A Facile Route for Synthesis of LiFePO4/C Cathode Material with Nano-sized Primary Particles*
XIAO Zhengwei (肖政偉)**, HU Guorong (胡國(guó)榮), DU Ke (杜柯)and PENG Zhongdong (彭忠東)1Faculty of Metallurgical and Energy Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, ChinaSchool of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
A Facile Route for Synthesis of LiFePO4/C Cathode Material with Nano-sized Primary Particles*
XIAO Zhengwei (肖政偉)1,**, HU Guorong (胡國(guó)榮)2, DU Ke (杜柯)2and PENG Zhongdong (彭忠東)21Faculty of Metallurgical and Energy Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China2School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
A facile and practical route was introduced to prepare LiFePO4/C cathode material with nano-sized primary particles and excellent electrochemical performance. LiH2PO4was synthesized by using H3PO4and LiOH as raw materials. Then, as-prepared LiH2PO4, reduced iron powder and α-D-glucose were ball-milled, dried and sintered to prepare LiFePO4/C. X-ray diffractometry was used to characterize LiH2PO4, ball-milled product and LiFePO4/C. Differential scanning calorimeter-thermo gravimetric analysis was applied to investigate possible reactions in sintering and find suitable temperature for LiFePO4formation. Scanning electron microscopy was employed for the morphology of LiFePO4/C. As-prepared LiH2PO4is characterized to be in P21cn(33) space group, which reacts with reduced iron powder to form Li3PO4, Fe3(PO4)2and H2in ball-milling and sintering. The appropriate temperature for LiFePO4/C synthesis is 541.3-976.7 °C. LiFePO4/C prepared at 700 °C presents nano-sized primary particles forming aggregates. Charge-discharge examination indicates that as-prepared LiFePO4/C displays appreciable discharge capacities of 145 and 131 mA·h·g?1at 0.1 and 1 C respectively and excellent discharge capacity retention.
lithium ion cell, reduced iron powder, ball-milling, LiFePO4/C, nano-sized primary particle
1 INTRODUCTION
Owing to exhausting of fossil fuels and increasingly severe greenhouse gases pollution, the development of electric vehicles (EVs) has long been an intense issue since it appeared in 1899 [1]. There are several candidates of rechargeable system for EVs batteries, such as Pb acid, Ni Cd, NiMH [2], but with respect to specific power (W·kg?1) and specific energy (W·h·kg?1), these technologies are outmatched by Li-ion battery technology. Since its commercialization by Sony in the early 1990s, this advanced system has become the prior consideration for vehicles.
In view of the electrochemical properties of cathode materials for lithium ion cells, among LiCoO2and its derivatives, LiMn2O4and LiFePO4, LiFePO4owns the best holistic evaluation for EVs application: medium voltage, cheap raw materials, environmental friendliness, high temperature stability and safety, and appreciable theoretical capacity of 170 mA·h·g?1, which is comparable to the actual capacity of commercialized and widely used LiCoO2[3-6]. As regard to the application to EVs, LiMn2O4has the “seemingly” insurmountable problem of electrochemical instability at elevated temperatures [7].
However, LiFePO4has the disadvantage of very low electronic conductivity, 10?9-10?10S·cm?1. Many studies have been carried out to improve its electronic conductivity and electrochemical performance. Conductive carbon coating/mixing [8], metal coating/mixing [9], aliovalent ion doping [10] and nano-sizing LiFePO4particles [11] have been introduced and proved to be effective. Among these improved methods, the effectiveness of carbon coating/mixing to obtain cathode material LiFePO4/C composite with excellent electrochemical performance has been confirmed by many research groups. Aliovalent ion doping remains to be controversial in that: (1) the theoretical calculation indicates that doping is not energetically favorable [12], (2) the formation of conductive phases between active particles may account for the improved electronic conductivity of “doped LiFePO4” [13].
LiFePO4has been commercialized, and A123 Systems is one of the most famous and best suppliers of this cathode material. A123 Systems is noted for its LiFePO4product of well-separated nano-sized LiFePO4particles, which can provide very short routes for Li+intrusion/extrusion in electrochemical processes and effect excellent rate capability as a cathode material in lithium ion cells. However, its shortcoming is obvious: nano-sized particles need much more binder for cathode fabrication, greatly reducing the volumetric energy density of cathode. Therefore, it will be meaningful to synthesize LiFePO4aggregates with nano-sized primary particles to keep the advantage of short routes for Li+intrusion/extrusion in electrochemical process and reduce the amount of binder used in cathode fabrication.
