Volumetric and Transport Properties of Aqueous NaB(OH)4Solutions*
ZHOU Yongquan (周永全), FANG Chunhui (房春暉)*, FANG Yan (房艷) and ZHU Fayan (朱發(fā)巖)
1CAS Key Laboratory of Salt lake Resources and Chemistry, Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qinghai 810008, China
2Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Beijing 100039, China
Volumetric and Transport Properties of Aqueous NaB(OH)4Solutions*
ZHOU Yongquan (周永全)1,2, FANG Chunhui (房春暉)1,*, FANG Yan (房艷)1, and ZHU Fayan (朱發(fā)巖)1,2
1CAS Key Laboratory of Salt lake Resources and Chemistry, Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qinghai 810008, China
2Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Beijing 100039, China
Density, pH, viscosity, conductivity and the Raman spectra of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions precisely measured as functions of concentration at different temperatures (293.15, 298.15, 303.15, 313.15 and 323.15 K) are presented. Polyborate distributions in aqueous NaB(OH)4solution were calculated, covering all the concentrationrange,is the most dominant species, other polyborate anions are less than 5.0%. The volumetric and thetransport properties were discussed in detail, both of these properties indicate thatbehaves as a structure-disordered anion.
aqueous NaB(OH)4solution, volumetric property, transport property, polyborate distribution
1INTRODUCTION
Hydroxy-hydrated borates constitute the bulk of the mineral and optical ma?terial kingdom. Especially the tetrahy?dridoborate (BH4), as the reduction product of B(OH)4, are versatile reducing agents in various organic and inorganic processes [1]. The percentage of hydrogen presented in NaBH4and released by hydrolysis are 10.6% and 10.8%, respectively. Therefore, NaBH4is the most attractive chemical hydride for H2generation and storage in automotive fuel cell applications [2, 3]. However, the extensive use of NaBH4fuel would require the disposal of large quantities of the product NaB(OH)4. NaBH4can be regenerated from NaB(OH)4chemically [4-7]. Unfortunately, most chemical regeneration syntheses proposed so far involve several reaction steps with high cost. Furthermore, the by-products, wastes, and greenhouse gas emissions have already aroused the growing concern from the public. Luckily, the use of an electrolytic cell to reduce NaB(OH)4would not create large quantities of by-products, wastes, or emissions. There are a number of patents indicating the possibility ofelectroreductionciency and 20% to 80% yield on electrocatalytic hydrogenation cathodes [8-10]. However, reproduction of these claims was facing a number of difficulties, some researchers even got the conclusion that direct electroreduction of NaB(OH)4into NaBH4was impossible [11].
Physicochemical properties such as density, electrical conductivity, viscosity, and acidity at moderate temperatures, affect the H2generation and storage system as well as the electrochemical recyclability of sodium metaborate. The density of NaB(OH)4solutions has been measured at moderate temperatures by Ward et al. [12], Corti et al. [13] and Ganopolsky et al [14]. The conductivity and viscosity have been studied by Corti et al. [13, 15], and Cloutier et al. [16] reported the properties (pH, density, conductivity and viscosity) of saturated NaB(OH)4in aqueous alkaline solutions. However, all those studies were under the concentration of 1.0 mol·L?1or a saturated single point. In the present paper, the density, electrical conductivity, viscosity, acidity and Raman spectra of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions were assembled systematically. Not only the volumetric and transport properties of aqueous NaB(OH)4solution were deliberated, but also the chemical species distribution was given for the first time.
2EXPERIMENTAL
Commercially available metaborate [NaB(OH)4·2H2O, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., AR] was recrystallized twice from double-distilled water [17] (electrical conductivity, κ<1.0 μS·cm?1). The entire sample solutions were prepared by mass using double-distilled water, and the overall relative uncertainty in the solution preparation was 0.1%. The borate solutions were carefully protected from atmospheric CO2and can be used about one week without concentration changes.
Densities, ρ, of all the solutions were determined using a DMA4500 apparatus (Anton Paar, Austria) with an uncertainty of 0.00003 g·cm?3and temperature was controlled to ±0.03 K. The instrument was calibrated prior to initiation of each series of measurements, using air and double-distilled water as reference substances. Electrical conductivity, κ, was measured with an YSI 3200 conductivity meter (YSI, USA) using black-platinized electrode with a reproducibility of 0.3%. The constant of electrode was calibrated using six NaCl standard solutions (0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 0.5 and 1.0 mol·kg?1). A standard solution was measured every five measurements, the constant recalibrated if the deviation ≥0.3%. Acidity, pH, of all the solutions was measured using an Orion 310P-01 pH meter(Thermo, USA) with a reproducibility of 0.5%. The pH electrode was calibrated using three pH standard solutions (4.003, 6.864 and 9.182), a standard solution was used for checkup after every five measurements, the electrode recalibrated if the deviation ≥0.5%. In all the pH and conductivity measurements, a thermostat (GDH-1015W, Sayfo Analytical Instrument Factory, Ningbo, China) was used to maintain the temperature of the solutions within ±0.01 K uncertainty. Viscosity, η, was measured with a single Ubbelohde viscometer (Jingliang Precise Instrument Co., Shanghai, China), which was placed in a well-stirred constant temperature water bath and the temperature of the solutions was kept within ±0.05K uncertainty. The flow time was measured with an accurate 0.01 s stopwatch and the double-distilled was used for calibration. Measurements were repeated at least 4 times for each solution and temperature. The uncertainty of the viscosity measurements was estimated to be 0.5%. Raman spectra of solid and liquid samples were recorded in the ranges of 300-4000 cm?1, respectively, with a Nicolet Almega Dispersive Raman spectrometer (laser: 532 nm, exposure time: 8 s) at room temperature. The solid samples were put in the microscope slide (number of exposures: 1). The liquid samples were held in a quartz glass tube (number of exposures: 32).
3RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1Chemical species in solutions
Measured pH of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions were collected in Table 1 as functions of molality (m), at 298.15 and 323.15 K.
pH of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions raises with concentration increasing, but at different concentration range different increasing rate can be found. In extreme low concentration (m<0.07 mol·kg?1), pH rises sharply with concentration increase. This maybe because the polyborates do not show any significant extent of polymerization, and the dominant species are B(OH)?4and B(OH)3in the extremely dilute solution. The dehydration and polymerization make pH changes complicated with concentration increase in moderate concentration (0.07<m<1.46 mol·kg?1). A good linear relationship between pH and concentration can be seen in high concentration (m>1.46 mol·kg?1), which may be due to the low acidity makes B(OH)?4become the dominant borate.
