Polymeric nanocomposites loaded with fluoridated hydroxyapatite Ln3+ (Ln = Eu or Tb)/iron oxide for magnetic targeted cellular imaging
Jie Pan, Wei-Jiao Liu, Chao Hua, Li-Li Wang, Dong Wan, Jun-Bo Gong
1State Key Laboratory of Hollow Fiber Membrane Materials and Processes, School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering,Tianjin Polytechnic University, Tianjin 300387, China; 2Key Laboratory of Green Process and Engineering, Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100190, China; 3Department of Chemical Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Introduction
With the advances in molecular and cellular techniques, research about the diagnosis of disease has been directed toward the underlying molecular and genomic aberrations, rather than toward clinical signs and symptoms alone.Molecular imaging is a developing research discipline aimed at visually characterizing normal and pathologic processes in living organisms at the cellular and molecular levels1-4.Modalities used in molecular imaging includes positron emission tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, single-photon emission computed tomography, optical imaging, and ultrasound5.These modalities differ in terms of spatial resolution, temporal resolution,sensitivity in probe detection, depth of signal penetration,availability of biocompatible molecular imaging agents, and cost.Optical imaging, an emerging molecular imaging mode,is based on the detection of photons after their interaction with the tissue.This technique has high sensitivity and spatial resolution, features fast and easy to perform procedures, and requires inexpensive and available optical reporters and dyes for simultaneous imaging of multiple processes3.As an optical approach, fluorescence imaging is used for molecular imaging.
As hydroxyapatite (HAP) is the main inorganic component of bones and teeth of humans and animals, it exhibits good biocompatibility in biological applications6-8.HAP doped with rare earth elements has been used as luminescent materials for biological imaging8-17.Hui et al.16used a hydrothermal approach to dope rare earth elements with fluorine ions to fabricate fluoridated HAP nanocrystals, which demonstrated excellent luminescent properties for biological imaging.The quenching of the excited state of rare earth elements is caused by ?OH ions in the lattice, which were replaced with F?ions to prepare materials with low vibrational energies for rare earth fluorescent transition8.Hui et al.16described doped HAP nanoparticles (NPs) as fluorescing probes with excellent biocompatibility, good biodegradability, and prominent luminescent features.Compared to traditional fluorescent dyes, doped HAP NPs exhibit high fluorescence intensity,enhanced photostability, improved stability, and high resistance to photobleaching.Quantum dots (QDs) have been widely used as luminescence probes.QDs have various advantages,including tunable emission from visible to infrared wavelengths by changing their size and composition, broad excitation spectra because of high absorption coefficients, high quantum yield of fluorescence, strong brightness, photostability, and high resistance to photobleaching18-20.Although QDs are suitable for biological imaging, they exhibit toxicity caused by the oxidative degradation of their heavy metal contents, thereby limiting their applications in biological fields21-23.The toxicity of QDs can only be partly resolved through surface modification or encapsulation in biodegradable NPs24-29.As an alternative to QDs, fluoridated HAP:Ln3+NPs present lower toxicity; these NPs are also inexpensive and feature anti-corrosion properties.Therefore,fluoridated HAP:Ln3+NPs can be potentially used for molecular imaging.
Targeted molecular imaging of cancer is generally achieved through passive and active targeting30-33.In passive targeting,probes accumulate at tumor sites through an enhanced permeability and retention effect, which can be attributed to two factors34-36.First, angiogenic tumors produce vascular endothelial growth factor, which hyperpermeabilizes tumorassociated neovasculature and results in the leakage of circulating probes.Second, tumors lack an effective lymphatic drainage system, which causes subsequent probe accumulation33.In active targeting, targeting agents, such as ligands, attach on the surface of small particles through various conjugation mechanisms2,33,37,38.The targeted probes can recognize and bind to specific ligands unique to cancer cells; subsequently, the probes largely accumulate in cancer cells while minimizing distribution in noncancerous cells adjacent to the targeted tissue.Although active targeting is superior in molecular imaging, it is limited for clinical applications because of patient-to-patient variation in receptor expression levels and non-specific expression of receptors in normal tissues.Unlike active targeting, magnetic targeting utilizes magnetic field to accumulate magnetic probes in the cellular area where the magnet is placed39-47.Magnetic targeting is a general targeting approach because it is based on physical interactions and not limited by specific receptor expression.Gu et al.46fabricated magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles(M-MSNs) and found that the internalization of M-MSNs by A549 cancer cells could be accelerated and enhanced under magnetic field; the internalization is mainly through an energydependent pathway, namely, clathrin-induced endocytosis,rather than passive diffusion or magnetic pull-down process.
