Identifying the Unknown Tags in a Large RFID System
Yu Fu, Zhihong Qian, Xue Wang, Guiqi Liu
College of Communication Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
* The corresponding author, email: dr.qzh@163.com
I.INTRODUCTION
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a type of non-contact, non-line-of-sight reading and low-power wireless communication technology [1].With the rapid development of Internet of Things, RFID is the key technology of its perception layer.RFID technology has been widely used in various applications,including logistics/inventory management, object tracking and health care [2-4], etc.
An RFID system mainly consists of one or multiple readers, numerous tags and a backend server [5].An RFID reader, read-write (or read-only) device equipped with the ability of memory and computing, can identify and communicate with tags via wireless channel.RFID tags are usually attached to the designated objects (e.g., products and living beings).Each tag, consisting of antenna, coupling components and chip set, has a unique ID to store the specific information.The back-end server, a control center that provides service and management, integrated with the application layer software of RFID system stores data information collected by readers.
Most existing protocols aim at addressing tag collision problem.These protocols can collect all tag IDs within the interrogating range of the reader.In recent years, two types of tag detection protocols, including missing tag identification protocol and unknown tag identification protocol, have efficiently solved RFID tag monitoring problem.In many practical applications, when some items are stolen or lost, the tags attached these items are called missing tags.When some tagged items are new entering or misplaced, the tags, of which IDs are not stored in the database of back-end server, are called unknown tags.Consider that,in the inventory management, some products are new-coming and not recorded in the list.Obviously, manual searching is slow-speed and low-efficiency.We can solve this problem by using RFID technology.And unknown tag identification has practical significance and is an under-investigated problem.
In this paper, we focus on identifying unknown tags.And the major contributions can be summarized as follows:
1) We propose a baseline protocol, in which information of known tags is used directly to deactivate them (i.e.let the tags do not take part in the following interrogating process)and consequently the remaining tags are unknown ones.
2) We further propose a novel unknown tag identification protocol (NUTIP), which consists of two phase: tag identification &unknown tag labeling phase, and labelled tag identification phase.The proposed NUTIP identifies unknown tags to meet the predefined identification accuracy.This protocol is efficient in RFID system for both sparse unknown tags environment and dense unknown tags environment.
3) To minimize the execution time of unknown tag identification, this paper investigates the optimal parameter settings: the optimal frame length and the minimum round count of NUTIP.
4) To evaluate the performance of NUTIP,we carry out some simulation experiments and the results show that the NUTIP outperforms relevant protocols.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.Section II presents the related work.Section III describes the system analysis.The baseline protocol and NUTIP are introduced in section IV.Analysis of NUTIP is presented in section V.Section VI shows the experimental results of proposed protocols and compares them with BUIP, BUIP-CE and BUIP-CF.Finally, this paper is concluded in section VII.
This paper proposes a baseline protocol and a novel unknown tag identification protocol(NUTIP) to identify the unknown tags efficiently.
I.RELATED WORK
In RFID tag identification research, extensive works focus on solving tags-to-reader collision problems to collect all tag IDs.The anti-collision protocols can be classified into two categories: Aloha-based probabilistic protocols [6-8]and tree-based deterministic protocols [9-11].Bueno-Delgadoet al[12] and Gandinoet al[13] solved the transmission collision problem for dense reader environments.Wuet alproposed a novel tag anti-collision protocol considering capture effect environment to enhance the efficiency of tag identification in [14].The protocol reduces collision between the hidden tags by capture effect and the other tags.The purpose of these studies is to collect tag IDs in static RFID system.However, the actual RFID system is dynamic, such as loss of tags, entry of new tags and faulty position of tags.
Some researchers focus on detecting the missing tags.Liet al[15] designed five missing tag identification protocols based on probabilistic methods.To achieve better time efficiency, the protocol that is proposed by Liuet alin [16] leverages the expected collision slots for improving the utilization of time frame.Liuet al[17] proposed a slot filter-based missing tag identification protocol.Some expected collision slots are reconciled into singleton slots.On the other hand, empty slots and irreconcilable collision slots are able to filter out.

Fig.1 The system model
In recent years, the problem of unknown tag identification has attracted more attentions.Liuet al[18] proposed two protocols:filtering-based unknown tag identification protocol (FUTI), and interactive filtering-based unknown tag identification protocol (IFUTI).These protocols employ hash functions and filters to label unknown tags until predefined identification accuracy is satisfied.In the execution of FUTI protocol or IFUTI protocol,unknown tag identification is interfered with known tags because known tags may collide with unlabeled unknown tags in the RFID system.Liuet al[19] proposed three protocols to identify unknown tags: a basic unknown tag identification protocol (BUIP), a BUIP with collision-empty slot pairing (BUIP-CE) and a BUIP with collision-fresh slot paring (BUIPCF).In BUIP all known tags are deactivated and all unknown tags are labeled.By using BUIP-CE known tags deactivation efficiency has further improved.Expected collision slot is paired with an expected empty slot.Hence,the number of expected singleton slots increases.However, unknown tags may collide with the known tags in expected empty slots after paring.In order to overcome the shortage of BUIP-CE, BUIP-CF pairs expected collision slots with additional slots in this frame, which increases the probability of singleton slots and makes known tags to deactivate quickly.The three protocols spend more time to deactivate all known tags when the number of known tags is very large.
