Co-expression of HBZ, TAX and FOXp3 and HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis development in HTLV-1-infected individuals: A systematic review
Ana Carolina Marinho Monteiro Lima, Greice Carolina Santos da Silva, Fernanda Khouri Barreto, Filipe Ferreira de Almeida Rego, Luana Leandro Gois,3, Luciane Amorim Santos,,4?
1Catholic University of Salvador, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
2Multidisciplinary Institute in Health, Federal University of Bahia, Vitoria da Conquista, Bahia, Brazil
3Bahia School of Medicine and Public Health, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
4Postgraduate Program in Health Sciences, Faculty of Medicine of Bahia, Federal University of Bahia, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
ABSTRACT Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is associated with the development of HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). It has been reported that the HTLV-1 proteins (specifically TAX and HBZ) can modulate FOXp3,resulting in an immune imbalance that can favor the progression of HAM/TSP. This review aims to summarize the literature in order to clarify the relationship between the expression of HTLV-1 mRNAs and/or viral proteins (TAX and HBZ) with the expression of mRNA and/or protein FOXp3 and their correlation with HAM/TSP development. This systematic review was conducted according to the recommendations of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis. The search strategy was performed on the Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online and Latin American and Caribbean Literature in Health Sciences Platform using subject descriptors. After screening, six articles were included in this review. The studies suggested that TAX and HBZ have a directly proportional correlation with FOXp3 in individuals with HAM/TSP, which also presented an increased expression of FOXp3 compared to asymptomatic controls and/or healthy donors. This systematic review indicates that TAX and HBZ can interact with FOXp3 and that interaction may influence HAM/TSP development.
KEYWORDS: HTLV-1; HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP); FOXp3; HBZ; TAX
1. Introduction
The human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) was discovered in 1979[1] and since then, different subtypes have been identified. The most prevalent are the cosmopolitan subtype 1a[2]and the African subtype 1b[3]. The cosmopolitan subtype 1a can also be divided into five different subgroups (subgroup A-E)[4].
It is estimated that HTLV-1 has infected around five to ten million people worldwide[2], being endemic in Japan, the Caribbean islands,Equatorial Africa and South America[2,5]. This retrovirus is the etiological agent of many severe diseases, including the adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma (ATLL), HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP), among others[6,7]. It is important to note that the most HTLV-1-infected individuals are classified as asymptomatic carriers (ACs). However, some of these individuals have non-specific symptoms resulting from HTLV-1 infection, which are not directly related to any diseases associated with HTLV-1, like overactive bladder[8,9] and muscle weakness[10].It remains unclear what causes the development of disease in the infected patient. It is assumed that viral factors and host factors may be related to different clinical outcomes of infection[11].
The HTLV-1 genome is flanked by two long terminals repetition sequences (LTR) and presents genes that encodes the structural proteins antigenic group (gag), polymerase (pol) and envelope (env),and the pX region, which encodes the accessory and regulatory proteins[12]. The regulatory, tax and rex genes, and the accessory genes, p12, p13, p21 and p30, are transcribed from the 5' LTR, while the HTLV-1 bZIP factor (hbz) is read in the complementary pro-viral chair in the sense 3' LTR[12].
During the infectious process the HTLV-1 infects T cells, with special tropism for CD4T lymphocytes[13]. These lymphocytes can differentiate into regulatory T cells (Tregs) and play an important role in immunological regulation. The Tregs lymphocytes are essential in maintaining immune system homeostasis since they are able to regulate the inflammatory profile during infections by suppressing T cell proliferation and releasing anti-inflammatory cytokines[14]. In this sense, the expression of the forkhead box p3 transcription factor(FOXp3) seems to be important, once this protein acts on specific DNA regulatory regions, increasing or suppressing the transcription of specific genes[14]. It has been reported that HTLV-1 proteins,especially TAX and HBZ, impair the functionality of Treg cells by modulating the FOXp3 expression, causing an immune imbalance and favoring the progression of diseases associated with HTLV-1[15].
Studies describe that TAX protein is associated with a reduction of FOXp3 expression, therefore, inhibits the Treg cells regulatory function[16]. On the other hand, the HBZ protein induces higher expression of FOXp3, directly interacts with it, leading to Treg function impairment[17].
