Novel virulence factor dupA of Helicobacter pylori as an important risk determinant for disease manifestation: An overview
Jawed Alam, Avijit Sarkar, Bipul Chandra Karmakar, Mou Ganguly, Sangita Paul, Asish K Mukhopadhyay
Abstract Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a microaerophilic, Gram-negative, human gastric pathogen found usually in the mucous lining of stomach. It infects more than 50% of the world’s population and leads to gastroduodenal diseases. The outcome of disease depends on mainly three factors: Host genetics, environment and bacterial factors. Among these, bacterial virulence factors such as cagA, vacA are well known for their role in disease outcomes. However, based on the global epidemiological results, none of the bacterial virulence (gene) factors was found to be associated with particular diseases like duodenal ulcer (DU) in all populations. Hence, substantial importance has been provided for research in strain-specific genes outside the cag pathogenicity island, especially genes located within the plasticity regions. dupA found within the plasticity regions was first demonstrated in 2005 and was proposed for duodenal ulcer development and reduced risk of gastric cancer in certain geographical regions. Due to the discrepancies in report from different parts of the world in DU development related to H. pylori virulence factor, dupA became an interesting area of research in elucidating the role of this gene in the disease progression. In this review, we shed light on the detailed information available on the polymorphisms in dupA and their clinical relevance. We have critically appraised several pertinent studies on dupA and discussed their merits and shortcomings. This review also highlights dupA gene as an important biomarker for DU in certain populations.
Key words: Helicobacter pylori; Plasticity region; Duodenal ulcer; Gastric cancer; dupA gene
INTRODUCTION
Helicobacter pylori(H. pylori) is a curved rod-shaped, Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found usually in the mucous lining of the stomach.H. pyloriinfects more than 50% of the world’s population and 70%-80% of the Indian population[1,2].H. pyloriis acquired during childhood and remains in the stomach throughout the life if not treated effectively[3]. Infection withH. pyloricauses duodenal ulcer (DU), gastric ulcer (GU), gastric cancer (GC) and gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma[4-7]. Considering its clinical importance, the World Health Organization has declaredH. pylorias a class I carcinogen and enlisted GC as the fifth most common cancer and the third most common cause of cancer-related death[8,9]. Infection ofH. pyloriis comparatively more prevalent in developing countries than Western countries due to socioeconomic and sanitary conditions[10]. The mode of transmission ofH. pyloriis not clearly understood. However, most of the studies suggest thatH. pyloriis transmitted from person to personviaoral-oral and fecal-oral route and also through contaminated food and water[11-14].
The enigma ofH. pyloriresearch is that the majority of infected patients remain asymptomatic, whereas around 15%-20% of infected individuals develop symptoms of peptic ulcer (duodenal or gastric) as a long-term consequence of infection. It is not clear what governs the manifestation ofH. pyloriinfection in some people. This apparent puzzle prompted the proposal that the sheer presence ofH. pyloriin the stomach is inadequate to develop acute gastric disease and that other conditions are required. However, it is assumed that the responsible factors inH. pylori-associated diseases are due to its virulence factors, host genetics, immunity and environmental influences. Host factors like polymorphism in the genes (pro-inflammatory cytokine genes) increase the risk of the specific clinical outcome[15]. None of theH. pylorivirulence factors such ascagA,vacA, the blood group antigenbabAandoipAhave been linked with specific diseases like DU or GC uniformly in all populations[16-20].
Analysis of the full genome sequences of differentH. pyloristrains reported specific genetic locus whose G+C content was lower than that of the rest of theH. pylorigenome. This indicates the possibility of horizontal deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) transfer from other species.H. pyloricarry an open pan-genome, which maintain a discrete group of strain-specific genes. These strain-specific genes mostly reside in genomic regions that had earlier been coined as plasticity zones. This term was previously used to describe a specific genetic segment with high variation between theH. pylorigenome sequences[21,22]. The complete genome sequence ofH. pylorireveals that part of the plasticity zone is normally arranged as genomic islands that may be integrated in the genetic loci. About 50% of the strain-specific genes ofH. pyloriare located in the plasticity region. Here, our focus is on the genedupA, which is located within the plasticity region. This gene was first reported in 2005 as an important biomarker for DU[23]. During subsequent years, several investigations were carried out ondupA, and this has become an interesting area of research, as shown in Table 1.