For this purpose, a novel unknown tag identification protocol (NUTIP) is proposed.The NUTIP consists of two phases: tag identification & unknown tag labeling phase, and labelled tag identification phase.In the first phase, NUTIP employs an indicator vector to identify tags of actual singleton slots.Known tags are deactivated to avoid making collision with unknown ones.Additionally, unknown tags of actual collision slots, which are supposed to empty slots, are labeled (i.e.let the tags not take part in the first phase, but keep active in the second phase).In the second phase, EDFSA is used for identifying all labeled unknown tags.Specially, NUTIP identifies unknown tags to satisfy the predefined identification accuracy.
III.SYSTEM MODEL
3.1 Assumption and problem
We consider a large-scale RFID system with a single reader and two kinds of tags, which are known tags and unknown tags, as illustrated in Fig.1.The number of known tags and unknown tags arekandu, respectively.K={kt1,kt2,…,ktk}, representing the set of known tags.U={ut1,ut2,…,utu}, representing the set of unknown tags.Each tag possesses a unique ID and is equipped with the uniform hash functionH(·).
Note that we consider the single reader case.However, a large RFID system consists of multiple readers and a large number of tags.So we extend our solutions to the multi-reader case.The system uses a back-end server to control all readers inquiring the field at the same time.And the parameters and the indicator vector have the same value with all readers.Moreover, each reader sends the received data to the back-end server.In other words, the multiple synchronized readers are considered as a single reader logically.To simplify this discussion, we assume a single reader scenario.
Assume that the RFID reader has right to access to a database of the back-end server where all known tag IDs are stored.And unknown tag IDs are not available in the database.The reader communicates with the backend server and all the RFID tags via a highspeed link and an error-free wireless channel,respectively.Besides, all known tags exist in the interrogating range of reader during the execution of our protocols.Some tags may be unexpectedly missing, such as move out of the system and stolen by theft.Then the system operates existing excellent missing tag identification protocols (e.g., [15-17]) to detect them and remove their IDs from the database.
The problem we want to solve in this paper is to quickly collectuunknown tag IDs with a given accuracy, which is denoted asμ.Letμbe the quotient of unknown tags that are expected to be identified divided by all unknown tags.For example, there are 1000 unknown tags exist in the RFID system, 950 unknown tag IDs should be collected on average whenμis equal to 95%.Table I summarizes the notations used in the following proving process.
3.2 Time slot
It is in time-slotted way for communication between a reader and tags.The reader sends signal to synchronize the clock of the tags.And some tags select one slot to respond after they are queried by a reader.This interactive communication, applied in our protocols,called as Reader Talks First mode.The status of time slot has three categories based on the number of responded tags in the slot: empty slot, singleton slot and collision slot.If zero tag responds to the reader, it is called empty slot.If only one tag responds in the slot, it is called singleton slot.In this case the reader identifies the tag successfully and let the tag deactivate.If more than one tag respond, it is called collision slot.The reader cannot identify these tags in the slot.
Furthermore, according to the length of response, the time slot includes three categories:tag slot, long-response slot and short-response slot [20].The length of tag slot, denoted asttag,allows the transmission of a 96-bit tag ID.The length of long-response slot, denoted astl, allows the transmission of long response carrying 10-bit information.The length of short-response slot, denoted asts, affords transmitting a short response with only 1-bit information.The tags usetlto decide whether the status of time slot is empty/singleton/collision.On the other hand,the tags usetsto determine whether the status of time slot is empty/nonempty.Besides, the tags also usetsto know the tags that are supposed to respond.According to the specification of the Philips I-Code system [21],ttag,tlandtsare set to 2.4ms, 0.8ms and 0.4ms, respectively.
IV.UNKNOWN TAG IDENTIFICATION PROTOCOLS
4.1 Baselιne protocol
We know the reader has right to access to the database that stores known tag IDs.Each known tag is identified and deactivated after reader broadcasting its ID.Then the remaining tags are unknown tags and could be identified by running tag IDs collection protocols [8-11].In our baseline protocol, EDFSA [22]is used to identify the remaining tags.The optimal system efficiency of EDFSA protocol is 36.8%, it means that EDFSA need at least 2.72uμto identifyutags with a given accuracyμ.The identification of known tag takesk(ttag+ts).Therefore the total execution time of baseline protocol isk(ttag+ts)+2.72u·μ·ttag.Comparing with the traditional protocols [23-25] of tag IDs collection, it effectively reduces the total execution time by avoiding re-collect known tag IDs.However, the transmission of known tag IDs is very time-consuming.Therefore, it motivates us to design a more time-efficient unknown tag identification protocol.