It is essential to understand the mechanisms involved in the modulation of FOXp3 by HTLV-1 proteins (HBZ and TAX),in order to contribute to knowledge of HAM/TSP pathogenesis mechanisms. This understanding is fundamental to identify the early diagnosis markers and therapeutic targets. This systematic review was designed to clarify the relationship between the expression of mRNA and/or proteins of HTLV-1 with the expression of mRNA and/or cellular protein FOXp3, and the relationship with the HAM/TSP development.
2. Materials and methods
This systematic literature review was conducted according to the recommendations of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis[18] guidelines. The study was also registered in PROSPERO (No. CRD42021225356).
2.1. Search strategy
A search was performed using Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (Medline) or PubMed and Latin American and Caribbean Literature in Health Sciences (LILACS) databases on the December 10th, 2020. The combination of the following keywords selected from Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) was used for the search: [(“HTLV-1” OR “Human T-Lymphotropic Virus 1” OR “Human T Lymphotropic Virus 1”) AND (“FOXp3” OR“Forkhead Box p3” OR “Scurfin” OR “IPEX”) AND (“HBZ” OR“bzip Factor” OR “Basic-Leucine Zipper Transcription Factors” OR“TAX OR P40”)].
2.2. Eligibility criteria
The following inclusion criteria were applied to select the studies:1) only articles in Portuguese, English or Spanish; 2) observational original studies, 3) studies on HTLV-1-infected individuals with HAM/TSP and 4) studies that presented the expression of mRNA and/or FOXp3 protein and mRNAs and/or viral proteins HBZ and/or TAX. The exclusion criteria were: 1) studies evaluated other microorganisms, 2) literature review articles and 3) studies that did not show results related to the effect of the expression relationship of mRNAs and/or viral proteins HBZ and/or TAX with mRNA and/or cellular protein FOXp3 in individuals with HAM/TSP.
2.3. Study selection and data collection
The identification of eligible articles was performed by reading the titles and abstracts. This screening was performed by two authors independently (A.C.M.M.L and G.C.S.S). The eligible full articles were then read by the authors and the inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied again. The included articles were determined by consensus among the authors. The following data was extracted from the included articles: authors, year of publication, country of samples, study design, host, and method used to detect genes/proteins expression, genes/proteins of interest and type of interaction between FOXp3 and HBZ and/or TAX genes/proteins expression.
2.4. Evaluation of the studies quality
The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal Checklist for Analytical Cross-Sectional Studies protocol was used to assess the risk of study bias. The studies were classified as low risk of bias if 70% or more of the answers on the checklist were “yes”, medium risk of bias for 50%-69% and high risk of bias for 50% or less. Only articles with low or medium risk of bias were included in this study.Considering the differences between the articles eligible for this review, such as the different variables evaluated and the methodologies applied in each of the studies, we were unable to make statistical comparison between the articles or meta-analysis.
2.5. Data analysis
The data collected from the articles were tabulated using Microsoft Excel. The relation of HBZ and/or TAX expression with FOXp3 was classified according to the rate of gene expression or the quantification of these proteins. In order to answer the objectives of this systematic review, a “directly proportional” relationship was considered when the correlation analyses were positive, that is, when the genes or proteins were expressed in the same direction (both down-regulated or both up-regulated). On the other hand, they were considered “inversely proportional” when the correlation analysis was negative, that is, when the genes or proteins were expressed in opposite directions (one upregulated and the other downregulated).The studies that did not identify any type of relationship between the expression of proteins and/or genes (one does not influence the expression of the other), were considered as “not found”.

Figure 1. Flow diagram summarizing systematic search and study selection.
3. Results
The literature search identified a total of 40 articles on the PubMed platform and no study was found in the LILACS database. Among the 40 articles, 28 were eligible from reading the title and summary.Among these, 14 did not show results regarding the relation between the expression of FOXp3 with the expression of HBZ and/or TAX in HAM/TSP patients and eight review articles were excluded.Therefore, a total of six articles were included in the systematic review (Figure 1).
The six articles included were published between 2006 and 2018.All articles were observational cross-sectional studies and the methodological quality analyses indicated that 66.67% (n=4) of the studies were considered with low risk of bias and 33.33% (n=2) were considered medium risk of bias (Table 1).
