Variational quantum semi-supervised classifier based on label propagation
Yan-Yan Hou(侯艷艷), Jian Li(李劍), Xiu-Bo Chen(陳秀波), and Chong-Qiang Ye(葉崇強(qiáng))
1College of Information Science and Engineering,ZaoZhuang University,Zaozhuang 277160,China
2School of Artificial Intelligence,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
3School of Cyberspace Security,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
4Information Security Center,State Key Laboratory Networking and Switching Technology,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
Keywords: semi-supervised learning,variational quantum algorithm,parameterized quantum circuit
1.Introduction
Classification,one of the most common problems in machine learning, is devoted to predicting the labels of new input data based on labeled data.Classification algorithms have been widely applied in image processing,speech recognition,and other fields.With the development of artificial intelligence and cloud computing, data in classification tasks are expanding rapidly.Still,most of them are unlabeled and need to be labeled by experienced annotators in advance.As labeling data is expensive and time-consuming work,[1]researchers began to study how to add unlabeled data into the training set and utilize labeled and unlabeled data to build semi-supervised classifiers.Label propagation,a crucial semi-supervised learning method,predicts the labels of unlabeled data based on graphs.Semi-supervised classifiers based on label propagation pay more attention to the internal relevance of data and have good effects on the classification of multiple correlation data.However, as the scale of data grows, creating a graph requires a higher computational cost.Implementing the semi-supervised classifier based on label propagation becomes a challenging task for classical computers.
Quantum machine learning, the intersection of quantum physics and machine learning,offers potential speed-ups over classical machine learning algorithms.Variational quantum algorithms (VQAs) are the dominant strategy in the noisy intermediate-scale quantum(NISQ)era.It is devoted to building hybrid quantum-classical models, where parameterized quantum circuits construct the cost function of issues, and classical computers train the parameters of quantum circuits by minimizing cost functions.In VQAs,quantum devices focus on classically intractable problems and transfer the problems difficult to implement on quantum devices to classical computers.Therefore, VQAs have lower requirements for quantum resources and have become important methods for implementing quantum machine learning tasks.At present,VQAs have been applied in classification,[2–5]clustering,[6,7]generative models,[8–10]dimensionality reduction,[11–13]etc.
Quantum systems represent data in the Hilbert space of exponential dimension.Inspired by the advantages of quantum systems in processing high-dimensional data,researchers proposed a series of quantum classification algorithms.[14–17]Considering the high computational complexity of kernel computation,Rebentrostt[18]offered a quantum support vector machine (QSVM) algorithm.This algorithm adopted quantum matrix inversion[19]and a density matrix exponentiation method[20]to implement binary classifier tasks,and achieved exponential speed-ups over corresponding classical classifiers under certain conditions.Schuld[21]proposed a quantum distance-based classifier,which only used Hadamard gates and two single-qubit measurements to implement binary classification tasks.Blank[22]designed a quantum kernel classifier based on quantum swap test operation,which is called a swap test classifier.This classifier achieves good classification accuracies in non-linear classification tasks.
The label propagation method predicts labels of unlabeled data by minimizing energy function, which is similar to cost function optimization of VQAs.Inspired by the similarity between VQAs and label propagation,we adopt VQAs to design a quantum label propagation method, and further implement a quantum semi-supervised classifier based on predicted labels.Our work has two main contributions.(i)A variable label propagation method based on locally parameterized quantum circuit is designed for the first time.The locally parameterized quantum circuit can be used to implement VQAs with only some unknown parameters.(ii)A classifier based on hybrid Bell andZbases measurement is designed,and this measurement method reduces circuit depth and is more suitable implemented on NISQ devices.We organize the paper as follows.Section 2 gives a review of classical label propagation.Section 3 outlines the variational quantum label propagation method.Section 4 designs a quantum semi-supervised classifier based on hybrid Bell andZbases measurement.Section 5 verifies the accuracies of label propagation and the semisupervised classifier.Finally,we get a conclusion and discuss future research directions.
2.Review of label propagation
Label propagation begins with mapping a data set into an undirected weight graph, where nodes represent data and edges reflect the similarities between data.If two data have a great similarity, the edge between them has a higher weight;otherwise, the edge has a lower weight.Labeled data propagates their labels to the neighboring unlabeled data based on undirected weight graphs.Since a graph corresponds to a matrix, matrix operations can be used to implement semisupervised learning.LetD={Dl,Du}denote a training data set,including labeled dataDl={(x1,y1),(x2,y2),...,(xl,yl)}and unlabeled dataDu={xl+1,xl+2,...,xl+u},wherexi ∈Rmis theithdata described bymreal-valued attributes andyi ∈{+1,?1}represents the corresponding label.knearest neighbors method is a common method for constructing undirected weight graphsG=(V,E),whereV={xi}i∈nrepresents nodes,E={ei j}i,j∈ndenotes the edges between the nodesxiandxj,andn=l+u.Ifxjis one ofknearest neighbors ofxi,there is an edge between the nodesxiandxj; otherwise, there are no edges.
LetW={wij}i,j∈ndenote the weight matrix of edges,
represents the weight of the edgeei j,whereNk(xi)means the set ofknearest neighbors ofxi.Letf(xi) represent the predicted label ofxi.Similar samples should have similar labels,the more similar the samples, the smaller the difference between the labels,then the energy function of all training data[1]is
wheredi=∑1wijrepresents the sum of theithrow ofWandD=diag(d1,d2,...,dn)denotes the degree matrix.Equation(2)can be rewritten in the matrix form as
wheref= () represents the predicted label vector of all training data.fl= (f(x1),...,f(xl)) andfu=(f(xl+1),...,f(xl+u)) correspond to the label vectors of labeled and unlabeled data,respectively.OnceE(f)obtains the minimum value,f(xi)for labeled data will be equal to the correct labelyi,andf(xi)for unlabeled data will be closest to the correct label.Thus,predicting the labels of unlabeled data can be implemented by solving the optimization problem
whereL=D ?Wis the Laplacian matrix.Figure 1 shows a simple example of label propagation.