Raman spectrum is an effective method for polyborate study [18]. In order to get a clear picture of the main polyborates and their equilibria in aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions, Raman spectra of the labeled solutions in Table 1 were recorded and displayed in Fig. 1. Range of 500-1200 cm?1is the most favorable zone for the investigation of borate solution, which might be considered as the characteristic absorption bands of polyborates [19-21]. The only obvious band near 741 cm?1in Raman spectra of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions is the characteristic peak of the
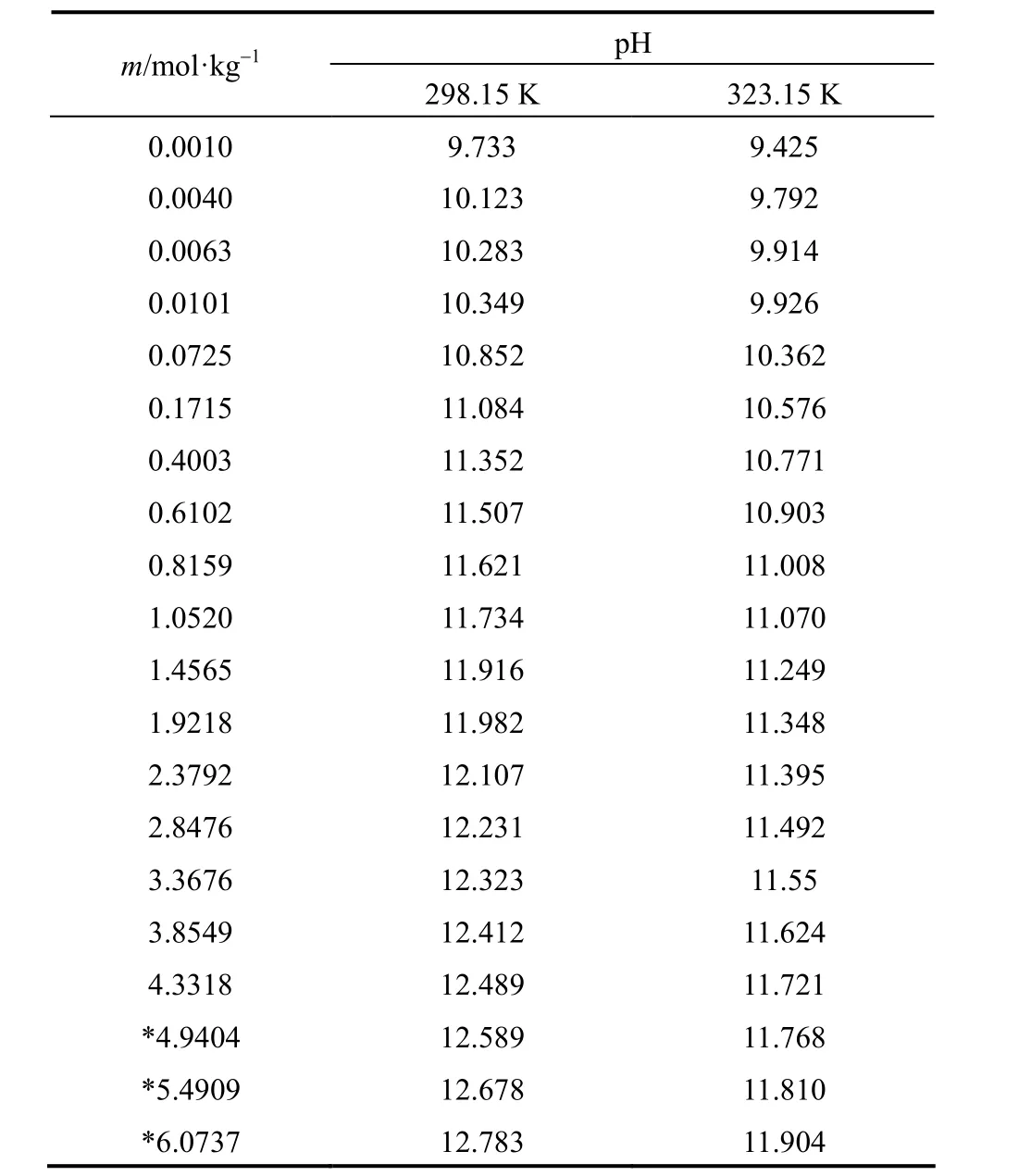
Table 1pH of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions as functions of concentration at 298.15 and 323.15 K
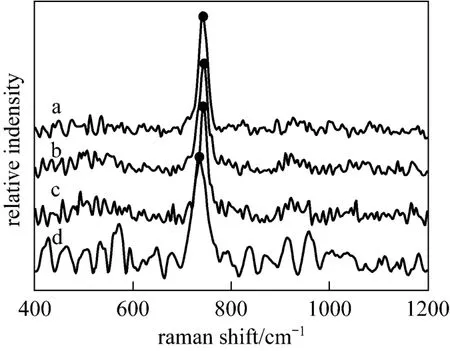
Figure 1microcrystals; ● characteristic peak
Polyborate distributions in aqueous NaB(OH)4solution at 298.15 and 323.15 K were calculated using measured pH values and the literature equilibrium constants [22-24] by Newton iteration algorithm, as Fig. 2 shown. δ is the moles of boron for individual polyborate divided by the moles of total boron. As Fig. 2 shown, the dominating borate anions is B(OH)?4, the other polyborates (H3BO3, B3O3(OH)?4, B3O3(OH)52?, B4O5(OH)24?and B5O6(OH)?4are less than 5% in NaB(OH)4solution.
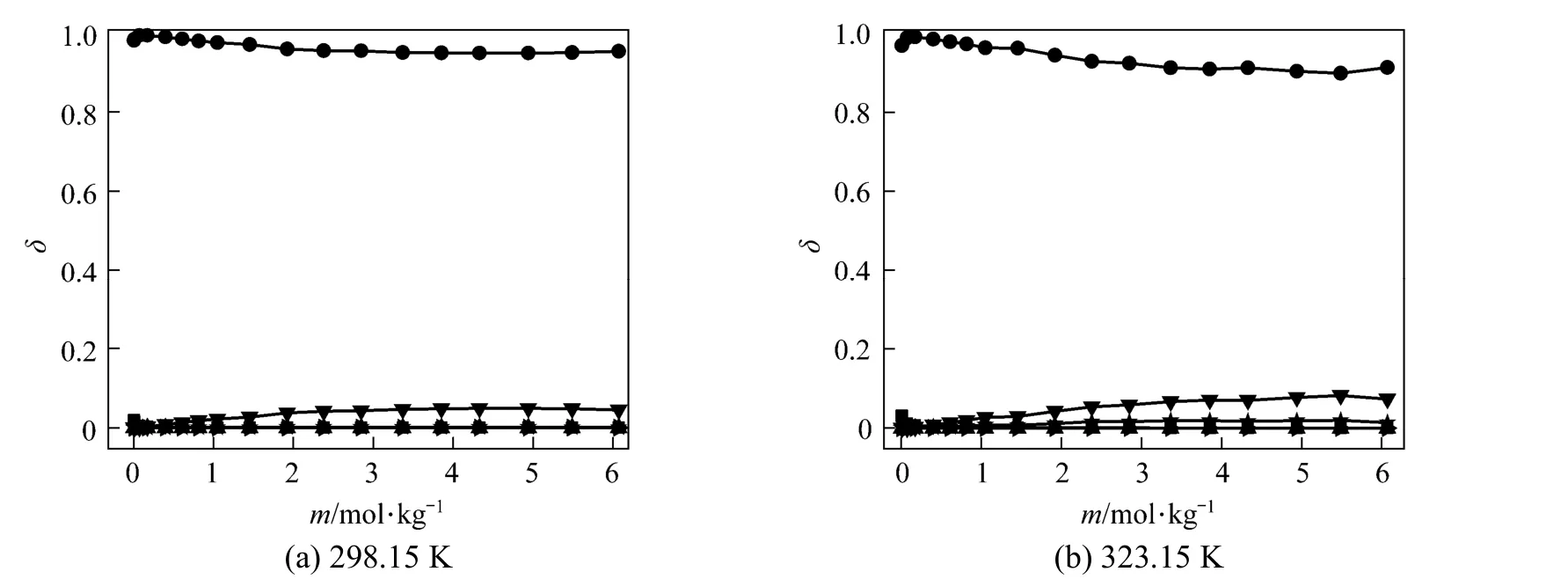
Figure 2Variation in the distribution of boron species with concentration in aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions at 298.15 and■ H3BO3;
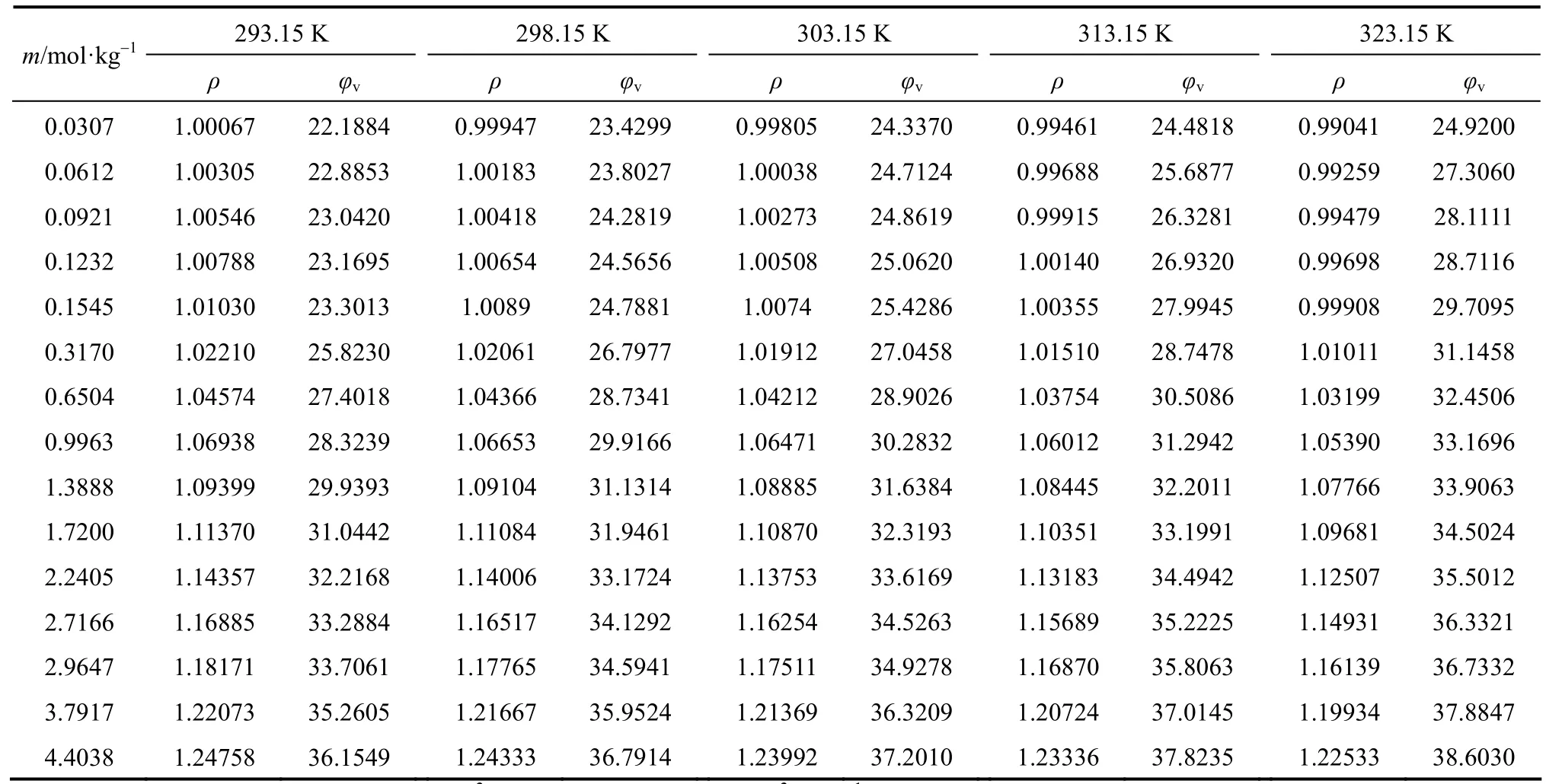
Table 2Density and φvof aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions at various temperatures
So the sodium metaborate [NaB(OH)4·2H2O] was assumed to dissociate in aqueous NaB(OH)4solution as follows:
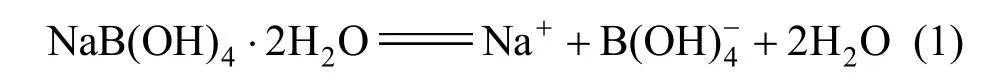
Therefore, all our results reported for sodium metaborate were denoted as NaB(OH)4 which dissoci
3.2Volumetric properties
3.2.1Density
The densities of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions were measured at 293.15, 298.15, 303.15, 313.15 and 323.15 K. The density and apparent molar volume of the solution, as a function of concentration and temperature are shown in Table 2.
The apparent molar volumes φvfor these solutions, given in Table 2 were calculated from the equation
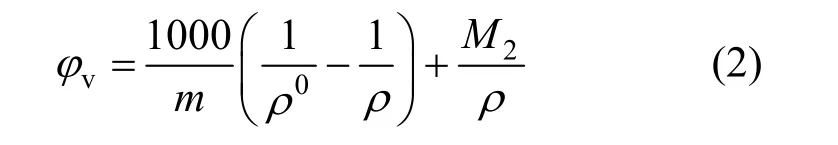
where ρ0is the density of water at corresponding temperatures, ρ0=0.99823, 0.99707, 0.99568, 0.99225 and 0.98807 g·cm?3at 293.15, 298.15, 303.15, 313.15 and 323.15 K, respectively; m is the molality (mol·kg?1) of solution and M2is the molecular weight of the compounds, 101.828 for NaB(OH)4here.
Most of the equations reported in the literature [25] with only two variables, i.e. the density and theconcentration or temperature. Here we proposed a new expression, Eq. (3), which takes the density as a function of both concentration and temperature.
ρ=A+Bm+Cmt+Dmt2+Em1.5+Fm1.5t+Gm1.5t2(3) where A, B, C, D, E, F, G are empirical constant determined by least-squares fit; m is the concentration in units of mol·kg?1; t is the temperature in units of °C. Herein, for the aqueous NaB(OH)4solution, an empirical equation
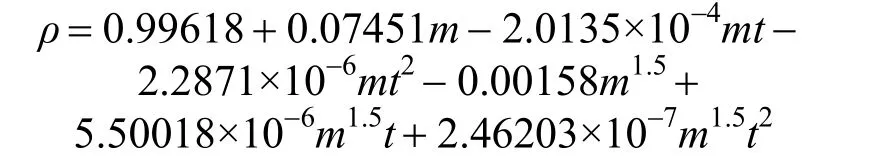
with R2=0.9988 was deduced in temperature range from 20 to 50 °C. Fig. 3 displays the measurements and the empirical density correlation of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions vs. concentration at 293.15, 298.15, 303.15, 313.15 and 323.15 K. As shown in Fig. 3, our experimental data are also in good agreement with the literature [12].
