Progress in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with immune combination therapy
Di Pan,Hao-Nan Liu,Peng-Fei Qu,Xiao Ma,Lu-Yao Ma,Xiao-Xiao Chen,Yu-Qin Wang,Xiao-Bing Qin,Zheng-Xiang Han
Abstract Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a severe malignancy that poses a serious threat to human health.Owing to challenges in early diagnosis,most patients lose the opportunity for radical treatment when diagnosed.Nonetheless,recent advancements in cancer immunotherapy provide new directions for the treatment of HCC.For instance,monoclonal antibodies against immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) such as programmed cell death protein 1/death ligand-1 inhibitors and cytotoxic t-lymphocyte associated antigen-4 significantly improved the prognosis of patients with HCC.However,tumor cells can evade the immune system through various mechanisms.With the rapid development of genetic engineering and molecular biology,various new immunotherapies have been used to treat HCC,including ICIs,chimeric antigen receptor T cells,engineered cytokines,and certain cancer vaccines.This review summarizes the current status,research progress,and future directions of different immunotherapy strategies in the treatment of HCC.
Key Words: Hepatocellular carcinoma;Ⅰmmunotherapies;Ⅰmmune checkpoint inhibitor;Clinical efficacy;Adverse reactions
lNTRODUCTlON
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains among the most prevalent malignant tumors worldwide[1] and represents the primary form of liver cancer[2].Diagnosis typically occurs during the middle to late stages for the majority of patients with HCC[3].For patients with mid to late-stage HCC diagnosis,systemic therapy is the main treatment method[4].The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has undergone an extensive approval process for systematic liver cancer treatments (Figure 1),encompassing chemotherapy,targeted therapy,and immunotherapy[5].While traditional systemic chemotherapy lacks significant efficacy in improving the survival of patients with HCC and often triggers severe adverse reactions (AEs)[6],combined chemotherapy results have proven suboptimal in clinical studies[7].FDA-approved molecular targeted drugs (such as sorafenib and lenvatinib) have demonstrated survival advantages of up to 3 months[8,9].Nonetheless,their clinical benefits are limited by toxicity,low overall survival (OS) benefits,and drug resistance[10].
Establishing an immuno-suppressive state within the tumor microenvironment (TME) stands as a critical capability of malignant tumors[11].Recent advancements in comprehending the immune escape mechanisms of malignancies have led to the development of various immune drugs,yielding promising outcomes[12-15].Immunotherapy is a systemic treatment approach that stimulates the human immune system,enhances immune response,strengthens immune cells’ capability to resist tumor cells,and overcomes tumor cells’ evasion of immune surveillance[16].Tumor immunotherapy,a highly anticipated innovative therapy,holds broad application prospects in mid to late-stage HCC,with numerous notable clinical trials in HCC immunotherapy (Table 1).
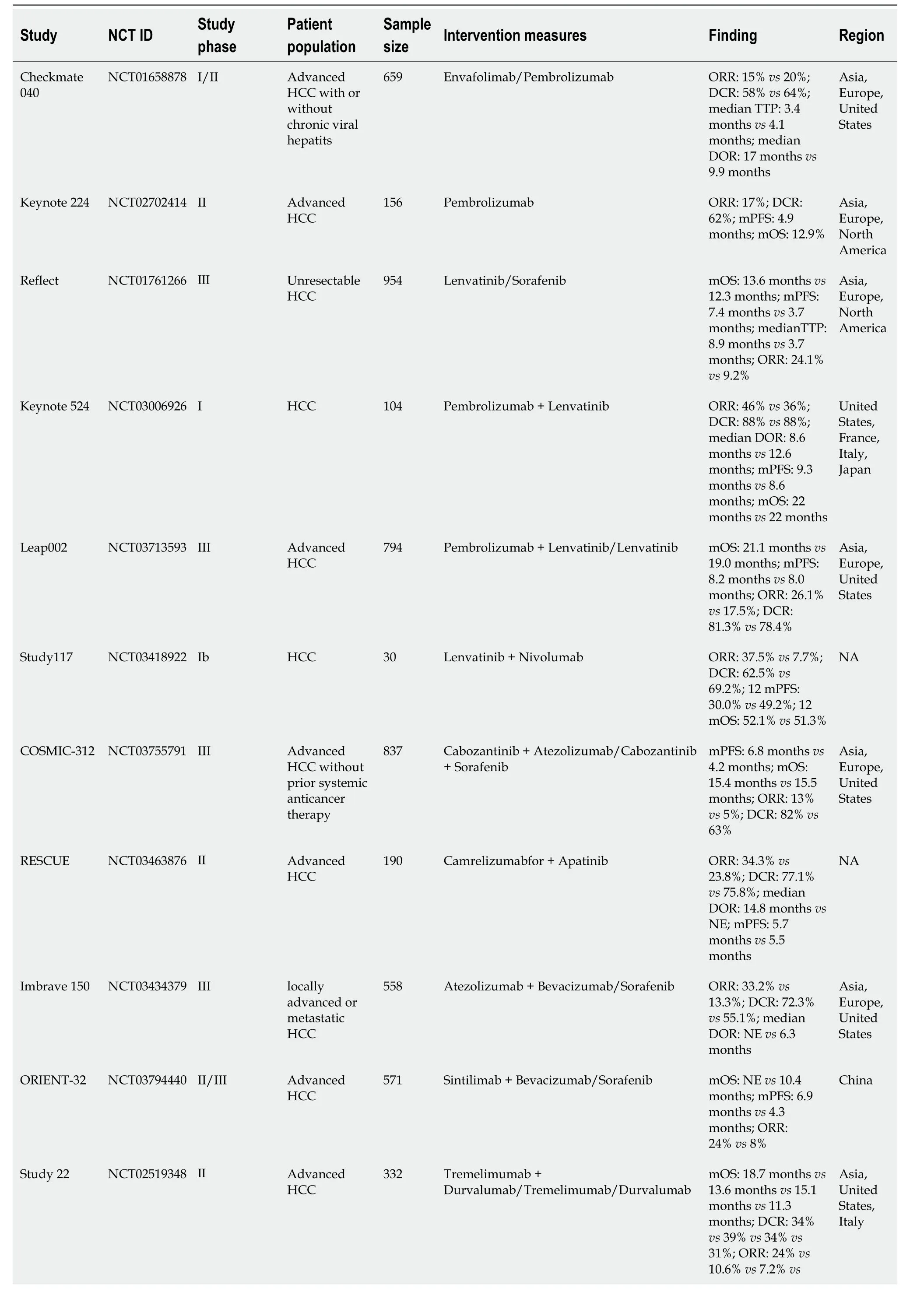
Table 1 Summary of clinical study data for hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy
Currently,diverse immunotherapy methods exist for HCC,including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs),peptide vaccines,dendritic cell vaccines,chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T),and oncolytic viruses[17].However,ICIs have emerged as the primary research focus in HCC treatment[18].We conducted a comprehensive review of completed ICI treatment trials for HCC in the past five years using the Clinical Trials website (ClinicalTrials.gov;Table 2).
