proft,F.Int.J.Quantum Chem.2000,80,227.doi:10.1002/1097-461X(2000)80:2<227::AID-QUA17>3.3.CO;2-E
(33)Heidar-Zadeh,F.;Richer,M.;Fias,S.;Miranda-Quintana,R.A.;Chan,M.;Franco-Perez,M.;Gonzalez-Espinoza,C.E.;Kim,T.D.;Lanssens,C.;Patel,A.H.G.;et al.Chem.Phys.Lett.2016,660,307.doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2016.07.039
(34)Kohn,W.Phys.Rev.Lett.1996,76,3168.doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.76.3168
(35)Prodan,E.;Kohn,W.Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA 2005,102,11635.doi:10.1073/pnas.0505436102
(36)Fias,S.;Heidar-Zadeh,F.;Geerlings,P.;Ayers,P.W.Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA 2017,114,11633.doi:10.1073/pnas.1615053114
(37)Berkowitz,M.;Ghosh,S.K.;Parr,R.J.Am.Chem.Soc.1985,107,6811.doi:10.1021/ja00310a011
(38)Ghosh,S.K.;Berkowitz,M.J.Chem.Phys.1985,83,2976.doi:10.1063/1.449846
(39)Ghosh,S.K.Chem.Phys.Lett.1990,172,77.doi:10.1016/0009-2614(90)87220-L
(40)Harbola,M.K.;Chattaraj,P.K.;Parr,R.G.Isr.J.Chem.1991,31,395.
(41)Langenaeker,W.;De Proft,F.;Geerlings,P.J.Phys.Chem.1995,99,6424.doi:10.1021/j100017a022
(42)Chamorro,E.;De Proft,F.;Geerlings,P.J.Chem.Phys.2005,123,154104.doi:10.1063/1.2072907
(43)Torrent-Sucarrat,M.;Salvador,P.;Sola,M.;Geerlings,P.J.Comp.Chem.2007,28,574.doi:10.1002/jcc.20535
(44)Chattaraj,P.;Roy,D.R.;Geerlings,P.;Torrent-Sucarrat,M.Theor.Chem.Acc.2007,118,923.doi:10.1007/s00214-007-0373-8
(45)Polanco-Ramirez,C.A.;Franco-Perez,M.;Carmona-Espindola,J.;Gazquez,J.L.;Ayers,P.W.Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.2017,19,12355.doi:10.1039/c7cp00691h
(46)Liu,S.;Parr,R.G.J.Chem.Phys.1997,106,5578.doi:10.1063/1.473580
(47)Lieb,E.H.Int.J.Quantum Chem.1983,24,243.doi:10.1002/qua.560240302
(48)Eschrig,H.The Fundamentalsof Density Functional Theory;Teubner:Stuttgart-Leipzig,Germany,1996.
(49)Kvaal,S.;Ekstrom,U.;Teale,A.M.;Helgaker,T.J.Chem.Phys.2014,140,18A518.doi:10.1063/1.4867005
(50)Perdew,J.;Parr,R.;Levy,M.;Balduz,J.L.J.Phys.Rev.Lett.1982,49,1691.doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.49.1691
(51)Fias,S.;Geerlings,P.;De Proft,F.;Ayers,P.W.in preparation.
(52)Ghosh,S.K.;Berkowitz,M.;Parr,R.G.Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA 1984,81,8028.doi:10.1073/pnas.81.24.8028
(53)Nagy,A.;Parr,R.G.Proc.Indian Acad.Sci.1994,106,217.
(54)Nagy,A.;Parr,R.G.J.Mol.Struct.THEOCHEM 2000,501–502,101.doi:10.1016/S0166-1280(99)00418-2
(55)Nagy,A.Int.J.Quantum Chem.2017,117,e25396.doi:10.1002/qua.25396
(56)Callen,H.B.Thermodynamicsand an Introduction to Thermostatistics;John Wiley:New York,NY,USA,1985.
(57)Prigogine,I.;Defay,R.Chemical Thermodynamics;Longman:London,UK,1954.
(58)Berry,R.S.;Rice,S.A.;Ross,J.Physical Chemistry;Wiley:New York,NY,USA,1980.
(59)Cardenas,C.;Echegaray,E.;Chakraborty,D.;Anderson,J.S.M.;Ayers,P.W.J.Chem.Phys.2009,130,244105.doi:10.1063/1.3151599
(60)Ayers,P.W.Phys.Rev.A 2006,73,012513.doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.73.012513
(61)Franco-Perez,M.;Ayers,P.W.;Gazquez,J.L.;Vela,A.J.Chem.Phys.2015,143,244117.doi:10.1063/1.4938422
(62)Franco-Perez,M.;Gazquez,J.L.;Ayers,P.W.;Vela,A.J.Chem.Phys.2015,143,154103.doi:10.1063/1.4932539
- 物理化學學報的其它文章
- Synthesis of Mn O x-CeO2 Using Metal-Organic Framework as Sacrificial Template and Its Performance in the Toluene Catalytic Oxidation Reaction
- Reactivity of Indoles through the Eyes of a Charge-Transfer Partitioning Analysis
- Thermodynamic Dual Descriptor
- Multiply Charged Anions, Maximum Charge Acceptance, and Higher Electron Affinities of Molecules, Superatoms, and Clusters
- Quantitative Electrophilicity Measures
- Kohn-Sham Density Matrix and the Kernel Energy Method

