Kinetics of Reaction-Crystallization of Struvite in the Continuous Draft Tube Magma Type Crystallizers—Influence of Different Internal Hydrodynamics
Joanna Koralewska, Krzysztof Piotrowski, Boguslawa Wierzbowska and Andrzej Matynia
?
Kinetics of Reaction-Crystallization of Struvite in the Continuous Draft Tube Magma Type Crystallizers—Influence of Different Internal Hydrodynamics
Joanna Koralewska1, Krzysztof Piotrowski2,*, Boguslawa Wierzbowska1and Andrzej Matynia1
1Department of Chemistry, Wroclaw University of Technology, 50-370 Wroclaw, Poland2Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, Silesian University of Technology, 44-101 Gliwice, Poland
reaction-crystallization, struvite, phosphorus recycling, nucleation, crystals growth, DTM MSMPR crystallizers, size-dependent growth kinetics, liquid jet pump, propeller agitator
1 INTRODUCTION
The new, original constructions of jet-pump crystallizers can be generally classified as DTM (draft tube magma) type units [1]. A jet-pump situated inside the crystallizer provides good mixing of the circulated suspension, thus enables one to receive a non-classified product of representative crystal size distribution (CSD). It may be approximately assumed that such apparatus fulfills the requirements of MSMPR (mixed suspension mixed product removal) crystallizer [2]. Essential advantages of a jet-pump crystallizer include absence of troublesome moving (especially rotating) elements and practical utilization of simple hydrodynamic phenomena. This results in lower probability of failure and relative simplicity in use [3].

Figure 1 A general scheme of the three crystallizer constructions under study
1—feeding inlet; 2—pH-correction agent inlet; 3—outlet of crystal suspension
Internal circulation of suspension generated by liquid jet-pump device is based on advantageous hydrodynamic effects connected with the merge of two circulated streams (see Fig. 1). It causes relatively fast and effective blending of the reagents, resulting in homogenization of concentration and temperature in the process environment, as well as prevention of excessive agglomeration of crystals. Incrustation inside the apparatus body is also strongly inhibited to achieve longer failure-free exploitation time possible.
Jet-pump crystallizers have been designed and adopted for various mass crystallization processes [3], including the most complex reaction-crystallization ones (barium sulphate [4, 5], hydroxyapatite [6, 7] and struvite [6, 8, 9]).
