A DFT/TD-DFT study of effect of different substituent on ESIPT fluorescence features of 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl)-4-chloromethylthiazole derivatives
Shen-Yang Su(蘇申陽), Xiu-Ning Liang(梁秀寧), and Hua Fang(方華)
Department of Chemistry and Material Science,College of Science,Nanjing Forestry University,Nanjing 210037,China
Keywords: excited-state intramolecular proton transfer(ESIPT),TD-DFT,substitution
1. Introduction
As a typical weak interaction, hydrogen bond (Hbond) plays a significant part in biology, chemistry, and physics, especially in many photochemical and photophysical processes.[1-6]Proton transfer (PT) usually occurs in molecules with acidic and basic groups, and the H-bond between the acidic group and basic group i acts as the bridge of proton transfer. Since the excited state proton transfer process was reported first by Weller,[7]a strong upsurge to study the excited state intramolecular and intermolecular proton transfer has sustained for decades.
Excited-state intramoecular proton transfer(ESIPT)reaction is a sub-picosecond ultrafast photo-induced tautomerization process,in which the ground-state normal form(N)converts into the corresponding tautomer form(T)by undergoing a four-stage photocycle.[8-10]The transformation between N and T results in great changes in the physical and chemical properties of the compound, especially in the spectral behaviors. In the photocycle process,dual fluorescent emission and large Stokes shift are observed in ESIPT compound. Based on the unique photophysical features, ESIPT molecules are widely applied to photostabilizer,sensing technology,molecular switches,and laser dyes.[11-17]
The fluorescent properties of ESIPT compound are obviously affected by the media environment, such as pH, solvent polarity, solvent type, viscosity,etc. Many researchers have performed a large number of studies on the effects of surrounding media on ESIPT process and luminescent properties.[18-22]In addition,the changes of geometrical structures of ESIPT compound can also control the spectral features. The substitution of functional groups may provide an effective way to fine-tune the ESIPT process and photophysical properties of compounds.[23-26]According to the previous reports, Maet al.[27]studied the substituent effect on ESIPT process of 1-(aclamino)-anhraquinones. Takagiet al.[28]probed the ESIPT fluorescence properties of methoxysubstituted 2-hydroxyphenylbenzimidazole. Songet al.[29]investigated the effect of different substiuents on ESIPT of 3-hydroxychromone. Zhanget al.[30]examined the relationship between the substituted position and ESIPT fluorescence features of 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]-pyridine(HPIP).Zhanget al.[31]synthesized a series of new NH-type pyrroleindole compounds and discussed the effects of different functional groups on the ESIPT process and photophysical properties. Obviously,an approporiate substituent can greatly improve the properties of ESIPT materials. Therefore,structural modification with different functional groups can usually be used to design and develop new ESIPT compounds with good applications.
Recently, a series of thiazole-based organic molecules[32-37]was synthesized experimentally and successfully used as fluorescent chemosensors with high selectivity in identifying metal ions (e.g., Ga3+, Al3+, Zn2+, Cu2+) and anions (e.g., CN-, F-, I-, HSO-4, H2P2O3-7). The diversities of fluorescence recognition functions of the parent thiazole molecule are due to the chemical modification in the positions 2 and 4 of the thiazole ring. Inspired by the previous reports, we investigate the effects of different substituents on the ESIPT process and photophysical properties of fluorescent probe molecule in the present work. We design four novel ESIPT compounds via chemical substitution based on 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl)-4-chloromethylthiazole(HCT).[33]Two electron-donating groups(CH3,OH)and two electron-withdrawing groups (CF3, CHO) are introduced in the para position of hydroxyl group in the benzene ring of HCT, and denoted as R-HCT. The structures of the designed probes R-HCT are shown in Fig. 1. We employ the density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT)to investigate the effects of different substituents on the intramolecular H-bond,the absorption/fluorescence spectra and ESIPT process of R-HCT. Detailed calculation results, such as structural parameter,vibrational spectra,topology analysis,reduced density gradient analysis, frontier molecular orbital,ESIPT process, and photophysical properties are investigated as follows. We hope our studies may provide much useful information for the design of ESIPT-based fluorescent probes with better photophysical properties.

Fig.1. Structures of R-HCT(R:H,CH3,OH,CF3,CHO).
2. Computational details
In this work,all the calculations were performed by using the Gaussian 09 package.[38]The ground-state (S0) and the first excitedstate (S1) normal form (N), transition state (TS),and tautomer form (T) of R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3, CHO)molecules were fully optimized by using the DFT and TDDFT methods with B3PW91 functional[39-41]and 6-31+G(d,p) basis set. The frequency calculations were carried out at the same computational level to verify the minima(N and T)and transition state, which have no imaginary frequency and only one imaginary frequency, respectively. Acetonitrile solvent and the integral equation polarizable continuum model(IEFPCM)[42-44]were chosen in order to be consistent with the experimental environment.[33]The absorption and fluorescence emission spectra were simulated at a TD-B3PW91/6-31+G(d,p)level based on the optimized S0structure and optimized S1structure, respectively. The topology analysis and the reduced density gradient isosurfaces were performed by using the Multiwfn program[45]and VMD program,[46]respectively.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Optimized structures and infrared spectra
All the structures of HCT derivatives R-HCT (R: CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in the normal(N)and tautomer(T)forms in the S0and S1states are completely optimized and shown in Fig.2. The corresponding structural parameters related to intramolecular H-bond in R-HCT,such as bond lengths O1-H2,H2-N3,and bond angle O1-H2-N3,are listed in Table 1.
