Effects of Low Anisotropy on Generalized Ghost Dark Energy in Galileon Gravity
H.Hossienkhani, V.Fayaz, A.Jafari, and H.Youse fi
1Department of Physics,Hamedan Branch,Islamic Azad University,Hamedan,Iran
2Department of Science,Hamedan University of Technology,Hamedan 65155,Iran
1 Introduction
The verification of the late-time acceleration of the universe(see Ref.[1]for a detailed discussion of the recent astronomical observations)has led to extensive research towards its explanation.This result is based on fitting a Friedman-Robertson-Walker type geometry,together with the corresponding cosmology,to the existing astronomical data.However,by taking into account the present day astronomical observational information,at this stage,the only model independent conclusion is that the observations do favor the pressureless Einstein-de Sitter model.According to recent observational data sets,[2?3]our current universe is flat and undergoing a phase of the accelerated expansion,which started about five billion years ago.In principle,this phenomenon can be explained by either dark energy(DE)(see,e.g.,Ref.[4]),in which the reason of this phenomenon is due to an exotic component with large negative pressure,or modified theories of gravity.[5]DE is believed to dominate the mass-energy budget of the universe,it violates the strong energy conditions and it can cluster at the largest accessible scale.But,aside from these two features,nothing is known for certain about the nature of DE,which has become a matter of intense debate.[6]Although the nature of neither dark matter(DM)nor DE is currently known,it is felt that both DM and DE are non-baryonic in origin,and that DM is distinguished from DE by the fact that the former clusters on sub-Megaparsec scales.Indeed,the need for DM was originally pointed out by Zwicky[7]who realized that the velocities of individual galaxies located within the Coma cluster were quite large,and that this cluster would be gravitationally bound only if its total mass substantially exceeded the sum of the masses of its component galaxies.Several independent techniques like cluster mass-to-light ratios[8]baryon densities in clusters[9]weak lensing of clusters[10]and the existence of massive clusters at high redshift[11]have been used to obtain a handle on DM.On larger scales,evidence for DM in clusters comes from gravitational lensing,[12]virial analyses,[13]or X-ray halos of hot gas.[14]Wang and Steinhardt[15]first argued that the cluster abundance can be used to probe the properties of DE,and Haiman et al.[16]showed that a survey with several thousand clusters can yield precise statistical constraints on both the DE densities and the equation of state.Since then,a series of papers has focused on the prospects of high yield cluster surveys as probes of DE model.[17]These papers also show that constraints from cluster surveys will be complimentary to those from cosmic microwave background(CMB)anisotropy and SNe Ia distance measurements.Thus far,the most successful candidate for DE is the cosmological constant Λ,which together with cold dark matter(CDM)and radiation form the standard cosmological model,ΛCDM.Besides the conventional choice of the cosmological constant,a good number of DE candidates,such as quintessence,kessence,phantom,tachyon,and Ricci DE,have been proposed in recent years to handle the issue of late time cosmic acceleration.[18?31]
Recently the so-called QCD ghost DE(GDE)has been proposed in Refs.[32]–[34].The Veneziano ghost field plays a crucial role in the resolution of the U(1)a problem in QCD.[35]One clarification is that there are some DE models where the ghost plays the role of DE(see,e.g.,Ref.[36])and becomes a real propagating physical degree of freedom subjected to some severe constraints.In Ref.[37],the author discussed that the contribution of the Veneziano QCD ghost field to the vacuum energy is not exactly of order H and a subleading term H2appears due to the fact that the vacuum expectation value of the energy-momentum tensor is conserved in isolation.[38]It was argued that the vacuum energy of the ghost field can be written as H+O(H2),where the subleading term H2in the GDE model might play a crucial role in the early stage of the universe evolution,acting as the early DE.[39]It was investigated the GGDE model in the framework of Brans-Dicke cosmology in Ref.[40].There has been a lot of interest in recent years in establishing a connection between DE and scalar field models.[41]
Scalar-tensor theories of gravity have experienced a resurgence of sorts,over the last twenty years.This is due in part to string theory,where the plethora of compactification moduli generically appear in the 4D effective theory with kinetic mixing with the graviton.Moreover,the discovery of accelerated expansion makes the possibility that General Relativity is modified on the largest scales plausible.The simplest model of a scalar-tensor theory is due to Brans and Dicke(BD).[42]But an interesting scalar field,“Galileon”,theory,[43]inspired by the decoupling limit of the Dvali-Gabadadze-Porrati(DGP)model[44]and its cosmological consequences,[45]was introduced.The self-interacting solution for Galileon gravity has been constructed in Ref.[46].Recently,Jamil et al.[47]and Ranjit et al.[48]have studied the observational constraints of some parameters in Galileon gravity.Also,Biswas and Debnath[49]have discussed the GGDE in Galileon gravity.All the above reasons motivate us to investigate the GGDE model with subleading term H2in the framework of FRW universe.
It is natural to assume that the geometry at very early epoch more general than just the isotropic and homogeneous FRW.Although the universe,on large scale,seems homogeneous and isotropic at present,there is no observational data that guarantees the isotropy in an era prior to the recombination.In fact,it is possible to begin with an anisotropic universe,which isotropizes during its evolution.Fayaz et al.[50]discussed the perfect fluid and DE with time varying G and Λ in an anisotropic universe.We investigate the general theory of Galileon gravity about a Bianchi I(BI)background spacetime.We will try to generalize the work in Ref.[49]in order to obtain a general and we reconstructed field equations in the BI anisotropic space.Recently,Hossienkhani et al.[51]investigated the various DE models in a sense of BI model by considering a Brans-Dicke framework in,which there is a non-minimal coupling between the scalar field.Consequently,it would be worthwhile to explore anisotropic DE models in the context of Galileon theory.
In this work,we have obtained some accelerating models in the framework of the Galileon gravity for an anisotropic BI universe.For this purpose,we consider theflat anisotropy BI universe.The arrangement for the paper is as follows.In Sec.2,we provide the preliminary formalism for Galileon gravity.The exact solutions of thefield equations are derived for an anisotropic BI universe in Sec.3.In Sec.4,we consider the GGDE model in the framework of Galileon gravity and we reconstruct the BI field equations of the GGDE model,which describes accelerated expansion.We obtain numerical solutions in Sec.5.Conclusions and discussions on our work are given in the last section.