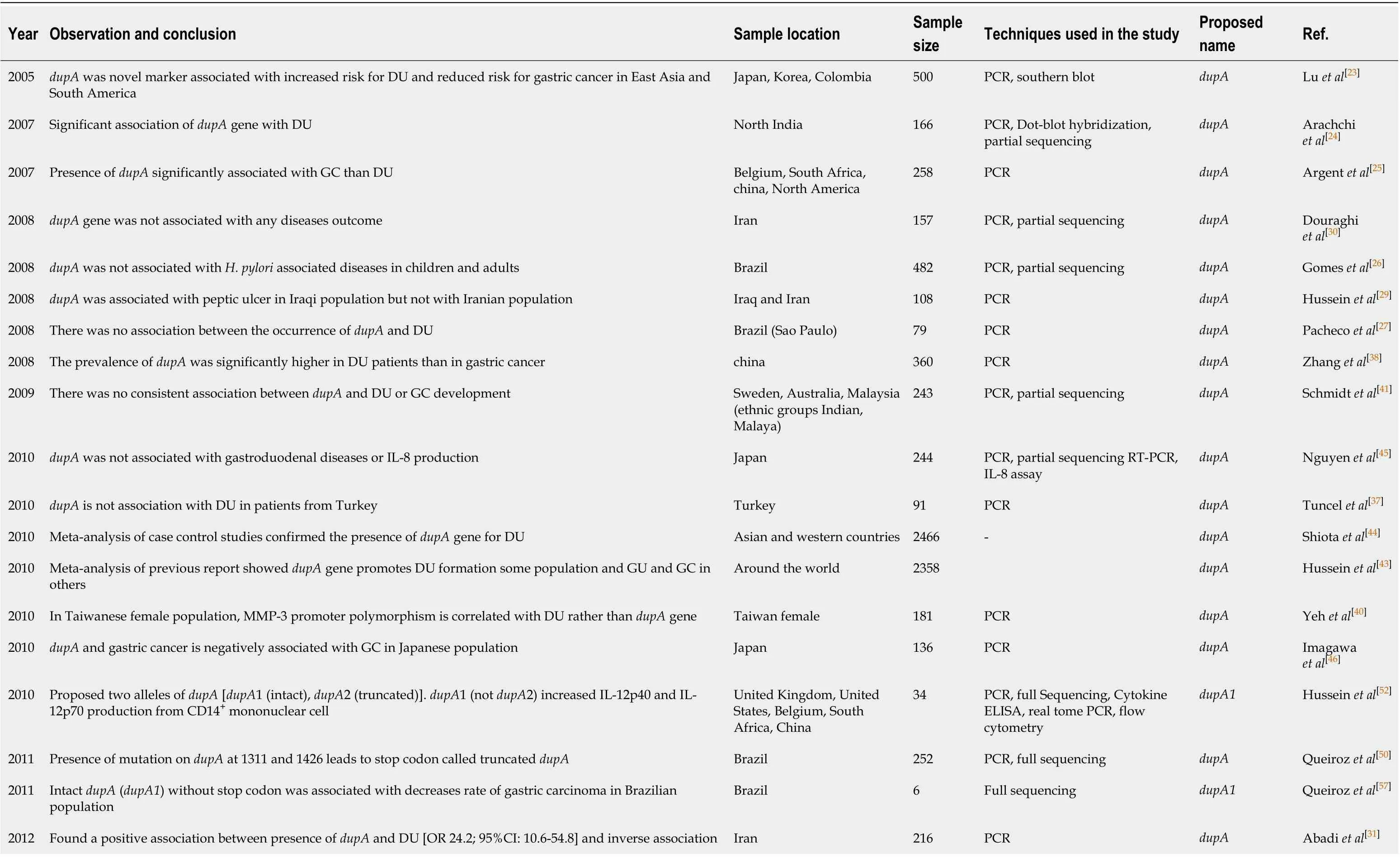
Table 1 Important finding on dupA of Helicobacter pylori in chronological order
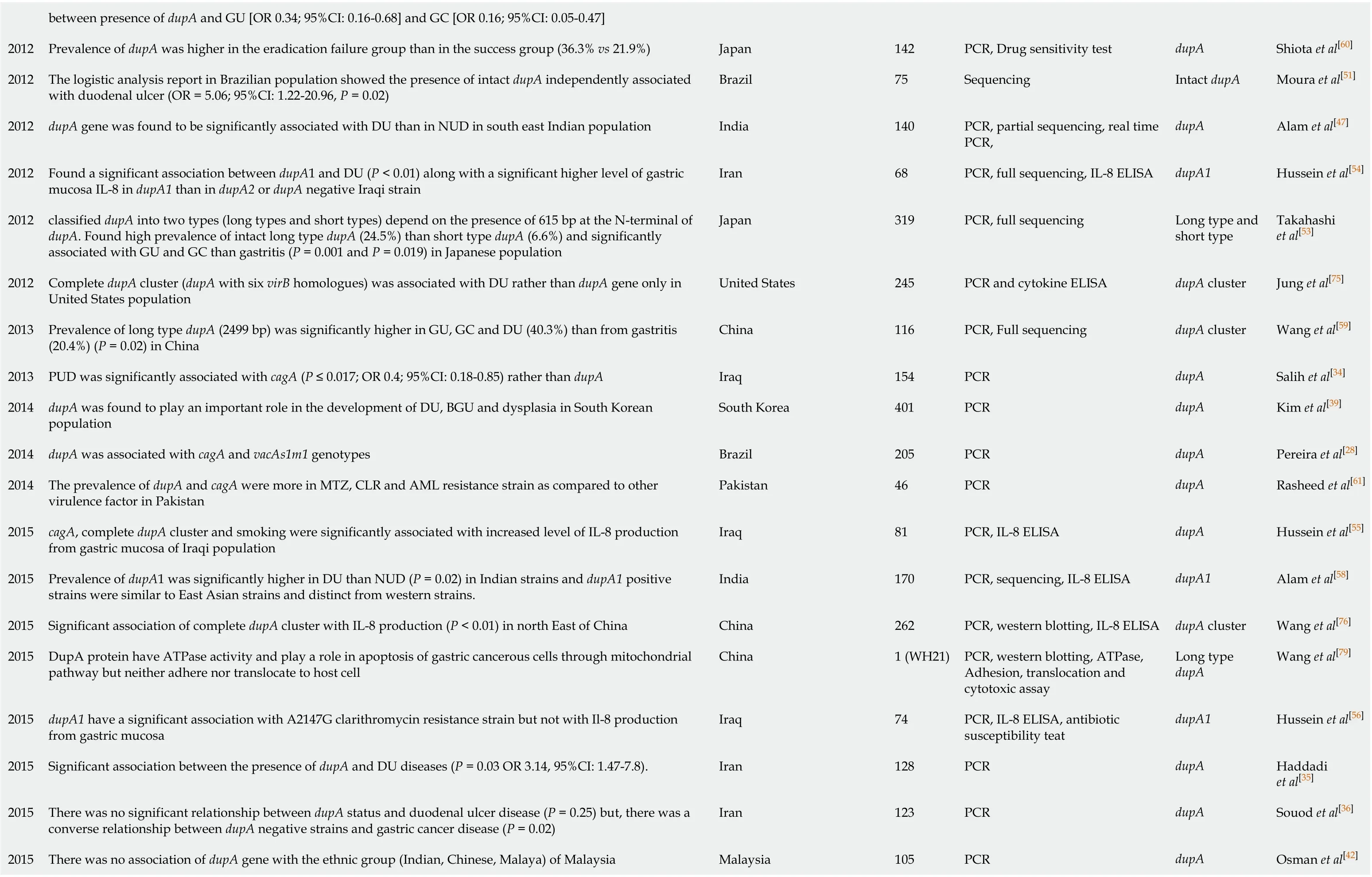
between presence of dupA and GU [OR 0.34; 95%CI: 0.16-0.68] and GC [OR 0.16; 95%CI: 0.05-0.47]2012 Prevalence of dupA was higher in the eradication failure group than in the success group (36.3% vs 21.9%)Japan 142 PCR, Drug sensitivity test dupA Shiota et al[60]2012 The logistic analysis report in Brazilian population showed the presence of intact dupA independently associated with duodenal ulcer (OR = 5.06; 95%CI: 1.22-20.96, P = 0.02)Brazil 75 Sequencing Intact dupA Moura et al[51]2012 dupA gene was found to be significantly associated with DU than in NUD in south east Indian population India 140 PCR, partial sequencing, real time PCR,dupA Alam et al[47]2012 Found a significant association between dupA1 and DU (P < 0.01) along with a significant higher level of gastric mucosa IL-8 in dupA1 than in dupA2 or dupA negative Iraqi strain Iran 68 PCR, full sequencing, IL-8 ELISA dupA1 Hussein et al[54]2012 classified dupA into two types (long types and short types) depend on the presence of 615 bp at the N-terminal of dupA. Found high prevalence of intact long type dupA (24.5%) than short type dupA (6.6%) and significantly associated with GU and GC than gastritis (P = 0.001 and P = 0.019) in Japanese population Japan 319 PCR, full sequencing Long type and short type Takahashi et al[53]2012 Complete dupA cluster (dupA with six virB homologues) was associated with DU rather than dupA gene only in United States population United States 245 PCR and cytokine ELISA dupA cluster Jung et al[75]2013 Prevalence of long type dupA (2499 bp) was significantly higher in GU, GC and DU (40.3%) than from gastritis (20.4%) (P = 0.02) in China China 116 PCR, Full sequencing dupA cluster Wang et al[59]2013 PUD was significantly associated with cagA (P ≤ 0.017; OR 0.4; 95%CI: 0.18-0.85) rather than dupA Iraq 154 PCR dupA Salih et al[34]2014 dupA was found to play an important role in the development of DU, BGU and dysplasia in South Korean population South Korea 401 PCR dupA Kim et al[39]2014 