Transition from isotropic to polar state of self-driven eccentric disks
Jinghan Wang(王靜晗), Tianliang Xu(許天亮), Jingxi He(何景熙), Kang Chen(陳康), and Wende Tian(田文得)
Center for Soft Condensed Matter Physics&Interdisciplinary Research,School of Physical Science and Technology,Soochow University,Suzhou 215006,China
Keywords: eccentric disk,Langevin dynamics,polar order,alignment effect
1.Introduction
Active matter,whose agents convert either internal energy into directed motion or utilize energy from the environment,is inherently out of equilibrium.Active agents include not only natural living species ranging from,e.g.,cytoskeletons[1]and microtubule–kinesin bundles[2]to living liquid crystals (suspensions of motile bacteria in liquid crystals),[3,4]but also a lot of artificial self-driven particles such as synthesized Janus particles[5]and chiral rotors.[6,7]The non-thermal motion is the origin of many rich and interesting phenomena of active matter,e.g., giant fluctuations,[8,9]spontaneous phase separation,[10,11]pattern formation,[12,13]vortex formation,[14]active turbulence,[15,16]and swarming.[17–19]Understanding behavior of active systems is an intense area of research from the fundamental aspect.Most theoretical knowledge about such active matter and its transitions has been developed on the dependence of active Brownian particles (ABP) model[20–22]and Vicsek-like model.[23]
For ABP model,[24]active agents are composed of selfdriven isotropic particles with isotropic pairwise interactions subjected to Brownian dynamics.A typical phenomenon in the ABP model is the motility-induced phase separation(MIPS).For Vicsek-like model, point particles travel at a speed and their direction changes according to interaction rules which comprise both explicit alignment and noise,to account for external or internal perturbations.The model shows a phase transition from disordered motion to large-scale ordered motion.[23]Also, there exist other models incorporating explicitly the body-fixed axis of particles.The alignment mechanism depends on the axis through the steric interaction of elongated objects.[11–13]Alternatively,for circular or spherical particles,a natural way of producing alignment is to incorporate inelasticity or softness in the interaction rules.[24]Recently, our group designed an eccentric robot composed of a Hexbug Nano and a circular foam(Fig.1(a)).The foamed disk adheres to the back of the Hexbug Nano, which is supported by twelve flexible legs that all bends slightly backwards.A vibration motor when turned on can set the Hexbug Nano into forward hopping motion on a solid substrate.The behavior of single robot and two-robot collision are given in supporting information (Figs.S1–S4).The interacting center of robots when colliding is the geometric center of the disk,not its center of mass.Because it is hard to eliminate the boundary effect in experiment when focusing on the collective behavior(Robots prefer to aggregate around the boundary,data not shown)and it is also difficult to control the system parameters such as activity and frictional coefficients, for the first step,here we proposed a computational model for the individual robot(Fig.1(b))to study their multi-body behaviors.
In contrast to the ABP model, the prominent feature of this model is mutual coupling of translational and rotational freedoms, which, to a certain extent, gives rise to an orientational alignment through collision.Meanwhile, the collision-induced alignment is different with the purely effective mesoscopic (anisotropic) alignment in Vicsek-like models.Through the control of parameters such as rotational friction coefficient and rotational noise, we find that a homogeneous system without rotational noise exhibits a sharp discontinuous transition from an isotropic to a polar state when increasing rotational friction coefficient.The transition becomes continuous when adding angular noise.The formation of polar state originates from the velocity alignment effect due to the cascading-collision-induced rotation.We also find that the existence of rotational noise could reduce the alignment effect and lead to a large spatial density inhomogeneity.