All studies used peripheral blood mononuclear cells from HTLV-1-infected individuals as a sample. Regarding the clinical condition,five articles (83.33%) studied only HTLV-1-infected individuals with HAM/TSP and one article (16.67%) studied HTLV-1-infected individuals with HAM/TSP and ATLL. Four articles (66.67%)evaluated only the expression of the viral protein TAX, one (16.67%)evaluated both TAX and HBZ, and one (16.67%) evaluated only HBZ (Table 1). Five articles (83.33%) detected the HTLV-1 proviral load, all using the real-time quantitative PCR technique.
Five articles evaluated the correlation between the expression of TAX and FOXp3 in HAM/TSP patients. Of these, two found an inversely proportional correlation[19,20] and three found a directly proportional correlation[21-23](Figure 2). Yasuma et al.[23] detailed that the directly proportional relation between the expression of TAX and FOXp3 existed only in infected individuals with the cosmopolitan subtype 1a subgroup-A of HTLV-1 (HTLV-1aA),while in subgroup B (HTLV-1aB) no interaction was found between the expression of TAX and FOXp3 (Table 2).
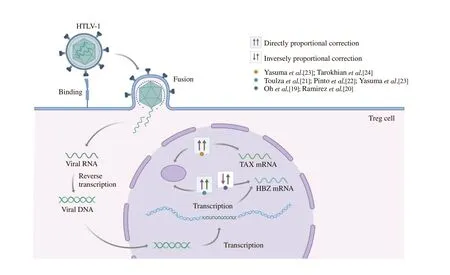
Figure 2. Correlation between the expression of TAX and HBZ with FOXp3 in HAM/TSP patients. Adapted from “Retrovirus Life Cycle”, by BioRender.com (2021).Available from: https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates/t-5e14fab8a853ac0084826ca2-retrovirus-life-cycle. Copyright 2021 by BioRender.
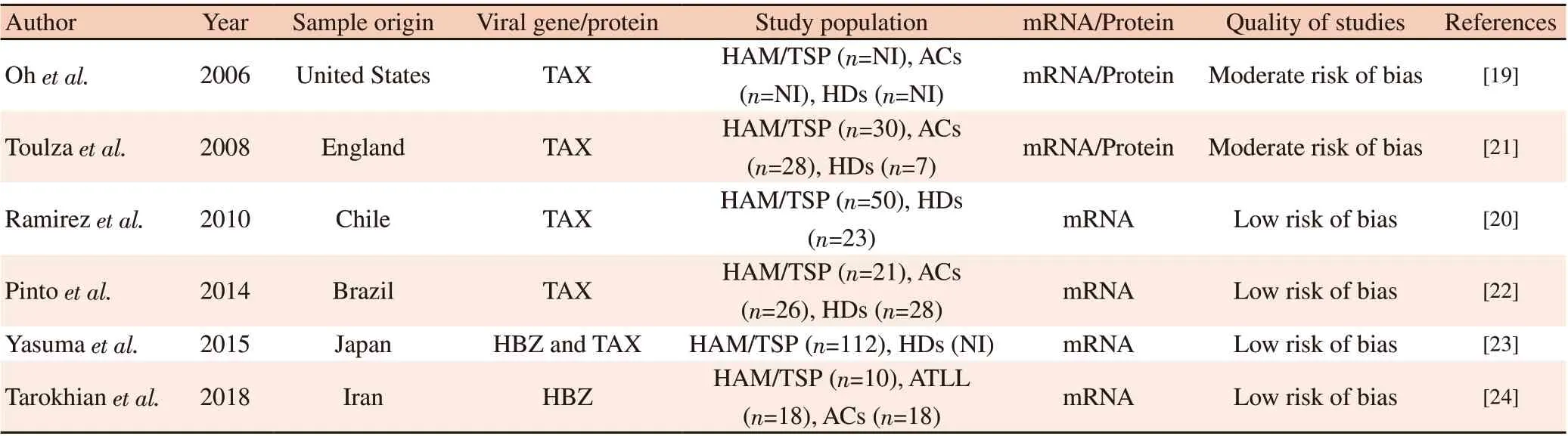
Table 1. Characteristics of the six included studies.
Out of the two articles that evaluated the expression of HBZ, both described a directly proportional relation between the expression of HBZ and FOXp3 in HTLV-1-infected patients with HAM/TSP[23,24](Figure 2). Moreover, Yasuma et al. identified this relation only in individuals infected with HTLV-1aA, but not in those infected with HTLV-1aB (Table 2).