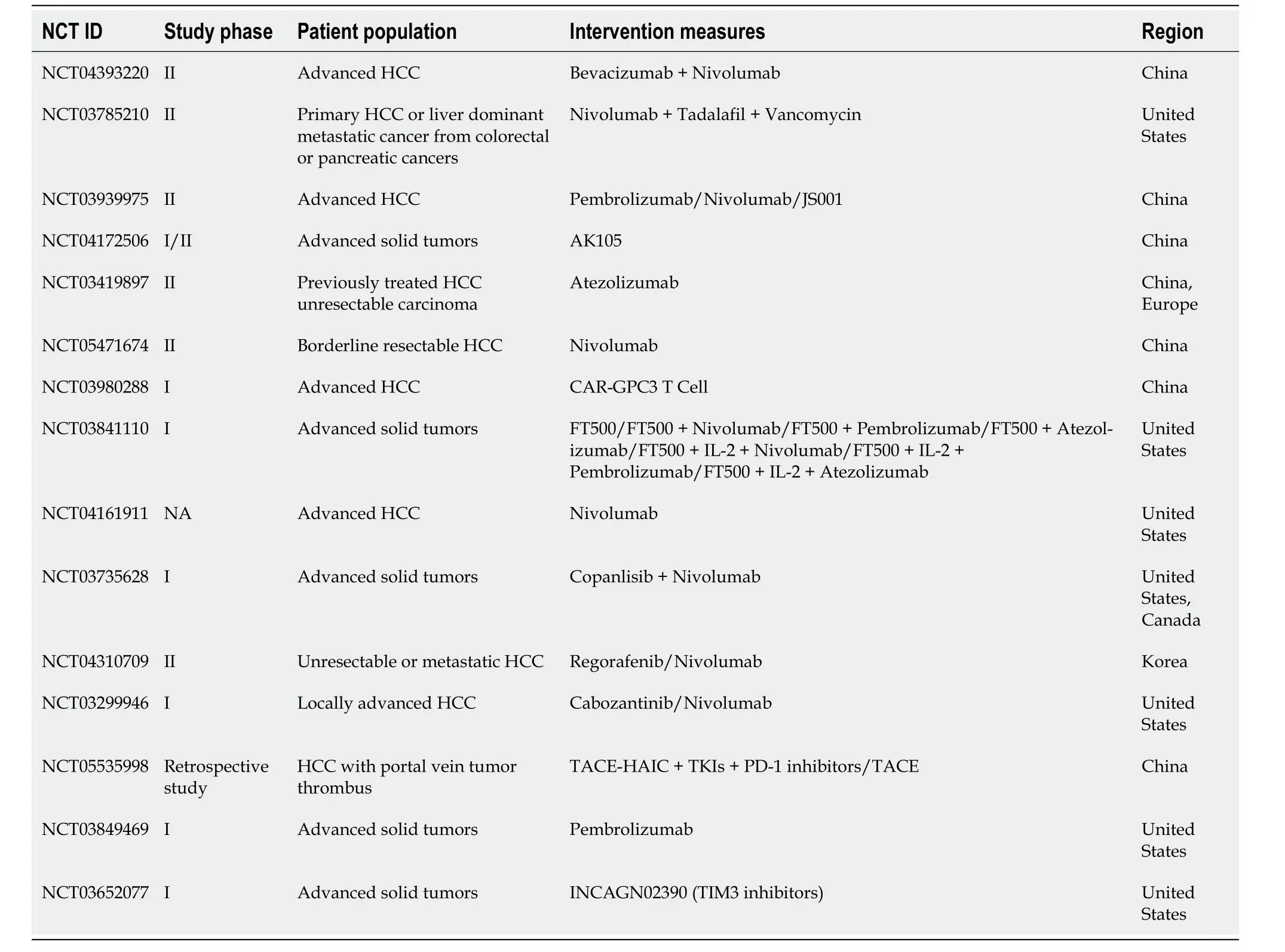
Table 2 Clinical Trials of hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy completed in the last five years (ClinicalTrials.gov)
ICIs represent monoclonal antibodies that obstruct checkpoint proteins from binding to their ligands,reactivating and maintaining the tumor immune cycle,thereby enabling T cells to eliminate tumor cells[19].Currently,three types of ICIs,namely programmed cell death receptor 1 programmed cell death protein 1/death ligand-1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors and cytotoxic t-lymphocyte associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) inhibitors,have garnered FDA approval for HCC treatment[20].The data from the Checkmate 040 study phase I-II revealed an objective response rate (ORR) of 14%,a disease control rate (DCR) of 56%,and an average OS of 15.6 months in patients with advanced HCC treated with nivolumab monotherapy[9].The keynote-224 study documented the clinical efficacy of pembrolizumab in the treatment of patients with HCC who had undergone prior sorafenib treatment,showcasing a 17% ORR and a median OS (mOS) of 13 months[21].Following these findings,the FDA has approved pembrolizumab and nivolumab for second-line monotherapy in patients with HCC.However,despite positive outcomes from Phase I and Phase II clinical studies,subsequent Phase III randomized controlled trials for nivolumab and pembrolizumab failed to meet their primary endpoints[22-23].Consequently,the FDA retracted the indication for nivolumab monotherapy as a second-line treatment for patients with HCC.The response rate for ICI monotherapy ranges from 15% to 23%,escalating to approximately 30% after combination therapy[24].Although ICIs have exhibited clinical efficacy in HCC treatment,the limited response rate with monotherapy necessitates exploring combined strategies to further enhance treatment efficacy.In recent years,ICIS monotherapy and combination therapy have emerged as crucial pillars in HCC treatment (Figure 2).In this review,we explore current immunotherapy approaches and future directions.

PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1;CTLA-4: Cytotoxic t-lymphocyte associated antigen-4.
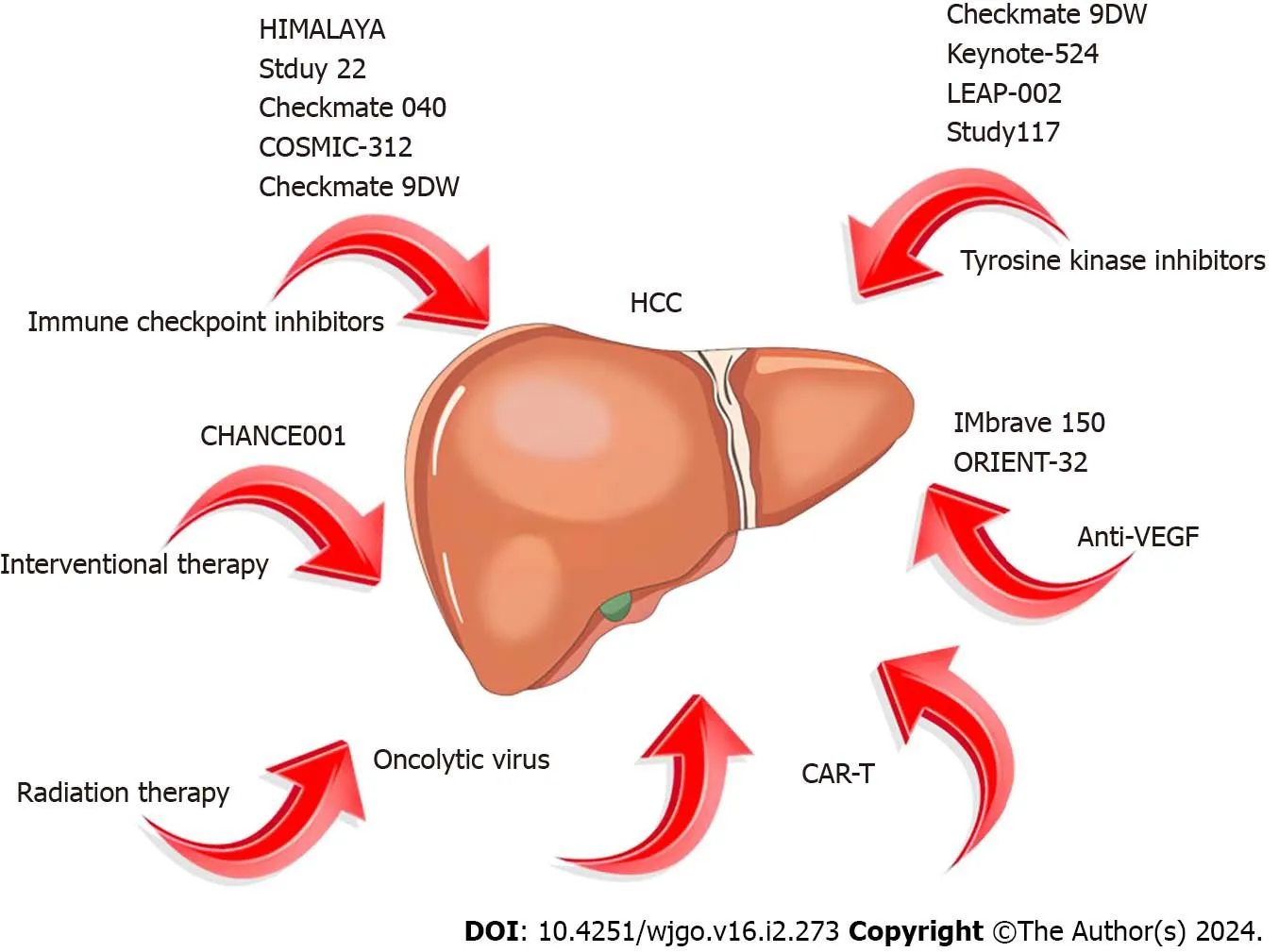
Figure 2 Concepts of hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy,immunotherapy combination therapy,and related trials in recent years.HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma;CAR-T: Chimeric antigen receptor T cells;VEGF: Vasoactive endothelial growth factor.
lClS COMBlNED WlTH TYROSlNE KlNASE lNHlBlTORS
Lenvatinib,a selective,multi-target drug [such asVEGFR 1-3,FGFR 1-4,PDGFR-α,tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) of RET and KIT][25] that has gained approval from the European Drug Administration,FDA,and the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) as a first-line treatment for advanced HCC in 2018,based on the Reflect study[26],along with lenvatinib and joining sorafenib as the standard first-line therapy.TKIs possess anti-immunosuppressive properties,wherein tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) are reduced and CD8+T cell proliferation and activation are enhanced[27,28].In the TME,TAMs are pivotal immune modulators implicated in tumor immune escape by producing cytokines like interleukin-10,prostaglandin E2,and transforming growth factor.Therefore,inhibiting TAM production supports immune activation[29,30].
