Separation of Eu3+ Using a Novel Dispersion Combined LiquidMembrane with P507 in Kerosene as the Carrier*
PEI Liang (裴亮), WANG Liming (王理明) and FU Xinglong (付興隆)
?
Separation of Eu3+Using a Novel Dispersion Combined LiquidMembrane with P507 in Kerosene as the Carrier*
PEI Liang (裴亮)1,2,**, WANG Liming (王理明)2and FU Xinglong (付興隆)2
1Key Laboratory of Water Cycle and Related Land Surface Processes, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China2Faculty of Water Resources and Hydraulic Power, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an 710048, China
The separation of Eu3+is studied with a dispersion combined liquid membrane (DCLM), in which polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (PVDF) is used as the liquid membrane support, dispersion solution containing HCl solution as the stripping solution, and 2-ethyl hexyl phosphonic acid-mono-2-ethyl hexyl ester (P507) dissolved in kerosene as the membrane solution. The effects of pH value, initial concentration of Eu3+and different ionic strength in the feed phase, volume ratio of membrane solution to stripping solution, concentration of HCl solution, concentration of carrier, different stripping agents in the dispersion phase on the separation are investigated. The optimum condition for separation of Eu3+is that concentration of HCl solution is 4.0 mol·L-1, concentration of carrier is 0.16 mol·L-1, and volume ratio of membrane solution to stripping solution is 30︰30 in the dispersion phase, and pH value is 4.2 in the feed phase. The ionic strength has no significant effect on separation of Eu3+. Under the optimum condition, when the initial concentration of Eu3+is 0.8×10-4mol·L-1, the separation percentage of Eu3+is 95.3% during the separation time of 130 min. The kinetic equation is developed in terms of the law of mass diffusion and the theory of interface chemistry. The diffusion coefficient of Eu3+in the membrane and the thickness of diffusion layer between feed phase and membrane phase are obtained and their values are 1.48×10-7m2·s-1and 36.6 μm, respectively. The results obtained are in good agreement with literature data.
dispersion combined liquid membrane, 2-ethyl hexyl phosphonic acid-mono-2-ethyl hexyl ester, separation, europium3+
1 INTRODUCTION
Liquid membranes (LMs) involve extraction and stripping processes simultaneously, and they have benefits of nonequilibrium mass transfer and up-hill effect, where the solute can move from low to high concentration solution [1-4]. The main liquid membrane systems include emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) [5], supported liquid membrane (SLM) [6], bulk liquid membrane (BLM), flowing liquid membrane (FLM) [7], electrostatic pseudo liquid membrane (EPLM) [2], supported emulsion liquid membrane (SELM) [8, 9], hollow fiber liquid membrane (HFLM) [10], supported liquid membrane with stripping dispersion (SLM-SD) [11, 12],. The potential advantages of LM techniques, over traditional separation techniques and solid membrane techniques, are low capital and operating costs, low energy and extractant consumption, high concentration factors and high fluxes. However, LM techniques have not been adopted for large-scale industrial processes [13-19], primarily due to the lack of longtime stability, difficult operation and larger membrane resistance,[20]. For example, SLM will lose the carrier because of the turbulent shear force of liquid in both phases and concentration difference between organic phase and aqueous phase, and the operation of ELM involves the complexity of emulsification and de-emulsification techniques [10-12].
A new liquid membrane technique, named dispersion combined liquid membrane (DCLM), has been proposed [21]. The DCLM technique is based upon surface renewal and diffusion theory, with the advantages of fiber membrane extraction, liquid film permeation and most of other liquid membrane systems, resulting in more stable membrane, lower costs, simpler operation, extremely efficient stripping of target species from the organic phase with high flux, and high concentration of target species in the stripping solution. However, more studies are needed for the application of DCLM in industry [22, 23]. The scale-up for the new liquid membrane configuration requires a complete understanding of the efficiency parameters, reported in such a way that a concise and global insight of the separation characteristics of a given system can be easily drawn. For example, the study on the separation of a single cation and a new permeability coefficient equation are needed, and more data for the separation of two or more competitive solutes are required for some applications, such as waste liquid of metallurgical industry.
The present study is concerned with the technical feasibility for separation of metal ions by DCLM. Eu3+is playing an increasingly important role in high technology. We choose DCLM to separate Eu3+. The effects of various experimental parameters on separation of rare earth Eu3+ions are investigated. The separation of Eu3+is carried out with a DCLM, which consists of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (PVDF) as the support, dispersion solution concluding HCl solution as the stripping solution, and 2-ethyl hexyl phosphonic acid-mono-2-ethyl hexyl ester (P507) dissolved in kerosene as the membrane solution. Although the separation of metal ions by SLM containing the same carrier (P507) has been extensively studied, there is little research by DCLM. The effects of pH value, initial concentration of Eu3+and different ionic strength in the feed phase, volume ratio of membrane solution to stripping solution, concentration of HCl solution, concentration of P507, and different stripping agents in the dispersion phase on separation of Eu3+are investigated. The results with DCLM are compared to those with conventional SLM. A kinetic equation for DCLM process is derived from the law of mass diffusion and the theory of interface chemistry and tested.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
2.1 Reagent
All the reagents such as Eu(CH3COO)3·4H2O, arsenazo III(C22H18As2O14N4S2), CH3COONa, HCl, and CH3COOH used in the present work were of analytical grade. 2-ethyl hexyl phosphonic acid-mono-2- ethyl hexyl ester (P507) is a commercial extractant (purity>95%) and used without any further purification. Kerosene was washed with concentrated sulfuric acid and distilled at 180-220°C.
2.2 Preparation of solutions
Eu3+stock solution was prepared by dissolving Eu(CH3COO)3·4H2O in 1 mol·L-1HCl solution, and analyzed by arsenazo III as the chromogenic agent. For Eu3+feed solution, a certain amount of the Eu3+stock solution was diluted with 0.01 mol·L-1HCl solution after adding a calculated amount of CH3COONa and CH3COOH. Arsenazo III stock solution was prepared by dissolving the powder of arsenazo III in deionized water. To obtain the stripping solution, the required amount of HCl was solved and diluted with deionized water to a certain concentration. P507 solution was obtained by diluting a certain amount of extractant with kerosene.
2.3 Experimental procedure
The separation with the DCLM was determined as follows. The experiments were accomplished at (25±1)°C in a simple diffusion cell, which consists of two-compartment perspex half-cells, each with effective volume of 70 ml. The membrane impregnated with P507 dissolved in kerosene was clamped between the two half-cells. A microporous PVDF membrane was used as the solid support, the thickness of which is 65 μm, with nominal porosity of 75%, tortuosity of 1.67 and effective area of 10.5 cm2. The feed phase (50 ml) consisted of Eu3+and buffer solution was poured into the perspex half-cell. The mixed dispersion phase consisted of certain volume ratio of the membrane solution containing the carrier P507 to HCl stripping solution was placed into another half-cell. The stability of the SLM was ensured by a modified SLM with stripping dispersion phase, where the aqueous stripping solution was dispersed in the organic membrane solution in a mixer. The stripping dispersion formed in the mixer went to the membrane module to provide a constant supply of the organic solution to the membrane pores. Samples of the feed phase were taken at intervals. The stirred dispersion phase were allowed to stand until the phase separation occurred, and then the Eu3+sample was collected from the dispersion phase. Samples containing Eu3+in the feed phase were analyzed for ion concentration with a UV-1200 spectrophotometer using arsenazo III as the chromogenic agent (under the detection wave length 652 nm). Fig. 1 is the experimental installation of the DCLM process.