Nao-sized LiFePO4synthesis often needs sophisticated techniques and harsh conditions in liquid or sol-gel [14, 15]. In this work, we choose an easy and simple method to introduce carbon to synthesizeLiFePO4/C composite cathode material for lithium ion cells. LiH2PO4is prepared by making use of H3PO4and LiOH. Then, LiH2PO4, reduced iron powder and α-D-glucose (C6H12O6·H2O) are ball-milled and sintered to prepare LiFePO4/C. The as-prepared composite cathode material is characterized for its characteristics and charge-discharge performance.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
At room temperature, 1.5 mol·L?1LiOH aqueous solution was slowly added into 85% (by mass) H3PO4aqueous solution under vigorous agitation, with the molar ratio of 1︰1. The product solution was left to stand for hours until its pH value became constant. The solution was then heated on stirring to vaporize and white solid LiH2PO4was derived.
LiH2PO4and reduced iron powder with molar ratio of 1︰1 and a certain amount of α-D-glucose (C6H12O6·H2O) were mixed and ball-milled at a speed of 400-500 r·min?1for 5 h with pure ethanol as grinding medium. The obtained slurry was dried at 100 °C to remove volatile constituents to get dried lump, which was sintered in an argon atmosphere at 700 °C for 15 h to obtain LiFePO4/C.
The dried lump was examined with differential scanning calorimeter-thermo gravimetric analysis (DSC-TGA) on SDTQ 600 using V 8.0 Build 95 software to investigate the reactions of constituents to form LiFePO4, with heating rate of 10 K·min?1and argon flow rate of 100 ml·min?1. As-prepared LiH2PO4, dried lump and synthesized LiFePO4/C were characterized by X-ray diffractometry (XRD) with Philips X-pert powder diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation. The morphology of LiFePO4/C was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) on JSM-6360LV (JEOL).
LiFePO4/C, poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) binder and acetylene black with mass ratio of 75︰10︰15 were mixed and ground with the addition of suitable amount of N-methyl pyrrolidinone (NMP) solvent. The slurry was spread uniformly over an aluminum foil current collector and was dried at 120 °C under vacuum. The slurry with a mass ratio 2︰1 for acetylene black︰PVDF binder (with NMP as the solvent) was uniformly coated onto the dried electrode, which was also dried at 120 °C under vacuum. Circular cathode sheets were punched with an area of 0.785 cm2for each. For coin cell fabrication, the electrolyte was 1 mol·L?1LiPF6in a mixture of ethylene carbonate, ethyl methyl carbonate and dimethyl carbonate with volume ratio of 1︰1︰1. Metallic lithium wafer was used as the counter electrode, and Celgard 2400 polypropylene microporous membrane as separator. Coin cell 2025 with the prepared cathode electrode was assembled in an argon-filled glovebox free from oxygen and water vapor. At room temperature, the rate capability (1C=170 mA·h·g?1) for LiFePO4/C cathode material was galvanostatically examined in the voltage window of 2.5-4.1 V on Land BTI-40. The specific capacity of the cathode in this work referred to that of LiFePO4/C loaded.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION

Figure 1 XRD pattern for as-prepared LiH2PO4
Figure 1 gives the XRD result for as-prepared LiH2PO4. The characteristic peaks for the compound are sharp and perfect, indicating a high degree of crystallinity. The pattern agrees well with that of LiH2PO4indexed in P21cn(33) space group [International Centre for Diffraction Data/Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (ICDD/JCPDS) 21-0498] and no impurity phase is found, indicating a high purity product. Therefore, the method employed is a practicable way of soft chemistry synthesis for LiH2PO4of high purity and crystallinity.
Figure 2 shows the XRD pattern for the dried lump, obtained by ball-milling the mixture of LiH2PO4, reduced iron powder and α-D-glucose, revealing the presence of crystallized Li3PO4and iron residue in the mixture. Therefore, LiH2PO4and reduced iron powder have reacted in the ball-milling process, but the reaction is not complete. From the color of blueness, it can be deduced that Fe3(PO4)2forms in the process. Nocharacteristic peaks of LiH2PO4are observed, suggesting its consumption by chemical reactions and decrease in crystallinity in the ball-milling. Since bubbling was observed in the ball-milling process, the principal reaction in this step is

Figure 2 XRD pattern for dried lump from ball-milled mixture of LiH2PO4, reduced iron powder and α-D-glucose

Therefore, the main constituents of the dried lump are residual LiH2PO4and Fe, products Li3PO4and Fe3(PO4)2.