In 2020,Finnet al[31] reported the results of a single-arm Phase Ib clinical trial (keynote-524)[31].The trial enrolled 140 patients with advanced HCC as the study subjects,showing that pembrolizumab combined with lenvatinib as a first-line treatment regimen achieved an ORR of 36% (RECIST 1.1 standard) and 46% (mRECIST standard).Additionally,this combination significantly extended the median progressive free survival (PFS) to 9.3 months (95%CI=5.6-9.7) and mOS to 22 months [95%CI=20.4-not estimable (NE)].Based on these promising findings,the LEAP-002 study[32],a randomized,controlled,double-blind large phase III trial,compared pembrolizumab combined with lenvatinib (1:1 ratio) against lenvatinib alone in 794 patients with HCC who did not undergo systemic treatment.The results indicated a significantly higher mOS (21.2 months) with pembrolizumab combined with lenvatinib compared to lenvatinib alone (19 months) [hazard ratio (HR)=0.840,P=0.0227],and it also significantly improved median PFS (mPFS) (8.2 monthsvs8.0 months,HR=0.867,P=0.0466).The ORR for combination therapy was 26.1%,surpassing the monotherapy group’s 17.5%.However,while combination therapy showed trends toward improved OS and PFS,it did not achieve the predetermined statistical significance in efficacy.
Sudy117[33] assessed 30 patients with advanced HCC treated with lenvatinib combined with nivolumab.The primary endpoint of the study was tolerance and safety,while the secondary endpoint was ORR.All patients experienced AEs,predominately hand and foot syndrome (56.7%) and dysphonia (53.3%),which were manageable.The combination therapy demonstrated a remarkable ORR of 76.7% and a DCR of 96.7%,establishing its tolerability and robust anti-tumor effects.
Kelleyet al[34] evaluated the efficacy and safety of cabozantinib combined with atezolizumabvssorafenib alone in treating advanced HCC (COSMIC-312)[34].The results revealed significantly superior mPFS in the cabiralizumab reduction (40 mg)+atezolizumab group compared to sorafenib monotherapy (6.8 monthsvs4.2 months,P=0.0012),yet mid-term analysis showed no significant difference in the mOS between the two groups (15.4 monthsvs15.5 months,P=0.44).
The combination therapy of domestic programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitor camrelizumab and apatinib (Rescue)[35] displayed notable efficacy in advanced HCC treatment.Compared to sorafenib alone,the combination of camrelizumab and apatinib as first-line treatment for HCC significantly prolonged both PFS and OS.Notably,the OS rate at 12 months reached approximately 75%,with a mPFS of 5.6 months and a mOS of 20.1 months.Additionally,the ORR and DCR for this combined treatment regimen were 25.4% and 78.3%,respectively.Grade 3-4 AEs were experienced by 77.4% of patients,primarily manifesting as hypertension (34.2%).On January 31,2023,with NMPA approval,camrelizumab combined with apatinib became the first-line treatment for unresectable or metastatic liver cancer in China,establishing the "Shuang ai" combination as China’s first approved PD-1 inhibitor+small molecule anti-angiogenic drug regimen for advanced HCC.
lClS COMBlNED WlTH ANTl-VASOACTlVE ENDOTHELlAL GROWTH FACTOR DRUGS
Vasoactive endothelial growth factor (VEGF),originating from tumor cells and the surrounding matrix[36],not only facilitates tumor angiogenesis but also suppresses dendritic cell antigen-presenting function,hinders T cell activation and infiltration,and fosters regulatory T cells and myeloid suppressive cells,thereby disrupting the anti-tumor immune response[37,38].
The IMbrave150 study[39],conducted in over 70 countries,was a phase III,multicenter open-ended study.comparing the efficacy and safety of atezolizumab combined with bevacizumab (T+A scheme)vssorafenib alone in patients with advanced HCC who had not received prior systemic treatment.Results revealed a mOS of 19.2 months with the T+A regimen and 13.4 months with sorafenib monotherapy (P< 0.001),and mPFS of 6.9 and 4.3 months,respectively (P< 0.001).The Chinese subgroup exhibited a mOS of 24.0 months.The incidence of grade 3-4 AEs in the T+A regimen (43%) was similar to sorafenib monotherapy (43%).The study also found that the ORR of the T+A combination reached 30%.Additionally,the T+A regimen significantly improved patients’ quality of life compared to sorafenib alone (HR=0.63,95%CI: 0.46-0.85),leading to its approval as a first-line treatment for HCC.
The ORIENT-32 phase III clinical trial[40] assessed sintilimab combined with bevacizumabvssorafenib in first-line treatment for hepatitis B-related advanced liver cancer.The combined regimen significantly improved the mOS (NEvs10.4 months,HR=0.57,P< 0.0001) and mPFS (4.6 monthsvs2.8 months,HR 0.56,P< 0.0001) compared to sorafenib alone.This study encompassed a Chinese population,reflecting real-world scenarios in China.Consequently,the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) guideline included "sintilimab in combination with bevacizumab biosimilar" as a treatment option.