2 A Brief Galileon Gravity
The Galileon gravity is described by the action[43,46,52?53]
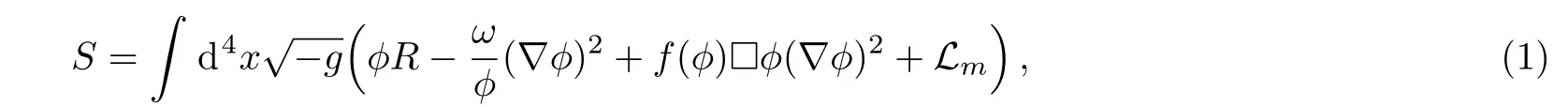
where R is the Ricci scalar curvature,? is the Galileon field and the coupling f(?)has dimension of length,(??)2=gμν?μ??ν?,?? =gμν?μ?ν?,and Lmstands for the matter Lagrangian.The matter Lagrangian does not depend on the Galileon field ?.The Einstein and field equations are given by[46,52]
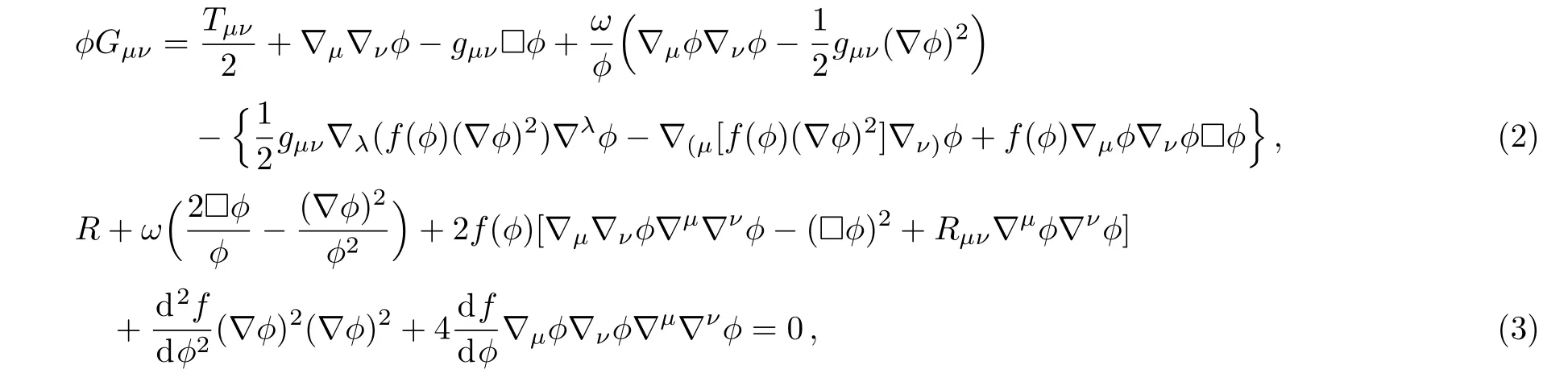
where Tμνis the energy-momentum tensor for matter.For the case of ω =0 and f(?)=r2M2p/?3(where Mpis the Planck scale and r is the crossover scale),the model reduces to the DGP braneworld.[54]
3 Background Anisotropy Cosmology
Recently,the existence of anisotropy at the early times is a natural phenomenon for investigation,based on theoretical arguments and observational data.Therefore,it considers models of a universe with an initially anisotropic background.The anisotropic Bianchi models may provide an adequate description of anisotropic phase in the history of the universe.The simplest models of the anisotropic universe are the BI model,which spatial sections are flat,but the scale factors are different in each direction.
The anisotropic BI geometry is described by
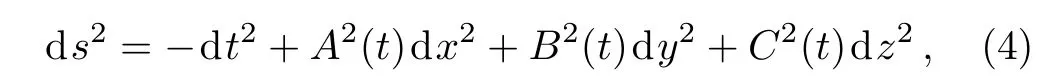
where A(t),B(t),and C(t)are the scale factors for each of the three spatial directions.It reduces to the FRW case when A(t)=B(t)=C(t)=a(t).Given this metric the connection components are
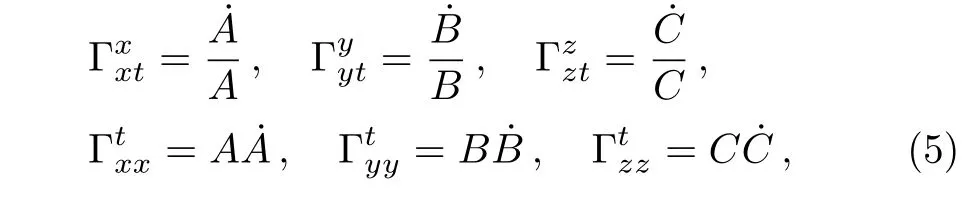
where the over dot on the scale factors denotes differentiation with respect to time t.Now,we assume that the universe is filled with isotropic fluid i.e.,px=py=pz.In presence of anisotropy,the Einstein and field equations,Eqs.(2)and(3)give
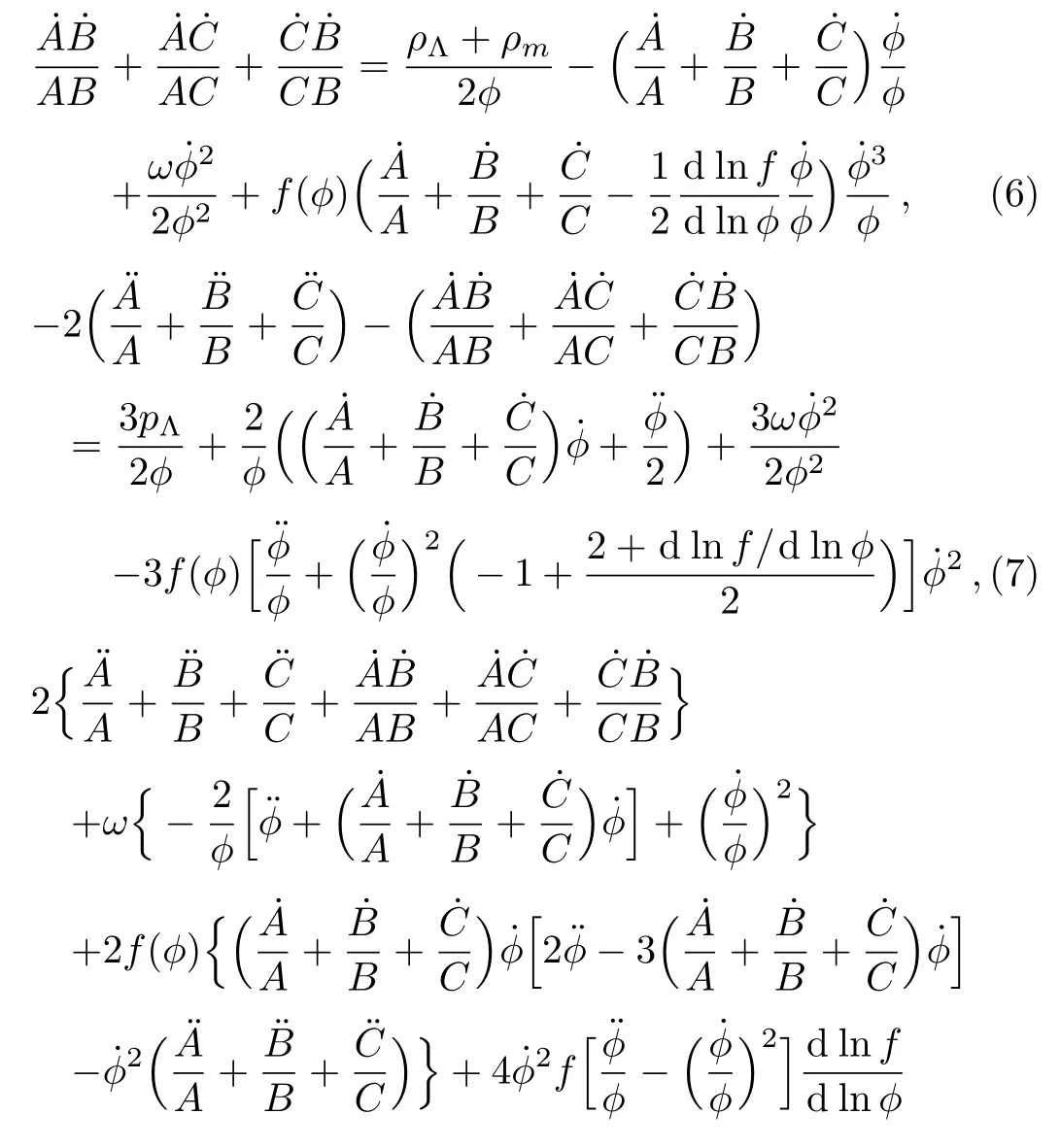
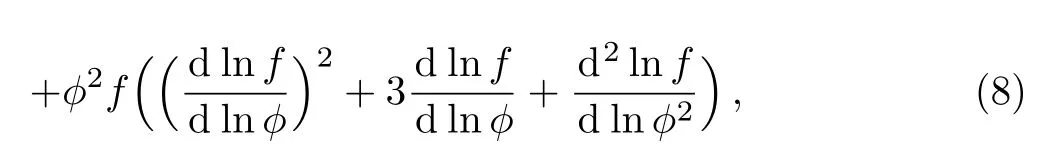
where ρΛand pΛare respectively,the energy density and pressure of DE.Defining the time-like hyper surfaceorthogonal vector u= ?/?t,we can define the generalized mean Hubble’s parameter,H,and the shear,σμν,as follows:
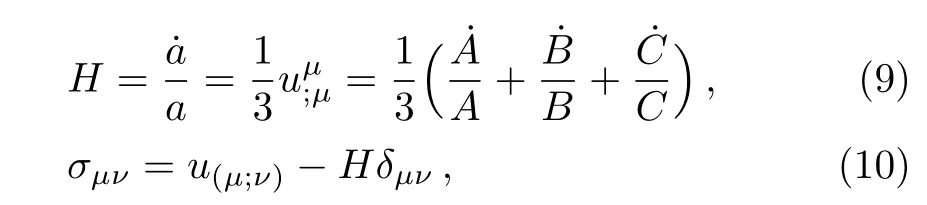
where a=(ABC)1/3is the mean scale factor.The corresponding shear scalar and Ricci scalar become
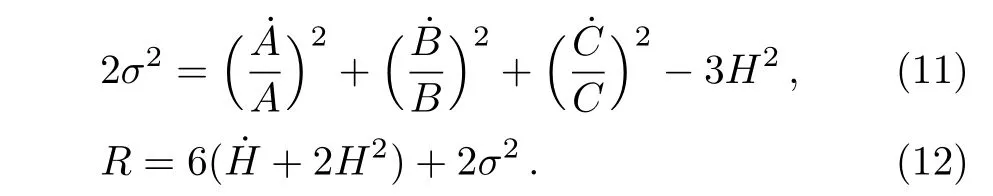
By using Eqs.(9),(10),(11),and(12),we can rewrite thefield equations(6),(7),and(8)as follows
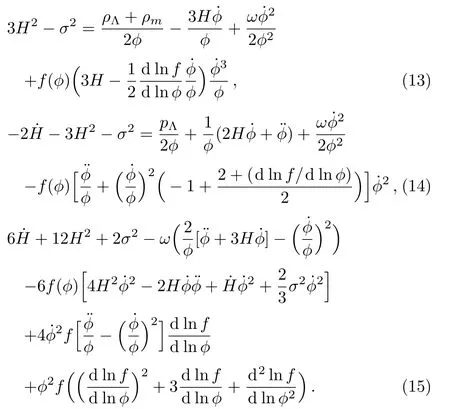
As above,Eqs.(13),(14),and(15)are independent equations,which have unknown parameters such as ?,H,f(?)and σ.Here,our task is to solve these equations simultaneously. To this end,we use the ansatz ?= ?(r,a(t))=S(a)P(r).It can be shown that,[55]in a cosmological background,P(r)=constant and we are led to ? = ?(a)=S(a).In BD theory 1/? plays the role of effective gravitational coupling G.Here,we assume ?=?0a?,[55]where ? is any integer,implies that=?H?.Also,since f(?)is the arbitrary function,so we may assume f(?)=1/(M2?2)[46,52]where M is the parameter of the model.From this we have,d lnf/d ln?=?2.So,Eq.(13)leads to
