Spatial Dependent Spontaneous Emission of an Atom in a Semi-In finite Waveguide of Rectangular Cross Section?
Hai-Xi Song(宋海希),Xiao-Qi Sun(孫曉祺),Jing Lu(盧競),and Lan Zhou(周蘭)
Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Quantum Structures and Quantum Control of Ministry of Education,Department of Physics and Synergetic Innovation Center of Quantum Effects and Applications,Hunan Normal University,Changsha 410081,China
1 Introduction
Any quantum system inevitably interacts with its surroundings,which possess a huge amount of uncontrollable degrees of freedom.Such interaction causes the rapid destruction of quantum coherence,which is an essential requirement for quantum information processing to fully exploit the new possibilities opened by quantum mechanics.For example,the information stored in two-level systems(we refer to atoms hereafter)can be destroyed by their surrounding electromagnetic field.Spontaneous emission(SE)is one of the most prominent effects in the interaction of atoms with vacuum.It is an atomic radiation as follow:an atom is initially in an excited state relax to its ground state and emit a quanta of energy to its surrounding vacuum electromagnetic(EM) field,which carries away the difference in energy between the two levels.
SE is not only useless but also harmful to quantum information process.However,recently studies have shown that it is useful to build a device in a quantum network for controlling single photon by a local atom,e.g.the atomic radiation leads to the total re flection of the single-photon propagating in one quantum channel,[1?2]the frequency converter for single photon,[3]and the transfer of single photon from one quantum channel to the other.[4]Nowadays,great interest has been paid on the use of atoms to act as a quantum node in extended communication networks and scalable computational devices.[15?18]As the SE rate of a single atom can be modi fied by a succession of short and strong pulses or measure to the quantum system,[19?22]a dynamical Quantum-Zeno-Effect(QZE)switch for single photon is proposed.[5]The quantum interference between multiple transition pathways of atomic internal states has been exploited to modify the transport property of the single photon in a quantum channel.[9]With the well-known result that the atomic SE depends on the electromagnetic vacuum environment that the atom is subjected to,a boundary has been used to increase the efficiency of the quantum router.[12]
Actually,the SE rate of a single atom is one of the basic topic of quantum electrodynamics,numerous studies of the SE rates[23]have been carried out for atoms in free space(e.g.Ref.[24]),in a cavity(e.g.Ref.[25]),near a metallic mirror(e.g.Ref.[26])or a dielectric interfacer(e.g.Ref.[27]),between two mirrors(e.g.Ref.[28])or two dielectric interfaces(e.g.Ref.[29]).However,photons used to transmit information or distribute the entanglement along the network,are con fined in a one-dimensional(1D)waveguide.Similar to cavities,1D waveguide has a well-de fined mode spectrum and a relatively loss-free environment.However,unlike cavities,modes are available in waveguide for photons to propagate.The geometry constraint not only con fines the propagating direc-tion of photon,but also gives rise to an increasing of the interference effects.Since photons do not interact with each other,atoms implanted in waveguide are necessary to mediate the photon-photon interaction or redirect the possible propagating directions.The coupling strength of atoms to the waveguide is enhanced by decreasing the mode volume.Consequently,the atomic radiation in 1D waveguide plays an important role in controlling photons in quantum networks.And the studies on the atoms in 1D waveguide are now referred to by the term“waveguide quantum electrodynamics(QED).”
Since the radiative properties of an atom in a con fined space differ fundamentally from that in free space,considerable interest has been paid on atoms in a semi-in finite or in finite 1D waveguide.However most works focus on 1D waveguide without a cross section.[30?34]In this paper,we study the radiative properties of an atom in a semiin finite waveguide of rectangular cross section,which is a typical 1D QED system.The termination of the waveguide is regarded as a perfect mirror,which re flects emitted photons back to the atom.We analyze the interaction of an initially excited two-level atom with the waveguide in vacuum.The Markovian approximation is first used to analyze the dependence of the SE rate on the density of states and the spatial pro file of the waveguide.To find the in fluence of the time that one-photon wave packet requires to bounce back and forth between the atom and the mirror,we perform the linear expansion of the dispersion relation for the atomic transition frequency far away from the cuto fffrequencies,and obtain a delay-differential equation.Then the atomic SE dynamics is studied by varying the cross section of the waveguide as well as the atomic location.
This paper is organized as follows.In Sec.2,we introduce the system we have studied.In Sec.3,we derive the relevant equations describing the dynamics of the system in single-excitation subspace.In Sec.4,we do the Markovian approximation to study the effect of the mode pro file on the spontaneous rate.In Sec.5,the atomic dynamics is studied by linearly expanding the dispersion relation around the transition frequency,which is valid far from the branch threshold,where the delay time is introduced.Finally,we conclude this work in Sec.6.