Figure 1 Experimental installation of DCLM process
1—feed pool; 2—PVDF membrane; 3—feed phase; 4—dispersion pool; 5—membrane solution; 6—stripping phase; 5+6—dispersion phase; 7—magnetic stirrer apparatus
2.4 Experimental principle and theoretical analysis
Figure 2 shows the principle of DCLM process, in which concentration change and separation processes are depicted, where subscripts m, f and s stand for membrane phase, feed solution, and dispersion phase, respectively. The co-separation involves following steps.
(a) Eu3+diffuses from the feed phase to interface A.
(b) In the membrane phase near interface A, the extraction of Eu3+from the feed solution with carrier P507 [such as (HR)2] in kerosene can be expressed as [24, 25]:
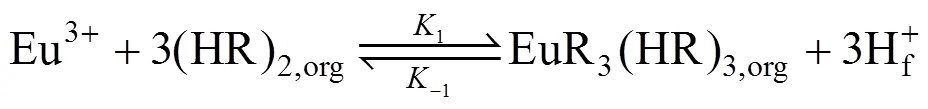
where1and-1are the reaction percentage constants of the reversible reaction at the interface between the feed phase and membrane phase.
Figure 2 The principle of DCLM process
(c) The metal-complex [EuR3(HR)3] diffuses through the membrane A-B.
(d) In the stripping side near interface B, EuR3(HR)3dissolves in the membrane solution and Eu3+are stripped by stripping agent. At the drop interface, Eu3+in the organic phase interchanges H+in the stripping phase, then Eu3+diffuses to the bulk of the stripping phase and the extractant is regenerated. The stripping reaction can be written as

