Motion of the moonlet in the binary system 243 Ida
L.Lan·Y.Ni·Y.Jiang·J.Li
1 Introduction
Asteroid 243 Ida is an S-type asteroid with an average diameter of 31.4 km in the Koronis family,which is the most abundant type in the inner main belt[1,2].It was discovered by an Austrian astronomer,Johann Palisa,on 29th September 1884.Spacecraft Galileo,destined for Jupiter,flew by the asteroid 243 Ida on 28th August 1993,thus,it is the second asteroid that a spacecraft has flown by(the first was 951 Gaspra,and Spacecraft Galileo also did a flyby).The primary’s observed semi-major axis of revolution is 2.8616 AU with an orbital period of~4.841 years.The asteroid seems to be composed of two connected objects for an elongated shape.
Moreover,243 Ida is the first asteroid found to have a natural moonlet,called Dactyl,which was discovered in pictures returned from spacecraft Galileo.Dactyl has an average diameter of only 1.4 km,which is about 1/22 the size of the primary.The surfaces of the binary are both heavily covered with craters and composed of similar materials,which suggests the same origin from a parent-body fragment in the Koronis family[3].
As a delicate system with tiny divergence velocities,binary asteroids such as 243 Ida draw much attention to their formation and evolution[4].However,it is hard to determine the orbit of Dactyl accurately for its remote location from the earth.The ratio of separation to primary’s average radiusas/rpis about 6.9 and the eccentricity of the moonlet is over0.2,according to observation.The over all dimensions of Dactyl were found to be 1.6 km×1.4 km×1.2 km,which is quite insignificant compared with the primary;therefore,it is modeled as a massless particle in this paper for the large size ratio of the binary system[5–8].
Irregular asteroids are quite common in solar systems because hardly any bodies have sufficient mass for gravity to overcome the inner solid stress[9–11].The study on the gravitational field of the irregular primary is the basis to investigate the motion of the moonlet.The separation between a particle and the primary is an important factor affecting the required sophistication of model.Therefore,several models with various degrees of sophistication have been developed to date.If a particle is adequately remote from the primary,a perturbation expansion method with low-order Legendre coefficients can be used.Moreover,simple-shape models can be adopted,such as a logarithm and a massive finite segment],a simple planar plate],a rotating homogeneous cube[14],a dumbbell-shaped body[15],and a dipole[16].In addition,the ellipsoid–sphere and ellipsoid–ellipsoid systems are used to study the motion of probe near the binary system in the case that the pairs are in relative equilibrium[17,18].
If a particle is close to the primary,the gravity of an irregular body dominates a conclusive effect,thus the solar gravitation and sunlight pressure can be neglected[19].In this case,using simple-shape models,it is hard to reveal the complicated shape of asteroids,as well as the gravity potential near an irregular body.Moreover,the spherical-harmonic method fails within the reference sphere,and the expansion method with low-order Legendre coefficients is insufficient for calculation since higher-order terms may take numerous iterations to converge or diverge in some cases[11,12].Therefore,the absolute importance of a high-precision polyhedral model with sufficient vertices and faces is underscored for the research on the motion near an irregular asteroid[20–22].Based on the method,Yu and Baoyin[23]investigated 29 families of periodic orbits in the vicinity of 216 Kleopatra using hierarchical grid searching method.Also,Jiang et al.[11]discussed the topological classifications and bifurcations of the periodic orbits near the highly irregular bodies.Moreover,Ni et al.[24]studied the multiple bifurcations in the continuation of periodic orbits near the asteroid 433 Eros.The work of Lan et al.[25]investigated the gravity field of heterogeneous asteroids using method improving upon polyhedron.
In this paper,calculations are conducted using polyhedral method to investigate the periodic orbits near the primary and motion of the moonlet.First,the periodic orbits around the equilibrium points and large-scale periodic orbits are calculated and analyzed.They indicate that geometric natures of periodic orbits in the vicinity of an irregular asteroid are very sophisticated[11].However,most of these orbits are unstable.
It is worthy mentioned that two period-doubling bifurcations(PDBs)and one Neimark–Sacker bifurcation(NSB)occur during the continuation of the retrograde near-circular periodic orbits near the equatorial plane,thus orbits of the family appear stable or unstable in different regions divided by three bifurcations.Moreover,we find many quasi-periodic orbits existing near the equatorial plane.The motion of these quasi-periodic orbits differ greatly in region I and region II shown by Poincare sections.Dactyl orbits the primary in the stable region I.Associated with the observed orbital parameters,it can be concluded seriously that Dactyl is likely to be in a quasi-periodic orbit in region I.
This paper is organized as follows:some basic theories are introduced in Sect.2.Then,several families of periodic orbits in the vicinity of the primary are studied in Sect.3.The stabilities of the retrograde periodic orbits in four regions are also investigated in this section.Moreover,Poincare sectionsVz?Zof quasi-periodic orbits are analyzed in Sect.4,and we propose a possible orbit of Moonlet Dactyl in this section as well.In the final section,we discuss the results and draw our conclusions.
2 Irregular asteroid’s gravity field and periodic motion of a particle
In this section,basic theories are introduced,including the gravitational potential of a polyhedral body,dynamic equation of a particle near an asteroid,a hierarchical grid orbital searching method,as well as an orbital continuation method.Moreover,the topological cases of Floquet multipliers are introduced to study the stabilities of periodic orbits.