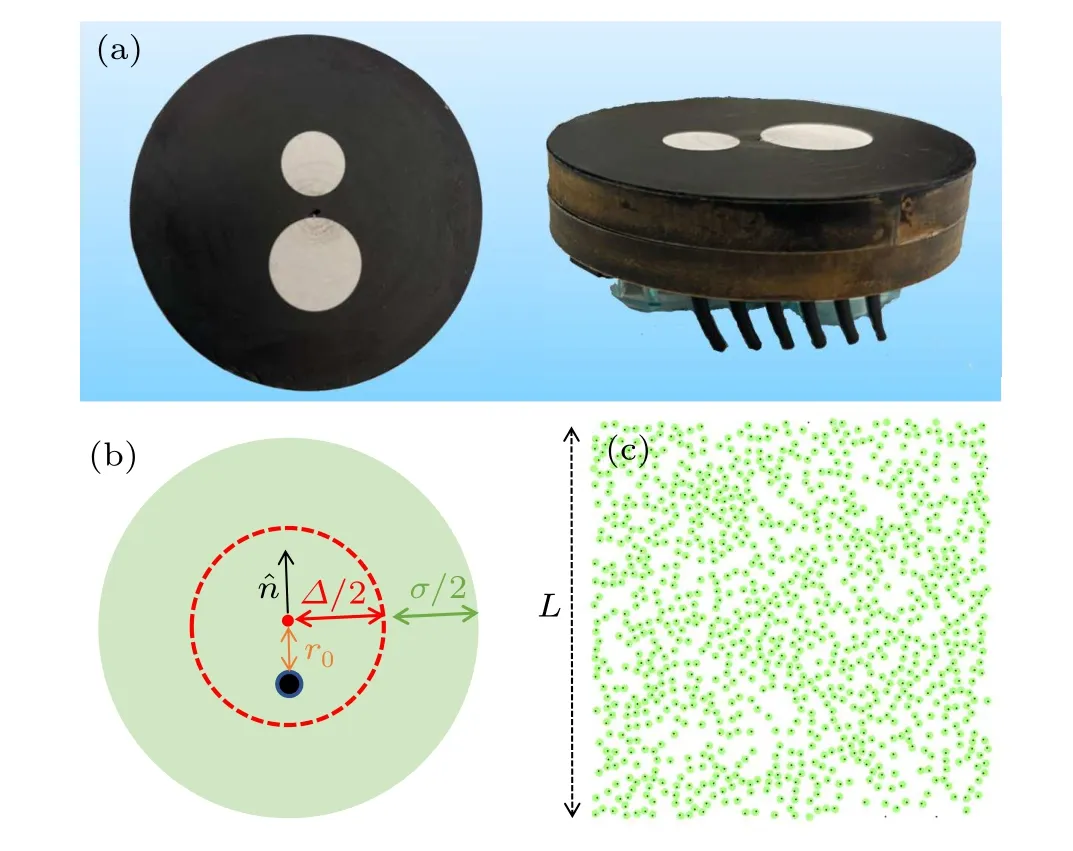
Fig.1.(a)Top and side view of the eccentric robot composed of a Hexbug Nano and a circular foam.(b) Schematic diagram of our model used in the simulation.The red point denotes the geometric center (GC) of the robot, while the black point denotes the center of mass (COM) of the robot.The robot is self-driven along the orientation, ?n, from the center of mass to the geometric center.The dotted circle denotes a hard core with diameter,?.(c)A typical snapshot of initial configuration.
This paper is organized as follows.After the definition of our model and introduction of simulation methods in Section 2,the structure and phase behavior of the system are systematically analyzed in Section 3.Finally, we conclude our main findings in Section 4.
2.Model and methods
The disk was modelled by a rigid body characterized by two centers(Fig.1(b)): one is the geometric center,the other is the center of mass off-centered with a distancer0=1/3σ.Initially,Ndisks were randomly placed in a square box of sizeL×L(Fig.1(c)).A diskiis described by its geometric center(GC),ri(t),center of mass(COM),rci(t),and orientation,?ni(t)([cosθ,sinθ]), which goes from COM to GC,as shown in Fig.1(b).All disks interact with a repulsive Lennard–Jones potential,with a distance shifted by?,
whereri jis the distance of GCs between disksiandj.
The dynamics of each disk is described by the following equations:
wheremcis the mass of COM,Iis the rotary inertia,γtis the translational friction coefficient,γrthe rotational friction coefficient,Fathe strength of self-propelled force,kBthe Boltzmann constant.TtandTrare used as parameters of strength of translational and rotational noises,respectively.For the granular system,theTt=Tris not mandatory.Γdenotes the torque on diskidue to collision.Besides,ηi(t)andξi(t)are Gaussian white noises on the COM with zero mean and unit variances,
whereηαorηβis thex/y-th component of the vectorη(t).
We used the home-modified LAMMPS software to perform all simulations.The equations of motion were solved using a velocity-Verlet algorithm.Periodic boundary conditions were applied in theXandYdirections in two dimensions.Reduced units were used by settingm=1,σ=1,andε=1.The corresponding time unit,.Additionally, we setmc=1.1m,I=0.01mσ2(except for investigating the effect of eccentricity),the reduced translational noise,kBTt=1.0ε,self-propelled force,Fa=500ε/σshift distance,?=σ,L=100σ,and,which results in the motion of disks effectively overdamped.We mainly paid attention to the influence of rotational noise and eccentricity on the collective behavior of disks.All simulations began from random initial configurations (Fig.1(c)).Disks with random orientation are placed homogenously in the box at the beginning.For each case,it ran in a minimum time of 1×107τwith a time step,10?4τ.
3.Results and discussion
We establish the phase behavior of the system and focus on the rotational noise and rotational friction coefficient.The order parameter in two dimensions was defined as〈ψ〉=2〈cos2θ〉?1,hereθis the angle between the velocity of each disk and the average velocity of all disks in the system.We distinguish two states: one is the isotropic state with a random orientation of disks,the other is the polar state with a dominant orientation(see Fig.2).The appearance of two states depends on the rotational friction coefficient which controls the time scale of its rotation.Additionally, the state transition is also affected by number density,ρ,of disks.