where2and-2are the reaction rate constant of the reversible reaction at interface B.
(e) Carrier P507 returns from interface B to interface A.
The equation for permeability coefficient can be defined as [26]

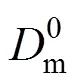
We define

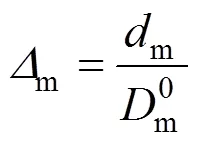
so that Eq. (1) is expressed as

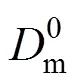
In previous study, we obtained [26]


3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Effect of volume ratio of membrane solution to stripping solution
The effect of volume ratio of membrane solution to stripping solution in the dispersion phase on separation of Eu3+is shown in Fig. 3. The volume ratio is increased from 10︰50 to 50︰10. Volume ratio 50︰10 is better.

Figure 3 Effect of volume ratio of membrane solution to stripping solution on separation of Eu3+
(pH in feed phase: 4.0, initial concentration of Eu3+: 1.0×10-4mol·L-1, concentration of HCl solution in dispersion phase: 4.0 mol·L-1, concentration of P507: 0.16 mol·L-1)
■?10︰50; ▲?20︰40; ×?30︰30; □?40︰20;◆?50︰10
At ratios of 50︰10, 40︰20 and 30︰30, the separation percentage of Eu3+are 83.5%, 81.5% and 81% respectively. These separation percentages are satisfactory, so we choose the ratio 30︰30 during the following experiments.
3.2 Effect of concentration of HCl solution in the dispersion phase
The effect of concentration of HCl solution in the dispersion phase on separation of Eu3+is shown in Fig. 4. As the acid concentration increases, the separation percentage increases. At the concentration of 5.0 and 4.0 mol·L-1, the separation percentages of Eu3+are 82.5% and 81%, respectively. The increasing of concentration of HCl solution from 2.0 mol·L-1to 3.0 mol·L-1has no significant effect on separation percentage of Eu3+, and it is less than 70%, because the number of Eu3+complex and the concentration of membrane solution which separation through the membrane per unit area of the membrane per unit time are definite. However, under the condition of 6.0 mol·L-1HCl solution, the separation percentage is a little lower than 5.0 mol·L-1and 4.0 mol·L-1, due to higher concentration of HCl solution resulting in a large number of volatilization of HCl during a certain time. The concentration of HCl solution 4.0 mol·L-1in the dispersion phase can be chosen during the following experiments.

Figure 4 Effect of concentration of HCl solution on separation of Eu3+
(pH in feed phase: 4.0, initial concentration of Eu3+: 1.0×10-4mol·L-1, volume ratio of membrane solution to stripping solution in the dispersion phase: 30︰30, concentration of P507: 0.16 mol·L-1)
concentration/mol·L-1: ■?2; ▲?3; ×?4; □?5;◆?6
3.3 Effect of pH in the feed phase
Based on mechanism of mass transfer process, the concentration difference between feed phase and dispersion phase is the driving power of mass transfer process. So in the feed phase the lower the H+concentration is, the stronger the driving power of mass transfer process will be. Stronger power will promote the separation percentage of Eu3+. Equally, the greater the pH value in the feed phase is, the higher the separation percentage of Eu3+is. The effect of pH in the feed phase on separation of Eu3+is studied in the pH range of 3.3 to 4.6, which is adjusted with an HAc-NaAc buffer solution. Initial concentration of Eu3+in the feed phase is 1.0×10-4mol·L-1. The results are shown in the Fig. 5. The separation percentage of Eu3+increases when the pH in the feed phase increased from 3.3 to 4.6, and a maximum separation percentage observed at pH 4.2 is 90.8%. Above the pH of 4.2 in the feed phase, the separation percentage of Eu3+decreases to 86%. When pH value was higher than 4.6, hydroxy complex of Eu3+was formed in the feed phase and the separation percentage of Eu3+decreased. Contrast to the previous cases, the literature [28] suggested the influence of pH on distribution coefficient of extraction process. It is large because the separation process is mainly governed by the driving power of mass transfer caused by the distribution equilibrium, when the renewal effect of the liquid membrane and the diffusion mobility of Eu3+ions are determined under specific experimental conditions [29, 30]. The pH of 4.2 as the optimum pH condition in the feed phase was chosen during the following experiments.