2.1 Gravitational potential and dynamical equation
The overall dimensions of asteroid 243 Ida are 59.8 km×25.4 km×18.6 km,and its rotation period is~4.634 h.The bulk density of the asteroid is estimated to be 2.4 g/cm3,and its total mass is 4.121×1016kg.We use a polyhedral model of the primary with 2161 vertices and 4318 faces[26].The gravitational potential can be expressed as[21]
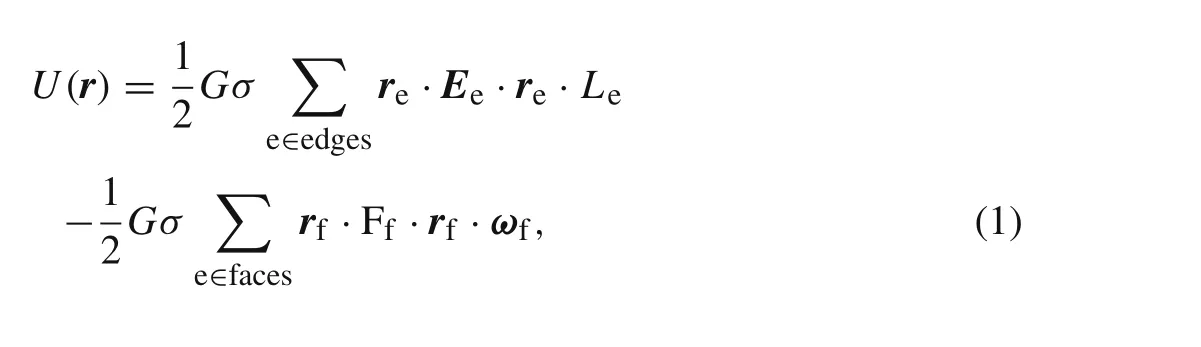
and the gravitational force can be written as
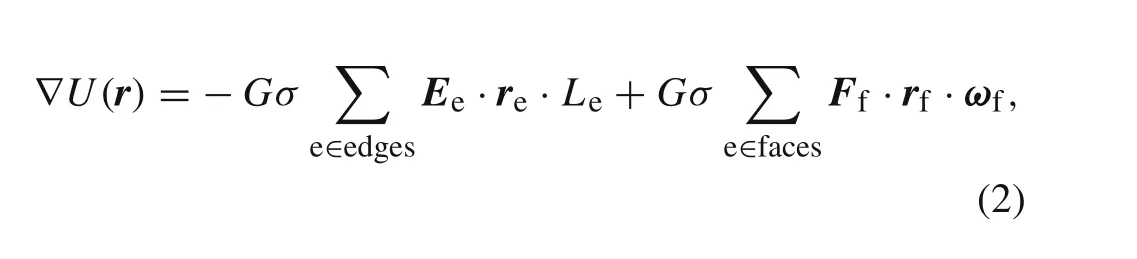
where“?”denotes the gradient operator.G=6.67×10?11m3·kg?1·s?2is the gravitational constant;σis the asteroid’s bulk density;Ledenotes the integration factor between field points and edgese;ωfdenotes the signed angle relative to field points;reandrfdenote the body-fixed vectors from field points to edge e and face f,respectively;EeandFfdenote geometric parameters of edges and faces,respectively.

The sunlight pressure and solar gravitation are neglected because all considered motion are within the influence sphere of the primary.The dynamical equation of a particle can be written as[22]whereris a vector from origin to the particle;ωdenotes the rotational angular velocity of the primary relative to the inertial frame;τdenotes the angular acceleration of the primary.An inertial principal axis system is used in this paper with an origin at the barycenter of the primary.andIz≥Iy≥Ix,whereIx,Iy,Izare the principal moments of inertia.Equation 3 can be expressed in this body-fixed frame as
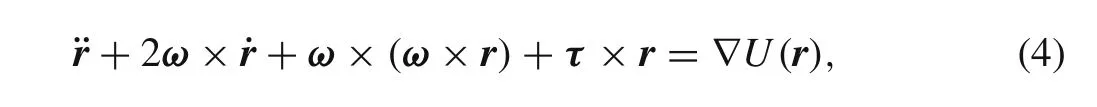
where “.”and “..”are differential and second-order differentials of time.Considering the variation of asteroid’s angular velocity is quite slow,we assumeτ=0 andωremains constant in this paper.The sum of the centrifugal potential and gravity potential are always introduced as the effective potential[27]

The Coriolis term 2ω×˙rhas no effect on the generalized energy of the system and the term?V(r)is a potential force;therefore,Eq.(6)is conserved for the explicit time independence.The system keeps a symplectic form and conserves phase volume in each extended phase space,resulting in unpredictability of long-range dynamical motions[23].The integral of generalized energy can be expressed as a Hamiltonian function[28]
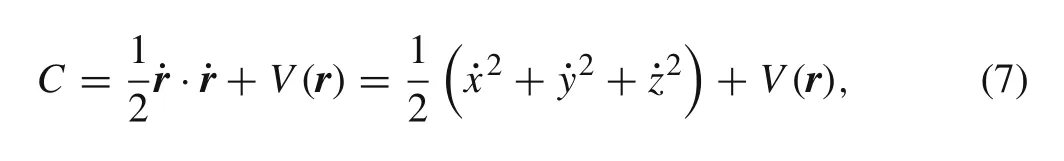
which is always called the Jacobi integral.Certain Jacobi integrals divide the entire space into an allowable region withV(r)<C,and a forbidden region withV(r)>Cfor the motion of a particle[29].The zero-velocity surfaces,generated byV(r)=C,are the boundaries of these regions[23].

Fig.1 Six families of periodic orbits around the equilibrium points
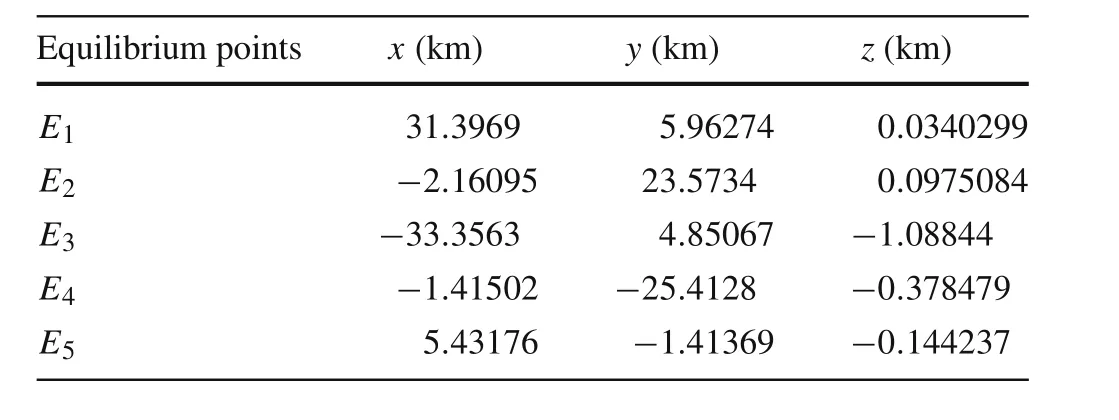
Table 1 The equilibrium points in the vicinity of the primary
The kinetic energy of a particle with respect to the body-fixed frame can be calculated from the difference betweenCandV(r)[30]

The equilibrium points are the spots satisfying?V(r)=0.This means˙r=0 and¨r=0 derived from Eq.(6).A method proposed by Wang et al.[20,31]is used to calculate relative equilibrium points in the vicinity of the primary.As shown in Fig.1,there are four unstable equilibrium points outside the body and one stable equilibrium point inside the body,as listed in Table 1[20].Thereinto,E1andE3are two saddle points,andE2andE4are two extreme points.Asaddle point is a stationary point,but is not a local extremum on all axes.The saddle point always occurs at a relative minimum along one axial direction and at a relative maximum along the crossing axes.