In this study, a facile method was used to fabricate novel nanocomposites for magnetic targeted cellular imaging of cancer.Fluoridated Ln3+-doped HAP (Ln3+-HAP) NPs and iron oxides (IOs) can be encapsulated with biocompatible polymers[such as poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), PLGA] via a modified solvent exaction/evaporation technique to prepare polymeric nanocomposites with fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/iron oxide.The fabricated composite can be used to improve specificity and sensitivity of cellular imaging through magnetic targeting.In this study, an external magnetic field was used for targeting to allow the nanocomposites to be as close as possible to A549 cancer cells.Most nanocomposites around A549 cells can be internalized by the cells via an energy-dependent pathway.This study utilizes magnetic field to achieve targeted cellular imaging of cancer with fluoridated Ln3+-HAP NPs for cancer diagnosis.The scheme of synthesis and applications of fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites is presented in Figure 1.
Materials and methods
Materials
Ca(NO3)2·4H2O, Na3PO4·12H2O, NaF, NaOH, octadecylamine,oleic acid, ethanol, cyclohexane, FeSO4·(NH4)2SO4·6H2O,dichloromethane (DCM), and PVA (MW: 30,000-70,000) were obtained from Beijing Chemical Reagents Company (China).Eu(NO3)3·6H2O, Tb(NO3)3·6H2O, and PLGA (L:G molar ratio:75:25, MW: 100,000-130,000) were purchased from Sigma(St.Louis, MO, USA).Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium(DMEM), antibiotics (penicillin-streptomycin solution), Triton X-100, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT), diethyl ether, chloroform, and cholesterol were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St.Louis, MO, USA).Fetal bovine serum (FBS) was purchased from Gibco (Life Technologies, AG, Switzerland).Millipore water was produced using the Milli-Q Plus System (Millipore Corporation, Bedford,USA).
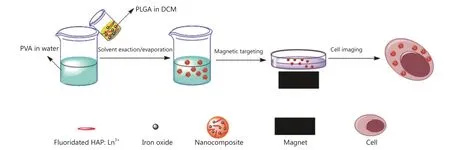
Figure 1 Scheme of the synthesis and applications of the fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites.
Preparation of fluoridated Ln3+-HAP (Ln = Eu or Tb) NPs
Fluoridated Ln3+-HAP NPs were prepared using the protocol described in the literature8.Briefly, octadecylamine (0.5 g)were dissolved in oleic acid, (4 mL) in a Teflon-lined autoclave(50 mL).The solution was mixed with ethanol (16 mL) and an aqueous solution of Ca(NO3)2(0.28 M, 7 mL) under agitation.The solution was then added with aqueous solutions of Eu(NO3)3or Tb(NO3)3(0.28 M, 0.7 mL), NaF (0.28 M,1.4 mL), and Na3PO4(0.16 M, 7 mL).The mixture was agitated for 5 min, sealed, and hydrothermally treated at 180 ℃ for 12 h.The obtained fluoridated Ln3+-HAP NPs were collected through centrifugation and washed several times with cyclohexane and ethanol.
Preparation of IOs
IOs were fabricated according to the method reported in the literature48.Briefly, 0.6275 g of FeSO4·(NH4)2SO4·6H2O was dissolved in 16 mL of water.The solution was mixed with 0.8 g of NaOH, 8 mL of oleic acid and 8 mL of ethanol under stirring at room temperature.The solution was then added with an aqueous solution of FeSO4·(NH4)2SO4·6H2O.The mixed reactants were then transferred to a 50 mL sealed autoclave and heated at 180 ℃for 10 h.The products were collected through centrifugation and washed at least 3 times with cyclohexane and ethanol.Finally,IOs were obtained through drying and stored for further use.