Most articles evaluated the expression of FOXp3 in individuals with HAM/TSP comparing to ACs or healthy donors (HDs)individuals. Among the three articles that found a directly proportional relationship between TAX and FOXp3, two found an increase in FOXp3 in HAM/TSP individuals compared to HDs and/or ACs[21,22]. Yasuma et al. found this increase in the HTLV-1aA subtype compared to the HTLV-1aB. Two articles found an inversely proportional relationship with a decrease of FOXp3 in HAM/TSP individuals compared to HDs and/or ACs[19,20]. On the other hand,one article[24] found a directly proportional relationship between HBZ and FOXp3 with a decrease in the expression of FOXp3 in HAM/TSP individuals compared to ATLL individuals (Table 2).
4. Discussion
This study performed an analysis of the correlation between the expression of TAX and/or HBZ with FOXp3 in individuals with HAM/TSP. This analysis can provide insights regarding the modulation of HTLV-1 viral proteins in the host organism when interacting with the FOXp3 protein. This interaction can impair the immune regulatory response and, therefore, contribute to thepathogenesis mechanisms of HAM/TSP. This systematic review identified that most articles reported a directly proportional interaction between TAX and FOXp3 and between HBZ and FOXp3.Studies indicate that the HBZ viral protein induces FOXp3 expression through activation of TGF-β/Smad pathway[25],corroborating with the directly proportional interaction in HAM/TSP found in this review. Despite that, the direct interaction between the HBZ protein and FOXp3 destabilizes its regulatory function[17],which may cause a loss of functional capacity from Treg cells.HBZ is also capable of increasing the number of Treg cells with unstable FOXp3 expression, inducing the production of IFN-γ by these cells and, therefore, exacerbating the inflammatory profile in HAM/TSP[26]. However, this correlation still needs to be further investigated in the literature, as there are more studies investigating the influence of HBZ on FOXp3 in the course of ATLL disease, than the effect of HBZ on FOXp3 on HAM/TSP disease.
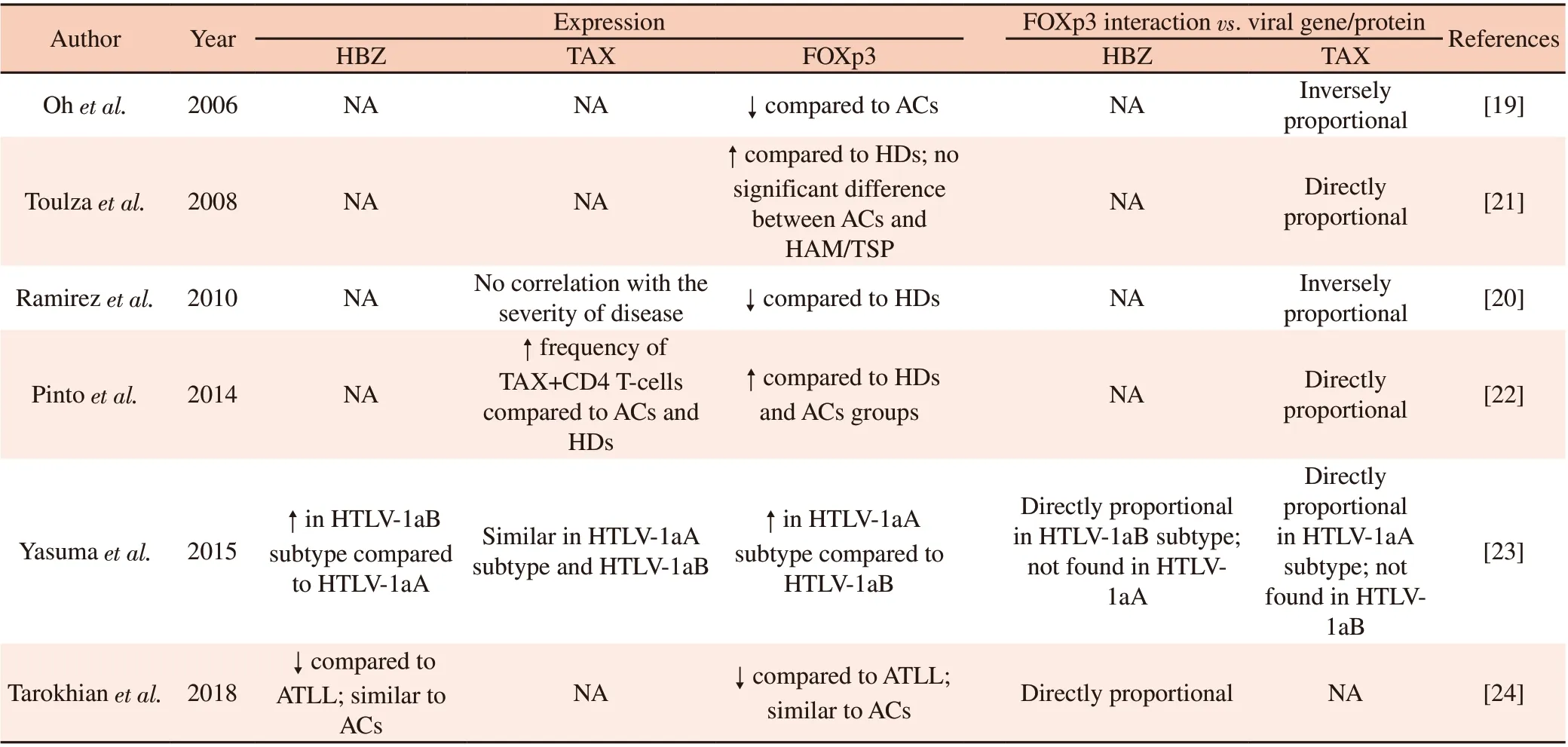
Table 2. Evaluation of HBZ, TAX and FOXp3 expression in patients with HAM/TSP.