In 2022,ESMO reported on the CARES-310 study,a multicentre open phase III clinical trial[41] involving 543 patients with advanced HCC randomly assigned to apatinib+karelizumab or sorafenib treatment groups in a 1:1 ratio.The results indicated that the abatinib+karelizumab group improved mPFS (5.6 monthsvs3.7 months) and increased mOS (22.1 monthsvs15.2 months) compared to the sorafenib group.Consequently,CSCO has now adopted "apatinib+carilizumab" as a treatment option.
A phase Ib/II study[42] explored tivozanib combined with duvalizumab in second-line treatment for advanced HCC following initial treatment or after T+A progression.With a total of 27 enrolled patients,the median follow-up time was 13.2 months for group A and 3.4 months for group B.Data were available for 25 of the 27 patients enrolled in group A,revealing an ORR of 25% and a 1-year OS of 76%.
Renet al[43] reported a phase II clinical study evaluated serplulimab in combination with bevacizumab biosimilar in advanced HCC across four groups.Groups A,B,and C received 3 mg/kg serplulimab with 5 mg/kg HLX04 (bevacizumab biosimilar),3 mg/kg serplulimab with 10 mg/kg HLX04,or 3 mg/kg serplulimab monotherapy,whereas group D included first-treatment patients following the same combination regimen and dose as group B.The results showed that the ORR was 30.0% in group A and 14.3% in group B.Median during of response was not reached (95%CI,3.3-NE) in group A and was 9.0 months (95%CI,7.9-NE) in group B.MPFS was 2.2 months (95%CI,1.4-5.5) and 4.1 months (95%CI,1.5-NE),and mOS was 11.6 months (95%CI,6.4-NE) and 14.3 months (95%CI,8.2-NE) in groups A and B,respectively.
Grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse event incidence was 70.0%,57.1% in groups A and B,respectively.Most immune-related adverse events were grade ≤ 3.Yet the overall safety of serplulimab in combination with bevacizumab was manageable.Based on several key efficacy indicators such as ORR,PFS,and OS,the first-line application of serplulimab combined with bevacizumab biosimilar appeared more beneficial than second-line use,highlighting its preference as an immunological combination regimen for patients with advanced HCC at the time of diagnosis.
DUAL lMMUNE COMBlNATlON THERAPY
Studies have found that CTLA-4 inhibitors and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors target different sites and timeframes within the same T cell[44].CTLA-4 inhibitors activate T cells in lymph nodes,while PD-1 inhibitors reactivate T cells suppressed in the TME[45,46].Combining these two agents can concurrently stimulate the same T cell,whether in the activated site (lymph node) or TME,ensuring continuous T cell stimulation over a prolonged period[47].This combination may intensify co-stimulation,further enhancing T cell activation.Based on this theoretical foundation,various clinical studies exploring dual immune combination therapy for HCC have been conducted.
The Checkmate 040[48] study initially demonstrated the substantial treatment efficacy of nivolumab and ipilimumab,reporting a 31% ORR with a mOS of 22.8 months.It is the earliest clinical study of HCC immunotherapy and plays a pivotal role in pioneering the development of dual immunotherapy.
ASCO 2023 reported another study evaluating the efficacy of nivolumab combined with ipilimumab as a backline treatment for HCC[49].The results showed that of the 30 evaluable patients in the cohort experiencing ICIs,1 achieved confirmed partial response (PR) and 14 achieved stable disease (SD),with ORR of 3.3% and DCR of 50.0%.Of the 30 evaluable patients in the ICIs-nave cohort,4 achieved confirmed PR and 10 achieved SD,with an ORR of 13.3% and DCR of 46.7%.Furthermore,the mPFS was 2.4 and 3.1 months for the ICIs-and ICIs-na?ve cohorts,respectively.Although mOS was not reached in either group,these results offer hope to patients with advanced HCC.
A global,open-label,randomized controlled phase I/II trial[50] involving multiple countries enrolled 332 patients with advanced HCC across four treatment groups to evaluate the toxicity and efficacy of tremelimumab and duvalizumab combination therapy in first and second-line treatments.The tremelimumab (300 mg) plus Furvalumab (1500 mg) followed by the durvalumab (1500 mg) group exhibited the most significant benefit,achieving a mOS of 18.73 months and a 24% ORR.The dual immunotherapy group had a lower incidence of grade 3-4 treatment-related AE (37.8%) compared to the tremelimumab monotherapy group.This study suggests that the combination of tremelimumab with nivolumab significantly improves OS with good safety profiles.Subsequently,based on these favorable results,the Phase III HIMALAYA study was initiated to evaluate duvalizumab+tramelumab and sorafenib in first-line HCC treatment[51].The study also introduced the STRIDE regimen (conventional interval administration of duvalizumab+single high initiation dose of tremelimumab).The STRIDE regimen reduced the risk of death by 22% (HR=0.78,95%CI=0.65-0.93),with a mOS of 16.4 months comparable to sorafenib alone (13.8 months).In terms of ORR,the ORR of the STRIDE regimen group was three times higher than that of the sorafenib monotherapy group (20.1%vs5.1%),the median duration of remission was up to 22.3 months,and the incidence of ≥ grade 3 treatment-related AEs was 30% lower than that of the control group,without increasing serious liver injury and bleeding events.It became the first dual immunization combined with sorafenib study to show positive OS results in the first-line treatment of HCC,leading to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines including "duvalizumab+tremelimumab" as a treatment option (Class 1 recommendation).