Preparation of fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites
Fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites were prepared through a modified solvent exaction/evaporation technique.Briefly, 30 mg of the mixture of fluoridated Ln3+-HAP NPs and IOs (2:1, 1:1, and 1:2; mass ratio) were dissolved in 4 mL of DCM containing 50 mg of PLGA.The solution was added to 60 mL of aqueous solution with 300 mg of PVA.The mixture was then sonicated for 100 s at 75 W.The emulsion was agitated overnight to evaporate DCM.The formed suspension was centrifuged with deionized water.Finally, fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites were obtained through centrifugation.
Characterization
The morphologies of the nanocomposites were observed with a HITACHI H-7650B transmission electron microscope (TEM)at 100 kV and a FEI Tecnai G2 F20 S-Twin high-resolution TEM at 200 kV.The nanocomposite suspension was dropped on the surface of copper grid with carbon film and dried at room temperature.The fluorescence spectra of the nanocomposites were recorded using a HITACHI F-4500 fluorescence spectrophotometer with an excitation wavelength of 405 and 488 nm for the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites and fluoridated Tb3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites, respectively.The magnetic properties of the fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites were determined with a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) at room temperature.Dried nanocomposites of known mass were placed in non-magnetic aluminum sheet and then subjected to varied magnetic fields that ranged from ?2×104to 2×104Oe.
Cell experiments
Cell culture
Human cervical HeLa cell line A549 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection.All cell culture related reagents were purchased from Invitrogen.The cells were grown in DMEM with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin.The fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites containing a 1:1 mass ratio of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP and IOs were used for cell experiments.
Cytotoxicity of nanocomposites
The viability of A549 cells incubated with the nanocomposites was evaluated with MTT assay.Briefly, the cells were seeded in 96-well microplates at a density of 5×104cells/mL.After 24 h of cell attachment, the cells were incubated with 10, 20, 40, 80, 150, and 300 μg/mL nanocomposites for 8 and 24 h.The nanocomposites were then removed, and the cells were washed with PBS three times.The wells were washed twice with PBS and added with 10 μL of MTT supplemented with a culture medium.After 4 h of incubation, the culture medium was removed and the precipitate was dissolved in isopropanol.The absorbance of the wells was determined with a microplate reader (VictorШ, Perkin-Elmer)with a wavelength of 570 nm and reference wavelength of 620 nm.Cell viability was calculated with the following equation:
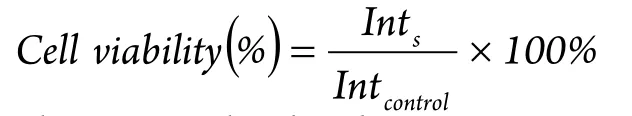
where Intsis the absorbance intensity of the cells incubated with the nanocomposites suspension and Intcontrolis the absorbance intensity of the cells incubated with the incubation medium only(positive control).
Magnetic targeted cellular imaging
A549 cells were maintained at 37 ℃ in a culture medium under a humidified condition of 5% CO2.On the day prior to treatment,the cells were seeded in a glass bottom dish with a density of 50,000 cells/mL.For magnetic targeted cellular imaging, a cubic permanent magnet (1.3T) was placed under the edge of the dish and the cells were incubated with 250 μg/mL nanocomposites for 2 h at 37 ℃.Control groups were incubated with the nanocomposites at the same concentration for 2 h without the magnetic field.The cells were then washed with PBS, and the nuclei were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride for 30 min.The stained cells were washed twice with PBS, and cell images were obtained using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM, Zeiss 710 3-channel; Zeiss,Germany) with an excitation wavelength of 405 nm.
Results and discussion
Charactarization of fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites
Surface morphology
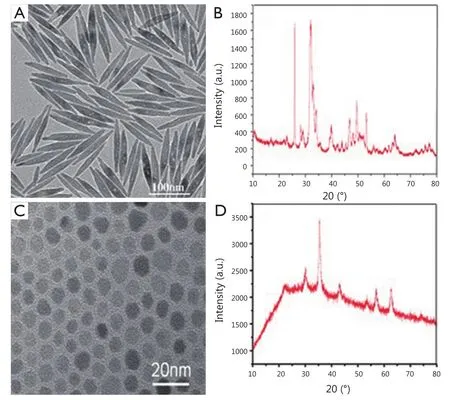
Figure 2 (A) TEM image of hydrophobic fluoridated Eu3+-HAP NPs.(B) TEM image of hydrophobic IOs.(C) XRD patterns of fluoridated Eu3+-HAP NPs.(D) XRD patterns of IOs.TEM, transmission electron microscope; HAP, hydroxyapatite; NP, nanoparticle; IO, iron oxide.