Among the articles that evaluated the relation between TAX and FOXp3 in HAM/TSP, most studies observed a directly proportional interaction. On the other hand, only two articles found an inversely proportional correlation. This is because, in the literature, there are already articles that provide strong evidence that TAX interacts with the FOXp3 protein, modulating the expression of this gene to increased or decreased, according to the results found in this systematic review. Therefore, we propose two hypotheses for both findings: TAX has a suppressive role in the expression of FOXp3 in T cells[16,27], triggering a loss of the functional capacity of the Tregs cells[28,29], suggesting that this suppression may collaborate with the chronic inflammatory state and the development of HAM/TSP; and the presence of TAX increases the frequency of FOXp3CD4T cells[30] and induces the CD25 expression[31,32]. Indeed, the frequency of FOXp3TaxCD4T cells is greater than FOXp3TaxCD4T cells[21].
It is worth considering that individuals with HAM/TSP have higher proviral loads[33,34]. The proviral load is positively correlated with the frequency of FOXp3CD4T cells[30]. In addition, it has been previously reported that the level of TAX is higher in patients with HAM/TSP than in asymptomatic patients[35]. Because of this, it is necessary to clarify whether this directly proportional relationship is an effect of the modulation of TAX under FOXp3 or the other associated factors. In this sense, it is suggested that it may not reflect the interaction of TAX on FOXp3, but the TAX effect on the entire immune system. We hypothesize that generalized lymphoproliferation stimulated by TAX may result in the preferential expansion of FOXp3CD4T cells, since CD4CD25cells are the predominant viral reservoir in patients with HAM/TSP and are increased[36].
Three hypotheses are supported for this: Treg cells are highly susceptible to transmission of the HTLV-1 viral particle by proximity to dendritic cells[37-39]; viral proteins induce Treg cells differentiation[40,41]; or HTLV-1 infection induces overexpression of genes, including the FOXp3 gene[30]. This last hypothesis is supported by the evidence that the TAX protein has the role of inducing host genes. More precisely, this protein can influence the expression of perforin 1 gene (prf1)[22] associated with the cytotoxic activity of CD8T cells, and the genes associated with lymphocyte activation,such as the CD3 gene of T cells, lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase and guanine nucleotide exchange factor vav 1[42]. Therefore,it is evident that the factors that determine the interaction between TAX and FOXp3 remain unknown and incongruous in the literature.Because of that, it is possible to suggest that several factors act to generate an induction or inhibition of the FOXp3 gene in individuals with HAM/TSP.