Figure 3 shows DSC-TGA curves of the ball-milled mixture, with three thermal peaks. The first one at 107.7 °C corresponds to a heavy mass loss on TGA curve, which can be attributed to the loss of crystalliferous water and decomposition of the mechanically activated α-D-glucose, further reaction of residual LiH2PO4and reduced iron powder to form Li3PO4and Fe3(PO4)2, and liberation of H2. Some studies have reported the application of the mixture of an inert gas (Ar or N2) and H2for synthesizing LiFePO4cathode material with excellent electrochemical performance [16, 17]. In this work, the release of H2in the sintering is favorable to the formation of LiFePO4, providing a strong reductive atmosphere for ferrous iron. The mass of the sample stays unchanged after 383.3 °C, which is the evidence for

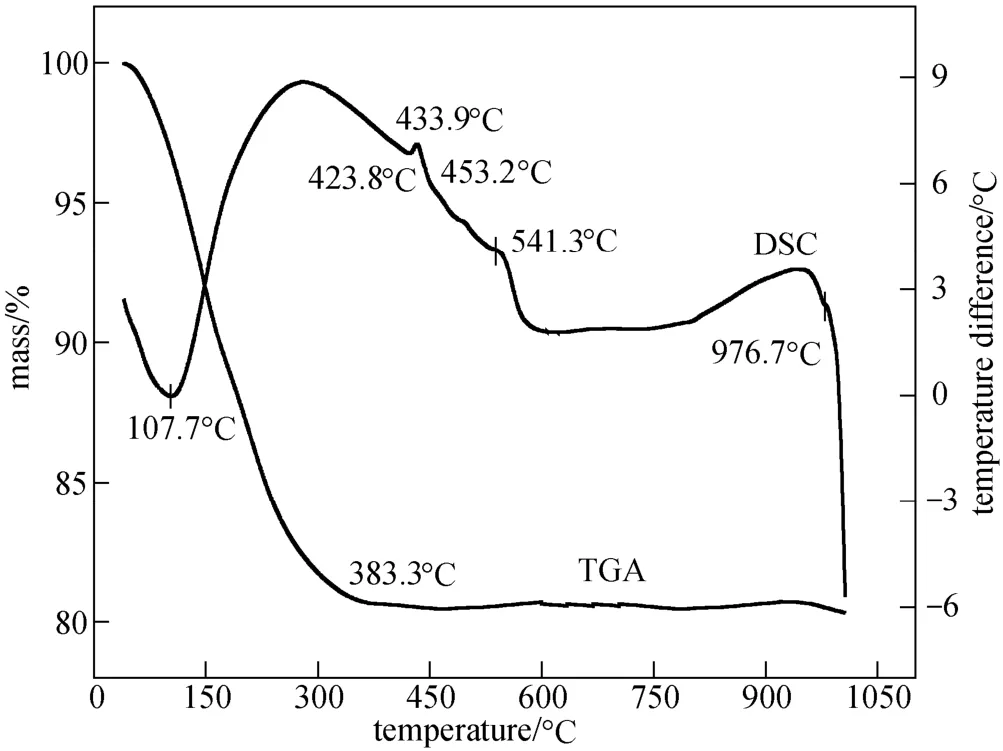
Figure 3 DSC-TGA for the dried lump of ball-milled mixture of LiH2PO4, reduced iron powder and α-D-glucose
The last peak of DSC curve at 976.7 °C reflects the decomposition of LiFePO4with the loss of Li at high temperatures. Therefore, at a temperature between 541.3 and 976.7 °C, LiFePO4can be synthesized via the approach adopted in this work. It is worth mentioning that LiFePO4can not be successfully prepared when LiH2PO4, reduced iron powder and α-D-glucose are simply mixed and ground but not ball-milled before sintering in argon.
Figure 4 gives the XRD pattern for LiFePO4/C synthesized at 700 °C. The diffraction result is indexed in the orthorhombic space group Pnma. The peaks on the diffraction line are sharp and perfect, suggesting a high degree of crystallinity for as-prepared LiFePO4/C. The pattern agrees well with that for triphylite (JCPDS NO. 40-1499), and no impurity phases consisting of lithium, iron, or phosphorous can be detected, indicating that the iron residue in the dried lump is completely consumed in the sintering process. No diffraction peaks for crystallized carbon are revealed in Fig. 4, indicating the amorphous form of the conductive reagent resulting from anaerobic pyrolysis of α-D-glucose.
