Parahellenia,a new genus segregated from Hellenia (Costaceae) based on phylogenetic and morphological evidence
Jun Chen ,Sijin Zeng ,Liny Zeng ,Khng Sinh Nguyen ,Jiwei Yn ,b ,Hu Liu ,Ninhe Xi ,*
a Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Botany/Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Digital Botanical Garden,South China Botanical Garden,Chinese Academy of Sciences,510650,Guangzhou,People's Republic of China
b Department of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture,Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering,510225,Guangzhou,People's Republic of China
c Institute of Ecology and Biological Resources,Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology,18 Hoang Quoc Viet,Hanoi,Vietnam
d Graduate University of Science and Technology,Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology,Hanoi,Vietnam
Keywords:Molecular phylogenomics New genus New species Cheilocostus
ABSTRACT Previous studies recognized three major lineages of the family Costaceae: a South American clade,an Asian clade and a Costus clade.However,the genus Hellenia within the Asian clade has been shown to be non-monophyletic and its morphology has not been studied carefully.Therefore,the complete plastid genomes of Hellenia species were obtained and the monophyly of Hellenia was tested through four different datasets in this study.Plastid phylogenomic analyses of Costaceae revealed that Hellenia is strongly supported as paraphyletic.Two major clades are recovered,namely the Hellenia s.s.subclade and the Parahellenia subclade.Phylogenetic analyses based on an enlarged taxon sampling of the Asian clade using a two chloroplast markers dataset (trnK intron and trnL-F spacer) confirmed the paraphyly of Hellenia.Meanwhile,morphological analyses suggested that members of the Parahellenia subclade differ from the remaining Hellenia species in many characters including inflorescences,bracts,stigma,axillary buds,floral tubes and labellum.According to the present molecular and morphological evidence,the latter subclade is recognized as a new genus,Parahellenia.Two new species are described,four new combinations are made,and identification keys are also provided.
1.Introduction
Costaceae Nakai,commonly known as the spiral ginger family,is a small family of Zingiberales and easily distinguished from other families within the order by well-developed and sometimes branched aerial shoots that have a characteristic spiral phyllotaxy,tubular leaf sheaths and petaloid labellum formed by fusion of five sterile staminodes (Kirchoff and Ruitshauser,1990;Kress,1990;Kress et al.,2001;Larsen,1998;Wu and Larsen,2000;Specht and Stevenson,2006).It consists of seven genera and more than 120 species,pantropically distributed with species abundant in the Neotropics (Specht,2006a;André et al.,2016;van Caspel,2019;Valderrama et al.,2020).Previous phylogenetic analyses of the family Costaceae based on multiple molecular marks from chloroplast(trnK intron and trnL-F spacer)regions and nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) as well as morphological and biogeographic information recognized three major lineages:a South American clade (consisting of Chamaeocostus C.D.Specht &D.W.Stev.,Dimerocostus Kuntz and Monocostus K.Schum.),an Asian clade (comprising Cheilocostus C.D.Specht,Paracostus C.D.Specht and Tapeinochilos Miq.) and an African-Neotropical Costus clade(Costus L.) (Specht et al.,2001;Specht,2006a,2006b;Specht and Stevenson,2006).However,the relationships remained unresolved for some clades,notably the Asian and Costus clades.Recent phylogenetic studies have mainly focused on the Costus clade (see Kay et al.,2005;Salzman et al.,2015;André et al.,2016;Maas-van de Kamer et al.,2016;Valderrama et al.,2020) while few studies have so far been conducted on phylogenetic relationships within the Asian clade.Within this clade,Paracostus and Tapeinochilos were supported as distinct monophyletic groups (Specht et al.,2001;Specht,2006a,2006b;André et al.,2016;Carlsen et al.,2018),but the relationships among the remaining members are uncertain,in particularly,the genus Cheilocostus (≡Hellenia Retz.).
Cheilocostus was established to accommodate a group of Southeast Asian and Malesian species classified at that time as members of the broadly defined genus Costus (Specht and Stevenson,2006).The widespread Cheilocostus speciosus (J.Koenig) C.D.Specht (≡Banksea speciosa J.Koenig) was designated as the generic type.Three other species,Costus globosus Blume,C.lacerus Gagnep.and C.sopuensis Maas &H.Maas,were also transferred to Cheilocostus in that study.They accepted Maas’treatment in 1979 to recognized Cheilocostus globosus(Blume)C.D.Specht,C.lacerus(Gagnep.)C.D.Specht and C.speciosus as different species complexes.Among them,Cheilocostus globosus group as circumscribed by Maas (1979) referred to 15 names: Costus acanthocephalus K.Schum.(Indonesia),C.chrysocephalus K.Schum.(New Guinea),C.clemensae Ridl.(Philippines),C.dhaninivatii K.Larsen (Thailand),C.globosus (Indonesia),C.kingii Baker[≡C.globosus var.kingii(Baker)Holttum,Malaysia],C.microcephalus K.Schum.(Malaysia),C.oligophyllus K.Schum.(Malaysia),C.ridleyi K.Schum.[≡C.globosus var.ridleyi(K.Schum.)Holttum,Malaysia],C.sulfureus K.Schum.(Indonesia),C.tonkinensis Gagnep.(Vietnam),C.velutinus Ridl.[≡ C.globosus var.velutinus (Ridl.) Holttum,Malaysia].Later,Costus mulus Meekiong,Ipor &Tawan (Malaysia)was defined within this group (van Caspel,2019).This group is characterized by inflorescences borne on separate leafless shoots and bracts that are spiny at their apices.However,Dutta(2010)and Govaerts (2013) argued that Cheilocostus is an illegitimate superfluous name(ICN Art.52.1,Thurland et al.,2018)because it includes the type of Hellenia,which would be adopted for the genus.Morphologically,Hellenia is characterized by having an open and showy labellum,woody bracts,leaf-bearing shoots with axillary branching,a bilamellate stigma with dorsal bilobed appendage(Specht and Stevenson,2006).Till now,only 10 species were currently transferred to Hellenia (Dutta,2010;Govaerts,2013;Kumar et al.,2016a;Chen et al.,2021),and some Asian species have not been transferred to this genus,e.g.,C.tonkinensis.On the other hand,those species complexes,especially Hellenia globosa(Blume)S.R.Dutta,appear to be highly variable taxa,which need intensive field studies particularly with regards to floral characters like shape and structure of the labellum and colour of the various other floral parts before it can be determined where the boundaries are between species.To sum up,this genus is in urgent need of comprehensive revision.
Since only three Hellenia species,namely H.globosa,H.lacera(Gagnep.) Govaerts and H.speciosa (J.Koenig) S.R.Dutta,were sampled in previous studies (Specht,2006a;2006b),the relationship of Hellenia within Asian clade is not well resolved.Phylogenetic trees reconstructed from limited plastid regions (trnK and trnL-F)suggested that Hellenia is paraphyletic because H.globosa was not in a clade with the remaining Hellenia species but had a unique phylogenetic position sister to the Hellenia s.s.subclade plus Tapeinochilos (Specht,2006a).However,phylogenetic study based on molecular[ITS,RPB2(RNA polymerase II the second largest subunit),trnK,trnL-F] and morphological data indicated that Hellenia was monophyletic only with weak overall support and collapsed with Tapeinochilos,and thus this genus was only upheld by morphological support (Specht,2006b).It is worth emphasizing in that study H.globosa formed a distinct and strongly supported subclade which was sister to the remaining members of Hellenia plus Tapeinochilos.This rather surprising result prompted our closer examination of the H.globosa subclade,which consists of four currently accepted species,viz.Costus mulus,C.tonkinensis,Hellenia borneensis (A.D.Poulsen)Govaerts and H.globosa.The species of this subclade can be morphologically distinguished from other Hellenia species by a suite of characters,such as inflorescences arising on leafless shoots from the rhizomes,laxly imbricated bracts,a bilamellate stigma with two equal lobes and glabrous leaf blades.
The poor phylogenetic resolution of Hellenia may be due to limited taxon sampling or insufficient informative sites for the molecular markers selected (Specht et al.,2001;Specht,2006a,2006b;André et al.,2016;Carlsen et al.,2018).To further assess the phylogenetic relationship of Hellenia,a comprehensive taxon sampling of Hellenia and its relatives and more sequence data are necessary.Phylogenomics provides us with an effective means to resolve difficult phylogenetic problems (Wen et al.,2015;Zimmer and Wen,2015).Nowadays,the genome skimming method can generate a large amount of data and has been used to obtain complete chloroplast genomes,entire nuclear ribosomal DNA(nrDNA) repeats,which has been successfully applied to reconstruct the phylogenetic history of various plant lineages(Mabry and Simpson,2018;Thomson et al.,2018;Liu et al.,2019,2020;Marinho et al.,2019;Yang et al.,2021;Yao et al.,2021).However,resolution within the Asian clade collapses based on the ITS dataset,indicating that this rapidly evolving region provides strong phylogenetic signal at the tips while potentially causing conflict at the base(Specht,2006b).
We herein reconstruct the phylogeny of Hellenia s.l.by sampling more species from China and Vietnam,using chloroplast genomes and two chloroplast DNA (trnK and trnL-F) regions.By integrating these molecular findings with a morphological investigation using both herbarium specimens and living samples,our studies aim to test the monophyly of Hellenia.Based on these data,a new genus is established and a taxonomic revision for this genus is presented.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Taxon sampling and outgroup selection for phylogenetic analyses
To obtain a more accurate phylogeny of Hellenia,three datasets of plastid genomes [coding regions (CDS),non-coding regions(non-CDS) and complete plastid genomes respectively] and one dataset of two plastid markers (trnK+trnL-F)were utilized.
Firstly,plastid phylogenomic analyses of Costaceae (three datasets of plastid genomes) were conducted to reveal the approximate position of Hellenia within the family.15 species representing six genera and three clades of Costaceae were sampled based on previous phylogenetic relationships reported in Specht and Stevenson (2006).Two species (Alpinia oxyphylla Miq.and Zingiber officinale Roscoe)from Zingiberaceae were selected as outgroups according to phylogenetic relationships reported in Kress et al.(2001).Detailed information of all species sampled are provided in Table S1.
Then,the dataset of two plastid markers (trnK+trnL-F) was used to conduct phylogenetic studies of the Asian clade with enlarged taxon sampling.A total of 21 ingroup taxa of four genera(six Hellenia species,four Tapeinochilos species,two Paracostus species from the Asian clade and nine Costus species)were used for molecular analyses.Four species belonging to three genera (Chamaecostus,Dimerocostus and Monocostus) were selected as outgroups,which were representatives of the South American clade in the sense of Specht and Stevenson(2006).Sequences of these two DNA regions of Hellenia species were extracted from the assembled complete plastid genomes.Other available sequences were downloaded from GenBank (from Pederson,2004;Specht,2006b;Salzman et al.,2015;Givnish et al.,2018;Cui et al.,2019;Li et al.,2020).Detailed information of all species sampled and sequences used are available in Table S2.