2.2 Periodic motions in the vicinity of the primary
Periodic motions were identified as the foundation to comprehend the creation of celestial systems and their stabilities[23,29];therefore,we first need investigate the periodic orbits near the primary in order to understand the motion of moonlet Dactyl.The dynamical equation of the periodic motion can be written simply as follow

Xis a six-dimensional variate relative to the moonlet’s position and velocity.
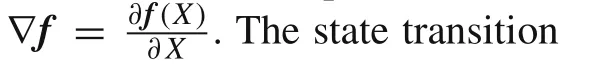

The monodromy matrix represents the state transition matrix with a transition time of a periodt=T:

The Floquet multipliers are Eigenvalues of the monodromy matrix.There must be a pair of “1”,determined by the orbital periodicity and generalized energy conservation of the system.The remaining Floquet multipliers should be the combination of following forms:a pair of 1,? 1,α±1,cosβ± i sinβorσ±1(cosθ± i sinθ),where|α|∈(0,1),β∈(0,π),θ∈(0,π),which are determined by the symplectic construction of matrixM[11].It is hard to find all periodic orbits near an irregular asteroid because of orbit richness and denseness,but all orbits can be classified by different topological cases of Floquet multipliers[34].
Seven topological cases of pure-periodic orbits,which are all non-collisional and non-degenerate-real-saddle,were discussed by Jiang et al.[11].Four of these cases are mentioned in this paper,and are listed in Table 4.A periodic orbit is unstable if it has Floquet multipliers outside the unit circle in the complex plane.In contrast,the Floquet multipliers for a stable periodic orbit should be all on the unit circle.
2.3 Bifurcations in the continuation of the periodic orbits
The orbital continuation is an effective method to search for plentiful periodic orbits with similar parameters.We find a basic periodic orbit in an orbital family first,and other orbits of the same family are continued from the basic orbits.The Jacobi constant is always chosen as the continuous dependence,and multiple parameters will change correspondingly in the continuation as well[23].The continuation follows[35]
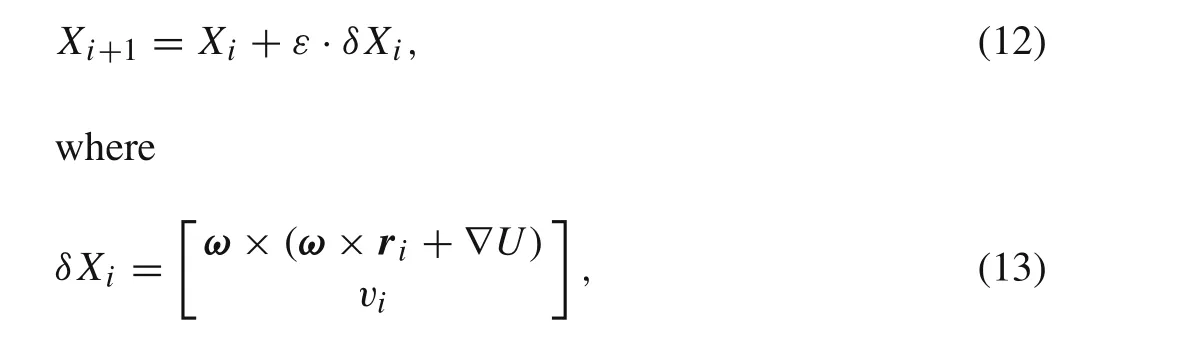
in whichδX iis the gradient direction;εis the step size chosen to get an optimal value ofX i+1in the gradient direction.The procedure of continuation ends if the orbit intersects the asteroid.
In the orbital continuation,bifurcations might occur,the topological cases of Floquet multipliers might transfer,and stabilities of periodic orbits mights witch[33,36].PDB takes place when and only when two or four Floquet multipliers crash at(?1,0)and leave thex-axis or unit cycle[11].The NSB takes place when and only when two Floquet multipliers collide at eiβ(β∈(0,π))and 2 Floquet multipliers crash at e?iβ(β∈(0,π))synchronously,then all leave the unitcycle.
3 Periodic orbits around the equilibrium points and large-scale periodic orbits
The periodic orbits in the vicinity of the primary can be classified as two types.Type 1:the orbital families of this type extend like a tree ring around a certain equilibrium point,as shown in Fig.1.They are periodic orbits around the equilibrium points.Type 2:the families of this type usually extend to greater area in the vicinity of asteroid and are not dominated by a certain equilibrium point.They are large-scale periodic orbits.However,whether Type 1 or Type 2,most of the orbits are unstable,except the periodic orbits near the equatorial plane.We pay our attention to bifurcations in the continuation of retrograde near-circular orbits near the equatorial plane.Moreover,four regions and their stabilities are studied in this section.
3.1 The periodic orbits around equilibrium points of the primary
The number of orbital families of this type of periodic orbit depends on the topological structures of the eigenvalues of non-degenerate and non-resonance equilibrium points,specifically the dimension of central manifolds[37].Through calculation,six families of periodic orbits around the equilibrium points are found,as shown in Fig.1.Family 1(a)and Family 1(b)are around equilibrium pointE1,Family 2 is around equilibrium pointE2,Family 3(a)and Family 3(b)are around equilibrium pointE3,and Family 4 is around equilibrium pointE4.Family 1(b)and Family 3(b)are near the equatorial plane,but the others are approximately perpendicular to the plane.These show a typical distribution of the periodic orbits around the equilibrium points for elongated asteroids,such as asteroids216 Kleopatra and 433 Eros[6,23].Orbit 1(a),Orbit 1(b),Orbit 2,Orbit 3(a),Orbit 3(b),and Orbit 4 are the basic orbits of these six orbital families,respectively.The other orbits of the same family are continued from these basic orbits.The initials of these basic orbits with respect to the body-fixed frame are listed in Table 2.Figure 2 presents the transfers of the Floquet multipliers during the continuations.Two real-saddle bifurcations occur during the orbital continuation of Family 2.A real-saddle bifurcation is a type of bifurcation where in the continuation of orbits,two pairs of conjugated Floquet multipliers run into each other at the real axis synchronously and then run on the realaxis[38].These show that these six families of orbits are all unstable.

