Effects of postmastectomy radiotherapy on prognosis in different tumor stages of breast cancer patients with positive axillary lymph nodes
Miao-Miao Jia*, Zhi-Jie Liang*, Qin Chen, Ying Zheng, Ling-Mei Li, Xu-Chen Cao
1The First Department of Breast Cancer, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Key Laboratory of Breast Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin Medical University, Ministry of Education, Tianjin 300060, China;
2Department of Pathology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center of Cancer, Tianjin 300060, China
Effects of postmastectomy radiotherapy on prognosis in different tumor stages of breast cancer patients with positive axillary lymph nodes
Miao-Miao Jia1*, Zhi-Jie Liang1*, Qin Chen1, Ying Zheng1, Ling-Mei Li2, Xu-Chen Cao1
1The First Department of Breast Cancer, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Key Laboratory of Breast Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin Medical University, Ministry of Education, Tianjin 300060, China;
2Department of Pathology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center of Cancer, Tianjin 300060, China
Objective: To explore the effects of postmastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT) on the locoregional failure-free survival
(LRFFS) and overall survival (OS) of breast cancer patients under di ff erent tumor stages and with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes (ALNs).
Methods:We conducted a retrospective review of 527 patients with one to three positive lymph nodes who underwent modi fi ed radical or partial mastectomy and axillary dissection from January 2000 to December 2002.e patients were divided into the T1-T2N1and T3-T4N1groups.e e ff ects of PMRT on the LRFFS and OS of these two patient groups were analyzed using SPSS 19.0, Pearson’s χ2-test, Kaplan-Meier method, and Cox proportional hazard model.
Results:For T1-T2N1patients, no statistical signi fi cance was observed in the e ff ects of PMRT on LRFFS [hazard ratio (HR)=0.726; 95% con fi dence interval (CI): 0.233-2.265; P=0.582] and OS (HR=0.914; 95% CI: 0.478-1.745; P=0.784) of the general patients. Extracapsular extension (ECE) and high histological grade were the risk factors for LRFFS and OS with statistical significance in multivariate analysis. Stratification analysis showed that PMRT statistically improved the clinical outcomes in high-risk patients [ECE (+), LRFFS: P=0.026, OS: P=0.007; histological grade III, LRFFS: P<0.001, OS: P=0.007] but not in low-risk patients [ECE (–), LRFFS: P=0.987, OS: P=0.502; histological grade I-II, LRFFS: P=0.816, OS: P=0.296]. For T3-T4N1patients, PMRT e ff ectively improved the local control (HR=0.089; 95% CI: 0.210-0.378; P=0.001) of the general patients, whereas no statistical e ff ect was observed on OS (HR=1.251; 95% CI: 0.597-2.622; P=0.552). Absence of estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors (ER/PR) (–) was an independent risk factor. Further strati fi cation analysis indicated a statistical di ff erence in LRFFS and OS between the high-risk patients with ER/PR (– ) receiving PMRT and not receiving PMRT [ER/PR (–), LRFFS: P=0.046, OS: P=0.039]. However, PMRT had a bene fi cial e ff ect on the reduction of locoregional recurrence (LRR) but not in total mortality [ER/PR (+), LRFFS: P<0.001, OS: P= 0.695] in T3-T4N1patients with ER/PR (+) who received endocrine therapy.
Conclusion:PMRT could reduce ECE (+), histological grade III-related LRR, and total mortality of T1-T2N1patients. T3-T4N1patients with ER/PR (–) could bene fi t from PMRT by improving LRFFS and OS. However, PMRT could only reduce LRR but failed to improve OS for T3-T4N1patients with ER/PR (+) who received endocrine therapy.
Breast cancer; positive lymph nodes; postmastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT); locoregional failure-free survival (LRFFS); overall survival (OS)
Introduction
Postmastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT), as a treatment modality for postoperative patients with breast cancer, is primarily used to reduce locoregional recurrence (LRR) and improve survival, although modestly, in patients with high-risk factors1-4.