The TEM images of fluoridated Eu3+-HAP NPs and IOs are shown in Figure 2A,B.The length of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP NPs is about 100 nm, the size of IOs is around 8 nm, and both are well monodispersed.Figure 2C,D represent the XRD patterns of fluoridated Eu3+-HAP NPs and IOs, respectively.The XRD image of fluoridated Eu3+-HAP NPs shows the absence of impurities in the final products, thereby demonstrating that Eu3+has been successfully doped into HAP.The XRD image of IOs displays that the final product is a pure phase of IOs.Figure 3A-C show the TEM images of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites with different Eu3+-HAP and IOs mass ratios (2:1, 1:1, and 1:2).These nanocomposites are dispersed as individual nanocomposite with a uniform size of about 200 nm in diameter under each ratio.Figure 3D displays the high-resolution TEM image of the nanocomposite at 1:1 mass ratio of fluoridated Eu3+-HAP and IOs.Fluoridated Eu3+-HAP and IOs can be well encapsulated into PLGA NPs, and the encapsulation does not result in morphological changes.The EDS map in Figure 4 presents the element distribution of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites,thereby demonstrating that fluoridated Eu3+-HAP and IOs can be well encapsulated into PLGA NPs.The nanocomposites with fluoridated Eu3+-HAP and IOs at a mass ratio of 1:1 were used for the following study because of their fluorescence and magnetic property.
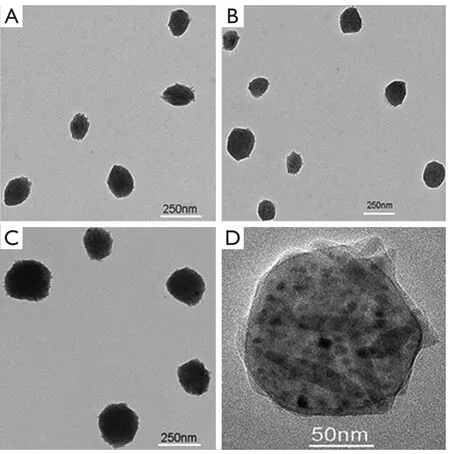
Figure 3 TEM images of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites under different mass ratios of fluoridated Eu3+-HAP and IOs.(A) 2:1.(B) 1:1.(C)1:2.(D) HTEM image of the fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites at 1:1 mass ratio of fluoridated Eu3+-HAP and IOs.TEM, transmission electron microscope; HAP, hydroxyapatite; IO, iron oxide.
Emission spectrum
The emission spectra of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites and fluoridated Tb3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites in water are demonstrated in Figure 5.The emission spectrum of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites was determined from 550 to 750 nm under 405 nm excitation (Figure 5A), and the main emission peak of nanocomposites is located at 615 nm.Figure 5B shows the emission spectrum of the fluoridated Tb3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites under 488 nm exitation, and the main emission peak is located at 548 nm.The spectra of the fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites demonstrate that the strong fluorescence of the nanocomposites remains, despite the encapsulation of fluoridated Ln3+-HAP NPs into PLGA NPs.As the nanocomposites are stable with the existence of IOs, they are considered suitable for targeted cellular imaging.
Magnetic property
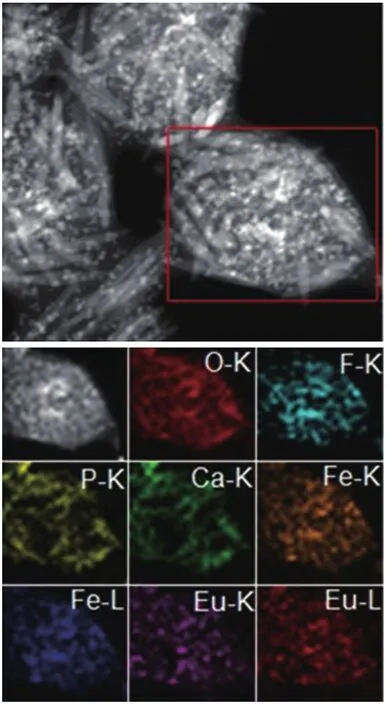
Figure 4 EDS map of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites.HAP, hydroxyapatite; IO, iron oxide.