dupA was associated with cagA and vacAs1m1 genotypes Brazil 205 PCR dupA Pereira et al[28]2014 The prevalence of dupA and cagA were more in MTZ, CLR and AML resistance strain as compared to other virulence factor in Pakistan Pakistan 46 PCR dupA Rasheed et al[61]2015 cagA, complete dupA cluster and smoking were significantly associated with increased level of IL-8 production from gastric mucosa of Iraqi population Iraq 81 PCR, IL-8 ELISA dupA Hussein et al[55]2015 Prevalence of dupA1 was significantly higher in DU than NUD (P = 0.02) in Indian strains and dupA1 positive strains were similar to East Asian strains and distinct from western strains.India 170 PCR, sequencing, IL-8 ELISA dupA1 Alam et al[58]2015 Significant association of complete dupA cluster with IL-8 production (P < 0.01) in north East of China China 262 PCR, western blotting, IL-8 ELISA dupA cluster Wang et al[76]2015 DupA protein have ATPase activity and play a role in apoptosis of gastric cancerous cells through mitochondrial pathway but neither adhere nor translocate to host cell China 1 (WH21)PCR, western blotting, ATPase, Adhesion, translocation and cytotoxic assay Long type dupA Wang et al[79]2015 dupA1 have a significant association with A2147G clarithromycin resistance strain but not with Il-8 production from gastric mucosa Iraq 74 PCR, IL-8 ELISA, antibiotic susceptibility teat dupA1 Hussein et al[56]2015 Significant association between the presence of dupA and DU diseases (P = 0.03 OR 3.14, 95%CI: 1.47-7.8).Iran 128 PCR dupA Haddadi et al[35]2015 There was no significant relationship between dupA status and duodenal ulcer disease (P = 0.25) but, there was a converse relationship between dupA negative strains and gastric cancer disease (P = 0.02)Iran 123 PCR dupA Souod et al[36]2015 There was no association of dupA gene with the ethnic group (Indian, Chinese, Malaya) of Malaysia Malaysia 105 PCR dupA Osman et al[42]
CI: Confidence interval; DU: Duodenal ulcer; GC: Gastric cancer; GU: Gastric ulcer; IL-8: Interleukin-8; MMP-3: Matrix metalloproteinase -3; NUD: Non-ulcer dyspepsia; OR: Odds ratio; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction.