According to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines5, PMRT should be considered for patients with T3-T4breast cancer with more than three positive lymph nodes or with T1-T2breast cancer with one to three positive lymph nodes. Given that several clinical and pathological factors may affect prognosis of patients with intermediate-risk breast cancer, using T/N classi fi cation only is an imprecise method in determining whether a patient should be considered for PMRT6-9. Several researchers have aempted to identify the risk factors for LRR and mortality aer mastectomy to select patients who are most likely to bene fi t from PMRT1-4,6-18. However, these patient subgroups have not been clearly de fi ned, and the contribution of PMRT to locoregional control and survival remains unclear.
The function of PMRT is not clearly defined in breast cancer patients with one to three positive lymph nodes. In this retrospective study, we identified prognostic factors for LRR and mortality of T1-T2N1and T3-T4N1breast cancer patients. In addition, we compared the locoregional failure-free survival (LRFFS) and overall survival (OS) of the high-risk patients with and without PMRT to define a subgroup of patients who might bene fi t from PMRT.
Materials and methods
Clinical data
From January 2000 to December 2002, breast cancer patients with pathologically proven one to three positive axillary lymph nodes (ALNs) were treated with modified radical mastectomy plus axillary dissection at the Tianjin Cancer Hospital. Of the 527 patients with one to three positive lymph nodes, the median age was 48.73 years (range, 26 to 79 years).e median number of involved ALNs was 1.93 (range, 1 to 3). A total of 432 patients with T1-T2disease and 95 patients with T3-T4disease were included in the study, 75.7% (327/432) and 70.5% (67/95) of whom received PMRT, respectively.e study was approved by the institutional ethics commiee.
Systemic treatment
All patients received TEC-based (docetaxel, epirubicin, cyclophosphamide) or docetaxel-containing regimens as adjuvant chemotherapy. Adjuvant endocrine therapy was performed for 5 years in all patients who had positive hormone receptors. Among 527 patients, 74.8% (394/527) underwent PMRT, which was delivered to the breast, chest wall, internal mammary, supraclavicular, and axillary fossa drawing region by medial and lateral-tangential fields with external-beam irradiation (4 or 6 MV photons/60 Co). The standard dose to the entire chest wall was 50 Gy (range, 46 to 54 Gy), 1.8 to 2 Gy/d, and five times weekly. The supraclavicular region and the full axilla were treated with a dose of 50 Gy using an anterior fi eld. An additional external boost with electrons (2 Gy/10 Gy to 14 Gy) was performed in patients who had locally advanced disease.
Follow-up
The median time of follow-up was 127.82 months (range, 15 to 155 months). All intervals were calculated from the date of completion of surgery, and the endpoint was de fi ned as the last follow-up or death. Evaluation of tumor control was performed for patients in 4-month intervals for the first 2 years and in 6-month intervals for the next 3 years. Subsequently, these patients were observed on a yearly basis. Clinical examinations, which included blood sampling, routine chest radiograph, mammograph, and ultrasound, were performed as evaluation during the follow-up. Further evaluations were conducted only if the clinical findings indicated a disease progression. Survival period was calculated from the date of surgical resection to the date of last follow-up.e endpoints of interest included LRFFS and OS.
Recurrence
LRR was identified as local recurrence (chest wall alone) or regional recurrence (axillary, supraclavicular, and internal mammary lymph nodes alone). Any recurrence outside these areas was de fi ned as distant metastasis (DM).
Statistical analysis
All analyses were performed using SPSS 19.0. Pearson’s χ2-test was used to compare the proportions of categorical covariates among the groups of patients with different T stages. OS and LRFFS were analyzed with Kaplan-Meier method. Univariate and multivariate hazard ratios (HR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using Cox’s proportional hazard model. A probability level of ≤0.05 was considered statistically signi fi cant.
Results
Basic information
With a median follow up of 127.82 months (range, 15 to 155 months), 3.7% (16/432) and 14.7% (14/95) of patients developed LRR in T1-T2N1and T3-T4N1patient groups, respectively. OS was 93.5% (404/432) and 45.3% (43/95) in the T1-T2N1and T3-T4N1groups, respectively. The Kaplan-Meier curves of LRFFS and OS in different T stages confirmed the statistically significant difference in LRFFS and OS between the T1-T2N1and T3-T4N1patients (Figure 1A,B).e distribution patterns of clinico-pathologic characteristics for the PMRT and non-PMRT groups are presented in Table 1. A statistically significant difference was observed between the two groups regarding the status of extracapsular extension (ECE) and the number of involved ALNs (P<0.05).