The experimental data concerning reaction- crystallization of struvite in two continuous laboratory liquid jet-pump crystallizers of various internal hydrodynamic regimes [denoted as DTM↑ and DTM↓, see Figs. 1 (a) and 1 (b)] and—for comparison purposes—in a crystallizer equipped with a propeller agitator [1] [denoted later as DT—see Fig. 1 (c)] are presented in this study. Laboratory test stand was precisely controlled by automatic control system driven by PC computer. Nucleation and growth rates of struvite crystals were estimated from the population density distributions of crystal product taking into account size-dependent growth (SDG) kinetic mechanism.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
2.1 Setup and procedure
The simplified schemes of laboratory crystallizers used in the present research are shown in Fig. 1:
A liquid jet-pump device [Figs. 2 (a), 2 (b)] installed in the laboratory crystallizers is characterized by the following dimensions:
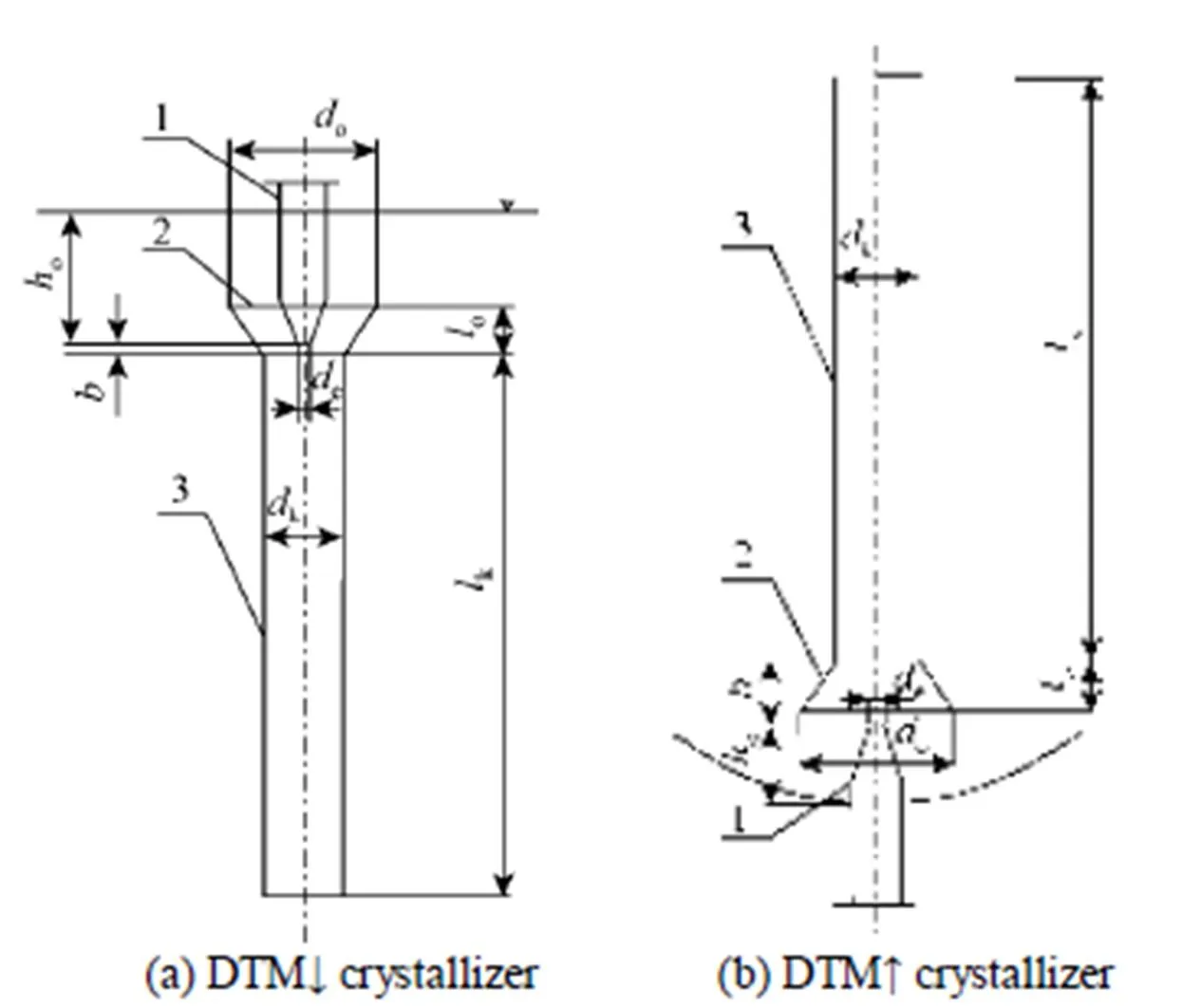
Figure 2 Liquid jet-pump device applied in a laboratory DTM↓ and DTM↑ crystallizers under study
1—feeding nozzle; 2—confusor; 3—mixing chamber

Figure 3 Connection scheme of a test stand for reaction-crystallization of struvite
1—DTM↓ crystallizer with internal circulation of suspension; 2—circulating pump; 3—rotameters; 4—heat exchanger; 5—PC computer; 6—feeding tank (MgCl2solution blended with NH4H2PO4solution); 7—peristaltic pump; 8—alkaline agent’s tank (NaOH solution); 9—NaOH dosing pump; 10—pump for removal of crystal suspension from the crystallizer; 11—storage tank for crystal product suspension; 12,13,14—electronic balances; pH—control of the reaction environment’s pH; T—temperature control
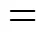
The experiments were carried out under the predetermined, constant conditions:
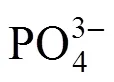
Minimal unit power of a jet-pump feeding stream (however sufficient enough for stable circulation of suspension) was used [19, 20]. Its value can be calculated using the following equation:

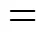
Continuous reaction-crystallization process of struvite was run through the time of 5starting from the moment as the assumed parameter values stabilized. After this period the solid phase concentration in the product suspension (T) and its crystal size distribution (CSD) (laser particle size analyzer COULTER LS-230) were determined. Chemical analysis of mother liquor (plasma emission spectrometer ICP-AES Philips PU 7000) and solid phase (spectrometer IR Philips PU 9712) were done as well.