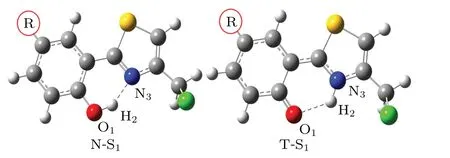
Fig.2. Optimized geometries of normal form(N)and tautomer form(T)of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in S1 state.
For the normal forms of CH3-HCT and OH-HCT compound,it can be seen in Table 1 that the bond distances of O1-H2and H2-N3,and the bond angle O1-H2-N3in the S0state are 0.996 °A,1.703 °A,147.9°,and 0.995 °A,1.709 °A,147.8°respectively.Comparing with HCT,[47]the H2-N3bonds and the angles O1-H2-N3of CH3-HCT and OH-HCT in the S0state are elongated and shortened, respectively, which means that the intramolecular H-bonds O1-H2...N3of CH3-HCT and OH-HCT in the S0state are weaker than those of HCT. The electron-donating groups CH3and OH evidently weaken the intramolecular H-bond of HCT in the S0state. For the CHOHCT compound and CF3-HCT compound, the H2-N3bond distances and the bond angles O1-H2-N3averagely decrease by 0.024 °A and increase by 0.15°,respectively,compared with the corresponding data of HCT. The shortened H2-N3bond and the enlarged O1-H2-N3angle confirm the existence of the strong intramolecular H-bond O1-H2...N3in CF3-HCT and CHO-HCT compounds in the S0state. However, the effects of different functional groups(CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)on the structure of HCT in the S1state are quite opposite. From Table 1 it follows that the bond distance of H2-N3and bond angle of O1-H2-N3for each of CH3-HCT and OH-HCT are averagely shortened by 0.059 °A and enlarged by 1.1°,respectively, and the corresponding parameters of R-HCT (R: CF3,CHO) are averagely elongated by 0.022 °A and reduced by 0.9°,respectively,compared with those of HCT.These results indicate that the intramolecular H-bond of HCT in the S1state is enhanced by the electron-donating group (CH3, OH) and weakened by the electron-withdrawing group(CF3,CHO).In addition, the O1-H2and H2-N3bond lengths and O1-H2-N3bond angle of R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3, CHO) are in a range of 0.995 °A-1.003 °A, 1.670 °A-1.709 °A, and 147.8°-148.4°in the S0state, and in a range of 1.023 °A-1.057 °A,1.508 °A-1.610 °A, and 150.7°-152.9°in the S1state, respectively. The elongating O1-H2bond, the shortening H2-N3bond,and the enlarging O1-H2-N3bond angle of the R-HCT(R:CH3, OH,CF3, CHO)confirm that the intramolecular Hbond O1-H2...N3are strengthened in the S1state,which will be favorable to occur in the ESIPT process.
For the R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3, CHO) compounds,the tautomer forms cannot be obtained in the S0state. Each attempt to find the tautomer structures fails. These results suggest that the R-HCT compounds radioatively return to the ground state in the tautomer form, subsequently return to the normal forms in a barrierless manner.

Table 1. Primary structural parameters(bond length(in unit °A)and bond angle in unit(°))of HCT and its derivatives R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in S0 state and S1 state.
The changing of intramolecular H-bond of R-HCT (R:CH3, OH, CF3, CHO) can be confirmed by the infrared (IR)vibration spectra of the O1-H2bond (normal form) in the RHCT compounds in acetonitrile(shown in Fig.3). In general,the strengthening or weakening of H-bond corresponds to the red-shift or blue-shift of O1-H2bond stretching vibrational frequency, respectively.[48-50]As shown in Fig. 3, the O1-H2stretching vibrational frequencies for CH3-HCT,OH-HCT,CF3-HCT, and CHO-HCT in the S0state are at 3189 cm-1,3215 cm-1, 3110 cm-1, and 3063 cm-1, respectively. When R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3, CHO) compounds are in the S1state, the corresponding vibrational frequencies are situated on 2153 cm-1, 2266 cm-1, 2680 cm-1, and 2551 cm-1,respectively. The O1-H2stretching vibrational frequencies of HCT replaced by electron-donating group and electronwithdrawing group are slightly blue-shifted and red-shifted in the S0state, respectively, in comparison with the corresponding value of HCT.[47]These results confirm the electrondonating group (CH3and OH) and electron-withdrawing group (CF3, CHO) weaken and strengthen the intramolecular H-bond O1-H2...N3in the S0state,respectively. In the S1state,the substituents have opposite effects on the intramolecular H-bond based on the changes between HCT and R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CHO,CF3). In addition,the apparent red-shifts 1036 cm-1,949 cm-1,430 cm-1,and 512 cm-1of the O1-H2stretching vibrational frequency of CH3-HCT,OH-HCT,CF3-HCT,and CHO-HCT in the S1state,respectively,represent the strengthening intramolecular H-bond O1-H2...N3,compared with the corresponding IR frequencies in the S0state. The proton might transfer more easily in the S1state than in the S0state. The red-shift values between S0and S1states in CH3-HCT and OH-HCT are larger than those values in R-HCT(R:CHO,CF3),which means that the electron-donating group has stronger effects on enhancing the intramolecular H-bond than electron-withdrawing group. The conclusion obtained by the structural parameters is proved by the analysis of IR vibration.