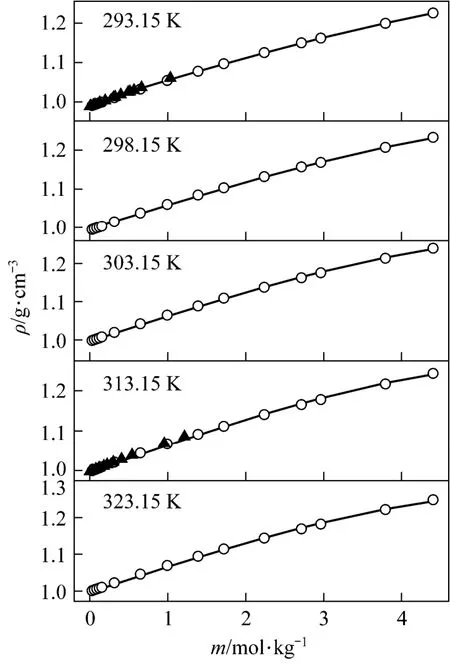
Figure 3Density vs. concentration plots for aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions at various temperatures○ experimental values; ▲ literature data for NaB(OH)4[12]; calculated data from nonlinear fitting
3.2.2Apparent molar volumes
The concentration dependence of the φvof NaB(OH)4is shown in Fig. 4. Correspondingly, we fi tted the experimental data to a three constant polynomial of concentration (mol·kg?1)
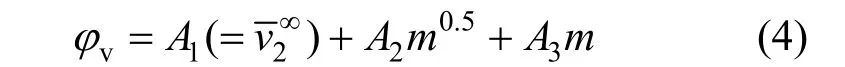
Figure 4Plot of apparent molar volume (φv) against molality of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions at different temperatures■ 313.15 K; ● 323.15 K; ▲ 303.15 K; ▼ 298.15 K;293.15 K
The temperature dependence of theof NaB(OH)4, shown in Fig. 5, can be expressed by the equation
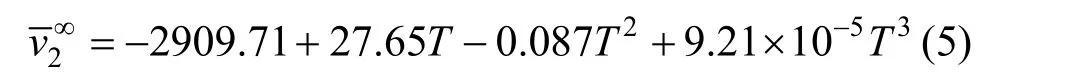
Table 3Least-squares parameters of Eq.for aqueous NaB(OH) solutions4
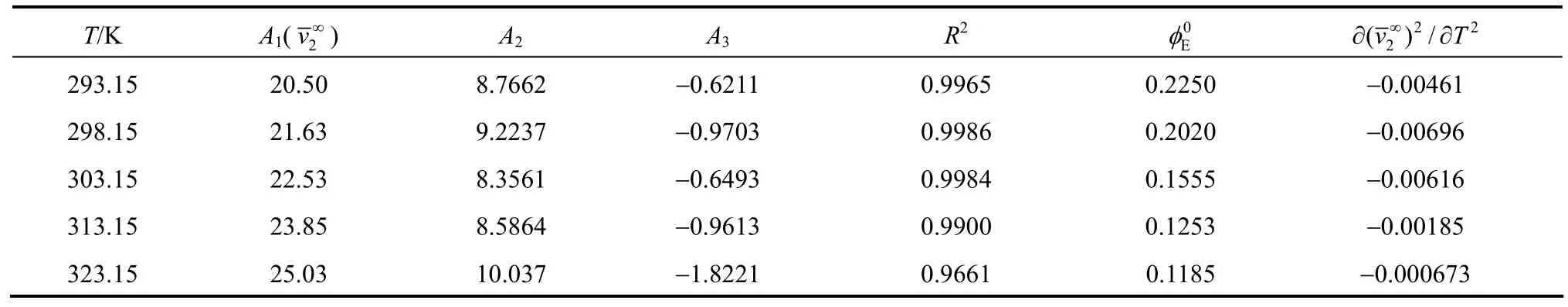
Table 3Least-squares parameters of Eq.for aqueous NaB(OH) solutions4
T/K A1(v∞) A2A3R20Eφ 2??( )/vT 2 2 2∞293.15 20.50 8.7662 ?0.6211 0.9965 0.2250 ?0.00461 298.15 21.63 9.2237 ?0.9703 0.9986 0.2020 ?0.00696 303.15 22.53 8.3561 ?0.6493 0.9984 0.1555 ?0.00616 313.15 23.85 8.5864 ?0.9613 0.9900 0.1253 ?0.00185 323.15 25.03 10.037 ?1.8221 0.9661 0.1185 ?0.000673
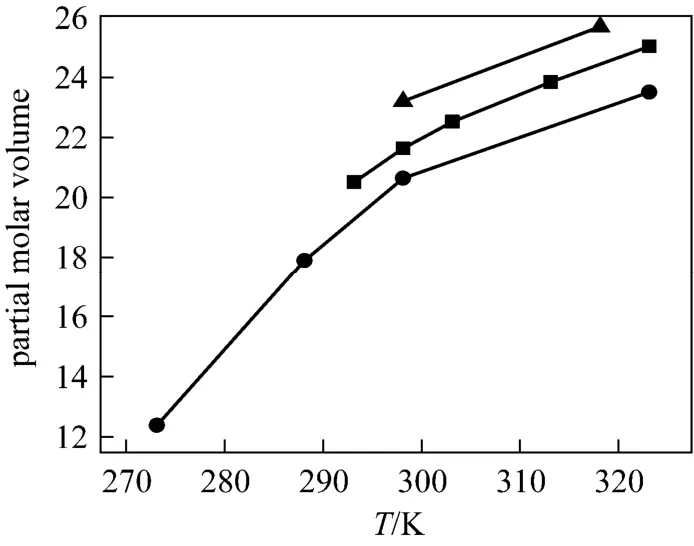
Figure 5Partial molar volumes at infinite dilution of NaB(OH)4as a function of temperature■ present work; ● Ward et al.; ▲ Corit et al.
As Fig. 5 shown, the agreement among the different data sources is satisfactory. Using Hepler’s [26] reasoning,would be classified as a “structure breaking” solute between 298.15 and 323.15 Kute has the hydrophilic character, while if the behaviorsolute has hydrophobic character) , this may due to the unique structure ofanion (four tetrahedrons OH groups) [27].
3.3Transport properties
3.3.1Viscosity
Measured viscosities for aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions were collected in Table 4. The viscosity data are plotted in Fig. 6 at two temperatures. A semi-empirical equation [28-30]:
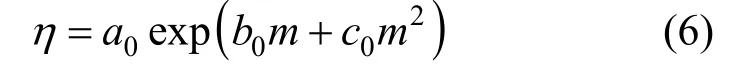
has been shown to be useful for data fi tting over wide concentration range, where a0, b0, and c0are the adjustable temperature dependent parameters. Theleast-squares fitted parameters in Eq. (6) are summarized in Table 5.