Univariate and multivariate analyses
The factors affecting OS varied between the T1-T2N1and T3-T4N1patients. ECE (HR=1.086; 95% CI: 1.012-1.164; P=0.022) and histological grade III (HR=3.365; 95% CI: 1.332-8.602; P=0.010) were the risk factors in T1-T2patients. However, the risk factor in T3-T4patients was ER/PR (–) tumors. ER/PR (+) tumors (HR=0.307; 95% CI: 0.154-0.610; P=0.001) had a signi fi cant e ff ect in improving OS (Tables 2 and 3).
E ff ects of PMRT on LRFFS and OS of T1-T2N1patients based on ECE status and histological grade
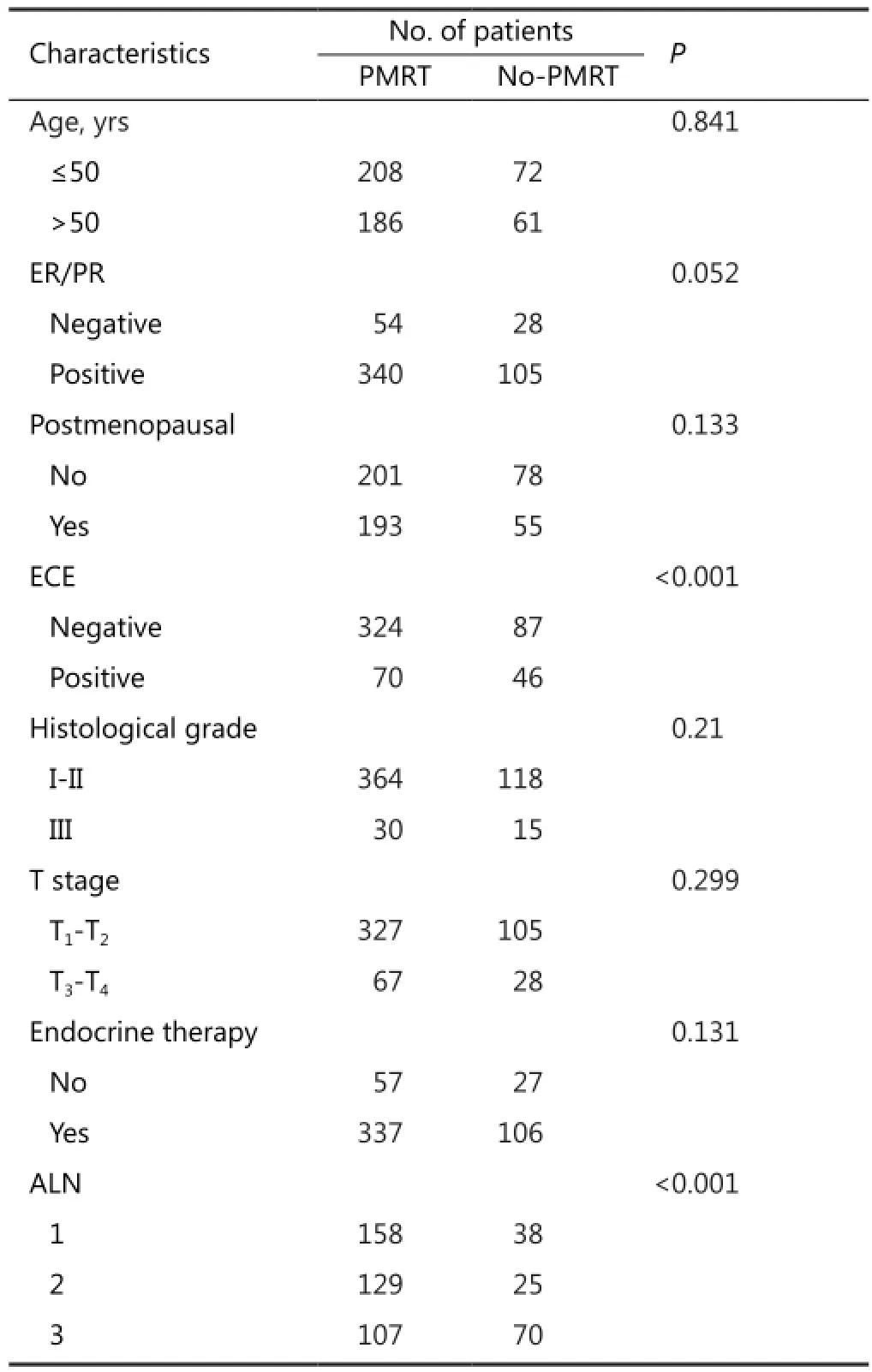
Table 1 Clinicopathologic features of patients in the study
E ff ects of PMRT on LRFFS and OS of T3-T4N1
patients based on hormone receptor status
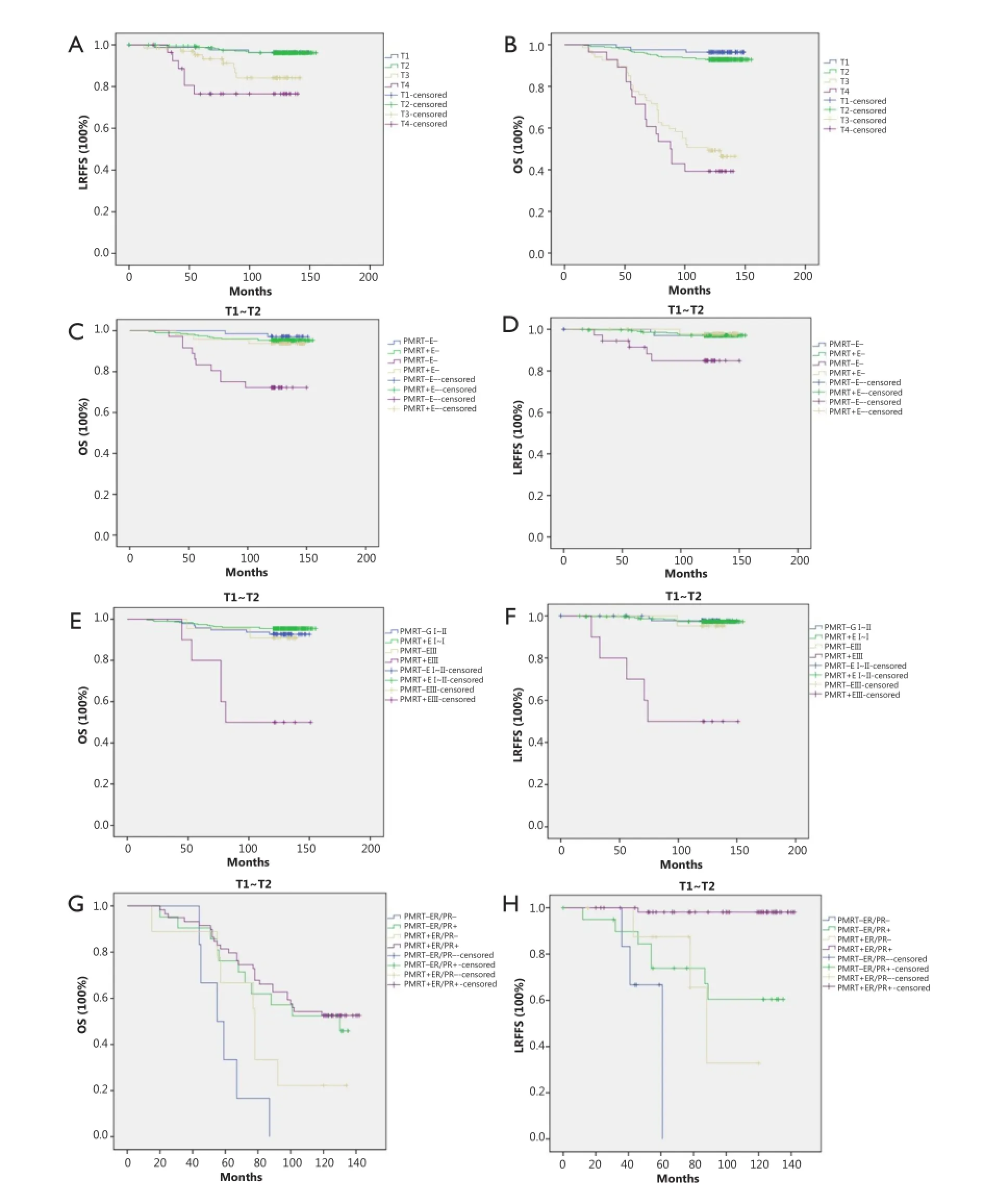
Figure 1 (A) Kaplan-Meier curve of LRFFS in different T stages; (B) Kaplan-Meier curve of OS in different T stages; (C) Kaplan-Meier curve of OS in patients with different ECE in T1-T2N1patients. PMRT+E— vs. PMRT—E—: P=0.502; PMRT+E+ vs. PMRT—E+: P=0.007 (PMRT—, non-PMRT; PMRT+, PMRT; E—, ECE—; E+, ECE+); (D) Kaplan-Meier curve of LRFFS in patients with different ECE in T1-T2N1patients. PMRT+E— vs. PMRT—E—: P=0.987; PMRT+E+ vs. PMRT-E+: P=0.026; (E) Kaplan-Meier curve of OS in patients with different histological grades in T1-T2N1patients. PMRT+ GI-II vs. PMRT— GI-II: P=0.296; PMRT— GIII vs. PMRT+ GIII: P=0.007. (GI-II, grade I-II; GIII, grade III); (F) Kaplan-Meier curve of LRFFS in patients with different histological grades