2 An Atom Inside a Rectangular Pipe Waveguide
The system we studied is shown in Fig.1.A waveguide made of ideal perfect conducting walls is formed from surfaces at,and is placed along thezaxis.The waveguide is assumed to be in finite along thezdirection.The boundary condition restricts photons to travel without loss of power in two independent guiding modes:[35?36]TE modes whose electric field has no longitudinal component,and TM modes whose magnetic field has no longitudinal component.Letbe the wave vector.The relationskx=mπ/aandky=nπ/awith positive integersn,mcan be imposed by the condition that the tangential components of the electric field vanish at all the conducting wall,however,there is no constraint onk.Therefore,the waveguide allows a continuous range of frequencies described by the dispersion relation
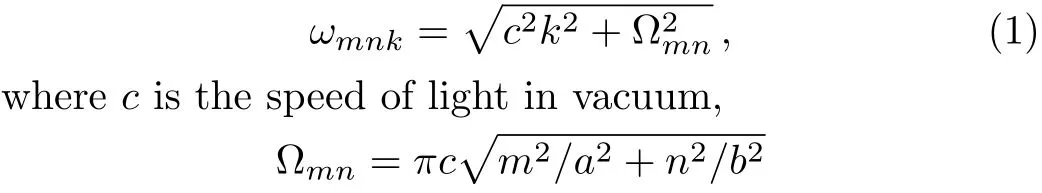
is the minimum frequency for a traveling wave.We note thatmandncannot both be zero.Ifa>b,TE10is the lowest guiding mode for the waveguide,[37]and the lowest TM modes occur form=1,n=1.Obviously,the waveguide modes form a one-dimensional continuum.Each guiding mode provides a quantum channel for photons to travel from one location to the other.
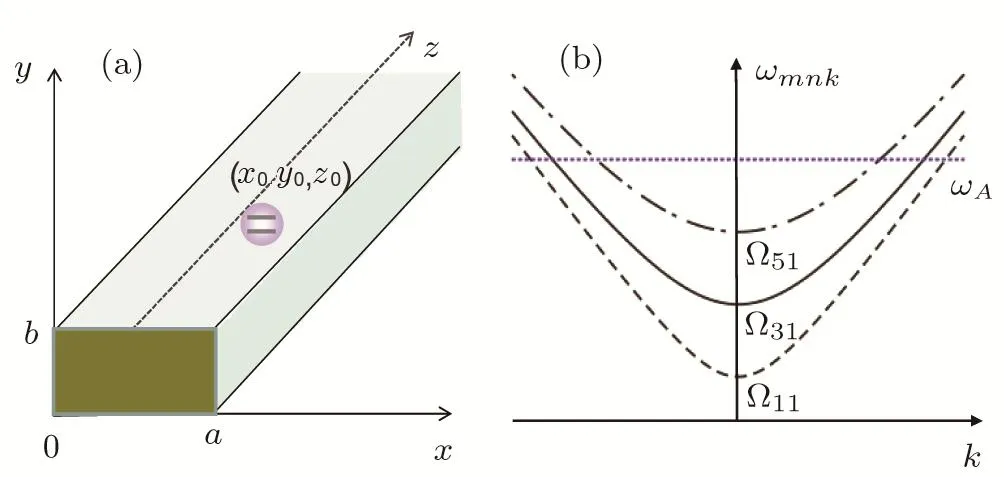
Fig.1 (Color online)Schematic illustration for(a)the two-level atom embedded in a semi-in finite waveguide of rectangular cross section,and(b)the dispersion relation of the guiding modes,which interact with the atom atr=(a/2,b/2,z0)with a=2b.
Atis an atom with transition frequencyωAbetween upper level|e>and lower level|g>,which is excited initially.The atom sits inside the hollow waveguide.z0is the distance between the atom to the wall(or the mirror)atz=0.The free Hamiltonian for the atom is described by

whereis the rising(lowering)atomic operator.For the purpose of simplicity,the electric dipole of the stationary atom is assumed to be oriented along thezdirection,which means that the atom only interacts with the TMmnmodes.Since the number(m,n,k)speci fies the mode function of this air- filled metal pipe waveguide,we label the annihilation operator for each TM guiding mode byamnk.The free Hamiltonian for the waveguide is described by


where the coupling strength Here,?0the permittivity of free space,dthe magnitude of the transition dipole moment of the atom and assumed to be real,A=abthe area of the rectangular cross section.Using the dispersion relation,the coupling strength can be rewritten as
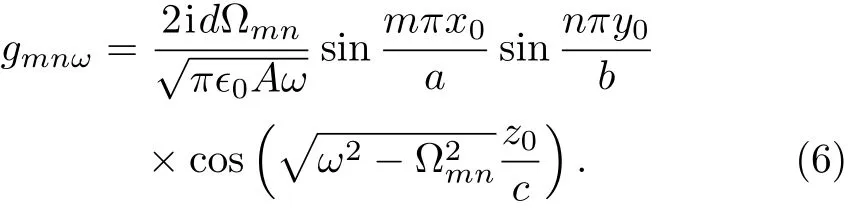
The cosine function in Eqs.(5)and(6)occurs due to the termination of the waveguide,which presents the difference from the in finite waveguide.Obviously,the atom located atx0=a/2 andy0=b/2 decouples to the TMmnguiding mode with even integermorn.The total system are described by Hamiltonian
3 Evolution of the Atom-Vacuum System
In this section we study the dynamics of the system when the atom is initially in the excited state|e>and the field is in the vacuum state|0>.Since the number of quanta is conserved in this system,we can write the wavefunction of the system as:

in one quantum subspace.The first term in Eq.(7)describes the atom in the excited state with no photons in the field,ε(t)is the corresponding amplitude,whereas the second term in Eq.(7)describes the atom in the ground state with a photon emitted at a modekof the TMmnguiding mode,φmn(k,t)is the corresponding amplitude.The initial state of the system is denoted by the amplitudesε(0)=1,φmn(k,0)=0.The Schr¨odinger equation results in the following coupled equation of the amplitudes
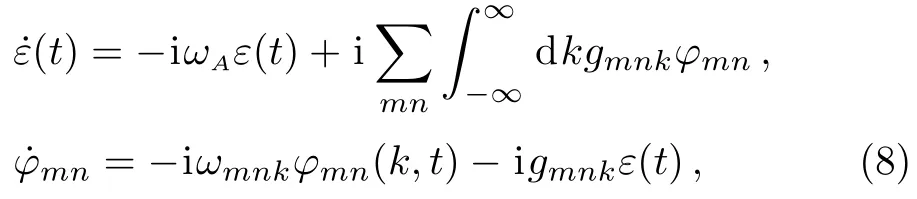
where the overdot indicates the derivative with respect to time.The population of the atomic excited state are usually analyzed by eliminating the field variables and focusing on the dynamics of the radiating system.We start by removing the high frequency term in Eq.(8)via the transformation
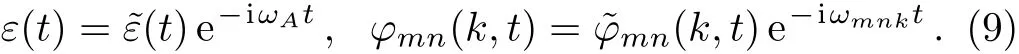
Then we formally integrate equation of,which is later inserted into the equation for.The probability amplitude for the excited atomic state is determined by the following integro-differential equation
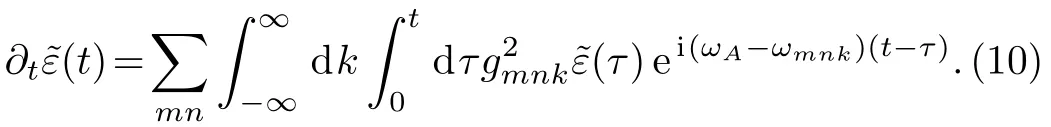
Equation(10)shows that the value ofdepends on the values ofat all earlier time.
4 Spatial Dependence of the Spontaneous Rate
To see how the mode distribution of the quantum vacuum fluctuation modi fies the atomic spontaneous rate,weon the right-hand side of Eq.(10),and the amplitude of levelreads

weighted by the strength of the coupling to the continuum.Since the dispersion relation of the semi-in finite waveguide is the same as that of the in finite rectangular waveguide,ρ(ω)in Eq.(14)is also the density of state of the in finite rectangular waveguide.For weak atom- field coupling,the amplitude of level|e>decays exponentially


The modal pro file affects on the decay rate via location of the atom.If the atom is located atx0=a/2 andy0=b/2,no photons are radiated into the TMmnguiding mode with even integermornsince the guiding mode is standing waves in the transverse direction.The cuto fffrequencies also affect the decay rate via the local density of states.In Fig.1(b),we have given a schematic diagram of the dispersion relation of the guiding modes,which interact with the atom atr=(a/2,b/2,z0)fora=2b.If the transition frequencyωA
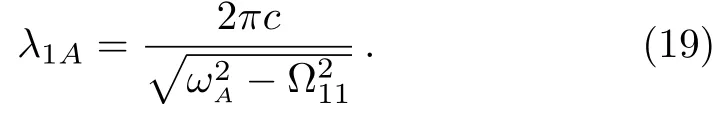
In Fig.2(a),we have plotted the probability of finding the atom in its excited state as a function of Γtfor three different values ofz0=0,λ1A/8,λ1A/4,where
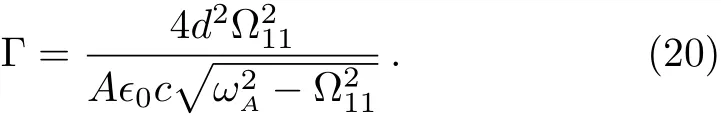
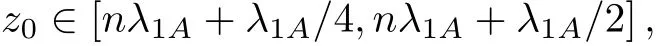
It can be seen that in the intervalz0∈[nλ1A,nλ1A+λ1A/4]with integern,the SE rate decreases as the atommirror separation increases.However in the interval its SE rate increases asz0increases.Since cosxis a periodical function of the argumentx,the figure is only plotted inz0∈[0,λ1A/4].It can be seen that atz0=nλ1A+λ1A/4,the SE is completely suppressed.Since we have set thata=2b,TM51and TM13is the third and fourth guiding modes,which might be interacting with the atom.When ?31<ωA
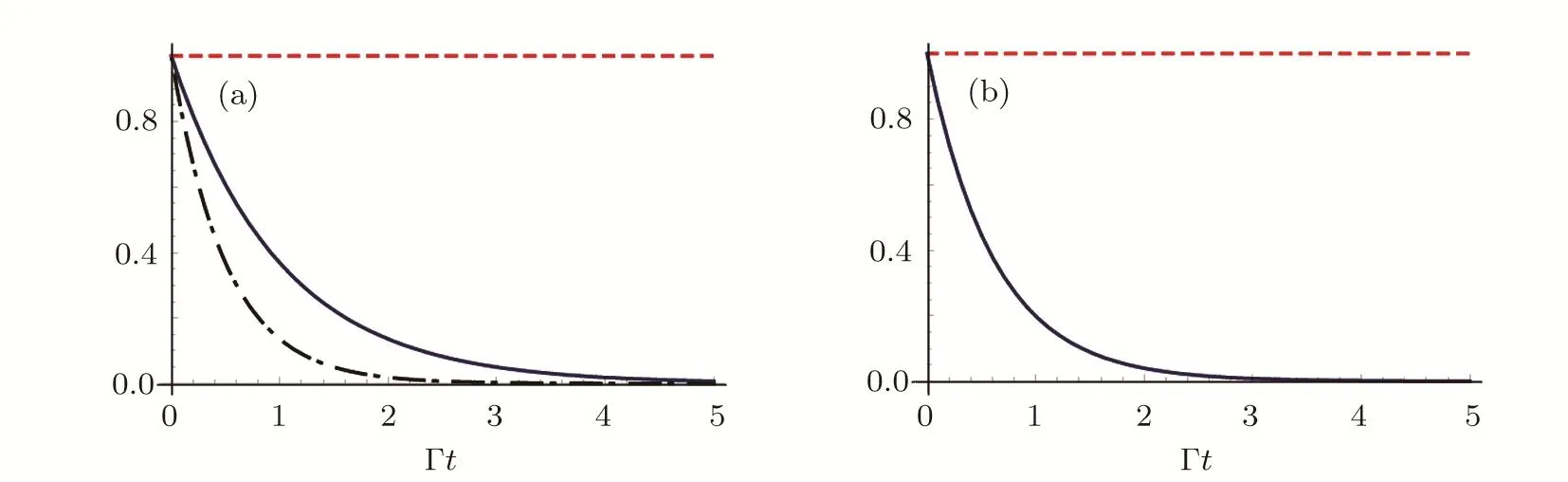