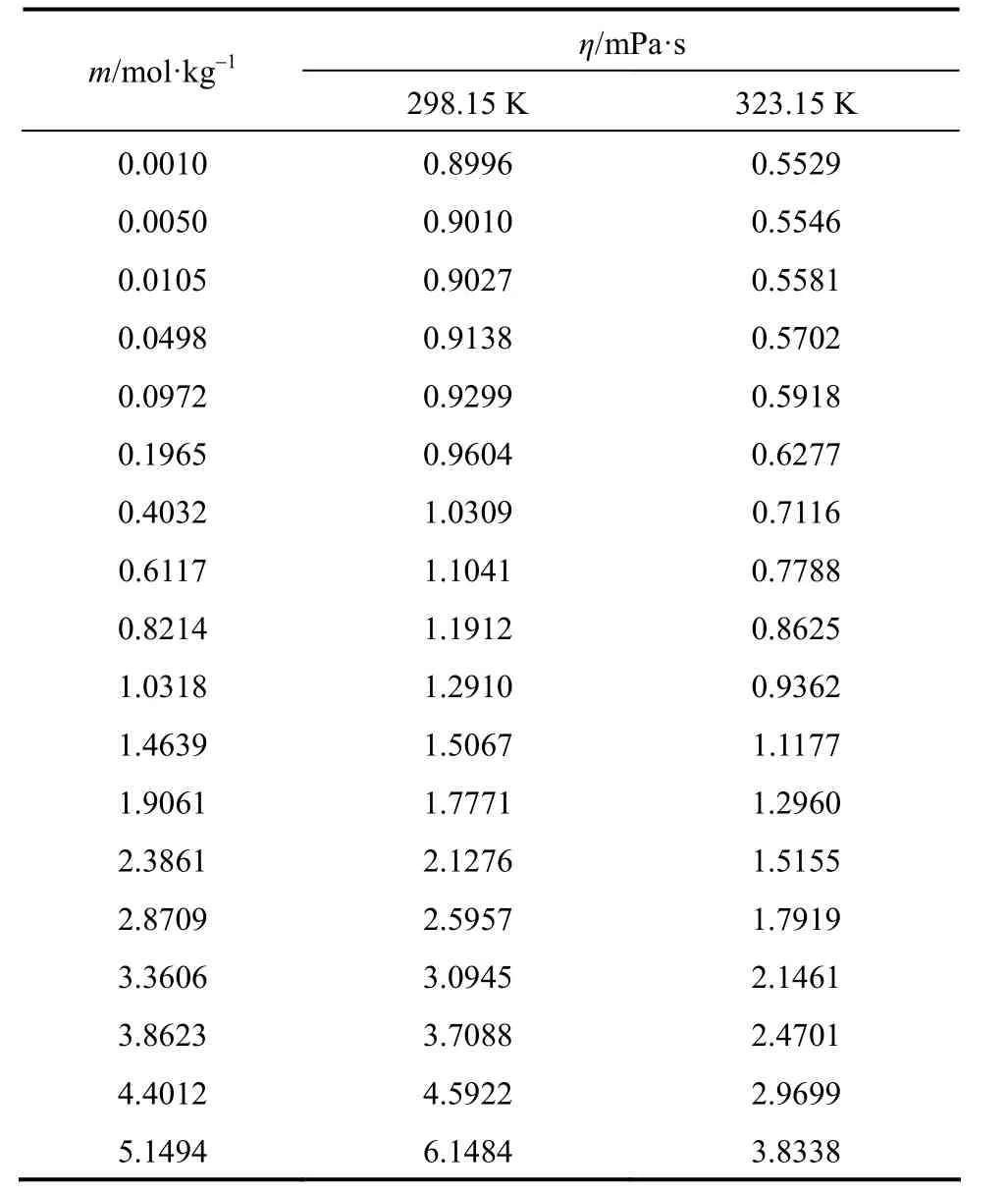
Table 4Viscosity of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions at as functions of concentration at 298.15 and 323.15 K
The viscosity data of concentration less than 0.1 mol·L?1were analyzed in terms of the extended Jones-Dole viscosity equation:
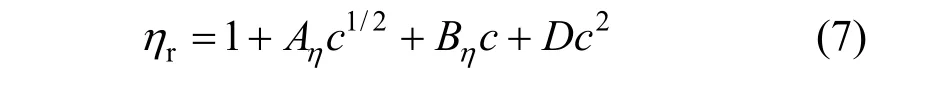
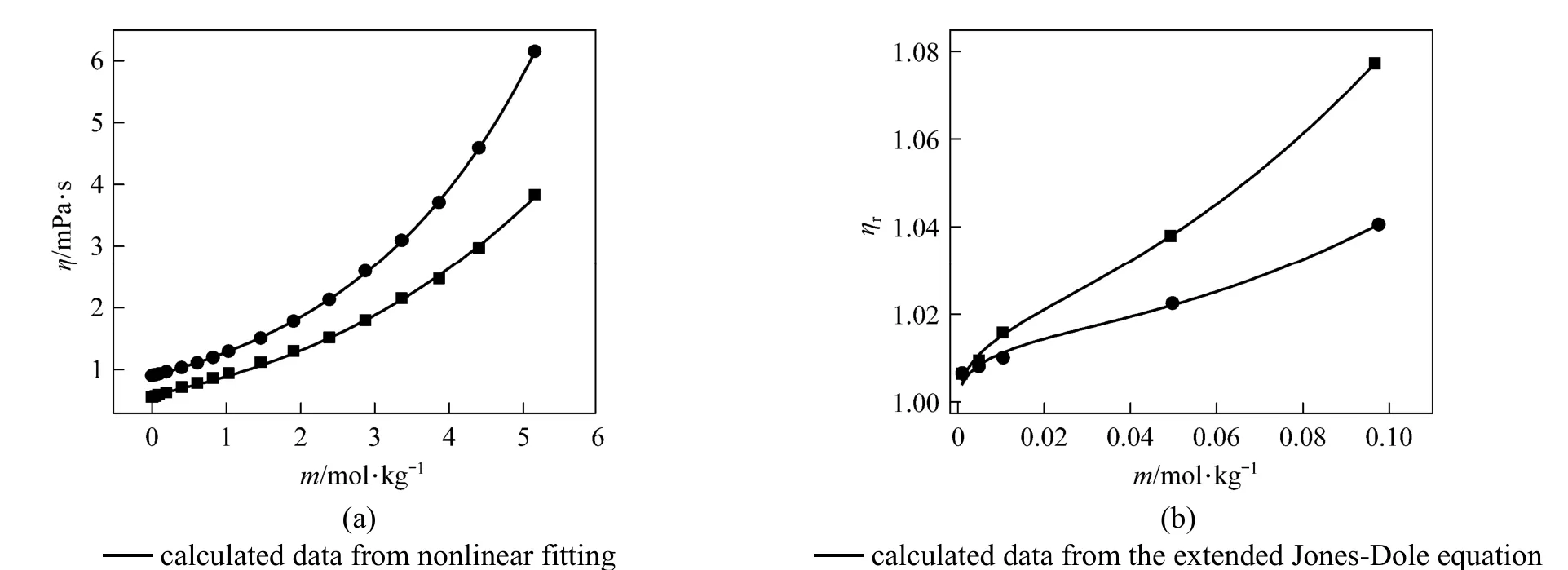
Figure 6(a) Viscosity vs. concentration plots for solutions at 298.15 K and 333.15K and (b) relative viscosity vs. concentration (<0.01 mol·L?1)● experimental values at 298.15 K; ■ experimental values at 333.15 K
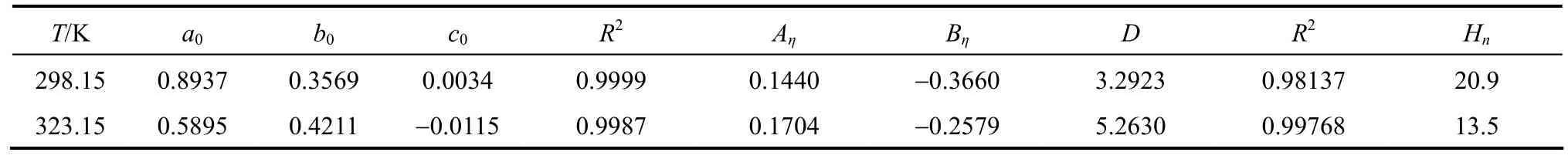
Table 5Coefficients for Eqs. (6) and (7) and the hydration number
where ηr=η/η0·ηr, η and η0are the relative viscosity, viscosity of the solution and viscosity of the solvent, respectively, and c is the molar concentration. Coefficient (Aη) is a measure of ion-ion interactions and may be calculated from equilibrium theory, as summed by Jenkins and Marcus [31]. Coefficient (Bη), also called the Jones-Dole coefficient, is an empirical constant, qualitatively correlating on the size of solute particle and on ion-solvent interaction characteristic for electrolyte and solvent [31]. Bηof B(OH)?4were calculated by subtracting the Bηof Na+ion [25] from the values of NaB(OH)4at 298.15 and 323.15 K, respectively, that is Bη,B(OH)?4,298.15=?0.452 L?mol?1and Bη,B(OH)?4,323.15=?0.339 L·mol?1, which are well consistent with the literature values of dilute aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions at 298.15 K [32]. The calculated Bηof B(OH)?4(Bη<0) indicated it behaves as a structure disordering ion between 298.15 to 323.15 K, which is consistent with our study on volumetric properties of aqueous NaB(OH)4solution.
For a dilute solution of spherical colloidal suspensions, Einstein derived the relation

where φ is the volume fraction of the solute. For 1︰1 type electrolyte, Eq. (9) becomes

where Vhis the hydrodynamic volume. Where Vhisthe partial molar volumeof the unsolvated solute particle in a continuum solvent. Thus, the value of the hydration number (Hn) can be calculated as

Hnlies between 0 and 2.5 for unsolvated species and has higher valu?es for solvated species. The calculated Hnof B(OH)4are 20.9 and?13.5 at 298.15 and 323.15 K indicated the B(OH)4are solvated in aqueous solution [33]. It’s maybe another evidence?for a tight hydration sphere is formed around B(OH)4in aqueous solutions.
