Prevalence of anxiety among gestational diabetes mellitus patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kai Wei Lee, Hong Chuan Loh,Seng Choi Chong, Siew Mooi Ching, Navin Kumar Devaraj, Maiza Tusimin, Habibah Abdul Hamid, Fan Kee Hoo
Kai Wei Lee, Siew Mooi Ching, Navin Kumar Devaraj, Department of Family Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang 43400, Selangor, Malaysia
Hong Chuan Loh, Clinical Research Centre, Hospital Seberang Jaya, Ministry of Health Malaysia, Perai 13700, Penang, Malaysia
Seng Choi Chong, Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang 43400, Selangor, Malaysia
Maiza Tusimin, Habibah Abdul Hamid, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang 43400, Selangor, Malaysia
Fan Kee Hoo, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang 43400, Selangor, Malaysia
Abstract
Key words: Prevalence; Anxiety; Gestational diabetes; Psychiatry; Meta-analysis; Systematic review
INTRODUCTION
The prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) has been increasing over the past decades[1,2].Globally, GDM has been reported as a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among both the infants and their mother[3,4].Mothers with GDM are at increased risk of getting pregnancy complications such as preterm delivery, preeclampsia, abnormal birth weight, metabolic and electrolyte disorders[5].Studies also indicated that GDM may persist after postpartum and subsequently develop into overt diabetes mellitus, and it was estimated that the risk for developing diabetes mellitus after GDM increased linearly with the duration of follow-up ranged from 19.72% at 10 years.The estimated risks for type-2 diabetes mellitus ranged from 19.7% at 10 years to 39.0% at 30 years[6].Neonates born to GDM mothers are at higher risk of suffering from adverse neonatal outcomes such as abnormal birth weight, congenital anomalies, hypoglycaemia and longer duration in neonatal intensive care unit for further investigation[7-9].
Previous studies showed that the prevalence of depression among mothers with GDM were ranging from 25.9% to 56.7%[10,11]and the prevalence of anxiety was within a range of 4.8% to 57.7%[12,13].Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress which involves both psychological and physical reactions.It becomes clinically significant when the anxiety grows out of proportion to the situation and causes functional impairment.Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental illnesses, and are characterized by feelings of tension, worrying thoughts and physical changes such as increased blood pressure.People with anxiety disorders usually have recurring intrusive thoughts or concerns.They may avoid certain situations out of worry.They may also have physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling, dizziness or a rapid heartbeat[14].With a remarkable increase in lifetime prevalence, anxiety has become a public health burden worldwide, causing increased use of mental health services and loss of productivity[15].In particular, anxiety is a common psychiatric condition that affects up to one-fifth of the pregnant mothers[16]and is significantly associated with postpartum depression (odds ratio = 2.6, 95%CI: 2.0, 3.5) and reduced odds of breastfeeding (odds ratio = 0.63, 95%CI: 0.5, 0.7)[17].Thus, anxiety and related mental conditions could pose negative effects on child development[18].A high state of anxiety is found in 15.8% of pregnant women, while 12.5% of women suffer high trait anxiety[19].Similarly, pregnant mothers with GDM were more anxious than pregnant women with other medical problems or healthy pregnant women[20].
①蔣哲倫《論周邦彥的羈旅行役詞》:“羈旅行役,是我國(guó)古典詩(shī)歌的傳統(tǒng)題材之一,主要是抒發(fā)統(tǒng)治階級(jí)中某些人物遭受斥逐后去國(guó)懷鄉(xiāng)的牢愁,中下層官吏為職操勞而旅途奔波的磋嘆,以及一般文人墨客失意流落的哀怨?!?/p>
There are multiple factors associated with anxiety during pregnancy, including current or past pregnancy-related complications, previous pregnant loss and personal history of mental illness[21].Study have also shown that women with GDM experience significantly worse quality of life[22].However, findings from previous studies indicate that there is a lack of data on the epidemiology of antenatal anxiety among GDM patients.Therefore, we aimed to determine the pooled prevalence of anxiety among GDM patients by conducting a meta-analysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This present study was registered in the Medical Research and Ethics Committee, Ministry of Health Malaysia (registration number: NMRR-20-117-52644), and conducted according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses[23].As this work only involved secondary data retrieval and analysis, no ethical approval was sought.