in T1-T2N1patients. PMRT+ GI-II vs. PMRT— GI-II: P=0.816; PMRT— GIII vs. PMRT+ GIII: P<0.001; (G) Kaplan-Meier curve of OS in patients with different hormone receptor status in T3-T4N1patients. PMRT+ER/PR— vs. PMRT—ER/PR—: P=0.039; PMRT+ER/PR+ vs. PMRT—ER/PR+: P=0.695; (H) Kaplan-Meier curve of LRFFS in patients with different hormone receptor status in T3-T4N1patients. PMRT+ER/PR— vs. PMRT—ER/PR—: P=0.046; PMRT+ER/PR+ vs. PMRT—ER/ PR+: P<0.001.
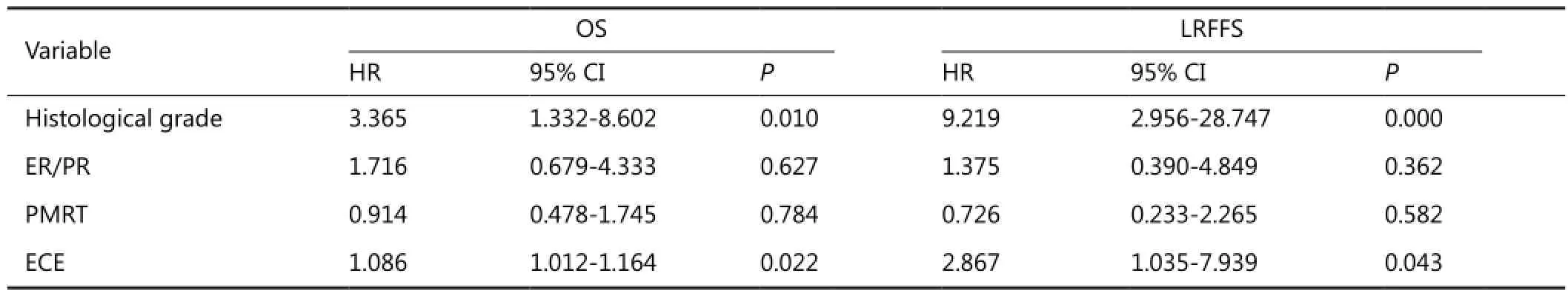
Table 2 Multivariate analysis with Cox proportional hazards model for OS and LRFFS of T1-T2N1patients
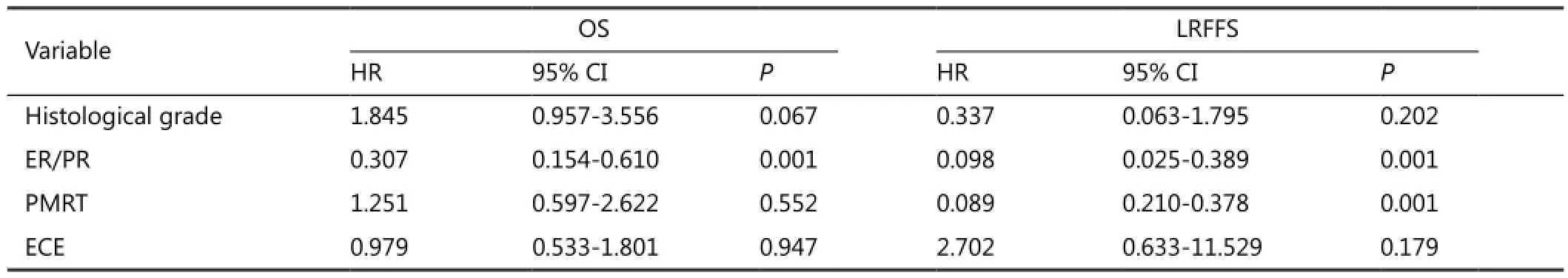
Table 3 Multivariate analysis with cox proportional hazards model for OS and LRFFS of T3-T4N1patients
With regard to LRFFS and OS of T3-T4N1patients, ER/PR (+) was a statistically significant factor on multivariate analysis. PMRT was beneficial on LRFFS of all patients regardless of the hormone receptor status. The effects of PMRT on LRFFS and OS of the patients with di ff erent ER/PR statuses were examined. All T3-T4N1patients were first stratified into subgroups of ER/PR (+) and ER/PR (–). We observed that PMRT was useful for the reduction of LRR (P<0.001) of T3-T4N1patients with ER/ PR (+) but failed to improve OS (P=0.695). However, patients with ER/PR (–) could bene fi t from PMRT on improving LRFFS (P=0.046) and OS (P=0.039) (Figure 1G,H).
Discussion