Advancing research has introduced bispecific antibodies targeting both CTLA-4 and PD-1 simultaneously,potentially offering lower toxicity than dual immune drug combinations[52].China’s first bispecific antibody drug,candonilimab (AK104)[53],showed promise in a phase II clinical trial when combined with lenvatinib for advanced HCC first-line treatment[54].A total of 30 patients were included in the study.Among 18 patients with evaluable anti-tumor activity,the post-treatment ORR was 44.4% and DCR was 77.8%.Moreover,the mPFS has not been reached thus far.
Tebotelimab,a bispecific antibody targeting PD-1 and LAG-3,demonstrated good safety profiles and modest efficacy in a multicentre Phase I-II clinical trial[55] involving patients with treated HCC in a dose-escalation phase and a doseexpansion phase.It enrolled 30 immunotherapy-treated patients and 30 immunotherapy-na?ve patients.Overall,the safety profile of the treatment was good,with a 19% incidence of treatment-related AEs at G3 and above in the doseescalation phase,similar to that of PD-1 antibodies in general.In terms of efficacy,the ORR was 3% in immunotherapytreated patients and 13.3% in immunotherapy-na?ve patients.Thus,its efficacy appears to have a slight advantage over PD-1 antibodies.
Additionally,other ICIs beyond those targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 have likewise demonstrated favorable outcomes.A phase II study[56] explored the efficacy of cobolimab (TIM-3 antibody) in combination with dostarlimab for first-line HCC treatment,exhibiting a 46% ORR (n=13,with six patients experiencing remission)
Another phase II study[57] investigated bavituximab (phosphatidylinositide antibody) combined with pembrolizumab for first-line advanced HCC treatment,revealing a 32% ORR.This study also identified a diagnostic marker for the immune microenvironment.A total of 19 patients were monitored for marker identification,and 5 of the 8 positive patients experienced remission,while only 1 of the 11 negative patients experienced remission and 9 experienced tumor progression.Thus,such a dual immune combination regimen has notable potential in HCC.
lClS COMBlNED WlTH lNTERVENTlONAL THERAPY
The landscape of first-line treatment has undergone significant improvement with the approval of the T+A scheme and sindilimab+bevacizumab regimens,marking a successful blend of targeted and immune therapy in HCC treatment.Recent years have witnessed a deeper exploration of combinational therapies,shining a light on the role of interventional therapy.Various triple schemes involving targeted+immune+interventional therapies have showcased notable efficacy in treating HCC.
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) remains the standard treatment for mid-term HCC and has also been applied to advanced HCC[58-64].While TACE exhibits a local anti-tumor effect and boosts the anti-tumor immune response,its induced ischemic and hypoxic conditions often trigger VEGF overexpression,ultimately leading to HCC neovascularization[65,66].Targeted drugs not only inhibit angiogenesis,but also exert immunomodulatory effects on the TME[27,67].Hence,the synergy between targeted,immune,and interventional therapies is evident.Caiet al[68] reported that compared to TACE combined with lenvatinib alone[68],the addition of PD-1 inhibitors significantly prolonged mOS in patients with advanced HCC (16.9 monthsvs12.1 months,P=0.009),with manageable AEs.Caoet al's study[69] observed that for unresectable HCC,the treatment regimen of TACE combined with lenvatinib and sintilimab resulted in a mOS of 23.6 months and an ORR of 46.7%[69].Notably,the CHANCE001 study,a large sample,multicenter retrospective study,compared the clinical efficacy of TACE combined with targeted PD-1 inhibitorsvsTACE alone[70].Results demonstrated significantly longer mOS (19.2 monthsvs15.7 months,P=0.001) and PFS (9.5 monthsvs8.5 months,P=0.002) in the combination therapy group.The ORR was 60.1% for the combination therapy group compared to 32.0% for the TACE group,marking it as the largest sample size study on TACE combined with immunotherapy and targeted drug therapy for HCC.
Hepatocellular arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) is another interventional method for the treatment of HCC,delivering chemotherapy drugs directly to the arterial branches related to HCC,thereby increasing local drug concentration[71].Meta-analyses indicates superior efficacy of HAIC over TACE[72-74].Laiet al[75] observed that after treatment with the HAIC combined with an envatinib and toripalimab regimen,patients with advanced HCC achieved a mOS of up to 17.9 months,with an ORR of 66.7%,and experienced minimal overlapping toxicities.
Baeet al[76] reported a study on local high-dose autologous Natural killer (NK) cells combined with HAIC for HCC treatment.Among the 11 enrolled patients,the ORR was 63.6% and the DCR was 81.8%.The mPFS and OS were 10.3 and 41.6 months,respectively.No compensatory losses or serious AEs occurred during HAIC,and no AEs related to NK cell infusion were noted.
lClS COMBlNED WlTH RADlATlON THERAPY
Compared to invasive techniques like TACE,the integration of radiation therapy and immunotherapy stands out for its non-invasiveness,high safety profile,and easy acceptance by patients,gradually becoming a research hotspot in the comprehensive treatment of HCC.Radiation therapy excels in exposing more tumor-related antigens and releasing damage-related molecules,thus promoting anin situvaccine effect.It also reshapes the TME,enhancing dendritic cell antigen presentation,activating CD8+T cells,and improving cytotoxicity[77,78].Moreover,radiation therapy also promotes the secretion of cytokines by recruiting cytotoxic T lymphocytes,thereby promoting the infiltration of immune killer cells into tumor tissue[79].
The START-FIT phase II clinical trial[80] explored the efficacy and safety of TACE+stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in combination with avelumab for HCC treatment.Results showcased a 42% CR,24% PR,and a 67% ORR.PFS stood out at 20.7 months and OS at 30.3 months,with a local control rate of 92% at two years.Although clinical studies with avelumab in HCC are limited,the exploration continues.
