可見(jiàn)光輻射下活性炭-鐵酸鎳雜化催化劑光催化氧化氨氮
肖 波 劉守清
(蘇州科技學(xué)院,化學(xué)生物與材料工程學(xué)院,江蘇省環(huán)境功能材料重點(diǎn)實(shí)驗(yàn)室,江蘇蘇州215009)
1 Introduction
Nickel ferrite(NiFe2O4)is a promising photo-Fenton catalyst in practical application due to its easy immobilization,separation,recovery,and reuse by external magnetic field.The literature has shown,however,a single component of NiFe2O4has no photocatalytic activity to hydrogen peroxide due to the inhibition of nickel atoms in the crystal lattice.1,2Thus,it is necessary to modify the single NiFe2O4.Wang′sgroup3,4utilized graphene and multiwall carbon tubes to fabricate hybrid catalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants.Doet al.5applied activated carbons(ACs)to prepare Fe3O4and MnFe2O4hybrid materials as heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the oxidation decomposition of methyl orange(MO).Huet al.6prepared an activated carbon-titanium dioxide composite for the degradation of dyes.Other carbon materials were also utilized to synthesize photocatalysts to promote the photocatalytic efficiency.7-9However,the activated carbonnickel ferrite(AC-NiFe2O4)hybrid catalyst has not been employed to degrade ammonia in the presence of hydrogen peroxide.
Aqueous ammonia(NH3/NH4+)is a major aquatic pollutant,which comes from livestock waste and agricultural fertilizer.The excess of its existence in soil and waters makes eutrophication and depletion of dissolved oxygen,and increases biological oxygen demand.Therefore,some techniques such as the breakpoint chlorination,ion exchange,air stripping,and biological nitrification and denitrification for the removal of ammonia have been developed.10The photocatalytic technique was also developed to oxidize ammonia using TiO2.11-21The advantage of the TiO2catalyst is that it is stable and nontoxic.However,TiO2,especially,nano-sized TiO2is not easy to be immobilized,consequently,it runs off with effluent.And moreover,it is not response to visible light.Therefore,it is necessary to develop novel photocatalysts that have high activities,respond to visible light,and are easy to be immobilized.Therefore,herein we present the activated carbonnickel ferrite as a hybrid catalyst for the photo-Fenton oxidization of ammonia in the presence of hydrogen peroxide under visible light irradiation and explore the mechanism of oxidation of ammonia.
2 Experimental
2.1 Chemicals
Activated carbon was purchased from Shanghai General Chemical Factory(Shanghai,China).Ferric chloride hexahydrate(FeCl3?6H2O),and sodium hydroxide(NaOH),sodium carbonate,and sodium bicarbonate were purchased from Tianjin Damao Chemical Factory,China.Ni(II)sulfate hexahydrate(NiSO4?6H2O)was obtained from Nanjing Chemical Reagent Co.,Ltd.All reagents were of analytical grade and used without further purification.All solutions were prepared with deionized Milli-Q water(18.2 MΩ?cm).
2.2 Synthesis of AC-NiFe2O4catalyst
NiSO4?6H2O(2.6285 g,0.01 mol)and FeCl3?6H2O(5.4058 g,0.02 mol)were separately dissolved in 15.0 mL of water.Both of the solutions were mixed under stirring.The activated carbon was pretreated by heating to 110°C and maintained for 1 h.Then,the pretreated activated carbon(0.2344 g)was added in the mixed solution,and was continuously stirred for 30 min.NaOH(3.2000 g,0.08 mol)was dissolved in 10.0 mL of deionized water,the NaOH solution was added dropwise to the mixed suspension solution.Another 20.00 mL of deionized water was added in the suspension solution up to the final volume of 60.0 mL,and it continued to be stirred for 30 min.The suspension solution including nickel ferrite paste and activated carbon was transferred into a 100 mL Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave that was sealed and maintained at 180°C for 10 h.The suspension was filtered to obtain AC-NiFe2O4precipitates,which were rinsed thrice with water to remove the excess of NaOH and other electrolytes.Finally,magnetic powder was obtained after sintering at 200°C for 4 h.The magnetic powder was utilized for the characterization and photocatalytic degradation of ammonia.The single NiFe2O4was prepared for comparison.
2.3 Characterization for structure and magnetism
X-ray diffraction(XRD)measurements were performed using anX′Pert-ProMPD X-ray diffractometer(Panalytical,Netherland).The X-ray source was Cu-Kαradiation with a wavelength of 0.154 nm,tube voltage of 40 kV,and tube current of 40 mA.Morphological observations were conducted using a transmission electron microscopy(TEM)system(TecnaiG220,FEI,USA)and a scanning electronic microscopy(SEM)system(Quanta 400 FEG,FEI,USA).AC-NiFe2O4and activated carbon powder were dispersed in water using an ultrasonic device,placed on carboncoated copper grids,and dried under ambient conditions for morphological observation.A Fourier-transform infrared(FTIR)spectrophotometer(Spectrum BX,PerkinElmer Ltd.,USA)was used for the characterization of group vibrations at an optical resolution of 4 cm-1.The mulls of AC-NiFe2O4were supported by a KBr plate.Magnetic measurements were made using a vibrating sample magnetometer(Lake Shore 7410,Lake Shore Cryotronics,Inc.,USA)at(25±2)°C.
2.4 Degradation tests and analytical methods
All photocatalytic experiments were conducted under visible light irradiation(λ>400 nm).A300 W UV-visible lamp(OSRAM,Germany)was used as a light source.Photo-Fenton degradation of ammonia was performed in a 100 mL beaker at room temperature((25.0±0.2)°C).The distance between the lamp and test solution was approximately 10 cm.The wall of the beaker was shielded from the surrounding light with tinfoil.Visible light was obtained with a cut-off filter(λ>400 nm),which covered the window of the beaker to absorb UV light and allow visible light ofλ>400 nm to pass through.Atest solution of about 50 mL was typically used in the photo-Fenton experiments.The pH value of solutions was adjusted by 0.1 mol?L-1NaHCO3-Na2CO3buffer,and the AC-NiFe2O4(0.20 g)was utilized as the catalyst.The absorbance at 425 nm was measured at regular intervals using a double beam TU-1901 spectrophotometer during the photo-Fenton process to probe the concentration of ammonia by Nessler reagent.Atest solution of 1.0 mL was taken out and diluted into 25.0 mL to track the content of ammonia during the photocatalytic degradation of ammonia.