Literature search
Two investigators (Lee KW and Loh HC) independently searched MEDLINE, Cinahl, PubMed and Scopus databases for potential studies published in journals from inception to 31 October 2019.We used following search terms: (Anxiety OR anxiety symptom OR anxiety disorder OR generalized anxiety disorder OR panic disorder OR panic attack OR agoraphobia OR phobia OR specific phobia OR specific phobic disorder OR medication-induced anxiety disorder OR medical condition induced anxiety disorder OR social anxiety disorder) AND (prevalence) AND (gestational diabetes OR GDM OR gestational diabetes mellitus OR diabetes in pregnancy).The search strategies with the Boolean or phrase operators were shown in the Supplementary material 1.Studies in English, available in full-text and conducted among humans were searched.Then, we removed duplications using Endnote, after that we screened the title and abstracts for its suitability.Finally, articles with their full text were assessed for eligibility to be recruited into the quantitative analysis.
Inclusion criteria
Any studies that reported the prevalence or percentage for anxiety symptoms or anxiety disorders among GDM patients and fulfilled the inclusion criteria were analysed.The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Diagnosing or screening of anxiety was made according to Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders/International Classification of Diseases diagnostic criteria or by any screening tools; (2) Participants in the study were diagnosed with GDM; and (3) Studies were published in English peer-reviewed journal from inception to 31 October 2019.Other related studies were also included through careful review of the reference lists of related review articles and reverse-forward citation tracking.Studies were excluded if they included only pregnant mothers with pre-existing diabetes mellitus, were of case-control design or examined anxiety prior to the diagnosis of GDM.
Study selection
All relevant articles identified through the above databases were imported into Endnote programme X5 version.Initially, we performed de-duplication.Two investigators independently screened each title and abstract for suitability based on the search strategies mentioned above.Then, full-text articles were assessed based on the inclusion criteria mentioned above.Any disagreements between the investigators were resolved through discussions before the final consensus for quantitative analysis was reached.
Data extraction
The following data were extracted from every study: The last name of the first author, year of publication, country, sample size, study design, recruitment duration, timing of GDM diagnosis, GDM diagnosis guidelines, assessment of anxiety guidelines, and timing of anxiety assessment.The outcomes measures included the numbers of GDM patients with anxiety symptoms or disorders and total number of GDM patients.Two investigators (Lee KW and Loh HC) individually extracted the data and assessed the study quality, with differences resolved through discussion with the third and fourth investigators (Ching SM and Hoo FK).
Quality assessment
The quality of the individual studies was determined using the checklist of Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE)[24].
The aim and use of STROBE were to assess the strengths and weaknesses of the studies reported in the medical literature.STROBE results also helps readers to know what was planned, done and found, as well as what is incomplete and inadequate in the reporting of the articles.The tool consists of 22 items to help assess the important components found in observational studies.In certain instances where the information provided was insufficient in order to make judgement for a certain item, that item was graded with a “0”, rendering the item as having a high risk of bias.Each article’s quality was graded as “good” if the STROBE score was ≥ 14; or graded as “poor” if the STROBE score was < 14.Two investigators (Devaraj NK and Maiza T) individually assessed the study quality, with differences resolved by discussion with the third and fourth investigators (Ching SM and Hoo FK).Studies were included in analysis regardless of STROBE score and grade.
Statistical analysis
A random-effects (DerSimonian and Laird Method) meta-analysis method was employed to pool the prevalence estimated from these related studies and was reported with a 95%CI.I2index was used to assess the studies heterogeneity (i.e.low is < 25%, moderate 25%–50%, and high > 50%) that indicated the total percent of discrepancy due to variation in the included studies[25].For statistical analysis, Open Meta (Analyst) software was used, this software can be accessed and downloaded from http://www.cebm.brown.edu/openmeta/index.html[26].Funnel plot was generated using The Jamovi project computer Software which can be retrieved from https://www.jamovi.org[27].