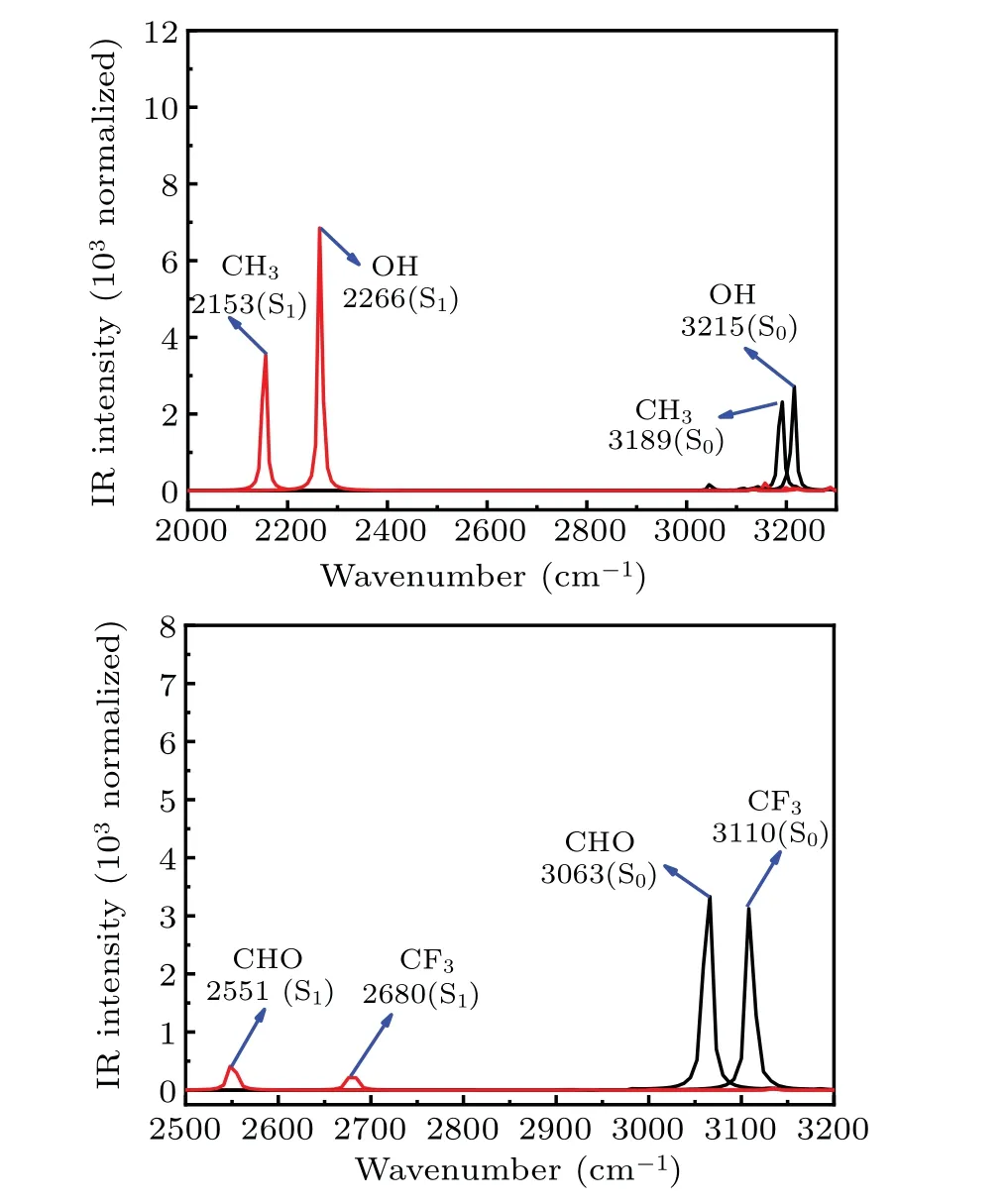
Fig.3. IR spectra for R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in the normal form in a region of O1-H2 stretching vibration spectra in S0 state and S1 state.
3.2. Topology analysis and reduced density gradient analysis
To further explore the strength of intramolecular H-bond of R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3, CHO), the topological analysis based on the electron density is performed. Topology parameters (ρ(r), ?2ρ(r),V(r),EHB,G(r),H(r), and ELF)are obtained at the bond critical point (BCP, [3,-1] type) between H2atom and N3atom and listed in Table 2. The value of ?2ρ(r)can be used to determine the type of interaction,and the value ofρ(r)andEHBare closely related to the strength of the H-bond.[51]The positive or negative value of ?2ρ(r)represents the closed-shell interaction(e.g.,ionic bond and H-bond)or shared interaction (e.g., covalent bond), respectively. The H-bond strength can be divided into three types based on the value ofρ(r)at BCP:[52](i)weak,ρ(r)≤0.02;(ii)medium,0.02<ρ(r)<0.03; (iii)strong,ρ(r)≥0.03. The bigger the values ofρ(r)andEHBare,the stronger the H-bond is. It can be found in Table 2 that the electron densityρ(r) of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in the S0and S1states are in a range of 0.0512 a.u.-0.0547 a.u. and 0.0648 a.u.-0.0845 a.u., respectively, and the value of Laplacian ?2ρ(r) in the S0state and the S1state are larger than 0.10 a.u.