2.2 Reaction-crystallization kinetics
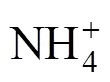
For the basic, simplified approach to the mass crystallization process kinetics, assuming steady state in a continuous crystallizer with ideally mixed content and withdrawal of a non-classified, representative product (MSMPR type crystallizer), the population balance equation can be formulated in a general form of simple differential equation [21]:
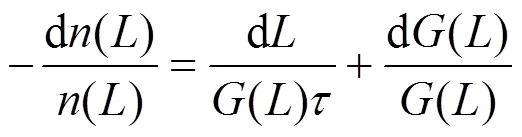
This characteristic behavior can be theoretically interpreted as the symptom of a complex kinetic mechanism—Size-Dependent Growth (SDG). Its consequence—a nonlinear increase in the number of fines—is very essential from the practical point of view since within this size range the largest fraction of the overall crystals number is located. Considering fine-grained morphology, this crystal fraction characterizes itself by the largest specific surface area in respect to the whole population. A more detailed description of the process kinetics, considering the SDG mechanism, thus rendering the experimentally observed strong nonlinearity of ln() function course for struvite crystals of<10mm requires assuming some form of() dependency before solving the general population balance equation of MSMPR crystallizer, Eq. (2).
Empirical or semiempirical() equations [22-29] were analyzed in detail [30]. Theoretical analysis regarding mathematical construction of these functions proved that equations proposed in Refs. [22, 28, 29] are valid only for the crystals of finite size. Assumption of zero-size nucleus makes its further growth impossible from mathematical point of view. Thus, for practical application of these formulas it becomes necessary to assume arbitrarily starting size for nucleusz, which value can introduce some unpredictable calculation error.
Selected analytical solutions of Eq. (2), derived as() expressions comply with the assumed() forms, are presented below [30]:
Abegg, Stevens and Larson (ASL) model [24], Eqs. (3), (4) and (6):
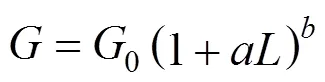
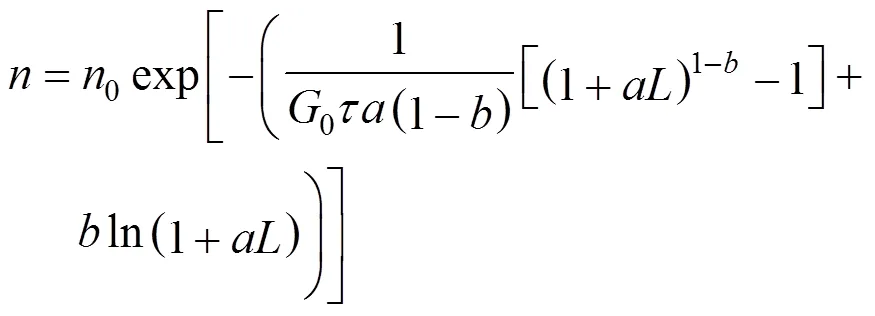
Canning-Randolph (CR) model [23], Eqs. (5) and (6):