The Nessler reagent(alkaline solution of dipotassium tetraiodomercurate(II))was prepared according to the following procedure:10 g HgI2and 7 g KI were dissolved in water and added to NaOH solution(16 g NaOH in 50 mL of water)and finally diluted to 100 mL by deionized water.22The Nessler reagent was stored in dark bottle and diluted properly before analysis.Ammonia reacts with the Nessler reagent to yield colored solutions by reaction(1):
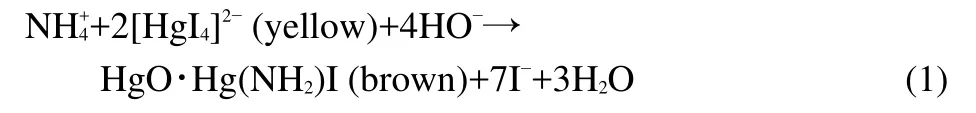
The absorbance at 425 nm was measured to obtain the concentration of ammonia during the photo-Fenton process.
3 Characterization results and discussion
3.1 XRD characterization
Fig.1 shows the XRD patterns of the as-synthesized ACNiFe2O4and NiFe2O4samples.The diffraction angle positions of the characteristic peaks(2θ)for both samples are in good agreement with the data in the JCPDS card(No.74-2081)of NiFe2O4,confirming the same crystal structure of theAC-NiFe2O4sample as that of the NiFe2O4sample.It is a cubic spinel ferrite,crystallizing in the cubic spinel type structure(a=0.8433 nm),space groupFd3m.Considering atomic occupancy,NiFe2O4is written as(Fe3+)A[Ni2+Fe3+]BO42?,where A and B represent tetrahedral and octahedral sites,respectively.23
The peaks of the AC-NiFe2O4and NiFe2O4samples are distinctly broad,indicating that the AC-NiFe2O4particles are very small.The average diameter(D)of the as-synthesized ACNiFe2O4particles was calculated to be 10.7 nm using the Debye-Scherrer equation24D=Kλ/(Wcosθ)at a diffraction angle of 35.59°(2θ).Wis the breadth of the observed diffraction peak at its half height,Kis the so-called shape factor(usually approximately 0.89),andλis the wavelength of the X-ray source used(0.154 nm by our measurement).TheDvalue based on the Debye-Scherrer equation is consistent with that obtained from the SEM and TEM observations.
3.2 FTIR characterization
All spinels,particularly ferrites,show two characteristic bands in their infrared spectra.The higher bandν1,observed from 600 to 550 cm-1,corresponds to intrinsic stretching vibrations of the metal at the tetrahedral site Mtetra?O.The lower bandν2,which is observed from 450 to 385 cm-1,corresponds to octahedral metal stretching Mocta?O.25Thus,the absorption bandν1is caused by stretching vibrations of the tetrahedral metal-oxygen bond,whereas the absorption bandν2is caused by metal-oxygen vibrations at the octahedral sites.
Fig.2 shows an absorption band located at 598 cm-1,which is assigned to the tetrahedral metal stretching vibrations.Another band is observed at 412 cm-1,corresponding to the octahedral metal stretching vibrations.These results agree with the data from the literature,25also confirmed by the data of XRD.The absorption band at 1622 cm-1is assigned to adsorbed water hydroxyl ions,that at 1125 cm-1is assigned to sulfate ions adsorbed on the surface of the particles,and that at 2366 cm-1is assigned to carbon dioxide.The absorption bands at 1026 and 3414 cm-1are attributed to stretching vibrations of C―O groups and O―H stretching vibrations,25respectively,indicating the activated carbon partially oxidized.
3.3 Morphology and spectific area
Fig.3 shows the TEM images of the NiFe2O4and AC-NiFe2O4samples.The elaborative observations found that the size of ACNiFe2O4particles is almost the same as that of NiFe2O4particles,being equal to about 10 nm.This diameter of AC-NiFe2O4particles is also close to that calculated by the Debye-Scherrer equation.However,Brunauer-Emmett-Teller(BET)surface area measurements show that the specific areas of theAC-NiFe2O4and NiFe2O4samples are very different,147.83 m2?g-1forAC-NiFe2O4and73.14 m2?g-1for NiFe2O4,showing the enhanced effect of the activated carbon in specific area.
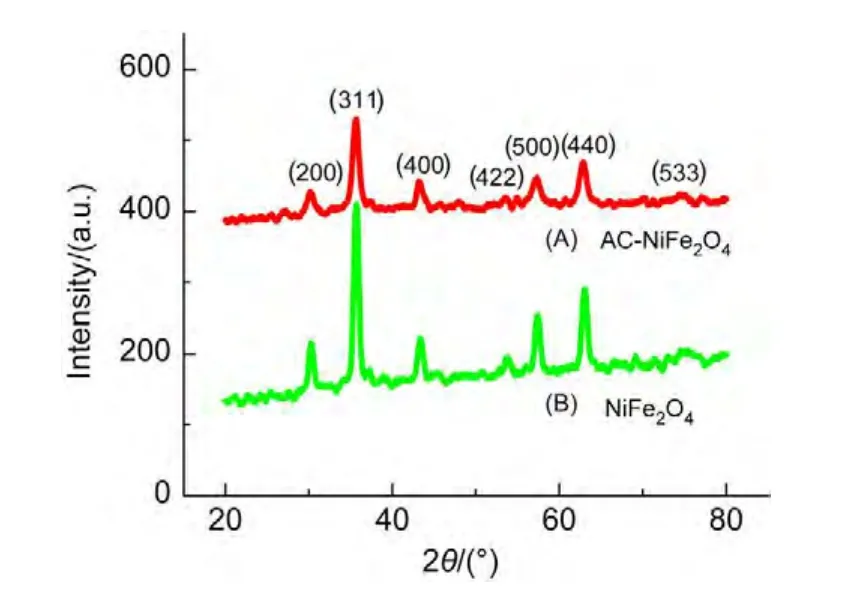
Fig.1 XRD patterns of the samples