Table 2. Calculated BCP parameters associated with intramolecular H-bond of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in S0 state and S1 state.

Fig.4. Scatter plots of S versus sign(λ2)ρ and gradient isosurfaces of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in S0 state and S1 state.
These results mean that the strong intramolecular Hbonds exist in the R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in the S0state and S1state, and the H-bond in the S1state is stronger than that in the S0state. The same conclusion is obtained from the value ofEHBof R-HCT. Evidently, the introduction of different substituents gives rise to different effects on the H-bond strength. In the S0state, the electron-donating group(CH3,OH)weakens the intramolecular H-bond of HCT,and the electron-withdrawing group (CF3, CHO) strengthens the corresponding H-bond. In the S1state, the introducing electron-donating group(CH3,OH)and electron-withdrawing group (CF3, CHO) make the intramolecular H-bond of HCT strengthen and weaken,respectively. The above conclusion is consistent with that drawn from the structures.
We also employ the reduced density gradient (RDG)function to analyze the intramolecular H-bond of R-HCT.The RDG analysis proposed by Johnsonet al.[53]and Garc′?aet al.[54]is based on the electron densityρa(bǔ)nd its reduced gradientS, and can be used to distinguish non-covalent bond interaction. Herein, a real space function sign(λ2)ρis defined,in whichρis the electron density in corresponding region andλ2is the second largest eigenvalue of Hessian matrix ofρ.Large negative or positive value of sign(λ2)ρrepresents the interaction such as H-bond or steric effect, respectively. The near zero value of sign(λ2)ρrepresents weak van der Waals interactions.
The RDGversussign(λ2)ρof R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in the S0state and S1state are shown in Fig.4. For the S0and S1R-HCT compounds, their spike peaks are located at-0.06<ρ <-0.05 a.u.and-0.09<ρ <-0.06 a.u., respectively, which confirms that the strong intramolecular Hbond O1-H2...N3exists separately in the S0state and S1state,and the intramolecular H-bonds in the S1state are stronger than those in the S0state. In comparison with HCT,[47]the introduced electron-donating/electron-withdrawing group weakens/enhances and enhances/weakens the intramolelcular H-bond of HCT in the S0and S1states, respectively. Based on the non-covalent interaction analysis,the above-mentioned conclusion is affirmed again.
3.3. Excited-state intramolecular proton transfer
In order to further study the effects of different substitutents on ESIPT process of HCT, we completely optimize the structure of transition state(TS).The TS structures of R-HCT(R: CH3, OH, CF3, CHO) are verified by frequency calculations as shown in Fig. A1 in Appendix A. The reaction barrier and reverse reaction barrier in the S0state and S1state of the studied compounds are calculated and displayed in Table 3. The corresponding energy diagram for proton transfer in R-HCT is shown in Fig. 5. It is worth noting that only S1tautomer geometries of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)are obtained. All the attempts to obtain the tautomer structures of CH3-HCT, OH-HCT, CF3-HCT, and CHO-HCT fail and end in their corresponding normal structures. This is probably because the energy values of forming the stable tautomer structures in the S0state are too high.

Table 3. Calculated reaction barrier (in units kcal/mol) for forward and reverse proton transfer in R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in S1 state.
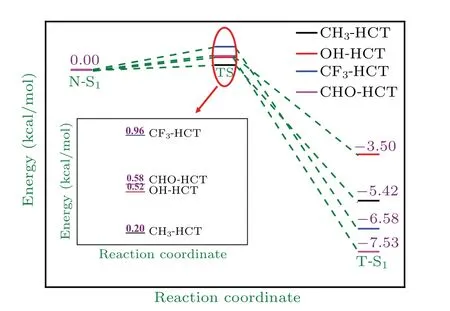
Fig.5. Potential energy profiles of proton transfer in R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in S1 state.
These result suggest that the proton transfer from O-H group to thiazolic nitrogen atom is impossible for R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in the ground state. However,it should be mentioned that there is a low reaction barrier less than 1 kcal/mol in the S1state for proton transfer process from N to T.Obviously, the low reaction barrier is prone to ESIPT process. The ESIPT process should be an ultrafast process due to the lower barrier. After ESIPT behavior,the S1tautomer form of R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3, CHO) will transform into the corresponding unstable S0tautomer structure through emission fluorescence,then occur a barrierless reverse ground-state proton transfer(RGSPT)process and return to the most stable S0normal structure. We also find that the replacement of different substituents can modulate the ESIPT process of HCT.As shown in Table 3,the electron-donating group(CH3,OH)and electron-withdrawing group (CF3, CHO) reduce and increase the ESIPT reaction barrier of HCT, respectively. Evidently, the introduction of electron-donating group into the HCT is more favorable to the ESIPT process. In addition,the reverse proton transfer barrier of CH3-HCT, OH-HCT, CF3-HCT,and CHO-HCT are 5.62,4.02,7.54,and 8.11 kcal/mol,respectively, and they are all higher than the corresponding ESIPT barrier. The larger reaction barrier implies that the reverse ESIPT process is difficult to occur,and the corresponding tautomer structures of R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3, CHO)are the stable structures in the S1state.