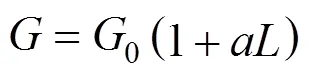
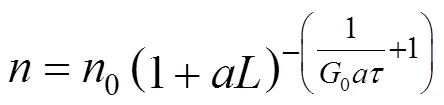
Rojkowski exponential (RE) model [25], Eqs. (7) and (8):
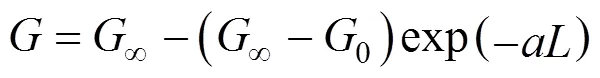
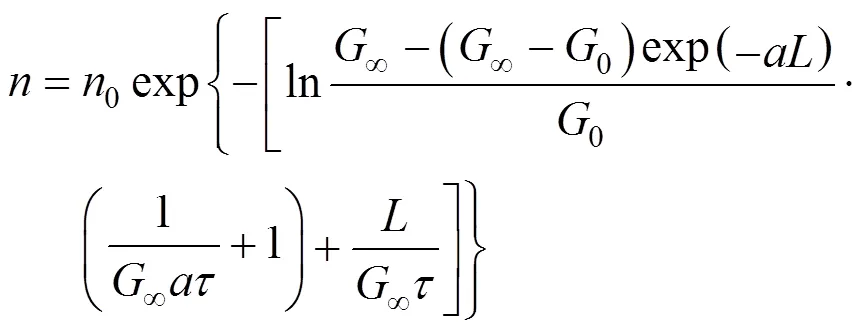
Rojkowski hyperbolic (RH) model [26], Eqs. (9) and (10):

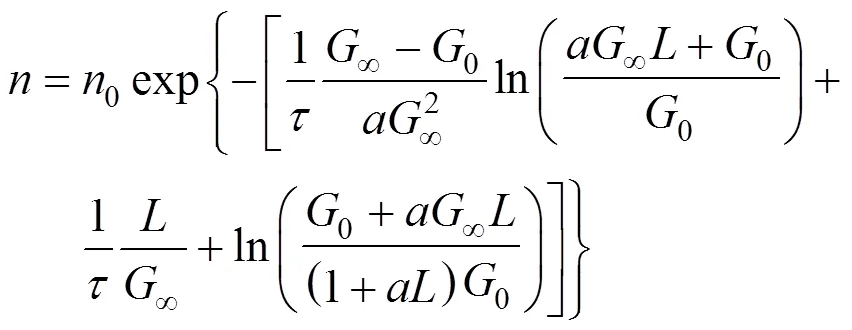
Rojkowski hyperbolic II (RH II) model [27], Eqs. (11) and (12):
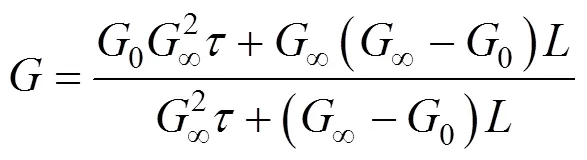
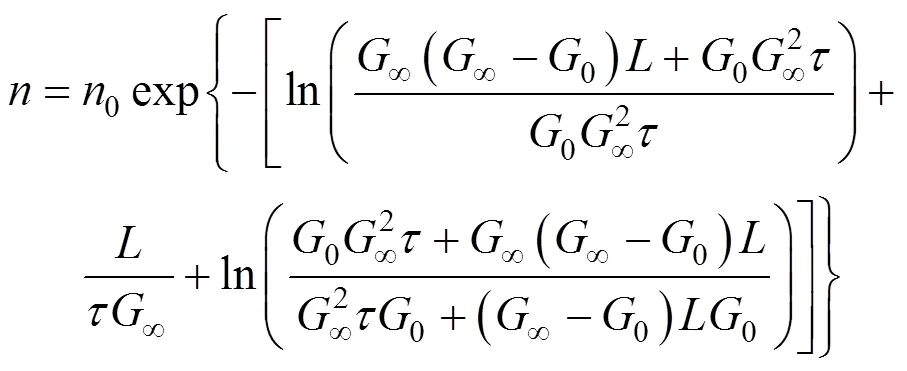
Knowing nuclei population density,0, and their linear growth rate,0, the (overall) nucleation ratecan be calculated from the following relation:
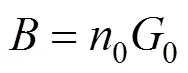
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Estimation of kinetic parameters of the model
On the basis of own experimental data the following parameters:0,0,¥,,values in() functions corresponded to the selected() equations were determined. For each() function (thus SDG model) and each experimental data set a mean square deviation (variance) was calculated by:
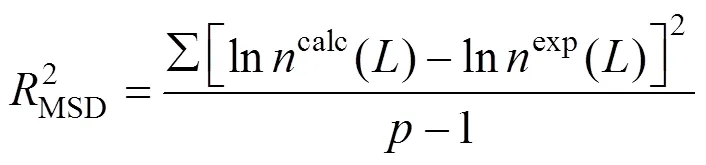
Table 1 Kinetic models of struvite crystallization in DTM↑, DTM↓ and DT crystallizers:??and??values for the selected SDG equations
3.2 DTM↑ crystallizer performance
Kinetic parameter values of reaction-crystallization process of struvite in a jet-pump DTM↑ crystallizer, calculated with the RH SDG model, can be summarized as follows. Increase in Mg2+ions mass concentration in a feeding solution from 0.25% to 2.0% results in:
Table 2 The values of nucleation and crystal growth rate for the selected SDG models acquired in DTM↑, DTM↓ and DT crystallizers (Struvite crystals obtained for Mg2+ ions mass concentration in a feeding solution equals to 0.25% atpH9, t900 s and kv1)
Table 3 The values of nucleation and crystal growth rate for the selected SDG models acquired in DTM↑, DTM↓ and DT crystallizers (Struvite crystals obtained for Mg2+ ions mass concentration in a feeding solution equals to 2.0% at pH9, t900 s and kv1)
Increase in maximal linear growth rate,¥, from 9.03×10-9to 2.11×10-8m·s-1;
Increase in nucleation rate,, from 9.40×1012to 1.63×1014m-3·s-1.