The significance of PMRT to reduce LRR and total mortality in the subgroup of patients with one to three positive lymph nodes remains unclear7,11-16. Currently, the indication of PMRT is mainly determined by the number of positive lymph nodes and the T stage. However, some studies10,16,19,20have reported the comparatively more effective prognostic predictors other than T and N stage that guide the PMRT treatment.ese predictors include age, hormone receptor status, ECE status, histological grade, lymphovascular invasion, menstrual status, and lymph node ratio.
Huang et al.12highly recommends the PMRT to breast cancer patients with T1-T2and one to three positive lymph nodes for reducing LRR and improving disease-free survival. Tendulkar et al.16suggested that PMRT provides excellent locoregional control for patients with one to three positive lymph nodes, regardless of PMRT patients in more advanced stage (about 40% had stage T3-T4disease) and a greater number of risk factors, such as pathological grade III and ECE. However, Geng et al.17suggested that PMRT does not signi fi cantly improve the LRFFS for patients with one to three positive axillary nodes, regardless of the ECE status. Kong et al.18found that PMRT does not improve LRR, DM-free survival, or OS in T1-T2N1breast cancer patients. However, PMRT might be beneficial in a subgroup of patients with histological grade III disease, ECE, or triplenegative subtype. PMRT is important in identifying the risk factors associated with increased risk of LRR and total mortality in patients with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes to establish its indications.
According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology21, insufficient evidence exists to formulate recommendations or suggestions for the routine use of PMRT in patients with T1-T2breast cancer and one to three positive lymph nodes. However, PMRT has been considered for T1-T2N1patients based on the NCCN guidelines5. Our retrospective study provided some new information with regard to patients with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes, who may bene fi t from PMRT.
Based on our study, di ff erent e ff ects of PMRT on improving LRFFS or OS were found between the T1-T2N1and T3-T4N1patients. Previous studies have reported15,16that the LRFFS and OS of T1-T2N1breast cancer patients treated with radicalmastectomy are dependent on several prognostic factors other than T and N stage. Our analysis revealed that ECE (+) and histological grade III were the high-risk factors for LRR and mortality of T1-T2N1patients. The stratification analysis results revealed that PMRT had a positive effect in reducing ECE (+) or histological grade III-related LRR and mortality. However, the remaining patients with ECE (–) or histological grade I-II experienced extremely low LRR and mortality rates after mastectomy treatment, and the benefit from PMRT was minimal. Although PMRT had no protective function in improving LRFFS and OS of the general T1-T2N1patients, high-risk patients with ECE (+) and histological grade III could bene fi t from PMRT.