3.4. Frontier molecular orbitals and electronic spectra
As is well known, the analysis of frontier molecular orbitals(FMOs),as an effective method,is often used to explore the charge distribution characteristics in the excited state.[55,56]Therefore,the calculated FMOs of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO) are displayed in Fig. 6. The calculated absorption and fluorescence emission wavelengths, corresponding oscillator strength(f)and the orbital compositions are listed in Tables 4 and 5.Obviously,the first singlet transition(S0-S1)of R-HCT corresponds to the electronic transition from the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) to the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital(LUMO),making large orbital contributions(see Table 4). Hence,only the HOMO and LUMO orbitals of R-HCT in the S1state are displayed in Fig. 6. From Fig. 6,we can draw the conclusion that the HOMOs of R-HCT (R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)haveπcharacter while the corresponding LUMOs haveπ*character. The transition process from HOMO to LUMO hasππ*-type features in view of the charge distribution between HOMO and LUMO.
For the R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3, CHO), the electron density of hydroxyl O1atom (proton donor) decreases,while the electron density of N3atom (proton acceptor) increases after the transition from HOMO to LUMO. Namely,the intramolecular charge transfer exists in the S0→S1transition, and renders the hydroxyl O1atom and N3atom more acidic and basic, respectively, which is more favorable to the occurrence of ESIPT. However, the remarkable intramolecular charge transfer features in R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3,CHO)compound are totally different because of different substituents.We find that the HOMOs of CH3-HCT and OH-HCT are mainly located on the hydroxyl benzene ring,whereas the LUMOs are distributed mainly on phenol-thiazole ring due to push-pull electron effect(CH3and OH as electron donor and thiazole as electron acceptor). While for the CF3-HCT compound and CHO-HCT compound, electron densities of both HOMOs and LUMOs are mainly in phenol-thiazole ring due to the electron-withdrawing effects of CF3and CHO.
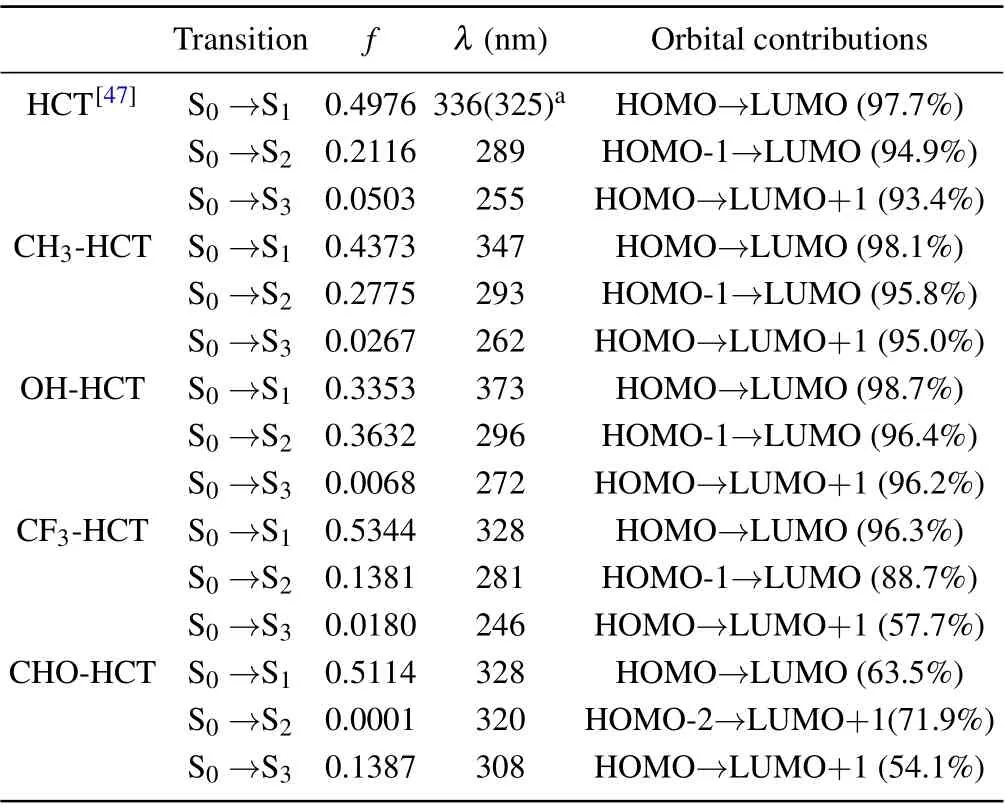
Table 4. Values of vertical excitation energy of S0 →Sn (n=1-3)and oscillator strength(f),and major orbital contributions of R-HCT(R:H,CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)obtained at TD-B3PW91/6-31+G(d,p)level in acetonitrile.