The articles included in this systematic review also analyzed the functional capacity of Tregs cells (data not shown). This is important because FOXp3 is the differentiating factor for Treg cells and plays a crucial role in the function of this cell type[14]. Treg cells are essential for the control of infections, and they act by suppressing the inflammatory state of the tissue, thus avoiding major damage to the organism[43]. It was observed in the articles included in this systematic review that circulating regulatory T cells are functionally impaired.When analysing the phenotypic profile of Treg cells, it was found that there is a phenotype marked decrease in the expression of CTLA-4,GITR and CD27, molecules essential for the functionality of Treg cells, in HAM/TSP patients[14]. In addition, it is known that patients with HAM/TSP presented an increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines(IFN-γ) and a decrease in regulatory cytokines (TGF-β)[44,45]. These abnormalities were found both in articles included in this review that found a directly and inversely proportional relationship between TAX and FOXp3. Therefore, this may suggest that, even though the viral TAX protein has effects of induction or inhibition of FOXp3,the HTLV-1 has modulation strategies in FOXp3 that triggers continuous losses in the cell’s ability to regulate the immune system by decreasing the phenotype markers or release of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
The HAM/TSP pathogeneses is characterized by chronic inflammatory profile with high spontaneous proliferation,hyperactivation of immune cells and high level of cytokines[46].However, the mechanism of HAM/TSP development remains unclear. One hypothesis about it indicates that there is a chronic inflammation in the central nervous system caused by cellular infiltration of HTLV-1-infected cells, resulting in neuronal damage[47]. Therefore, the physiological mechanisms of suppression of inflammation and activation of the immune response during HTLV-1-infection are essential to control the course of the pathogeneses. In regard to this, we propose that the interaction of viral proteins and FOXp3, demonstrated in this review, may contribute to the dysregulation of the natural Treg function and loss of the ability to control the inflammatory response. Then, the hyperinflammatory environment prevails and the HAM/TSP disease progresses.
The small number of screened articles that evaluated the interaction between HTLV-1 viral proteins/mRNA with FOXp3 indicates that the mechanisms of interaction between TAX and HBZ with FOXp3 still need to be studied, and further studies are still needed for this relationship to be established. It is also important to note that the divergent results in relation to TAX may indicate that TAX is expressed in different ways from individual to individual, in view of the differences between the populations studied in the evaluated articles, such as geographic region. In addition, most of the studies selected in this systematic review evaluated only TAX, with HBZ little objectified as a study element. All of this implies a better understanding of the pathogenesis mechanisms of HTLV-1 for the development of HAM/TSP.
The analysis of the articles selected by this systematic review indicated that TAX and HBZ can interact with FOXp3 in HAM/TSP patients. These articles pointed out that the expression of HBZ is directly proportional to FOXp3 expression. On the other hand, it is not yet clear if TAX has a directly or indirectly proportional relationship with FOXp3. The results indicate that TAX can be expressed in different ways according to the individual host. Furthermore, it is suggested that HTLV-1 has modulation mechanisms aimed at affecting the regulation of the immune system and, thus, being able to establish an optimized chronic inflammation.Further studies analyzing this relationship should be carried out,since FOXp3cells can be crucial elements to better understand the pathogenesis of HTLV-1 and the development of HAM/TSP.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This research was funded by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (426196/2018-0). ACMML was supported by a scholarship from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (127049/2019-3 and 115208/2020-8).
Authors’ contributions
A.C.M.M.L. and G.C.S.S. performed the search and analysis of the data. L.L.G. and L.A.S. designed and coordinated the study.A.C.M.M.L., G.C.S.S., L.L.G., F.F.A.R., F.K.B and L.A.S. wrote the article and contributed to the final version of the manuscript.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2021年8期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2021年8期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Pediatric perspectives on treating uncommon genotypes of hepatitis C in the United States
- Determinants of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and encountered side-effects among the vaccinated in Bangladesh
- Failure of space spraying to eliminate dengue virus-infected Aedes aegypti may explain failure to prevent secondary cases in Southern Thailand
- EWMA control chart based on its first hitting time and coronavirus alert levels for monitoring symmetric COVID-19 cases
- Predictors of in-hospital mortality by logistic regression analysis among melioidosis patients in Northern Malaysia: A retrospective study
- Prevalence and clinical significance of antiphospholipid antibodies among hospitalized COVID-19 patients