3.1.Effect of γr
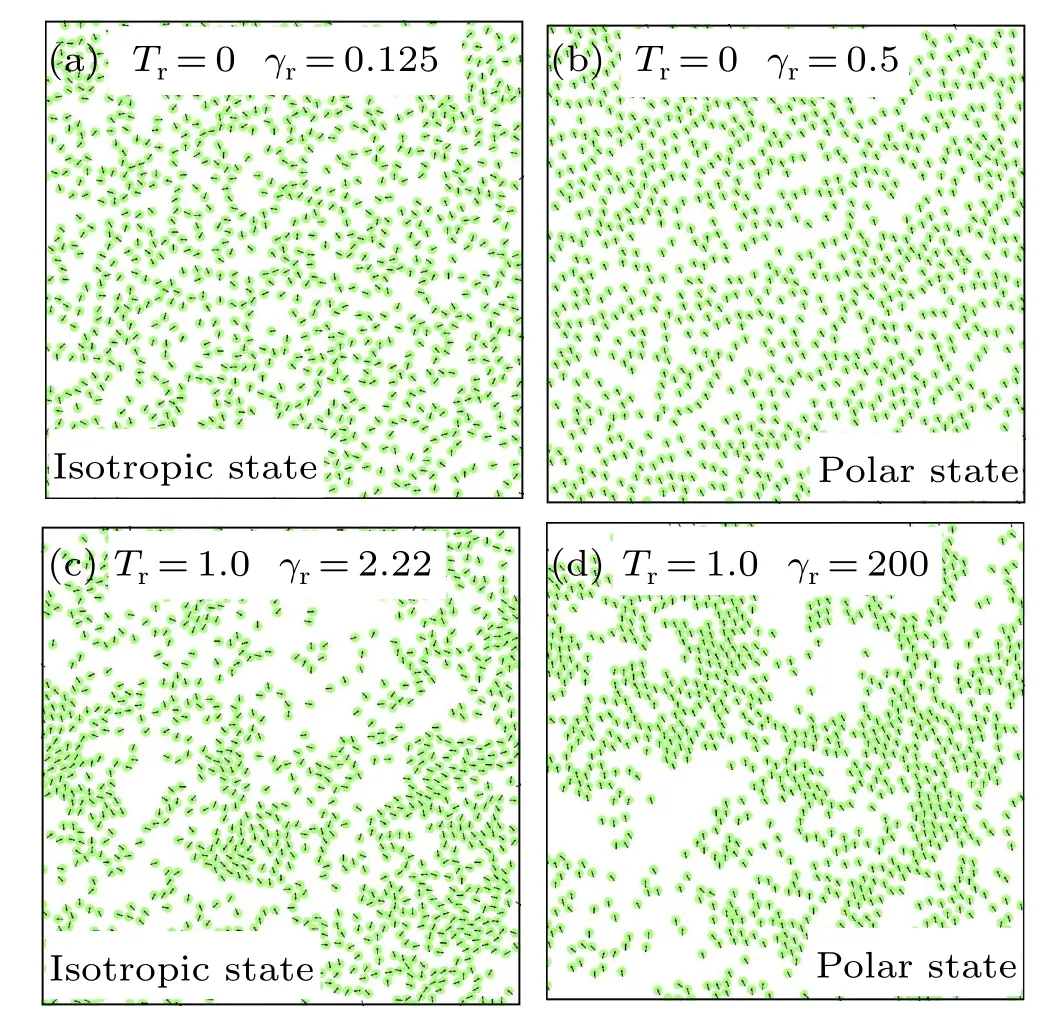
Fig.2.Typical snapshots for the systems without (Tr =0) or with rotational noise(Tr =1)at various value of γr.The black arrow denotes the orientation of each disk.
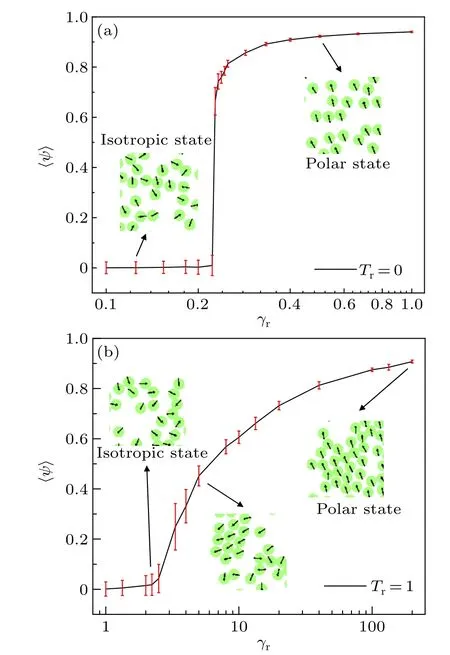
Fig.3.Order parameter, 〈ψ〉, of the system as a function of γr without,Tr=0(a),and with,Tr=1(b)rotational noise at ρ =0.1.The insets are typical snapshots at the corresponding γr.The error bar is the standard deviation of ψ.