Table 5. Values of vertical emission energy of S1 →S0 and oscillator strength (f), and major orbital contributions of R-HCT (R: H, CH3, OH,CF3,CHO)obtained at TD-B3PW91/6-31+G(d,p)level in acetonitrile.
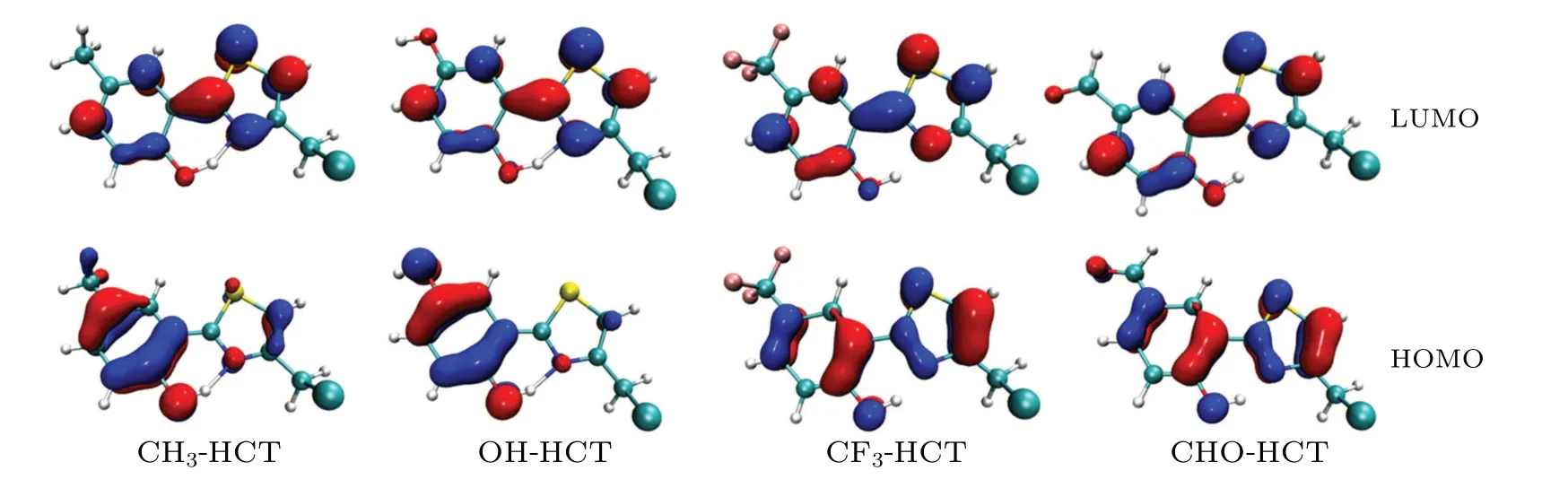
Fig.6. Frontier molecular orbitals(HOMO and LUMO)of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in acetonitrile.
The related energy values of HOMO,LUMO,energy gap of R-HCT (R: H, CH3, OH, CF3, CHO) in the S1states are listed in Table 6. It can be seen that the HOMO and LUMO energy values of CF3-HCT and CHO-HCT are all a little lower than those of HCT, which does not render the energy gaps of CF3-HCT and CHO-HCT significantly different from those of HCT. For compounds with electron-donating group (CH3,OH),the LUMO energy values are obviously increased while their LUMO energy values are a little increased,which results in the smaller energy gaps than that of HCT.The smaller energy gaps of CH3-HCT, OH-HCT are corresponding to the red-shift absorption peaks. The smaller the energy gap, the stronger the red-shift absorption peak is.

Table 6. Energy values (in unit eV) of HOMO, LUMO, and the HOMOLUMO gaps(in unit eV)of HCT and their derivatives R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in S1 state.