The CA 209-678 study evaluating Y90 radiation embolization combined with navolizumab treatment[81] revealed an 81% regression of radiation field target lesions,achieving an ORR of 30.6% in all patients with HCC and 43.5% in those limited to intrahepatic lesions.Zhonget al[82] conducted a retrospective study on stage C patients with HCC in Barcelona,exploring the safety and clinical outcomes of a triple regimen involving radiotherapy,targeted immunotherapy,and other therapies.Sixteen patients received a treatment regimen comprising PD-1 inhibitor,anti-angiogenesis,and radiotherapy.According to the mRECIST standard,six patients experienced PR and seven exhibited SD,with no CRs observed.The ORR and DCR were 40.0% and 86.7%,respectively.Additionally,a study by Lukeet al[83] assessing the safety of SBRT+pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors (including HCC) revealed a comparable adverse reaction rate between the radiation+immunotherapy regimen and radiation therapy alone,with a dose-limiting adverse reaction rate of 9.7%.
lClS COMBlNED WlTH OTHER REGlMENS FOR TREATMENT
Oncolytic viruses are capable of selectively targeting and killing cancer cells and hold promise in cancer treatment.They exist in nature or can be obtained through genetic engineering[84].Despite their potential,their therapeutic efficacy needs improvement as the body tends to swiftly eliminate these viruses[85].Hence,trials often combine oncolytic viruses with other treatments to enhance their anti-tumor effects.The goal is to leverage the dual efficacy of oncolytic viruses and immune cells in combating cancer.This subtype of immunotherapy is widely combined with ICIs in both preclinical and clinical studies,yet application in the field of HCC remains limited,mostly in the developmental phase.
An ongoing clinical trial is recruiting patients to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SynOV 1.1 adenovirus injection combined with tislelizumab in patients with advanced HCC through a single-arm,open-label,and dose-increasing evaluation.
As molecular biology and cellular immunology advance,CAR-T therapy emerges as a novel approach in cellular immunotherapy,widely used in hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.In exploring CAR-T targets for HCC,Glypican-3,MUC-1,EpCAM,and CD147 stand out[86].However,there is currently a lack of clinical research on the combination of CAR-T and ICIs for the treatment of mid to late-stage HCC.The future focus will remain in this direction.Furthermore,attention should be paid to the limitations of clinical trials.For example,most clinical trials overlook the etiology of HCC,and incorporating assessments of patients’ quality of life post-treatment could illuminate the negative impacts of appropriate treatment and clinical decisions.Unfortunately,the main endpoints of most trials do not include quality-of-life assessments,necessitating solutions for better evaluation (Table 3).
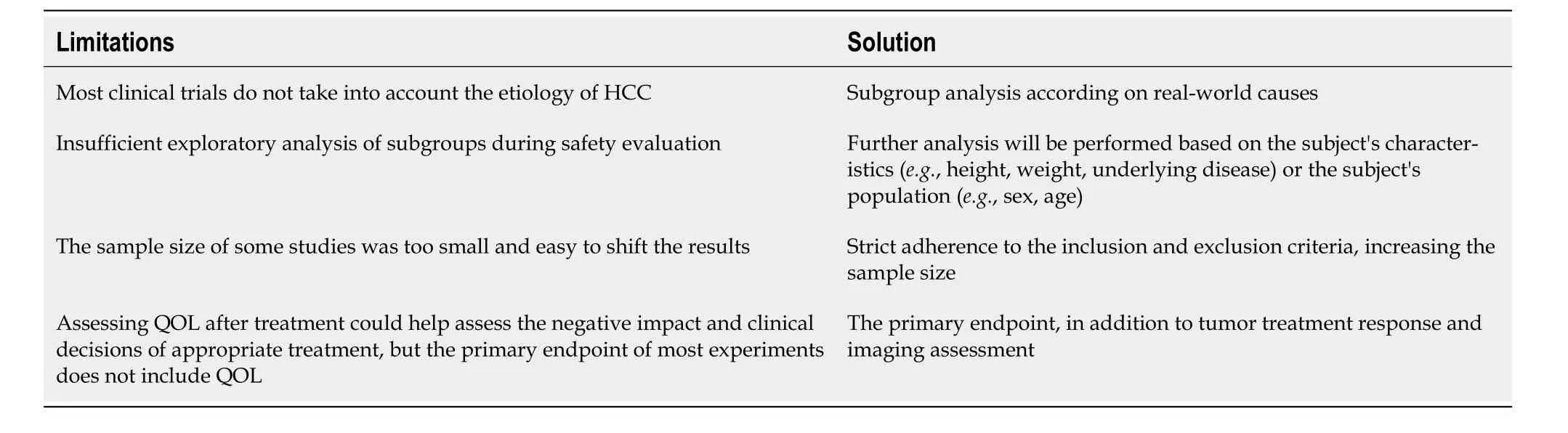
Table 3 Summarize the limitations of current clinical trials and propose solutions
CONCLUSlON
Summary and outlook
Although the incidence of HCC in various age groups in China is on a downward trend[87],the immunosuppressive characteristics of HCC often yield poor treatment outcomes with single ICI regimens.With continued advances in molecular biology,several drugs have gained approval for HCC treatment (Table 4).In the era predominantly focused on anti-angiogenic drug therapy,the publication of initial CARES-310 study data[41] at ESMO 2022 brought about positive dual endpoints-PFS and OS-inspiring hope in clinics for immunotherapy combined with an anti-angiogenic small molecule TKI.The significant strides made in molecularly targeted therapy and immune checkpoint therapy for advanced HCC will benefit many patients,yet they also pose challenges in drug selection and sequencing.As these drugs eventually become available,combination therapy using targeted therapies and ICIs is expected to yield better outcomes than current treatments.Currently,various immunological combination regimens for HCC exist,but direct comparison between different clinical studies is challenging,lacking "head-to-head" trials.Thus,selecting the appropriate treatment regimen has become a new challenge.A meta-analysis[88] evaluated the clinical benefits of each first-line regimen,highlighting atirizumab in combination with bevacizumab and sindilizumab in combination with bevacizumab as having significant clinical benefits.Furthermore,the study encompassed four targeted immune combination regimen trials,indicating no significant difference in mOS