4.2 Novel unknown tag identification protocol
To solve the problem of unknown tag iden-tification, we propose a novel unknown-tag identification protocol (NUTIP) in this section.We present the NUTIP description firstly, and then analyze how to optimize the parameter settings for achieving its best performance.
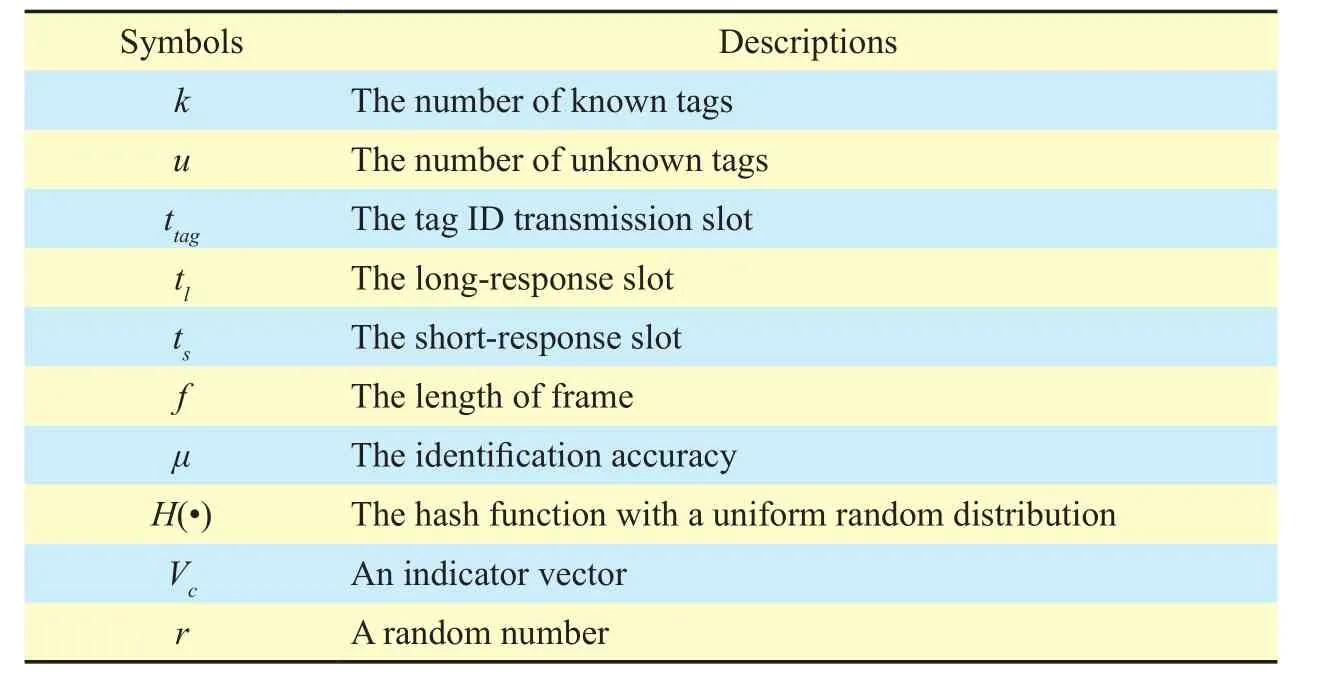
Table I Notations used in the following proving process
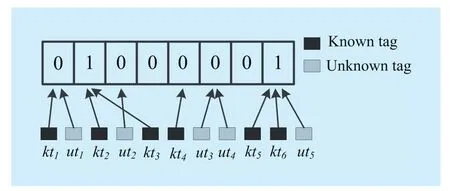
Fig.2 Exemplification of the indicator vector Vc
The NUTIP consists of two phase: tag identification & unknown tag labeling phase, and labelled tag identification phase.In the first phase, some known tags are deactivated.And lots of unknown tags are identified or labeled.In order to identify and label a percentageμof unknown tags, the first phase consists of several rounds.The total number of these unknown tags is expected to beμ·u.In the second phase,only the labeled unknown tags are identified.