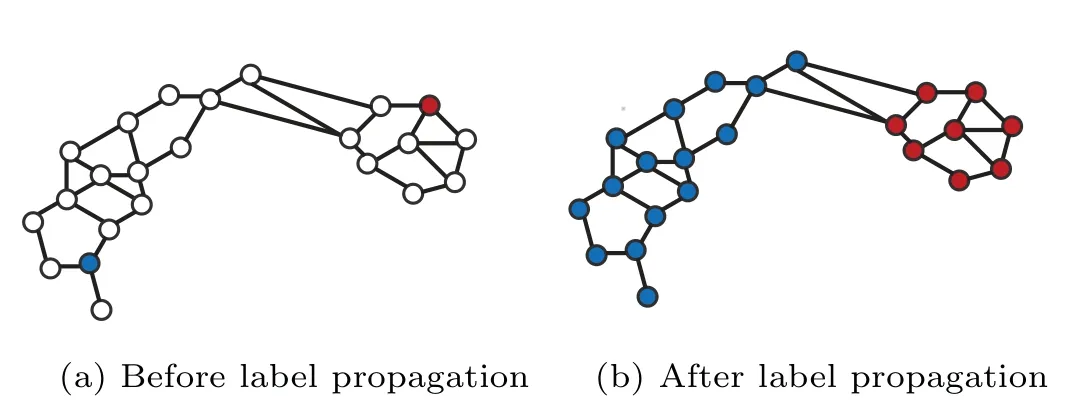
Fig.1.Label propagation.Red nodes represent labeled data belonging to the +1 class.Blue nodes mean labeled data belonging to the ?1 class.White nodes indicate unlabeled data.Panel(a)shows the graph before label propagation.Panel (b) gives the graph after label propagation.After label propagation,labeled data propagate their labels to their neighboring unlabeled data according to the k nearest-neighbors principal.
3.Variational quantum label propagation method
In this section, we reformulate the original label propagation and design a variational quantum label propagation(VQLP) method according to the similarity between the energy functionE(f)and cost functions of VQAs.
3.1.Reformulation of label propagation
3.2.The overall structure of the VQLP algorithm
The VQLP algorithm adopts an iterative optimization method to predict the optimal label vector.In each iteration,the work includes evaluation cost function, learning parameters, and predicting label vectors.Figure 2 shows the overall structure of the VQLP algorithm.In the first stage, the state|ψ〉for the incidence matrixBis prepared by conditionally accessing the state of weight matrixW.The label vector|?f(θ)〉 represents labels of labeled data and unlabeled data.As only the labels of unlabeled data are unknown,we design a locally parameterized quantum circuitV(θ)to build the label vector|?f(θ)〉.After preparing|ψ〉and|?f(θ)〉,a hybrid Bell andZbases measurement,called asU2,is applied on|ψ〉and|?f(θ)〉 to construct the cost functionC(θ).The label vector|?f(θ)〉based on initial parameters may not correspond to the correct labels of training data.Thus, the second work is to search for the optimal label vector.The cost function valueC(θ)is transmitted to a classical optimizer and minimized by tuning the parametersθ.OnceC(θ)reaches the maximum iteration numberτor is less than the specified error thresholdετ,the optimal parametersθ?are gotten.V(θ)consists of parameterized quantum circuit for building labels of unlabeled data and unparameterized quantum circuit for building labels of labeled data.In the third stage,parameterized quantum circuitV′(θ?) (partial circuit ofV(θ)) acts on the initial state|0〉 to construct the label vector|?u(θ?)〉 for unlabeled data.Algorithm 1 shows the outline of the VQLP algorithm.
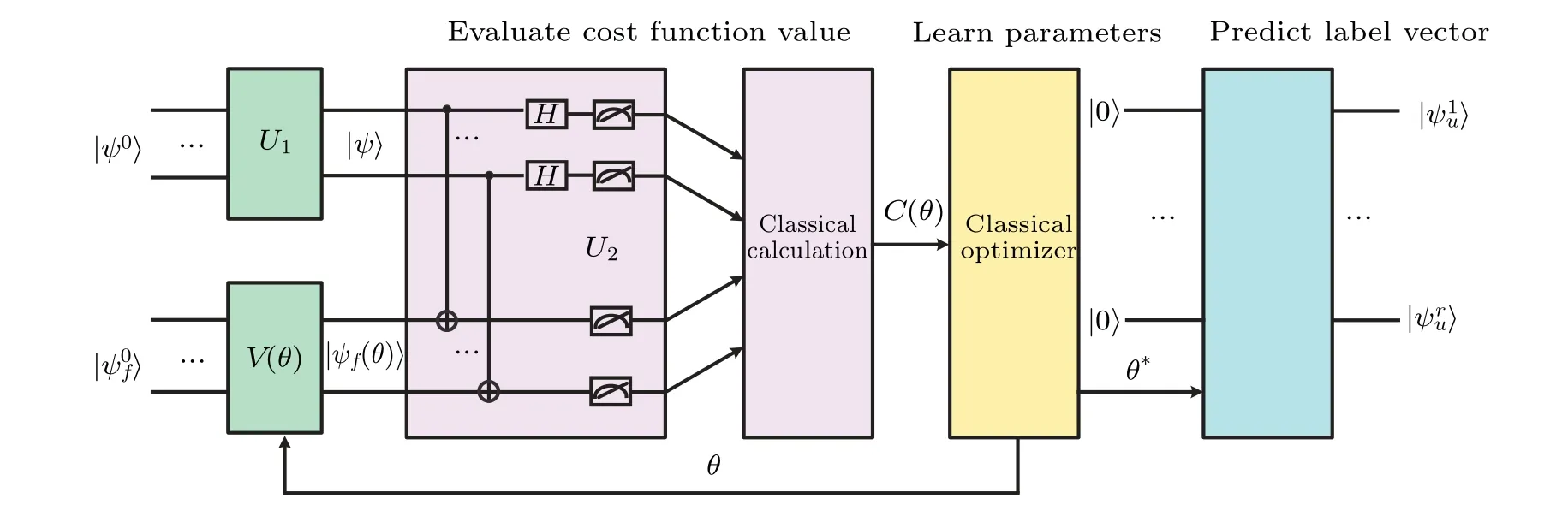
Fig.2.The overall structure of the VQLP algorithm. U1 acts on the initial state|ψ0〉to construct the state|ψ〉of the incidence matrixB.The parameterized quantum circuit V(θ)acts on the initial state|?0f〉to produce the state|?f(θ)〉of the label vector f.Cost function C(θ)is gotten by performing the unitary operation U2 followed by classical post-processing,where U2 is responsible for computing the Hibert–Schmidt inner product between |ψ〉 and |?f(θ)〉.In each iteration, the classical computer minimizes C(θ) to get the optimized parameters θ.Once the optimal parameter θ?is obtained,the ansatz V′(θ?)acts on the state|0···0〉r to build the label vector|?u(θ?)〉=|···〉for unlabeled data,where|?iu〉represents the ith qubit of|?u(θ?)〉.