3.3 DTM↓ crystallizer performance
It can be supposed, that the main reason responsible for such behavior is the advantageously modified hydraulic regime of internal circulation. It influences the distribution of supersaturation within the process environment and suspension hydrodynamics. It should be noted, that in a DTM↓ type crystallizer (similarly to a DTM↑ construction) the smallest-size crystal mass fraction (3%-5%) reached the pump in external circulation loop. However, it did not visibly influence mean crystal size since in this configuration other kinetic effects predominated. Theoretical confirmation of these observations is provided in the form of kinetic parameter values corresponding to a DTM↓ apparatus type, as well as their interrelations. Increase in Mg2+ions mass concentration in a feeding solution (0.25%→2.0%) results—in this operation regime—in:
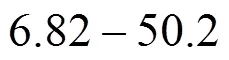
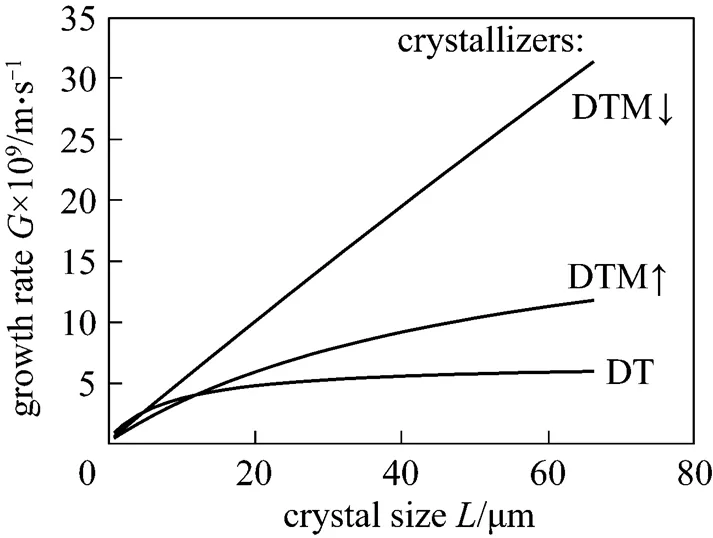
From this analysis it results that in a DTM↓ crystallizer the considerably higher values of maximal linear growth rate are attainable. In consequence the product crystals of nearly 2-times larger mean sizes (compared to DTM↑ and DT constructions) are obtained. Nuclei population density,0, as well as nucleation rate,, are clearly lower in a DTM↓ crystallizer compared to a DTM↑ one.
Lower mixing intensity, thus not effective enough blending of reagents with mother solution, leads to the occurrence of temporary, local supersaturation peaks responsible for higher nucleation rate in a DTM↓ crystallizer compared to a DT one (being free of these drawbacks). Attrition effects in external circulation pump contribute to this effect, as well. Elimination or at least significant reduction in these negative tendencies should be employed. Rational modification of DTM↓ construction can provide crystal product of higher quality.
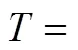
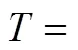
3.4 Size-dependent growth phenomena in DTM crystallizers
Character of() courses is qualitatively similar in DT and DTM↑ crystallizer types, where some rapid approach to an asymptotical, limiting¥value is observed. In case of DTM↓ constructionincreases practically linearly with crystal size within a 0<<80mm range, what corresponds to the larger mean sizes in a crystal product population (Fig. 5).