Table 2 The initials of basic orbits belonging to six orbital families around the equilibrium points with respect to the body-fixed frame
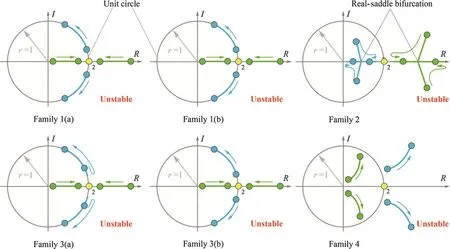
Fig.2 The transfers of the Floquet multipliers of six orbital families around the equilibrium points during the continuations.“2”means two Floquet multipliers overlap together.“R”and“I”refer to real axis and image axis of the complex plane,respectively
3.2 Large-scale periodic orbits
These families of periodic orbits are not around certain equilibrium points and usually have large scales.Six families of large-scale periodic orbits are found,as shown in Fig.3.Orbit 5,Orbit 6,Orbit 7,Orbit 8,Orbit 9,and Orbit 10 are basic orbits of Family 5,Family 6,Family 7,Family 8,Family 9,and Family 10,respectively.Initials of six basic orbits with respect to the body-fixed frame are listed in Table 3.The transfers of the Floquet multipliers during the continuations of six families are presented in the Fig.4.A PDB occurs during the continuation of Family 9.These six families of periodic orbits are also unstable.

Fig.3 The transfers of the Floquet multipliers of six families of large-scale periodic orbits during the continuations.“2”means two Floquet multipliers overlap together

Table 3 The initials of basic orbits belonging to six families of large-scale periodic orbits with respect to the body-fixed frame
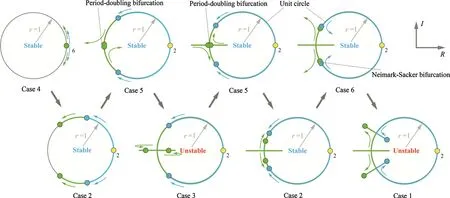
Fig.4 The transfer of topological cases of Floquet multipliers’topological cases in the continuation of the retrograde near-circular periodic orbits near the equatorial plane.“6”and “2”mean six and two Floquet multipliers overlap together,respectively
3.3 Stabilities of retrograde near-circular periodic orbits near the equatorial plane
It is convincing that there exist more families of large-scale periodic orbits around the primary.However,most of these orbits are unstable,which are less meaningful to the missions since probes are more likely to escape from nominal orbits with out control.Dactylisn’t supposed to be in an unstable orbit since it has been flying around the primary for a long time.However,we find that most of retrograde nearcircular periodic orbits near the equatorial plane are stable.Several orbits of the family have similar orbital parameters to that of Dactyl,making the research on this family has much scientific meaning.This family of periodic orbits were first proposed by Scheeres et al.[22],and their stable conditions are given in Ref.[39].
Periodic orbits of the family are continued based on Jacobi constant varying from 4.833×10?3m2/s2to 8.789×10?4m2/s2in steps of? 1.2× 10?7m2/s2.The direction of continuation is shown by the arrow in Fig.5.The orbital scale decreases and other parameters vary correspondingly.When a particle is sufficiently remote from the primary,the primary’s irregularity has little effect on the gravity.Therefore,the particle orbits a body that is almost the same as a uniform mass sphere.The Floquet multipliers’topological case appears as Case 4 at infinity,as shown in Fig.4.During the continuation,two PDBs and one NSB occur one by one.These bifurcations divide the space into two stable regions and two unstable regions,as shown in Fig.5.They can be called stable region I,unstable region II,stable region III,and unstable region IV,respectively.Periodic orbits in stable regions are all stable,but in unstable regions are all unstable.The ranges of Jacobi constants for these regions are listed in Table 5.The entire transfer process of the Floquet multipliers’topological cases are listed as follows:

as shown in Fig.4,and the forms of these cases are listed in Table 4.The first PDB occurs when the Jacobi constantC=1.052 and orbital periodT=2.699;the second PDB occurs when Jacobi constantC=1.01986 and orbital periodT=2.62683;the Neimark-Sackerbifurcation occurs when Jacobi constantC=0.949763 and orbital periodT=2.46352.IfC<0.878945,the orbits intersect the primary;therefore,C=0.878945 is the end of the continuation.Two PDBs occur at the orbits near two unstable saddle equilibrium pointsE1andE3,and the Neimark-Sackerbifurcation occurs where the orbit is very close to the surface of the primary,since asteroid’s irregularity makes a leap effect.Long-term integrations indicate that periodic orbits in unstable regions are more likely to diverge,but in stable regions can remain stable for a long time.If there is a ring formed by dust near the primary similar to that of Saturn,a division may exist between two stable regions(Table 5).
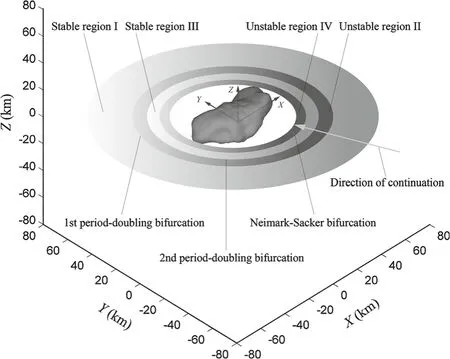
Fig.5 Stable regions and unstable regions
4 Quasi-periodic orbits near the equatorial plane and the motion of moonlet Dactyl
The moonlet Dactylorbits the primary in stable region I.The observed parameters of Dactyl’s orbit around the primary are presented in Table 6(the data is from website:http://www.johnstonsarchive.net/astro/asteroidmoons.html).The periodic orbits with similar parameters in stable region I are also listed in Table 6.The periodic orbit 11 has a similar semimajor axis to that of Dactyl,and the periodic orbit 12 has a similar orbital period to that of Dactyl.However,it is obvious that Dactyl is not in these orbits.These orbits are more circular and closer to equatorial plane.However,the similarities imply Dactyl may be in a quasi-periodic orbit near the region.