Figure 5 Effect of pH in the feed phase on separation of Eu3+
(concentration of HCl solution in dispersion phase: 4.0 mol·L-1, initial concentration of Eu3+: 1.0×10-4mol·L-1, volume ratio of membrane solution and stripping solution in the dispersion phase: 30︰30, concentration of P507: 0.16 mol·L-1)
pH: ■?3.3; ▲?3.6; ×?4.0; □?4.2;◆?4.6
3.4 Effect of initial concentration of Eu3+ in the feed phase
Effect of initial concentration of Eu3+on separation percentage of Eu3+is studied in the Eu3+concentration range from 0.16×10-4mol·L-1to 1.50×10-4mol·L-1. The results obtained are presented in Fig. 6. With the increasing of initial concentration of Eu3+in the feed phase from 0.16×10-4mol·L-1to 1.50×10-4mol·L-1, the separation percentage of Eu3+decreased during the same time. This is because the number of P507 is definite through the membrane when the interface between the feed phase and the membrane phase is definite. That is to say, the number of Eu3+separated is definite in this separation process. When the Eu3+concentration is 0.8×10-4mol·L-1, 1.0×10-4mol·L-1, and 1.5×10-4mol·L-1, the separation percentage is up to 95.3%, 90.8% and 73.1% in 130 min, respectively. Further more, the separation percentage is up to 97.3% in 100 min, when initial concentration of Eu3+is adjusted to 0.16×10-4mol·L-1, and after 100 min Eu3+is hardly determined, because the concentration of Eu3+is too low to determine, that is to say the Eu3+is exhausted in the feed phase and concentration of Eu3+is below the analytical determination limits.

Figure 6 Effect of initial concentrations of Eu3+on separation of Eu3+
(concentration of HCl solution in dispersion phase: 4.0 mol·L-1, pH in feed phase: 4.2, volume ratio of membrane solution and stripping solution in the dispersion phase: 30︰30, concentration of P507: 0.16 mol·L-1)
concentration/mol·L-1: ■?0.16×10-4; ▲?0.50×10-4; ×?0.80×10-4;□?1.00×10-4;◆?1.50×10-4
3.5 Effect of different stripping agents on separation of Eu3+
The effects of different stripping agents in the dispersion phase on separation of Eu3+are studied. The effect of different stripping agents in the dispersion phase on the separation percentage of Eu3+is shown in Fig. 7. Using hydrochloric acid (HCl) 4 mol·L-1, sulphuric acid (H2SO4) 2 mol·L-1and nitric acid (HNO3) 4 mol·L-1as the stripping agent respectively, it was found that hydrochloric acid is the most efficient stripping agent in this investigation. Under the conditions of hydrochloric acid solution, sulphuric acid solution and nitric acid solution, the separation percentage of Eu3+is up to 95.3%, 92% and 82% respectively. During the following experiment we have still chose the hydrochloric acid as the stripping agent.
3.6 Effect of concentration of P507 on separation of Eu3+
Concentration of P507 in the membrane phase and dispersion phase also plays a significant role in separation of Eu3+. Effect of concentration of P507 on separation percentage of Eu3+is studied in the P507 concentration range from 0.036 mol·L-1to 0.23 mol·L-1. The results are shown in the Fig. 8. With the increasing of concentration of P507 in the membrane phase from 0.036 mol·L-1to 0.23 mol·L-1, the separation percentage of Eu3+increases, however, when concentration of P507 increases to 0.23 mol·L-1from 0.16 mol·L-1, the increasing of separation percentage of Eu3+is near. So 0.16 mol·L-1can be chosen as the optimum concentration of carrier.
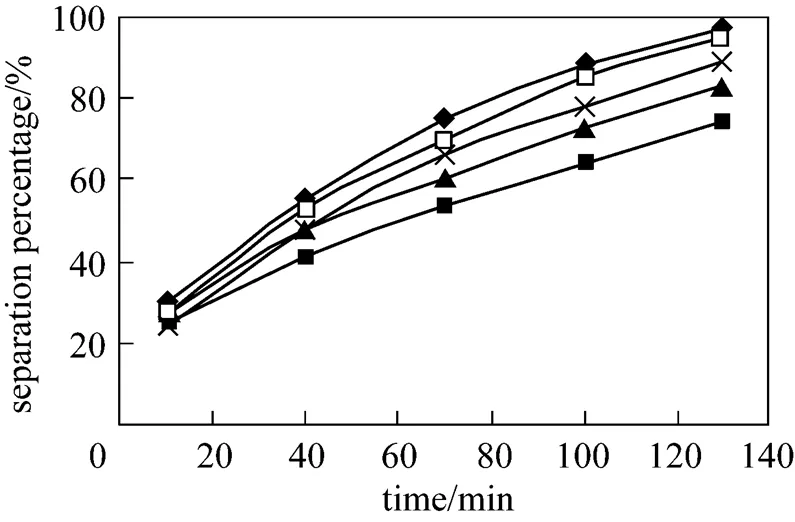
Figure 8 Effect of concentration of P507 on separation of Eu3+
(concentration of HCl solution in dispersion phase: 4.0 mol·L-1, pH in feed phase: 4.2, initial concentration of Eu3+: 0.8×10-4mol·L-1, volume ratio of membrane solution and stripping solution in the dispersion phase: 30︰30)
concentration/mol·L-1: ■?0.016; ▲?0.065; ×?0.100; □?0.160;◆?0.230
3.7 Effect of ionic strength in the feed phase
Above experiments, we did not consider the influence of ionic strength. Under the optimum condition, the effect of ionic strength in the feed phase on separation percentage of Eu3+is studied in this section under the same concentration of Eu3+0.8×10-4mol·L-1.The reagent KNO3was used to adjust the ionic strength to 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 mol·L-1respectively. The results are shown in Fig. 9. It indicates that the ionic strength has not influence on the separation percentage of Eu3+.
4 KINETIC ANALYSIS
Constructing based on the data of effect of pH in the feed phase, and the relationship developed between 1/cand [H+]3[Eq. (4)], When concentration of carrier is definite.