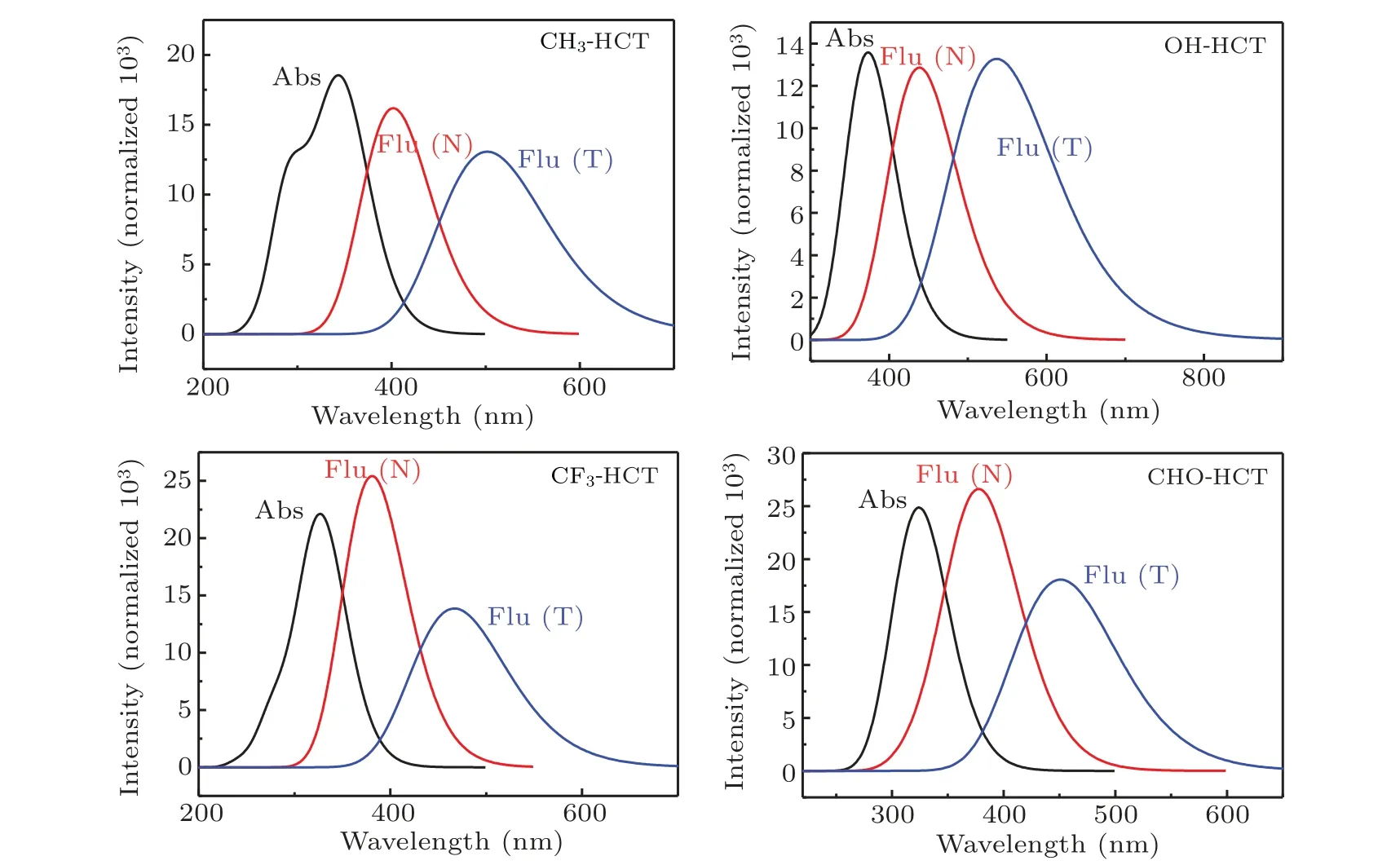
Fig.7. Calculated absorption(Abs)and fluorescence(Flu)emission spectra of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in acetonitrile.
The absorption and fluorescence spectra of R-HCT (R:CH3, OH, CF3, CHO) at the normal and tautomer forms are also simulated and the results are shown in Fig.7.The detailed transition properties of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)are listed in Tables 4 and 5.As shown in Tables 4 and 5 and Fig.7,it can be found that the maximum absorption peaks of CH3-HCT, OH-HCT, CF3-HCT, and CHO-HCT are at 347 nm,373 nm, 328 nm, and 328 nm, respectively. And the corresponding maximum fluorescent peaks are at 402 nm,438 nm,381 nm,and 379 nm. The electron-donating group(CH3,OH)gives rise to a red-shift in both the absorption and fluorescent peaks of HCT,which results in an increase in the Stokes shift (from 48 nm (HCT) to 55 nm (CH3-HCT) and 65 nm(OH-HCT)). However, the electron-withdrawing group (CF3,CHO)makes the electronic spectra blue-shift a little. The redshift or blue-shift electronic spectral wavelengths imply that the intramolecular H-bond is strengthened or weakened.[57,58]Obviously, electron-donating group (CH3, OH) and electronwithdrawing group(CF3,CHO)strengthen and weaken the intramolecular H-bond O1-H2...N3in the S1state,respectively.
The calculated fluorescence spectra of R-HCT (R: CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)show dual fluorescent emission bands which correspond to their normal and tautomer forms, respectively.For the tautomer forms of R-HCT, the fluorescence peaks of CH3-HCT, OH-HCT, CF3-HCT, and CHO-HCT are at 502 nm,536 nm,467 nm,and 451 nm,respectively,showing the corresponding Stokes shift of 155 nm, 163 nm, 139 nm,and 123 nm. The effects of different substituents on the fluorescent emission peaks in the tautomer form are consistent with those on the absorption peaks and fluorescent peaks in the normal form.
4. Conclusions
In summary, DFT and TD-DFT methods with IEFPCM solvent model have been used to investigate the effects of different substituents on the H-bond strength, ESIPT behaviors and photophysical properties of R-HCT (R: CH3, OH, CF3,CHO)compounds in acetonitrile. From the results of primary structural parameters,infrared(IR)vibration spectra,topological analysis and reduced density gradient(RDG)analysis,the strengths of intramolecular H-bond of all title compounds enhanced in the S1state are confirmed, which will be favorable for the ESIPT process. The electron-donating groups (CH3,OH)and electron-withdrawing groups(CF3,CHO)strengthen and weaken the intramolecular H-bond in the S1state,respectively. The enhanced intramolecular H-bond in the CH3-HCT and OH-HCT and the weakened H-bond in the CF3-HCT and CHO-HCT make ESIPT process take place much more easily and more difficultly, respectively. The substitution effect on the H-bond strength in the S0state is opposite. The frontier molecular orbitals prove that the transition process from HOMO to LUMO in R-HCT compounds showππ*-type feature. The electron-donating groups (CH3, OH) narrow the energy gaps of HCT, and electron-withdrawing groups (CF3,CHO)do not show significant difference from those of HCT.The smaller the energy gap,the stronger the red-shift absorption peakis. In addition, the electron-donating groups (CH3,OH) red-shift both the absorption and fluorescence emission peaks of HCT,respectively,and then causing the Stokes shift to increase. The electron-withdrawing groups (CF3, CHO)have a little effect on electronic spectra.