Dozens of quasi-periodic orbits exist in the stable region I.They can be obtained by adding perturbations at the initial parameters of periodic orbits.Perturbations of 0.25%,0.5%,1.0%are added at the initials of periodic orbit 11,respectively.The Poincare sectionsVz?Zare calculated for 2000 days based on RK 7(8)integration methods to show the behaviors of the orbits,as shown in Fig.6.The graphics are similar to petalages and the particles run within a closed area like an egg in the order of tens of meters with respect toZ-axis,and in the order of microns per second with respect toVz-axis.Particles intersect the cores of the graphics at a higher rate.
Poincare sectionsVz?Zare also calculated in region II.Perturbations of 0.25%,0.5%,1.0%are added at the initials of a periodic orbit in region II,as shown in Fig.7.The graphics in Fig.7 are extremely different from those in Fig.6.These graphics resemble an oblique figure“8”,and the particles are active at the joining region of two rings.The oblique figure“8”is on the order of several kilometers with respect to theZ-axis,and on the order of meters per second with respect to theVz-axis.These reflect that the intersection points in Fig.7 distribute in a much largerrange comparing with those in Fig.6.There are remarkably different motions of quasiorbits in region I and region II,and orbits in region II are more reactive to perturbations.
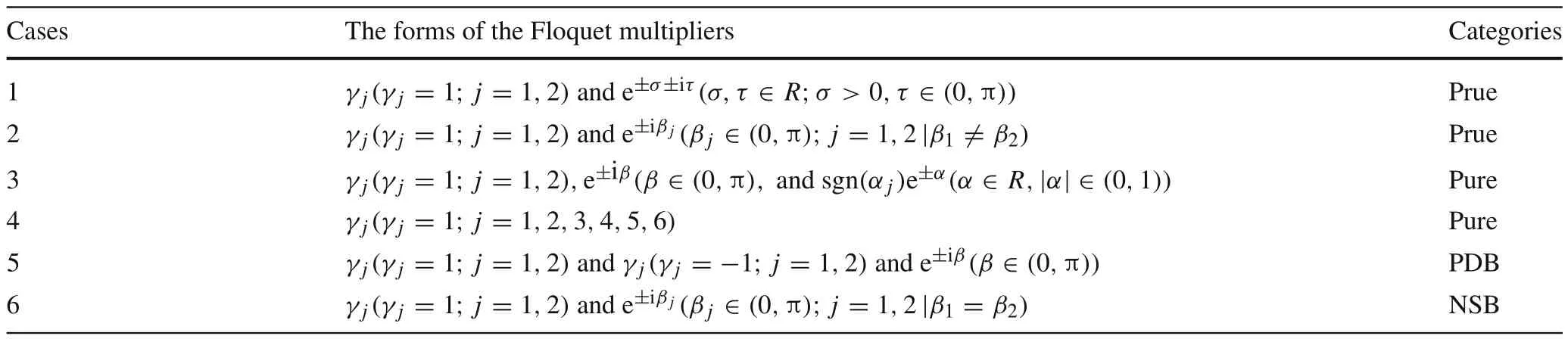
Table 4 Topological cases of Floquet multipliers belonging to pure-periodic cases,PDB,and NSB,respectively[34]

Table 5 Parameters for the regions represented in Fig.5
We choose a group of orbital initials similar to those of Dactyl from the two-body model and calculate its evolution for 2000 days.The orbit is called quasi-orbit 13.The calculation result suggests that the particle orbits the primary stably.The trajectory is within a 3-D space similar to a tire around the body,as shown in Fig.8.The Poincare sectionsVz?Zrelative to the orbit is also shown in Fig.8,and it is very similar to those in Fig.6.Figure 9 presents the evolutions of the orbital parameters,which coincide well with Dactyl’s observed parameters.Short-term and longterm periodic variations coexist in the evolution of each parameter.It has serious possibility that Dactyl is in a suchlike quasi-periodic orbit in region I around the primary.