We first pay attention to the influence of rotational friction coefficient,γron the collective behavior atρ=0.1.Here,we choose two typical systems without(Tr=0)and with(Tr=1)rotational noise from the systematic studies ofTr(Fig.S5).The order parameters,〈ψ〉, are shown in Fig.3.AtTr=0,〈ψ〉≈0 at smallγr, implying an isotropic phase (see Fig.2 and the inset of Fig.3).At largeγr,the system shows a polar phase with〈ψ〉≈0.94, where most disks move in one direction.There exists a sharp transition from isotropic phase to polar phase with the increase ofγr.AtTr=1.0, there also exists isotropic phase at smallγrand polar phase at largeγrSurprisingly, the transition of two phases becomes continuously with the increase ofγr.The interesting questions are that: (i) what is the structural difference between two kinds of systems? (ii)How does the system evolve into the ordered structure and why does the phase transition occur?
We analyze the structure of polar and isotropic state without and with rotational noise by radial distribution function,g(r)=n(r)/ρ·2πr·δr, wheren(r)is the number of disks at the distance interval, [r,r+δr], from a centra disk,ρthe average number density of system.As shown in Fig.4,the first and second peaks for the system atTr=1 are higher than that for the system atTr=0.This means that local density of disks is higher for the noisy system.What is more interesting,without rotational noise,the first peak ofg(r)for the system in the isotropic state shows slightly higher than that in polar state,implying polar state is more homogeneous.
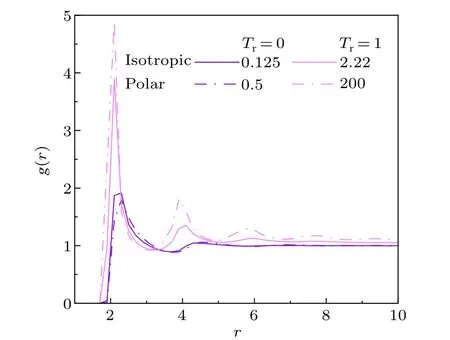
Fig.4.Radial distribution function g(r), of disks for the isotropic and polar state without or with rotational noise at the corresponding γr and ρ =0.1.
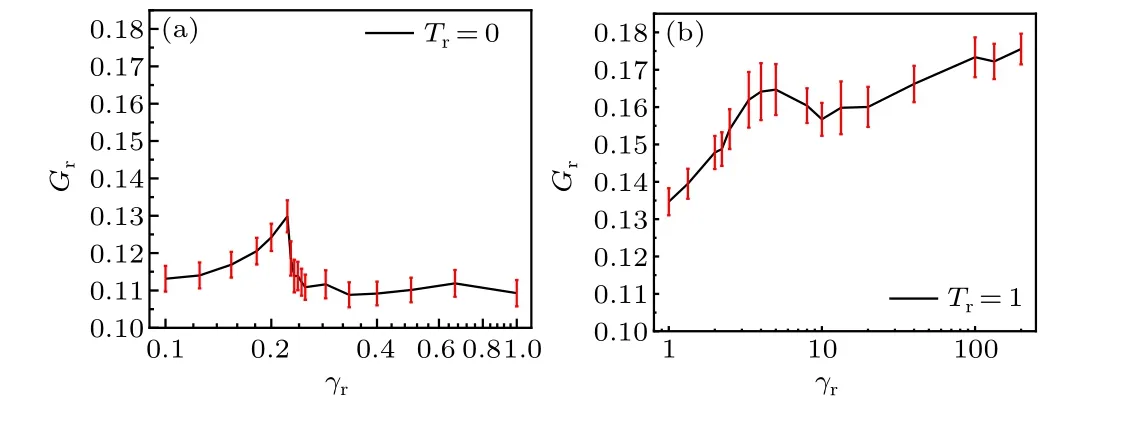
Fig.5.The Gini coefficients Gr,as a function of γr without(a)and with(b)rotational noise at ρ =0.1.The error bar is the standard deviation of Gr.
To explore the density heterogeneity of the whole system,we define and calculate the Gini coefficient
as our previous work,[25–27]where ˉρis the mean density,ρithe number density of particles in thei-th partitioned space,andNthe total number of partitioned spaces.The Gini coefficients as a function ofγrwithout and with rotational noise are given in Fig.5.Without rotational noise,Grincreases firstly and then decreases with the increase ofγr.The largestGr(close to 0.13)occurs atγr=0.225.TheGrshows the similar behavior for the systems with rotational noise.The difference is thatGr(>0.13)is larger for the noisy system.This indicates that the rotational noise has a significant effect on the collective behavior of disks, which makes the collisions between disks more frequent and leads to a larger density fluctuation.Specially in Fig.5(b),Grof the noisy system increases with a larger rotational friction coefficient.This is because,in the noisy system,the increase of rotational friction coefficient indicates the increase of persistent length of self-driven disks, which promotes cluster formation due to the self-trapping mechanism,similar to the ABP model.