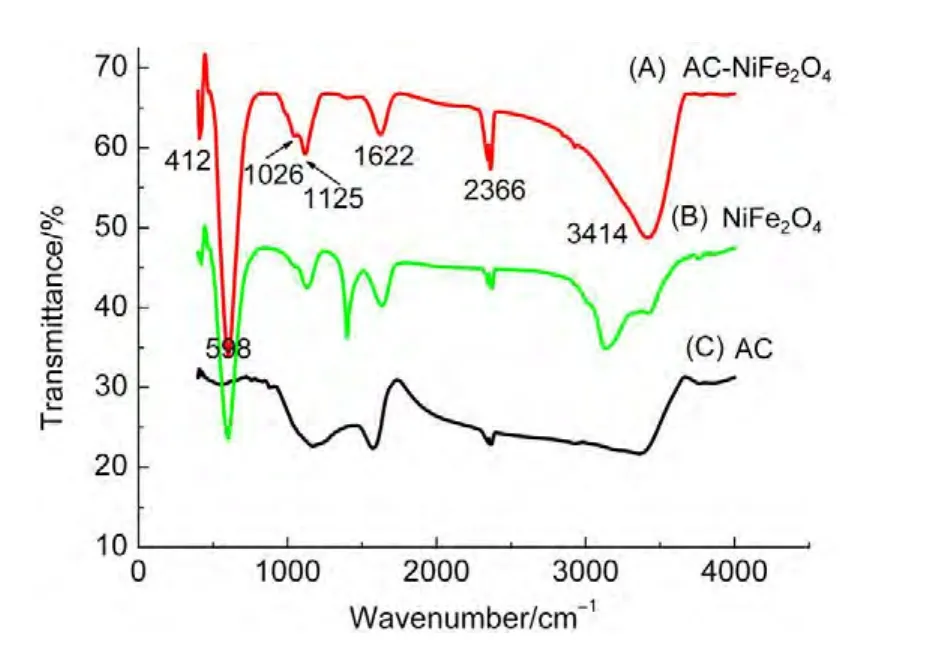
Fig.2 FTIR spectra of the samples
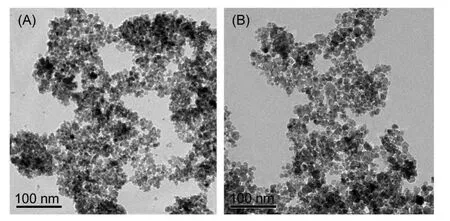
Fig.3 TEM images of the NiFe2O4(A)and AC-NiFe2O4(B)samples
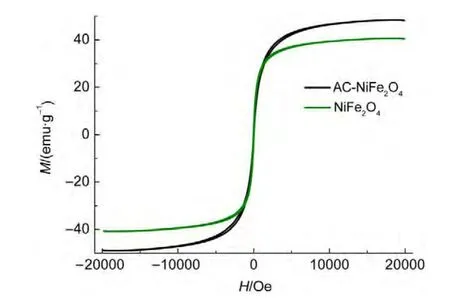
Fig.4 Hysteresis loops for the NiFe2O4andAC-NiFe2O4 samples at room temperature
3.4 Magnetic characterization
Magnetization hysteresis loops of the as-synthesized ACNiFe2O4and NiFe2O4samples at room temperature were measured using a vibrating sample magnetometer,as shown in Fig.4.The saturation magnetization of AC-NiFe2O4is 48.4 emu?g-1,whereas that of NiFe2O4is 40.4 emu?g-1.The saturation magnetization of the AC-NiFe2O4sample is larger than that of the NiFe2O4sample,showing that the activated carbon enhances the order of the microstructure for NiFe2O4particles.
4 Degradation of ammonia by AC-NiFe2O4 catalyst
4.1 Photo-Fenton degradation of ammonia in the presence of H2O2
Fig.5 presents the degradation curves of ammonia using ACNiFe2O4and NiFe2O4as catalysts in the presence or absence of H2O2under visible light irradiation or in dark in solutions with pH 10.5.Curve 1 shows an abatement of 91.0%for ammonia using AC-NiFe2O4as the Fenton-like catalyst in the presence of 1.0 mmol?L-1H2O2under visible light irradiation,while only an abatement of 30.0%(curve 2)for ammonia using NiFe2O4as the catalyst under similar conditions in 10 h.The results indicate that the AC-NiFe2O4catalyst is capable of responding to visible light and the activated carbon plays an indispensable role in absorbing visible light.

Fig.5 Photo-Fenton degradation of ammonia in 50.0 mLsolutions
Curve 3 shows a low abatement efficiency of 24.0%after a 10.0 h irradiation in the absence of the AC-NiFe2O4catalyst.Compared with this curve,curve 1 indicates that the AC-NiFe2O4material plays a vital role of catalyst.Curve 4 shows a low degradation ratio of 23.0%without H2O2under similar conditions.Compared with this curve,curve 1 indicates that the AC-NiFe2O4catalyst is capable of utilizing hydrogen peroxide to oxidize ammonia.
The abatement of 9.3%in dark at 10.0 h(curves 6)shows that ammonia can be adsorbed on the AC-NiFe2O4catalyst or be volatized a little.Curve 5 shows that hydrogen peroxide degraded ammonia slightly in the dark.Compared with curves 6 and 5,curve 1 indicates that the visible light irradiation plays a significant promotion role of degradation of ammonia.
4.2 Effects of AC content
A series of AC-NiFe2O4hybrid materials containing various mass concentrations of activated carbon from 0.0%to 8.0%were synthesized by the above mentioned methods,and the as-synthesized products were utilized as the photo-Fenton catalyst for the degradation of ammonia.The degradation curves were shown in Fig.6.The results show that at the initial stage the degradation ratio increases as the mass concentration of AC rises in the composite,the degradation ratio reaches a top of 86.0%when the AC content is equal to 4.0%.Then,the degradation ratio starts to fluctuate when the AC content continues to increase.Both 6.0%and 8.0%contents of AC do not result in any expected increase of degradation ratio.Contrary to what it was expected,the degradation ratio decreased slightly.Thus,an optimal mass concentration of AC is equal to 4.0%in the composite catalyst for the degradation of ammonia.The reason for the fluctuation could involve the adsorption of ammonia on nickel ferrite.On the one hand,the increase of AC content in the composite catalyst can improve the absorption to visible light,resulting in promoting the degradation rate for ammonia.On the other hand,the overload of AC could inhibit the adsorption of ammonia on the surface of nickel ferrite catalyst because AC decreased the concentration of transition metal atoms exposed on the surface of the composite catalyst.