These quasi-periodic orbits are very appropriate to park probes,since less propulsion is required for station-keeping for their st abilities.Moreover,the stable relative motion to the primary makes it easy for global mapping of the asteroid.In addition,alternative distances between probe and the primary will balance the requirement of the safety and observation.
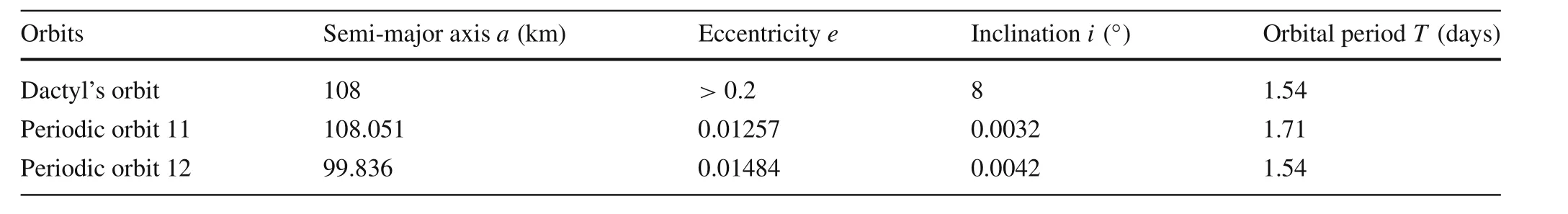
Table 6 Comparison of average orbital parameters between Dactyl’s orbit and the periodic orbits in region I
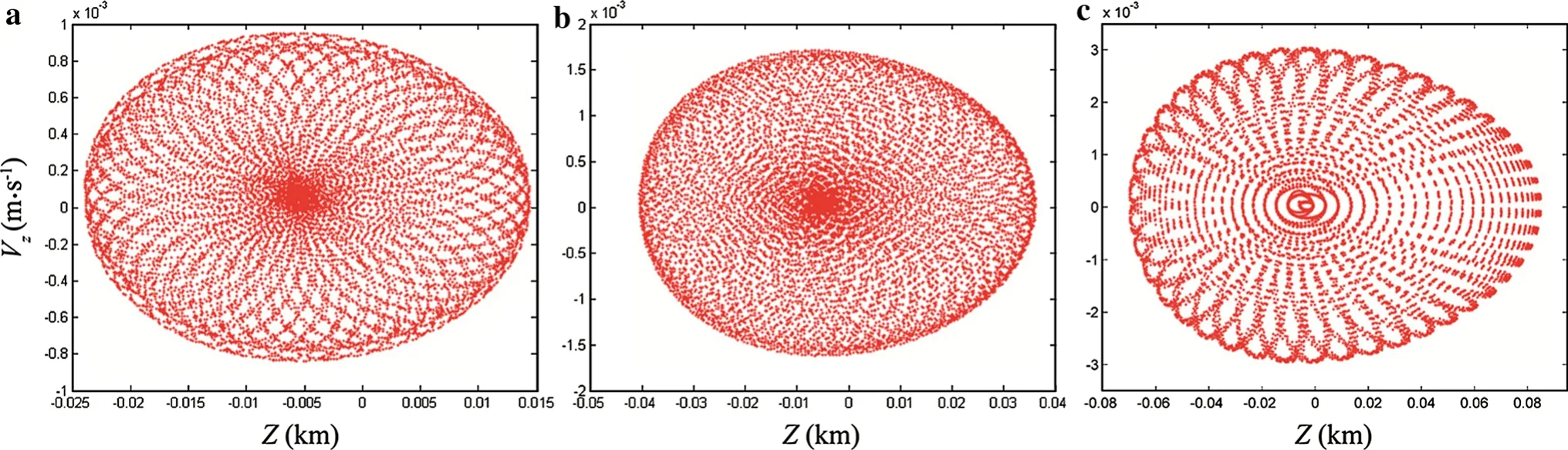
Fig.6 The Poincare sections Vz?Z calculated in stable region I.a 0.25%perturbation.b 0.5%perturbation.c 1.0%perturbation
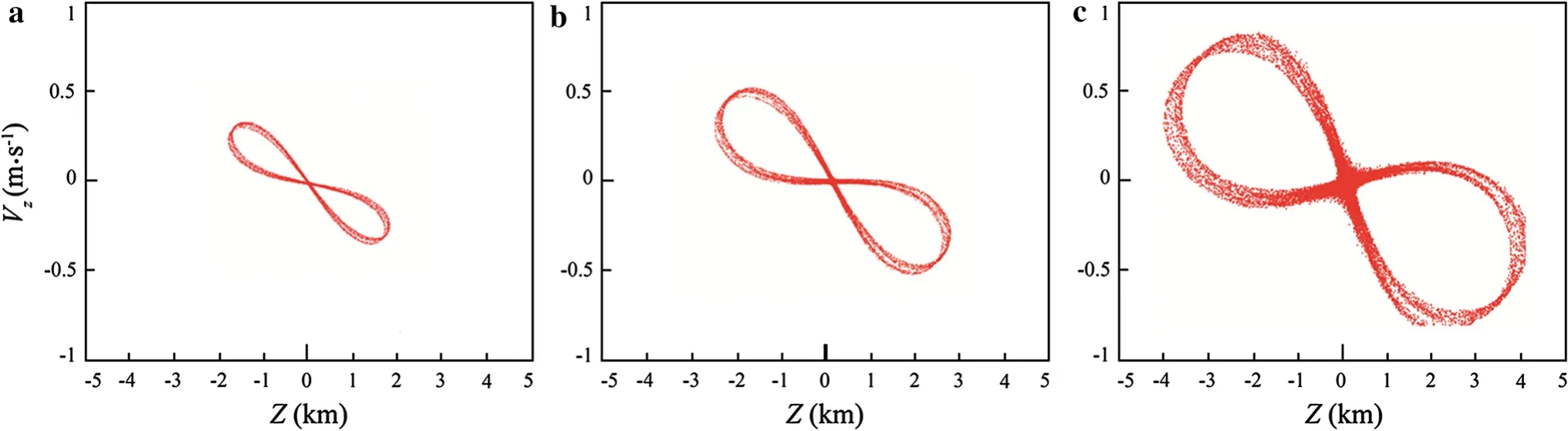
Fig.7 The Poincare sections Vz?Z calculated in unstable region II.a 0.25%perturbation.b 0.5%perturbation.c 1.0%perturbation
5 Conclusions
Periodic orbits around the primary found in the binary system 243 Ida show sophisticated geometric natures.They can be classified as the orbits around equilibrium points and largescale orbits.The continuation results suggest the abundance and denseness of periodic orbits.The transfers of the Floquet multipliers’topological cases relative to each family indicate most of mentioned periodic orbits are unstable,except the orbits near the equatorial plane.These orbits are near circular.During the continuation of the retrograde orbits,two PDBs and one NSB occur one by one,leading to two stable regions and two unstable regions.Periodic orbits in the stable regions are all stable,but in the unstable regions are unstable.Moreover,many stable quasi-periodic orbits exist in these regions.Poinc are sectionsVz?Zcalculated in region I and region II show different styles of motions of quasi-periodic orbits.Orbits in unstable region II are more likely to diverge.Combining with the observed orbital parameters of Dactyl,it has serious possibility that Dactyl is in a quasi-periodic orbit around the primary in stable region I,which gives an explanation for the motion stability of the binary system.Furthermore,these also suggest a feasible region to park probes in missions.