3.3.2Electrical conductivity
The experimental electrical conductivities of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions are listed in Table 6.
Figure 7 (a) shows that a break can be found, the conductivity increases as concentration and temperature. The conductivity data over the whole concentration range studied were fi tted to the Casteel-Amisequation [30, 34]:
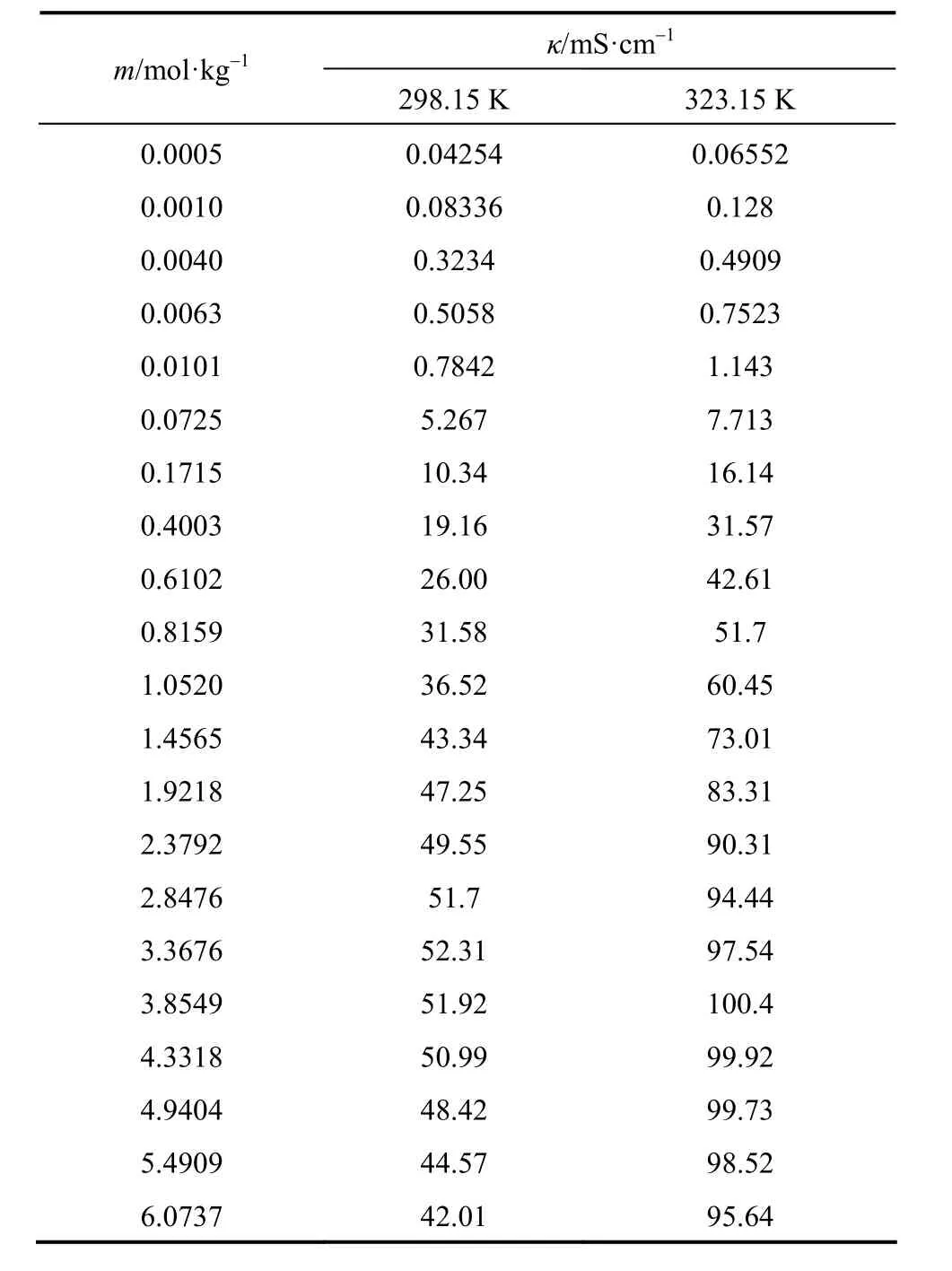
Table 6 Electrical conductivity of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions at as functions of concentration at 298.15 and 323.15 K
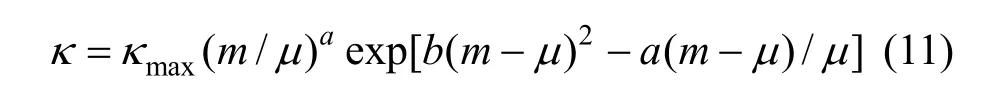
where μ is the concentration corresponding to the maximum conductivity κmaxat a given temperature; a and b are empirical parameters; m is molality in units of mol·kg?1. In all the concentration range a function between conductivity and concentration can be given though nonlinear fitting.
The decrease of molar conductivity with increasing concentration must be due to the increase of viscosity of the aqueous solution and polymerization. The polymerization makes charge carriers in unit volume decrease, and higher polyborate anions and their hydration also means the charge carriers are large in size, and the increasing viscosity make migration rateslower.In extremely dilute solution (smaller than 0.01to any significant e?xtent polymerization so the main species are B(OH)4and B(OH)3with an equilibrium as follows:
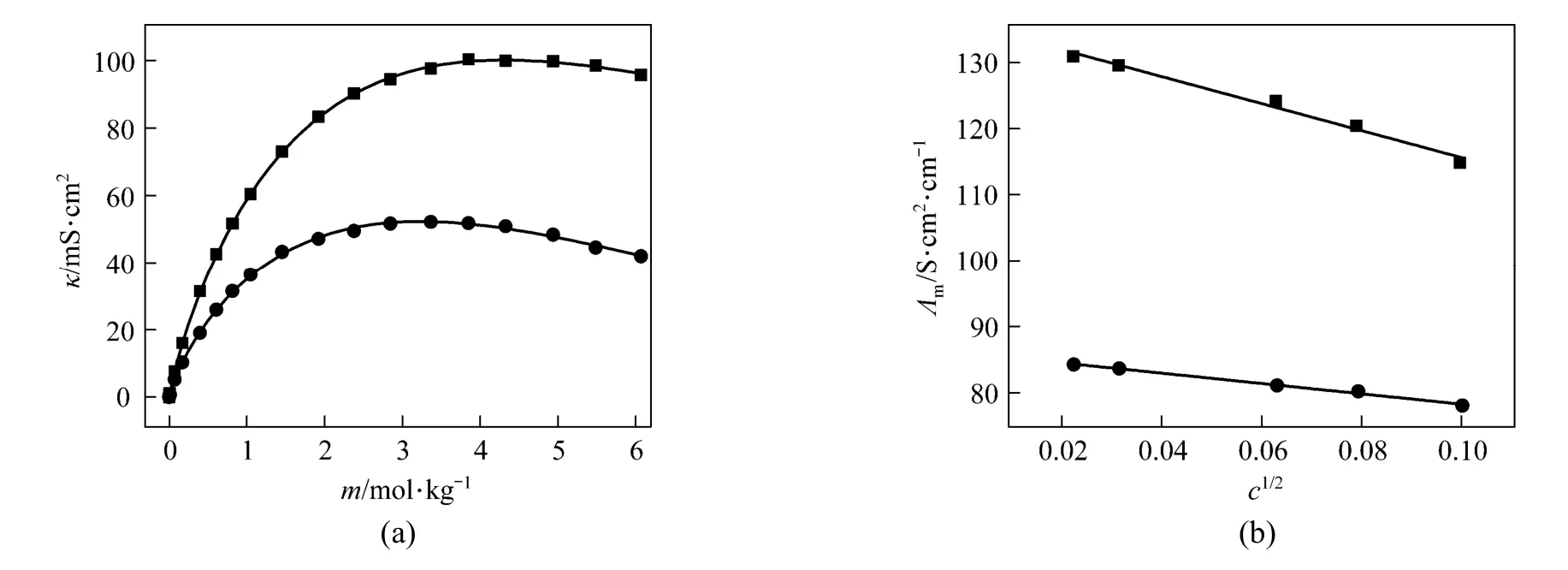
Figure 7(a) Conductivity vs. concentration plots for solutions at 298.15 and 323.15 K and (b) molar conductivity vs. concentration (<0.01 mol·L?1) to zero● experimental values at 298.15 K; ■ experimental values at 323.15 K; calculated data from nonlinear fitting
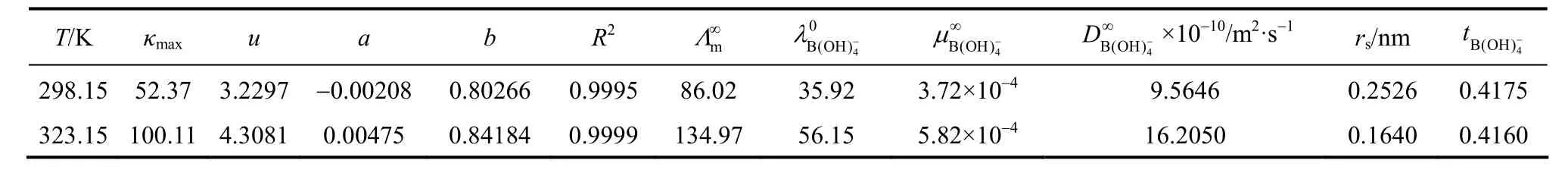
Table 7Values of kmax, u, a and b coefficients for Eq. (11) and the transport properties of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions
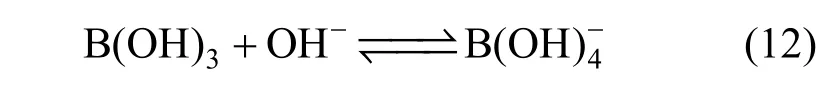
Limiting molar conductivity (mΛ∞) of NaB(OH)4can be gotten by extrapolate to c=0 mol·L?1through the Kohlrausch correlations. As Fig. 7 (b) shown, the plot ofmΛ against c1/2is a line withmΛ∞as intercept to slope A at concentration (c<0.01 mol·L?1) where Λ∞,298.15=86.02 and Λ∞,323.15=136.05 S·cm2·mol?1. The limiting ionic conductivities for the B(OH)?4ion were calculated by+subtracting the limiting ionic conductivities of Na ion [25] from the limiting molar conductivity of NaB(OH)4,well consistent with Corti’s conclusion at 298.15 K [15].
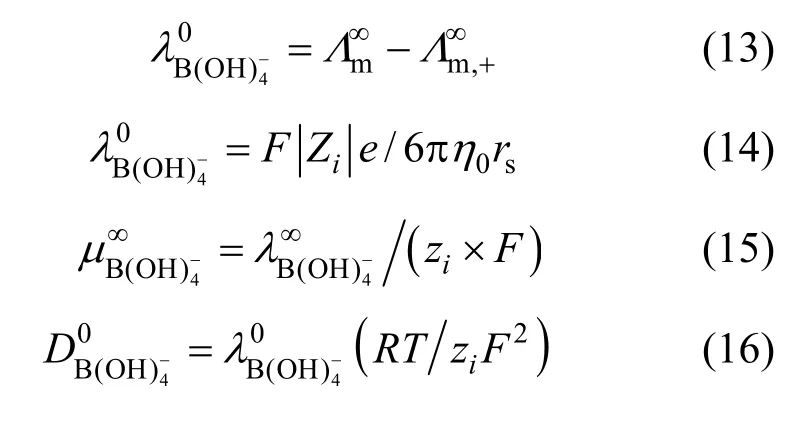
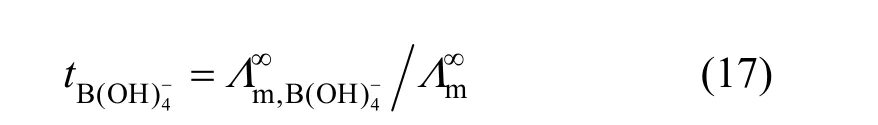
4CONCLUSIONS