Fig.6 Effect of the content of activated carbon on degradation ratio of ammonia under visible light irradiation
4.3 Effects of pH
The pH value of solutions is capable of greatly affecting the degradation rate,even standstill due to protonation of ammonia in acidic solutions.Thus,ammonia solutions with various pH values were utilized to examine the photo-catalytic degradation efficiency shown in Fig.7.The results indicated that the solutions with pH value less than 9.0 have very low degradation ratios.A pH 7.0 solution has only 10.0%of the degradation ratio for ammonia,another pH 8.0 solution responds to a 14.0%of degradation ratio.However,the solutions with pH value larger than or equal to 9.0 yield high degradation ratios.And the degradation ratio increases with the incease of pH value.The 86.0%degradation ratio was achieved in pH 10.5 solution while only the 10.0%degradation ratio in pH 7.0 solution.
For phenomenon,it is attributed to the protonation of ammonia.11The pKaof NH4+is equal to 9.3,so it is predominantly protonated in pH<9.3 solutions.The protonated ammonia is charged positively,which is not easy to coordinate to the nickel ferrite surface.The higher pH values of solutions favor to adsorption of ammonia on the catalyst.Thus,the degradation rate is faster and faster with the increase of pH value in solutions.In addition,the hydroxyl radicals(?OH)can oxidize NH3but not NH4+,26the more concentration of NH3led to the faster degradation rate in a higher pH solution.
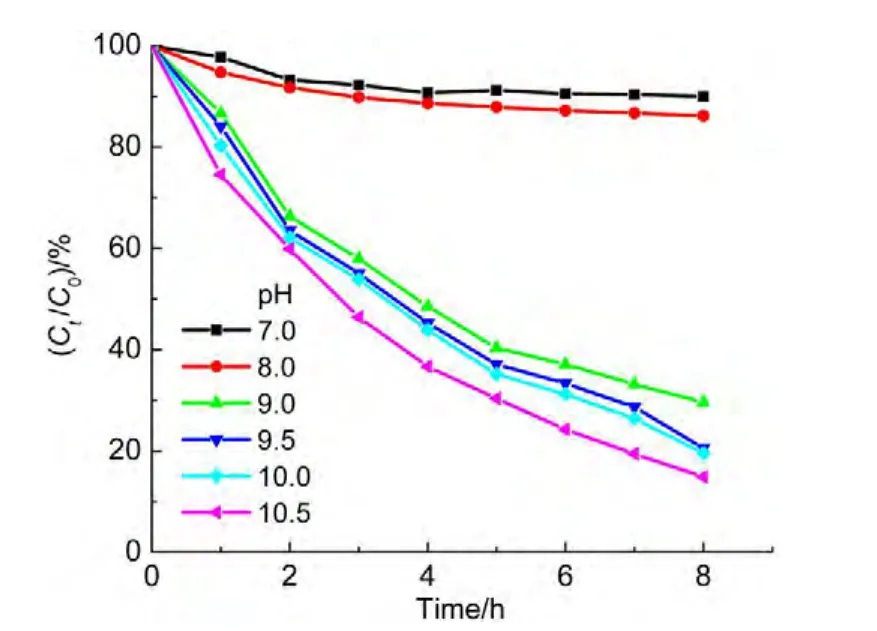
Fig.7 Effect of pH values on degradation ratio of ammonia during photo-Fenton process
4.4 Effects of H2O2concentration
In order to obtain the optimal concentration of H2O2,a series of solutions containing 0.5,1.0,and 10.0 mmol?L-1H2O2solution were tested.The results showed that at 8.0 h the degradation ratios for ammonia approached to 71.3%,86.0%,and 87.0%with respect to three concentrations of H2O2,respectively.As seen in Fig.8,the degradation ratio for ammonia rose with the increase of H2O2concentration.However,the degradation ratio of ammonia did not go up sharply when the concentration of H2O2is more than 1.0 mmol?L-1.Compared with the concentration of 1.0 mmol?L-1,a 10-fold H2O2concentration resulted only in a rise of 1.0%in the degradation ratio of ammonia.Thus,the concentration of 1.0 mmol?L-1H2O2is proper in economy.
4.5 Effects of catalyst loading
The impact of AC-NiFe2O4dosage on the degradation of ammonia was investigated in the range of 2.0-6.0 g?L-1(0.1-0.3 g in 50 mL solution).As shown in Fig.9,the degradation efficiency increased with the catalyst dosage up to 4.0 g?L-1,and then slightly decreased upon further addition of the catalyst.The phenomenon is similar to that reported by literature.27,28The inhibition effect of iron species is considered as the reason for this decrease because the scavenging of hydroxyl radicals or other radicals will occur when excessive catalyst is exposed to the radicals,which can be expressed by the following equations.29,30
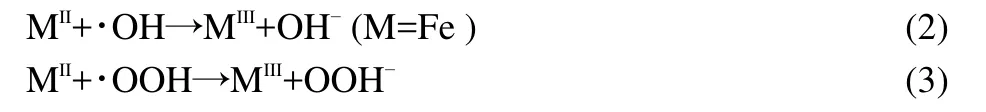
4.6 Effects of Anions
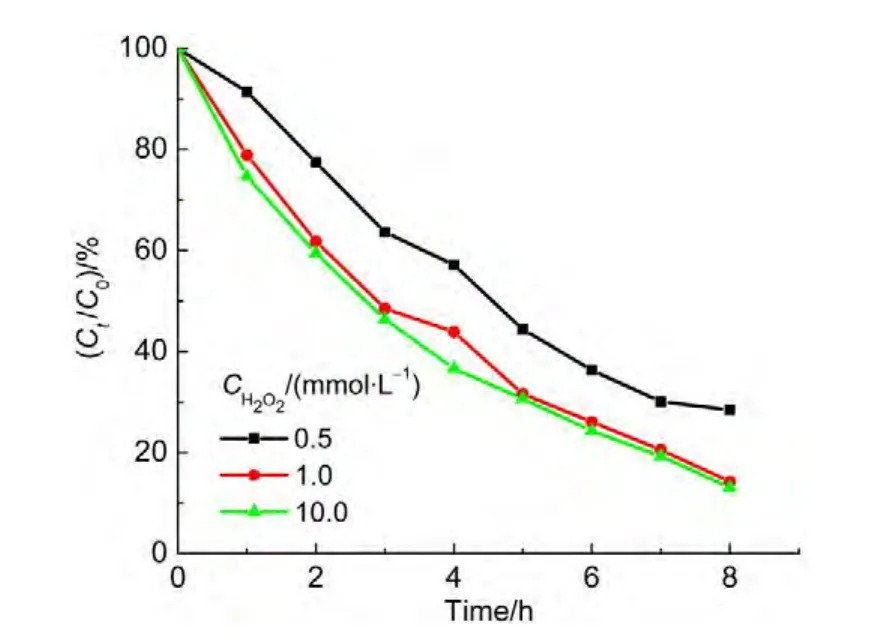
Fig.8 Effect of initial concentrations of H2O2on degradation ratio of ammonia
Fig.10 demonstrates the dependence of the degradation ratio on the different anions under similar conditions.As seen in Fig.10,the degradation ratios of ammonia are slightly different in the presence of such anions,The order of the degradation rate followssuggesting the acceleration of degradation of ammonia in the presence of chloride.The reason is that chloride ions are oxidized by hydroxyl radicals to[ClOH]-?(Eq.(4)),subsequently,the ClO-species are formed(Eq.(5)).31,32Finally,ammonia is removed quickly33by equations(6)and(7).