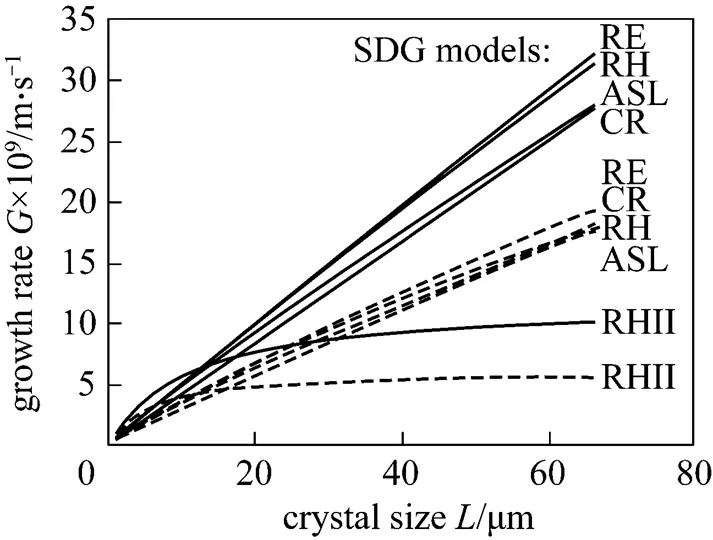
The() dependences for DTM↑ and DTM↓ constructions are presented in Figs. 6 and 7 for all five SDG models used [ASL, CR, RE, RH and RH II, Eqs. (3)-(12)]. Generally, from Fig. 6 it can be concluded that all five kinetic SDG models provide highervalues for higher [Mg2+]RMvalue within the whole size range tested (0-80mm). Relatively large initial increase in growth rate is observed (especially visible in RE, RH and RH II model courses where the maximal possibleis theoretically upper-limited by some asymptotical¥value; in case of CR and ASL models the theoretically unlimited() increase is observed). Contrary, different hydrodynamic regime in a DTM↓ construction is clearly demonstrated by modified arrangement of the() curves family in Fig. 7. Both RE and RH models present apparent linear courses, suggesting location of asymptotical¥value in a considerably higher level compared to a DTM↑ variant (see also differentscale in both figures). Generally, all SDG kinetic models from Fig. 7, except RH II model, provide higher() values in comparison with the data in Fig. 6. This confirms previous conclusions concerning a more convenient process environment for the crystal phase growth provided by a DTM↓ construction. The discrepancies between all five SDG model predictions for the analyzed systems are also visible in Table 1 (statistical analysis of variance).
Comparison between experimental and simulated PDDs proves, that the suggested SDG equation provides adequate description of ln() courses, both in characteristic, highly nonlinear segment corresponding to the smallest sizes and in apparently linear fragment for the larger ones. This flexibility enables one to apply a recommended SDG model in the calculation- design works, covering a more detailed estimation of cumulative distribution of specific surface area() or cumulative crystal mass distribution()—the “derivative relationships” based on the fundamental() course. Contrary, frequent application of oversimplified SIG (size-independent growth) kinetic model, based on the assumption of ln() function’s linearity in the whole crystal size range, thus excluding clear, nonlinear increment (even by several orders of magnitude) invalues within the smallest sizes, results in a significant accumulation of error thus incorrect prediction of(()) or(()) distributions within this the most interesting size range.
3.5 Hydrodynamic problems-overcoming suggestions
Among two jet-pump DTM crystallizer constructions tested: DTM↑ with a feeding nozzle situated in the apparatus bottom (upward circulation of suspension in a mixing chamber) and DTM↓ with a feeding nozzle located under free level of medium (downward circulation) a more convenient design proved to be a DTM↓ one. It was technically possible by appropriate arrangement of a DTM↓ crystallizer interior (.. appearance of the stable pseudo-fluidal layer in a “crystal growth zone”). Higher concentration of solid phase in a working volume acted here advantageously by creating local whirls, making better distribution of MAP supersaturation within the reaction environment possible. Relatively large specific surface area of crystal phase (positive influence of attrition—however considerably restricted) reduces the mass transfer resistances. It protects also against appearance of the excessive supersaturation peaks, thus improves the process stability. As a result, larger crystals were withdrawn from a DTM↓ construction, of the size increasing with the increase in Mg2+ions concentration in a feeding solution. Other considered criteria were: location and mode of introduction of a feeding solution, stability of operation and the final results (CSD of product). It should be emphasized, that both DTM crystallizers produce crystal populations of comparable or larger mean sizes than a DT crystallizer does.
The only disadvantage observed during laboratory- scale tests of jet-pump DTM crystallizers was undesirable presence of crystal fines in the external circulation loop (however of small mass fraction in relation to the whole suspension). It resulted in their appearance in a circulation pump (intensive attrition and breakage of crystals). Constructional corrections in a classical design,.. increase in a cross-section area of overflow part, can only slightly improve the separation effectiveness in a sedimentation zone. However, decrease in a removable size is not sufficient enough for the total elimination of this unintentional behavior for the sake of extreme small size range (even below 1mm) of particles created in reaction-crystallization processes. It seems that the only rational engineering strategy to provide larger product-crystals is to eliminate the external loop totally, providing jet-pump with compressed gas stream (.. air). In reaction- crystallization processes of struvite and hydroxyapatite application of air (aeration) is also well-grounded by technological requirements [10-12]. Application of compressed gas stream provides stable internal circulation coupled with efficient micro-and macromixing within the complex three-phase dispersed systems [31]. It should be noted, however, that in industrial-scale mass crystallization processes, where mean crystal sizes are several hundred times larger compared to the specific reaction-crystallization products, introduction of external circulation loop in a jet-pump DTM apparatussystem does not affect the process run and its results substantially while other advantages predominate.