Figure 5 shows the SEM morphology of as-prepared LiFePO4/C. Nano-sized primary particles with narrow size distribution agglomerate to aggregates in micrometers. The formation of aggregates is favorable to cathode fabrication because nano-sized particles cause wetting problems and need much more PVDF binder, which will greatly reduce the volumetric energy density of the cathode. In the ball-milling step, LiH2PO4and reduced iron powder reacted in such a way that the latter is dissolved and consumed gradually. The primary particle size of the product, dried lump, can reach nano-scale after the milling the completion of chemical reactions accompanied by mass loss. The second thermal peak is at 433.9 °C, without mass loss in the corresponding part of TGA curve. The thermal effect can be ascribed to the substantial formation of LiFePO4until 541.3 °C:process, without serious agglomeration in milling. Nano-sized particles of ball-milled product are beneficial to the formation of LiFePO4in the following sintering, in which the presence of carbon from decomposition of α-D-glucose also prohibits the growth of LiFePO4particles [18]. As shown in Fig. 5, pores distribute between nano-sized LiFePO4/C primary particles. These pores can be well wetted by electrolyte and provide more sites for electrochemical reactions which only occur at those points where the active material, conductive diluent and electrolyte meet [7]. Meanwhile, the nano-size of LiFePO4primary particles provides very short routes for Li+intrusion/ extrusion in electrochemical processes [19]. Moreover, the diffusivity of Li+is inversely proportional to the square of particle size of LiFePO4[20]. Therefore, nano-sized primary particles of as-prepared LiFePO4/C in this work help Li+ions migrate and diffuse in LiFePO4crystals. It can be predicted that as-synthesized LiFePO4/C cathode material may exhibit very good electrochemical performance.

Figure 4 XRD pattern of LiFePO4/C synthesized at 700 °C

Figure 5 SEM image for LiFePO4/C synthesized at 700 °C

Figure 6 Typical charge-discharge profiles for as-prepared LiFePO4/C at 0.1 and 1 C
Figure 6 shows the typical charge-discharge profiles for as-prepared LiFePO4/C at 0.1 and 1 C. The 0.1 C charge-discharge curves for the cathode electrode present a flat plateau at around 3.45 V, the voltage at which both the lithium intrusion and extrusion at room temperature proceed in a two-phase reaction [21] between LiFePO4and FePO4crystallizing in space group Pnma. The as-prepared LiFePO4/C displays discharge capacities of 145 and 131 mA·h·g?1at 0.1 and 1 C, respectively, which are comparable to those reported in literature. It is noted that at 0.1 C the discharge curve for LiFePO4/C exhibits a higher voltage plateau than that at 1 C. In addition, the higher the rate is, the bigger the gap is between charge-discharge plateau voltages, but the charge-discharge plateau voltages at 0.1 C are much better kept at around 3.45 V than those at 1 C. These results suggest that higher rates can swiftly increase the polarization during the charge-discharge process.
The olivine structure is thought to be the intrinsic reason for the low electronic conductivity of the compound. This group is exemplified by LiFePO4which has a hexagonally-close-packed oxygen array, with the octahedra sharing edges (LiO6) or corners (FeO6). The poor electronic conductivity of pristine LiFePO4is imputed to the absence of continuous edge-shared FeO6network [22]. Carbon coating/mixing treatment on pure LiFePO4particle can greatly improve its electronic conductivity and then rate capability in electrochemical process. In this work, the nano-sized primary particles also contribute to the improvement in electrochemical capability. The very short Li+migration routes in the primary particles facilitate the diffusion of Li+ions, which has been proved to beanother factor to limit the rate performance of LiFePO4[23]. Magasinski et al. introduced C-Si granules with nano-sized primary particles which exhibit excellent electrochemical performance when used as anode in lithium ion cells [24].
Figure 7 shows the rate capability and capacity retention for LiFePO4/C in the first 50 cycles of charge-discharge process. At 0.1 and 1 C, the capacity retention is well maintained. Even at 1 C, LiFePO4/C displays a discharge capacity of 131 mA·h·g?1, which is comparable to that reported [25]. The excellent capacity retention can be attributed to carbon coating/ mixing and as-prepared LiFePO4/C cathode material itself, whose primary particles with uniform size alleviate the sluggish migration and diffusion of Li+[26]. Moreover, nano-sized primary particles are more endurable to the strain in expansion and contraction of LiFePO4unit cell during Li+intrusion and extrusion [19], leading to good cycling ability.