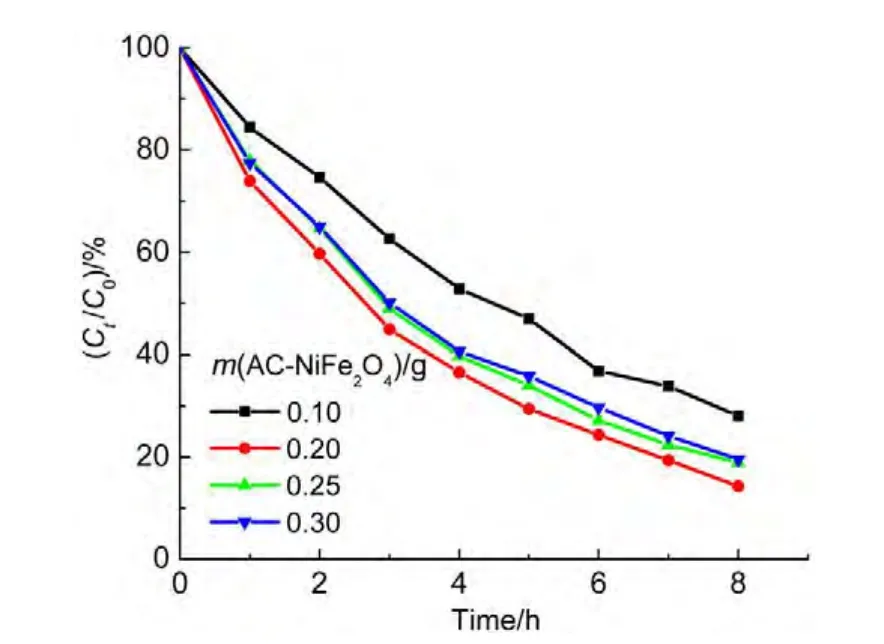
Fig.9 Influence of AC-NiFe2O4catalyst dosage on the degradation ratio of ammonia

4.7 Stability and reuse
The cyclic tests were performed in order to evaluate the catalytic activity and stability during a series of experiments and to observe the possibility of catalyst reuse.The catalyst was tested in eight consecutive experiments by using the fresh ammonia solutions under conditions(50.0 mg?L-1ammonia,1.0 mmol?L-1H2O2with pH 10.5,and 0.2 g catalyst in 50.0 mL solution).The reaction time was about 8 h each run.At the end of the previous experiment,the catalyst was collected by using an external magnetite,and then separated and washed with deionized water for three times.It was observed that the degradation rate was almost unchanged for eight runs(Fig.11),indicating that theACNiFe2O4catalyst is very stable,recoverable and reusable.A XRD measurement was also conducted on the hybrid catalyst after the photocatalytic reaction,the result showed that the positions of major peaks are almost unchanged(not shown here),confirming the stability of the catalyst again.
The leaching tests showed that it is very difficult for iron leaching due to forming the hydrolysis of iron ions in the alkali solutions.As a matter of fact,the concentration of iron ions is very low(2.9×10-5mol?L-1),even if nickel ferrite is in an acidic medium of pH 3.0,this value is far lower than that of leaching from Fe2O3.2Hence,the iron leaching during the reaction is negligible.
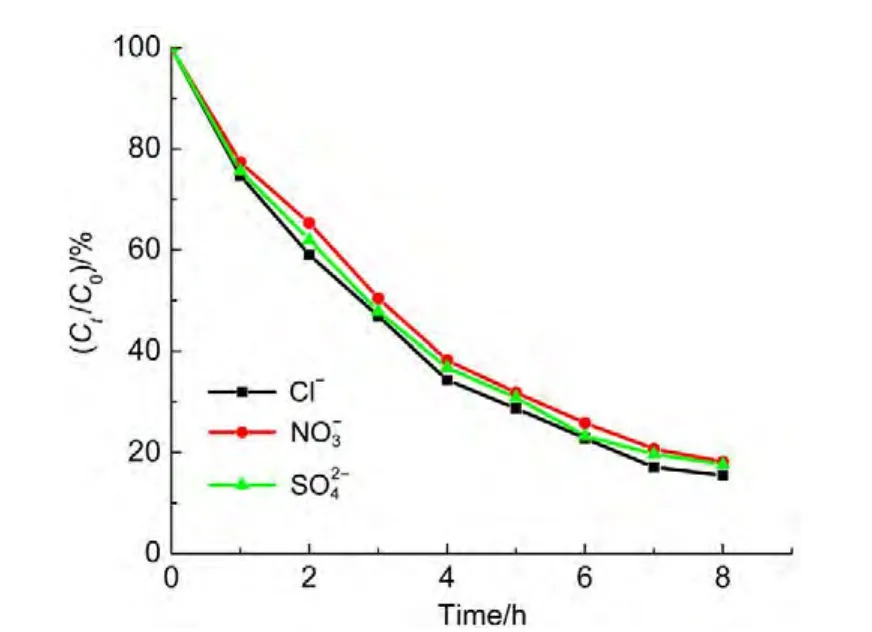
Fig.10 Effect of anions on degradation of ammonia
4.8 Kinetic analysis
The initial concentration of ammonia was varied as desired while the concentration of 1.0 mmol?L-1H2O2,0.2 g catalyst in 50.0 mL solution with pH 10.5 were constant.The degradation curves for the various ammonia concentrations were shown in Fig.12.The studies showed that the ammonia degradation follows a pseudo-first order kinetic law.The parameter ln(C0/Ct)is linearly proportional to the irradiation timet,shown in Fig.13.According to the integral equation(8)and experimental data,the average value of an apparent rate constantkappcan be obtained,which is equal to 3.538×10-3min-1.

4.9 Reaction mechanism
There are two pathways for the oxidization of ammonia after ammonia is adsorbed on the catalyst surface.34,35The one is through a series of NH2,NH,N2Hx+y(x+y=0,1,2)intermediates including hydrazine to release nitrogen gas.The other one is through HONH2,NO2-intermediates,finally,to form nitrate ions.These two pathways could be denoted as follows
Reaction pathway 1:

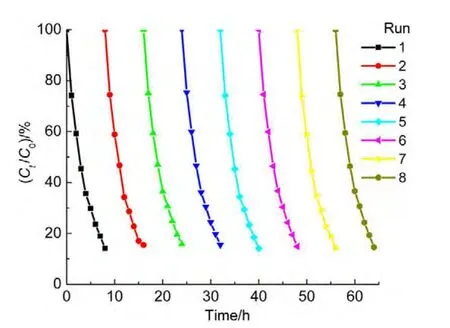
Fig.11 Cyclic tests of AC-NiFe2O4catalyst for stable check
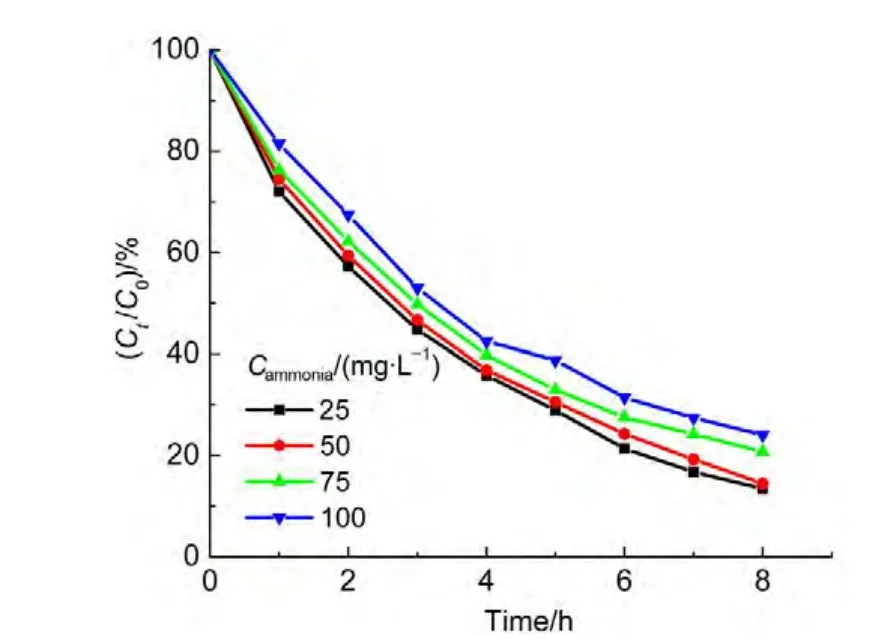
Fig.12 Effects of the initial concentrations of ammonia on degradation rate
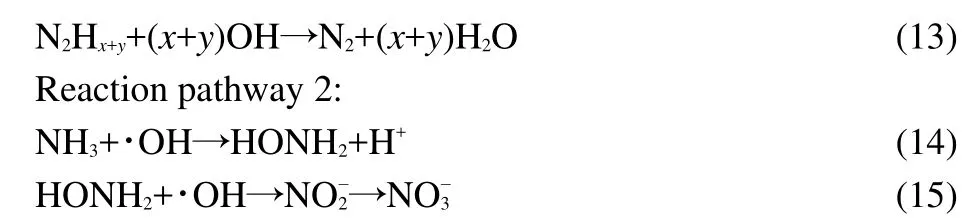
The absorption peaks for NO3?and NO2?anions are at 203 and 210 nm,respectively.To decline the interference of NO3?,the absorbance at 220 nm was measured.Atest for the degradation of ammonia was performed.The results showed that the absorbance for nitrite increased from zero to 1.63 over the irradiation time,whereas the absorbance for ammonia decreased from 1.68 to 0.12 shown in Fig.14,indicating the major product ofyielded by oxidization of ammonia.In order to confirm the oxidization pathway of ammonia,p-dimethylamino-benzaldehyde,a chromogenic agent for hydrazine intermediate(it will lead to absorbance at 460 nm if there is hydrazine in solution),was utilized to detect if there was any hydrazine intermediate during photo-Fenton degradation of ammonia.The result showed that no hydrazine was found.Therefore,consideration of abatement of ammonia in solution in dark(curve 6 in Fig.5),the mechanism for ammonia oxidization suggested that ammonia was first adsorbed on the catalyst surface,then,it was oxidized through HONH2tounder visible light irradiation.