2.2.DNA extraction,sequencing and assembly
Silica-gel dried leaves were sent to Novogene(Tianjin,China)to extract total genomic DNA for library (350 bp) preparation for genome skimming sequencing.Paired-end (150 bp) sequencing was conducted on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000(San Diego,CA,USA),generating ca.20 Gb raw data for each sample.After quality control of the raw data,all paired reads were extracted for plastid assembly using GetOrganelle 1.7 (Jin et al.,2020).The plastid genome of Tapeinochilos ananassae K.Schum.(MH603446) was downloaded from Genbank as the reference.
2.3.Plastid genome annotation
Plastid Genome Annotator(PGA)with the reference mentioned above and GeSeq with default settings were used to annotate the newly assembled plastid genome of Hellenia speciosa(Tillich et al.,2017;Qu et al.,2019).Geneious Prime 2019(https://www.geneious.com)was used to check and integrate these two annotations.Then,the newly annotated plastome sequence of H.speciosa was used as the reference to annotate the other plastid genomes using PGA.
2.4.Plastid genome alignment and phylogenetic inference
The coding regions and non-coding regions of plastid genomes were extracted by Python script (http://github.com/Kinggerm/PersonalUtilities/blob/master/get_annotated_regions_from_gb.py)and aligned by MAFFT 7.4 (FFT-NS-i × 1000 strategy) separately(Katoh and Standley,2013).Poorly aligned regions were removed by trimAl 1.2 with default settings before subsequent analyses(Capella-Gutiérrez et al.,2009).In addition,two DNA makers(trnK and trnL-F)were extracted from plastid genomes by Geneious,then were aligned using MUSCLE in MEGA 7 separately (Edgar,2004;Kumar et al.,2016b).Later,the cpDNA dataset including trnK and trnL-F regions were constructed and used in the subsequent phylogenetic analyses.
Maximum likelihood (ML) analyses were conducted in IQTREE 1.6 using SH-aLRT test and ultrafast bootstrap (UFBoot) feature(-alrt 1000-bb 1000-nt AUTO)(Nguyen et al.,2015;Hoang et al.,2018)on CentOS 7.6.Graphical representation of the plastid circular map of H.speciosa was generated with OGDRAW (Greiner et al.,2019).
2.5.Morphological comparisons
Morphology and distribution of Hellenia and related genera identified in the past phylogenetic analyses(Specht,2006a,2006b;Specht and Stevenson,2006) were compared.A total of 17 characters were examined to understand their possible distinctions.The selection of morphological characters was mainly based on Maas(1972)and Specht(2004).Morphological data of Hellenia was based on field and herbarium collections or published accounts(Maas,1979;Specht,2004;Specht and Stevenson,2006;Larsen,2008;Meekiong et al.,2008;Poulson and Specht,2010).Morphological data of Tapeinochilos was obtained from relevant literature(Miquel,1869;Schumann,1904;Maas,1979;Smith,1987;Gideon,1996;Specht,2004) or website (http://www.gingersrus.com) and herbarium collections.
3.Results
3.1.Plastid genome structure
Nine chloroplast genomes of Costus tonkinensis (three samples)and Hellenia species (six samples) were newly sequenced and assembled with lengths ranging from 166,129 to 168,082 bp.All chloroplast genomes have a typical quadripartite circular structure with a pair of inverted repeats regions(IRs)that separate the large single-copy (LSC) and small single-copy (SSC) regions.The representative gene map of the H.speciosa chloroplast genomes is presented in Fig.1.
3.2.Phylogenetic analyses
Our datasets included 3759 bp of two plastid markers data,74,662 bp of plastid CDS data,50,002 bp of plastid non-CDS data and 124,664 bp of complete plastid genome data.Summary features of sampled sequences of these four datasets are provided in Table S3.
The phylogenetic trees using three different datasets of plastid genomes have identical topologies (Fig.2,Figs.S1-S2),and thus only the plastid CDS tree is presented here (Fig.2).The phylogenomic tree recovered three main clades: an Asian clade,a Costus clade and a South American clade.The Asian clade is strongly supported(SH-aLRT 100%,UFBoot 100%)and includes species of Hellenia s.l.plus Tapeinochilos.The Costus clade is mainly composed of the genus Costus (SH-aLRT 100%,UFBoot 100%).The South American clade contains Chamaecostus,Dimerocostus and Monocostus (SHaLRT 100%,UFBoot 100%).As currently circumscribed,Hellenia is non-monophyletic but is strongly supported as paraphyletic(Fig.2).Two subclades were recognized within Hellenia,namely the Hellenia s.s.subclade including the generic type H.speciosa and the Parahellenia subclade including C.tonkinensis and two unknown species.The former subclade appears as sister to Tapeinochilos (SH-aLRT 100%,UFBoot 100%),while the latter subclade is distantly related to the core Hellenia with strong support(SH-aLRT 100%,UFBoot 100%).
The phylogenetic tree based on the dataset of two plastid markers (trnK+trnL-F) is a little different from those of plastid genomes and recovered the Asian clade to be paraphyletic (Fig.3)because Paracostus was found to be sister to the Costus clade not to the Asian clade (SH-aLRT 82%,UFBoot 61%).The Asian clade contains only two genera,Hellenia s.l.and Tapeinochilos.Hellenia s.l.can be further divided into two subclades:the Hellenia s.s.subclade and the Parahellenia subclade.Tapeinochilos forms a well-supported monophyletic subclade (SH-aLRT 97%,UFBoot 48%) as sister to the Hellenia s.s.subclade,and this pair is then sister to the Parahellenia subclade.
3.3.Morphological analyses
The comparison of 17 characters yielded two groups of Hellenia.Group I includes the species of the Parahellenia subclade,such as Costus tonkinensis;group II includes the rest species of Hellenia.The species of group I usually have glabrous leaves,mostly lateral inflorescences(Fig.4A)and a bilamellate stigma with two equal lobes(Fig.4C),while those of group II have glabrous upper leaf sides,pubescent lower leaf sides,always terminal inflorescences(Fig.4D)and a bilamellate stigma with one lobe larger than the other one(Fig.4F).Group I species always possess a solitary bud at each node and laxly imbricated bracts,while group II species sometimes have more than one bud at each node and densely imbricated bracts.Group I species have slender and long floral tubes fused more than halfway with the style base(Fig.4B)and a funnel-shaped labellum due to its small tube,whereas group II possess nearly hollow floral tubes (Fig.4E) and a horizontally flattened labellum.

Fig.1.Map of the Hellenia speciosa plastid genome.Genes shown outside the outer circle are transcribed counterclockwise and those inside are transcribed clockwise.Genes in different functional groups are color coded following the legend.The dark shading in the inner circle indicates GC percent.LSC indicates large single copy;SSC,indicates small single copy and IR,indicates inverted repeat.
Group I also differs from the genus Tapeinochilos in having an open and conspicuous labellum (the open floral form) and three locules per ovary,while the latter has a tubular and inconspicuous labellum(the ornithophilous floral form)and two locules per ovary.Group I possesses laxly imbricated bracts,slender and long floral tubes fused more than halfway with the style base,while the members of Tapeinochilos have densely imbricated bracts and hollow floral tubes.In contrast to group I,the species of Tapeinochilos always have toothlike lateral staminodes but lack a stigma appendage and a bracteole.More detailed comparisons are provided in Table 1.
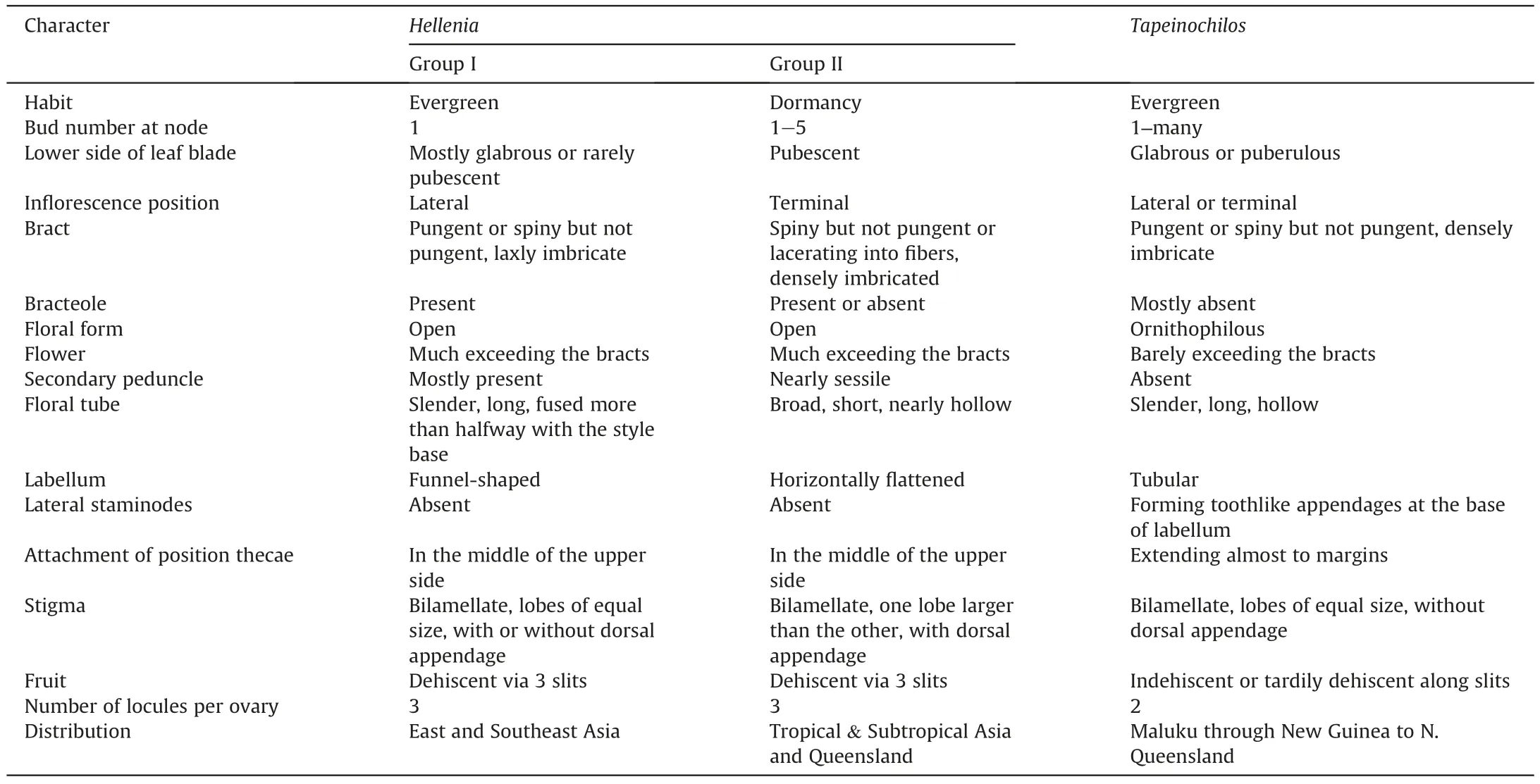
Table 1 Comparison of morphology and distribution of Hellenia and Tapeinochilos.