among the first-line combination regimens.However,atilizumab in combination with bevacizumab,sindilizumab in combination with IBI305 (a bevacizumab analog),and karelizumab in combination with abatinib significantly prolonged patients' mPFSvssorafenib,while tesilizumab in combination with duvarizumabvssorafenib did not significantly prolong patient mPFS.In terms of safety,atelizumab in combination with bevacizumab exhibited a significantly lower risk of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) compared to karelizumab+apatinib,sindilizumab+lBl305,and sorafenib,and a similar risk to tesirizumab+doxorubicin.Additionally,carilizumab+apatinib had a significantly higher RR for greater than grade 3 TRAEs compared to atalizumab+bevacizumab.With sorafenib no longer deemed the standard control arm,future trials aim to challenge new benchmarks by exploring further treatment options for patients with HCC,utilizing first-line immunotherapy-based combinations.In conclusion,the necessity for cross-disciplinary systemic therapy for inoperable HCC will intensify in the future.Cellular immunotherapy technologies,including CAR-T cells (except for the three launched CAR-T variants),dendritic cell vaccines,NK cells,tumor infiltrating lymphocytes cells,T cell receptor-gene engineered T cells therapy,and cancer vaccines,are in clinical trial stages and are yet to gain approval for use in Chinese hospitals.The future holds numerous unexplored facets in HCC immunotherapy.First,recent studies indicate a lower immune therapy response rate in non-viral-associated liver cancer compared to viral-associated liver cancer,urging exploration into the etiological mechanisms of HCC for selecting combined immunotherapy[89,90].Second,while alpha-fetoprotein remains a valuable biomarker for guiding treatment and prognosis prediction in HCC[11],discovering other biomarkers for efficacy prediction in screening patients with HCC could significantly benefit immunotherapy.Lastly,active research on the mechanisms underlying acquired drug resistance in immune combination regimens is necessary to guide further investigation.
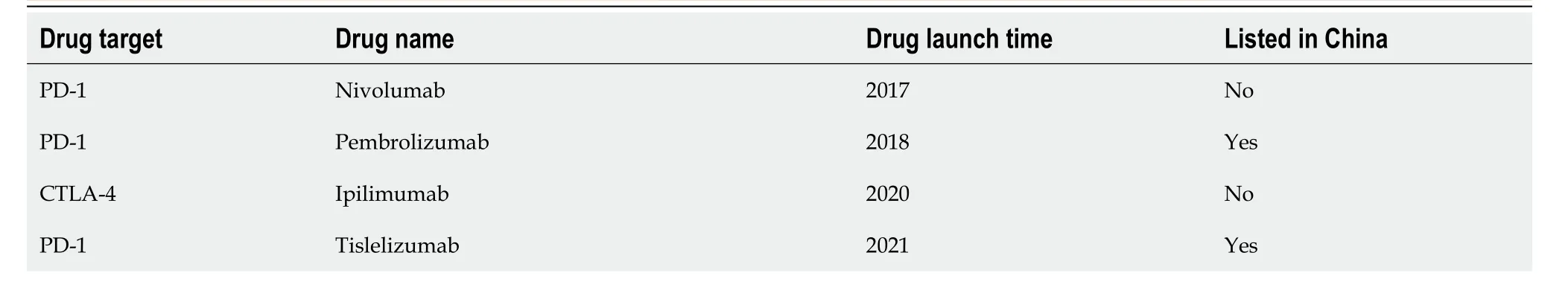
Table 4 lmmunotherapy drug approved for hepatocellular carcinoma
FOOTNOTES
Co-first authors:Di Pan and Hao-Nan Liu.
Co-corresponding authors:Xiao-Bing Qin and Zheng-Xiang Han.
Author contributions:Han ZX and Qin XB were the leaders in actually co-ordinating the processing of submissions and undertaking the work of responding to review comments,and were often responsible for the research involved in the manuscripts,and contributed to the subject matter regardless of size.Pan D and Liu HN not only made the most and most important graphical contributions to this article,but also wrote the first draft of the article,making roughly equal contributions from article design to manuscript submission.Qin XB and Han ZX generated the idea for the study;Pan D and Liu HN analyzed and interpreted the content;Wang YQ,Qu PF,Ma X,Ma LY and Chen XX prepared the original draft;Pan D,Liu HN,Wang YQ and Qin XB are responsible for image processing;Han ZX is responsible for revising and finalizing the manuscript;All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript submitted for publication.
Conflict-of-interest statement:The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations,or those of the publisher,the editors,and the reviewers.Any product that may be evaluated in this article,or any claim that may be made by its manufacturer,is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:China
ORClD number:Di Pan 0009-0000-8992-0281;Zheng-Xiang Han 0000-0003-2463-8933.
S-Editor:Li L
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Li L
 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2024年2期
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2024年2期
- World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology的其它文章
- Does enhanced recovery after surgery programs improve clinical outcomes in liver cancer surgery?
- Cardiotoxicity induced by fluoropyrimidine drugs in the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors
- Effect of screening colonoscopy frequency on colorectal cancer mortality in patients with a family history of colorectal cancer
- Preoperative controlling nutritional status as an optimal prognostic nutritional index to predict the outcome for colorectal cancer
- Tumour response following preoperative chemotherapy is affected by body mass index in patients with colorectal liver metastases
- Expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 is positively correlated with the autophagy level in colon cancer