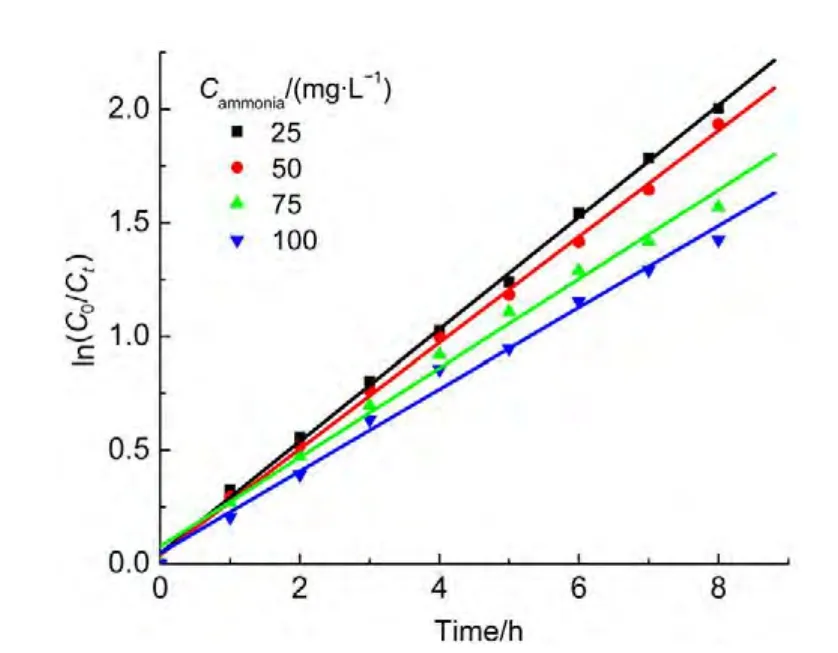
Fig.13 Dependence of ln(C0/Ct)on irradiation time for ammonia degradation
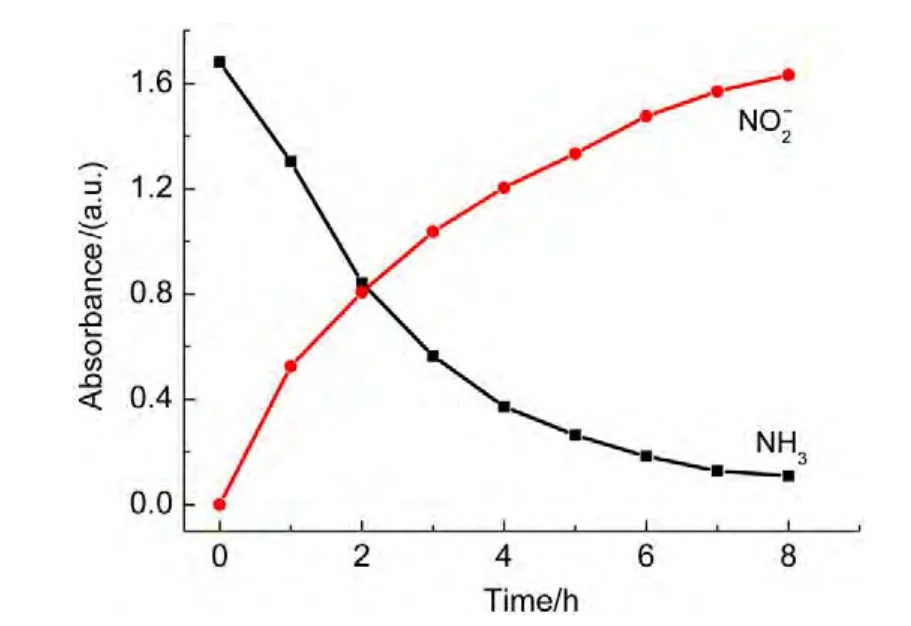
Fig.14 Dependence of absorbance for nitrite anions on irradiation time
Compared with that of the NiFe2O4sample,the diffuse reflection spectrum of theAC-NiFe2O4catalyst shows a red shift and an enhanced absorption of visible light shown in Fig.15,indicating that AC-NiFe2O4can utilize visible light more effectively than NiFe2O4for photocatalytic degradation of ammonia.Another photoelectrochemical test showed that the NiFe2O4composite on indium tin oxide(ITO)glass electrode has no photo-currents(not shown)at 0.8 V(vsSCE)in 0.1 mol?L-1Na2SO4solution,suggesting that the photocatalytic process is a photo-Fenton process.Thus,the electron transfer mechanism may be suggested as follows shown in Fig.16.
There are graphene sheets in activated carbon materials,and grapheme sheets are semiconductor materials,when photons hit on the semiconductor materials,a fraction of the incident photon flux provokes the photo-generated electrons,which will diffuse through the graphene sheets to the Fe 3dorbital.Therefore,photons trigger the catalytic reaction.The role of the graphitic sheets of carbons would be of paramount importance for the migration of the photo-generated electrons,minimizing recombination,and favoring the electron transfer to the Fe 3dorbital to form Fe(II)ions.36-39Therefore,the activated carbon plays the role in absorbing photons,forming photo-generated electrons,and transferring the photo-generated electrons to the Fe 3dorbital.When H2O2approached Fe(II)ions diffusively,the reaction oc-curred to yield radicals?OH,thus,triggering the Fenton oxidization process by Eq.(14).
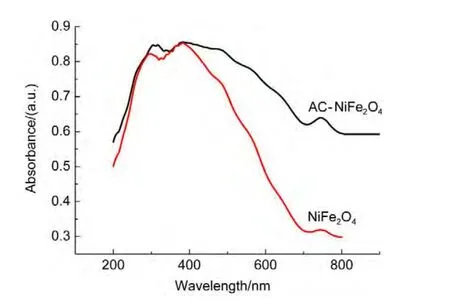
Fig.15 Diffuse reflectance spectra of AC-NiFe2O4and NiFe2O4
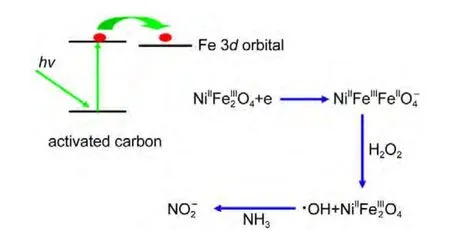
Fig.16 Photochemical process mediated by activated carbon in theAC-NiFe2O4material
5 Conclusions
Activated carbon-Nickel ferrite hybrid can be utilized as a heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst to degrade ammonia in the presence of hydrogen peroxide under visible light irradiation.Activated carbon plays a vital role in absorption of visible light.The oxidization pathway for ammonia is through HONH2intermediate to form nitrite ions.The kinetic studies show that the oxidization of ammonia follows the pseudo-first order kinetic law,the rate constant is equal to 3.538×10-3min-1.Eight runs show the catalyst is very stable,recoverable,separable and reusable,suggesting its potential application at the disposal of ammonia.
(1) Costa,R.C.C.;Lelis,M.F.F.;Oliveira,L.C.A.;Fabris,J.D.;Ardisson,J.D.;Rios,R.R.V.A.;Silva,C.N.;Lago,R.M.J.Hazard.Mater.B2006,129,171.doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.028
(2)Liu,S.Q.;Feng,L.R.;Xu,N.;Chen,Z.G.;Wang,X.M.Chem.Eng.J.2012,203,432.doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.071
(3)Fu,Y.S.;Chen,H.Q.;Sun,X.Q.;Wang,X.AIChE J.2012,58,3298.doi:10.1002/aic.13716
(4)Pan,X.;Fu,Y.;Wang,L.;Wang,X.Chem.Eng.J.2012,149,195.