pH of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions were precisely measured as functions of concentration from dilute to saturation at 298.15 and 323.15 K. Coupling with Raman spectra of some concentrated samples, polyborate distribution calculated using measured pH values and literature equilibrium constants of aqueousNaB(OH)4solutions shows?that covering all the concentration range, B(OH)4is the most dominant species, other polyborate anions are less than 5.0%. Densities of aqueous sodium borate solutions as functions of concentration (from diluted to saturate) and temperatures (293.15, 298.15, 303.15, 313.15 and 323.15 K) were summed, and semi-empirical equations for those properties vs. concentration were also suggested. Apparent molar volumes (φv), limit partial molar volumesand apparent molar expansibilitiesof sodium metaborate have been determined from those precision density. Conductivity data were analyzed with a semi-empirical equation over range concentration, and the limiting molar conductivity of298.15 and 323.15 K by the Kohlrausch correlations. From those values, the ionic mobility, diffusion coefficients and transference number for the4B(OH)?anion were given. Viscosity data were analyzed with a semi-empirical equation over range concentration, and the ion-solvent and ion-ion interactions were analyzed with an extended Jones-Dole type correlation at the extremely dilute concentration. Values of ?0.452 and?0.339 L·mol?1were estimated for the4B(OH)?B-coefficient at 298.15 and 323.15 K, respectively. Both of the volumetric and transport properties of aqueous NaB(OH)4solutions indicate that the B(OH)?4behaves like “structure breakers” between 293.15 and 323.15 K.
NOMENCLATURE
m molality, mol·kg?1
R universal gas constant, 8.314 J·mol?1·K?1rsstokes radius, m
T absolute temperature, K
t temperature, °C
ηrrelative viscosity
ρ density of solution, g·cm?3
ρ0density of pure water, g·cm?3
φvapparent molar volumes, cm3·mol?1
REFERENCES
1 Periasamy, M., Thirumalaikumar, P., “Methods of enhancement of reactivity and selectivity of sodium borohydride for applications in organic synthesis”, J. Organomet. Chem.,609(1-2), 137-151 (2000).
2 Li, H.W., Yan, Y.G., Orimo, S., Zuttel, A., Jensen, C.M., “Recent progress in metal borohydrides for hydrogen storage”, Energies,4(1), 185-214 (2011).
3 Jain, I.P., Jain, P., Jain, A., “Novel hydrogen storage materials: A review of lightweight complex hydrides”, J. Alloys Compd.,503(2), 303-339 (2010).
4 Ved, A.S., Miley, G.H., Seetaraman, T.S., “Recycling sodium metaborate to sodium borohydride using wind-solar energy system for direct borohydride fuel cell”, In: Proceedings of the ASME 8th International Conference on Fuel Cell Science, Engineering and Technology, USA, 139-141 (2010).
5 Kong, L.Y., Cui, X.Y., Jin, H.Z., Wu, J., Du, H., Xiong, T.Y.,“Mechanochemical synthesis of sodium borohydride by recycling sodium metaborate”, Energy Fuels,23(10), 5049-5054 (2009).
6 Kojima, Y., Haga, T., “Recycling process of sodium metaborate to sodium borohydride”, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,28(9), 989-993 (2003).