METHODOLOGY
To review the importance ofdupA, we have searched the “NCBI-PubMed” using the keywords: “dupA”, “H. pylori” and a total of 80 articles were found, of which 76 were published in English till January 2020. Out of 76, 13 are published as review articles and two as meta-analysis of previous data. The remaining 61 documented as research articles. The research ondupAhas spanned 15 years with contradictory findings. In this review, we summarize the result of relevant studies and discuss the pathogenesis ofdupAsince its early stage to recent advancements. Finally, this review highlights the significance ofdupAgene ofH. pylorias a virulence factor (virulence marker) and its role in pathogenesis including the progression of DU.
DISCREPANCIES OF DUPA WITH CLINICAL OUTCOMES
Studies conducted withH. pyloristrains from East Asia and South America identified a novelH. pylorivirulence factor encoded in thedupAthat was associated with increased risk of DU and decreased risk of GC. However, this perception seems to be region specific. ThisdupAwas homologous tovirB4 gene, located in the plasticity zone ofH. pylori. dupAcontained two open reading frames (ORFs),jhp0917andjhp0918, with an overlap of twelve bases and an insertion of either base thymine (T) or cytosine (C) after the position 1385 of thejhp0917that leads to continuous gene of 1839 bp. Since 2005, several studies have been conducted from different geographical areas to check the association ofdupAwith disease outcome considering thedupAhas two ORFs (jhp0917/jhp0918) with the insertion of one base (T/C) at position 1385 ofjhp0917. Studies performed in North India during 2007 support the finding of Luet al[24]. However, studies conducted in different countries (Belgium, South Africa, China, North America and Brazil) found thatdupAis not associated with DU in the respective population[25-27].
Investigations made in Sao Paulo, Brazil showed thatdupAwas detected inH. pyloristrains of 41.5% patients, which was less from a previous study made by Gomeset al[26](2008), in whichdupAwas present in 89.5% patients[28]. This study showed an association ofdupAwithcagAandvacA s1m1genotypes but without any link to disease outcome. The difference in the results of these two studies from Brazil could be explained by variation in geographic regions, a re-arrangement in the plasticity zone distribution inH. pyloriand various methods used for the analysis.
The distribution ofdupAinH. pyloriwas similar in Iraqi and Iranian population, but there was an association between peptic ulcer anddupAonly in the Iraqi population[29]. An independent study by Douraghiet al[30](2008) reported a nonsignificant higher distribution ofdupAin DU than non-cardia GC patients in the Iranian population[30]. Another study by Talebi Bezmin Abadiet al[31](2012) found a positive association between the presence ofdupAand DU along with an inverse association betweendupAand GU in Iranian population[31]. The discrepancy in the finding of Douraghiet al[30](2008) and Talebi Bezmin Abadiet al[31](2012) may be due to differences in the study populations. Douraghiet al[30](2008) focused mainly in Tehran (the densely populated capital of Iran), whereas Talebi Bezmin Abadiet al[31](2012) collected samples from the extremely rural northern areas of Iran. Recently, Fatahiet al[32](2019) tested a highly conserved region ofdupAand showed a significant relationship between the occurrence of DU and the presence of an 112 bp segment ofdupAin the Iranian population[32]. Another group from Iran studied the relationship between antibiotic resistance pattern and virulence genotype among 68H. pyloristrains and found that metronidazole resistance was significantly associated with the strains harboringcagA, sabAanddupA[33]. One study from Kurdistan region of Northern Iraq reported thatcagAgene was significantly associated with peptic ulcer disease rather thandupA, which contradict the result of Husseinet al[29](2008). This might be due to the differences in sample size and also in the geographical location of Iraq[34]. In the Shiraz area of Iran, a significant relationship was found between strains withdupA, CagA motif (ABC types) and DU disease, which supports the previous finding in this region[35]. Another study from Western Iran indicated that presence ofdupAgene could be considered as a marker for the onset of severe gastroduodenal diseases[36]. However, there was no association ofdupAwith DU in the results obtained from the Turkish population[37].
In China and South Korea, presence ofdupAin clinicalH. pyloriisolates is significantly associated with DU and peptic ulcer (DU, benign GU, dysplasia), respectively[38,39]. In the Taiwanese female population, the host factor matrix metalloproteinase-3/tissue inhibitor matrix metalloproteinase-1 genotypes rather thandupAwas found to increase the risk of DU inH. pyloriinfected cases[40]. A case control study conducted in Sweden, Australia, Malaysia and Singapore showed that there was significant variation in the prevalence ofdupAin different locations and among different ethnic groups (Chinese, Indian and Malaya) within a country[41]. Another study in ethnic groups (Indian, Chinese and Malaya) of Malaysia reported that the prevalence ofdupAwas 22.9% in patients, which was in line with previous data (21.3%) conducted in Malaysia by Schmidtet al[41](2009). In the later study, there was no association betweendupAand clinical outcome[42].