To help tags select more appropriate slot,we use the indicator vector, which has already been adopted by many existing papers [16-19].At the beginning of the first phase, the reader broadcasts anf-bit indicator vectorVcto all of the tags within its interrogating range.Besides,the reader transmits a request
Each tag is pseudo-randomly mapped to a slot after receivingrandffrom the RFID reader.Assume that a certain tagtxis mapped to a slot at indexw, wherew=H(IDx,r) modf.Then the tagtxchecks thewth index ofVc.Here, we call thewth bit ofVcas the representative bit oftx.It is easy to draw the following conclusions:
(1) When the representative bit is ‘1’, it means that the expected collision slot is selected by the tag.Since missing tag doesn’t appear in system during our protocol execution, the expected collision slot must be an actual collision slot.However, it cannot be determined the tag is known or unknown.Let the tagtxdo not respond in this round, but remain active status in the following round.
(2) When the representative bit inVcis ‘0’,it means the expected empty/singleton slot is selected by the tag.Note that, the reader only checks expected empty slots and expected singleton slots.The tag usestltime to transmit information and then actual status of slot is determined by the reader.
In fact, the expected empty/singleton slot may be actual empty/singleton/collision slot.The reader executes the appropriate operation to the tags in different time slots, which as following:
(1) If an empty slot turns out to be empty,no tag responds;
(2) If an empty slot turns out to be singleton, only one unknown tag exists and it could be identified by the reader;
(3) If an empty slot turns out to be collision,all tags of this slot must be unknown and then they need to be labeled by the reader;
(4) If a singleton slot turns out to be singleton, only one known tag exists and then it needs to be deactivated;
(5) If a singleton slot turns out to be collision, the tags of this slot, including known tags and unknown tags, don’t respond in this round.However, these tags remain active status in the following round.
In the first phase, some known tags are set to deactivate to avoid interfering with unknown tag identification.On the other hand,some unknown tags responded in actual singleton slots are identified by reader.And lots of unknown tags, responded in actual collision slots that supposed to be empty, are labeled.
In the second phase, we simply identify all labeled unknown tags.The reader collects all labeled unknown tag IDs by using the EDFSA protocol as the same as BUIP.
V.ANALYSIS OF NUTIP
5.1 Choosing the optimal frame length
Assume that there arekiknown tags anduiunknown tags in theith round.Andfiis the length of the current frame.The probability that a slot is expected empty, denoted asis given as follows
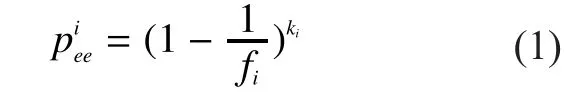
The probability that a slot is expected singleton, denoted asis given as follows
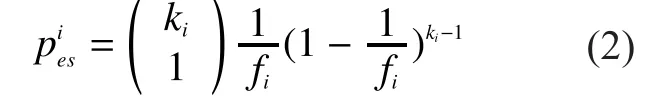
The probability that a slot is expected collision, which is

For any slot, the probability that unknown tags can be labeled is given by
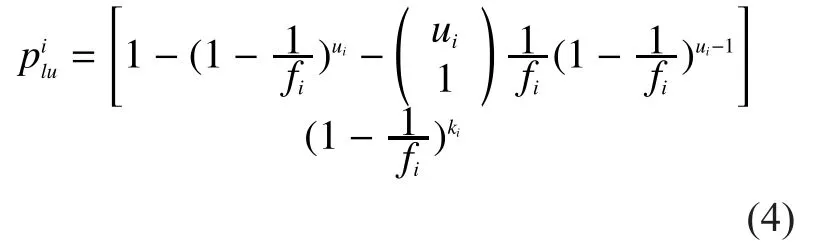
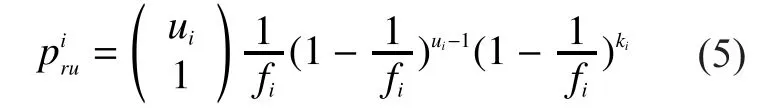

Thus theith round hasfislots.The total number of identified tags isand the total number of labeled tags isThe probability that a certain unknown tag can be identified and the probability that a certain unknown tag can be labeled areandrespectively.
Table II lists some values ofwith differentui, whenki=10000 andμ=99%.With the number of unknown tags increases, the valueremains at about 0.36.It is mainly because the frame lengthfiis optimal in each frame.From equation (7),fiis associated with the change ofkiandui.In table III, some value ofwith differenti, whenki=10000,ui=10000 andμ=99% are listed.We can see thatis substantially improved withiincreases during the first phase execution.
5.2 Choosing the minimum round count
The first phase is repeated for several rounds.Assume that the first phase usesLrounds to identify and label with a percentageμof unknown tags.In fact, the probability that unknown tags are identified or labeled in the first phase, denoted asp, is given as follows

In order to achieve the target of identified unknown tags with the accuracy ofμ, we need to make sure thatpis not less thanμ, i.e.p≥μ.
We already know both the number of known tags and the number of unknown tags.Thus the frame length of the current round can be achieved.Combining equations (6), (7) and(8), we can get the actual probabilitypthat unknown tags are identified.Thus the round countLcan be obtained.