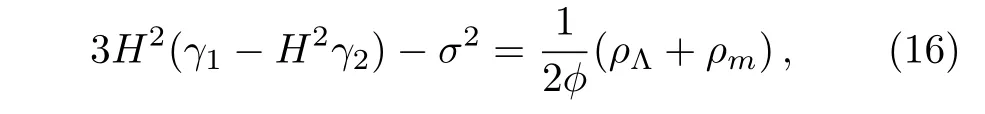
where
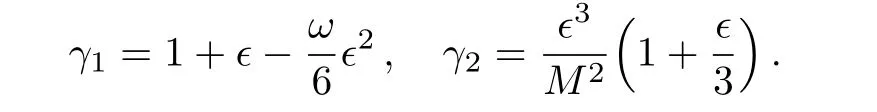
It is straightforward to show that this equation of motion reduces to the Einstein gravity in the limiting case corresponding to ?=0(γ1=1,γ2=0).
4 Bianchi Type I Field Equations and Generalized Ghost Dark Energy in Galileon Cosmology
In the Galileon gravity,the GGDE can be assumed as[56?58]in the following form
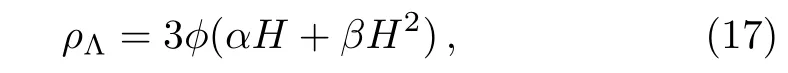
where α is a constant of order(with ΛQCDbeing the QCD mass scale)and β is another constant parameter of the model with dimension of[energy]2.In the original GDE(β =0)with ΛQCD~ 100 MeV and H ~ 10?33eV,gives the right order of magnitude~(3×103eV)4for the observed DE density.[33]In the GGDE,β is a free parameter and can be adjusted for better agreement with observations.In this work we are interested to suggest a phenomenological modification of the generalized ghost DE and investigate cosmological consequences of such modification.As usual the fractional energy densities are defined as
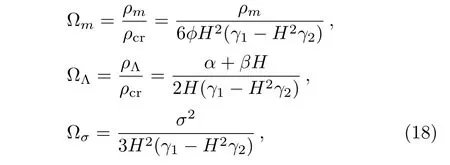
where the critical energy density(i.e.,the energy density required in order to obtain flatness)is given by ρcr=6?H2(γ1? H2γ2).Thus,the BI equation can be rewritten as follows:
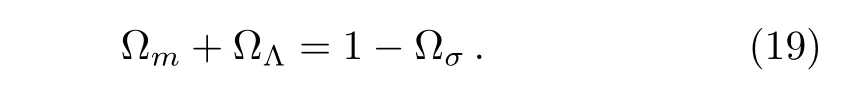
In noninteracting scenario the energy conservation laws for spatially non-isotropic universe are as follows
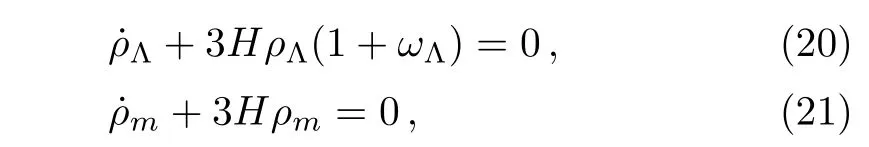
where ωΛ=pΛ/ρΛis the equation of state parameter of DE.Differentiating Eq.(16)with respect to time,we obtain
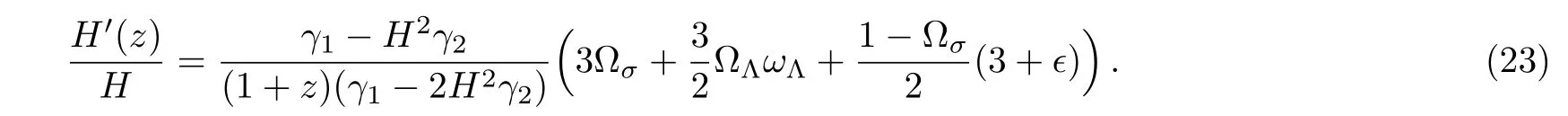
Taking the derivative of Eq.(17)with respect to time i.e.,˙ρΛ=3(?˙H(α+2βH)+˙?H(α+βH))and using Eqs.(20)and(23),the EoS parameter can be obtained as
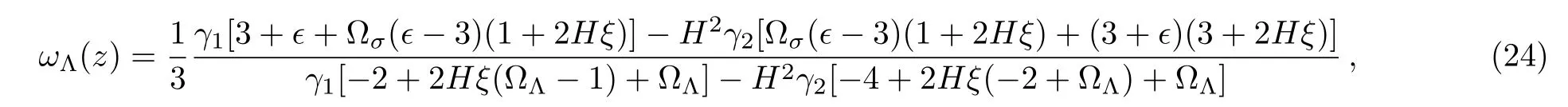
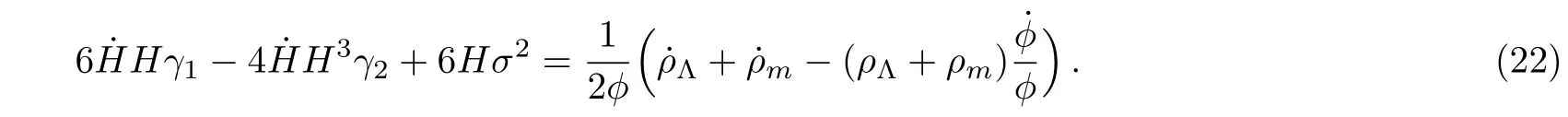
Using Eqs.(18),(19),(20),and(21)and with the help of u= ρm/ρΛ=(1??σ??Λ)/?Λ,we find

A case of particular interest is that when ? is small whereas ω is high so that the product ?ω results of order unity.[61?62]This is interesting because local astronomical experiments set a very high lower bound on ω;[63]in particular,the Cassini experiment implies that ω >104.[5,64]Also,Sheykhi et al.[40]obtained the result for the value of ? is ?<0.01.The GGDE model in Galileon framework has an interesting feature compared to the GGDE model in BI universe.Also,the deceleration parameter is obtained as
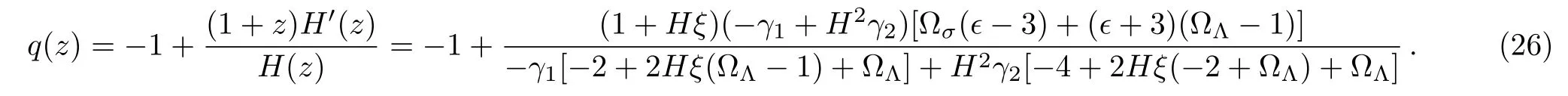
where ξ is given by β/α.In the absence of Galileon scalar field,i.e.,for ?=0(γ1=1,γ2=0)and the original GDE(ξ= β =0)we obtain[59?60]
When ?= β =0 we obtain the deceleration parameter in BI models for the original GDE[59]
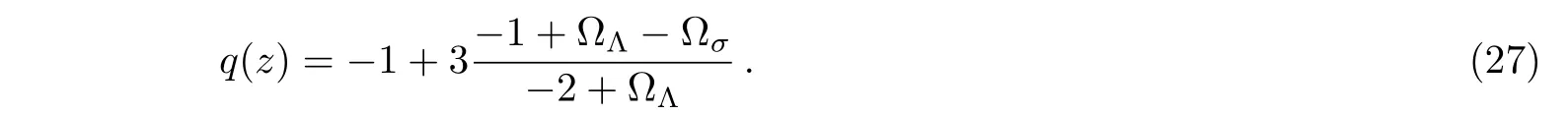
We can also obtain the evolution behavior of the DE.Taking the derivative of Eq.(18),we find
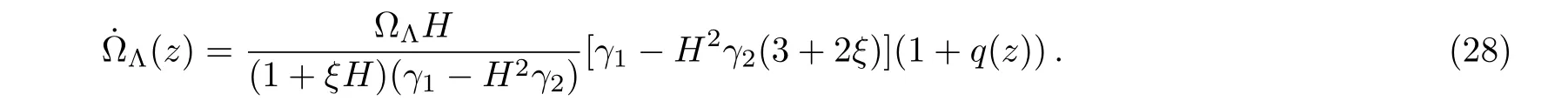