Two independent systematic review and meta-analyses showed thatdupAis more associated with DU in some Asian populations than in Western populations[43,44]. Between 2005 and 2009, almost all the studies used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of two ORFsjhp0917, jhp0918and sequencing to identify thedupA. Functional analysis ofdupAin the Japanese population showed no association with DU but another study from different parts of Japan showed thatdupAis inversely related to GC[45,46].
Results from a study using different molecular methods [PCR, dot-blot hybridization, sequencing and reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR)] indicated thatdupAgene was prevalent more than six times in DU than in non-ulcer dyspepsia patients, indicating its significant association in India[47]. This result also corroborated the finding of Arachchiet al[24](2007) from North India. The RT-PCR analysis of South and East Indian population revealed that all PCR positive strains were not able to producedupAtranscripts, which was inconsistent with the finding of Nguyenet al[45](2009) where all thedupApositive strains showed the expression of the gene[47]. Further, the real-time PCR analysis revealed that the expression level of thedupAtranscripts varied from strain to strain in this study.
Studies conducted in Chile supported a significant association ofdupAgene with non-severe clinical outcome like DU and also played a role in protecting severe diseases like GC[48]. The Costa Rica study with 151 dyspeptic patients showed that presence ofdupAwas significantly associated with decreased risk of DU[49].
Some of the above-mentioned studies verified the finding of Luet al[23](2005), but others could not find an association betweendupAand disease outcome in their study populations. The differences in the results could be explained due to variation in the distribution of plasticity region genes and differences in the study population and techniques chosen for detection ofdupAgene. Several studies ondupAwere restricted to PCR ofjhp0917andjhp0918along with sequencing of only the 3' region ofjhp0917to find the insertion of T/C at 1385 position ofjhp0917. Numerous studies have shown the presence of frame shift mutation withindupAgene leading to the formation of truncated non-functional DupA. These findings provide evidence that only PCR based analysis ofdupAmay yield erroneous interpretation. Studies conducted by Queirozet al[50](2011) and Mouraet al[51](2012) from Brazil showed the presence of a mutation indupAthat results in a stop codon, making the gene truncated or non-functional. In addition, these studies revealed the importance of sequence analysis ofdupAamplicons[50,51]. TruncateddupAmight not be involved in the pathogenesis ofH. pylori.
Husseinet al[52](2010) coined the term “dupA1”. ThedupApositiveH. pyloristrains were categorized into two alleles based on the sequence;dupA1(intact 1884 bp) anddupA2(truncated). It was shown that the intactdupA1positive strains induced the production of interleukin (IL)-12 subunit p40 (IL-12p40) and IL-12p70 from CD14 (+) mononuclear cells and IL-8 expression in the human stomach, respectively[52]. Takahashiet al[53](2012) first reported the presence of an additional 615 bp in the 5' region of ORFjhp0917(absent in strain J99) and 45 bp in the 3' ofjhp0918(consist of 37 bp of intergenic region ofjhp0918-jhp0919and 8 bp of 5' region ofjhp0919in J99)to make 2499 bp ofdupAin the Japanese population (Figure 1). This variation formed the basis for classification ofdupAinto two types; “l(fā)ong and short types”. The long type of intact 2499 bp (with an additional 615 bp at 5' region ofjhp0917) has been considered as an actual virulence factor, and the absence of the additional segment should be interpreted with caution[53].
None of theH. pyloristrains from Iraq carried the completedupAcluster containingvirB8,virB9,virB10,virB11,virD4andvirD2, but there was a significant association betweendupA1 and DU. Moreover, higher levels of gastric mucosa IL-8 production were documented indupA1than indupA2ordupAnegative strains[54]. Further studies withH. pyloriinfected patients showed thatcagA, completedupAcluster and smoking habit were associated with increased levels of IL-8 production from gastric mucosa[55]. It was also shown in another study that the high IL-8 level in gastric mucosa was neither significantly associated withdupA1positive strains nor withdupAnegative strains[56]. A significant association has also been found betweendupA1and A2147G clarithromycin resistance mutation. However, the result ofdupA1and IL-8 association in the Iraqi population was not well elucidated. In BrazilianH. pyloristrains, it was found thatH. pyloristrains had the 45 base at the 3' end ofdupA, similar to that ofdupA1[57].
dupAgene of IndianH. pyloristrains has been classified into two forms based on the presence of additional 615 bp at the 5' region ofdupAfollowedbya stop codon. This includesdupA1 without any frameshift mutation (either long type or short type) anddupA2 with the truncated version having frameshift mutation[58]. Among these,dupA1 (intactdupA) was significantly associated with DU. Phylogenetic analysis of completedupAgene sequencing revealed that IndianH. pyloristrains intermingled with the East Asian strains, but differed from European strains[58].dupAis the first known genetic element of IndianH. pyloristrains, which phylogenetically formed the same cluster with the East Asian strains.In vitrostudy showed that IL-8 production was significantly associated with DU in intactdupA1 rather than truncateddupA2 ordupAnegative strains[58]. In Chinese strains, the prevalence of long typedupA(2499 bp) was significantly higher in patients with GU, GC and DU than in those with gastritis[59].
