Effects of sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations on chondrocytes, IL-1β and NO in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis
Yao Meng-li (姚夢(mèng)莉), Chen Zhao-hui (陳朝暉), Chen Xiang-hua (陳向華), Xu Han (徐寒), Wang Ting-ting (王婷婷),Hu Rong-ting (胡榮庭), Jin Xiang-yu (金祥雨), Jin Han (金晗)
1 Clinical College of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230012, China
2 College of Acupuncture-moxibustion and Tuina, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230038, China
3 Graduate School, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230038, China
Abstract
Keywords: Tuina; Massage; Manual Therapies; Nitric Oxide; Interleukin-1; Apoptosis; Osteoarthritis, Knee; Rabbit
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a common chronic progressive joint disease and more liable to affect the elderly. Its incidence rate is as high as 85.0% in people over 65 years old. KOA is only less harmful than ischemic heart disease, seriously affecting the quality of life and social participation degree of the patients[1-2].KOA is originated from articular cartilages which are composed of 1.0% cartilage cells and 99.0% cartilage matrix. The development of KOA is accompanied by a series of pathological processes such as excessive chondrocyte apoptosis, an imbalance between cartilage matrix synthesis and degradation, and degenerative changes of articular cartilages. However, the specific pathogenesis is still unclear. In recent years, studies have revealed that KOA is the result of an imbalance between pro-inflammatory factors and antiinflammatory factors. Pro-inflammatory factors such as interleukin (IL)-1β promote articular cartilage degeneration[3]. The clinical efficacy of sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations in KOA treatment has been confirmed[4], but the mechanism is still unclear. In this experiment, KOA rabbit model was established to observe the effects of the sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations on the levels of IL-1β and nitric oxide (NO)in serum and knee joint fluid, as well as the chondrocytes in the KOA model rabbits, to explore the action mechanisms and provide experimental basis for clinical application of the sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Animals and groups
Thirty healthy specific pathogen-free New Zealand adult white rabbits with a body mass of 2.0-2.5 kg, half male and half female, were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine and raised separately (one/cage) with free access to water and food. The experiments followed the national guidelines for the management and use of laboratory animals, and were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (Approval No. AHUCM-rabbits-2019010). After one week of adaptive feeding, the rabbits were divided into a normal group (n=9) and a modeling group (n=21, three of which were used for model identification) according to the random number table method. The 18 successfully modeled rabbits were randomly divided into a model group (n=9) and an intervention group (n=9).
1.2 Main reagents and equipment
Rabbit IL-1β enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA) kit (Cat. No. JYM0011Rb, Wuhan ColorfulGene Biological Technology Co., Ltd., China); rabbit NO kit (Cat.No. A012-1, Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute,China);in situterminal deoxynucleotidyl transferasemediated nick and labeling (TUNEL) reaction kit (Cat. No.30967400, Roche, China); RT-6000 model microplate reader (Rayto, China); RM2245 model paraffin microtome (Leica, Germany); BX41 model optical microscope (Olympus, Japan).
1.3 Modeling method
The modified Hulth method was used for model preparation[5]. Each rabbit was fasted for 12 h before surgery, followed by injection of 3% sodium pentobarbital into the ear vein at a dose of 3.0 mL/(kg·bw) for anesthesia, and then the rabbit was fixed in a supine position. The skin within the operation scope was routinely shaved and disinfected; a longitudinal incision was made on the inside of the right knee joint to open the joint cavity. The medial collateral ligament was cut under orthophoria, and then the patella was manually pushed away; the knee joint was dislocated and flexed to the maximum angle; the joint cavity was completely exposed; the medial meniscus was removed and the anterior cruciate ligament was cut off. Given that the lateral separation and drawer tests were positive, hemostasis, saline rinsing, and suture of the incision layer by layer were performed. To prevent infection, penicillin (200 000 U/d) was injected intramuscularly for three consecutive days after operation. The rabbits were chased for 30 min every day from the fourth day to the eighth week after the operation. It would be a good sign to observe rabbit claudication behavior at the 8th week.
1.4 Modeling evaluation
Eight weeks after the operation, three model rabbits were sacrificed to verify whether the model was successful. The success of model was verified according to the behavioral changes of rabbits, general observation, and pathological examination of articular cartilages. Behavioral observation found knee joint swelling and claudication. The general observation of articular cartilages revealed typical cartilage degeneration, joint swelling, osteophyte hyperplasia, as well as depression, and defects and erosion of the articular cartilage surface. Pathological examination of articular cartilages showed that the cartilage surface was thinned, rough, or even broken; cartilage cells were pyknotic and clustered; and cartilage structure was disordered.
The model was successful when the above conditions were met, and further intervention could be performed.The success rate of model preparation in this experiment was 100%.
1.5 Groups and interventions
1.5.1 Normal group
The rabbits were reared routinely without any treatment.
1.5.2 Model group
After the models were successfully prepared, the rabbits were reared routinely without any treatment.
1.5.3 Intervention group
The affected knee joints of the rabbits in the intervention group were treated with the sinewregulating bone-setting manipulations.
Method: Na-Grasping and Nie-Pinching manipulations were performed on the muscle regions of Foot Yangming, Foot Taiyang, Foot Shaoyin, and Foot Shaoyang meridians from top to bottom for 3 min to relax the tense muscles, focusing on the cords or nodular reaction points that could be touched on the above-mentioned meridian routes. Then the knee joint around the patella was digital An-Pressed and Rou-Kneaded 50 times on the left, right, upper and lower sides. Both sides of the patellar ligament [Dubi (ST 35)and Neixiyan (EX-LE 4)] were digital An-Pressed with the thumbs. Held the calf with the rest fingers, and rotated the knee joint six times at the same time. Then flexed and extended the affected knee joint ten times. Each treatment lasted for 10 min and was performed every other day for 20 consecutive sessions.
1.6 Testing indicators and methods
1.6.1 Lequesne MG function rating of knee joints[6]
After the experiment, the local pain stimulus response, gait changes, joint range of motion and joint swelling status of the rabbits in each group were observed. The rabbit knee joints were evaluated by the Lequesne MG knee function rating. A higher rating score indicated more severe knee joint symptoms.
1.6.2 General observation of articular cartilages and Pelletier score[7]
The rabbits were sacrificed by air embolism. After opening rabbit knee joint cavity of the affected side, the articular cartilage color and defect degree of articular surface were observed, and pictured for Pelletier scoring. The highest score was 4 points, and the lowest score was 0 point. A higher score indicated more serious cartilage abrasion of the knee joint.
1.6.3 Morphological observation and the Mankin score of articular cartilage tissue[8]
After the general observation, the intact knee joint was removed and fixed in 10% formalin solution for 48 h. Then the specimens would go through the following steps: decalcification, secondary sampling(only the cartilage tissue of the medial femoral condyle),dehydration, embedding, wax block making, cutting into slices of 4 μm in thickness, and hematoxylin-eosin(HE) staining. Cartilage cell numbers, cartilage matrix staining, cartilage tidal lines, and cartilage structure in the articular cartilage tissue were observed and photographed under a light microscope. The Mankin score was evaluated. The maximum accumulated Mankin score was 14 points. A higher score indicated more severe articular cartilage degeneration. The specific classification criteria were: normal cartilage (0-1 point); early osteoarthritis (2-6 points); mid-term osteoarthritis (7-10 points); and advanced osteoarthritis(11-14 points).
1.6.4 ELISA and nitrate reductase method to determine the expression levels of IL-1β and NO in serum and synovial fluid
Before the general observation, the abdominal aortic blood of the rabbits in each group was first collected into labeled coagulation tubes, and then centrifuged for 10 min at 2 000 r/min. The upper layer of serum was transferred into a 2 mL EP tube and stored at -20℃.
Synovial fluid collection: After the blood was collected, 0.5 mL sodium chloride solution was injected into the knee joint cavity with a 1 mL syringe. The needle was inserted at the intersection of the lower edge of the patella and the lateral 1 cm of the patellar ligament. A small depression could be seen, equivalent to the position of Dubi (ST 35). Pay attention to avoid damaging the articular cartilage surface when inserting the needle. After repeated flexion and extension of the knee joint 10 times, 0.5-1.0 mL synovial fluid was collected into a 2 mL labeled EP tube, and stored in a refrigerator at -20 ℃ for testing. Before the test, the frozen joint fluid and serum were thawed step by step,and then the test was performed strictly following the instructions of the kit.
1.6.5 Chondrocyte apoptosis measured by TUNEL
The slices of 3 μm in thickness were prepared with the wax blocks and detected strictly following the instructions of the TUNEL kit. After the detection,chondrocyte apoptosis was observed under a light microscope. The apoptotic cells appeared brownish yellow and the normal cells appeared blue. Then calculated the apoptosis index[9]. Five high-power fields(×400) containing the relatively largest apoptosis number in each slice were randomly selected, and the percentage of apoptotic cells in 100 chondrocytes was calculated.
1.7 Statistical methods
SPSS version 23.0 software was used for statistical analysis of all data. The measurement data meeting normality and homogeneity of variance were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s). The pairedsamplet-test was used for comparisons within groups and one-way analysis of variance was used for comparisons between groups. The data not satisfying normality and homogeneity of variance were expressed as the rank average (Ri), and the non-parametric ranksum test was used. Of which, the Lequesne MG score was compared using the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test.P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
2 Results
2.1 Behavioral observation and comparison of the Lequesne MG function rating result
Rabbits in the normal group were insensitive to painful stimulation; had no knee joint swelling or movement limitation; showed continuous and powerful jumping, and normal gait. Rabbits in the model group had knee joint swelling, claudication, and limited joint activities, especially knee extension activities. They showed obvious struggles and resistance toward local painful stimulation and knee extension activities.Moreover, jumping activities were significantly reduced,and the action was not continuous when pushing the ground, mainly using the healthy side (left hind limb) as the support point. Rabbit joint swelling in the intervention group was reduced, with increased pain tolerance and smoother knee extension activities.During the test, rabbits were less struggling and the continuous jump numbers were increased. The situation was improved compared to that of the model group though the left side was still the main support point.
The three groups had statistically significant differences in the Lequesne MG function rating results(the four items including local response, gait response,joint range of motion, and joint swelling), (P<0.05).Compared with the normal group, rabbits in the model group and the intervention group had increased local reactions, joint range of motion, and joint swelling(P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the degrees of the above three items in the intervention group were significantly decreased (P<0.05). Compared with the normal group, the gait response of the model group was significantly worse (P<0.05), while the difference between the intervention group and the model group was statistically insignificant (P>0.05), (Table 1).
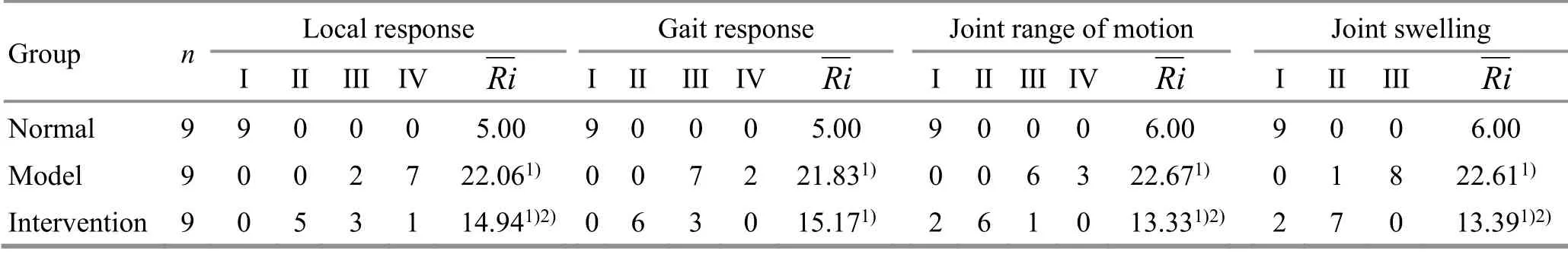
Table 1. Lequesne MG function rating of rabbit knee joints in each group
2.2 General observation and comparison of the Pelletier score
There was no swelling or osteophyte hyperplasia in the right knee of the rabbits in the normal group. The bilateral knee joints were basically the same size, the articular cartilage surface was smooth and flat, and the synovial fluid appeared pale white. There were defects and erosions on the articular cartilage surface of rabbits in the model group. Some of the subchondral bones were exposed. The cartilage surface was dim and swollen with osteophyte hyperplasia in the surrounding;and the synovial fluid was light yellow. In the intervention group, there were scattered dot-like depressions on the surface of rabbit cartilage, showing fair smoothness and pale white (Figure 1).
The difference in the Pelletier score among the three groups was statistically significant (P<0.05). Compared with the normal group, the cartilage damage in the model group was more severe (P<0.05), and the cartilage damage in the intervention group was slightly milder (P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the intervention group had a statistical difference in the articular cartilage score (P<0.05), (Table 2).
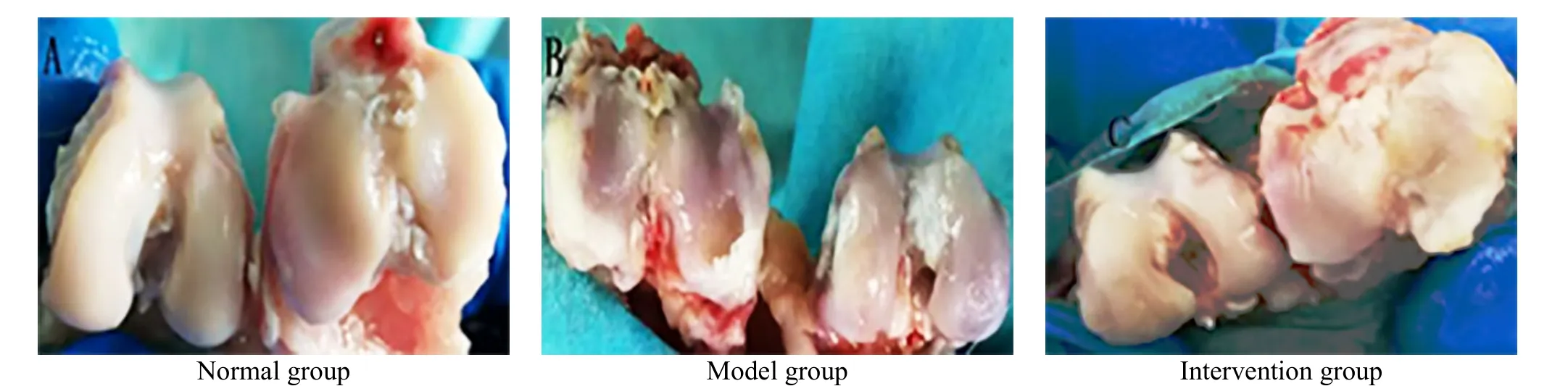
Figure 1. General observation of the rabbit articular cartilage in each group
Table 2. Comparison of Pelletier score of the articular cartilage in each group ( ±s point)
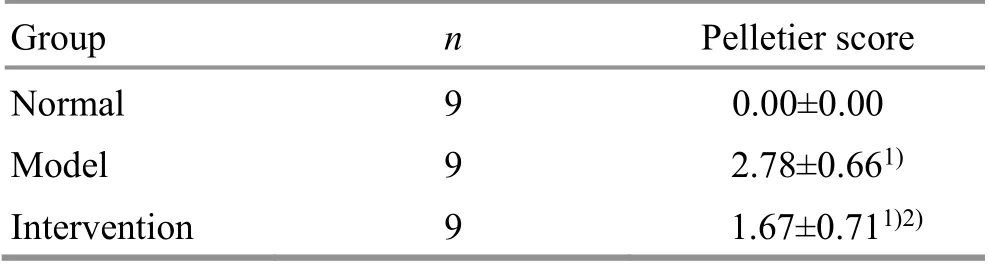
Table 2. Comparison of Pelletier score of the articular cartilage in each group ( ±s point)
Note: Compared with the normal group, 1) P<0.05; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.05
Group n Pelletier score Normal 9 0.00±0.00 Model 9 2.78±0.661)Intervention 9 1.67±0.711)2)
2.3 Pathological observation of the articular cartilage and comparison of the Mankin score
The articular cartilage surface of rabbits in the normal group was smooth and flat; each layer structure was clear; the chondrocytes were evenly distributed,arranged in columns with normal shape and size, and complete tidal lines without clusters. In the model group, the articular cartilage surface became thin,rough or even ruptured; the structure was disordered with irregular cracks, interrupted or disappeared tidal lines, pyknotic shape and changed size of cartilage cells;and the cartilage matrix was stained unevenly. In the intervention group, the overall hierarchical structure of the articular cartilage was basically complete; the cartilage surface was thin but basically flat; the shape and size of cartilage cells were close to normal with a slightly increased number and clustering in the superficial layer. Please see Figure 2 for details.
Compared with the normal group, the cartilage tissue of the model group and the intervention group was significantly damaged (P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the damage degree of the intervention group was significantly reduced (P<0.05), (Table 3).
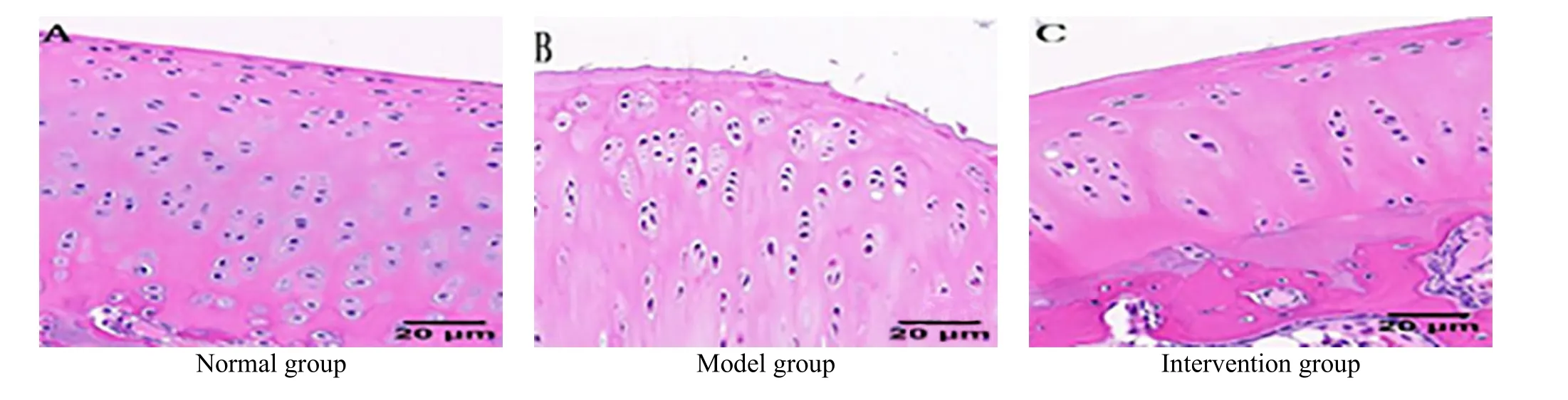
Figure 2. HE staining results of the rabbit articular cartilage in each group (×400)
Table 3. Comparison of Mankin score of articular cartilage in each group ( ±s point)
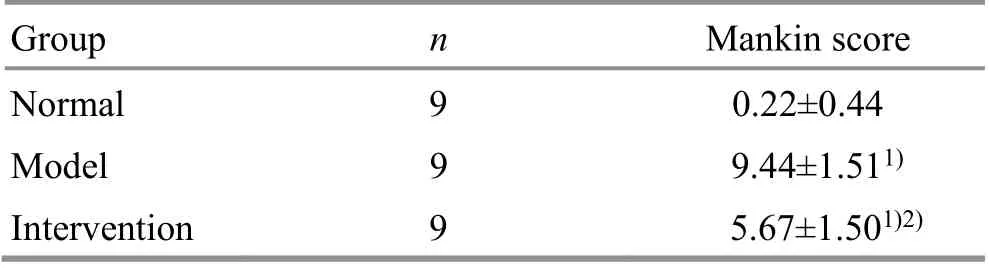
Table 3. Comparison of Mankin score of articular cartilage in each group ( ±s point)
Note: Compared with the normal group, 1) P<0.05; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.05
Group n Mankin score Normal 9 0.22±0.44 Model 9 9.44±1.511)Intervention 9 5.67±1.501)2)
2.4 Comparison of the IL-1β and NO levels
Compared with the normal group, the IL-1β and NO levels in rabbit’s serum and synovial fluid of the model group were significantly increased (P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the levels of IL-1β and NO in serum and synovial fluid of the intervention group were significantly decreased (P<0.05), (Table 4).
2.5 Comparison of the chondrocyte apoptosis rate
The TUNEL results showed that compared with the normal group and the intervention group, the rabbit articular cartilage in the model group was seriously damaged and the chondrocyte apoptosis rate was significantly increased (P<0.05), which proved the success of rabbit KOA modeling. Compared with the model group, the chondrocyte apoptosis rate in the intervention group was decreased (P<0.05), suggesting the effectiveness of sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations. However, the chondrocyte apoptosis rate in the intervention group was still statistically higher than that in the normal group (P<0.05), (Figure 3 and Table 5).
Table 4. Comparison of the IL-1β and NO levels in serum and synovial fluid of each group ( ±s)
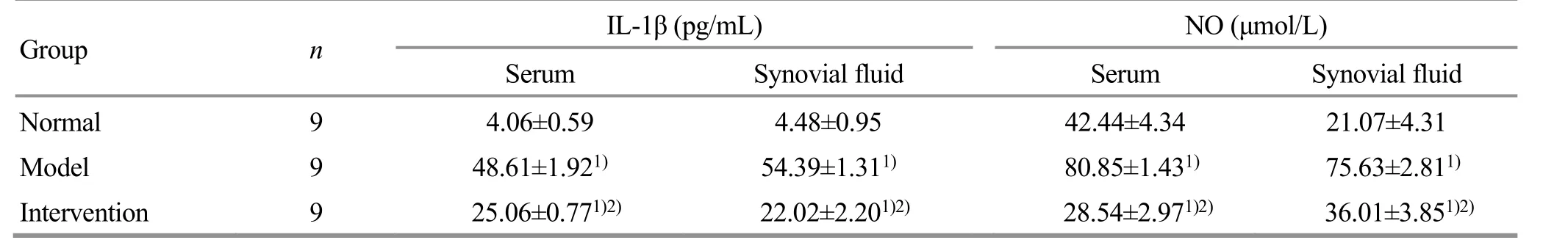
Table 4. Comparison of the IL-1β and NO levels in serum and synovial fluid of each group ( ±s)
Note: Compared with the normal group, 1) P<0.05; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.05
Group n IL-1β (pg/mL) NO (μmol/L)Serum Synovial fluid Serum Synovial fluid Normal 9 4.06±0.59 4.48±0.95 42.44±4.34 21.07±4.31 Model 9 48.61±1.921) 54.39±1.311) 80.85±1.431) 75.63±2.811)Intervention 9 25.06±0.771)2) 22.02±2.201)2) 28.54±2.971)2) 36.01±3.851)2)

Figure 3. TUNEL staining results of rabbit’s chondrocytes in each group (×400)
Table 5. Comparison of the chondrocyte apoptosis rate in each group ( ±s %)
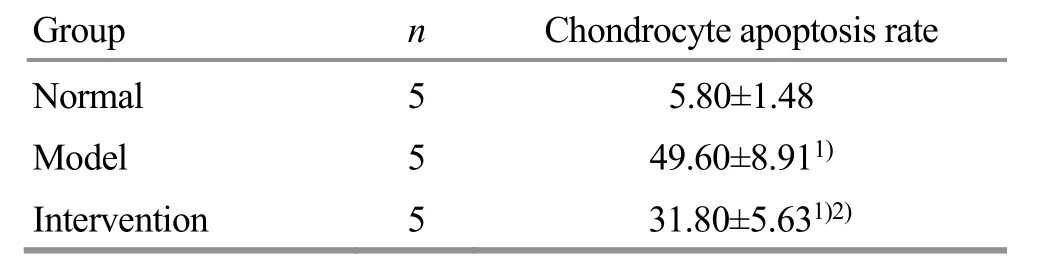
Table 5. Comparison of the chondrocyte apoptosis rate in each group ( ±s %)
Note: Compared with the normal group, 1) P<0.05; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.05
Group n Chondrocyte apoptosis rate Normal 5 5.80±1.48 Model 5 49.60±8.911)Intervention 5 31.80±5.631)2)
3 Discussion
The prevalence of KOA is high and its pathogenesis is very complicated. Some scholars reported that the occurrence of KOA was closely related to inflammatory factors[10-11]. IL-1 is the initiating factor regulating the inflammatory response, including two subtypes of IL-1α and IL-1β. IL-1β is more closely related to KOA. Its expression levels in serum and synovial fluid have a strong positive correlation with the severity of KOA, and thus it is considered to be the core factor in promoting KOA development[12-13]. KOA mainly affects the cartilage.There are IL-1β receptors on the surface of the cartilage cell membrane in cartilage tissue. When osteoarthritis occurs, the receptor number on the membrane surface increases exponentially, forming a hormone-receptor complex to interfere with the outside information transmission and affect normal cell metabolism[14]. The damage of IL-1β to cartilage tissue is also manifested in two aspects of chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage matrix degradation. In one study, when IL-1β was added to chondrocytes culturedin vitro, the morphology of chondrocytes was irregularly changed, and the apoptosis rate was significantly increased; the degeneration still existed even when the chondrocytes were passaged to the third generation[15]. Besides, IL-1β up-regulates the expression levels of matrix metalloproteinase and prostaglandin E2, accelerates the degradation of extracellular matrix components of cartilage tissue, and enhances the decomposition of articular cartilage[16-17]. IL-1β promotes the chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage matrix degradation, ultimately damaging articular cartilage and accelerating the course of osteoarthritis. NO is also an important inflammatory mediator involved in osteoarthritis. It inhibits cartilage matrix synthesis and induces chondrocyte apoptosis.Under IL-1β stimulation, chondrocytes activate inducible nitric oxide synthase to produce a large amount of NO, which excessively degrades the proteoglycan and collagen in the cartilage matrix, and damages the structures protecting the chondrocytes.This results in insufficient nutrient supply to the cartilage, eventually leading to excessive apoptosis of cartilage cells[18]. Therefore, this study focused on IL-1β and NO to detect their expression levels and the chondrocytes. The results showed that compared with the normal group, the IL-1β and NO levels and the chondrocyte apoptosis rate in the model group were significantly increased (P<0.05). This also directly shows that the IL-1β and NO over-expression eventually leads to excessive chondrocyte apoptosis and participates during the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis.
Pain is one of the main symptoms of KOA. It is chronic,persistent, and progressive. KOA pain includes both subjective sensory pain signals released by the brain and local pain in the knee joint, which may be related to the release of inflammatory mediators. The muscles,synovium, and ligaments around the knee joint have nerve distributions and abundant sensory receptors.When knee joint is injured, the corresponding sensory receptors will receive noxious stimulations (mechanical stimulation or chemical stimulation of the released inflammatory mediator) through the peripheral nerves,which are afferent into the posterior horn of the spinal cord and finally into the central nervous system, and induce pain. Due to the activation of nociceptors and the patient’s subjective feelings, inflammatory mediators such as lactic acids and prostaglandins released in the joint cavity can lower the patient’s peripheral receptor threshold, which makes the patient more susceptible to painful stimulation and further promotes the release of more inflammatory mediators.During this process, the inflammatory response intensifies and the information of joint pain spreads,which will sensitize the peripheral fibers and make the pain susceptible[19-20]. Long-term pain also affects the patient's mental health. In KOA patients, the pain threshold and the anxiety index are generally decreased,and the serum levels of some inflammatory mediators are increased, making the disease more difficult to manage[21]. Both IL-1β and NO are inflammatory mediators with the effect of causing pain. In this experiment, the Lequesne MG function rating was used as the evaluation indicator to observe the effect of the sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations on the expression levels of IL-1β and NO in serum and synovial fluid, the response to painful stimulation, and the degree of knee swelling. The results showed that the levels of IL-1β and NO in serum and synovial fluid, the local knee joint reaction, joint mobility, and joint swelling in the Lequesne MG function rating of the intervention group were differently improved, and were statistically different from those of the model group(P<0.05), confirming the therapeutic effect of the sinewregulating bone-setting manipulations.
Biomechanical abnormalities of the lower limbs induce KOA, mainly manifesting as the imbalance between bones and tendons. Tendons are closely related to the knee joint function. The coordination of tendons and bones maintains the normal functional activities of knee joint. In this experiment, the ligaments and meniscus of rabbit's knee joint were destroyed by the modified Hulth method to simulate the secondary KOA in humans. The experimental observations showed that the knee joint range of motion was decreased, the exertion way of lower limbs was changed, and the articular cartilage was damaged in the model rabbits,which can directly explain the damage of the imbalance between bones and tendons. The Na-Grasping and Nie-Pinching manipulations in this study made the model rabbits quiet and relieved their muscle spasms to make the muscles in a relaxed state. Then stimulating techniques such as digital An-Pressing were used to treat along the relevant meridian and tendon routes,especially focusing on the nodules and trigger points, so as to achieve the effect of releasing adhesions,unblocking the meridians, harmonizing Qi and blood,invigorating blood, and relieving pain. Finally, Yao-Shaking, flexion, and extension manipulations were used to correct the abnormal anatomical positions of the joint. The full set of manipulations can rearrange and regulate the tendons, lubricate the joints, and correct the abnormal weight-bearing posture and gait of the model rabbits, improving the joint range of motion and dysfunction, and ultimately achieving the therapeutic result of “normal bone, soft tendons, and smooth flow of Qi and blood”. The results of this study showed that compared with the model group, the intervention group rabbits had different degrees of improvement in the joint range of motion and articular cartilage damage, and the between-group difference was statistically significant (P<0.05), but the difference in gait response between the two groups had no statistical significance (P>0.05). We speculate that it may be related to the decline in knee muscle strength and endurance, and may require additional functional exercises for effective improvement.
In summary, the sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations can down-regulate the expression levels of IL-1β and NO in serum and synovial fluid of KOA model rabbits and reduce the apoptosis rate of chondrocytes. Thus, it can protect cartilage tissue,relieve knee joint pain and swelling, and improve movement. This study has provided experimental evidence for KOA treatment with the sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (國(guó)家自然科學(xué)基金項(xiàng)目, No.81674076); Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province Education Office (安徽省教育廳自然基金重點(diǎn)項(xiàng)目, No. KJ2018A0273).
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria in this experiment.
Received: 14 November 2020/Accepted: 3 February 2021
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2021年6期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2021年6期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Efficacy observation of auricular point sticking in combination with a healthy diet for simple obesity in children
- Clinical efficacy of sticking-needle acupuncture plus tendon-regulating manipulation in the treatment of acute ankle sprain
- Therapeutic efficacy observation of warm needling moxibustion plus spine subtle adjusting manipulation for cervical radiculopathy
- Evaluation of the clinical efficacy of muscle regions of meridians needling method for refractory facial paralysis based on infrared thermal imaging technology
- Clinical study on Tuina plus umbilical therapy for senile functional constipation
- Effect of acupuncture on serum PYY and nesfatin-1 in obese patients with insulin resistance