The magnetic properties of IOs and the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites were obtained with a VSM.The hysteresis M–H curves are shown in Figure 6.Saturation magnetizations are 38.4 and 11.5 emu/g for IOs and the nanocomposites, respectively.The decrease in saturation magnetization for the nanocomposites may be due to the encapsulation of the PLGA matrix..
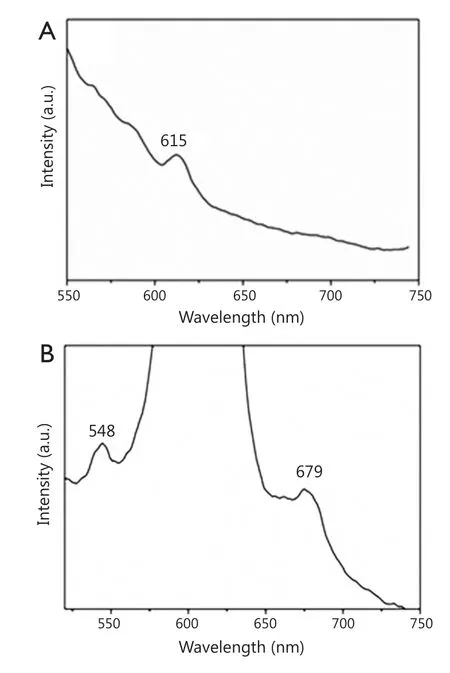
Figure 5 (A) Luminescent spectrum of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites under excitation at 405 nm.(B) Luminescent spectrum of the fluoridated Tb3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites under excitation at 488 nm.HAP, hydroxyapatite; IO, iron oxide.
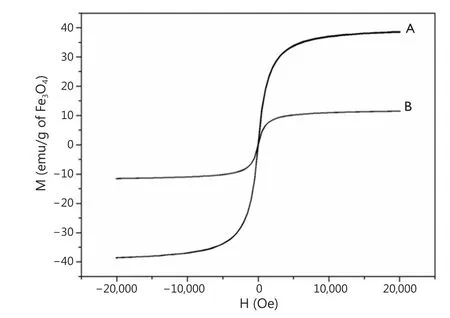
Figure 6 Hysteresis curve at room temperature.(A) Hydrophobic IOs NPs.(B) Fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites.IO, iron oxide; NP,nanoparticle; HAP, hydroxyapatite.
In vitro cytotoxicity of nanocomposites
The cytotoxity of the fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites to A549 cells was evaluated using MTT assay to examine their suitability for biological applications.Figure 7 shows that the fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites display low cytotoxicity to A549 cells.The cell viability values are higher than 90% even when the concentration of the nanocomposites reached 300 μg/mL.This finding further confirms the low toxicity of the nanocomposites.Therefore, the fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites could be potentially used for biological applications.
Magnetic targeted cellular imaging
The application of the fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites for magnetic targeted cellular imaging was investigated with CLSM with or without magnetic field.Figure 8 demonstrates the CLSM images of A549 cells incubated with 250 μg/mL fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites at 37 ℃ for 2 h without the magnetic field (Row 1) and under a magnetic field of 1.3T (Row 2).The CLSM images in red channel in Figure 8 show the fluorescence images of fluoridated Eu-HAP NPs at an excitation wavelength of 405 nm.The enhanced fluoresence signals in Row 2 reveal the high cellular uptake of the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites under external magnetic field for 2 h, whereas fluoresence signals are low witout external magnetic field (Row 1).The enhanced uptake of the nanocomposites by A549 cancer cells under magnetic field may result from the internalization of A549 cells via an energy-dependent pathway.These findings indicate that the fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites can be efficiently used for magnetic targeted cellular imaging of cancer.