4.Discussion
4.1.Phylogenetic relationships within Costaceae and the Asian clade
Molecular evidence has been the main basis for splitting the Costaceae into three main clades.However,the phylogenetic relationships of some clades were weakly supported or even in conflict in previous studies (Specht,2006a,2006b;André et al.,2016;Carlsen et al.,2018).For example,previous phylogenetic analyses using several chloroplast and nuclear regions showed that the Asian clade was sister to the Costus clade although the node was not well supported (Specht,2006a,2006b;André et al.,2016).In contrast,phylogenetic analysis using up to 378 putatively orthologous low-copy nuclear genes suggested that the Asian clade was not sister to the Costus clade but was the basal clade of Costaceae(Carlsen et al.,2018).
The present plastid phylogenomic analyses revealed that Costaceae can be divided into three clades in agreement with previous studies(Specht,2006a,2006b;André et al.,2016).The Asian clade is strongly supported(SH-aLRT 100%,UFBoot 100%)as sister to the Costus clade,and the South American one is the basal clade of Costaceae with high support(SH-aLRT 100%,UFBoot 100%)(Fig.2).The phylogenetic relationships recovered here are largely consistent with that reported in Specht (2006a,2006b),but support values of relevant nodes increased markedly (Fig.2).This result indicates that the plastid phylogenomic approach is helpful in clarifying the relationships of Costaceae members.
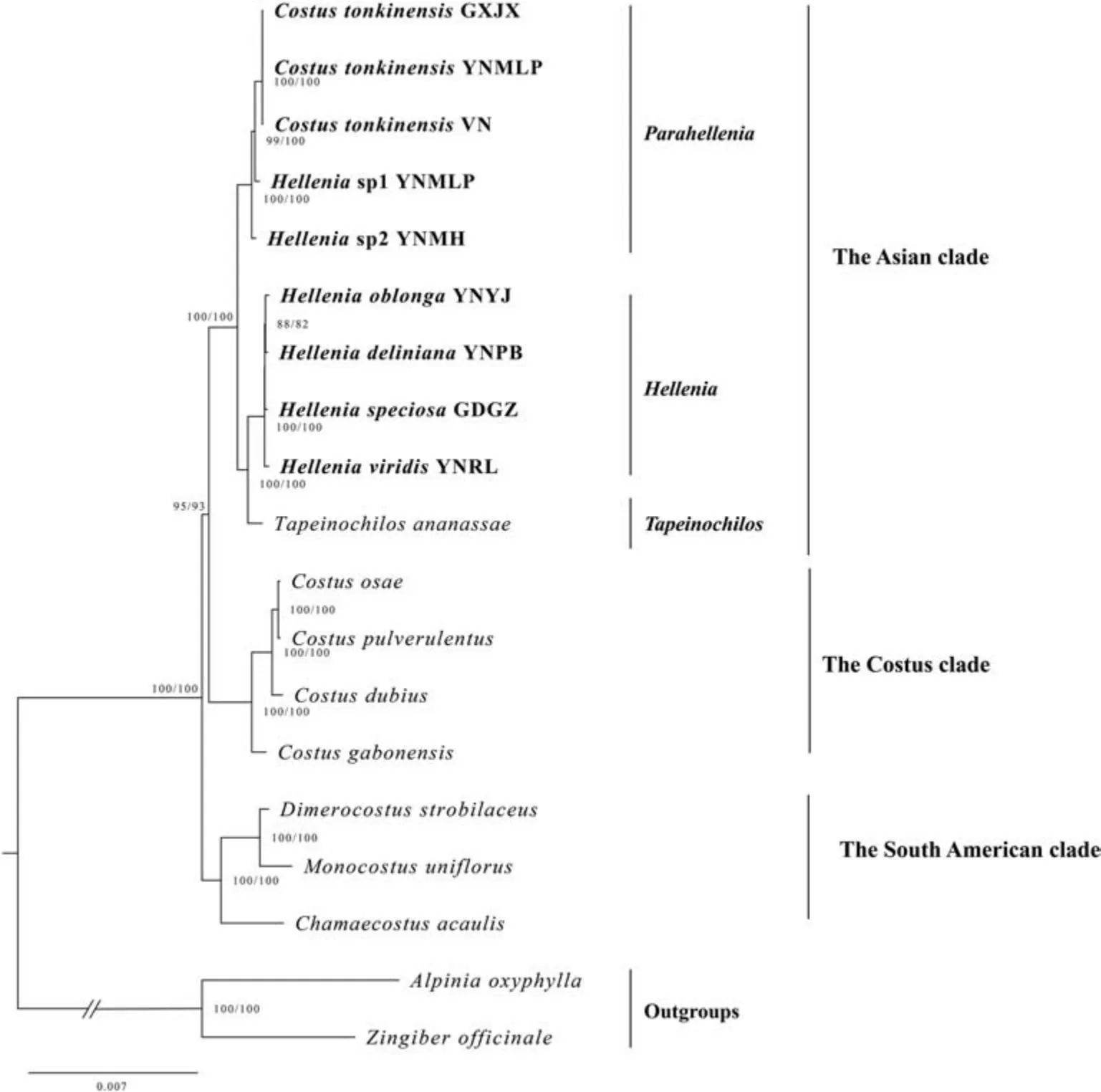
Fig.2.Phylogenetic relationships of Costaceae based on the coding regions(CDS dataset)of 19 plastid genomes.The value of the SH-aLRT test(left)and ultrafast bootstrap(right)are indicated at nodes and separated by a slash. Hellenia sp1= Parahellenia malipoensis, Hellenia sp2= Parahellenia yunnanensis.
The Asian clade in the sense of Specht(2006b)comprised three genera (Hellenia,Paracostus and Tapeinochilos).In line with previous studies (Specht,2006a,2006b;André et al.,2016),our phylogenetic analyses from four datasets all supported the close relationship between Hellenia and Tapeinochilos,and both grouped together within the Asian clade.Nevertheless,in conflict with those studies,the phylogenetic analysis based on two plastid regions(trnK and trnL-F) suggested that the Asian clade is nonmonophyletic but paraphyletic as Paracostus is not sister to the remaining members of the Asian clade but to the Costus clade(Fig.3).Costus as currently defined is the largest genus of Costaceae,which is restricted to the tropical moist forests of Africa and America with species diversity centered in the Neotropics.This genus has the broadest circumscription and includes most of the morphological diversity in the family (Specht and Stevenson,2006).However,Paracostus is limited to Borneo and Africa.This genus includes five species and is characterized by few-leaved prostrate stems,inconspicuous and not spiny bracts,and fewflowered inflorescences emerging from the nodes of lower part of the stem or rhizome (Specht and Stevenson,2006;Poulsen and Specht,2010).Therefore,increasing taxon sampling of the family,especially members of Paracostus not sampled in the current phylogenomic analyses,is necessary for improving our understanding of the evolutionary history of the family.
4.2.Paraphyly of Hellenia
Our phylogenetic results further recovered Hellenia s.l.as paraphyletic with two subclades divided.Subclade I is represented by Hellenia s.s.including the type H.speciosa,which is sister to Tapeinochilos.However,the species of subclade II form a highly supported group (the Parahellenia subclade) and are segregated from the remaining Hellenia species (the Hellenia s.s.subclade).The Parahellenia subclade was originally classified within Hellenia mainly by the general floral form (Specht and Stevenson,2006).However,there are differences in the structure of flowers of the Parahellenia subclade.All species of the Parahellenia subclade have a slender and long floral tube fused more than halfway with the style base and a funnel-shaped labellum due to its small tube.Furthermore,all species of the Parahellenia subclade share a combination of characters that also differentiate them from Hellenia,such as lateral and lax inflorescences and a bilamellate stigma with two equal lobes.They can also be easily recognized by vegetative characters,e.g.,their glabrous leaf blades,branches emerging from upper nodes(instead of breaking through the lower leaf sheaths) and a solitary axillary bud at each node.In addition,the plants of Parahellenia subclade mostly grow along ravines in East and Southeast Asia,while the other Hellenia species have a wider distribution (Tropical &Subtropical Asia and Queensland) and grow in forests,along roadsides or moist valleys.
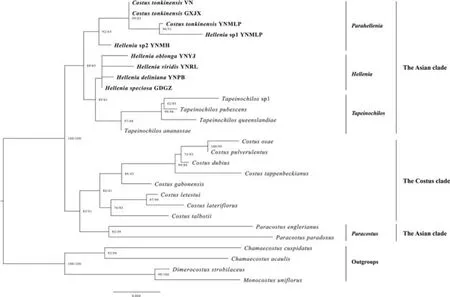
Fig.3.Phylogenetic relationships of Hellenia based on trnK intron and trnL-F spacer.The value of SH-aLRT test (left) and ultrafast bootstrap (right) are indicated on nodes and separated by a slash.Values at nodes of less than 80 (both parameters) are not shown. Hellenia sp1= Parahellenia malipoensis, Hellenia sp2= Parahellenia yunnanensis.

Fig.4. Parahellenia tonkinensis (Gagnep.) Juan Chen,N.H.Xia,L.Y.Zeng &S.Jin Zeng (A-C) and Hellenia speciosa (D-F).A.Lateral inflorescence;B.Flower bud (longitudinal view)showing corolla tube fused with style at base;C.Bilamellate stigma with two equal lobes and sharply-bilobed dorsal appendage;D.Terminal inflorescence;E.Flower bud (longitudinal view) showing nearly hollow corolla tube;F.Bilamellate stigma with one lobe larger than the other one and rounded-bilobed dorsal appendage.