To further inspect the structural difference,the local disk densities of final frames of our trajectories for the typical states are given in Fig.6.The blue color denotes the low-density region and the red color denotes the high-density region.It can be found that the density fluctuation is low for isotropic and polar states without noise.The system in polar state with noise exists large clusters and the density shows highly inhomogeneous.The results are consistent with the finding fromGr.The question is that,in the polar state,why the density heterogeneity is so different for two systems? This can be explained as follows: without noise, the change of disk’s orientation is mainly controlled by their collision.Otherwise, the disk will move along the self-driven direction.When one dominant direction of motion emerges,disks moving along the direction is rare to hit disks that are moving in the same direction with the same velocity.And disks deviating the direction have probability to change their direction via colliding with these disks.When all disks move in one direction, the distance of disks perpendicular to the direction will be adjusted by translational thermal noise.If there are angular noise,the orientation is also affected by rotational noise,the dominant direction maintains via increasing disk collision,i.e.,the increase of local density.
To understand the formation of polar order,the time evolution of system without noise atγr=0.5 is given in Fig.7(a)and Movie S1.The evolution ofGrand〈ψ〉are also plotted in Fig.8.The simulation was started from a randomly orientational and spatial distribution(Fig.7(a1)).It can be seen that small clusters forms firstly (Fig.7(a2)).The moving directions of disks in the small clusters are nearly same,but not for different small clusters.Then, the small clusters collide with each other to induce a velocity alignment and the formation of large clusters (Fig.7(a3)).This is accompanied by the increase of density heterogeneity and polar order(Fig.8).With the time evolution,nearly all disks move in a dominant direction (Fig.7(a4)) through cluster fusion and the system enters into the polar state.Interestingly, the clusters of disks gradually disappear after the polar state is formed and the system becomes more homogeneous (Figs.7(a5) and 8).The time evolution of system with rotational noise is also provided in Fig.S6 and Movie S2.The formation process of polar state is similar to the case without noise except the final density heterogeneity is higher(Fig.S7).
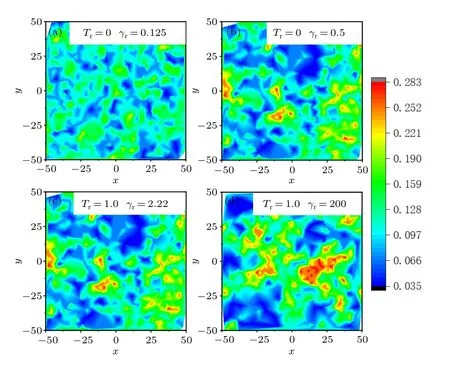
Fig.6.Local disk densities for the systems without (upper) or with(lower) rotational noise.Panels (a) and (b) are the local disk densities for the system without rotational noise at various values of γr.Panels(c)and(d)are for the noisy system.
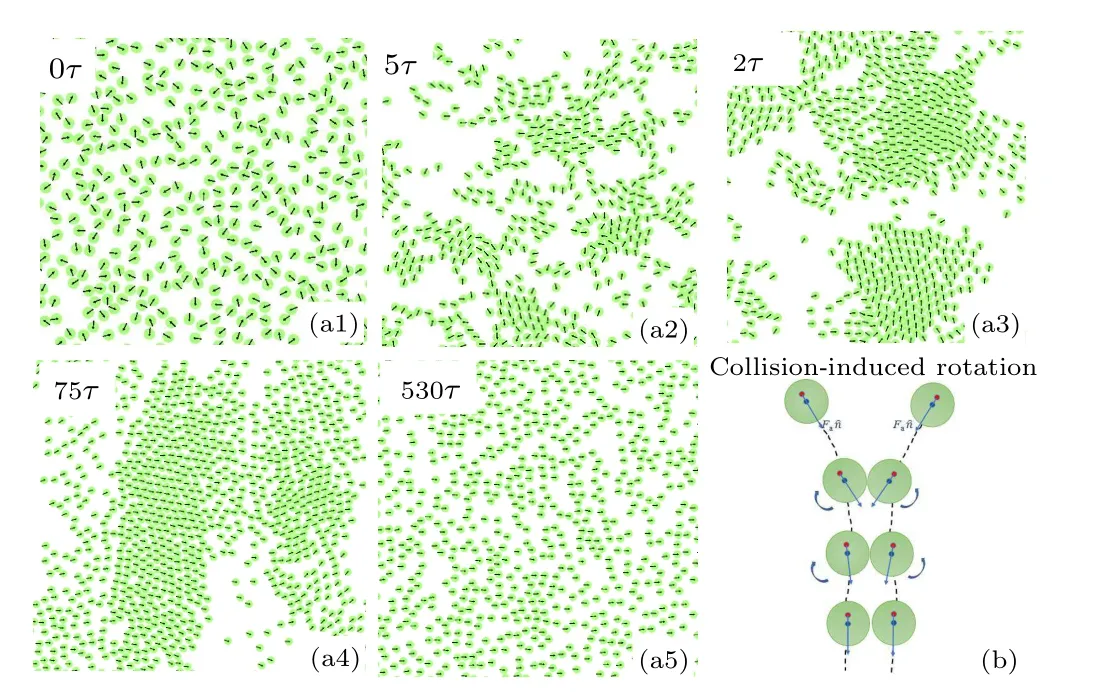
Fig.7.(a1)–(a5) Time evolution of the system at γr = 0.5 from the isotropic to the polar conformation and (b) a diagram for collisioninduced rotation of self-driven eccentric hard disks.