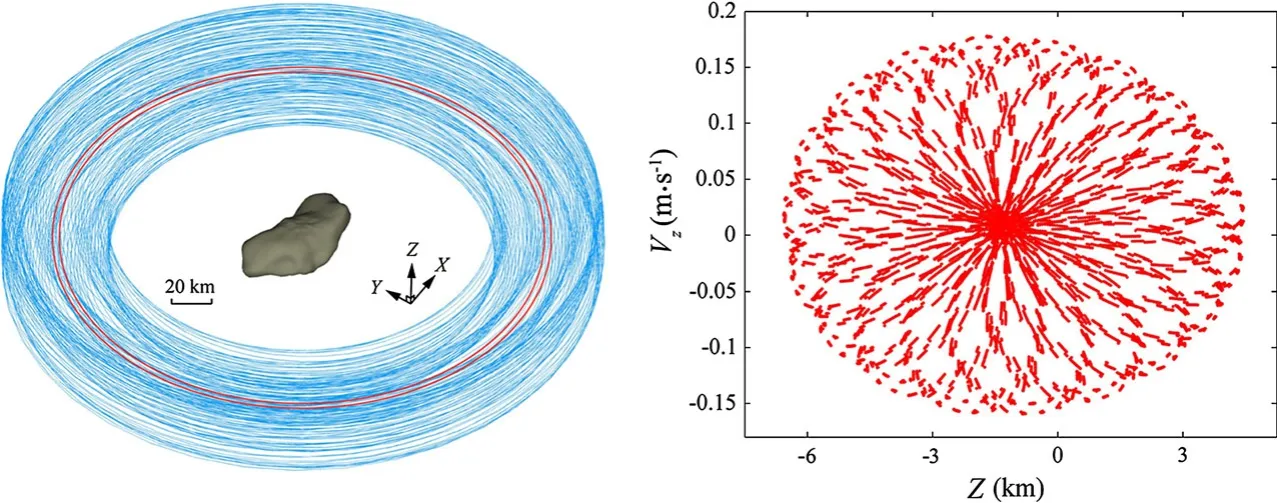
Fig.8 3-D Quasi-periodic orbit and Poincare sections Vz?Z relative to the quasi-periodic orbit.The red circles in left figure are periodic orbit 11 and 12
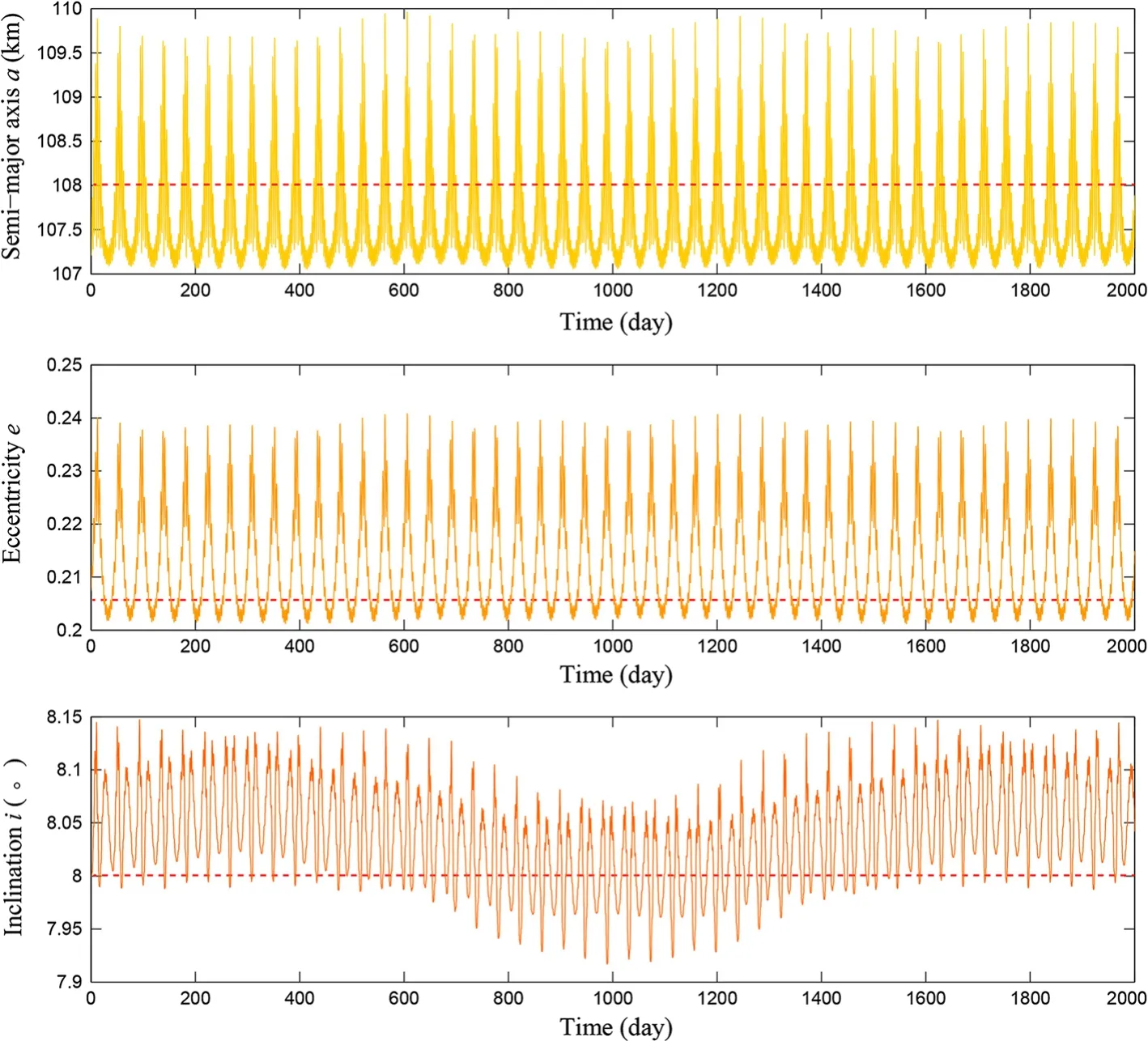
Fig.9 The evolution of the quasi-periodic orbit 13.The red dot lines represent the observed orbital parameters of Dactyl
AcknowledgementsWe are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for expeditious review and useful comments.This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant11572166).