Another close relative of the Parahellenia subclade is the genus Tapeinochilos,which is restricted to New Guinea and adjacent parts of Indonesia and northern Australia.Our results strongly supported Tapeinochilos as representing a distinct monophyletic clade,in accordance with the past studies (Specht,2006a;2006b).As mentioned above,this genus is easily distinguished from the Parahellenia subclade by bilocular ovules,a small and inconspicuous labellum,hollow floral tubes,densely imbricated bracts,absence of bracteoles,and lateral staminodes forming toothlike appendages at the base of labellum (Table 1).
In conclusion,our molecular phylogenetic analyses suggest that all species of the Parahellenia subclade are closely related to each other,comprising a monophyletic group with a rather isolated position within the Asian clade (Figs.2?3).The reconstructed phylogenetic relationships,together with a unique combination of morphological characters,support the recognition of a new genus to accommodate the species of the Parahellenia subclade and thus,a new genus Parahellenia is proposed.Morphological characteristics that distinguish Parahellenia from related taxa are given in Table 1 and a key is also provided to distinguish all genera within the Asian clade.Parahellenia currently comprises six species distributed in China,Indonesia,Malaysia,Thailand and Vietnam.Due to the limitations of sampling and accessibility,a broader taxonomic revision of the new genus is impossible currently.Thus,much more work is needed to resolve the relationships within the new genus in the future based on our results and previous studies (Maas,1979;Specht and Stevenson,2006;van Caspel,2019).
5.Taxonomic treatment
5.1.Key to the genus Parahellenia and related genera within the Asian clade
1 Plants prostrate;leaves few or solitary;inflorescence few-flowered;bracts inconspicuous………………………………Paracostus
1 Plants erect or slightly spiral;leaves many;inflorescence manyflowered;bracts conspicuous…………………………………………2
2 Ovary bilocular;labellum small,inconspicuous………………………………………………………………………………Tapeinochilos
2 Ovary trilocular;labellum large,showy…………………………………………………………………………………………………3
3 Inflorescence arising on a leafless shoot from the rhizome;bracts laxly imbricate,bilamellate stigma with two equal lobes;leaf blades mostly glabrous….…………………………………………Parahellenia
3 Inflorescence terminal on leafy shoot;bracts densely imbricate;bilamellate stigma with one lobe larger than the other one;lower side of the leaf blades pubescent………………………………Hellenia
5.2.Description of the new genus
ParahelleniaN.H.Xia,Juan Chen,L.Y.Zeng &S.Jin Zeng,gen.nov.
Type:Parahellenia tonkinensis(Gagnep.)Juan Chen,N.H.Xia,L.Y.Zeng &S.Jin Zeng,comb.nov.≡Costus tonkinensis Gagnep.
Diagnosis.This genus is similar to Hellenia,but differs in the lateral inflorescences (vs.terminal inflorescences),laxly (vs.densely) imbricated bracts,a bilamellate stigma with two equal lobes (vs.one lobe larger than the other one),a solitary (vs.1-5)axillary bud at each node,slender and long (vs.broad and short)floral tubes fused more than halfway with the style base(vs.nearly hollow),a funnel-shaped labellum due to its small tube (vs.horizontally flattened labellum).
Description.Evergreen perennial herbs.Rhizome thick and fleshy.Leafy shoot cane-like,slightly to highly spirally twisted,branches emerging from upper nodes,with secondary branching.Axillary bud 1 at each node.Leaves arranged spirally with closed sheaths;ligule short;petioles very short,terminal leaves sessile;lamina obovate or elliptic,smooth to lightly plicate,mostly glabrous on both sides.Inflorescence arising directly from the rhizome.Peduncle horizontal to ascending,covered with many tubular sheaths.Secondary peduncle short.Bracts coriaceous,pale green,red or brown,without appendage,mostly pungent at apex,each subtending a single flower.Bracteoles coriaceous,narrowly lanceolate to acerose,or cucullate,mostly pungent at apex.Flower sessile.Calyx tubular at base,3-lobed,lobes of equal size,mostly pungent at apex as bracts and bracteoles.Floral tube nearly as long as calyx,slender,long,fused more than halfway with the style base;lobes large,membranous,lanceolate.Labellum large,obovate,thin,funnel-shaped (forming a narrow tube that opens broadly at apex),never lobed;white,yellow to orange and sometimes red.Stamen 1,petaloid.Ovary trilocular.Stigma bilamellate,flattened 2-lobed,lobes of equal size,white,margin ciliate,dorsal appendage present or absent.Fruit a capsule,slightly fleshy,3-locular,dehiscing loculicidally by three longitudinal slits.Seeds numerous,irregularly barrel-shaped,aril white,basal and not enclosing the seed.
Etymology.The genus name reflects its similarity to Hellenia.
Chinese vernacular name.地萵筍花屬(dì wō sǔn huā shǔ) (新擬).
Distribution and habitat.It occurs in South and Southwest China,Indonesia,Malaysia,Thailand and Vietnam.Species of this genus grow in moist places along forest edges,in ravines in evergreen forests or bamboo forests,or from the foot to middle elevations of limestone hills,at 100-1100 m a.s.l.
5.2.1.Key to Parahellenia species
1 Bracts not pungent;leafy shoot mostly unbranched;leaf blades plicate……………………………………………………………………2
1 Bracts pungent;leafy shoot often branched;upper side of the leaf blades smooth……………………………………………………...3
2 Plants<90cm tall;leafblades small(22-28×3-5 cm);bracteoles narrowly lanceolate…………………….3.Parahellenia malipoensis
2 Plants >90 cm tall;leaf blades large (27-42 × 9-16 cm);bracteoles broadly cucullate………………1.Parahellenia borneensis
3 Bracts,bracteoles and calyces covered by stiff hairs……………………………………………………………….2.Parahellenia globosa
3 Bracts,bracteoles and calyces covered by short hairs or nearly glabrous………………………………………………………………….4
4 Leaf sheaths chartaceous;labellum white with orange center;stamen densely pilose abaxially …………4.Parahellenia mulus
4 Leaf sheaths coriaceous;labellum yellow or orange with red line at base;stamen sparsely pubescent abaxially……………………..5
5 Buds densely villous; bracts short and broad(3-4.5×2-2.6 cm);flowers yellow;upper margin of anther crest rounded;dorsal appendage of stigma bilobed,lobes acute……………………………………………5.Parahellenia tonkinensis
5 Buds villous at margin;bracts long and narrow(5.5-6 × 1.1-1.7 cm);flowers orange;upper margin of anther crest trilobed;dorsal appendage of stigma almost appressed or absent …………………………………6.Parahellenia yunnanensis
1.Parahellenia borneensis(A.D.Poulsen) N.H.Xia,Juan Chen &S.Jin Zeng,com.nov.≡Cheilocostus borneensis A.D.Poulsen,Gard.Bull.Singapore 62 (1): 136.2010 ≡ Hellenia borneensis (A.D.Poulsen) Govaerts,Phytotaxa 151(1): 64.2013 -Type: Malaysia,Sarawak,Batang Ai,Sungai Senkabang,small stream connecting to Sg.Delok opposite of Ng.Sumpa longhouse,1°12′S,112°3′E,alt.130 m,flowering on 8 December 2002,A.D.Poulsen and Bakir Raymond 1964 (holotype: SAR;isotypes: AAU,Sarawak Biodiversity Centre Flora Depository).
Phenology.Flowering from June to December;fruiting from July to February of following year.
Chinese vernacular name.婆羅洲地萵筍花(pó luó zhōu dì wō sǔn huā).
Distribution,habitat and conservation.It is endemic to Borneo and grows in lowland primary or secondary (logged)mixed dipterocarp forests,along riverbanks,at elevations of 100-200 m a.s.l.According to Poulsen and Specht (2010),this species was found at the foot hills of the central mountain range of Borneo in an area covering at least 2200 km2but with fewer than 10 localities and its sexual reproduction seemed dependent on natural pollinators that may not persist in degraded habitats(VU B1ab(iii);IUCN,2012).It was therefore regarded as Vulnerable.
Additional specimens examined.INDONESIA.West Kalimantan: Camp Betung Kerihun National Park,28 February 2000,Ambriansyah et al.AA2238 (BO,L,WAN).MALAYSIA.Sarawak:Batang Ai,flowering on 3 June 1993,H.Christensen &A.D.Poulsen 1997 (AAU);Gunung Mulu National Park,7 November 1990,M.C.Warwick MW177(E);Kapit,18 July 1987,L.Bernard S.54624(AAU,E),26 October 1988,H.Othman et al.S.56077(SAR),1 November 1988,H.Othman et al.S.56464 (AAU,E,K).
2.Parahellenia globosa(Blume) N.H.Xia,Juan Chen &S.Jin Zeng,com.nov.≡Costus globosus Blume,Enum.Pl.Javae 62.1827,nom.cons.prop.≡Costus roxburghii Hasselt,Bull.Sci.Nat.Geol.3: 189.1824 ‘Roxburghi’,nom.rej.prop.≡Cheilocostus globosus(Blume)C.D.Specht,Taxon 55(1):160.2006 ≡Hellenia globosa (Blume) S.R.Dutta,Pleione 4(1): 152.2010 ?Type:Indonesia,West Java,Bantam,Tjoeroek Dinding,November 1820,Van Hasselt s.n.[lectotype designated by Veldkamp(2018:443): L1480413!].
Phenology.Flowering from February to August.
Chinese vernacular name.球序地萵筍花(qiú xù dì wō sǔn huā).
Distribution,habitat and conservation.It is widespread in Indonesia,Malaysia and Thailand,and grows in moist evergreen forests near streams,at low elevations of 100-450 m a.s.l.However,due to lack of information on the extent of occurrence and population sizes,this species might be considered as Data Deficient (DD) according to IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria(IUCN,2012) until more comprehensive information permit a reevaluation.
Additional specimens examined.INDONESIA.Banten: Hinterland of Sanghijang (N.of Labuan),3 February 1954,A.G.L.Adolbert 279(L).Sulawesi:Dumoga Bone National Park,12 March 1985,E.F.Vogel&J.J.Vermeulen 6478(L).North Sumatra:Asahan,15-26 July 1936,R.S.Boeea 9572 (US);Padang Sidempuan,29 August?3 September 1933,R.S.Boeea 5267(US).West Java:Kebun Raya Bogor,8 July 1986,v.Balgooy &v.Setten 5684 (L).MALAYSIA.Sarawak:Sungai Batu,2 October 1974,J.D.Mamit S.35223 (L).THAILAND.Satun: Koh Talutao,20 June 1974,R.Geesink et al.7368 (L).
3.Parahellenia malipoensisJuan Chen,L.Y.Zeng,S.Jin Zeng&N.H.Xia,sp.nov.