The formation of polar state attributes to the collisioninduced rotation, which gives rise to the alignment effect of moving direction of disks due to the mutual coupling of the positional and orientational degrees of freedom in the dynamics of each disk (Fig.7(b)).The elastic collision results in a force acting on the GC of each disk.Due to the COM offset from the GC,the force produces a nonzero torque on the disk,which leads to the disk rotation.At a certain torque and rotational damping,the cascading collisions will eventually cause the velocity alignment.
To further understand why the system becomes homogenous, we performed an extra simulation of system without both translational and rotational noise.It can be found that all disks are moving in a direction and their spatial inhomogeneity in the polar state does not decrease over time(see Movie S3 and Fig.S8).This means that the translational noise is the key cause of homogenous distribution of disks.The dynamics of disks in the polar state is reminiscent of fluid with drift velocity.It can be manifested by the mean-squared displacement(MSD)and Gaussian distribution of velocity without drift(see Figs.9(a)and 9(b)).The MSD shows a normal distribution at a long-time scale.The probability distributions of the non-drift velocity,?vi=vi ?ˉv,(ˉvis the average velocity of the whole system) follows an approximate Gaussian distribution.The diffusion of disks due to thermal noise facilitates the formation of a spatially homogeneous state.However,the rotational noise has the opposite effect,which could enlarge the density heterogeneity accompanied by frequenter collision.
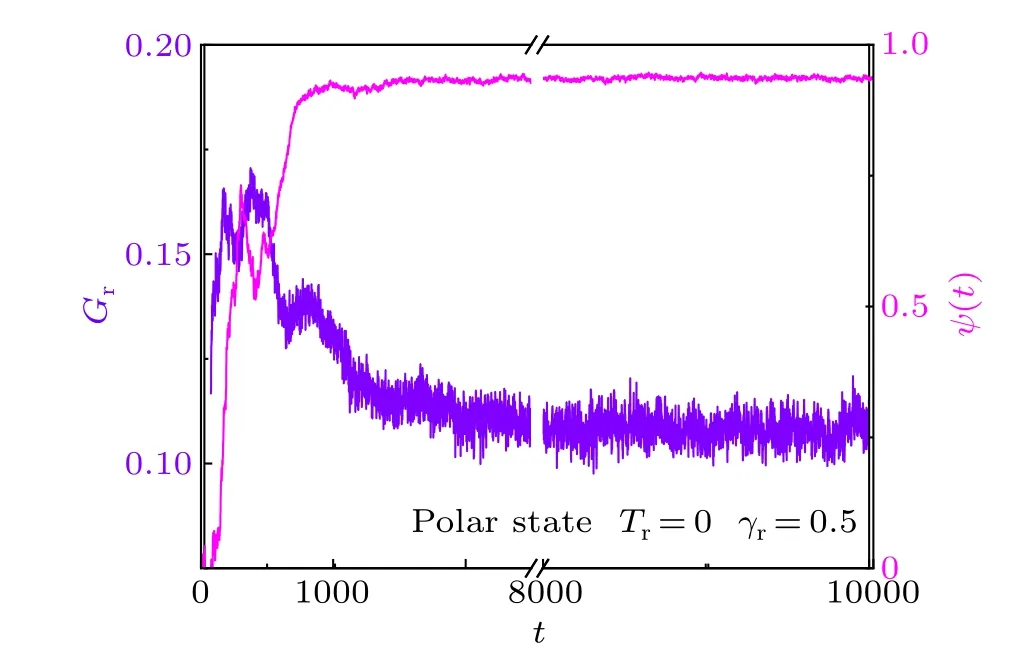
Fig.8.The Gini coefficients Gr and order parameter as a function of time for the system of ρ =0.1 in the polar state without rotational noise.

Fig.9.(a)Mean-squared displacement and(b)probability distribution of non-drift velocities of disks for the system without both translational and rotational noise at ρ =0.1.