In the Japanese population, prevalence ofdupAwas higher in the group whereH. pyloricannot be eradicated, indicating thatdupAmay be an associated risk factor in the eradication failure[60]. A study from Pakistan on the influence ofdupAin the eradication failure showed thatH. pyloristrains harboringdupAandcagAwere multidrug (metronidazole, clarithromycin and amoxicillin) resistant as compared to strains having other virulence factors. This finding was similar to the observation made in the Japanese population[61]. In the northern part of Spain,dupAwas more prevalent in mild diseases (peptic ulcer) than severe diseases (GC)[62]. In Switzerland and South Africa,dupAofH. pyloriwas not associated with severe gastritis or DU[63,64].

Figure 1 Schematic representation of the jhp0917, jhp0918 and jhp0919 gene in strain J99 and that of the dupA alleles in the clinical isolates. The long type dupA (2499 nt) in some clinical isolates contained an additional 615 nt in 5' region before jhp0917 gene and ended 5 bp after the start codon of jph0919 gene. The short type dupA (1884 nt) in some clinical isolates starts from the 5' region of jhp0917 gene and ended 5 bp after the start codon of jph0919 gene.
DUPA CLUSTER: THIRD TYPE IV SECRETION SYSTEM (T4SS) OF H. PYLORI
The T4SS is an important bacterial transport system, and it is involved in the transport of large molecules (e.g., DNA, protein,etc). across the bacterial cell envelope[65,66]. Till now, three types of T4SS have been identified inH. pylori, of which much work has been done for the first two categories (cagPAI and ComB) and little is known about the third T4SS termeddupAcluster ortfs3(Figure 2)[67,68]. The third putative type IV secretion system (tfs3)is a 16 kb gene fragment present in the plasticity zone ofH. pylori, whose seven ORFs (viB4,virB8, virB9, virB10, virB11, virD4andvirD2) were homologous to virB4/D ofAgrobacterium tumefecians(A. tumefecians). The function of thetfs3elements is not yet clear as there is no direct evidence to show its role in transformation, conjugation or mouse colonization[69,70]. Some researchers divided thetfs3intotfs3a(all sixvirBhomologues withdupA) andtfs3b(all sixvirBhomologues withvirB4), whereas others named all sixvirBhomologues with virB4 astfs3and all sixvirB homologues withdupAastfs4[71-73]. In order to avoid confusion, we will use the termtfs3aordupAcluster (all sixvirBhomologues withdupA). VirB8, VirB9 and VirB10 are expected to form the core complex that bridges cytoplasm and the outer membrane. The VirB4, VirB11, VirD4 may be localized to the inner bacterial membrane and recognize the substrate and energize translocation and assembly of T4SS[74]. Further, the novel putative T4SS (tfs3a) ordupAcluster has been divided into three groups: Viz, a completedupAcluster (dupA-positive and all sixvirBgenes-positive), an incompletedupAcluster (dupA-positive but one/more than onevirBgenes negative) anddupA-negative group (dupAnegative andvirBgene positive/negative).
The study ofdupAcluster from the United States population showed that the completedupAcluster (dupAwith sixvirBhomologues) was associated with DU rather thandupAgene only[75]. Another report from the northeast part of China showed a significant association of completedupAcluster with IL-8 production (P< 0.01), but it did not show any correlation betweendupAcluster and disease outcome[76]. The studies from United States and China were conducted to check the prevalence oftfs3aordupAcluster in their population by PCR only. However, the mere presence of the gene does not express functional protein and there is no direct evidence that showstfs3aordupAcluster forming a functional T4SS. The earlier studies ontfs3adid not find a direct pathogenic role oftfs3ainH. pylori, but found increased colonization fitness and up-regulation of pro-inflammatory signaling from cultured cells. A novel pathogenicity island (PAI) calledtfs3-PAI was identified in China that had 17 ORFs, of which six are functionally homologues of T4SS and coordinate with the well-studiedcag-PAI[77]. The completetfsplasticity cluster was associated with IL-8 induction. The expression of some of the genes oftfs3a/tfs4 (virB2,virB4,virB6,virB8,virB10) inH. pyloriis up-regulated in low pH and enhances bacterial adhesion that support the role oftfs3a/tfs4in the colonization and virulence[78]. It is not known whether thevirBgenes ofdupAcluster work independently or in a coordinated manner by interacting among themselves or complementing each other’s function. We checked the interaction ofdupAwith sixvirBgenes oftfs3ato identify the assembly and function of completetfs3usingin vivostudies (yeast two-hybrid system) and found thatdupAgene did not interact directly with anyvirBgene. It seems thatdupAmay interact with some intermediates or work independently (unpublished data). This interpretation supports our earlier finding thattfs3is not significantly associated with DU in Indian population. More studies are required to know the structure, assembly and functions of the VirB proteins inH. pylori.