Algorithm 1 Variational quantum label propagation(VQLP)algorithm
3.3.Construct normalized incidence matrix
In this subsection, our primary work is to construct the state|ψ〉 for the normalized incidence matrixB.To compensate for scaling effects, we firstly standardize all training data to zero mean and unit variance, then normalize them into unit vectors.represent the amplitude encoding of the training dataxp, where|·| representsl2-norm andxp jmeans thejthelement ofxp.Reference [28] proposed a quantum algorithm for estimating Euclidean distances between quantum states, and this algorithm corresponds to a mapping|p〉|q〉|0〉|p〉|q〉|d2(φxp,φxq)〉,whered2(φxp,φxq) =|φxp ?φxq|2represents the square of the Euclidean distance between|φxp〉 and|φxq〉.The first work of constructing incidence matrix is to prepare the weight matrixWby theknearest-neighbor method.To implement this work, we prepare the superposition stateof Euclidean distances between|φxp〉 and|φxq〉, and searchkminimum of|d2(xp,xq)〉 by the minimum search method.After searchingkminimum values of all training data,the state
for weight matrixWis constructed, wherewpqdescribes the neighbor relationship betweenxpandxq.Ifxqis one ofknearest neighbors ofxqorxpis one ofknearest neighbors ofxq,wpq=1;otherwise,wpq=0.
According to Eq.(15), the elements of incidence matrixBcome fromW.The second work is to build the state|ψ〉for the incidence matrixBbased on|ψW〉.We prepare the state
as input,where register 1 stores the indexes of nodes,and registers 2 and 3 store the indexes ofwpq.Registers 4, 5, and 6 with initial value|0〉|0〉|0〉will store comparison results.The specific steps of building the incidence matrixBare as follows.
(1) Do comparison operation (UC)[28]on registers 2 and 3, where the comparison result is stored in registers 4 and 6,and yield the state
Measure register 6 withZbasis, if the measurement result is 0,then get the state
(2)Extract the elements of the incidence matrixB.Equality comparison is firstly applied on registers 1 and 2.If registers 1 and 2 have the same value, register 5 is set to|1〉.If register 5 is still|0〉after performing the equality comparison,another equality comparison is performed on registers 1 and 3.If registers 1 and 3 have the same value,register 4 is set to|1〉.Through two equality comparisons,we get the state
(3)Perform CNOT operation on registers 5 and 4,where register 4 serves as control register, then measure register 5 withZbasis.If the measurement result is 1,the state
(4) Act Hadamard operation on register 4, then measure it into|1〉.The system yields the state
corresponding to the normalized incidence matrixB.Figure 3 shows the circuit implementation,and this circuit corresponds to the moduleU1in Fig.1.
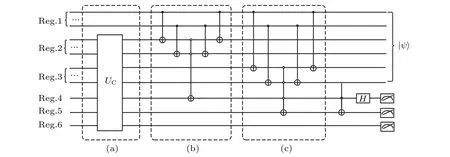
Fig.3.Circuit of constructing the incidence matrix.Reg.1–Reg.6 represent registers 1–6.The circuit in the dotted box (a) represents the comparison operation.The circuit in the dotted box (b) represents the equality comparison between Reg.1 and Reg.2, and the circuit in the dotted box(c)denotes the equality comparison between Reg.1 and Reg.3.The output state|ψ〉corresponds to the incidence matrixB.
3.4.Build label vector
In this subsection, our primary work is to build the state|?f(θ)〉of the predicted label vectorf=(fl,fu).As the correct label vector(y1,...,yl)of labeled data is known,the predicted label vectorfldoes not need to be updated in the optimization process.be the amplitude encoding offl, whereyi ∈{+1,?1}.As the predicted label vectorfuis unknown,we adopt parameterized quantum circuit(ansatz)to prepare the state
is gotten.In general, the number of unlabeled data is not less than the number of labeled data in semi-supervised learning.To make two terms of|(θ)〉meet a particular proportion, the controlled rotation operationRy(2α) is applied on added register 9 conditional on register 8 being|1〉, where.This operation yields the state
Subsequently,measure register 9 with theZbasis,if the measurement result is 0,get the state
whereyi ∈{+1,?1}andAs register 8 is redundant, apply Hadamard operation on register 8 followed by measuring it withZbasis, if the measurement result is 0,finally,get the state
where the amplitude of|?f(θ)〉is proportional to the predicted label vectorf.Figure 4 shows the circuit of constructing|?f(θ)〉, whereUlandV′(θ) are used to build the labels for labeled and unlabeled data,respectively.As part of the circuit is parameterized,the circuit is called as locally parameterized quantum circuit,corresponding to the moduleV(θ)of Fig.1.