Substituting q from Eq.(26)into Eq.(28)and using relationit follows that
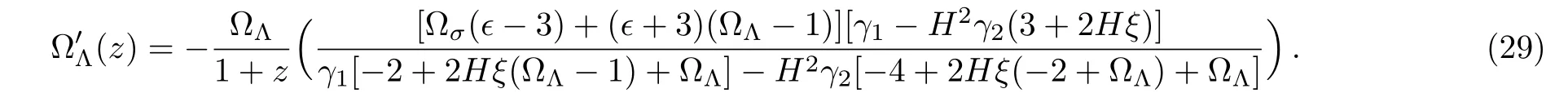
This is the equation of motion governing the evolution of GGDE in the framework of Galileon gravity.In the limit of standard cosmology ?=0 and σ = β =0,Eq.(29)reduces to its respective expression in GDE model.[65]
5 Numerical Solutions
It is easy to solve numerically for the intermediate regime between the early-time solution and the late-time accelerating one.We can solve Eqs.(13)–(15)numerically with appropriate initial conditions.We set initial conditions at GGDE domination and found the appropriate set of initial conditions in order to get acceleration at present time(defined by M=0.024 H0for ω = ?500).We computed the comoving distance r(z)=∫z0dz′/H(z′),for different ?σ0as a function of redshift z(:=1/a ? 1),which is plotted in Fig.1.For all values of ?σ0,the background evolution in GGDE BI and the GDE of FRW models in Galileon cosmology is almost indistinguishable from the ΛCDM model.Due the quintessence behaviour ωΛ> ?1(see Fig.4),the distance is smaller than in ΛCDM.This behavior can be explained by taking into account the evolution of Hubble parameter in Fig.2.The Hubble parameter is larger in the GGDE of the BI models,it takes intermediate values in the GDE of FRW and the smallest expansion appears to be in the ΛCDM model.Therefore the distance r(z)for the GGDE will always fall behind the GDE model in Galileon cosmology.The values of H(z)are fully compatible with ΛCDM,constraining the expansion rate very firmly.We analyze the model,using observed value of Hubble parameter at different redshifts(28 data points)listed in observed Hubble data by“SVJ”,“Clustering” and “DA” measurement are in the range of 0≤ z≤ 1.96[67?69]The Hubble parameter H(z)and the standard error σ′(z)for different values of redshift z are given in Table 1.Also from Fig.2,we can clearly see that for different ?σ0parameter values the process of cosmic evolution looks quite similar,that is,the bigger the value of the ?σ0parameter,the best the value of the Hubble expansion rate H(z).In other words,according to the curves,BI model shows that universe evolution(accelerated expansion)much faster than FRW universe.This implies that the BI model would play a more important role for constraining the models with more parameters.Note that the ΛCDM model Hubble’s parameter is H=H0(?m0(1+z)3+?σ0(1+z)6+?Λ)1/2and the EoS of DE is fixed to be ωΛ= ?1.The current fit value from cosmological observations is ?Λ=0.73±0.04.[70]For the ΛCDM cosmology,?m0is chosen to be 0.274 as given by the WMAP five-year observations.[71]The Hubble parameter is bigger in these models,which is compared to the ΛCDM universe.Therefore,from the above analysis,we will figure out that the parameters,?σ0,ξ and ω,can impact the cosmic expansion history in the GDE and GGDE of Galileon theory in BI model.