Type.CHINA.Yunnan:Malipo County,Mengdong Village,grows along riverbank,alt.1033 m,22°54′43.16′′N,104°45′24.33′′E,26 July 2021,J.Chen&J.W.Yan 21072604(holotype:IBSC0867971,isotypes:IBSC0867972,KUN,PE) (Figs.5?6).
Diagnosis.Parahellenia malipoensis is similar to P.borneensis,but differs in narrowly lanceolate (vs.cucullate) bracteoles,green(vs.reddish brown) leafless sheaths,small (70-90 cm vs.150-200 cm tall) stature,smaller leaves (22-28 × 3-5 cm vs.27-42×9-16 cm)and spike(5-6×2-4 cm vs.4-12×5-8 cm).
Description.Terrestrial,evergreen perennial herb.Rhizome horizontal,tuberous,1.0-1.5 cm in diam.,brown externally,white internally,glabrous.Leafy shoot 70-90 cm tall,base of leafy shoot to 1 cm in diam.;leafy sheaths green.Stem slightly spirally twisted,leafless in lower part,fragile,mostly unbranched at higher nodes;leafless sheaths closed,green with reddish brown tinge,membranous,caducous,glabrous,upper margin ciliate.Axillary bud 1 at each node,small,broadly triangle,up to 3 mm long,ca.2 mm wide,green tinged with red,margin pubescent.Leaves 9-15,consistently clustered toward the shoot apex;ligule 1-2 mm in height,upper margin fimbriate;petiole 5-11 mm long,dilated at base,yellowish green,cuneate,glabrous;lamina 21-28 × 3-5 cm,the lowest leaves obovate,the upper ones lanceolate,coriaceous,adaxial surface of the new forming leaves pinkish but become green later,plicate,abaxial surface pale green,glabrous,base narrowly attenuate,slightly oblique,apex acuminate,1-1.5 cm long.Infructescence lateral,8-11 cm long (including peduncle),lax.Peduncle horizontal to ascending,4.5-5 cm long,sheaths ± tubular,coriaceous,reddish brown,glabrous,margin ragged.Spike 5-6 × 2-4 cm (bracts only),7-12 flowers per spike.Rachis 1.5-2 cm long,glabrous.Secondary peduncle ca.3 mm long.Bracts 2-2.4×0.6-1.0 cm,elliptic,cucullate,apex spiny but not pungent,coriaceous,pale green or white with reddish brown dots,shortly pubescent,each with 1 bracteole and 1 flower.Bracteole 1.0-1.4 × ca.0.2 cm,narrowly lanceolate,apex spiny but not pungent,coriaceous,pale green or white with reddish brown dots,shortly pubescent.Calyx tube 6-8 mm long,3-5 mm wide,white,shortly pubescent;calyx limb 2.4-2.7 × 0.5-0.7 cm,tubular,reddish brown,coriaceous,shortly pubescent,apex 3-lobed,lobes 4-6 × 3-4 mm,slightly involute,apex spiny but not pungent,reddish brown.Fruit 1.5-1.8×0.6-0.9 cm,nearly elliptic,3-locular,nearly glabrous,reddish brown. Seeds (immature)1.2-1.9 × 1.2-1.5 mm,irregularly barrel-shaped,aril white,basal and not enclosing the seed.
Phenology.Flowering from late June to July;fruiting from July onwards.
Etymology.The species epithet‘Malipoensis’is derived from the locality,Malipo County,Yunnan in China,where the first author collected this species.
Chinese vernacular name.麻栗坡地萵筍花(má lì pō dì wō sǔn huā).
Distribution,habitat and conservation.This species is currently only known from Malipo County in China.During field surveys at the type locality,the first author encountered one population consisting of 20 adult individuals,growing along the riverbank in bamboo forests or evergreen forests,at an elevation of ca.1030 m a.s.l.Local people said there are many individuals in Vietnam.Thus,due to lack of information on the extent of occurrence and population sizes,this species might be treated as Data Deficient (DD) according to IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria(IUCN,2012) until more comprehensive information permit a reevaluation.
Additional specimens examined.CHINA.Yunnan: Malipo,Mengdong,14 September 2020,L.Y.Zeng 20091401 (IBSC).
Notes.Parahellenia malipoensis is rather distinct from other Parahellenia species by many characters,such as mostly unbranched stems,70-90 cm tall leafy shoots,plicate leaf blades,pinkish young leaves,small inflorescences and bracts spiny but not pungent at apex.Moreover,molecular evidence places this species in the Parahellenia subclade as sister to P.tonkinensis,which verifies that it is genetically distinct and supports its status as a new species(Figs.2-3,S1-S2).
4.Parahellenia mulus(Meekiong,Ipor &Tawan) Juan Chen,N.H.Xia&L.Y.Zeng.com.nov.≡Costus mulus Meekiong,Ipor&Tawan,Rheedea 18(2):87.2008-Type:Malaysia,Sarawak,Sungai Pangeh,Tutoh,Miri,21 May 2005,K.Meekiong&I.B.Ipor MK1406(holotype:SAR;isotypes: HUMS).
Phenology.Flowering &fruiting in May.
Chinese vernacular name.白花地萵筍花(bái huā dì wō sǔn huā).
Distribution,habitat and conservation.So far,it is only known from Sarawak,Malaysia and grows at open spaces along roadsides or near rivers at elevations of 500-800 m a.s.l.Due to lack of information on the extent of occurrence and population sizes,this species might be considered as Data Deficient (DD) according to IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria (IUCN,2012) until more comprehensive information permit a re-evaluation.
5.Parahellenia tonkinensis(Gagnep.)Juan Chen,N.H.Xia,L.Y.Zeng&S.Jin Zeng,com.nov.≡Costus tonkinensis Gagnep.,Bull.Soc.Bot.France 49: 248.1903 -Type: Vietnam,Hanoi [Tonkin],Mt.Ba Vi,above Van-maou,forests,alt.700 m,24 July 1886,B.Balansa s.n.(holotype: P 00686610!) (Fig.7).
Description.Terrestrial,evergreen perennial herb.Rhizome horizontal,tuberous,3-4 cm in diam.,brown externally,white internally,densely pubescent.Leafy shoot up to 3.5 m tall,base of leafy shoot to 2.5 cm in diam.;leafy sheaths closed,pale green when young,become reddish brown later.Stem slightly spirally twisted,leafless in lower part (from the base of stem to the first leaf);leafless sheaths closed,reddish brown,coriaceous,persistent,shortly pubescent,upper margin fimbriate;branches 6-11,emerging from upper nodes,consistently clustered toward the shoot apex.Axillary bud 1 at each node,up to 1.6 cm long,green tinged with red,densely pubescent.Leaves consistently clustered toward the shoot apex;ligule ca.2 mm in height,upper margin sparsely fimbriate;petiole 3-10 mm long,yellowish green,glabrous;lamina 21-30×6-10 cm,the lowest leaves obovate,the upper ones narrowly obovate,adaxial surface deep green,abaxial surface pale green,glabrous on both sides,base narrowly attenuate,slightly oblique,apex acuminate,1-1.7 cm long.Inflorescence lateral (i.e.,at the base of the plant terminating a separate leafless shoot that emerges directly from the rhizome),16-24 cm long(including peduncle and bracts only),lax.Peduncle horizontal to ascending,5-9 cm long,sheaths ± tubular,brownish,densely to sparsely pubescent,coriaceous.Spike 7-16×8-9 cm(bracts only).Rachis 7-13 cm long,glabrous.Secondary peduncle 5-9 mm long,shortly pubescent.Bracts 3-4.5 × 2-2.6 cm,free (not connate at base),the lowest bracts broadly elliptic,the upper ones elliptic,cucullate,apex pungent,coriaceous,white at base,reddish brown at upper half part,shortly pubescent,each with 1 bracteole and 1 flower.Bracteole 2-2.6 × 0.3-0.4 cm,narrowly lanceolate to acerose,apex pungent,coriaceous,white with reddish brown apex,shortly pubescent.Flower 10-14 cm long.Calyx tube (the fused bases of the calyx,corolla and stamens) 1.5-1.9 × 0.4-0.6 cm,ellipsoid,shortly pubescent;calyx limb 2-3.3×1-1.3 cm,tubular,pale green when young,become reddish brown when old,shortly pubescent,coriaceous,apex 3-lobed,lobes 7-10 × 3-6 mm,slightly involute,apex pungent,pale green with reddish brown apex when young,become reddish brown when old,glabrous.Floral tube (from apex of ovary to base of divergence of corolla lobes)3-3.2 cm long,fused with style in lowest 1.5-2.2 cm,white,glabrous externally;lobes 4.5-5.6×1.1-1.4 cm,narrowly obovate,yellow,glabrous.Labellum tube(from insertion of dorsal floral tube to base of divergence of labellum and stamen) 8-9 mm long with white long coarse hairs inside.Labellum 7.5-8 × 6-7.8 cm,flabellate after expansion,yellow with red lines at center,covered with glutinous papillae at center and base,margin undulate,glabrous.Stamen 2.4-3 cm long(when crest flattened),1.1-1.4 cm wide,petaloid,white,dorsal side sparsely pubescent.Anther crest 3-5 mm long,1-1.4 cm wide,round to slightly convex at top,whitish yellow with red bands,upper margin pubescent.Thecae 1.1-1.4 cm long,3-4 mm across both,in the middle of stamen.Style 4-4.5 cm long (free part),glabrous.Stigma 2-2.5 mm long,2-3.2 mm wide,fan?shaped,flattened 2?lobed,white,margin ciliate;dorsal appendage bilobed,lobes acute,white with red dots at base.Infructescence almost as same size as inflorescence,often still flowering at apex,with persistent bracts,bracteoles and calyces.Fruit 1.9-2.0 × 1.1-1.5 cm,nearly elliptic,3-locular,glabrous,brown.Seeds 3-4×ca.2 mm,irregularly barrel-shaped,aril white,basal and not enclosing the seed.