To understand the mechanism of phase transition,we define and calculate the time correlation function,and spatial correlation function,C(r)=of each disk.As shown in Fig.10,the spatiotemporal correlation of velocity of disks in the polar state (atγr=0.5,Tr=0 and atγr=200,Tr=1) is stronger than that in the isotropic state (atγr=0.125,Tr=0 and atγr=2.22,Tr=1), which means the moving direction of disks does not change over a long time and distance.The correlation time,which determines the persistence of the disk’s polarity,is important for the polar formation.The strong correlation originates from the high rotational diffusion coefficient,which suppresses the orientation deviation of disks after collision (see the inset of Fig.10(a)).Intuitively, the effective alignment roots in the collision-induced rotation and the ability of disks keeping their moving direction.
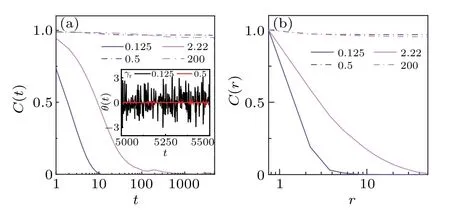
Fig.10.(a) The time correlation function C(t) and (b) spatial correlation function C(r) of disk’s orientation in the polar states with or without rotational noise.The inset is time evolution of the rotational angle of a disk for the system without noise at γr=0.125 and 0.5.
3.2.Effect of rotational noise intensity
Here, we focus on the effect of rotational noise at fixedγr= 1.The order parameter as a function ofTris presented in Fig.11(a).It can be found that the order parameter monotonously decreases with the increase ofTr, which implies that the orientation of disks gradually becomes disordered.The spatial correlation function (Fig.11(b)) and time correlation function(Fig.11(c))show that the increase of rotational noise causes the fast decrease of the spatiotemporal correlation of velocity.It not only decreases the spatial correlation length,also decrease the correlation time.This implies that the rotational noise destroys the persistence of velocity orientation and impedes the formation of polar state.
To further understanding the effect of rotational noise,theγr–Trphase diagram is given in Fig.11(d).It can be seen that,without rotational noise, the transition from an isotropic to a polar state is sharp(without green region)with the increase ofγr.The existence of rotational noise results in the continuous phase transition (with green region).However, the feature of the phase transition is independent of intensity of non-zero rotational noise.Here the critical rotational friction coefficient,was determined by choosing〈ψ〉≈0.25.As shown in Fig.11(e),theis linearly and monotonously increases withTrwith a slope≈2.2.This is because that the appearance of polar state depends on the ratio of rotational and translational characteristic time,α=γrFa/(σTrγt).The critical ratio turns out to be nearly 11 in our case.
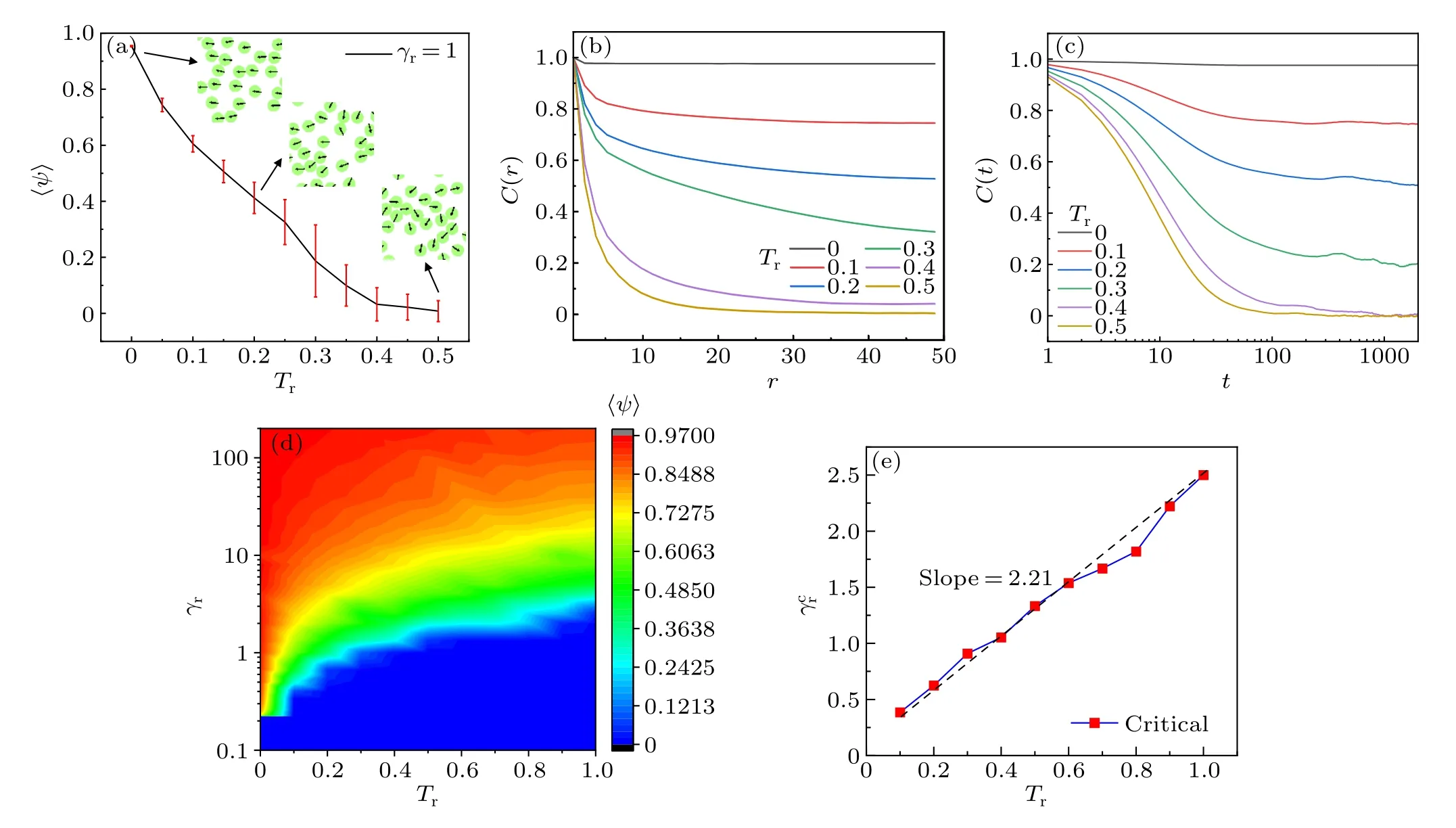
Fig.11.(a) Order parameter as a function of Tr, (b) spatial correlation function, and (c) time correlation function for the systems of ρ =0.1,γr =1.(d)γr–Tr phase diagram.The order parameter from 0 to 1 is colored from blue to red.(e)Critical rotational friction coefficient γcr as a function of Tr.
4.Conclusion