Fig.2 (Color online)Atomic excitation probability as function of Γt with a=2b.(a)The transition frequency ωA=(?11+?31)/2.The atom is located at three different positions z0=0(black dot-dashed line),z0= λ1A/8(blue solid line),z0= λ1A/4(red dashed line).(b)The transition frequency ωA=(?31+ ?51)/2.The atom is located at z0=λ1A/4.The red dashed line presents the contribution of the TM11mode.The blue solid line gives the contribution of both TM11and TM31modes.
One can also obtain the spontaneous rate in Eq.(18)by replacing?ε(τ)with?ε(t)in Eq.(10)and making the up limit of integral tend to in finite.Hence,the Markovian approximation yields the same phenomenon in the context below Eq.(18),which means that retardation effect is neglected.
5 Atomic Population of the Excited State
An excited atom relaxes to its ground state accompanied by a release of a photon to the EM vacuum.In this hollow waveguide,the emitted photon propagates along the positive and negativezdirections.Since the termination of the waveguide imposes a hard-wall boundary condition on the field,which behaves as a perfect mirror,the photon traveling along the negativezaxis is retrore flected to the atom,and re-excites the atom,which leads to a non-Markovian type dynamics of the system.[40]In this section,we study the spontaneous emission dynamics involving the retardation time for atom located atr=(a/2,b/2,z0)witha=2b.For the convenience of discussion,we denote the transversally con fined propagating modes,which couple to the atom as TMjwithj=(m,n)according to the ascending order of the cuto fffrequencies.By assuming that the transition frequencyωAis far away from the cuto fffrequencies ?j,we can expand frequencyωjkaround the transition frequencyωAup to the linear term
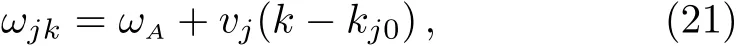

is different for different TMjguiding modes.We substitute Eq.(21)into integro-differential equation(10).Integrating over all wave vectorskgives rise to a linear combination ofδ(t±τj?τ)andδ(t?τ),whereτj=2z0/vjis the time that the emitted photon take the round trip between the atom and the mirror in the give transverse modej.We approximately obtain a delay-differential equation
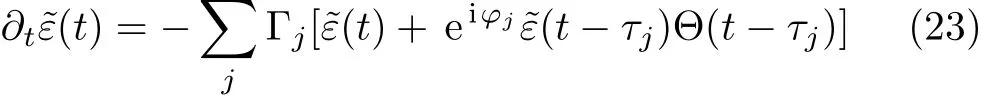
for the probability amplitude that the atom at timetis in the excited state,where

The first term on the right hand side of Eq.(23)leads to the exponential decay of the atom.The second term involved the timeτjthat the light needs for the distance atom-mirror-atom,which represents the effect of the reflected radiation on the atom that was emitted at timeτjin the TMmnmode before it interacts again with the atom.
5.1 SE Dynamics in Single Mode
In the frequency band between ?11and ?31,the waveguide is said to be single-moded.The atom with the transition frequencyωA∈(?11,?31)only interacts with the TM11(j=1)guiding mode,the delay-differential equation reduces to

where Γ1= Γ given in Eq.(20).For the case that the retarded argumentτ1→0,the memory effects inherent in the system disappear.The amplitude of state|e>becomes
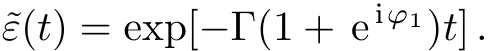
The SE rate and the frequency shift are presented by the real part 2Γ(1+cosφ1)and imagine part Γsinφ1,respectively.In the limitτ1→∞,the second term of Eq.(25)vanishes.Since the waveguide becomes in finite,the atomic population decays exponentially and the SE rate Γ is independent of the coordinatez0.