Figure 7 Rate capability and capacity retention for as-prepared LiFePO4/C
Further work will be done to improve the rate capacity of LiFePO4/C prepared via the procedure in this work by optimizing the experimental conditions, ball-milling speed and duration, choice of conductive carbon precursor, synthesis temperature and time, and so on. Even the reduced iron powder can be tailored to be as fine as possible which will need an inert atmosphere in ball-milling and subsequent steps for LiFePO4/C synthesis. At the same time, in the aggregates each nano-sized primary LiFePO4particle should be well coated by conductive carbon whose content in LiFePO4/C may be optimized.
4 CONCLUSIONS
LiFePO4/C cathode material with nano-sized primary particles was successfully synthesized by using as-prepared LiH2PO4, reduced iron powder and α-D-glucose, which were ball-milled, dried and sintered. In the sintering, H2release is favorable to the formation of LiFePO4. Nano-sized primary particles provide very short routes for Li+migration and diffusion in electrochemical processes. As-prepared LiFePO4/C
exhibits appreciable discharge capacities of 145 and 131 mA·h·g?1at 0.1 and 1 C respectively and excellent capacity retention at each of the tested rates. The facile route is a feasible approach for preparation of LiFePO4/C cathode material with nano-sized primary particles. Further work for the improvement on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C synthesized by the method will be carried out.
REFERENCES
1 Armand, M., Tarascon, J.M., “Building better batteries”, Nature, 451 (7), 652-657 (2008).
2 Ovshinsky, S.R., Fetcenko, M.A., Ross, J., “A nickel metal hydride battery for electric vehicles”, Science, 260 (5105), 176-181 (1993).
3 Yu, W.L., Zhao, Y.P., Rao, Q.L., “Rapid and continuous production of LiFePO4/C nano-particles in super heated water”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 17 (1), 171-174 (2009).
4 Yang, K.D., Tan, F.X., Wang, F., Long, Y.F., Wen, Y.X., “Response surface optimization for process parameters of LiFePO4/C preparation by carbothermal reduction technology”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 20 (4), 793-802 (2012).
5 Xiao, Z.W., Hu, G.R., Du K., Peng, Z.D., Deng, X.R., “High density LiFePO4/C composite cathode material for lithium ion batteries”, Chin. J. Nonferr. Metal., 17 (12), 2040-2045 (2007). (in Chinese)
6 Zhang, W.X., Zhao, F., Wang, Q., Yang, Z.H., “LiFePO4synthesized by hydrothermal method from Li3PO4and its modification”, CIESC. J., 61 (10), 2719-2725 (2010). (in Chinese)
7 Whittingham, M.S., “Lithium batteries and cathode materials”, Chem. Rev., 104 (10), 4271-4301 (2004).
8 Yoon, M.S., Islam, M., Park, Y.M., Ur, S.C., “Effect of synthesizing method on the properties of LiFePO4/C composite for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries”, Electron. Mater. Lett., 9 (2), 187-193 (2013).
9 Park, K.S., Song, J.T., Chung, H.T., Kim, S.J., Lee, C.H., Kang, K.T., Kim, H.G., “Surface modification by silver coating for improving electrochemical properties of LiFePO4”, Solid State Commun., 129 (5), 311-314 (2004).
10 Chung, S.Y., Bloking, J., Chiang, Y.M., “Electronically conductive phosphor-olivines as lithium storage electrode”, Nat. Mater., 1 (2), 123-128 (2002).
11 Jeong, E.D., Kim, H.J., Ahn, C.W., Ha, M.G., Hong, T.E., Kim, H.G., Jin, J.S., Bae, J.S., Hong, K.S., Kim, Y.S., Kim, H.J., Doh, C.H., Yang, H.S., “Synthesis and electrochemical studies of nano-scale carbon-coated LiFePO4electrodes for Li-ion batteries”, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 9 (7), 4467-4471 (2009).
12 Fisher, C.A.J., Prieto, V.M.H., Islam, M.S., “Lithium battery materials LiMPO4(M=Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni): Insights into defect association, transport mechanisms, and doping behavior”, Chem. Mater., 20 (18), 5907-5915 (2008).