Appendix A:Supporting information
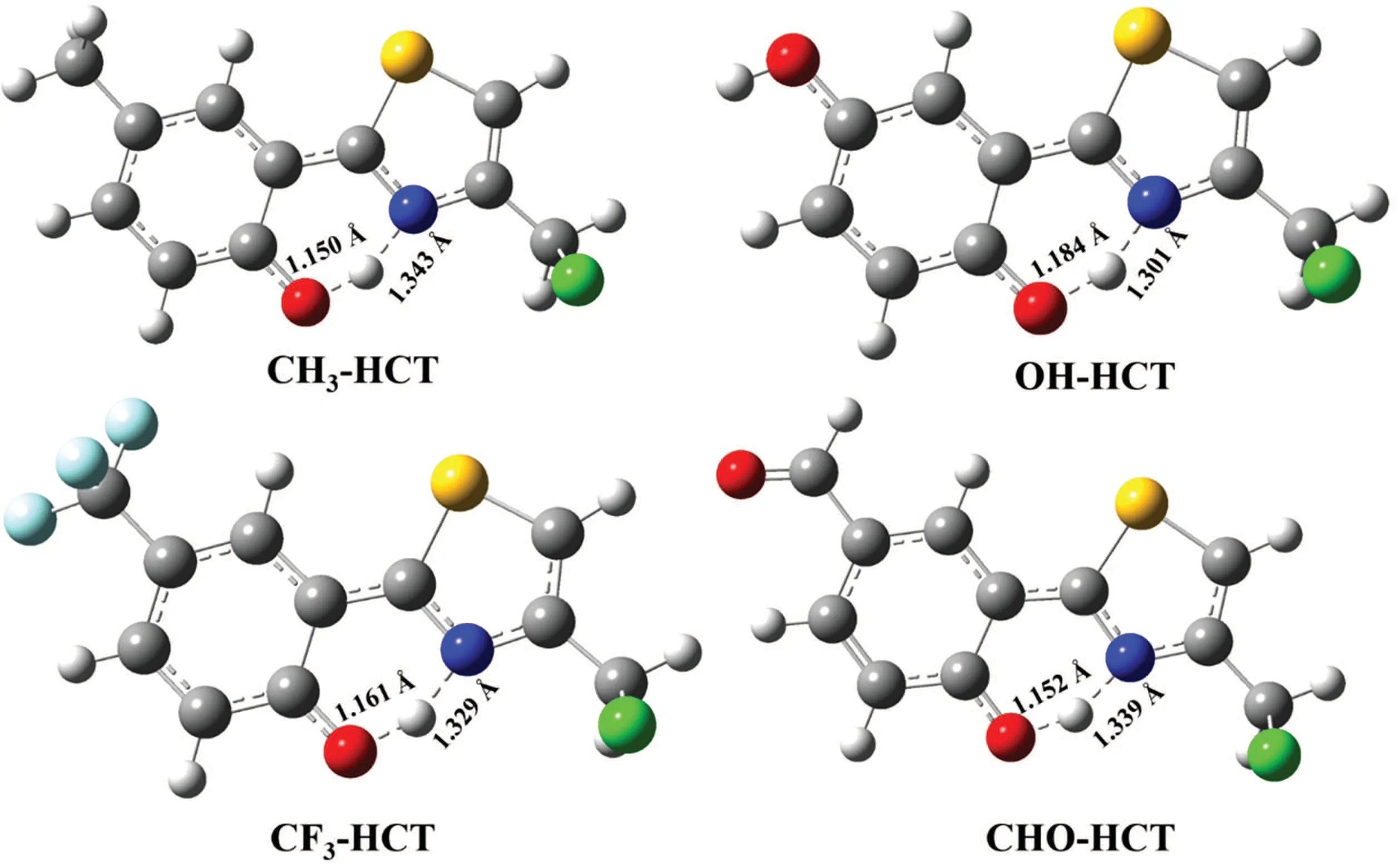
Fig.A1. Optimized transition state of R-HCT(R:CH3,OH,CF3,CHO)in the S1 state.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Surface modulation of halide perovskite films for efficient and stable solar cells
- Graphene-based heterojunction for enhanced photodetectors
- Lithium ion batteries cathode material: V2O5
- A review on 3d transition metal dilute magnetic REIn3 intermetallic compounds
- Charge transfer modification of inverted planar perovskite solar cells by NiOx/Sr:NiOx bilayer hole transport layer
- A low-cost invasive microwave ablation antenna with a directional heating pattern