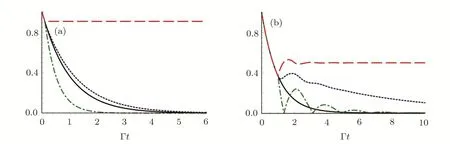
Fig.3(Color online)Amplitude|?ε(t)|versus Γt with delay Γτ1=0.1(a)and Γτ1=1(b)in the following cases:no termination(black solid line),phase φ1=2nπ+π/2(blue dotted line),φ1=2nπ+π (red dashed line),φ1=2nπ (green dash-dotted line).We have set the following parameters:a=2b,ωA=(?11+?31)/2.Since both φ1and τ1are related to the distance z0,different phases are achieved by adjusting the ratio a/d.
It can be seen from Eq.(25)that the time axis is divided into intervals of lengthτ1.We can formally integrate Eq.(25)and change the dummy integration variable,which is then substituted into the integrand.Proceeding inde finitely with iteration,the time behavior of the atomic state populations reads
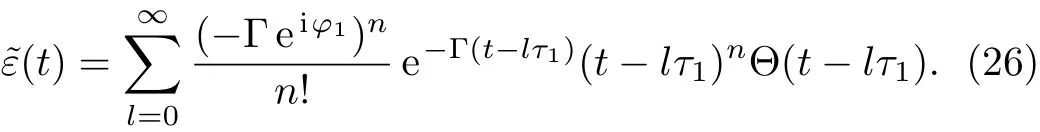
A step character is presented in Eq.(26).Fort∈[0,τ1],the atomic amplitude?ε(t)=exp(?Γt)decays exponentially,which coincides with the behavior of an excited atom in an in finite waveguide.The underlying physics is that the atom requires at least the timeτ1to recognize the mirror.Fort∈[τ1,2τ1],due to the emitted radiation re flected back to the atom,l=1 term has been included,which gives rise to the interference for finding the atom in the excited state.In Fig.3,we have plotted the norm|?ε(t)|of the atomic amplitude versus Γtwith delay Γτ1=0.1(a)and Γτ1=1(b).The exponential decay of the atom inside an in finite waveguide is plotted with the black solid line.When Γτ1?1,an exponential decay law is found,however,the SE can be either increased or descreased by the phase.The SE is completely suppressed when phaseφ1=(2n+1)π.When Γτ1≥1,the atom first decays exponentially,after the atom recognizes the mirror,it displays a behavior deviating from the exponential decay law,and a partial revival of the atomic population can be found.It is the interference between the emitted wave and the radiation wave re flected back to the atom,which makes the atom-mirror separationz0has signi ficant in fluence on the atomic dynamic via the phase.When the distance between the atom and the termination are further large(i.e.,Γτ1?1),it is found from Fig.5(a)that there is also a partial revival of the atomic population,however,the atom-mirror separationz0does not make any sense.In this case,the atom has already decayed to the ground state at the time that the photon bounces back to the atom,so there is no emitted wave to be interference with the wave re flected back to the atom,which means that the atomic revival is due to the atom being partially re-excited by the radiation.Since the light emitted in the positive direction has departed from the atom,the probability that the atom is re-excited becomes lower and lower.
5.2 SE Dynamics in Multiple Modes
An excited atom radiates waves into the continua of all modes resonant with the atom.When the cross area becomes larger,more modes are included in the resonance,then the atomic dynamics is not only affected by the timeτ1that light needs to bounce back and forth between the atom and the termination in the TM11mode,but also by other timeτjrequired for a photon emitted by the atom to propagate in the TMmnmode and reabsorbed by the atom.The de finition of delay timeτjtold us thatτj<τj+1.
In this section,we assume that the atomic transition frequency is in the regime[?31,?51],which means that only two TM modes(i.e.TM11,TM31)in resonance with the atom,the delay-differential equation reduces to