Contrary to T1-T2N1patients, the general T3-T4N1patients could benefit from PMRT in terms of LRFFS but not in OS. Stage T3-T4is a high-risk factor in breast cancer patients, who are more likely to develop DM than patients with early T stage disease. Breast cancer tends to be a systemic disease with potential sub-clinical DM in Fisher’s theory17. Our analysis revealed that PMRT could improve the LRR control in T3-T4patients, but no statistically significant effect on OS was observed among these patients. In addition, patients with ER/PR (+) benefited from endocrine therapy. All patients with ER/PR (+) who were included in our study received endocrine therapy. Endocrine therapy was a protective factor to improve LRFFS and OS of T3-T4N1patients according to the multivariate analysis results. Thus, the risks of LRR and mortality were positively associated with ER/PR (–). NCCN guidelines5suggested that T3-T4patients should receive PMRT. Rangan et al.22reported that LRR rate of patients with one to three positive lymph nodes who received chemotherapy and endocrine therapy is approximately 10% under the condition of non-PMRT. To further determine whether PMRT is essential for patients receiving endocrine therapy and whether ER/PR (–) patients could bene fi t from it, we analyzed its e ff ects on LRFFS and OS of T3-T4N1patients with ER/PR (–) and who received endocrine therapy, respectively. The results of stratification analysis indicated that PMRT caused a statistically significant improvement in LRFFS and OS of T3-T4N1patients with ER/ PR (–). For T3-T4N1patients who received endocrine therapy, PMRT could improve local control but no statistical change in OS was observed compared with non-PMRT.
PMRT alleviates local symptoms but often results in signi fi cant pathological damage to the heart, lungs, and skin. A meta-analysis by Taghian et al.19revealed a signi fi cant increase in non-breast cancer mortality in irradiated women.e mortality is mainly because of heart disease and lung cancer. Given the complications of PMRT, its necessity for T3-T4N1patients receiving endocrine therapy should be reconsidered because no statistical effect on OS was observed in this study despite the improvement in local control.
Conclusion
According to our results, PMRT is highly recommended to improve LRFFS and OS for T1-T2N1patients with ECE (+) or pathological grade III as well as for T3-T4N1patients with ER/ PR (–). However, PMRT has to be reconsidered for T3-T4N1patients with ER/PR (+) who bene fi ted from endocrine therapy on improving LRFFS and OS. Other prognostic factors should be considered, and the decision has to be made individually on the basis of endocrine therapy and request of the patient because PMRT could control LRR but not total mortality.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.11JCZDJC28000).
Con fl ict of interest statement
No potential con fl icts of interest are disclosed.
1. Overgaard M, Hansen PS, Overgaard J, Rose C, Andersson M, Bach F, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk premenopausal women with breast cancer who receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group 82b Trial. N Engl J Med 1997;337:949-955.
2. Overgaard M, Jensen MB, Overgaard J, Hansen PS, Rose C, Andersson M, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk postmenopausal breast-cancer patients given adjuvant tamoxifen: Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group DBCG 82c randomised trial. Lancet 1999;353:1641-1648.
4. Whelan TJ, Julian J, Wright J, Jadad AR, Levine ML. Does locoregional radiation therapy improve survival in breast cancer? A meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 2000;18:1220-1229.
5. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines?) (National Comprehensive Cancer Network ed., vol. 2012, v1. 2012 edition.Fort Washington, PA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2012. Breast cancer. Available online: hp://www.nccn.org/ professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf
8. Overgaard M, Nielsen HM, Overgaard J. Is the bene fi t of postmastectomy irradiation limited to patients with four or more positive nodes, as recommended in international consensus reports? A subgroup analysis of the DBCG 82 b&c randomized trials. Radiother Oncol 2007;82:247-253.
9. Cheng SH, Horng CF, Clarke JL, Tsou MH, Tsai SY, Chen CM, et al. Prognostic index score and clinical prediction model of local regional recurrence aer mastectomy in breast cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;64:1401-1409.
10. Neri A, Marrelli D, Roviello F, De Stefano A, Guarnieri A, Pallucca E, et al. Prognostic value of extracapsular extension of axillary lymph node metastases in T1 to T3 breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2005;12:246-253.
11. Hamamoto Y, Ohsumi S, Aogi K, Shinohara S, Nakajima N, Kataoka M, et al. Are there high-risk subgroups for isolated locoregional failure in patients who had T1/2 breast cancer with one to three positive lymph nodes and received mastectomy without radiotherapy? Breast Cancer 2014;21:177-182.