1.Belton,M.J.,Chapman,C.R.,Veverka,J.,et al.:First images of asteroid 243 Ida.Science 265,1543–1547(1994)
2.Helfenstein,P.,Veverka,J.,Thomas,P.C.,et al.:Galileo photometry of asteroid 243 Ida.Icarus 120,48–65(1996)
3.Chapman,C.R.,Klaase,K.,Belton,M.J.S.,etal.:Asteroid 243 Ida and its satellite.Meteoritics 29,455(1994)
4.Kevin,J.W.,Seth,A.J.:Formation and evolution of binary asteroids.In:Asteroids IV,375–393.University of Arizona,Tucson(2015)arXiv:1506.06689v1
5.Takahashi,Y.,Scheeres,D.J.,Werner,R.A.:Surface gravity fields for asteroids and comets.J.Guid.Control.Dyn.36,362–374(2013)
6.Chanut,T.G.G.,Winter,O.C.,Tsuchida,M.:3D stability orbits close to 433 Eros using an effective polyhedral model method.Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc.438,2672–2682(2014)
7.Marchis,F.,Berthier,J.,Burns,K.J.,etal.:Characteristics of known triple asteroid systems in the main belt.Bull.Am.Astron.Soc.42,1050(2010)
8.Taylor,P.A.,Margot,J.L.:Binary asteroid systems:tidal end states and estimates of material properties.Icarus 212,661–676(2011)
9.Ostro,S.J.,Hudson,R.S.,Nolan,M.C.,et al.:Radar observations of asteroid 216 Kleopatra.Science 288,836–839(2000)
10.Hartmann,W.K.:The shape of Kleopatra.Science 288,820–821(2000)
11.Jiang,Y.,Baoyin,H.,Li,H.:Periodic motion near the surface of asteroids.Astrophys.Space Sci.360,1–10(2015)
12.Elipe,A.,Riaguas,A.:Nonlinear stability under a logarithmic gravity field.Int.Math.J.3,435–453(2003)
13.Blesa,F.:Periodic orbits around simple shaped bodies.Monogr.Semin.Mat.García Galdeano 33,67–74(2006)
14.Liu,X.,Baoyin,H.,Ma,X.:Equilibria,periodic orbits around equilibria,and heteroclinic connections in the gravity field of a rotating homogeneous cube.Astrophys.Space Sci.333,409–418(2011)
15.Li,X.,Qiao,D.,Cui,P.:The equilibria and periodic orbits around a dumbbell-shaped body.Astrophys.Space Sci.348,417–426(2013)
16.Zeng,X.,Baoyin,H.,Li,J.:Updated rotating mass dipole with oblateness of one primary(II):out-of-plane equilibria and their stability.Astrophys.Space Sci.361,1–9(2015)
17.Gabern,F.,Koon,W.S.,Marsden,J.E.:Binary asteroid observation orbits from a global dynamical perspective.SIAM J.Appl.Dyn.Syst.5,252–279(2006)
18.Shang,H.,Wu,X.,Cui,P.:Periodic orbits in the doubly synchronous binary asteroid systems and their applications in space missions.Astrophys.Space Sci.355,69–87(2014)
19.Yu,Y.,Baoyin,H.:Routing the asteroid surface vehicle with detailed mechanics.Acta Mech.Sin.30,301–309(2014)
20.Wang,X.,Jiang,Y.,Gong,S.:Analysis of the potential field and equilibrium points of irregular-shaped minor celestial bodies.Astrophys.Space Sci.353,105–121(2014)
21.Werner,R.A.,Scheeres,D.J.:Exterior gravitation of a polyhedron derived and compared with harmonic and mascon gravitation representations of asteroid 4769 Castalia.Celest.Mech.Dyn.Astron.65,313–344(1997)
22.Scheeres,D.J.,Ostro,S.J.,Hudson,R.S.,et al.:Orbits close to asteroid 4769 Castalia.Icarus 121,67–87(1996)
23.Yu,Y.,Baoyin,H.:Generating families of3D periodic orbits about asteroids.Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc.427,872–881(2012)
24.Ni,Y.,Jiang,Y.,Baoyin,H.:Multiple bifurcations in the periodic orbit around Eros.Astrophys.Space Sci.361,1–15(2016)
25.Lan,L.,Yang,M.,Baoyin,H.,et al.:The periodic dynamics of the irregular heterogeneous celestial bodies.Astrophys.Space Sci.362,38(2017)
26.Stooke,P.:Stooke small bodies maps V2.0.MULTI-SA-MULTI-6-STOOKEMAPS-V2.0.NASA Planetary Data System(2012)
27.Wang,X.,Li,J.,Gong,S.:Bifurcation of equilibrium points in the potential field of asteroid 101955 Bennu.Mon.Not.R.Astron.Soc.455,3724–3734(2016)
28.Arnold,V.I.:Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics.Springer,Berlin(1978)
29.Szebehely,V.:Theory of Orbits—The Restricted Problem ofThree Bodies.Academic Press,New York(1967)
30.Jiang,Y.,Baoyin,H.:Orbital mechanics near a rotating asteroid.J.Astrophys.Astron.35,17–38(2014)
31.Jiang,Y.:Equilibrium points and periodic orbits in the vicinity of asteroids with an application to 216 Kleopatra.Earth Moon Planets 115,31–44(2015)
32.Scheeres,D.J.:Orbital mechanics about small bodies.Acta Astronaut.7,14–21(2012)
33.Hénon,M.:Exploration numérique du problème restreint.II.Masses égales,stabilité des orbites périodiques.Ann.Astrophys.28,992–1007(1965)
34.Jiang,Y.,Yu,Y.,Baoyin,H.:Periodic orbits,stability and bifurcations in the potential field of highly irregular-shaped celestial bodies.Nonlinear Dyn.81,119–140(2014)
35.Mu?oz-Almaraz,F.J.,Freire,E.,Galán,J.,et al.:Continuation of periodic orbits in conservative and Hamiltonian systems.Physica D Nonlinear Phenom.181,1–38(2003)
36.Tresaco,E.,Elipe,A.,Riaguas,A.:Computation of families of periodic orbits and bifurcations around a massive annulus.Astrophys.Space Sci.338,23–33(2012)
37.Jiang,Y.,Baoyin,H.,Li,J.,et al.:Orbits and manifolds near the equilibrium points around a rotating asteroid.Astrophys.Space Sci.349,83–106(2014)
38.Jiang,Y.,Yu,Y.,Baoyin,H.:Topological classifications and bifurcations of periodic orbits in the potential field of highly irregular-shaped celestial bodies.Nonlinear Dyn.81,119–140(2015)
39.Scheeres,D.J.,Williams,B.G.,Miller,J.K.:Evaluation of the dynamic environment of an asteroid:applications to 433 Eros.J.Guid.Control.Dyn.23,466–475(2000)
- Acta Mechanica Sinica的其它文章
- Adaptive ANCF method and its application in planar flexible cables
- Analytical modeling and simulation of porous electrodes:Li-ion distribution and diffusion-induced stress
- Macro and micro mechanics behavior of granite after heat treatment by cluster model in particle flow code
- Effect of a viscoelastic target on the impact response of a flat-nosed projectile
- Highly accurate symplectic element based on two variational principles
- Crack deflection occurs by constrained microcracking in nacre