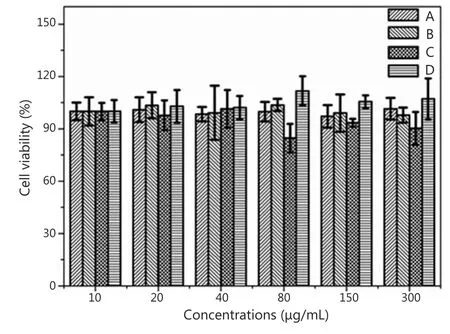
Figure 7 Cell viability of A549 cells at 37 ℃ under different nanocomposite concentrations.(A) Fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites cultured for 8 h.(B) Fluoridated Tb3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites cultured for 8 h.(C) Fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites cultured for 24 h.(D)Fluoridated Tb3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites cultured for 24 h.HAP,hydroxyapatite; IO, iron oxide.
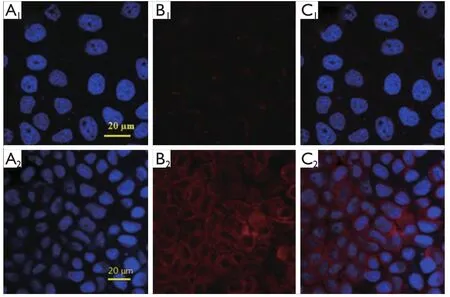
Figure 8 Confocal laser scanning microscopy images of A549 cells incubated with 250 μg/mL fluoridated Eu3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites at 37 ℃ for 2 h without magnetic field (Row 1) and under a magnetic field of 1.3T (Row 2).(A) The blue channel with excitation at 340 nm.(B) The red channel with excitation at 405 nm.(C)The combined red and blue channels.HAP, hydroxyapatite; IO, iron oxide.
Conclusion
Fluoridated Ln3+-HAP/IOs PLGA nanocomposites were prepared through a modified solvent exaction/evaporation technique.The fabricated nanocomposites show excellent photoluminescence, magnetic properties, and stability in aqueous solutions.Thus, the composites are suitable for targeted cellular imaging.The results of in vitro experiments further confirm that the nanocomposites exhibit low toxicity and can be successfully applied to improve the specificity and sensitivity of cellular imaging under magnetic field.The nanocomposites fabricated in this study will be a promising tool for magnetic targeted cellular imaging with improved specification and enhanced selection.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.21506161, 31270019),National Key Basic Research Program of China (973 Program)(Grant No.2011CB933100, 2011CB932402), Guangdong Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar (Grant No.2014A030306036) and open funds from the Key Laboratory of Biomedical Materials in Tianjin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
1.Jaffer FA, Weissleder R.Molecular imaging in the clinical arena.JAMA 2005;293:855-862.
2.Wang X, Yang L, Chen ZG, Shin DM.Application of nanotechnology in cancer therapy and imaging.CA Cancer J Clin 2008;58:97-110.
3.Weissleder R.Molecular imaging in cancer.Science 2006;312:1168-1171.
4.Weissleder R, Pittet MJ.Imaging in the era of molecular oncology.Nature 2008;452:580-589.
5.Louie A.Multimodality imaging probes: design and challenges.Chem Rev 2010;110:3146-3195.
6.Palmer LC, Newcomb CJ, Kaltz SR, Spoerke ED, Stupp SI.Biomimetic systems for hydroxyapatite mineralization inspired by bone and enamel.Chem Rev 2008;108:4754-4783.
7.Curtin CM, Cunniffe GM, Lyons FG, Bessho K, Dickson GR,Duffy GP, et al.Innovative collagen nano-hydroxyapatite scaffolds offer a highly efficient non-viral gene delivery platform for stem cell-mediated bone formation.Adv Mater 2012;24:749-754.
8.Hui J, Wang X.Luminescent, colloidal, F-substituted,hydroxyapatite nanocrystals.Chemistry 2011;17:6926-6930.
9.Chen F, Huang P, Zhu YJ, Wu J, Zhang CL, Cui DX.The photoluminescence, drug delivery and imaging properties of multifunctional Eu3+/Gd3+ dual-doped hydroxyapatite nanorods.Biomaterials 2011;32:9031-9039.