12. Huang CJ, Hou MF, Chuang HY, Lian SL, Huang MY, Chen FM, et al. Comparison of clinical outcome of breast cancer patients with T1-2 tumor and one to three positive nodes with or without postmastectomy radiation therapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2012;42:711-720.
13. Wu SG, He ZY, Li FY, Wang JJ, Guo J, Lin Q, et al.e clinical value of adjuvant radiotherapy in patients with early stage breast cancer with 1 to 3 positive lymph nodes aer mastectomy. Chin J Cancer 2010;29:668-676.
14. Yang PS, Chen CM, Liu MC, Jian JM, Horng CF, Liu MJ, et al. Radiotherapy can decrease locoregional recurrence and increase survival in mastectomy patients with T1 to T2 breast cancer and one to three positive nodes with negative estrogen receptor and positive lymphovascular invasion status. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2010;77:516-522.
15. Truong PT, Berthelet E, Lee J, Kader HA, Olivoo IA.e prognostic signi fi cance of the percentage of positive/dissected axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer recurrence and survival in patients with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes. Cancer 2005;103:2006-2014.
16. Tendulkar RD, Rehman S, Shukla ME, Reddy CA, Moore H, Budd GT, et al. Impact of postmastectomy radiation on locoregional recurrence in breast cancer patients with 1-3 positive lymph nodes treated with modern systemic therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012;83:e577-581.
17. Geng W, Zhang B, Li D, Liang X, Cao X.e e ff ects of ECE on the bene fi ts of PMRT for breast cancer patients with positive axillary nodes. J Radiat Res 2013;54:712-718.
18. Kong M, Hong SE. Which patients might bene fi t from postmastectomy radiotherapy in breast cancer patients with T1-2 tumor and 1-3 axillary lymph nodes metastasis? Cancer Res Treat 2013;45:103-111.
19. Taghian A, Jeong JH, Mamounas E, Anderson S, Bryant J, Deutsch M, et al. Paerns of locoregional failure in patients with operable breast cancer treated by mastectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy with or without tamoxifen and without radiotherapy: results from fi ve National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project randomized clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:4247-4254.
20. Nielsen HM, Overgaard M, Grau C, Jensen AR, Overgaard J. Locoregional recurrence aer mastectomy in high-risk breast cancer--risk and prognosis. An analysis of patients from the DBCG 82 b&c randomization trials. Radiother Oncol 2006;79:147-155.
21. Recht A, Edge SB, Solin LJ, Robinson DS, Estabrook A, Fine RE, et al. Postmastectomy radiotherapy: clinical practice guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol 2001;19:1539-1569.
22. Rangan AM, Ahern V, Yip D, Boyages J. Local recurrence aer mastectomy and adjuvant CMF: implications for adjuvant radiation therapy. Aust N Z J Surg 2000;70:649-655.
Cite this article as:Jia MM, Liang ZJ, Chen Q, Zhen Y, Li LM, Cao XC. Effects of postmastectomy radiotherapy on prognosis in different tumor stages of breast cancer patients with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes. Cancer Biol Med 2014;11:123-129. doi: 10.7497/ j.issn.2095-3941.2014.02.007
*These authors equally contributed to this work.
Xu-Chen Cao
E-mail: CXC@medmail.com.cn
Received December 25, 2013; accepted March 23, 2014. Available at www.cancerbiomed.org
Copyright ? 2014 by Cancer Biology & Medicine
 Cancer Biology & Medicine2014年2期
Cancer Biology & Medicine2014年2期
- Cancer Biology & Medicine的其它文章
- Polymeric nanocomposites loaded with fluoridated hydroxyapatite Ln3+ (Ln = Eu or Tb)/iron oxide for magnetic targeted cellular imaging
- An unusual case of aggressive systemic mastocytosis mimicking hepatic cirrhosis
- Spindle cell carcinoma of the breast as complex cystic lesion: a case report
- Clinico-pathological signi fi cance of extra-nodal spread in special types of breast cancer
- Incidence and mortality of female breast cancer in the Asia-Paci fi c region
- Research progress on the anticarcinogenic actions and mechanisms of ellagic acid