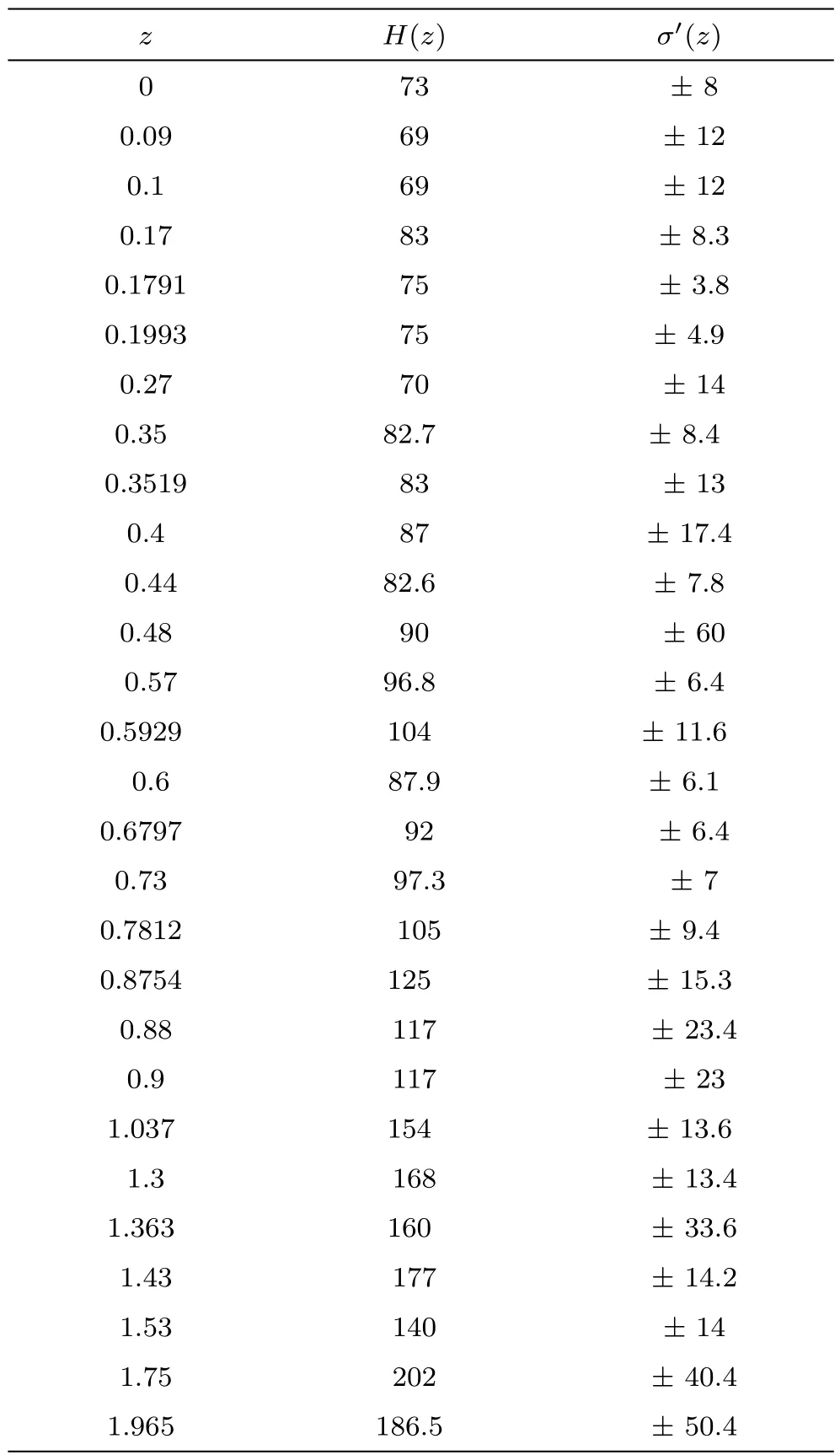
Table 1 The Hubble parameter H(z)and the standard error σ′(z)for different values of redshift z.
In Fig.3 we show the evolution of the DE density parameter ?Λand DM density parameter ?mas a function of the cosmic redshift z for three different values of the anisotropy energy density parameter ?σ0.The evolution of ?Λand ?mdepends on the value of the parameter ?σ0.From this figure it can be concluded that for smaller values of ?σ0the evolution of ?Λand ?mwill be flatter.
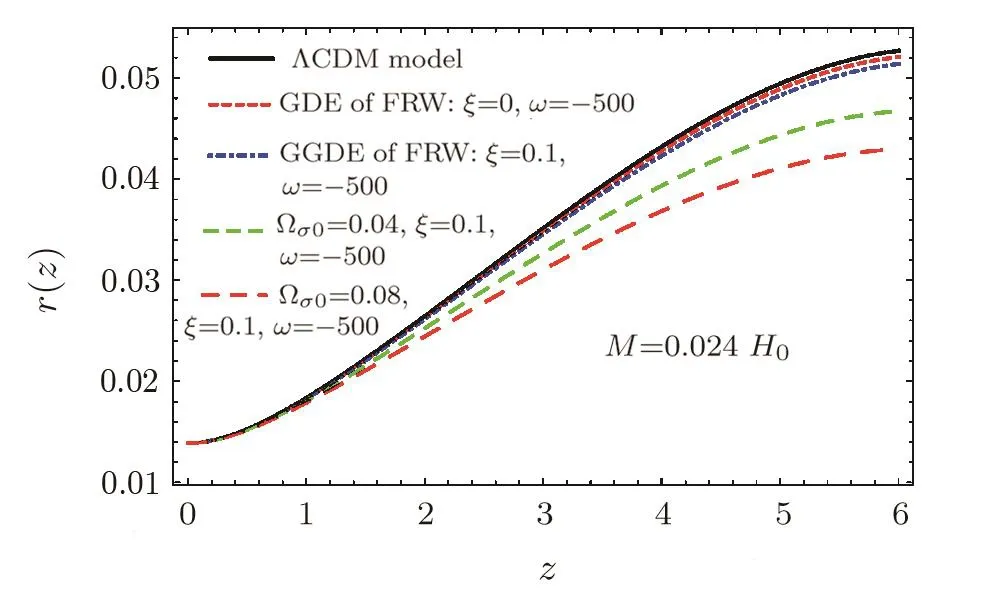
Fig.1 The comoving distance r(z)as a function of redshift for different values of ?σ0.
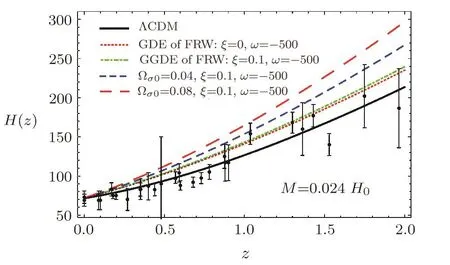
Fig.2 Comparison of the ΛCDM and GGDE models in the framework of Galileon gravity with the current H(z)measurements versus redshift z for different value of the anisotropy energy density parameter ?σ0,by considering H0=72 km·s?1·Mpc?1,[66]?m0=0.27,=0.69,ξ=0.1,?=0.003 and M=0.024H0.The data points with errorbars,and theoretical lines for different DE models and the observational H(z)data.[67?69]
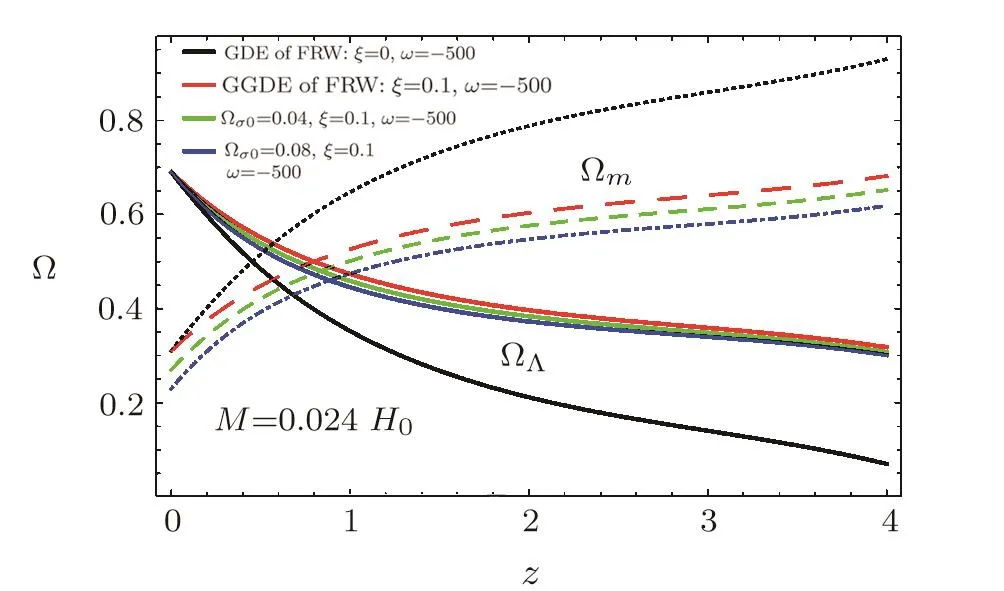
Fig.3 Evolutions of ?Λ and ?mversus the redshift for different ?σ0.Lines showing values increasing with z is ?m,and the decreasing lines are for ?Λ.The rest of parameters are as in Fig.2.
