Prevalence and clinical significance of antiphospholipid antibodies among hospitalized COVID-19 patients
Cesarius Singgih Wahono, Hani Susianti, Tri Wahyudi Iman Dantara?, Perdana Aditya Rahman, Mirza Zaka Pratama, Indah Adhita Wulanda, Khoirunisah Dwi Hartanti, Elvira Sari Dewi, Kusworini Handono
1Rheumatology and Immunology Division, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
2Department of Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
3Basic Nursing Department, Faculty of Medicine, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
ABSTRACT
KEYWORDS: Antiphospholipid antibodies; COVID-19; COVID-19 disease severity; Mortality
1. Introduction
In January 2020, a pneumonia outbreak caused by a novel coronavirus known as severe acute respiratory coronavirus-2(SARS-CoV-2) was first reported in Wuhan, China[1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) proclaimed the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) as a global health emergency since the confirmed infected cases spread throughout the globe[2]. In the meantime,the infection has rapidly spread, resulting in a pandemic that has affected more than 4.8 million individuals worldwide. In May 2021,the most significant numbers of new cases in South-East Asia were reported from Indonesia (26 908 new cases; 212.2 new cases per
100 000; an 8% increase); the enormous numbers of new deaths were also reported (1 125 deaths; 0.4 news per 100 000)[3]. Similarly,venous thromboembolism (VTE) has become a major concern in COVID-19. A recent meta-analysis study showed an increased risk of mortality associated with high thromboembolism events in COVID-19[4].
COVID-19 infection was associated with alterations in coagulation markers in the early reports[5,6]. A recent study shows that COVID-19 appears to have many coagulation abnormalities, including a significant increase in fibrin/fibrinogen breakdown products (i.e.D-dimers) and prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time(aPTT). Although the elevated D-dimer value is consistent with continued activation of the coagulation and fibrinolysis cascade,the combination of prolonged aPTT and arteriovenous thrombosis is unexpected. We have to remind clinicians of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)-like clinical conditions[6,7]. Several studies have attempted to explain the pathogenesis of thrombosis, one of which is the appearance of antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies[8].According to several recent studies, there is limited evidence on aPL antibodies in COVID-19 disease, and it is not clear whether they are incidental phenomena or whether they are related to any hemostatic abnormalities reported in COVID-19[9,10].
There are many ways to drive virus-induced autoimmunity. The production of aPL antibodies in patients infected with SARSCoV-2 can be calculated by two possible pathogenesis: neoepitope formation and molecular simulation[11,12]. These antibodies in COVID-19 mainly target β2GP1 and anticardiolipin (aCL)[9,13].However, several studies report that there are limited data on the occurrence of anti-phospholipid syndrome during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Positive antiphospholipid antibodies have been identified in a small number of patients. Their association with COVID-19 thrombotic events and clinical outcomes remains unclear[8,9,13].Therefore, this study aims to discover the correlation between antiphospholipid antibodies and coagulation dysfunction, clinical manifestations, disease severity, and mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, especially in Indonesia.
2. Subjects and methods
2.1. Study design and participants
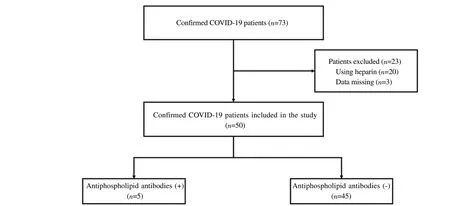
This is a descriptive single-center cross-sectional study considering COVID-19 patients admitted to Saiful Anwar General Hospital in Malang, East Java, Indonesia, between September and November 2020. This study has been approved by the Malang Saiful Anwar General Hospital, Indonesia Ethics Committee (ethics number 400/194/K.3/302/2020). We randomly selected 50 confirmed COVID-19 cases from the general and intensive care unit (ICU).Our inclusion criteria were confirmed COVID-19 cases according to the WHO definition: real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) SARS-CoV-2 test results were positive, and respiratory tract specimens collected from nasopharyngeal swabs[14].We excluded patients initially treated with heparin to reduce the interpretation bias of lupus anticoagulant (Figure 1).
2.2. Data collection
We collected patient demographic data, clinical characteristics,laboratory data, and clinical outcomes. Data were collected from the patients' medical records, including signs and symptoms,comorbidities, admission to ICU, and in-hospital mortality.
COVID- 19 severity is classified as mild, moderate, and severe based on the Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of COVID-19 in Indonesia[15]. Data were gathered comprehensively through a medical records review and communication with attending doctors and other health workers to fill in the missing data.
Thrombotic events, such as cerebrovascular accident (CVA),acute coronary syndrome (ACS), deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and pulmonary embolism, were defined as the presence of arterial or venous thromboembolism (PE). The appropriate examination to evaluate subjects who were clinically suspected with thrombotic events to establish the diagnosis, such as radiology examination,electrocardiography (ECG) and cardiac enzyme panel were performed.
Laboratory examinations, such as complete blood count,coagulation test, liver and renal function, were all measured for firsttime patients admitted to the hospital (Table 1). The antiphospholipid antibodies, including lupus anticoagulant, IgM/IgG anticardiolipin,IgM anti-β2-glycoprotein, were examined by ELISA (Orgentec Diagnostika GmbH).
2.3. Statistical analysis
Categorical variables were measured using percentages and frequency rates. Continuous variables with normal distribution were presented as mean ± SD and not-normal variables were reported as interquartile range (IQR). A t-test was employed to compare normally distributed data; otherwise, the Mann-Whitney test was utilized. The Chi-square test was used to compare proportions for categorical variables, and the Fisher exact test was utilized when data was insufficient. In studying the parameters associated with the occurrence of aPL antibodies, bivariate analysis was used. Variables with a P-value <0.05 according to a bivariate analysis were included in the multivariate analysis. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 25.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline characteristics of COVID-19 patients with and without antiphospholipid antibodies
We recruited 50 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 27 men (54.0%) and 23 women(46.0%), with an average age of (53.4 ± 14.4) years. The most common early signs and symptoms are dry cough (64.0%), shortness of breath (62.0%) and fever (60.0%). We found that the most common comorbidity in patients was diabetes (50.0%), followed by cardiovascular disease (34.0%), hypertension (32.0%) and chronic kidney disease (16.0%). We classify patients into mild (12.0%),moderate (64.0%), and severe (24.0%) based on the severityof COVID-19. Several manifestations of thrombosis have been reported: acute coronary syndrome (6.0%), cerebrovascular accident(6.0%), and deep vein thrombosis (4.0%) (Table 2). The laboratory profile is shown in Table 1. In addition, 9 patients (18.0%) were admitted to the ICU ward due to mechanical ventilators, 40 patients(80.0%) were discharged, and 10 patients (10.0%) died (Table 2).

Table 1. Laboratory findings of hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
3.2. Prevalence rates of aPL antibodies in COVID-19 patients
In our finding, from 50 patients with COVID-19, five patients(10.0%) had at least one circulating antiphospholipid antibody. The most frequently detected aPL antibodies were IgM anticardiolipin(80.0%) following by IgG anticardiolipin (20.0%), and IgM antiβ2-glycoprotein (20.0%). Three patients are positive for IgM anticardiolipin, one patient is positive for IgG anticardiolipin, and one patient is positive for both IgM anticardiolipin and IgM anti-β2-glycoprotein. No lupus anticoagulant was detected in this study.
3.3. Correlation of the clinical parameters in COVID-19 patients with antiphospholipid antibodies
The incidence of nausea and vomiting (80.0% vs. 24.4%, P=0.010),diarrhea (60.0% vs. 13.3%, P=0.010) and anosmia (60.0% vs. 15.6%,P=0.018) in COVID-19 patients with positive aPL antibodies statistically significantly higher than negative aPL antibody group,followed by fever, dry cough, shortness of breath, headache and chest pain, but there was no statistical difference (20.0%-80.0%,P<0.05). Interestingly, we found that all COVID-19 patients with aPL antibodies have cardiovascular disease (100.0% vs. 26.7%,P=0.001). In addition, There is a statistically significant higher prevalence of chronic kidney disease in aPL antibodies group as compared to negative aPL group (P=0.005) (Table 2). Multivariate analysis showed that the presence of aPL antibodies was significantly associated with a higher risk of nausea and vomiting (OR 12.4; 95%CI 1.2-122.6), diarrhea (OR 9.8; 95% CI 1.3-70.9), and anosmia (OR 8.1; 95% CI 1.1-57.9). Similarly, the risk of cardiovascular diseaseis higher (OR 1.4; 95% CI 1.0-1.9). Chronic kidney disease (OR 12.0; 95% CI 1.6-90.1) might be affected due to the presence of aPL antibodies (Table 3).

Table 2. Comparison between baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with and without antiphospholipids antibody.
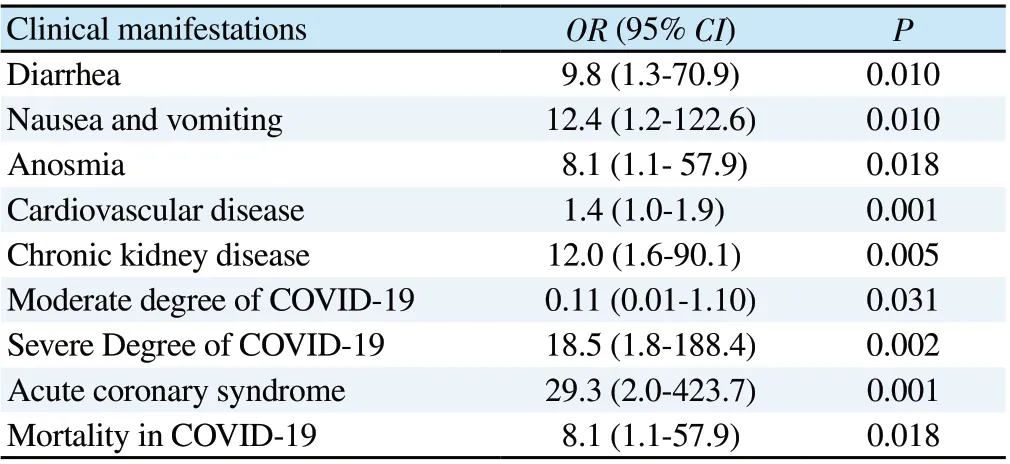
Table 3. Clinical parameters affected by antiphospholipid antibody positivity.
3.4. Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with antiphospholipid antibodies
Circulating aPL antibodies may aggravate the severity of COVID-19 disease. Our research shows that COVID-19 patients with aPL antibodies have a higher incidence of severe patients (80.0% vs.17.8%, P=0.002), and a lower incidence of moderate patients (20.0%vs. 68.9%, P=0.031). COVID-19 without aPL antibody is classified as mild. We recorded thrombotic events that occurred during hospitalization. Our results show that the incidence of acute corona syndrome in COVID-19 patients with aPL antibodies is significantly higher than that of patients without aPL antibodies (Table 2).Approximately 40.0% of COVID-19 patients with aPL antibodies are admitted to the ICU ward, but this is not significantly different from COVID-19 patients without aPL antibodies (P>0.05). We also found that COVID-19 patients with aPL antibodies have a higher mortality rate (60.0% vs. 15.6; P=0.018).
We performed multivariate analysis to measure the association of aPL antibodies with disease severity, thrombotic events, and mortality. We found that there were associations of aPL antibodies positivity in COVID-19 patients with a higher risk of severe degree(OR 18.5; 95% CI 1.8-188.4), lower risk of moderate degree (OR 0.11; 95% CI 0.01-1.10), higher risk of acute coronary syndrome events (OR 29.3; 95% CI 2.0-423.7), and higher risk of mortality(OR 8.1; 95% CI 1.1-57.9).
4. Discussion
This descriptive single-center cross-sectional study was conducted in Malang, Indonesia. This study evaluated the prevalence of aPL antibodies in COVID-19 patients and its association with this patient subgroup's clinical characteristics and clinical outcomes. Recent other single-center studies from China, Italy, and Mexico indicate that the prevalence of aPL antibodies in COVID-19 patients is low[9,13,16]. Similar to our findings, we studied the low incidence of aPL antibodies in COVID-19 patients, and the most commonly detected aPL antibodies are anticardiolipin and anti-β2-glycoprotein.We also found that the presence of aPL antibody is significantly related to the severity of COVID-19. The pathophysiology of the hypercoagulable state of COVID-19 is still unclear, but it is proven that most severe and critically ill patients have coagulopathy[17].However, in this study, no lupus anticoagulant was detected in all of our patients. In contrast with another recent study, it shows a more tremendous amount of lupus anticoagulant in COVID-19 patients but not in critically ill patients[18]. They are potentially biased due to heparin administration for hypercoagulable state prophylaxis[19].
Infection-induced aPL antibody production has been widely acknowledged[20]. The association between aPL antibody detection and SARS-CoV-2 viral infection remains unclear. The S1 may induce the generation of aPL antibodies, and the S2 subunits of S protein in the SARS-CoV-2 virus might produce a phospholipidlike epitope that stimulates the production of aPL antibodies[11]. A previous meta-analysis study reported a very high prevalence of aPL antibodies in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and hepatitis C virus (HCV), as well as gastrointestinal manifestation with COVID-19 infection[21,22]. Our findings show that gastrointestinal manifestations (diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting)have a significant association with the presence of aPL antibodies in serum.
Interestingly, the latest study found that IgA anti-β2-glycoprotein serum was the most common aPL antibody isotype in COVID-19.However, aPL antibodies may be temporary and disappear within a few weeks. As COVID-19 primarily affects the lung and intestines,preferential IgA isotype production could be linked to the breakdown of mucosal immune tolerance[13].
The circulating aPL antibody in COVID-19 has been considered to be one of the mechanisms leading to pro-inflammatory,hypercoagulable state and thrombotic events[23]. In this study,we found that aPL antibodies are present in many moderate and severe patients, which are associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease as comorbidities. Our study also reported an increased risk of thrombotic events. Approximately 40.0% of COVID-19 patients with aPL antibodies have the acute coronary syndrome, which is associated with a higher mortality rate. Although the aPL antibody in COVID-19 is related to disease severity and mortality, our findings and previous studies[8,13,19]found no significant association between aPL antibody and ICU admission. These findings suggest that aPL antibodies may be a marker of disease severity, thrombotic events, and mortality.Unfortunately, we cannot carry out long-term follow-up. There is still a lack of published evidence regarding the correlation between the presence of aPL antibodies and the clinical outcome of COVID-19. A prospective study of aPL antibodies in COVID-19 patients is urgently needed to investigate.
In conclusion, this study is a descriptive single-centered crosssectional study that is conducted in Malang, Indonesia. The purpose is to evaluate clinical characteristics, disease severity, and clinical outcome of COVID-19 patients with aPL antibody. The COVID-19 pandemic is an emerging global health problem that has high mortality rates. A vast population in Indonesia and the high number of new cases and death rates due to COVID-19 are emerging problems for the local government. We reported that a slight prevalence of aPL antibodies in COVID-19 had been associated with specific gastrointestinal manifestations. In addition, it has an increased risk of acute coronary syndrome and an increased mortality rate. Further studies using a larger scale and multi-center are needed to see the prevalence of clinical survival of COVID-19 patients that have aPL antibodies for its application to alertness,management and therapy of COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm no conflict of interests in this study.
Authors’ contributions
C.S.W., H.S., and K.H. designed, directed and supervised the project. T.W.I.D. and M.Z.P. processed the experimental data,performed the analysis, and wrote the manuscript in consultation with C.S.W., H.S., and K.H. P.A.R. helped supervise the project and contributed to the draft interpretation of the results. I.A.W., K.D.H.,and E.S.D. collected the data and performed the laboratorium analysis.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2021年8期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2021年8期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Pediatric perspectives on treating uncommon genotypes of hepatitis C in the United States
- Determinants of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and encountered side-effects among the vaccinated in Bangladesh
- Failure of space spraying to eliminate dengue virus-infected Aedes aegypti may explain failure to prevent secondary cases in Southern Thailand
- Co-expression of HBZ, TAX and FOXp3 and HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis development in HTLV-1-infected individuals: A systematic review
- EWMA control chart based on its first hitting time and coronavirus alert levels for monitoring symmetric COVID-19 cases
- Predictors of in-hospital mortality by logistic regression analysis among melioidosis patients in Northern Malaysia: A retrospective study