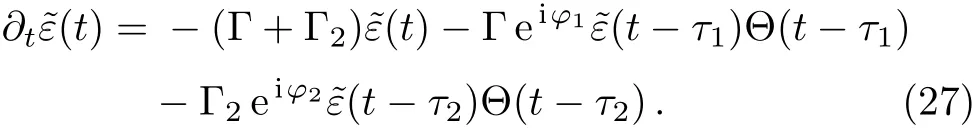
The space dependence enters via both the phasesφ1,φ2and the delay timeτ1,τ2of the different modes.If both argumentsτ1,τ2→0,the amplitude of state|e>becomes
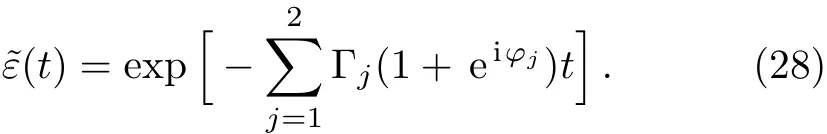
Two terms are consisted of in the above equation,the SE rateand frequency shift.Comparing to the single mode case,the SE rate is enhanced,however the frequency shift can be either increased or decreased due to the space dependence.In the limit,the second and third terms of Eq.(27)vanish.The amplitudeshows that the atomic population decays exponentially,Γ+Γ2is the SE rate that the atom interacts with the continuum of the TM11and TM31modes of an in finite waveguide,which is also independent of the coordinatez0.In the case thatτ1→0,the delay-differential equation reads

Using Laplace transformation and geometric series expansion,the solution reads
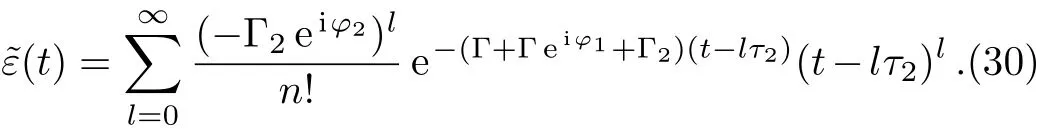
If the atom is located atz0satisfyingφ1=(2n+1)π,the SE that the TM11mode contributes to is completely suppressed,then one obtains the SE dynamics due to the emitted photon propagating only via the continuum of the TM31mode.In the case with finiteτ1andτ2→∞,the upper state amplitude becomes

However,it is impossible for an atom inside a realistic waveguide to appear the dynamics described by Eq.(31).In Fig.4,we have numerically plotted the amplitudeas a function of Γtwith Γτ1=0.1(a)and 1(b).It can be seen that in the interval[0,τ1],the upper state population of the atom decays exponential with a rate Γ+Γ2.After timeτ1,photons emitted by the atom are re flected back to the atom by the mirror so that the atom-mirror distance has great in fluence on the SE dynamics via phaseandτj.Phaseφ1first gives arise to deviation from the decay with a rate Γ + Γ2in the interval[τ1,τ2].As soon ast>τ2,the wave propagating in the TM31mode is reflected back to the atom by the mirror,phasedeviates the atomic dynamics from that of finiteτ1andτ2→∞.In the weak coupling case(see,Fig.4(a),the excited state probability decreases as the time increases.However,in the strong coupling case,several peaks can be observed in Fig.4(b),which present partial revivals of the atom probability when Γτ1≥1.Comparing to the time evolution in Fig.3,the SE is enhanced for a given phaseφ1.Phaseφ2and retardation timeτ2shift the position of the peak and the dip.
In Fig.5,we have numerically plotted the probabilityas a function of Γtwith delay Γτ1=10 for(a)single-moded and(b)double-moded cases.When the photon returns back to the atom,the atom has already decayed to its ground state,it is impossible for interference to occur so that the phasesφjhave no effect on the atomic dynamics.The peaks at timet>τ1owe to the re flected light reabsorbed by the atom.By comparing two figures in Fig.5,we found that the probability that the atom is reexcited by the radiation wave is lower in the multiple-mode case than that in the single-mode case,and more peaks appear in the intervalfor the multiple-mode case.Such observations are easy to understand because there are more transverse modes to interact with the atom.
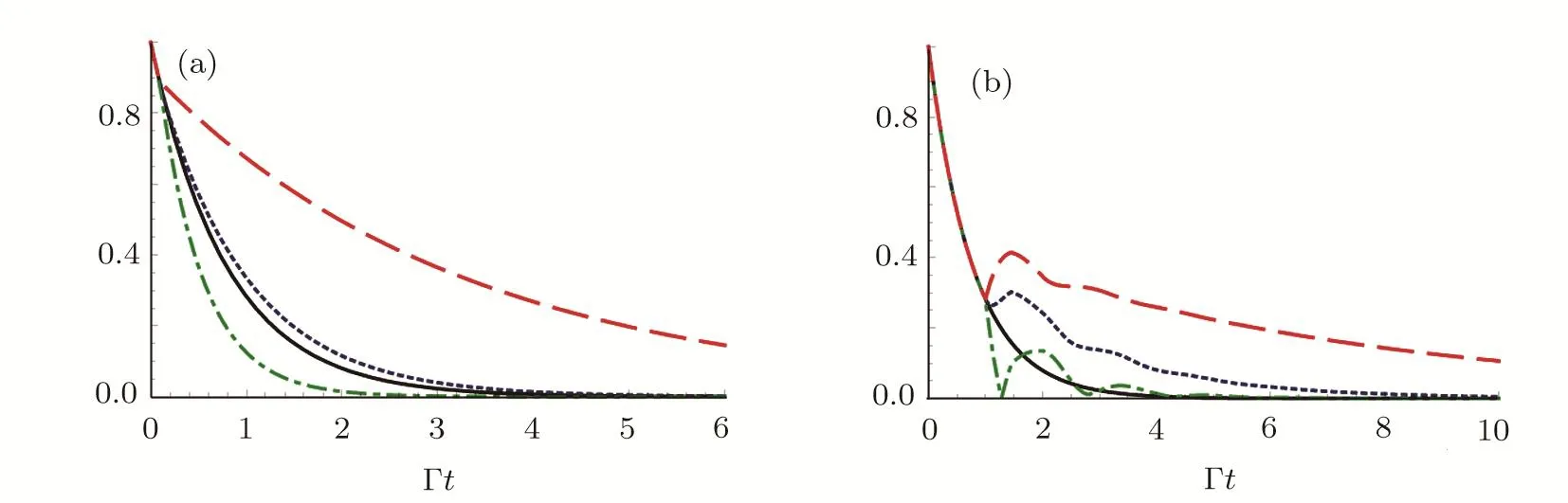
Fig.4(Color online)Amplitudeversus Γt with delay Γτ1=0.1(a)and Γτ1=1(b)in the following cases:no termination(black solid line),phase φ1=2nπ+π/2(blue dotted line),φ1=2nπ+π (red dashed line),φ1=2nπ (green dash-dotted line).We have set the following parameters:a=2b,ωA=(?31+?51)/2.

Fig.5(Color on line)Probabilityversus Γt with delay Γτ1=10 with phase φ1=2nπ+π/2(blue dotted line),φ1=2nπ+π (red dashed line),φ1=2nπ (green dash-dotted line)in the following cases:(a)single modetwo modes ωA=(?31+?51)/2.Here,a=2b.
6 Discussion and Conclusion
We have studed the dynamics of an atom inside a hollow waveguide of rectangular cross sectionA=ab,made of ideal perfect conducting walls.Such 1D waveguide generally consists of both TE and TM waves,the atom with dipole along thez-direction interacts only with the TMmntransverse modes,their coupling strength depends on the atomic location.A two-level atom with location fixed at(a/2,b/2,z0)is considered,which decouples to fields of the TM modes with even integerm,n.We have first discussed the dependence of the SE rate on the atommirror separation and the density of states by Markovian approximation(i)Since the density of state vanishes below ?11,the SE is completely suppressed whenωAτ1,two situations should be distinguished.For short retardation time,the interference between the radiation wave and the emitted wave makes the dynamics is strongly dependent onφj.For long retardation time,the atom has already decay to its ground state when the photon returns back to the atom,the partial revivals and collapses are due to the photon reabsorbed and re-emitted by the atom.
Appendix
The quantization of the waveguide field is based on the classical Maxwell equations with the boundary condition of metallic rectangular waveguides.The electric field can
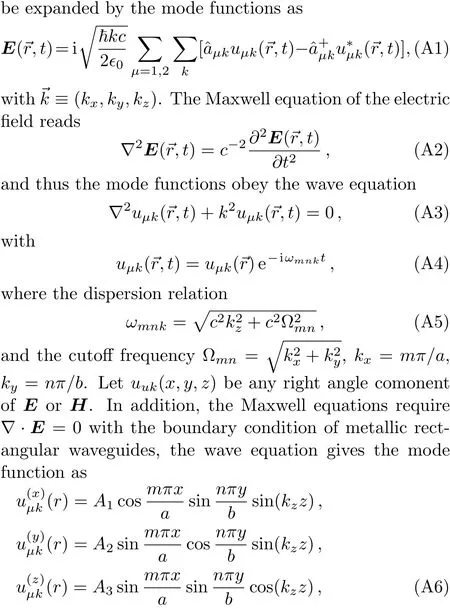
wheren,mare non-negative integers,andA1,A2,A3are the normalization constants.There are two mode functions in the waveguide,the transverse electric wave(TE mode function)and the transverse magnetic wave(TM mode function).For TE mode function,the Maxwell equation requires?·E=0,which meanskxA1+kyA2=0,so TE mode function reads

with the normalization condition.For TM mode function,the Maxwell equations require?·E=0,which means
[1]J.T.Shen and S.Fan,Phys.Rev.Lett.95(2005)213001;Opt.Lett.30(2005)2001;ibid.98(2007)153003;Opt.Lett.30(2005)2001.
[2]L.Zhou,Z.R.Gong,Y.X.Liu,et al.,Phys.Rev.Lett.101(2008)100501.
[3]Z.H.Wang,L.Zhou,Y.Li,and C.P.Sun,Phys.Rev.A 89(2014)053813.
[4]L.Zhou,L.P.Yang,Y.Li,and C.P.Sun,Phys.Rev.Lett.111(2013)103604;J.Lu,L.Zhou,L.M.Kuang,and F.Nori,Phys.Rev.A 89(2014)013805.
whereA=abis the crosssection of rectangular waveguide.The dipole of the TLS oriented along thezdirection is only coupled to the TM modes.The dipole coupling of the TLS to the TM field is given bydegEmnk(r0)wheredegis the dipole of the TLS andr0is the location of the TLS,withr0=(a/2,b/2,z0)the coupling coefficientgmnkis given by
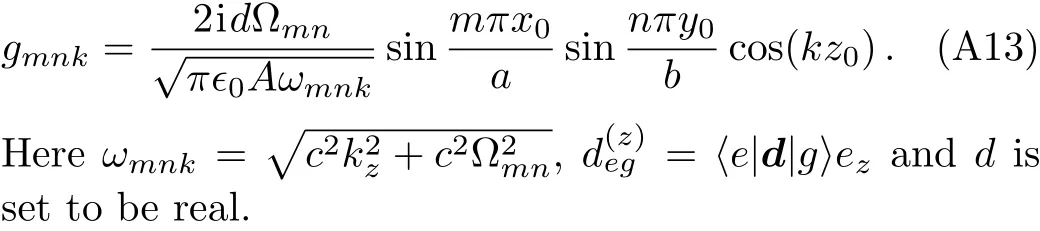
[5]L.Zhou,S.Yang,Y.X.Liu,et al.,Phys.Rev.A 80(2009)062109.
[6]H.X.Zheng,D.J.Gauthier,and H.U.Baranger,Phys.Rev.A 82(2010)063816;Phys.Rev.Lett.107(2011)223601;Phys.Rev.A 85(2012)043832;Phys.Rev.Lett.111(2013)090502.
[7]D.Roy,Phys.Rev.Lett.106(2011)053601;Phys.Rev.B 81(2010)155117;Phys.Rev.A 83(2011)043823.
[8]L.Zhou,H.Dong,Y.X.Liu,et al.,Phys.Rev.A 78(2008)063827;L.Zhou,Y.Chang,H.Dong,et al.,Phys.Rev.A 85(2012)013806.
[9]Z.R.Gong,H.Ian,L.Zhou,and C.P.Sun,Phys.Rev.A 78(2008)053806.
[10]T.S.Tsoi and C.K.Law,Phys.Rev.A 78(2008)063832.
[11]L.Neumeier,M.Leib,and M.J.Hartmann,Phys.Rev.Lett.111(2013)063601.
[12]L.Lu and L.Zhou,Opt.Express.23(2015)22955.
[13]F.Lecocq,J.B.Clark,R.W.Simmonds,et al.,Phys.Rev.Lett.116(2015)043601.
[14]C.H.Yan,L.F.Wei,W.Z.Jia,and J.T.Shen Phys.Rev.A 84(2011)045801.
[15]M.T.Cheng,X.S.Ma,M.T.Ding,et al.,Phys.Rev.A 85(2012)053840.
[16]P.Longo,P.Schmitteckert,and K.Busch,Phys.Rev.Lett.104(2010)023602;Phys.Rev.A 83(2011)063828(2011);P.Longo,J.H.Cole,and K.Busch,Opt.Express 20(2012)12326.
[17]M.Alexanian,Phys.Rev.A 81(2010)015805.
[18]T.Shi and C.P.Sun,Phys.Rev.B 79(2009)205111;T.Shi,S.Fan,and C.P.Sun,Phys.Rev.A 84(2011)063803;T.Shi and S.Fan,Phys.Rev.A 87(2013)063818.
[19]Qi-Cheng Wu,Ye-Hong Chen,Bi-Hua Huang,et al.,Opt.Express.24(2016)22847.
[20]Ye-Hong Chen,Qi-Cheng Wu,Bi-Hua Huang,et al.,Ann.Phys.2017(2017)00247.
[21]Ye-Hong Chen,Zhi-Cheng Shi,Jie Song,et al.,Phys.Rev.A 96(2017)043853.
[22]Qi-Cheng Wu,Ye-Hong Chen,Bi-Hua Huang,et al.,Phys.Rev.A 94(2016)053421.
[23]H.Walther,Phys.Rep.219(1992)263.
[24]J.Audretsch and R.M¨ullert,Phys.Rev.A 50(1994)1755.
[25]D.Kleppner,Phys.Rev.Lett.47(1981)233.
[26]R.J.Cook and P.W.Milonni,Phys.Rev.A 35(1987)5081;G.Alber,J.Z.Bern′ad,M.Stobi′nska,et al.,Phys.Rev.A 88(2013)023825.
[27]C.K.Carniglia and L.Mandkl,Phys.Rev.D 3(1971)280.
[28]W.Jhe,Phys.Rev.A 43(1991)5795;ibid.44(1991)5932.
[29]H.P.Urbach and G.L.J.A.Rikken,Phys.Rev.A 57(1998)3913.
[30]H.Dong,Z.R.Gong,H.Ian,L.Zhou,and C.P.Sun,Phys.Rev.A 79(2009)063847.
[31]K.Koshino and Y.Nakamura,New J.Phys.14(2012)043005.
[32]T.Tufarelli,F.Ciccarello,and M.S.Kim,Phys.Rev.A 87(2013)013820.
[33]M.Bradford and J.T.Shen,Phys.Rev.A 87(2013)063830.
[34]Y.L.L.Fang and H.U.Baranger,Phys.Rev.A 91(2015)053845.
[35]Q.Li,L.Zhou,and C.P.Sun,Phys.Rev.A 89(2014)063810.
[36]J.F.Huang,T.Shi,C.P.Sun,and F.Nori,Phys.Rev.A 88(2013)013836.
[37]Jin Au Kong,Electromagnetic Wave Theory,John Wiley&Sons,New York(1986)pp.166-170.
[38]A.G.Kofman and G.Kurizki,Nature(London)405(2000)546.
[39]A.G.Kofman and G.Kurizki,Phys.Rev.Lett.87(2001)270405.
[40]P.Zhang and M.W.Wu,Phys.Rev.B 76(2007)193312.
 Communications in Theoretical Physics2018年1期
Communications in Theoretical Physics2018年1期
- Communications in Theoretical Physics的其它文章
- Solitary Potential in a Space Plasma Containing Dynamical Heavy Ions and Bi-Kappa Distributed Electrons of Two Distinct Temperatures
- Ti Impurity Effect on the Optical Coefficients in 2D Cu2Si:A DFT Study?
- Simultaneous Effects of Impurity and Electric Field on Entropy Behavior in Double Cone-Like Quantum Dot
- Electron Acceleration by Beating of Two Intense Cross-Focused Hollow Gaussian Laser Beams in Plasma?
- Discrete Boltzmann Method with Maxwell-Type Boundary Condition for Slip Flow?
- Unique Outcomes of Internal Heat Generation and Thermal Deposition on Viscous Dissipative Transport of Viscoplastic Fluid over a Riga-Plate