The GGDE model in Galileon cosmology has an interesting feature compared to the GGDE and GDE models in Einstein’s gravity.Choosing ?Λ=0.72 for the present time,this inequality valid provided we take ?=0.003,which is consistent with observations.This indicates that one can generate a quintessence-like EoS for the GGDE in the Galileon framework.We see that for all value of?σ0,the EoS parameter for ghost and generalised ghost DE models is always bigger than ωΛ= ?1 and remains in the quintessence regime,i.e.,ωΛ>?1 as shown in Fig.4.
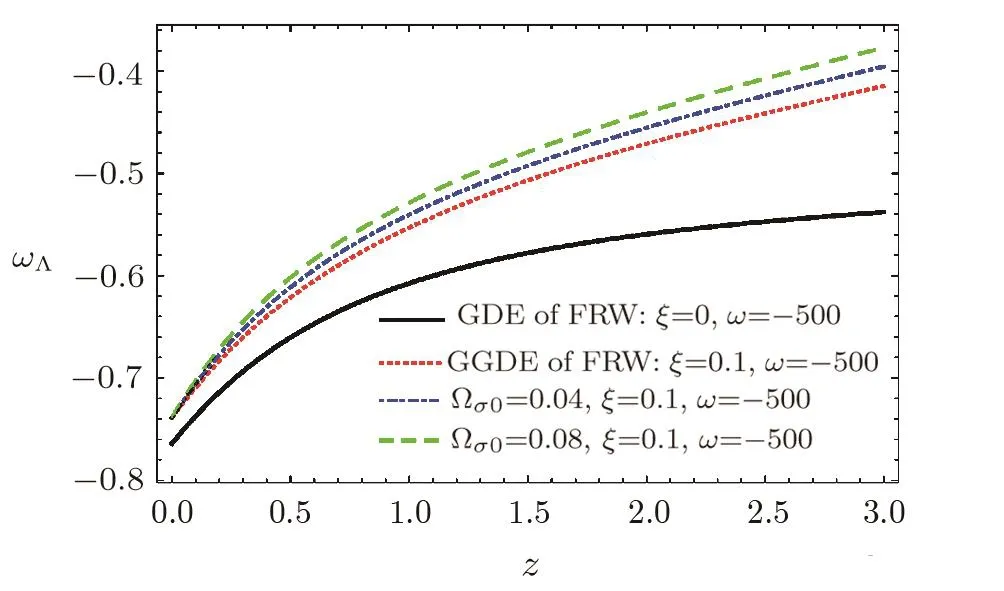
Fig.4 Evolution of the EoS parameter ωΛ(z)as a function of cosmic redshift z for the different value of the anisotropy energy density parameter ?σ0.As shown in the legend,the ghost DE is indicated by GDE,generalised ghost DE by GGDE.The same parameters as in Fig.2 are used.

Fig.5 Evolution of q(z)in terms of z for the GDE and GGDE of Galileon theory with different ?σ0and ΛCDM model with ?m0=0.3 and=0.7.
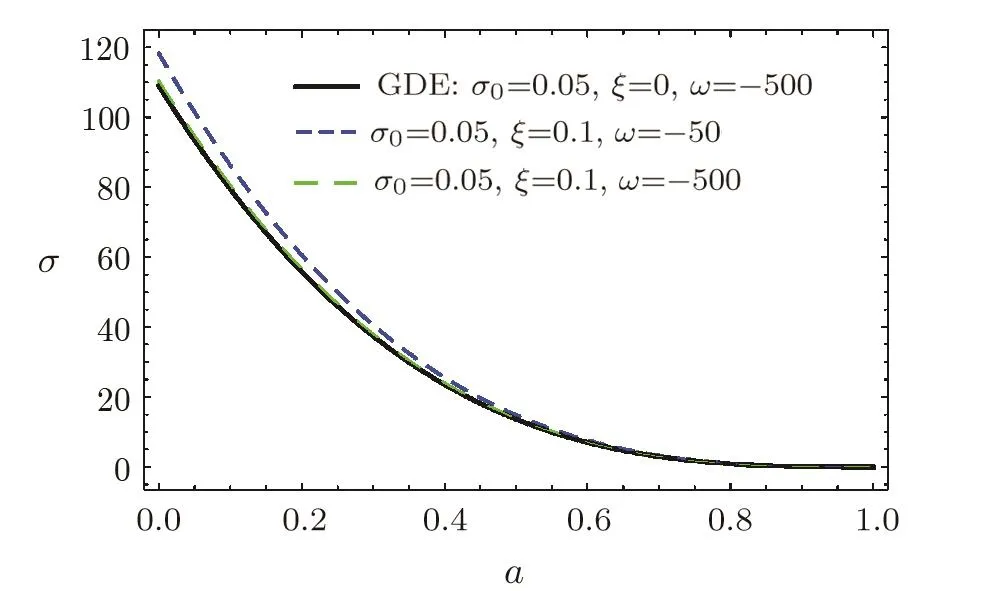
Fig.6 Time evolution of the shear scalar with respect to the scale factor a for both of GDE and GGDE of Galileon cosmology with σ0=0.05[72]for H0=72 km·s?1·Mpc?1, ?m0=0.27, ?0Λ =0.69, ξ=0.1,?=0.003,and M=0.024H0.
We figure out that the behaviour of the deceleration parameter for the best- fit universe is quite different from the ΛCDM cosmology as shown in Fig.5.We can also see that the best fit values of transition redshift and current deceleration parameter with ghost and generalized DE of Galileon theory are z=and q0=which is matchable with the observations[73]while for the case of ΛCDM,where z ~ 0.67 and q0= ?0.54.We can see that increasing ?σ0increases the value of q(z).

Fig.7 The evolution of the anisotropy parameter σ/H with respect to the scale factor a in a Galileon cosmology with σ0=0.05.[72]It becomes almost constant during the anisotropic inflationary phase.Then it falls rapidly down to O(σH).The initial data is same as in Fig.6.
The evolution of the σ is plotted in Fig.6.From Fig.6,it can be observed that evolution of shear depends on the initial conditions.Signature change of shear can be seen for both GDE and GGDE in the Galileon framework.Also,the shear scalar becomes negligible at late times and σ of GDE decreases slowly for walls compared to the GGDE.Finally we have considered,the model isotropize.The measure of the anisotropy is described by σ/H,describe the magnitude of the spacetime shear per the average expansion rate.However,as shown in Fig.7,during the inflationary phase,we find that the effect of shear cannot become as large as the Hubble parameter and the shear decreases at the end of the inflation.In other words,it becomes almost constant during the anisotropic inflationary phase.Then it falls rapidly down to O(σH).
5.1 Statefinder Parameters
In order to distinguish between the numerous dark energy models,et al.[76]proposed a cosmological diagnostic pair{r,s},which is known as statefinder parameters.Since the two parameters are derived from the cosmic scale factor alone,they are dimensionless and geometrical in nature.The diagnostic pair is defined as follows:
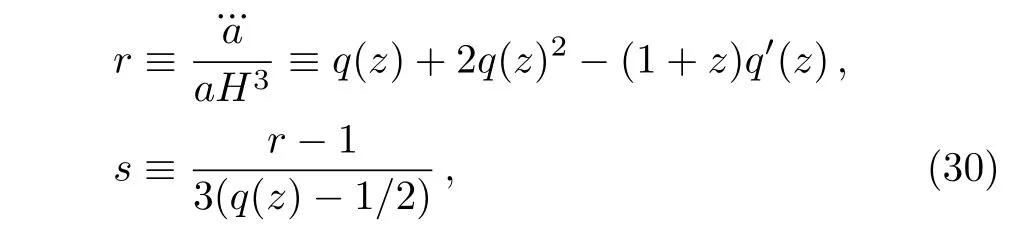
where q′=dq/dz and q is given by Eq.(26). The statefinder is a “geometrical”diagnostic in the sense that it depends upon the expansion factor and hence upon the metric describing space-time.As demonstrated in Refs.[77–78],the statefinder diagnostic can be effectively differentiate between a wide variety of DE models.We will soon see that it has a remarkable property for the basic flat ΛCDM BI model.The statefinder parameter s is a linear combination of r and q.In the{r,s}plane,s>0 corresponds to a quintessence-like model of DE and s<0 corresponds to a phantom-like model of DE.In Fig.8,we have studied the statefinder trajectories in the GGDE of Galileon gravity for the three cases we considered in this paper and we have observed that the flat ΛCDM point is attainable.The statefinder diagnostic can be discriminate between various DE models effectively.The r-s plane shows the GGDE behavior,ΛCDM limit and phantom and will also approach to quintessence behavior(see Fig.8(a)).When the anisotropy is absent(or FRW model),the endpoints of the r(s)curves could not arrive at the ΛCDM fixed point(1,0),though all of the evolution trajectories tend to approach this point.We have also studied the evolutionary behavior in the r-q plane in Fig.8(b).It shows that both ΛCDM and GGDE of Galileon gravity commence evolving from the same point in the past correspond to a matter dominated SCDM universe(r=1,q=0.5).As the universe is evolving,the value of r will be decreased from one.The star in the figure also corresponds to the ΛCDM fixed point and the dots marked on the curves represent the present values of the statefinder parameters.In Table 2 we have computed different values of r,s and q for the current universe(a=1)and for different choices of ?σ0.

Table 2 Today’s values of r,s,q.
6 Conclusion
In this paper,we have constructed the BI metric(which is spatially homogeneous and anisotropic)in the framework of the Galileon theory of gravity considering the GGDE model.We have discussed primary characters by choosing values of the parameters ? and ω and different values of the anisotropy energy density parameter ?σ0,and the discussion is summarized as follows.
We reconstructed the field equations of GGDE of Galileon theory in an anisotropic universe.With these considerations,we have evaluated the EoS,deceleration,and the evolution of the density parameter for GGDE models. We have also assumed that the evolution of the scalar field is related to that of the scale factor as ? ~ a?.First of all,the EoS parameter ωΛof the GGDE in Galileon theory with all values of ?σ0approaches to quintessence behavior.Then,the evolution of GGDE density parameter ?Λdepends on the anisotropy density parameter ?σ0.On the basis of the above considerations,it seems reasonable to investigate an anisotropic Universe,in,which the present cosmic acceleration is followed by a decelerated expansion in an early matter dominant phase.In other words,it indicates that the values of transition scale factor and current deceleration parameter areandfor the case of GGDE with Galileon theory while for the case of ΛCDM model,z=0.67 and q0= ?0.54,which is consistent with observations.[74?75]We have used the Hubble parameter versus redshift data to constrain cosmological parameters of GDE and GGDE of Galileon cosmology in BI universe.We found that,by choosing appropriate values of constant parameters,we figure out our model has more agreement with observational data than ΛCDM.Furthermore,we show that in an anisotropic universe with GGDE of Galileon cosmology,the Hubble parameter is greater than GDE of FRW and the ΛCDM models.Also,in the GGDE of BI model,the comoving distance evolves more slowly compared to the GDE of FRW in Galileon theory(see in Fig.1).Finally,we have studied the evolution of the σ and σ/H as shown in Figs.6 and 7.Although the shear is constant during the inflation,it can fall at the end of the inflation.Moreover,we have seen that the anisotropy of the universe σ/H can increase to O(1)at the end of the inflation.We have investigated the behavior of the state finder parameters r and s.These serve the purpose of distinguishing the model under consideration with other models,presenting a unique nature to it(the model).In other words,we can obtain various well-known limits through r-s and r-q planes such as,ΛCDM limit(r,s)=(1,0),de Sitter limit(r,q)=(1,?1),SCDM(r,q)=(1,0.5),phantom and quintessence DE eras(s<0 and s>0).In the case of GGDE model in Galileon theory,the trajectories of r-s plane with all values of ?σ0=0 approaches to quintessence behavior as well as ΛCDM limit as shown in Fig.8(a).But for the limiting case of ?σ0≠0 it shows the ΛCDM limit and phantom and also approaches to quintessence behavior.Also,the r-q plane has been used for discussion on the evolutionary property of the Galileon gravity(see in Fig.8(b)).

Fig.8 (a)Evolutionary trajectory in the statefinder r-s plane for GGDE of Galileon gravity in the cases of?σ0=0,0.04 and 0.08,respectively.The ΛCDM model corresponds to a fixed point{1,0}.(b)Evolution trajectory in the statefinder r-q plane for GGDE of Galileon gravity,and a star denotes the the ΛCDM model fixed point{1,?0.54}.[73]Color dots locate the current values of the statefinder pair r0,s0,q0.Selected curves of are plotted by fixing H0=72 km·s?1·Mpc?1,?m0=0.27,=0.69,ξ=0.1,?=0.003,and M=0.024H0.
[1]M.Betoule,R.Kessler,J.Guy,et al.,[SDSS Collaboration],A&A 568(2014)A22.
[2]A.G.Reiss,A.V.Filippenko,P.Challis,et al.,Astron.J.116(1998)1009.
[3]S.Perlmutter,G.Aldering,G.Goldhaber,et al.,Astro-phys.J.517(1999)565.
[4]E.J.Copeland,M.Sami,and S.Tsujikawa,Int.J.Mod.Phys.D 15(2006)1753.
[5]C.Brans and R.H.Dicke,Phys.Rev.124(1961)925;G.Dvali,G.Gabadadze,and M.Porrati,Phys.Lett.B 485(2000)208.
[6]T.Padmanbhan,Phys.Rep.380(2003)245;V.Sahni,Lect.Notes Phys.653(2004)141;J.A.S.Lima,Braz.J.Phys.34(2004)194.
[7]F.Zwicky,Helv.Phys.Acta 6(1933)110.
[8]R.G.Carlberg,H.K.C.Yee,and E.Ellingson,Astrophys.J.478(1997)462.
[9]J.J.Mohr,B.Mathiesen,and A.E.Evrard,Astrophys.J.517(1998)627.
[10]G.Wilson,N.Kaiser,and G.A.Luppino,Astrophys.J.556(2001)601.
[11]N.A.Bahcall and X.Fan,Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.95(1998)5956.
[12]Y.Mellier,ARA&A 37(1999)127.
[13]R.G.Carlberg,H.K.C.Yee,E.Ellingson,et al.,Astrophys.J.462(1996)32.
[14]D.A.White and A.C.Fabian,Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc.273(1995)72.
[15]L.Wang and P.J.Steinhardt,Astrophys.J.508(1998)483.
[16]Z.Haiman,J.J.Mohr,and G.P.Holder,Astrophys.J.553(2001)545.