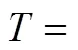
4 CONCLUSIONS
Experimentally verified RH SDG kinetic equation can be recommended for modeling of the struvite reaction-crystallization process in the presented conditions. It represents in practice the overall kinetics of closely integrated system: fast ionic reaction-struvite precipitation-MAP crystals growth, giving consideration to the essential dependency of growth kinetics on the crystal size, as well as incorporating the net effect of all, frequently opposite hydrodynamic and partial processes. Thus, adjusting the nucleation and growth kinetics by advisable modification of technological parameters vector it becomes possible to produce the crystal population of required CSD and quality, thus synthesize preliminary designed product demanding nofurther mechanical operations (.. milling, sieving,.).
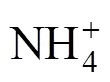
NOMENCLATURE
a parameter in ASL, CR, RE and RH SDG kinetic models, m-1
nucleation rate, m-3·s-1
exponent in ASL SDG kinetic model
efeeding nozzle diameter, m
() cumulative size-distribution of specific surface area of crystals, m2·m-3
linear growth rate of crystals, m·s-1
¥maximal linear growth rate of crystals, m·s-1
0minimal linear growth rate of crystals (growth rate of nuclei), m·s-1
spsolubility product of struvite, mol3·dm-9
vvolumetric shape factor of crystal
characteristic linear size of crystal, m
mmean size of crystal population, m
zlinear size of nucleus, m
Tconcentration of crystal phase in suspension, kgcryst·m-3
[Mg2+]RMmass concentration of magnesium ions in a feeding solution, %
() cumulative size distribution of crystals mass (undersize), kg·m-3
() population density (number of crystals within the specified size range in a unit volume of suspension per this size range width), m-1·m-3
calcpopulation density calculated, m-1·m-3
expexperimental population density, m-1·m-3
0population density of nuclei (zero-size crystals), m-1·m-3
euunit power of feeding stream, W·kg-1
number of experimental points
dedynamic pressure of feeding stream, Pa
vevolumetric flow rate of feeding stream, m3·s-1
vsvolumetric flow rate of crystal suspension, m3·s-1
MSDroot mean square deviation
process temperature, K
wcrystallizer working volume, m3
elinear velocity of feeding stream, m·s-1
solsolution density, kg·m-3
sussuspension density, kg·m-3
mean residence time of suspension in a crystallizer working volume (w/vs), s
1 Rojkowski, Z., Synowiec, J., Crystallization and Crystallizers, WNT, Warszawa (1991). (in Polish)
2 Mullin, J.W., Crystallization, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (1993).
3 Matynia, A., “Crystallizers with a jet pump”,..., 36 (6), 9-14 (1997). (in Polish)
4 Koralewska, J., Matynia, A., Piotrowski, K., Wierzbowska, B., “Precipitation of barium ions with solid ammonium sulphate in a continuous DTM crystallizer with liquid jet-pump of ascending suspension flow in a mixing chamber”,..., 27, 1555-1579 (2006).
5 Koralewska, J., Matynia, A., Piotrowski, K., Wierzbowska, B., “Crystallization of barium sulphate in a continuous DTM type crystallizer with a jet-pump of descending suspension flow in a mixing chamber”, In: Materials of the International Congress of Chemical and Process Engineering CHISA 2006, No. 278, Prague, Czech Republic (2006).
6 Matynia, A., Koralewska, J., Wierzbowska, B., Piotrowski, K., “Jet-pump crystallizers in the reaction-crystallization processes of sparingly soluble salts”,...., 7 (3), 56-64 (2005).
7 Koralewska, J., Matynia, A., Wierzbowska, B., Piotrowski, K., “Hydroxyapatite crystallization process in a DTM crystallizer of descending suspension flow in a mixing chamber”,...., 8 (3), 25-27 (2006).
8 Koralewska, J., Piotrowski, K., Wierzbowska, B., Matynia, A., “Nucleation and crystal growth rates of struvite in DTM type crystallizer with a jet-pump of descending suspension flow in a mixing chamber”,....., 2 (4), 260-266 (2007).
9 Koralewska, J., Piotrowski, K., Wierzbowska, B., Matynia, A., “Reaction-crystallization of struvite in a continuous liquid jet-pump DTM MSMPR crystallizer with upward circulation of suspension in a mixing chamber-an SDG kinetic approach”,..., 30 (11), 1576-1583 (2007).