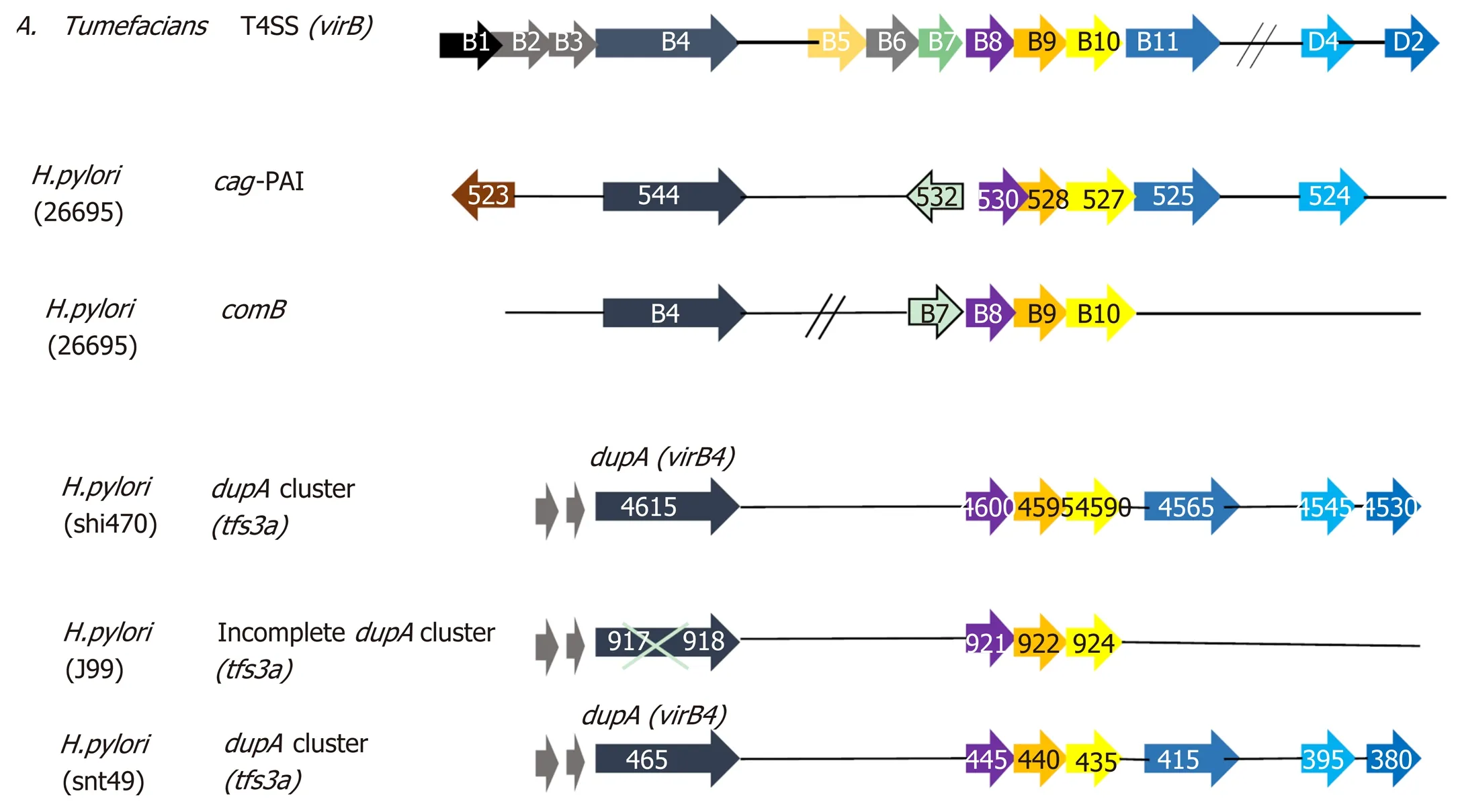
Figure 2 Organization of three types of type IV secretion system in the Helicobacter pylori compared to Agrobacterium tumefaciens prototype type IV secretion system. Genes are not drawn to scale. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; A. tumefaciens: Agrobacterium tumefaciens; T4SS: Type IV secretion system.
THE PROSPECTIVE FUNCTIONS OF DUPA
The bioinformatics analysis (PDB search tool, UniProt database) showed that thedupAgene is homologous to VirB4 adenosine triphosphate (ATP)ase of virB/virD ofA. tumefeciansand is predicted to be involved in DNA/protein transfer. The N-terminal of long type DupA has no homologous motif. Only the middle portion (jhp0917) and C-terminal (part ofjhp0918) showed homologous motifs suggesting that the Nterminal region might act as signal sequence. The amino acid sequence (210-406 AA) ofjhp0917gene protein was homologous to CagE_TrbE_VirB family, a component of type IV transporter secretion system. The first middle region of the DupA protein (430-500 AA) is homologous to FtsK/SpoIIIE family, which contains ATP binding P-loop motif. This was found in the Ftsk protein ofEscherichia coliinvolved in peptidoglycan synthesis and spoIIIE ofBacillus subtilis, facilitating in the intercellular chromosomal DNA transfer.
The second middle region (464-503aa) is homologous to TrwB, which has an ATP binding domain, and a part of T4SS may be responsible for the DNA binding and horizontal DNA transfer. The C-terminal region (668-738aa) is homologous to TraG_C_D, which is involved in the interaction of DNA-processing (Dtr) and mating pair formation (Mpf) system, leading to DNA transfer in bacterial conjugation. Many reports have shown that the growth rate ofdupApositive strains is higher in low pH as compared todupAdeleted/negative strains. This phenomenon indicates that DupA protein acts as an interactive protein and hence regulates urease secretion inH. pylori[79].
Thein vitroandin vivostudies showed the role ofdupAgene in the activation of transcription factors nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells and activator protein-1, which leads to IL-8 production. DupA protein act as an ATPase associated efflux pump, which probably confers its virulence. Evidence suggests thatDupAis involved in the pathogenesis ofH. pyloriby activating the mitochondria dependent apoptotic pathway of the host’s cell, which ultimately inhibits gastric cell growth.