[17]G.P.Holder,Z.Haiman,and J.J.Mohr,Astrophys.J.560(2001)L111;W.Hu and A.V.Kravtsov,Astrophys.J.584(2003)702;W.Hu,Phys.Rev.D 67(2003)081304;J.Weller,R.A.Battye,and R.Kneissl,Phys.Rev.Lett.88(2002)1301.
[18]R.R.Caldwell,M.Kamionkowski,and N.N.Weinberg,Phys.Rev.Lett.91(2003)071301.
[19]R.R.Caldwell and P.J.Steinhardt,Phys.Rev.D 57(1998)6057.
[20]P.J.Steinhardt,L.M.Wang,and I.Zlatev,Phys.Rev.D 59(1999)123504.
[21]S.Capozziello,S.Carloni,and A.Troisi,Recent Res.Dev.Astron.Astrophys.1(2003)625.
[22]M.Li,Phys.Lett.B 603(2004)1.
[23]R.G.Cai,Phys.Lett.B 657(2007)228.
[24]H.Wei and R.G.Cai,Phys.Lett.B 660(2008)113.
[25]M.X.Luo and Q.P.Su,Phys.Lett.B 626(2005)7.
[26]B.Feng,X.L.Wang,and X.M.Zhang,Phys.Lett.B 607(2005)35.
[27]C.Gao,X.Chen,and Y.G.Shen,Phys.Rev.D 79(2009)043511.
[28]Z.Zhang,S.Li,X.D.Li,et al.,JCAP 1206(2012)009.
[29]J.Zhang,X.Zhang,and H.Liu,Eur.Phys.J.C 54(2008)303.
[30]C.Armendariz-Picon,V.F.Mukhanov,and P.J.Steinhardt,Phys.Rev.Lett.85(2000)4438.
[31]A.Sen,J.High Energy Phys.0207(2002)065;T.Padmanabhan,Phys.Rev.D 66(2002)021301.
[32]F.R.Urban and A.R.Zhitnitsky,Phys.Lett.B 688(2010)9.
[33]N.Ohta,Phys.Lett.B 695(2011)41.
[34]R.G.Cai,Z.L.Tuo,H.B.Zhang,and Q.Su,Phys.Rev.D 84(2011)123501.
[35]E.Witten,Nucl.Phys.B 156(1979)269;G.Veneziano,Nucl.Phys.B 159(1979)213.
[36]F.Piazza and S.Tsujikawa,JCAP 0407(2004)004.
[37]A.R.Zhitnitsky,Phys.Rev.D 86(2012)045026.
[38]M.Maggiore,Phys.Rev.D 83(2011)063514.
[39]R.G.Cai,Z.L.Tuo,Y.B.Wu,and Y.Y.Zhao,Phys.Rev.D 86(2012)023511.
[40]A.Sheykhi,E.Ebrahimi,and Y.Yose fi,Can.J.Phys 91(2013)662.
[41]X.Zhang,Phys.Lett.B 648(2007)1;A.Sheykhi,Phys.Lett.B 682(2010)329.
[42]C.Brans and R.H.Dicke,Phys.Rev.124(1961)925.
[43]A.Nicolis,R.Rattazzi,and E.Trincherini,Phys.Rev.D 79(2009)064036.
[44]G.R.Dvali,G.Gabadadze,and M.Porrati,Phys.Lett.B 485(2000)208.
[45]C.Deffayet,Phys.Lett.B 502(2001)199.
[46]F.P.Silva and K.Koyama,Phys.Rev.D 80(2009)121301.
[47]M.Jamil,D.Momeni,and R.Myrzakulov,Eur.Phys.J.C 73(2013)2347.
[48]C.Ranjit,P.Rudra,and U.Debnath,Can.J.Phys 92(2014)1667.
[49]M.Biswas and U.Debnath,Commun.Theor.Phys.65(2016)121.
[50]V.Fayaz,H.Hossienkhani,and F.Felegary,Int.J.Theor.Phys.51(2012)2656.
[51]H.Hossienkhani,V.Fayaz,and N.Azimi,Astrophys.Space Sci.362(2017)55;H.Hossienkhani,Astrophys.Space Sci.361(2016)216;V.Fayaz,H.Hossienkhani,A.Pasqua,et al.,Can.J.Phys.94(2016)201.
[52]T.Kobayashi,H.Tashiro,and D.Suzuki,Phys.Rev.D 81(2010)063513.
[53]C.Deffayet,G.Esposito-Farese,and A.Vikman,Phys.Rev.D 79(2009)084003.
[54]N.Chow and J.Khoury,Phys.Rev.D 80(2009)024037.
[55]N.Riazi and B.Nasr,Astrophys.Space Sci.271(2000)237.
[56]W.Q.Yang,L.M.Song,Y.Y.Su,et al.,Mod.Phys.Lett.A 26(2011)191.
[57]M.Sharif and S.Waheed,Astrophys.Space Sci.348(2013)261.
[58]U.Debnath,Eur.Phys.J.Plus 129(2014)272.
[59]H.Hossienkhani,Astrophys.Space Sci.361(2016)136;V.Fayaz,H.Hossienkhani,Z.Zarei,and N.Azimi,Eur.Phys.J.Plus 131(2016)22.
[60]N.Azimi and F.Barati,Int.J.Theor.Phys.55(2016)3318.
[61]N.Banerjee and D.Pav′on,Phys.Lett.B 647(2007)447.
[62]A.Sheykhi,Phys.Lett.B 681(2009)205.
[63]C.M.Will,Theory and Experiment in Gravitational Physics,Cambridge University Press,2nd ed.,Basic Books/Perseus Group,Cambridge(1993).
[64]V.Acquaviva and L.Verde,JCAP 0712(2007)001.
[65]A.Sheykhi and M.S.Movahed,Gen.Relativ.Gravit.44(2012)449.
[66]D.N.Spergel,R.Bean,O.Dor′e,et al.,Astrophys.J.Suppl.170(2007)377.
[67]J.Simon,L.Verde,and R.Jimenez,Phys.Rev.D 71(2005)123001.
[68]C.Blake,et al.,Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc.425(2012)405.
[69]Y.L.Li,S.Y.Li,T.J.Zhang,and T.P.Li,Astrophys.J.789(2014)L15.
[70]T.M.Davis,E.Mortsell,J.Sollerman,et al.,Astrophys.J.666(2007)716.
[71]E.Komatsu,et al.,Astrophys.J.Suppl.180(2009)330.
[72]P.K.Aluri,S.Panda,M.Sharma,and S.Thakur,JCAP 12(2013)003.
[73]E.E.O.Ishida,et al.,Astropart.Phys,28(2008)547.
[74]Y.G.Gong and A.Wang,Phys.Rev.75(2006)043520.
[75]Y.S.Myung,Phys.Lett.B 652(2007)223;K.Y.Kim,H.W.Lee,and Y.S.Myung,Phys.Lett.B 660(2008)118.
[76]V.Sahni,et al.,JETP 77(2003)201.
[77]X.Zhang,Phys.Lett.B 611(2005)1.
[78]S.Chattopadhyay,Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,India Section A:Physical Sciences 84(2014)87.
 Communications in Theoretical Physics2018年4期
Communications in Theoretical Physics2018年4期
- Communications in Theoretical Physics的其它文章
- Influence of Non-linear Radiation Heat Flux on Rotating Maxwell Fluid over a Deformable Surface:A Numerical Study
- Numerical Study of Mixed Convective Peristaltic Flow through Vertical Tube with Heat Generation for Moderate Reynolds and Wave Numbers
- Melting Heat in Radiative Flow of Carbon Nanotubes with Homogeneous-Heterogeneous Reactions
- Controlling Thermal Conduction by Graded Materials?
- Direct Urca Processes Involving Proton1S0Superfluidity in Neutron Star Cooling?
- Effects of a Weakly Interacting Light U Boson on Protoneutron Stars Including the Hyperon-Hyperon Interactions?