13 Herle, P.S., Ellis B., Coombs, N., Nazar, L.F., “Nano-network electronic conduction in iron and nickel olivine phosphates”, Nat. Mater., 3 (3), 147-152 (2004).
14 Sides, C.R., Croce, F., Young, V.Y., Martin, C.R., Scrosati, B., “A high-rate, nanocomposite LiFePO4/carbon cathode”, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 8 (9), A484-A487 (2005).
15 Arumugam, D., Kalaignan, G.P., Manisankar, P., “Synthesis and electrochemical characterizations of nano-crystalline LiFePO4and Mg-doped LiFePO4cathode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries”, J. Solid State Electrochem., 13 (2), 301-307 (2009).
16 Rho, Y.H., Nazar, L.F., Perry, L., Ryan, D., “Surface chemistry ofLiFePO4studied by Mossbauer and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and its effect on electrochemical properties”, J. Electrochem. Soc., 154 (4), A283-A289 (2007).
17 Shi, Y., Chou, S.L., Wang, J.Z., Wexler, D., Li, H.J., Liu, H.K., Wu, Y.P., “Graphene wrapped LiFePO4/C composites as cathode materials for Li-ion betteries with enhanced rate capacity”, J. Mater. Chem., 22 (32), 16465-16470 (2012).
18 Hsu, K.F., Tsay, S.Y., Hwang, B.J., “Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized LiFePO4cathode materials prepared by a citric acid-based sol-gel route”, J. Mater. Chem., 14 (17), 2690-2695 (2004).
19 Arico, A.S., Bruce, P., Scrosati, B., Tarascon, J.M., Schalkwijk, W.V.,“Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices”, Nat. Mater., 4 (5), 366-377 (2005).
20 Ma, J.X., Wang, C.S., Wroblewski, S., “Kinetic characteristics of mixed conductive electrodes for lithium ion batteries”, J. Power Sources, 164 (2), 849-856 (2007).
21 Hu, G.R., Xiao, Z.W., Du, K., Peng, Z.D., Deng, X.R., “Preparation of LiFePO4for lithium ion battery using Fe2P2O7as precursor”, J. Cent. South Univ., 15 (4), 531-534 (2008).
22 Thackeray, M., “An unexpected conductor”, Nat. Mater., 1 (2), 81-82 (2002).
23 Churikov, A.V., Ivanishchev, A.V., Ivanishcheva, I.A., Sycheva, V.O., Khasanova, N.R., Antipov, E.V., “Determination of lithium diffusion coefficient in LiFePO4electrode by galvanostatic and potentiostatic intermittent titration techniques”, Electrochim. Acta, 55 (8), 2939-2950 (2010).
24 Magasinski, A., Dixon, P., Hertzberg, B., Kvit, A., Ayala, J., Yushin, G., “High-performance lithium-ion anodes using a hierarchical bottom-up approach”, Nat. Mater., 9 (4), 353-358 (2010).
25 Xu, Z.H., Xu, L., Lai, Q.Y., Ji, X.Y., “Microemulsion synthesis of LiFePO4/C and its electrochemical properties as cathode materials for lithium-ion cells”, Mater. Chem. Phys., 105 (1), 80-85 (2007).
26 Wang, C.S., Hong, J., “Ionic/electronic conducting characteristics of LiFePO4cathode materials”, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 10 (3), A65-A69 (2007).
2013-03-22, accepted 2013-07-07.
* Supported partially by the Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan Province (2010ZC051) and Analysis and Testing Foundation (2009-041) and Starting Research Fund (14118245) from Kunming University of Science and Technology.
** To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: csuxiao@163.com
 Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2014年5期
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2014年5期
- Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Soft Sensor Model Derived from Wiener Model Structure: Modeling and Identification*
- Kinetics of Forward Extraction of Boric Acid from Salt Lake Brine by 2-Ethyl-1,3-hexanediol in Toluene Using Single Drop Technique*
- Influence of Solvent on Reaction Path to Synthesis of Methyl N-Phenyl Carbamate from Aniline, CO2and Methanol*
- Effect of Adsorbent Diameter on the Performance of Adsorption Refrigeration*
- High-Thermal Conductive Coating Used on Metal Heat Exchanger*
- Filtering Surface Water with a Polyurethane-based Hollow Fiber Membrane: Effects of Operating Pressure on Membrane Fouling*