Compared with active Brownian particles and the Vicseklike model, here we proposed a model for self-driven eccentric disks,inspired by experimental design,to study their collective behavior via Langevin dynamics simulations.Without rotational noise, the variation of orientational order parameter with the increase of rotational friction coefficient demonstrates that the homogenous system can sharply convert from an isotropic to a polar state.With the rotational noise,the transition becomes continuous.Meanwhile, the order parameter monotonously decreases with the increase of noise strength.The formation of polar state can be understood by the alignment effect due to the mutual coupling of the positional and orientational degrees of freedom of each disk influenced by the rotational friction coefficient, which plays a critical role in the persistence of disk’s orientation.The rotational noise could weaken the alignment effect and cause the large spatial density inhomogeneity but the translational thermal noise facilitates the formation of a spatially homogeneous state.Our model make further conceptual progress on how the microscopic interaction among self-driven agents yields effective alignment due to the mutual coupling of the positional and orientational degrees of freedom,which deepens our understanding of the mechanism of the velocity alignment effect.It also provides ideas for future research on self-driven eccentric hard disks in complex and confinement systems.A similar velocity alignment phenomenon was also found in previous studies on self-propelled rods.[28,29]Due to the anisotropy of the shape of the self-propelled rods,the collision between two rods would generate an interacting torque,resulting in the velocity alignment between rods.In contrast, the shape of the self-driven eccentric disk used in our simulation is isotropic,and the diskto-disc collision interaction produces similar torques due to the deviation between center of gravity and geometric center of the disk.The steric interaction is different from the system of self-propelled rods.
It should be pointed out that it is the first step to understand the collective behavior of this kind of active matter, in which the interacting is the geometric center of the disk, not center of mass.It is different with the self-propelled rods,where the effective alignment results from the anisotropically steric interactions.Within the framework of our model,the effect of disk density on phase behavior can be further studied.Imaginably,high density will improve the collision frequency between disks,which is in favor of velocity alignment through mutual coupling of positional and rotational degrees of freedom of disks.Additionally, the effect of eccentricity is also interesting for further study(Fig.S9).We find the mutual coupling of the positional and orientational degrees of freedom of each disk is prerequisite for polar order and the degree of eccentricity does not affect the dynamics of polar formation atTr=0.
Acknowledgment
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.21674078, 21774091, and 21574096).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- First-principles calculations of high pressure and temperature properties of Fe7C3
- Monte Carlo calculation of the exposure of Chinese female astronauts to earth’s trapped radiation on board the Chinese Space Station
- Optimization of communication topology for persistent formation in case of communication faults
- Energy conversion materials for the space solar power station
- Stability of connected and automated vehicles platoon considering communications failures
- Lightweight and highly robust memristor-based hybrid neural networks for electroencephalogram signal processing