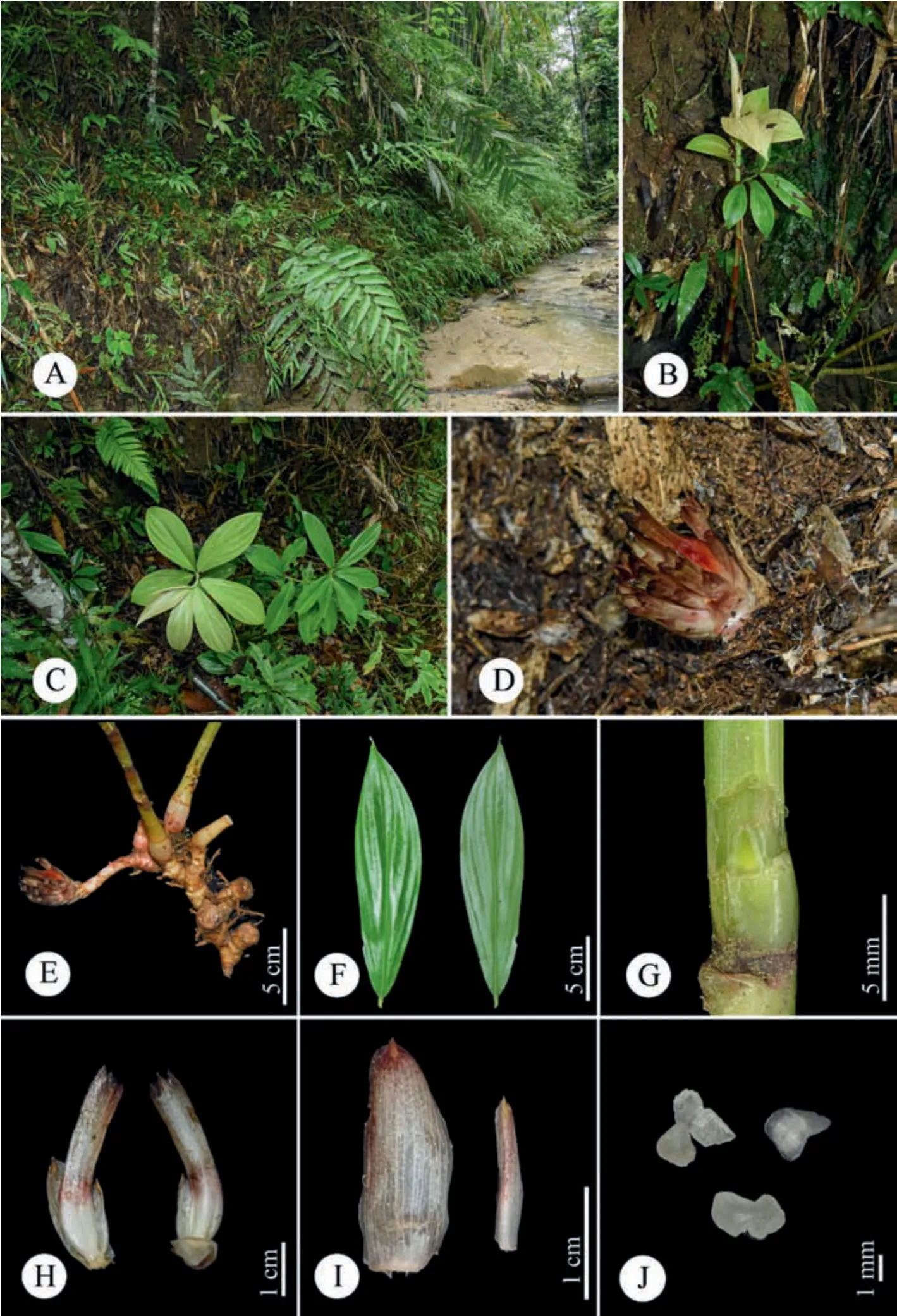

Fig.5. Parahellenia malipoensis Juan Chen,L.Y.Zeng,S.Jin Zeng &N.H.Xia.A.Habitat;B.New forming pinkish leaves (lateral view);C.New forming pinkish leaves (top view);D.Infructescence;E.Infructescence and rhizomes;F.Leaves(from left to right:front and dorsal views);G.Bud;H.Bracts,bracteoles and calyces;I.From left to right:bract,bracteole;J.Immature seeds.
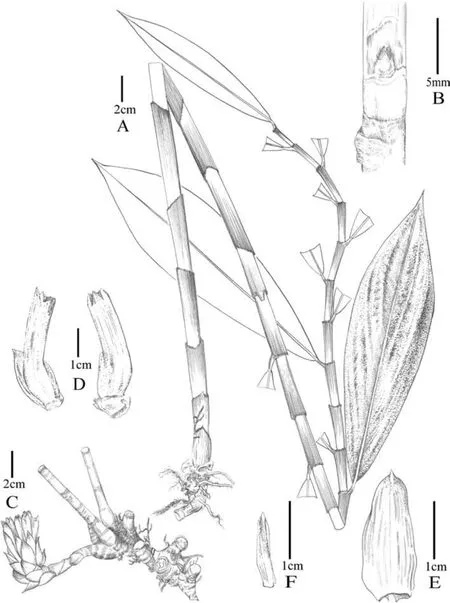
Fig.6. Parahellenia malipoensis Juan Chen,L.Y.Zeng,S.Jin Zeng&N.H.Xia.A.Leaf shoot;B.Bud;C.Inflorescence and rhizomes;D.Bracts,bracteoles and calyces;E.Bract;F.Bracteole.
Phenology.Flowering from July to August;fruiting from August to September.
Chinese vernacular name.地萵筍花(dì wō sǔn huā).
Distribution,habitat and conservation.This species is widespread in South and Southwest China and North Vietnam.It grows in damp valleys in limestone or shale mountains,at elevations of 130-1000 m a.s.l.Based on the georeferenced specimens cited in this study,the extent of occurrence (EOO) and area of occurrence(AOO) is estimated at 216,285.945 km2and 80 km2(GeoCAT -http://geocat.kew.org;Bachman et al.,2011),respectively.In addition,many populations of this species are from legally protected areas in China (e.g.,Shiwan Dashan Nature Reserve in Dongxing City and Qixingkeng Nature Reserve in Enping City) and Vietnam(Ba Vi National Park in Hanoi).Therefore,this species should be regarded as Least Concern (LC) according to IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria (IUCN,2012).
Additional specimens examined.CHINA: Guangdong: Enping,Qixingkeng Nature Reserve,13 July 2021,Chen et al.21071301(IBSC);Maoming,4 August 1956,L.Deng 1843(IBSC);Yangchun,Baichongshan Nature Reserve,11 September 1990,N.Liu et al.351 (IBSC);Zhaoqing,Dinghu Mountain,17 June 1964,G.Q.Ding&G.L.Shi 1518(IBSC).Guangxi: Baise,Yangxu Town,19 July 1958,Z.T.Li 601038(IBK);Bama,26 April 1957,Y.K.Li P01020 (IBSC);Chongzuo,Baili Town,25 August 2004,Baitouyehou Nature Reserve B0555 (IBK);Debao,21 February 2017,Debao Expedition 451024170221006LY(GXMG);Dongxing,18 October 1973,C.F.Liang 34005 (IBK),19 July 2021,Chen et al.21071901 (IBSC);Fangchenggang,Fulong Town,9 July 2010,Shiwan Dashan Expedition 2666(IBK);Jingxi,20 July 2021,Chen et al.21072001(IBSC);Linyun,11 September 1989,South China Expedition 1397 (IBSC);Long'an,5 September 2011,J.C.Yang et al.LH0677(IBK),10 November 2011,J.C.Yang&J.B.Liao LH1443(IBK),24 June 2014,Long'an Expedition 450123140624097LY (GXMG),18 July 2021,Chen et al.21071801(IBSC);Longlin,6 June 2009,X.F.Huang&L.H.Gao 20646 (GXMG);Longzhou,24 September 1979,Nonggang Expedition 10227(IBK),1 May 1980,Nonggang Expedition 12002(IBK),23 March 2009,Y.S.Huang&W.B.Xu 115(IBK).Guizhou:Luodian,Lofou,August 1909,A.Cavalerie 3654(P);Wangmo,22 July 2021,Chen et al.21072201 (IBSC).Yunnan: Hekou,China &Russia Expedition 2338 (PE);Jinping,17 January 2010,DNA barcode Southeast Yunnan Expedition GBOWS1352(KUN);Malipo,1 January 2010,DNA barcode Southeast Yunnan Expedition GBOWS459(KUN),12 July 2018,Z.D.Wei et al.Yezi453 (KUN).VIETNAM.Hanoi: Mt.Ba Vi,October 1887,B.Balansa 4206(K,P);Ba Vi District,Ba Vi National Park,19 July 2021,S.K.Nguyen&M.T.Trieu NSK1374(HN).
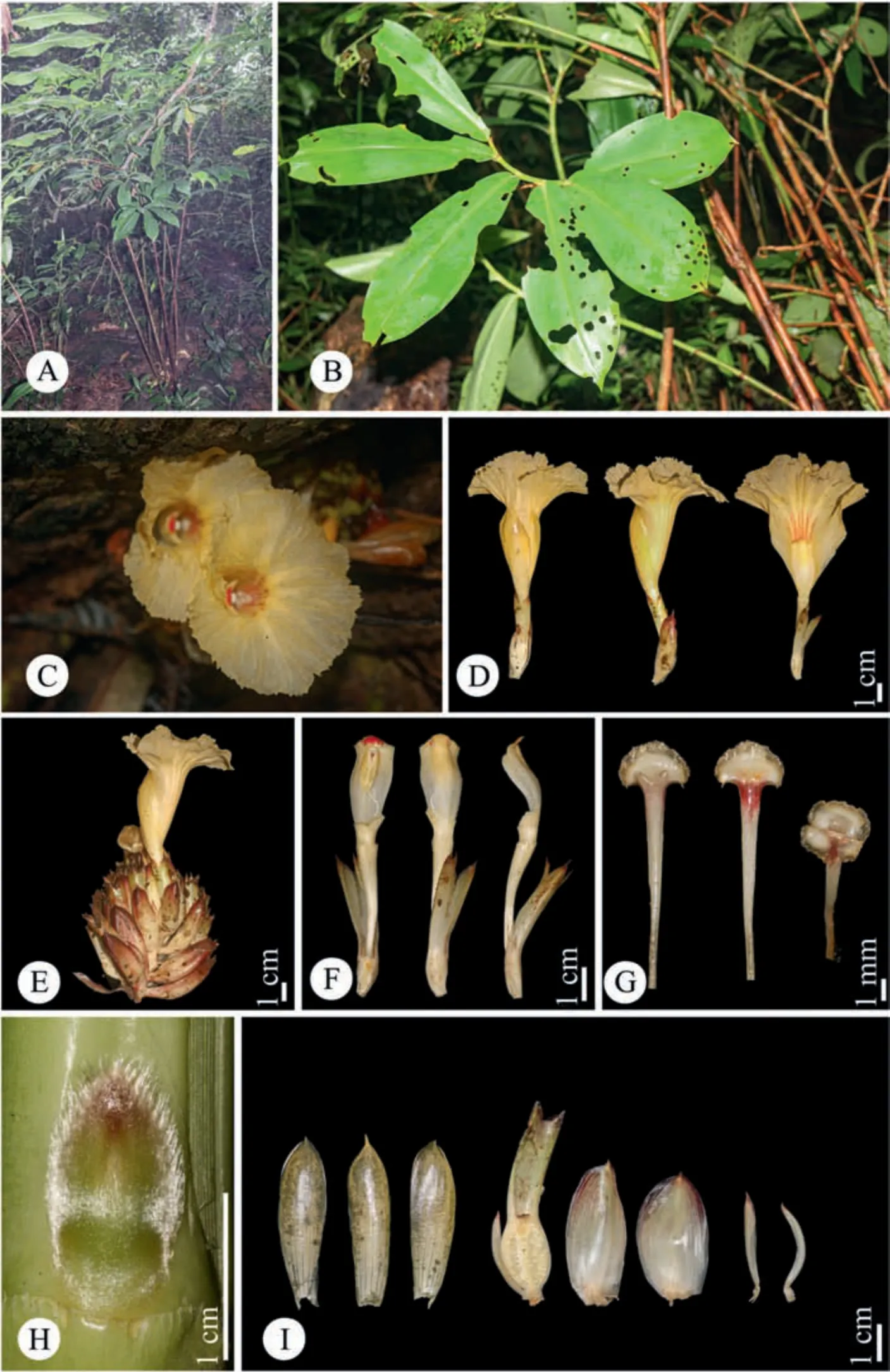

Fig.7. Parahellenia tonkinensis(Gagnep.)Juan Chen,L.Y.Zeng,S.Jin Zeng&N.H.Xia.A.Habit;B.Branches;C.Flowers(frontal view);D.Flowers(lateral view);E.Inflorescence with a flower;F.Stamen(from left to right:frontal,lateral and dorsal views);G.Stigma (from left to right:dorsal,frontal and top views);H.Bud;I.From left to right:three corolla lobes,ovary with a bracteole and a calyx,two bracts,two bracteoles.
Notes.Parahellenia tonkinensis differs from P.globosa in a number of floral characters: its yellow (vs.cherry red to bright orange yellow) labellum with (vs.without) red lines at center and base,dorsal appendage of stigma sharply (vs.rounded)bilobed,stamen not closed the throat (vs.wholly closed the throat),yellow (vs.deep yellow) anther crest with (vs.without)red bands,persistent (vs.dehiscing leaving a fibrous cover)leafless sheaths,shortly pubescent or nearly glabrous(vs.densely pubescent) bracts,bracteoles and calyces,glabrous (vs.pubescent) floral tubes,dorsal side of stamen sparsely pubescent (vs.densely covered with long white or yellow hairs) and glabrous(vs.fimbriate) margins of labellum.
Parahellenia globosa exhibits high variation of the indumentum and colour of the floral parts (van Caspel,2019).However,variability of the indumentum and colour of the floral parts was not observed in P.tonkinensis.
6. Parahellenia yunnanensis S.Jin Zeng,N.H.Xia,L.Y.Zeng&Juan Chen, sp.nov.
Type.CHINA.Yunnan: Ximeng County,Jiefang Village,open space along roadsides near rivers,alt.848 m,22°41′38.04′′N,99°36′5.63′′E,4 August 2021,J.Chen&J.W.Yan 21080403(holotype:IBSC0 867976;isotypes: IBSC0867970,KUN,PE) (Figs.8?10).
Diagnosis.Parahellenia yunnanensis is similar to P.tonkinensis,but differs in the 3-lobed (vs.rounded) anther crest,longer bracts and calyces,buds with villous margins (vs.densely villous buds),white stigma without (vs.with) red dots at base,appressed or absence of(vs.sharply-bilobed)stigma appendage and orange(vs.yellow)flowers.
Description.Terrestrial,evergreen perennial herb.Rhizome horizontal,tuberous,3-4 cm in diam.,brown externally,white internally,densely pubescent.Leafy shoot up to 4 m tall,base of leafy shoot to 3 cm in diam.;leafy sheaths closed,pale green when young,become reddish brown later.Stem slightly spirally twisted,leafless in lower part;leafless sheaths closed,reddish brown,coriaceous,persistent,glabrous,margin sparsely fimbriate;branches 9-15,emerging from upper nodes,consistently clustered toward the shoot apex.Axillary bud 1 at each node,up to 1.6 cm long,green at base,red at upper half part,margin densely pilose.Leaves consistently clustered toward the shoot apex;ligule ca.2 mm in height,margin sparsely fimbriate;petiole 5-14 mm long,yellow-green,glabrous;lamina 16-27 × 7-12 cm,the lowest leaves obovate,the upper ones narrowly obovate,adaxial surface deep green,abaxial surface pale green,glabrous on both sides,base narrowly attenuate,apex acuminate,1-2.2 cm long.Inflorescence lateral,18-28 cm long (including peduncle and bracts only),lax.Peduncle horizontal to ascending,8-15 cm long,sheaths±tubular,reddish brown,shortly pubescent,coriaceous. Spike 12-18 × 7.5-12 cm long (bracts only).Rachis 10-12.5 cm long,glabrous.Secondary peduncle 7-10 mm long,shortly pubescent.Bracts 5.5-6 × 1.1-1.7 cm,free (not connate at base),the lowest bracts broadly elliptic,the upper ones elliptic,cucullate,apex pungent,coriaceous,reddish brown,shortly pubescent,each with 1 bracteole and 1 flower.Bracteole 2-2.5 × 0.2-0.3 cm,narrowly lanceolate to acerose,cucullate,apex pungent,coriaceous,pale brown with reddish brown apex,shortly pubescent.Flower 12-16 cm long.Calyx tube(the fused bases of the calyx,corolla and stamens) 1.3-1.4 × 0.4-0.6 cm,ellipsoid,glabrous;calyx limb 3-3.6 × 0.6-0.9 cm,tubular,pale green when young,become reddish brown when old,glabrous,coriaceous,apex 3-lobed,lobes 4-9 × 4-6 mm,slightly involute,apex pungent,pale green with reddish brown apex when young,become reddish brown when old,glabrous.Floral tube (from apex of ovary to base of divergence of corolla lobes) 3.3-3.6 cm long,fused with style in lowest 1.8-2.5 cm,white,glabrous externally;lobes 4.7-5.5×1.3-1.7 cm,narrowly obovate,orange,glabrous.Labellum tube(from insertion of dorsal corolla tube to base of divergence of labellum and stamen)ca.1.1 cm long with long coarse white hairs inside.Labellum 7.5-8 × 7.5-9 cm,flabellate after expansion,orange with red center,densely covered with white glutinous papillae at center and base,margin undulate,slightly pubescent.Stamen 3-3.5 cm long(when crest flattened),1.5-1.7 cm wide,petaloid,white.Anther crest irregularly 3-lobed,recurved,1.2-1.4 cm long,1.5-2.5 cm wide,lateral lobes rounded,orange,medium lobe orange with red lines,margin pubescent.Thecae 1-1.2 cm long,0.3-0.4 cm across both,in the middle of stamen.Style 4.2-5 cm long (free part),glabrous.Stigma 2-2.5 mm long,2-3 mm wide,fan?shaped,flattened 2?lobed,white,margin ciliate;dorsal appendage absent or bilobed,white.Infructescence as same size as inflorescence,often still flowering at apex,with persistent bracts,bracteoles and calyces.Fruit 2.0-2.3 × 1.4-1.5 cm,nearly elliptic,3?locular,glabrous,brown.Seeds (immature) 3-4 × 1.5-2 mm,irregularly barrel-shaped,aril white,basal and not enclosing the seed.

Fig.8. Parahellenia yunnanensis S.Jin Zeng,N.H.Xia,L.Y.Zeng &Juan Chen.A.Habit;B.Branch;C.Infructescence;D.Flower;F.Inflorescence with a flower.
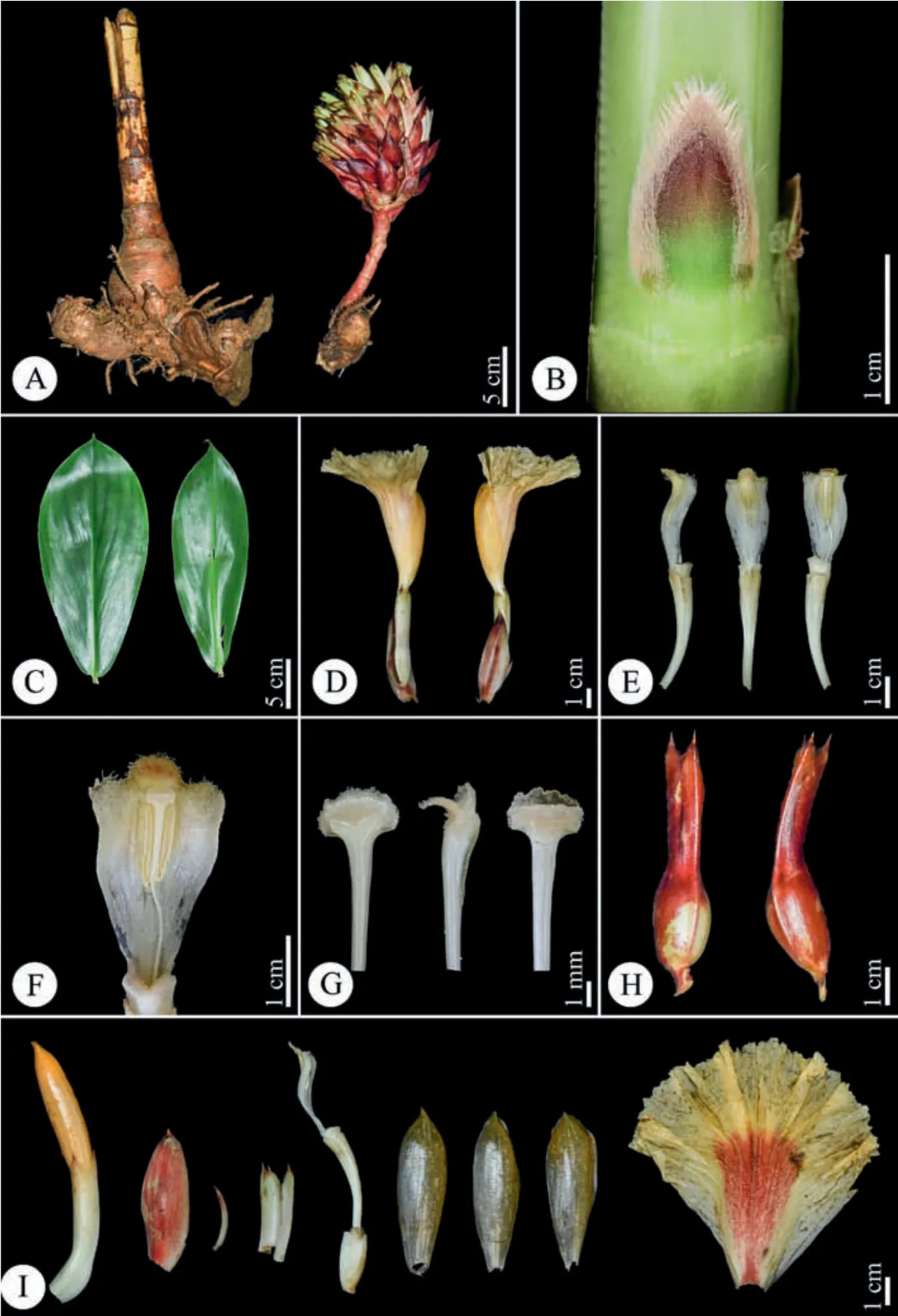

Fig.9. Parahellenia yunnanensis S.Jin Zeng,N.H.Xia,L.Y.Zeng &Juan Chen.A.Inflorescence and rhizomes;B.Bud;C.Leaves;D.Flowers;E.Stamens and floral tubers (from left to right:lateral,dorsal and frontal views);F.Stamen(enlarged view);G.Stigma(from left to right:dorsal,lateral and frontal views);H.Calyces and fruits;I.From left to right:flower bud,bract,bracteole,calyx,calyx tube with a corolla tube and a stamen,three corolla lobes and labellum.