Studies to understand the apoptotic effect ofdupAon human gastric adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line (commonly known as AGS) by propidium iodide staining and fragmentation assay determined thatdupAgene can induce apoptosis in AGS cells during an early stage of infection (unpublished data). This finding supports the results of Wanget al[79](2015) and finds thatdupAmay act as a pathogenic factor ofH. pylorito cause gastroduodenal diseases. Further studies are required to confirm the pathogenic effect ofdupAin anin vivomodel.
The growth kinetics between wild typedupApositive strains and its isogenic mutant strain showed that exponential phase was retarded indupAmutant cells as compared to the wild type strain. Our growth curve results, supported by the microarray data, showed that cell division gene in the mutantH. pyloriwas downregulated (unpublished data). It has also been suggested that motility is an essential feature in the colonization and therefore the pathogenicity ofH. pylori. The decrease in motility indupAmutant strain as compared to wild type inferred the role ofdupAgene in the motility. This motility result was further confirmed by the gene expression profile ofdupAmutant strain whose flagella proteins (FlgE, FliD and FliG) were found to be down-regulated (unpublished data). It might be possible thatdupAgene is directly or indirectly involved in negatively affecting the expression of cell division and flagellar genes ofH. pylori.
As predicted from the bioinformatics analysis, our experimental data (unpublished data) have shown that natural transformation ability indupAmutant strains has been totally inhibited in comparison to their wild type counterparts. There is a need for more studies on the heat-shock transformation efficiency, which will confirm the natural transformation assay, if any. Resistance to antimicrobials is of serious concern inH. pyloriinfection, as this may be the basis for eradication failure. It is important to use therapeutic regimens based on the results of antibiotic susceptibility testing. Metronidazole is considered a key drug in several therapies againstH. pyloriinfection. The results of the metronidazole susceptibility test showed that inactivation ofdupAgene transforms theH. pyloristrains to resistance phenotype. This phenomenon has not been explained very well. It is possible that thedupAgene might help in the DNA/protein/drug import (unpublished data).
ThedupAordupAcluster may have an intermediate function to linkcagPAI andcomBsystem, asdupAgene shows homology withcagEofcagPAI andcomB4ofcomBsystem. So, there is a need of anin vivostudy to establish the precise function ofdupA. It is assumed that thedupAin combination with other sixvirgenes form a novel third T4SS calledtfs3aordupAcluster that might play a pathogenic role in gastroduodenal diseases.
CONCLUSION
H. pyloriis one of the most diverse bacterial species.H. pyloridemonstrate panmictic population structure. DNA-fingerprint of two strains isolated from two different persons generally displays a non-identical pattern, which suggests genetic exchange along with co-evolution of this gastric pathogen with its host. One study from the Indian population demonstrated that all the tested patients carried multipleH. pyloristrains in their gastric mucosa[80]. Analyses of certain genetic loci showed the micro diversity among the colonies from a single patient, which may be due to the recombination events during long-term carriage of the pathogen. From the results of this study, researchers predicted that many patients from the developing world acquired infections ofH. pyloridue to repeated exposure to this pathogen with different genetic make-up[80]. This may enhance the probability of super infections, which favor genetic exchanges among these unrelatedH. pyloristrains. As a result, this led to the genesis of certainH. pylorivariants with different genetic makeup than the parental strain, which in turn increases the chance of the severe infection. Therefore, the exploration of appropriate biomarker(s) that envisage the clinical condition inH. pylori-infected patient is a challenging area of research.
There is a lack of relevant biomarker(s) capable of predicting important digestive diseases in clinical settings. Even though there is ample information regarding thedupAofH. pylori, many unanswered questions still exist, especially regarding the specificity of thedupAproposed for clinical manifestation.dupAwas categorized as long and short types in one study, but in another study, this gene was typed asdupA1 (intactdupA1may be long type or short type) anddupA2 (truncated version). This gene classification should be resolved for international use to avoid any misperception. We propose the longdupAasdupA1 and short typedupAasdupA2, and the truncated version ofdupAhas to be disregarded, as it has no role in pathogenesis.dupAshould be screened by PCR, sequencing of the full-length gene (1884 and 2499 nt) and western blotting. Nevertheless, the discrepancy prevails between the association ofdupA(short type or long type) ordupAcluster and the disease outcome. Currently, the prevalence of intactdupAin East Asian countries is lower than Western countries. DupA with another six Vir proteins (VirB8, VirB9, VirB10, VirB11, VirD4 and VirD2) predicted to form novel third type-IV secretion system (tfs3a), which may be involved in transformation/conjugation or injection of DNA/new effector molecules in gastric epithelial cells. However, the function of specific Vir protein of completedupAcluster (tfs3a) is not well characterized. Recent reports and other unpublished data showed that DupA has multifunctional biological activities, and it can be considered as an important biomarker for DU. It is also not clear whether the DupA works alone or in combination with other VirB proteins. There is an urgent need for reliablein vitroand animal models from diverse geographical areas of the world to elucidate further the pathogenic role ofdupAanddupAcluster in gastroduodenal diseases, particularly the DU and GC.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年32期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年32期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Association between human leukocyte antigen gene polymorphisms and multiple EPIYA-C repeats in gastrointestinal disorders
- Promising xenograft animal model recapitulating the features of human pancreatic cancer
- Immune and microRNA responses to Helicobacter muridarum infection and indole-3-carbinol during colitis
- Etiology and management of liver injury in patients with COVID-19
- Inactive matrix Gla protein is elevated in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
- Development of a novel score for the diagnosis of bacterial infection in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure