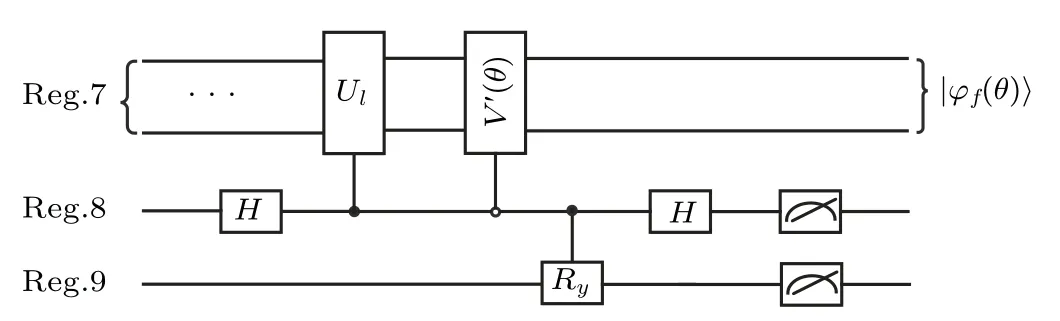
Fig.4.Circuit of constructing the label vector|?f(θ)〉.Reg.7, Reg.8,and Reg.9 represent registers 7,8,and 9,respectively. Ul means quantum access to labeled vector|?l〉,and V′(θ)is the parameterized quantum circuit for building|?u(θ)〉.
Many ansatzes can be used to implementV′(θ).Hardware-efficient ansatz uses lower circuit depth and fewer parameters to represent the solution space of problems,[29,30]and we adopt this ansatz to buildV′(θ).Hardware-efficient ansatz adopts a layered layout.Each layer consists of multiple 2-qubit unitary modules,where e?iHμrepresents 1-qubit parameterized gate,Hμis Hermitian operator, andWμrepresents unparameterized gate.Usually,the unitary moduleV(θik)includes multiple 1-qubit parameterized gates, thenθik={,,...,,...}.In the parameters optimization process,the error of|?u(θ?)〉decreases exponentially with the layers of the ansatzV′(θ?) increasing.To get the exact number of layers, we first prepare the ansatz with fewer layers and gradually increase the layers until the ansatz satisfies the specified error tolerance.[31]With increased data scale, Hardware-efficient ansatz shows an exponentially vanishing gradient(barren plateau).The VQLP algorithm adopts the alternating layered layout to solve the barren plateau problem.In this layout, the entangled gates in each layer only act on local qubits,[32]and the cost function is the combination of local functions, so the ansatz uses shallower circuit depth to solve the vanishing gradient problem.Figure 5 shows the circuit implementation,whereandWμare implemented by by rotationRyand CNOT,respectively.
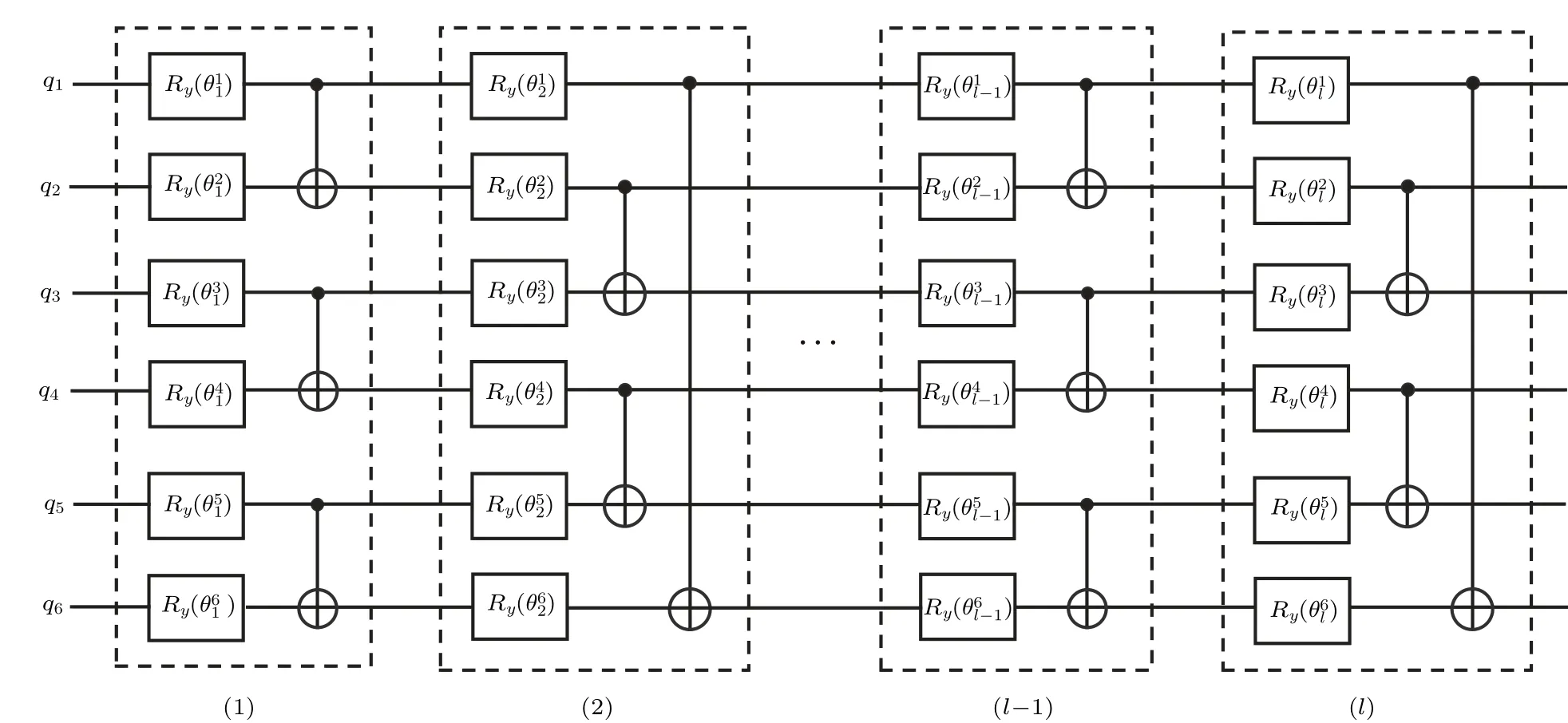
Fig.5.Parameterized quantum circuit V′(θ)(6-qubit input).This circuit includes l layers,where{q1,....,q6}represents the qubit sequence of |?u(θ)〉.The ith dashed box indicates the unitary operation in the ith layer.Each layer is composed of multiple unitary modules (θ j i ),consisting of single qubit rotations Ry(θ j i )and CNOT gates acting on neighboring qubit pairs.The circuit uses alternating layered layout,and unitary modules of adjacent layers act on alternating qubit pairs.
3.5.Compute cost function
After getting the incidence matrix|ψ〉and the label vector|?f(θ)〉,the sequent work is to compute the cost functionC(θ).According toρ1=tr2,3(ρ),the cost function in Eq.(7)can be rewritten as
which is the Hilbert–Schmidt inner product between|?f(θ)〉and|ψ〉.We adopt the Bell basis measurement method[33]to compute the cost functionC(θ).As|?f(θ)〉is stored in register 7 and|ψ〉is stored in registers 1,2,and 3,Eq.(21)is equal to?→c=(1,1,1,?1)?gdenote the post-processing vector of Bell basis measurement, and the cost function value can be computed byC(θ)=·.
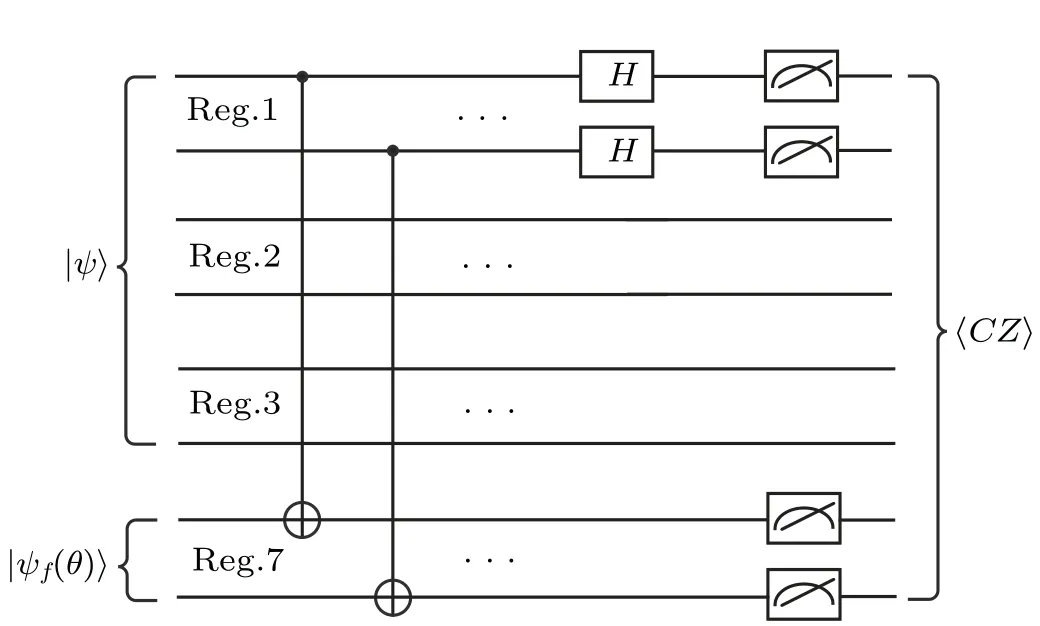
Fig.6.The circuit of computing the cost function C(θ).Reg.1, Reg.2,and Reg.3 store the incidence matrix |ψ〉, and Reg.6 stores the label vector |?f(θ)〉.Perform CNOT operation on registers 1 and 7, followed by Hadamard on register 7.After measuring the 2-qubit operator CZ on registers 1 and 7,the expectation value〈CZ〉1,7,corresponding to the cost function value C(θ),can be obtained by further classical computation.
4.Semi-supervised binary classifier
Quantum label propagation gets the labels of unlabeled data in training data set.In this section, we design a quantum semi-supervised binary classifier based on all training data.Let|φxi〉 represent training data, wherei ∈{1,...,n}andn=l+u.Ifi ∈{1,...,l},|φxi〉 represents labeled data;otherwise,|φxi〉 denotes unlabeled data.f′={f′1,f′2,...,f′n}denotes the predicted label vector got by label propagation,wheref′i=0 meansxibelonging to the +1 class andf′i=1 representsxibelonging to the?1 class.Let|φx?〉be test data,andk?i=|〈φx?|φxi〉|2represents the overlap between|φx?〉and|φxi〉.We adopt the weighted sum of overlaps between test and training data to predict the label
for the test data|φx?〉, wherec1andc2are the weight coefficients determined by the importance of labeled and unlabeled data.In semi-supervised learning,labeled data is more important than unlabeled data,thenc1>c2.
Quantum swap test operation can be used to compute|〈φx?|φxi〉|2, so it is also applied to predict the labelf?.However,this method needs multiple Toffoli gates,and the circuit has a higher depth as input qubits increase.Thus,implementing the classifier based on quantum swap test operation is not easy for current quantum devices.The Bell basis measurement method[33]is a novel method for computing the overlap of quantum states, which has a shallower circuit depth and is easy to implement on NISQ devices.Inspired by this method,we design a hybrid Bell andZbases measurement method to buildf?.
Given the superposition state
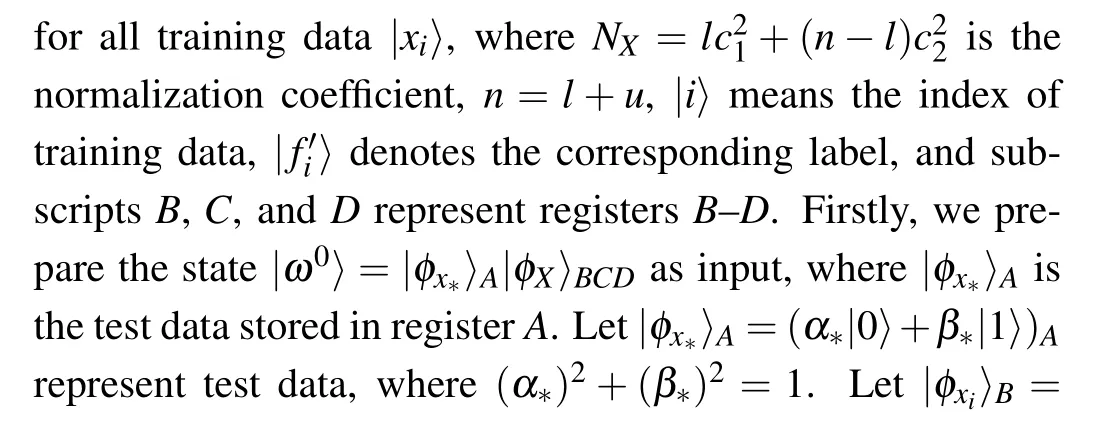

(1)Perform CNOT operation on registersAandB,where registerAserves as control register,then get the state
(2)Apply Hadamard operation on registerAand get
Through the first two steps, quantum state overlaps have been stored in the amplitudes of|ω2〉〈ω2|.
(3)Measure the expectation value of controlled-Zoperator for registersAandBandσZoperator for registerD,and this operation can be written as〈ω2|CZABσDZ|ω2〉, whereCZABdenotes controlled-Zoperator on registersAandB, andσDZdenotesσZoperator on registerD.AsCZAB=(|00〉〈00|+|01〉〈01|+|10〉〈10|?|11〉〈11|)ABandσDZ=(|0〉〈0|?|1〉〈1|)D,the expectation value is
where the superscriptsABDof operators are omitted for simplicity.When=0,registerDis|0〉;when=1,registerDis|1〉.According to the two values of registerD,Eq.(27)can be rewritten as
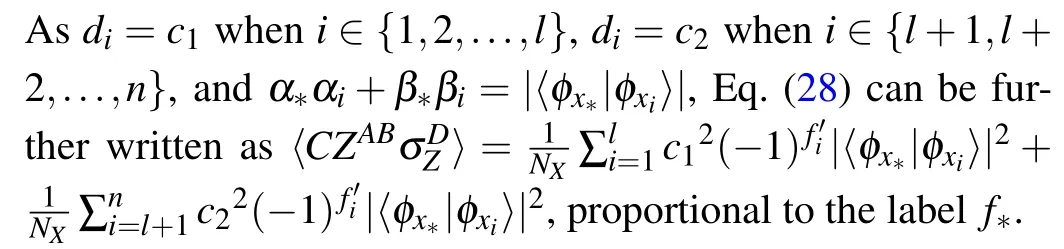
Quantum swap test can be used to compute the overlap between two quantum states withnqubits, where the qubits that form states can be entangled.According to the circuit equivalence of the Bell basis measurement and quantum swap test,[22]the Bell basis measurement in the quantum semisupervised classifier can be generalized to compute the overlap between|φx?〉A(chǔ)and|φxi〉Bwithnqubits.Figure 7 shows the circuit implementation.

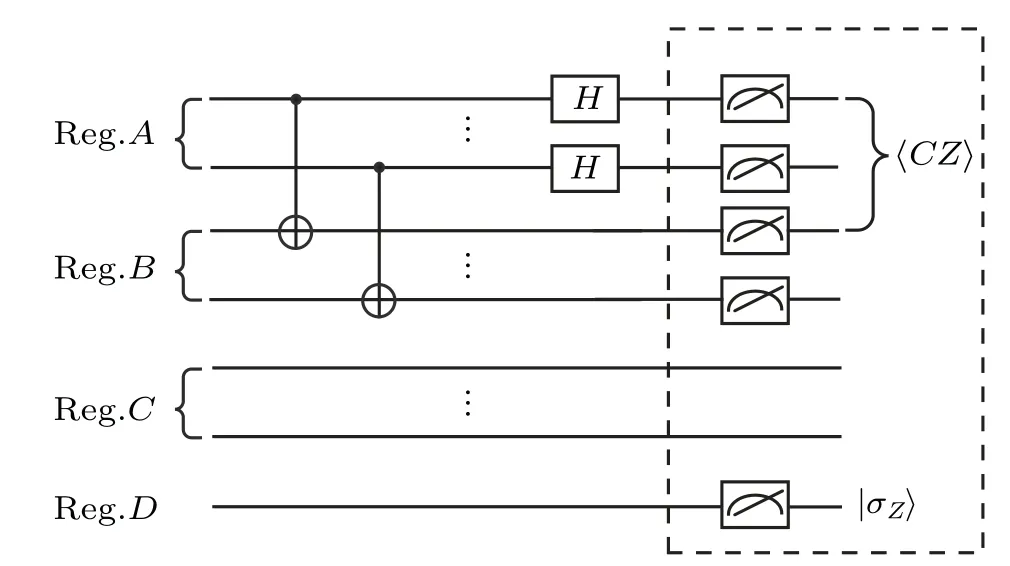
Fig.7.The circuit of the semi-supervised binary classifier.Reg.A stores|φx?〉.Reg.B, Reg.C, and Reg.D store |φxi〉, the index |i〉, and the corresponding label |fi〉, respectively.CNOT is performed on registers A and B, followed by Hadamard operation acts on register A.The label vector f?is gotten by measuring the expectation value of controlled-Z operator for registers A,B,and the expectation value of σZ operator for register D.
The quantum semi-supervised classifier based on the hybrid Bell andZbases measurement, shown in Fig.7, contains two layers.CNOT gates implement the first layer, and Hadamard gates implement the second layer.As CNOT gates act on different qubits, all CNOT gates can be executed in parallel.Similarly, Hadamard gates act on different qubits and can also be performed in parallel.No matter how many qubits of training or test data contains, the quantum semisupervised classifier based on hybrid Bell andZbases measurement needs only two layers,independent of the size of the classification problem.According to the method proposed in Ref.[24], the quantum semi-supervised classifier can also be implemented by swap test operation,shown in Fig.8.This circuit requires multiple CNOT and Toffoli gates, which cannot be implemented in parallel.One Toffoli gate requires multiple one-qubit and two-qubit gates to implement.Figure 9 shows Toffoli gate decomposition, where the Toffoli gate is implemented with CNOT, Hadamard,T, andT?gates.The quantum semi-supervised classifier based on the swap test operation needs 14 layers when training data or test data contains one qubit and 14mlayers when training data or test data hasmqubits.The circuit depth is linear with the size of the classification problem.Compared with the quantum semi-supervised classifier based on swap test operation,our proposed quantum semi-supervised classifier is more suitable for implementation on near-term quantum devices.
The quantum semi-supervised classifier based on hybrid Bell andZbases measurement requires more complex classical post-processing operations, which scale linearly with the system sizel.From the realization difficulty, the classical post-processing with higher complexity is more easily implemented than the quantum circuit whose depth scales linearly withl.The speed-up of the quantum semi-supervised classifier does not come from transmitting the exponential complexity work to the classical computer but from parallel quantum operations.To reduce the complexity of classical post-processing,we can convert the complex classical post-processing into quantum operations.Figure 10 shows the circuit implementation.This circuit adds an ancilla register and Toffoli gates,and the expectation value ofσZoperator for the ancilla register replaces the expectation value of the controlled-Zoperator for registersAandB.Compared with the circuit in Fig.7.This circuit has a higher depth but simpler classical post-processing.
Fig.10.The quantum semi-supervised binary classifier with simplified classical post processing.Compared with circuit Fig.7, this circuit converts the complex classical post-processing of the semi-supervised binary classifier into the quantum operation, where f?is obtained by measuring the expectation value of the σZ operator for the ancilla register(|0〉)and register D.The circuit in the dashed box has the same function as that in Fig.7.
5.Numerical simulations and performance analysis
In this section, we adopt the Iris dataset to test the performances of the quantum semi-supervised binary classifier based on hybrid Bell andZbases.The Iris dataset contains 150 samples, where samples 0–49 belong to class 1, samples 50–99 belong to class 2, and samples 100–149 belong to class 3.Classifying samples of classes 2 and 3 is the most difficult task for the Iris dataset, and we mainly analyze this task.We first choose 8 samples{x0,x1,x2,x3,x4,x5,x6,x7}to demonstrate label propagation,where samples{x0,x2,x4,x6}belong to class 2 and samples{x1,x3,x5,x7}belong to class 3.Let samples{x0,x1,x2,x3}represent labeled data.Assume the labels of samples{x4,x5,x6,x7}are unlabeled data, label propagation is to predict the labels of samples{x4,x5,x6,x7}.If the samplexibelongs to class 2, the labelyiis 1, and if the samplexibelongs to class 3, the labelyiis?1.Figure 11 shows the predicted labels of samples{x4,x5,x6,x7}.Simulation results show that the predicted labelf(xi)is close to the correct labelyi.represent the correct normalized label vector for samples{x4,x5,x6,x7},L=[f(x4),f(x5),f(x6),f(x7)] represents the predicted label vector,andS=L·LTdenotes the accuracy of the predicted labels.Figure 12 exhibits the accuracySunder different initial parameters.We can find that the accuracySreaches 99.5%after about 90 iterations regardless of the initial parameters.
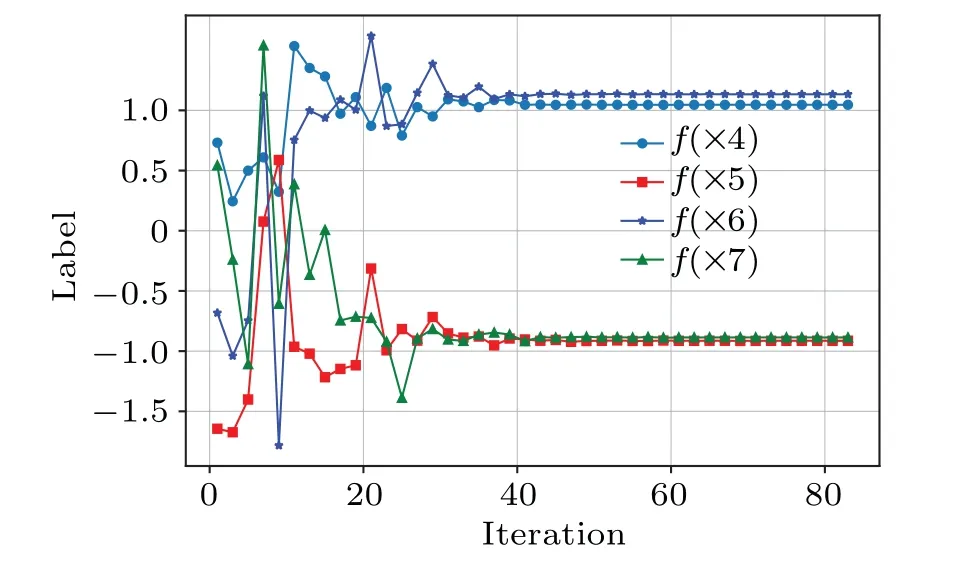
Fig.11.Predicted labels versus the number of iterations.The classical optimizer is the COBYLA method.Curves represent the estimated labels of unlabeled data.

Fig.12.Accuracy versus the number of iterations.Curves represent the accuracies under four different random initialized parameters.
Our second work is to demonstrate the accuracy of the semi-supervised binary classifier.Figure 13 presents the result for classifying samples of classes 1 and 2,where the predicted label greater than 0 represents the sample belonging to class 1;otherwise,the sample belongs to class 2.The result shows all samples of classes 1 and 2 can be correctly classified.Figure 14 shows the result for classifying samples of classes 1 and 3,where all samples can be correctly classified.Figure 15 shows the classification result of classifying samples of classes 2 and 3.As samples of classes 2 and 3 are not linearly separable,a few classification errors occurred in this task.

Fig.13.Classification results of semi-supervised binary classifier(classes 1 and 2).The horizontal axis represents the index i of samples,and the vertical axis shows the predicted label f(xi).Stars represent samples from class 1,and dots represent samples from class 2.
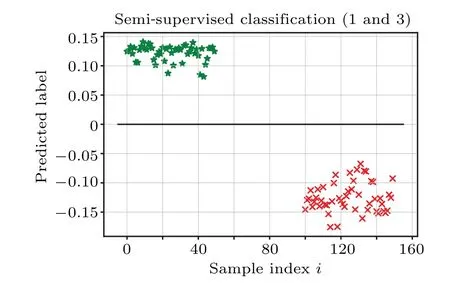
Fig.14.Classification results of semi-supervised binary classifier(classes 1 and 3).Stars represent samples from class 1, and crosses represent samples from class 3.

Fig.15.Classification results of semi-supervised binary classifier(classes 2 and 3).Dots represent samples from class 2, and crosses represent samples from class 3.
Table 1 shows mean accuracies and standard deviations for the quantum semi-supervised binary classifier based on Bell andZbases(semi-supervised classifier)and the quantum classifier based on swap test operation(swap test classifier)[22]under 10 random initial parameters, where each sample only contains two features.The cells of the format±m(xù)ean accuracy (standard deviation).For the semi-supervised classifier,the mean accuracy of classifying classes 1 and 2 is 100%,and the mean accuracy is also 100%for classifying classes 1 and 3.The mean accuracy of classifying classes 2 and 3 is 90.90%.Still, this accuracy of the semi-supervised classifier is higher than that of the swap test classifier.
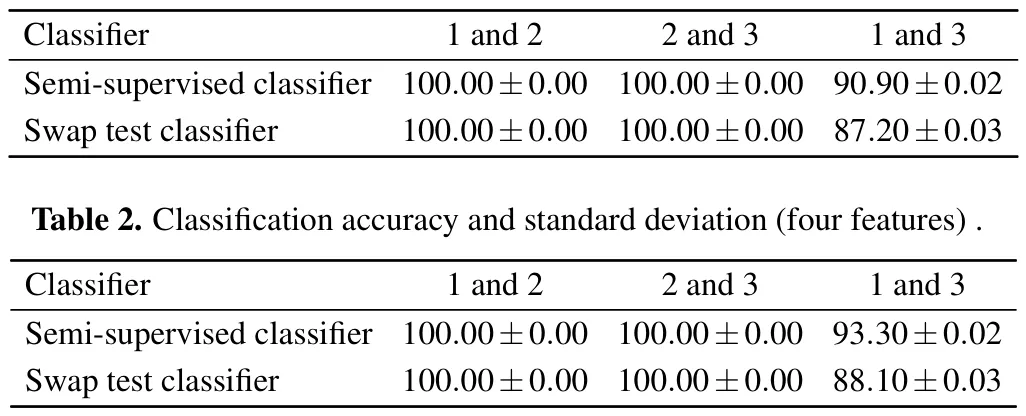
Table 1.Classification accuracy and standard deviation(two features).
To improve the separability of classes 2 and 3,we extract four features from the Iris dataset.Table 2 shows mean accuracies and standard deviations for samples containing four features.Compared with Tables 1 and 2,we can find that classifying the Iris dataset containing four features has higher accuracy than classifying the Iris dataset containing two features.
6.Conclusions and future work
In this paper, we adopt a quantum method to implement a quantum semi-supervised binary classifier.By converting the incidence matrix and label vector into quantum states,we design a variational quantum label propagation (VQLP)method.This method utilizes locally parameterized quantum circuits to reduce parameters required in the optimization and is more suitable for implementation on quantum devices.Based on the predicted labels, we further design a quantum semi-supervised classifier based on hybrid Bell andZbases measurement, which has a shallower circuit depth compared with the swap test classifier.Simulation results show that the VQLP method can predict the labels of unlabeled data with 99.5% accuracy, and the quantum semi-supervised classifier has higher classification accuracy than the swap test classifier.This algorithm assumes quantum operations under noiseless environments.However,hardware noise exists when the semisupervised learning algorithms are implemented on near-term quantum devices.The quantum semi-supervised classifier under noise environments needs to be researched in future work.Besides,we can further investigate how to adopt multiple data copies to build quantum semi-supervised classifiers based on kernel functions.The design method of theknearest neighbor graph in VQLP provides a novel idea for creating quantum machine learning models based on graphs.Simultaneously,this research promotes the development of VQAs in quantum semi-supervised learning fields.
Acknowledgements
Project supported by the Open Fund of Advanced Cryptography and System Security Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Grant No.SKLACSS-202108), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.U162271070),Scientific Research Fund of Zaozhuang University (Grant No.102061901).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- First-principles calculations of high pressure and temperature properties of Fe7C3
- Monte Carlo calculation of the exposure of Chinese female astronauts to earth’s trapped radiation on board the Chinese Space Station
- Optimization of communication topology for persistent formation in case of communication faults
- Energy conversion materials for the space solar power station
- Stability of connected and automated vehicles platoon considering communications failures
- Lightweight and highly robust memristor-based hybrid neural networks for electroencephalogram signal processing