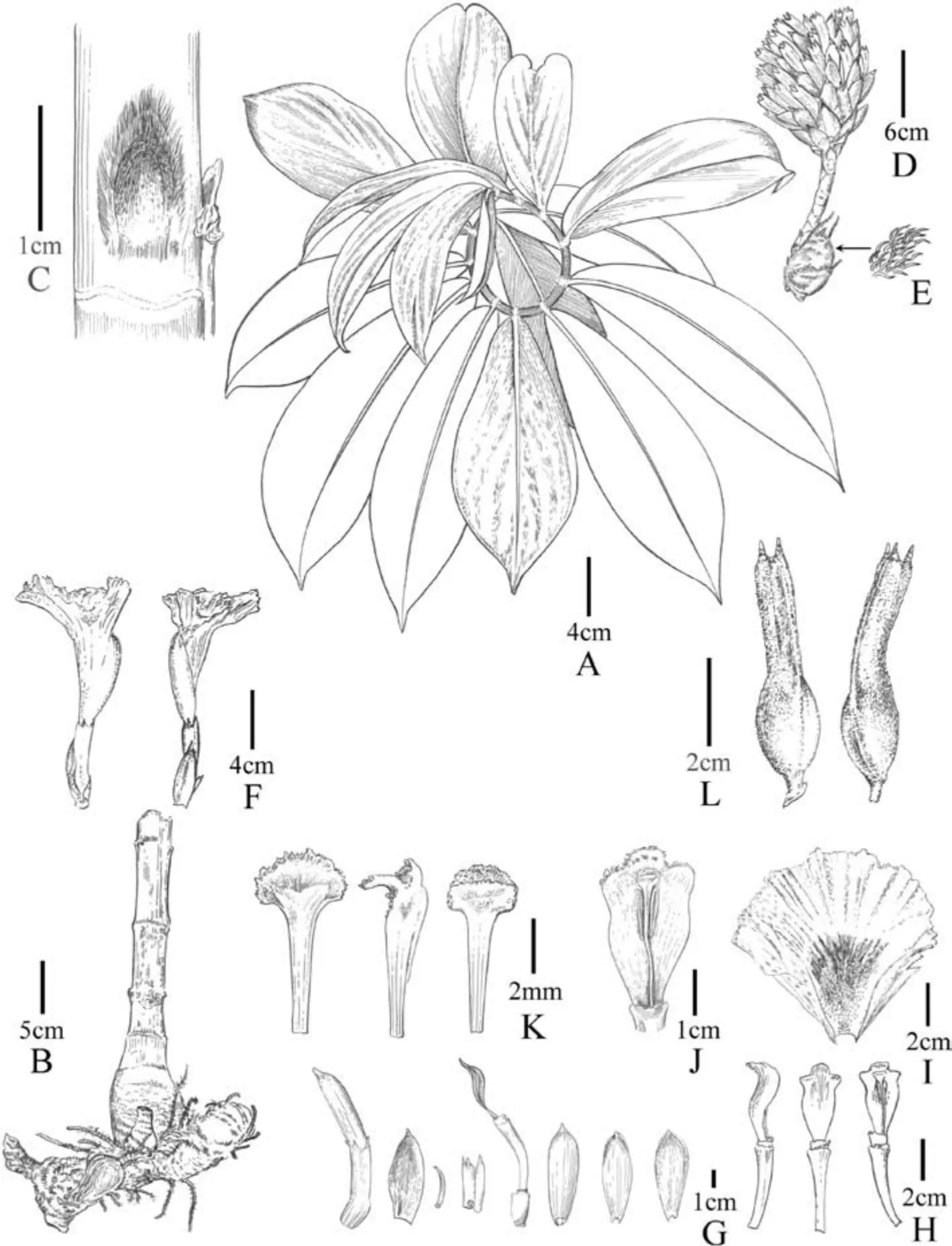
Fig.10. Parahellenia yunnanensis S.Jin Zeng,N.H.Xia,L.Y.Zeng&Juan Chen.A.Branch;B.Rhizomes;C.Bud;D.Inflorescence;E.Enlarge view of hairs on the rhizome;F.Flowers with bracts and bracteoles;G.From left to right:flower bud,bract,bracteole,calyx,calyx tube with a corolla tube and a stamen and three corolla lobes;H.Stamens and floral tubers(from left to right: lateral,dorsal and frontal views);I.Labellum;J.Stamen (enlarged view);K.Stigma (from left to right: dorsal,lateral and frontal views);L.Fruits.
Phenology.Flowering from July to August;fruiting from August to September.
Etymology.The specific epithet ‘yunnanensis’ is derived from the locality,Yunnan in China,where the first author collected this species.
Chinese vernacular name.云南地萵筍花(yún nán dì wō sǔn huā).
Distribution,habitat and conservation.This species is currently known in eight localities and grows along riverbanks or at roadsides near rivers in evergreen forests at elevations of 750-1085 m a.s.l.During field surveys at the type locality,the authors encountered three populations each consisting of 1-10 adult individuals.Several populations of this species are from legally protected areas in China(e.g.,Taiyanghe Provincial Nature Reserve in Pu'er City and Bulong State Nature Reserve in Menghai County).However,due to lack of information on the exact extent of occurrence and population sizes,this species might be considered as Data Deficient (DD) according to IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria(IUCN,2012)until more comprehensive information permit a re-evaluation.
Additional specimens examined.CHINA.Yunnan: Jinghong,Menglong,August 1936,C.W.Wang 77425 (PE);Jinghong,Kunge,October 1936,C.W.Wang 79214 (PE);Menghai,4 September 2020,L.Y.Zeng&S.J.Zeng 20090406(IBSC);Mengla,July 1991,Anonymous 0014(KUN),29 August 1984,Q.G.Wu&X.X.Huang 145(IBSC);Pu'er,Taiyanghe Provincial Nature Reserve,1 August 2021,J.Chen &J.W.Yan 21080102(IBSC).THAILAND.Chiang Mai:Muang,Doi Sutep-Pui National Park,26 July 1989,J.F.Maxwell 89-941 (L).
Notes.As elaborated in the diagnosis,P.yunnanensis most resembles P.tonkinensis by its glabrous leaves,lateral inflorescence and bracts pungent at apex but it can be distinguished by trilobed anther crest,longer bracts and calyces,buds with villous margins,white stigma without red dots at base,appressed or absence of stigma appendage and orange flowers.This species was also misidentified as P.tonkinensis in herbaria.However,P.tonkinensis only occurs in Guangxi,Guangdong,Guizhou and Southeast Yunnan(Hekou,Malipo and Jinping)in China.Molecular phylogeny studies show that P.yunnanensis is the basal species of the Parahellenia clade and genetically distant from P.tonkinensis and P.malipoensis,and thus support that this species is a new one(Figs.2-3,S1-S2).
Author contributions
JC and SJZ contributed equally to this work.NHX,JC and SJZ designed the studies.JC,SJZ and LYZ initiated the study.JC,LYZ,SJZ,KSN,HL and NHX collected and identified material.LYZ,JWY and SJZ carried out the laboratory work.LYZ and SJZ did the phylogenetic analysis.JC,NHX and ZLY did the taxonomic research.JC,LYZ,SJZ,KSN and JWY drafted the manuscript and figures.All authors have read,commented and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the staff of Qixingkeng Nature Reserve,Mr.Chaoyi Deng,Mr.Jianghua Huang,Mr.Jianjun Ou,Mr.Renbing Zhu,Mr.Shinian Lu and Mr.Yunfeng Huang for their help during field trips,Dr.Alex Dalberg Poulsen,Dr.Kalu B.Meeking and Mr.Yushi Ye for sharing images,Mr.Dave Skinner for sharing many images of Parahellenia species and Gideon's key to Tapeinochilos,Prof.Khoon Meng Wong for comments and corrections on a manuscript version of this paper,Mr.Dinghan Cui for preparing the illustration and the anonymous reviewers for their comments on the paper.The following herbaria are acknowledged for access to their collections:E,GXMG,GXMI,HITBC,IBK,IBSC,L,KUN,K,P,PE and US.We would also like to thank Chinese Virtual Herbarium (CVH,https://www.cvh.ac.cn),National Specimen Information Infrastructure (NSII,http://www.nsii.org.cn/2017/home.php),Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF,https://www.gbif.org) and Plants of the World Online (http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org) for providing digital images of specimens.This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant no.32070223) and the Biological Resources Programme,Chinese Academy of Sciences(Grant no.KFJ-BRP-017-19).
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pld.2022.02.001.
- 植物多樣性的其它文章
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
- Metabolome profiling of stratified seeds provides insight into the regulation of dormancy in Davidia involucrata
- Leaf fossils of Sabalites (Arecaceae) from the Oligocene of northern Vietnam and their paleoclimatic implications
- Plastid genome evolution of a monophyletic group in the subtribe Lauriineae (Laureae,Lauraceae)
- Reproduction and genetic diversity of Juniperus squamata along an elevational gradient in the Hengduan Mountains
- Ontogenetic trait variation and metacommunity effects influence species relative abundances during tree community assembly