Figure 9 Effect of ionic strengths on separation of Eu3+
(concentration of HCl solution in dispersion phase: 4.0 mol·L-1, pH in feed phase: 4.2, initial concentration of Eu3+: 0.8×10-4mol·L-1, volume ratio of membrane solution and stripping solution in the dispersion phase: 30︰30, concentration of P507: 0.16 mol·L-1)

Figure 7 Effect of different stripping agents on separation of Eu3+
(concentration of HCl solution in dispersion phase: 4.0 mol·L-1, pH in feed phase: 4.2, initial concentration of Eu3+: 0.8×10-4mol·L-1, volume ratio of membrane solution and stripping solution in the dispersion phase: 30︰30, concentration of P507: 0.16 mol·L-1)
■?hydrochloric acid (4 mol·L-1); ▲?sulphuric acid (2 mol·L-1); ×?nitric acid (4 mol·L-1)
It indicates that the relationship between 1/cand [H+]3is linear (Fig. 10). The value of2is 0.998, which is in good agreement with the theory from Eq. (4). The slope and intercept of the line are 2.3815×1015s·L4·m-1·mol-4and 6.0998×104s·m-1. The thickness of diffusion layerf, which is obtained by using diffusion coefficient of Eu3+in the aqueous solution (6.0×10-10m2·s-1) [27, 31] is thatff·f3.660×10-5m36.6 μm. Then the diffusion coefficientin the membrane, obtained by Eqs. (3) and (4), is thatm2·s-1.

Figure 10 Comparison between experimental and theoretical (I)
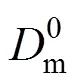

When+concentration in the feed phase is set, the effect of concentration of carrier on 1/cis studied. The results can be shown in Fig. 11. The value of2is 0.9924, which is in good agreement with the Eq. (4). In the same way, another kinetic equation can be developed as below:


Figure 11 Comparison between experimental and theoretical
5 Conclusions
Optimum separation condition of Eu3+in the DCLM system is that the concentration of HCl solution is 4.0 mol·L-1, volume ratio of membrane solution and stripping solution is 30︰30, the concentration of P507 is 0.16 mol·L-1in the dispersion phase, pH value is 4.2 in the feed phase. When initial concentration of Eu3+is 0.8×10-4mol·L-1, the separation effect of Eu3+is very obvious in the optimum condition and the separation percentage of Eu3+is up to 95.3% during the separation time of 130 min.

DCLM, owing to a large number of membrane solution is used in the dispersion phase, can supply the losing carrier of supported liquid membrane. As a result, the separation percentage of Eu3+increases, the stability of membrane is enhanced, and the life span of the membrane is extended.
NOMENCLATURE
surface area of membrane


fdiffusion coefficient of the metal ion in feed phase, m2·s-1
fthickness of diffusion layer between the feed phase and membrane phase, m
mthickness of the membrane, m
[H+] concentration of H+, mol·L-1
[HR] concentration of carrier P507, mol·L-1
1forward reaction rate constant at the left interface of the membrane
-1backward reaction rate constant at the left interface of the membrane
2forward reaction rate constant at the right interface of the membrane
-2backward reaction rate constant at the right interface of the membrane
exextraction equilibrium constant
cpermeability coefficient of metal ion, m·s-1
fvolume of feed phase
fseparation resistance due to diffusion by aqueous feed boundry layer, s·m-1
mseparation resistance due to diffusion through the membrane, s·m-1
porosity of the membrane
tortuosity of the membrane
Subscripts
f feed phase
m membrane phase
s stripping phase
1 Franken, T., “Liquid membranes-academic exercise or industrial separation proces”,.., 85, 6-10 (1997).
2 Gu, Z.M., Wu, Q.F., Zheng, Z.X., Li, Z.Q., Jiang, Y.L., Tang C.J., Lin, P.G., “Laboratory and pilot plant test of yttrium recovery from wastewater by electrostatic pseudo liquid membrane”,..., 93, 137-147 (1994).
3 Gaikwad, A.G., “Synergetic separation of europium through a contained supported liquid membrane using trioctylamine and tributyl phosphate as carriers”,, 63, 917-926 (2004).
4 Zhang, B.C., Gozzelino, G., Baldi, G., “State of art of the research on supported liquid membrane”,..., 20, 46-54 (2000).
5 Li, Q.M., Liu, Q., Li, K.A., Tong, S.Y., “Separation study of cadmium through an emulsion liquid membrane”, Talanta, 44, 657-662 (1997).
6 Bloch, R., Finkelstein, A., “Metal ion separation by dialysis through solvent membrane”,....., 6, 231-237 (1967).
7 Teramoto, M., Matsuyama, H., Yamashiro, T., Okmoto, S., “Separation of ethylene from ethane by a flowing liquid membrane using silver nitrate as a carrier”,..., 45 (3), 115-136 (1989).
8 Fouad, E.A., Bart, H.J., “Emulsion liquid membrane extraction of zinc by a hollow-fiber contact”,..., 307, 156-168 (2008).
9 Sonawane, J.V., Pabby, A.K., Sastre, A.M., “Au(I) extraction by LIX-79/-heptane using the pseudo-emulsion-based hollow-fiber strip dispersion (PEHFSD) technique”,..., 300, 147-155 (2007).
10 Gabelman, A., Hwang, S.T., “Hollow fiber membrane contactors”,..., 159, 61-106 (1999).
11 Basualto, C., Marchese, J., Valenzuela, F., Acosta, A., “Extraction of molybdenum by a supported liquid membrane method”,, 59, 999-1007 (2003).
12 Ho, W.S.W., Wang, B., “Strontium removal by new alkyl phenylphosphonic acids in supported liquid membranes with strip dispersion”,...., 41, 381-388 (2002).
13 Danesi, P.R., Reichley, Y.L., Rickert, P.G., “Lifetime of supported liquid membranes: the influence of interfacial properties, chemical composition and water separation on the long term stability of the membrane”,..., 31, 117-145 (1987).
14 Gu, Z.M., “State of the art and recent progress of liquid membrane separation process”,..., 23, 214-223 (2003).
15 Lin, C., He, G.H., Chen G.H., Tu, Z.H., “Stability of water-in-oil emulsion and its liquid membrane”,....., 18, 224-230 (2004).
16 Neplenbroek, A.M., Bargeman, D., Smolders, C.A., “Supported liquid membranes: instability effects”,..., 67, 121-132 (1992).
17 Neplenbroek, A.M., Bargeman, D., Smolders, C.A., “Mechanism of supported liquid membranes degradation: emulsion formation”,..., 67, 133-148 (1992).