10.Ciobanu CS, Iconaru SL, Massuyeau F, Constantin LV, Costescu A, Predoi D.Synthesis, Structure, and Luminescent Properties of Europium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanocrystalline Powders.J Nanomater 2012;2012.Available online: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/jnm/2012/942801/
11.Graeve OA, Kanakala R, Madadi A, Williams BC, Glass KC.Luminescence variations in hydroxyapatites doped with Eu2+ and Eu3+ ions.Biomaterials 2010;31:4259-4267.
12.Han Y, Wang X, Dai H, Li S.Synthesis and luminescence of Eu3+doped hydroxyapatite nanocrystallines: Effects of calcinations and Eu3+ content.J Lumin 2013;135:281-287.
13.Hasna K, Kumar SS, Komath M, Varma MR, Jayaraj MK, Kumar KR.Synthesis of chemically pure, luminescent Eu3+ doped HAp nanoparticles: a promising fluorescent probe for in vivo imaging applications.Phys Chem Chem Phys 2013;15:8106-8111.
14.Liu M, Liu H, Sun S, Li X, Zhou Y, Hou Z, et al.Multifunctional hydroxyapatite/Na(Y/Gd)F4:Yb3+,Er3+ composite fibers for drug delivery and dual modal imaging.Langmuir 2014;30:1176-1182.
15.Pan J, Wan D, Bian Y, Sun H, Zhang C, Jin F, et al.Fluorescent Hydroxyapatite-Loaded Biodegradable Polymer Nanoparticles with Folate Decoration for Targeted Imaging.AICHE J 2013;59:4494-4501.
16.Hui J, Zhang X, Zhang Z, Wang S, Tao L, Wei Y, et al.Fluoridated HAp:Ln3+ (Ln = Eu or Tb) nanoparticles for cell-imaging.Nanoscale 2012;4:6967-6970.
17.Pan J, Zhang J, Wang L, Wan D.Synthesis of iron oxide coated fluoridated HAp/Ln3+ (Ln = Eu or Tb) nanocomposites for biological applications.Chem Commun (Camb)2014;50:14010-14012.
18.Michalet X, Pinaud FF, Bentolila LA, Tsay JM, Doose S, Li JJ, et al.Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics.Science 2005;307:538-544.
19.Alivisatos AP, Gu W, Larabell C.Quantum dots as cellular probes.Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2005;7:55-76.
20.Smith AM, Duan H, Mohs AM, Nie S.Bioconjugated quantum dots for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging.Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2008;60:1226-1240.
21.Kirchner C, Liedl T, Kudera S, Pellegrino T, Mu?oz Javier A,Gaub HE, et al.Cytotoxicity of colloidal CdSe and CdSe/ZnS nanoparticles.Nano Lett 2005;5:331-338.
22.Derfus AM, Chan WC, Bhatia SN.Probing the Cytotoxicity of Semiconductor Quantum Dots.Nano Lett 2004;4:11-18.
23.Celik A, C?meleko?lu U, Yalin S.A study on the investigation of cadmium chloride genotoxicity in rat bone marrow using micronucleus test and chromosome aberration analysis.Toxicol Ind Health 2005;21:243-248.
24.Liu Y, Mi Y, Zhao J, Feng SS.Multifunctional silica nanoparticles for targeted delivery of hydrophobic imaging and therapeutic agents.Int J Pharm 2011;421:370-378.
25.Muthu MS, Kulkarni SA, Raju A, Feng SS.Theranostic liposomes of TPGS coating for targeted co-delivery of docetaxel and quantum dots.Biomaterials 2012;33:3494-3501.
26.Pan J, Feng SS.Targeting and imaging cancer cells by folatedecorated, quantum dots (QDs)- loaded nanoparticles of biodegradable polymers.Biomaterials 2009;30:1176-1183.
27.Pan J, Liu Y, Feng SS.Multifunctional nanoparticles of biodegradable copolymer blend for cancer diagnosis and treatment.Nanomedicine (Lond) 2010;5:347-360.
28.Pan J, Mi Y, Wan D, Liu Y, Feng SS, Gong J.PEGylated liposome coated QDs/mesoporous silica core-shell nanoparticles for molecular imaging.Chem Commun 2011;47:12886.
29.Pan J, Wang Y, Feng SS.Formulation, characterization, and in vitro evaluation of quantum dots loaded in poly(lactide)-vitamin E TPGS nanoparticles for cellular and molecular imaging.Biotechnol Bioeng 2008;101:622-633.