(5)Nguyen,T.D.;Phan,N.H.;Do,M.H.;Ngo,K.T.J.Hazard.Mater.2011,185,653.doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.068
(6)Xu,X.;Wang,X.J.;Hu,Z.H.;Liu,Y.F.;Wang,C.C.;Zhao,G.H.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2010,26,79.[徐 鑫,王曉靜,胡中華,劉亞菲,王晨晨,趙國(guó)華.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報(bào),2010,26,79.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB20100131
(7)Yang,H.P.;Zhang,Y.C.;Fu,X.F.;Song,S.S.;Wu,J.M.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2013,29,1327.[楊漢培,張穎超,傅小飛,宋雙雙,吳俊明.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報(bào),2013,29,1327.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201303212
(8)Long,M.;Cong,Y.;Li,X.K.;Cui,Z.W.;Dong,Z.J.;Yuan,G.M.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2013,29,1344.[龍 梅,叢 野,李軒科,崔正威,董志軍,袁觀明.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報(bào),2013,29,1344.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201303263
(9)Xing,W.N.;Ni,L.;Yan,X.S.;Liu,X.L.;Luo,Y.Y.;Lu,Z.Y.;Yan,Y.S.;Huo,P.W.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2014,30,141.[邢偉男,倪 良,顏學(xué)升,劉馨琳,羅瑩瑩,逯子揚(yáng),閆永勝,霍鵬偉.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報(bào),2014,30,141.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201311211
(10)Ou,H.H.;Hoffmann,M.R.;Liao,C.H.;Hong,J.H.;Lo,S.L.Appl.Catal.B2010,99,74.doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.06.002
(11) Bonsen,E.M.;Schroeter,S.;Jacobs,H.;Broekaert,J.A.C.Chemosphere1997,35,1431.doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00216-6
(12)Altomare,M.;Chiarello,G.L.;Costa,A.;Guarino,M.;Selli,E.;Chem.Eng.J.2012,191,394.doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.03.037
(13)Kominami,H.;Nishimune,H.;Ohta,Y.;Arakawa,Y.;Inaba,T.Appl.Catal.B2012,111,297.
(14) Kolinko,P.A.;Kozlov,D.V.Appl.Catal.B2009,90,126.doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.03.001
(15) Boulinguiez,B.;Bouzaza,A.;Merabet,S.;Wolbert,D.J.Photochem.Photobiol.A2008,200,254.doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2008.08.005
(16) Zhu,X.;Nanny,M.A.;Butler,E.C.Water Res.2008,42,2736.doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.02.003
(17) Shavisi,Y.;Sharifnia,S.;Hosseini,S.N.;Khadivi,M.A.J.Ind.Eng.Chem.2014,20,278.doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2013.03.037
(18) Dong,Y.;Bai,Z.;Liu,R.;Zhu,T.Atmos.Environ.2007,41,3182.doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.08.056
(19)Geng,Q.;Guo,Q.;Cao,C.;Zhang,Y.;Wang,L.Ind.Eng.Chem.Res.2008,47,4363.doi:10.1021/ie800274g
(20) Gou,H.H.;Liao,C.H.;Liou,Y.H.;Hong,J.H.;Lo,S.L.Environ.Sci.Technol.2008,42,4507.doi:10.1021/es703211u
(21) Altomare,M.;Selli,E.Catalysis Today2013,209,127.doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2012.12.001
(22) Niedzielski,P.;Kurzyca,I.;Siepak,J.Anal.Chim.Acta2006,577,220.doi:10.1016/j.aca.2006.06.057
(23) Lazarevic,Z.Z?.;Jovalekic,C.;Recnik,A.;Ivanovski,V.N.;Milutinovic,A.;Romcevic,M.;Pavlovic,M.B.;Cekic,B.;Romcevic,N.Z?.Mater.Res.Bull.2013,48,404.doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.10.061
(24) Klug,H.P.;Alexander,L.E.X-Ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials,2nd ed.;Wiley:New York,1974.
(25) Mouallem-Bahout,M.;Bertrand,S.;PeHa,O.J.Solid State Chem.2005,178,1080.doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2005.01.009
(26) Hoigne,J.;Bader,H.Environ.Sci.Technol.1978,12,79.doi:10.1021/es60137a005
(27) Liao,Q.;Sun,J.;Gao,L.Colloids Surf.A2009,345,95.doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.04.037
(28) Romero,A.;Santos,A.;Vicente,F.J.Hazard.Mater.2009,162,785.doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.123
(29) Ramirez,J.H.;Maldonado-Hódar,F.J.;Pérez-Cadenas,A.F.;Moreno-Castilla,C.;Costa,C.A.;Madeira,L.M.Appl.Catal.B2007,75,312.doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.05.003
(30)Lam,S.W.;Chiang,K.;Lim,T.M.;Amal,R.;Low,G.K.C.J.Catal.2005,234,292.doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2005.06.014
(31) Bacardit,J.;Sto1tzner,J.;Chamarro,E.Eng.Chem.Res.2007,46,7615.doi:10.1021/ie070154o
(32) Machulek,A.,Jr.;Moraes,J.E.F.;Carolina,Vautier-Giongo.;Silverio,C.A.;Friedrich,L.C.;Nascimento,C.A.O.;Gonzalez,M.C.;Quina,F.H.Environ.Sci.Technol.2007,41,8459.doi:10.1021/es071884q
(33) Li,M.;Feng,C.;Zhang,Z.;Zhao,R.;Lei,X.;Chen,R.;Sugiura,N.Electrochim.Acta2009,55,159.doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2009.08.027
(34) Zhu,X.;Castleberry,S.R.;Nanny,M.A.;Butler,E.C.Environ.Sci.Technol.2005,39,3784.doi:10.1021/es0485715
(35) Lee,J.;Park,H.;Choi,W.Environ.Sci.Technol.2002,36,5462.doi:10.1021/es025930s
(36) Velasco,L.F.;Fonseca,I.M.;Parra,J.B.;Lima,J.;Ania,C.O.Carbon2012,50,249.doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2011.08.042
(37) Leary,R.;Westwood,A.Carbon2011,49,741.doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2010.10.010
(38) Liu,S.Q.;Xiao,B.;Feng,L.R.;Zhou,S.S.;Chen,Z.G.;Liu,C.B.;Chen,F.;Wu,Z.Y.;Xu N.;Oh,W.C.;Meng,Z.D.Carbon2013,64,197.doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.07.052
(39)Guo,S.;Zhang,G.K.;Guo,Y.D.;Yu,J.C.Carbon2013,60,437.doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.04.058