7 Cakanyildirim, C., Guru, M., “Processing of NaBH4from NaBO2with MgH2by ball milling and usage as hydrogen carrier”, Renew. Energy,35(9), 1895-1899 (2010).
8 Amendola, S., “Borohydride ion generation/consumption system for electric vehicle, has electrochemical cell to electrochemically reduce aqueous solution of oxidized form of borohydride ions, at alkaline pH to form borohydride ions”, U.S. Pat., 6497973-B1 (2002)
9 Sharifian, H., Dutcher, J. S. , “Quat. ammonium and quat. phosphonium borohydride(s) prepn. by electrolysis, useful in paper prodn., fuel cells, detection and tracing of organic cpds. in biological systems”, U.S. Pat., 4904357-A (1990).
10 Jia, Y.Z., Li, J., Gao, S.Y., Xia, S.P., “Thermochemistry of dipotassium calcium octaborate dodecahydrate”, Thermochim. Acta,335(1-2), 1-4 (1999).
11 Gyenge, E. L., Oloman, C. W., “Electrosynthesis attempts of tetrahydridoborates”, J. Appl. Electroch em.,28(10), 1147-1151 (1998).
12 Ward, G.K., Millero, F.J., “The effect of pressure on the ionization of boric acid in aqueous solutions from molal volume data”, J. Solution Chem.,3(6), 417-430 (1974).
13 Corti, H., Crovetto, R., Fernandezprini, R., “Properties of the borate ion in dilute aqueous-solutions”, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans.,76, 2179-2186 (1980).
14 Ganopolsky, J.G., Bianchi, H.L., Corti, H.R., “Volumetric properties of aqueous electrolytes at high temperature: II. B(OH)3and B(OH)3-NaB(OH)4-NaOH mixtures up to 523 K”, J. Solution Chem.,25(4), 377-389 (1996).
15 Corti, H., Crovetto, R., Fernández-Prini, R., “Mobilities and ion-pairing in LiB(OH)4 and NaB(OH)4aqueous solutions: A conductivity study”, J. Solution Chem.,9(8), 617-625 (1980).
16 Cloutier, C.R., Alfantazi, A., Gyenge, E., “Physicochemical properties of alkaline aqueous sodium metaborate solutions”, J. Fuel Cell Sci. Tech.,4(1), 88-98 (2007).
17 Nies, N.P., Hulbert, R.W., “Solubility isotherms in the system sodium oxide-boric oxide-water. Revised solubility temperature curves of boric acid, borax, sodium pentaborate, and sodium metaborate”, J. Chem. Eng. Data,12(3), 303-313 (1967).
18 Zhou, Y.Q., Fang, C.H., Fang, Y., Zhu, F.Y., “Polyborates in aqueous borate solution: A Raman and DFT theory investigation”, Spectrochim. Acta A,83(1), 82-87 (2011).
19 Hirao, T., Kotaka, M., Kakihana, H., “Raman spectra of polyborate ions in aqueous solution”, J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem.,41(8), 1217-1220 (1979).
20 Liu, Z.H., Gao, B., Hu, M.C., Li, S.N., Xia, S.P., “FT-IR and Raman spectroscopic analysis of hydrated cesium borates and their saturated aqueous solution”, Spectrochim. Acta. A,59(12), 2741-2745 (2003).
21 Liu, Z.H., Gao, B., Li, S.N., Hu, M.C., Xia, S.P., “Raman spectroscopic analysis of supersaturated aqueous solution of MgO-B2O3-32%MgCl2-H2O during acidification and dilution”, Spectrochim. Acta. A,60(13),3125-3128 (2004).
22 Mesmer, R.E., Baes, C.F., Sweeton, F.H., “Acidity measurements at elevated temperatures. VI. Boric acid equilibriums”, Inorg. Chem.,11(3), 537-543 (1972).
23 Spessard, J.E., “Investigations of borate equilibria in neutral salt solutions”, J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem.,32(8), 2607-2613 (1970).
24 Weres, O., “Vapor pressure, speciation, and chemical activities in highly concentrated sodium borate solutions at 277 and 317 °C”, J. Solution Ch em.,24(5), 409-438 (1995).
25 Horvath, A.L., Handbook of Aquous Electralyte Solution: Pysical Properties, Estimation and Correlation Methods, Ellis Horwood, New York (1985).
26 Hepler, L.G., “Thermal expansion and structure in water and aqueous solutions”, Can. J. Chem.,47(24), 4613-4617 (1969).
27 Rajagopal, K., Jayabalakrishnan, S.S., “Volumetric and viscometric studies of 4-aminobutyric acid in aqueous solutions of salbutamol sulphate at 308.15, 313.15 and 318.15 K”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng.,17(5), 796-804 (2009).
28 Mahiuddin, S., Ismail, K., “Concentration dependence of viscosity of aqueous electrolytes. A probe into the higher concentration”, J. Phys. Chem. A,87(25), 5241-5244 (1983).
29 Wahab, A., Mahiuddin, S., Hefter, G., Kunz, W., “densities, ultrasonic velocities, viscosities, and electrical conductivities of aqueous solutions of Mg(OAc)2and Mg(NO3)2”, J. Chem. Eng. Data,51(5), 1609-1616 (2006).
30 Wahab, A., Mahiuddin, S., “Density, ultrasonic velocity, electrical conductivity, viscosity, and raman spectra of methanolic Mg(ClO4)2, Mg(NO3)2, and Mg(OAc)2solutions”, J. Chem. Eng. Data,54(2), 436-443 (2009).
31 Jenkins, H.D.B., Marcus, Y., “Viscosity B-coefficients of ions in solution”, Chem. Rev.,95(8), 2695-2724 (1995).
32 Cloutier, C.R., Alfantazi, A., Gyenge, E., “Physicochemical transport properties of aqueous sodium metaborate solutions for sodium borohydride hydrogen generation and storage and fuel cell applications”, In: 5th International Conference on Processing and Manufacturing of Advanced Materials, Chandra, 267-274 (2007).
33 Ali, A., Sabir, S., Shahjahan, H.S., “Physicochemical properties of amino acids in aqueous caffeine solution at 25, 30, 35 and 40 degrees °C”, Chin. J. Chem.,24(11), 1547-1553 (2006).
34 Casteel, J.F., Amis, E.S., “Specific conductance of concentrated solutions of magnesium salts in water-ethanol system”, J. Ch em. En g. Data,17(1), 55-59 (1972).
35 Mauerhofer, E., Zhernosekov, K., Rosch, F., “Limiting transport properties of lanthanide and actinide ions in pure water”, Radiochimica Acta,91(8), 473-477 (2003).
36 Mauerhofer, E., Rosch, F., “Dependence of the mobility of tracer ions in aqueous perchlorate solutions on the hydrogen ion concentration”, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.,5(1), 117-126 (2003).
10.1016/S1004-9541(13)60561-3
2012-05-07, accepted 2012-09-13.
* Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20873172) and Main Direction Program of Knowledge Innovation of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-EW-307).
** To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: fangch@isl.ac.cn; fangy8@isl.ac.cn
 Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2013年9期
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2013年9期
- Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Soft Sensor for Inputs and Parameters Using Nonlinear Singular State Observer in Chemical Processes*
- A New Tuning Method for Two-Degree-of-Freedom Internal Model Control under Parametric Uncertainty*
- Halloysite Nanotube Composited Thermo-responsive Hydrogel System for Controlled-release*
- Recent Advances in Separation of Bioactive Natural Products*
- A Novel γ-Alumina Supported Fe-Mo Bimetallic Catalyst for Reverse Water Gas Shift Reaction*
- Experimental and Theoretical Studies of CO2Absorption Enhancement by Nano-Al2O3and Carbon Nanotube Particles