Table II The value with different ui (ki=10000, f=fopi, μ=99%)

Table II The value with different ui (ki=10000, f=fopi, μ=99%)
Table III The valuewith different i (ki=10000, ui=10000, f=fopi, μ=99%)
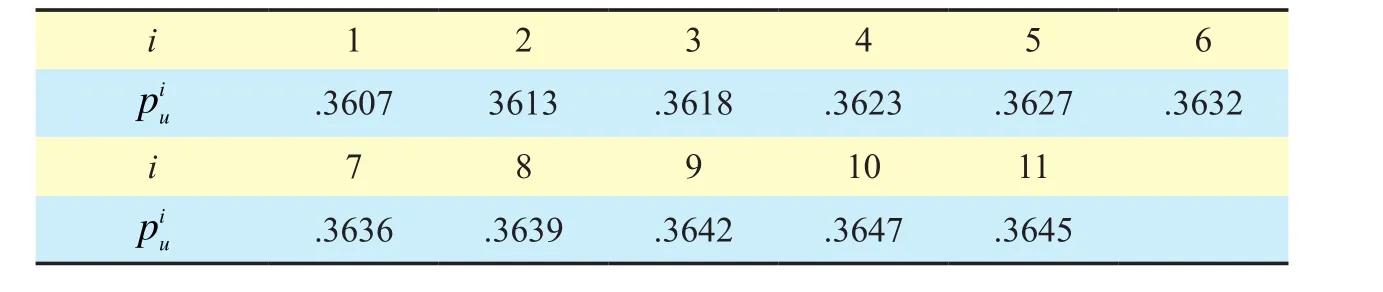
Table III The valuewith different i (ki=10000, ui=10000, f=fopi, μ=99%)
5.3 Total execution time
For the first phase, the execution time of NUTIP in theith round includes three parts.The first part is the time for transmitting the victorVc.We get the total number of slots isby the equation (7).The one bit in vectorVccorresponds to one slot in the frame, i.e.the number of bits inVcis the same as the number of slots in one frame.Assume that the vectorVcis divided into segments of 96 bits and transmitted inttag.Thus the time for transmittingVcis
The second part is the response time consumed by the tags.And the total number of slots, including expected empty slots and expected singleton slots, checked by reader in the frame isIn order to determine whether the status of time slot is actual empty/singleton/collision, these tags usetltime to transmit their 10 bits data.Thus the time of the second part is
The third part is the time of unknown tags identification.Tags needfi·pruslots to transmit their IDs by usingttagtime.The time needed to identify unknown tags isfi·pru·ttag.
Thus the execution time of theith round in the first phase is
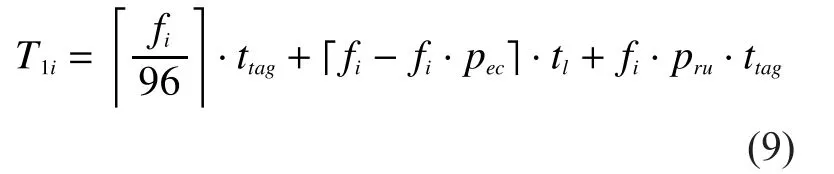
For the second phase, we run EDFSA protocol to identify the labeled unknown tags.These tags need to be identified by usinge·fi·plutime slots in the first sub-stage.Then the execution time of this round in the second phase is

Thus the total execution time of NUTIP is
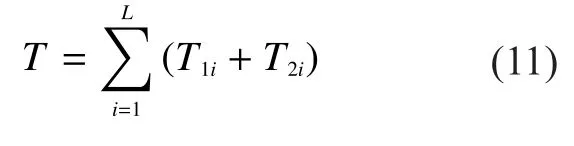
VI.SIMULATION RESULTS
In this section, we evaluate the performance of the proposed baseline protocol and NUTIP by using MATLAB simulation software.The length of each tag ID is set to 96 bits.The main performance metric is the execution time.We consider three system parameters:the number of known tagsk, the number of unknown tagsuand the identification accuracyμ.And we change their values to evaluate their impacts on the total execution time among different protocols.The default valuekis set as 10000, except Fig.3 (b).We adopt the same timing scheme as the specification of the Philips I-Code system [21]:ttag,tlandtsare set to 2.4ms, 0.8ms and 0.4ms, respectively to compute the execution time of different protocols.All the data reported here are averaged over 100 independent trials.
First, extensive simulation experiments are conducted to compare our protocols with BUIP,BUIP-CE and BUIP-CF in terms of the total execution time.The performance of our proposed NUTIP is the best and NUTIP is suitable for both sparse unknown tags environment and dense unknown tags environment.Second,another set of experiments are preformed to validate the identification accuracy of NUTIP.These simulations are conducted and displayed in the following detailed description.
6.1 Total execution time
The total execution time for identifying unknown tags is used as the performance criterion.We mainly compare our proposed protocols, i.e.baseline protocol and NUTIP, with BUIP, BUIP-CE and BUIP-CF.The detail analysis of NUTIP execution time is shown in section V.In this section, the identification accuracyμis predefined to 99%.
In Fig.3 (a), when the number of known tags is 10000 and the number of unknown tags changes with the range of [1000, 10000],obviously each of the five protocols execution time is increased with the increase ofu.The execution time of NUTIP is much lower than the other four protocols.Because each tag selected actual singleton slot can be identified to greatly reduce potential collision slots and not interfere with unknown tag identification.For example, when the number of unknown tags is 4000, the execution time of baseline protocol is 51.10s, which is lower than BUIP and BUIP-CE.And the execution time of NUTIP is just 34.14s, representing reduction of 42.6%,35.5% and 35.4% when compared with the BUIP, BUIP-CE and BUIP-CF respectively.
In Fig.3 (b), when the number of unknown tags is 2000 and the number of known tags changes with the range of [1000, 10000],each of the five protocols execution time is increased withkincreases.Compared with these protocols, NUTIP still perform best in terms of the total execution time.For example,when the number of unknown tags is 6000, the execution time of BUIP, BUIP-CE and BUIPCF is 32.21s, 29.18s and 27,72s respectively.And the execution time of baseline protocol is 28.05s, which outperforms BUIP and BUIPCE by 12.9% and 3.9% respectively.Moreover, the execution time of NUTIP is just 18.58s, indicating reduction of 42.3%, 36.3%and 33.0% when compared with the BUIP,BUIP-CE and BUIP-CF respectively.
Therefore, simulation results of the total execution time demonstrate that the proposed NUTIP outperforms baseline protocol, BUIP,BUIP-CE and BUIP-CF.
1) Sparse unknown tags environment
Ifu/kratio is low, it is called sparse unknown tags environment.As shown in Fig.4(a), when the number of known tags is 10000 and the number of unknown tags changes with the range of [100, 1000], i.e.in a sparse unknown tags environment, we evaluate the total execution time of five protocols in RFID systems.Here, the execution time of baseline protocol, BUIP, BUIP-CE and BUIP-CF are more than 25s.And proposed NUTIP requires execution time not more than 22s.Obviously,the performance of NUTIP is much better than the other four protocols.Baseline protocol,BUIP, BUIP-CE and BUIP-CF need deactivate all known tags.Thus they spend more time in a large-scale RFID system.However, NUTIP only need to label and identify unknown tags.Compared with these four protocols, proposed NUTIP is excellent in terms of the execution time, when the number of unknown tags is lower than the number of known tags.
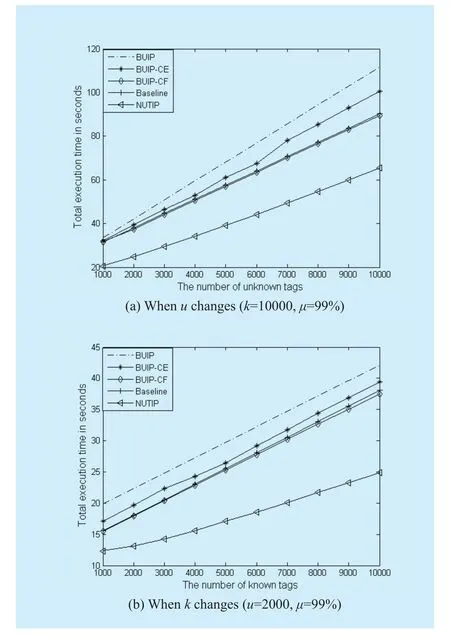
Fig.3 Total execution time of different protocols
2) Dense unknown tags environment

Fig.4 Total execution time under different environments
If u/k ratio is high, it is called dense unknown tags environment.As shown in Fig.4(b), when the number of known tags is 10000 and the number of unknown tags changes with the range of [6000, 15000], i.e.in a dense unknown tags environment, we evaluate the total execution time of five protocols.For example,when the number of unknown tags is 15000,the execution time of BUIP, BUIP-CE and BUIP-CF is 155.20s, 138.01s and 122.13s, respectively.And the execution time of baseline protocol is 122.86s, which is closer to BUIP-CF and lower than BUIP and BUIP-CE.While proposed NUTIP requires only 93.76s, indicating reduction of 39.6%, 32.1% 23.2% and 23.7%when compared with the BUIP, BUIP-CE,BUIP-CF and baseline protocol respectively.The simulation results show that the proposed NUTIP performs much better than BUIP, BUIPCE, BUIP-CF and baseline protocol.In BUIP,known tags deactivation phase is interfered with unknown tags.It prevents reader from deactivating known tags and increases the execution time.However, in NUTIP not only many known tags are deactivated, but also many unknown tags are identified.Meanwhile, many unknown tags are labeled to avoid disturbing identification of the remaining unknown tags.This can reduce more potential collisions in the following round.
We conclude that proposed NUTIP is optimal and applicable for both sparse and dense unknown tags environment.
6.2 Identification accuracy
Another important performance criterion is actual identification accuracy.
When the number of known tags is 10000 and predefined accuracy is 95%, the actual identification accuracy for sparse unknown tags environment and for dense unknown tags environment are shown in Fig.5 (a) and (b),respectively.When the number of unknown tags varies from 100 to 1000, the actual accuracy rate is up to 95.97% as shown in Fig.5(a).The actual accuracy remains stable when the number of unknown tags varies in a small count, e.g.100.As shown in Fig.5 (b), the number of unknown tags varies from 6000 to 15000 with a step of 1000.The actual accuracy rate decreases with the increase of the number of unknown tags.When the number of unknown tags is 15000, the actual accuracy rate of NUTIP is 95.53%.
When the number of known tags is 10000 and predefined accuracy is 99%, the actual identification accuracy for both two environments are shown in Fig.5 (c) and (d), respectively.When the number of unknown tags varies from 100 to 1000, the actual accuracy remains stable at 99.36% as shown in Fig.5(c).From Fig.5 (d) the actual accuracy rate decreases with the number of unknown tags increases.When the number of unknown tags is 15000, the actual accuracy of NUTIP is 99.26% higher than predefined accuracy 99%.
VII.CONCLUSION
RFID tag monitoring problems are important and need to be resolved urgently in many practical applications, such as inventory management.This paper has addressed the significance problem of unknown tag identification in a large-scale RFID system.In particular, our goal is to improve the time efficiency for unknown tag identification.This paper proposes a baseline protocol and a novel unknown tag identification protocol (NUTIP) to identify the unknown tags efficiently.In order to minimize the execution time, the optimal parameter settings of NUTIP: the optimal frame length and the minimum round count are investigated.Furthermore, the simulation experiments show that the proposed NUTIP outperforms BUIP,BUIP-CE, BUIP-CF and proposed baseline protocol.In our future work, we will investigate our protocols within multiple readers.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the reviewers for their detailed reviews and constructive comments, which have helped improve the quality of this paper.This paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61371092), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61540022),and the Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University Project (No.2016091).
[1] Z.Qian and X.Wang, “An Overview of Anti-Collision Protocols for Radio Frequency Identification Devices,” China Communications, vol.11,no.5, pp.44-59, Nov.2014.
[2] Y.Qi, Q.Yao, Y.Chen, and X.Zhong, “Study on RFID Authentication Protocol Theory,” China Communications, vol.8, no.1, pp.65-71, 2011.
[3] Y.Hu, I.C.Chang, and J.Li, “Hybrid blocking algorithm for identification of overlapping staying tags between multiple neighboring readers in RFID systems,” IEEE Sens.Journal, vol.15, no.7, pp.4076-4085, Jul.2015.
[4] W.Zhu, J.Cao, H.C.Chan, X.Liu, and V.Raychoudhury, “Mobile RFID with a High Identification Rate,” IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol.63, no.7, pp.1778-1792, 2014.
[5] C.H.Hsu, H.C.Chao, and J.H.Park, “Threshold jumping and wrap-around scan techniques toward effi cient tag identification in high density RFID systems,” Information Systems Frontiers,vol.13, no.4, pp.471-480, 2011.
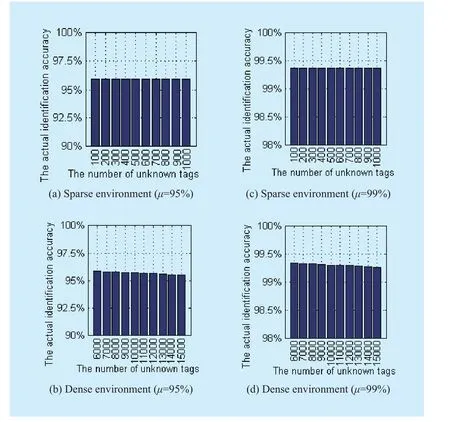
Fig.5 Actual identification accuracy of NUTIP when k=10000
[6] C.Wang, W.Wang, Y.Zhang, J.Qiao, and J Liu,“RFID Tag Management Scheme for Large-Scale Logistics System Based on LTE-A Structure,”China Communications, vol.8, no.8, pp.98-105, 2011.
[7] L.Zhu and T.S.P.Yum, “Optimal Framed Aloha Based Anti-Collision Algorithms For RFID Systems,” IEEE Transactions on Communications,vol.58, no.12, pp.3583-3592, 2010.
[8] A.Zanella, “Adaptive batch resolution algorithm with deferred feedback for wireless systems,”IEEE Trans.Wireless Commun., vol.11, no.10,pp.3528–3539, Oct, 2012.
[9] Y.Jiang and R.Zhang, “An adaptive combination query tree protocol for tag identification in RFID systems,” IEEE Commun.Lett., vol.16, no.8, pp.1192–1195, Aug.2012.
[10] C.Yang, L.Hu, and J.Lai, “Query tree algorithm for RFID tag with binary-coded decimal EPC,”IEEE Commun.Lett., vol.16, no.10, pp.1616–1619, Oct.2012.
[11] X.Liu, Z.Qian, Y.Zhao, and Y.Guo, “An adaptive tag anti-collision protocol in RFID wireless systems,” China Communications, vol.11, no.7, pp.117-127, 2014.
[12] M.V.Bueno-Delgado, R.Ferrero, F.Grandino,P.Pavon-Marino, and M.Rehaudengo, “A geometric distribution reader anti-collision protocol for RFID dense reader environments,”IEEE Trans.Automation Science and Engineering,vol.10, no.2, pp.296–306, Apr.2013.
[13] F.Gandino, R.Ferrero, B.Montruchio, and M.Rebaudengo, “DCNS: an adaptable high throughput RFID reader-to-reader anticollision protocol,” IEEE Trans.Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol.24, no.5, pp.893–905, May.2013.
[14] H.Wu, and Y.Zeng, “Passive RFID tag anticollision algorithm for capture effect,” IEEE Sens.Journal,vol.15, no.1, pp.218–226, Jan.2015.
[15] T.Li, S.Chen, and Y.Ling, “Identifying the missing tags in a large RFID system,” in Proc.ACM Int.Conf.Mobile ad hoc networking and computing, New York.USA, 2010, pp.1–10.
[16] X.Liu, K.Li, G.Min, Y.Shen, A.Liu, and W.Qu,“A multiple hashing approach to complete identification of missing RFID tags,” IEEE Trans.Commun., vol.62, no.3, pp.1046–1057, Mar.2014.
[17] X.Liu, K.Li, G.Min, Y.Shen, A.Liu, and W.Qu,“Completely pinpointing the missing RFID tags in a time-efficient way,” IEEE Trans.Comput.,vol.64, no.1, pp.87–96, Jan.2015.
[18] X.Liu, K.Li, G.Min, K.Lin, B.Xiao, Y.Shen, and W.Qu, “Efficient unknown tag identification protocols in large-scale RFID systems,” IEEE Trans.Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol.25,no.12, pp.3145–3155, Dec.2014.
[19] X.Liu, S.Zhang, K.Bu, B.Xiao, “Complete and fast unknown tag identification in large RFID systems,” in Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Mobile Adhoc and Sensor Systems, IEEE, pp.47-55, 2012.
[20] W.Luo, S.Chen, Y.Qiao, and T.Li, “Missing-tag detection and energy–time tradeoff in largescale RFID systems with unreliable channels,”IEEE/ACM Trans.Netw., vol.22, no.4, pp.1079–1091, Aug.2014.
[21] W.Luo, S.Chen, T.Li, and S.Chen, “Efficient Missing Tag Detection in RFID Systems,” Proc.IEEE INFOCOM, Shanghai.China, Apr.2011, pp.356-360.
[22] S.R.Lee, S.D.Joo, and C.W.Lee, “An enhanced dynamic framed slotted ALOHA algorithm for RFID tag identification,” in Proc.Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking and Services,2005, pp.166-172.
[23] L.Zhang, J, Zhang, and X.Tang, “Assigned tree slotted aloha RFID tag anti-collision protocols,”IEEE Trans.Wireless Commun., vol.12, no.11,pp.5493-5505, Nov.2013.
[24] Y.Wang, Y.Liu, H.Leung, and R.Chen, “A segment collision inversion protocol for RFID tag reading,” IEEE Commun.Lett., vol.17, no.10, pp.2008-2011, Oct.2013.
[25] Y.Wang, Y.Liu, H.Leung, and R.Chen, “A multibit identification protocol for RFID tag reading,”IEEE Sens.Journal, vol.13, no.10, pp.3527-3536, Oct.2013.
- China Communications的其它文章
- A Non-Cooperative Differential Game-Based Security Model in Fog Computing
- Dynamic Weapon Target Assignment Based on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Entropy of Discrete Particle Swarm
- Directional Routing Algorithm for Deep Space Optical Network
- Offline Urdu Nastaleeq Optical Character Recognition Based on Stacked Denoising Autoencoder
- Reputation-Based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm for Mobile Cognitive Radio Networks
- Toward a Scalable SDN Control Mechanism via Switch Migration