30.Cho K, Wang X, Nie S, Chen ZG, Shin DM.Therapeutic nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer.Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:1310-1316.
31.Danhier F, Feron O, Préat V.To exploit the tumor microenvironment:Passive and active tumor targeting of nanocarriers for anti-cancer drug delivery.J Control Release 2010;148:135-146.
32.Perrault SD, Walkey C, Jennings T, Fischer HC, Chan WC.Mediating tumor targeting efficiency of nanoparticles through design.Nano Lett 2009;9:1909-1915.
33.Wang M, Thanou M.Targeting nanoparticles to cancer.Pharmacol Res 2010;62:90-99.
34.Maeda H.Tumor-selective delivery of macromolecular drugs via the EPR effect: background and future prospects.Bioconjug Chem 2010;21:797-802.
35.Maeda H, Bharate GY, Daruwalla J.Polymeric drugs for efficient tumor-targeted drug delivery based on EPR-effect.Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2009;71:409-419.
36.Tyo JS, Goldstein DL, Chenault DB, Shaw JA.Review of passive imaging polarimetry for remote sensing applications.Appl Opt 2006;45:5453-5469.
37.Byrne JD, Betancourt T, Brannon-Peppas L.Active targeting schemes for nanoparticle systems in cancer therapeutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2008;60:1615-1626.
38.Davis ME, Chen ZG, Shin DM.Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008;7:771-782.
39.Cheng L, Yang K, Li Y, Zeng X, Shao M, Lee ST, et al.Multifunctional nanoparticles for upconversion luminescence/MR multimodal imaging and magnetically targeted photothermal therapy.Biomaterials 2012;33:2215-2222.
40.Veiseh O, Gunn JW, Zhang M.Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging.Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2010;62:284-304.
41.Takeda S, Mishima F, Fujimoto S, Izumi Y, Nishijima S.Development of magnetically targeted drug delivery system using superconducting magnet.J Magn Magn Mater 2007;311:367-371.
42.Arruebo M, Fernández-Pacheco R, Ibarra MR, Santamaría J.Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery.Nano Today 2007;2:22-32.
43.Chertok B, Moffat BA, David AE, Yu F, Bergemann C, Ross BD,et al.Iron oxide nanoparticles as a drug delivery vehicle for MRI monitored magnetic targeting of brain tumors.Biomaterials 2008;29:487-496.
44.Liu B, Li C, Ma P, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Hou Z, Huang S, et al.Multifunctional NaYF4:Yb, Er@mSiO2@Fe3O4-PEG nanoparticles for UCL/MR bioimaging and magnetically targeted drug delivery.Nanoscale 2015;7:1839-1848.
45.Reddy LH, Arias JL, Nicolas J, Couvreur P.Magnetic nanoparticles: design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications.Chem Rev 2012;112:5818-5878.
46.Liu Q, Zhang J, Xia W, Gu H.Magnetic field enhanced cell uptake efficiency of magnetic silica mesoporous nanoparticles.Nanoscale 2012;4:3415-3421.
47.Frey NA, Peng S, Cheng K, Sun S.Magnetic nanoparticles:synthesis, functionalization, and applications in bioimaging and magnetic energy storage.Chem Soc Rev 2009;38:2532-2542.
48.Liang X, Wang X, Zhuang J, Chen Y, Wang D, Li Y.Synthesis of nearly monodisperse iron oxide and oxyhydroxide nanocrystals.Adv Funct Mater 2006;16:1805-1813.
 Cancer Biology & Medicine2014年2期
Cancer Biology & Medicine2014年2期
- Cancer Biology & Medicine的其它文章
- An unusual case of aggressive systemic mastocytosis mimicking hepatic cirrhosis
- Spindle cell carcinoma of the breast as complex cystic lesion: a case report
- Effects of postmastectomy radiotherapy on prognosis in different tumor stages of breast cancer patients with positive axillary lymph nodes
- Clinico-pathological signi fi cance of extra-nodal spread in special types of breast cancer
- Incidence and mortality of female breast cancer in the Asia-Paci fi c region
- Research progress on the anticarcinogenic actions and mechanisms of ellagic acid