10 Donnert, D., Salecker, M., “Elimination of phosphorus from waste water by crystallization”,.., 20, 735-742 (1999).
11 Parsons, S.A., “Recent scientific and technical developments: Struvite precipitation”,., 41, 15-22 (2001).
12 Doyle, J., Parsons, S.A., “Struvite formation, control and recovery”,.., 36, 3925-3940 (2002).
13 Booker, N.A., Pristley, A.J., Fraser, I.H., “Struvite formation in wastewater treatment plants: Opportunities for nutrient recovery”,.., 20, 777-782 (1999).
14 Bridger, G., “Fertiliser value of struvite”,., 43, 3-4 (2001).
15 de-Bashan, L.E., Bashan, Y., “Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer”,.., 38, 4222-4246 (2004).
16 Matynia, A., Koralewska, J., Kwiecien, J., “The influence of the continuous crystallization process parameters on the crystal size distribution of struvite”,...., 5 (4), 83-89 (2003).
17 Matynia, A., Koralewska, J., Piotrowski, K., Wierzbowska, B., “The influence of process parameters on struvite continuous crystallization kinetics”,..., 193, 160-176 (2006).
18 Koralewska, J., Matynia, A., Piotrowski, K., Wierzbowska, B., “Reaction-crystallization process in a struvite precipitation technology—Application of a continuous DTM crystallizer with a jet-pump generating descending flow of suspension in a mixing chamber”,.., 7, 380-391 (2006).
19 Bechtold, Z., Malasinska, M., Matynia, A., Piotrowski, K., “Influence of selected jet-pump design parameters on a unit power of feeding stream in a DTM crystallizer with descending suspension flow in a mixing chamber”,.., 7, 371-379 (2006).
20 Bechtold, Z., Malasinska, M., Matynia, A., Piotrowski, K., “Influence of selected jet-pump design parameters in a DTM crystallizer with ascending suspension flow in a mixing chamber on a unit power of feeding stream”,..., 45 (4s), 13-15 (2006). (in Polish)
21 Randolph, A.D., Larson, M.A., Theory of Particulate Processes: Analysis and Techniques of Continuous Crystallization, Academic Press, New York (1988).
22 Bransom, S.H., “Factors in the design of continuous crystallizers”,..., 5, 838-844 (1960).
23 Canning, T.F., Randolph, A.D., “Some aspects of crystallization theory: Systems that violate McCabe’s Delta L Law”,., 13, 5-10 (1967).
24 Abegg, C.F., Stevens, J.D., Larson, M.A., “Crystal size distribution in continuous crystallizers when growth rate is size-dependent”,., 14, 118-122 (1968).
25 Rojkowski, Z., “New empirical kinetic equation of size dependent crystal growth and its use”,, 12, 1121-1128 (1977).
26 Rojkowski, Z., “New hyperbolic empirical model of size dependent crystal growth”,-, 26, 265-270 (1978).
27 Rojkowski, Z., “Two parameter kinetic equation of size dependent crystal growth”,, 13, 1277-1284 (1978).
28 Mydlarz, J., Jones, A.G., “On modeling the size-dependent growth rate of potassium sulphate in a MSMPR crystallizer”,..., 90, 47-56 (1990).
29 Mydlarz, J., “A hyperbolic crystal growth rate model”, In: Proceedings of 13th Symposium on Industrial Crystallization, Toulouse, France, 275-280 (1996).
30 Machej, K., Piotrowski, K., “Review and comparison of kinetic equations for mass crystallization design purposes”,..., 40 (5), 17-18 (2001). (in Polish)
31 Kamienski, J., Mixing Processes in the Multiphase Systems, WNT, Warszawa (2004). (in Polish)
2008-01-07,
2008-12-15.
* To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: krzysztof.piotrowski@polsl.pl
 Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2009年2期
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2009年2期
- Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Kinetics of Reactive Extraction of Nd from Nd2O3 with TBP-HNO3Complex in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide*
- Activity Coefficient Models to Describe Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium in Ternary Hydro-Alcoholic Solutions*
- Position Group Contribution Method for Predicting the Normal Boiling Point of Organic Compounds
- Experimental Study on the Initial Position Distribution of Taylor Bubbles in Cryogenic Upward Inclined Tubes*
- Enhancement of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Performance Using a Novel Tapered Gas Channel*
- Tert-butylation of Toluene with Tert-butyl Alcohol over Realuminated H-mordenite Zeolite*