18 Bechiri, O., Ismail, F., Abbessi, M., Samar, M.E.H., “Stability of the emulsion (W/O): application to the extraction of a dawson type heteropolyanion complex in aqueous solution”,..., 52, 895-902 (2008) .
19 Zha, F.F., Fane, A.G., Fell, C.J.D., “Effect of surface tension gradients on stability of supported liquid membranes”,..., 107, 75-86 (1995).
20 Ren, Z.Q., Zhang, W.D., Liu, Y.M., Dai, Y., Cui, C.H., “New liquid membrane technology for simultaneous extraction and stripping of copper(II) from wastewater”,..., 62, 6090-6101 (2007).
21 He, D.S., Luo, X.J., Yang, C.M., Ma, M., Wan, Y., “Study of transport and separation of Zn(II) by a combined supported liquid membrane/strip dispersion process containing D2EHPA in kerosene as the carrier”,, 194, 40-51 (2006).
22 Pei, L., Yao, B., Zhang, C., “Transport of Tm(III) through dispersion supported liquid membrane containing PC-88A in kerosene as the carrier”,..., 65 (2), 220-227 (2009).
23 Pei, L., Yao, B., Fu, X., “Study on transport of Dy(III) by dispersion supported liquid membrane”,.., 27 (3), 447-456 (2009).
24 Kubota, F., Goto, M., Nakashio, F., “Extraction of earth metals with 2-ethylhexyl phosphonic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester in the presence of diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid in aqueous phase”,...., 11, 437-453 (1993).
25 Choi, K.S., Lee, C.H., Kim, J.G., “Separating Ag, B, Cd, Dy, Eu, and Sm in a Gd matrix using 2-ethylhexyl phosphonic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester extraction chromatography for ICP-AES analysi”,, 71, 662-667 (2007).
26 Pei, L., Yao, B., Fu, X., Wang, L., “La(III) transport in dispersion supported liquid membrane including PC-88A as the carrier and HCl solution as the stripping solution”,...., 8 (6), 1041-1050 (2008).
27 Danesi, P.R., Vandegrift, G.F., ”Kinetics and mechanism of the interfacial mass transfer of Eu3+and Am3+in system bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate--dodecane NaCl-HCl-water”,..., 85, 36-46 (1981).
28 Yaftian, M.R., Burgard, M., Dieleman, C.B., Matt, D., “Rare-earth metal-ion separation using a supported liquid membrane mediated by a narrow rim phosphorylated calix(IV) arene”,..., 144 (2), 57-64 (1998).
29 Jyothi, A., Rao, G.N., “Solvent extraction behaviour of lanthanum(III), cerium(III), europium(III), thorium(IV) and uranium(VI) with 3-phenyl-4-benzoyl-5-isoxazolone”,, 37, 431-433 (1990).
30 Kandah, M.I., Meunier, J.L., “Removal of nickel ions from water by multi-walled carbon nanotubes”,..., 146, 283-288 (2007).
31 Chiarizia, R., Castagnola, A., Danesi, P.R., Horwitz, E.P., “Mass transfer rate through solid supported liquid membranes: influence of carrier dimerization and feed metal concentration on membrane permeability”,..., 14 (1), 1-11 (1983).
** To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: pellys_0311@163.com
2010-03-22,
2010-09-11.
the National Natural Science Foundation of China (90401009), the Foundation for Planning Project of West Action of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-XB2-13), the Research Fund for Excellent Doctoral Thesis of Xi’an University of Technology (602-210805).
 Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2011年1期
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2011年1期
- Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Dynamic Simulation and Analysis of Industrial Purified TerephthalicAcid Solvent Dehydration Process*
- Preparation of p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde by Hydrolysis of DiazoniumSalts Using Rotating Packed Bed*
- Liquid-solid Equilibria in Quinary System Na+, K+, Mg2+//Cl-,?at 25 °C*
- Pervaporation Separation of Butanol-Water Mixtures UsingPolydimethylsiloxane/Ceramic Composite Membrane*
- Reaction Kinetics of Biodiesel Synthesis from Waste Oil Using a Carbon-based Solid Acid Catalyst
- Enzyme-catalyzed Synthesis of Vitamin E Succinate Using aChemically Modified Novozym-435*