RESULTS
Description of included studies
Thirty manuscripts were identified in the initial screening as shown in Figure 1.After removal of duplicate articles (n= 11), a total of 19 studies were retrieved for further assessment.After screening for its suitability through title and abstract, 10 studies fulfilled both our inclusion and exclusion criteria.After careful evaluation of the 10 articles, only three studies were eligible for quantitative analysis in this study.
Characteristics of included studies
The main characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.A total sample of 12744 women diagnosed with GDM was included in the analysis.The respondents were diagnosed using either American Diabetes Association or World Health Organization guidelines.These studies were conducted in Canada[13], Ireland[12]and Malaysia[28].In terms of diagnosing or screening for anxiety, Bekaet al[13](2018) used the diagnostic criteria of the International Classification of Diseases- Ninth version (ICD-9) (prior to 2002) and the International Classification of Diseases- Tenth version (ICD-10) (2002 onward); while Eganet al[12](2017) and Leeet al[28](2019) used 21-item Depression Anxiety Stress Scale (DASS-21).For quality assessment, we assigned each study with an overall rating based on the tool derived from STROBE checklist.The overall quality of included studies appeared to be good.
Prevalence of anxiety
The overall pooled prevalence of anxiety was 29.5% (95%CI: 6.9, 52.0) (Figure 2).The pooled prevalence of anxiety using DASS-21 was higher than prevalence of anxiety using ICD-9/10 (42.4%vs4.8%).Sensitivity analysis reveals that study by Bekaet al[13]had substantial influences on the overall prevalence, which caused prevalence of anxiety to increase from 29.5% (95%CI: 6.9, 52.0) to 42.4% (95%CI: 13.2, 71.5).On the other hand, removal of studies by Eganet al[12], 2017 or Leeet al[28], 2019, it did not cause statistically significant changes to the overall prevalence of anxiety (Supplementary material 2).Indeed, funnel plot (Supplementary material 3) suggested that there was publication bias.Nevertheless, we did not exclude any studies from the meta-analysis in view there was only three studies available.
Quality assessment
We assigned the studies with an overall rating based on STROBE checklist.All three studies received an overall “Good” quality with a score of ≥ 14 over 22 (Supplementary materials 4-6).In summarizing the results, we concluded that all studies had methodological issues such as not describing any efforts to address potential sources of bias, how the missing data were addressed, and lacking of sensitivity analysis.

Table 1 Characteristics of the included studies
DISCUSSION
Our systematic review and meta-analysis offer preliminary evidence regarding the prevalence of anxiety among GDM patients.The results indicated that the pooled prevalence of anxiety among GDM patients was 29.5%.
Several reasons may have contributed to the high heterogeneity (I2= 99.12%) in the pooled prevalence that was seen in our systematic review and meta-analysis.First, there are differences in terms of the methodological approach used in different studies for the detection of anxiety.The diagnostic method would identify specific anxiety disorders with more stringent criteria, while the screening method served as case identification.Diagnostic versus screening criteria used by different studies for the clinically significant anxiety symptoms were omitted.For instance, Beka et al[13](2018) used ICD-9 and ICD-10 to diagnose anxiety disorder while Egan et al[12](2017) and Lee et al[28](2019) used DASS-21 for screening of anxiety symptoms.Unlike ICD, DASS-21 is a screening tool with 21 items which consists of three domains assessing depression, anxiety and stress[29].DASS-21 English version has been translated and validated into Malay version by Musa et al[30].DASS-21 has distinctive cut-off value for severity rating; anxiety is detected if anxiety domain score is ≥ 8 (Mild and above)[29], however it should be noted that clinically significant anxiety symptoms should be of moderate and above in its severity.
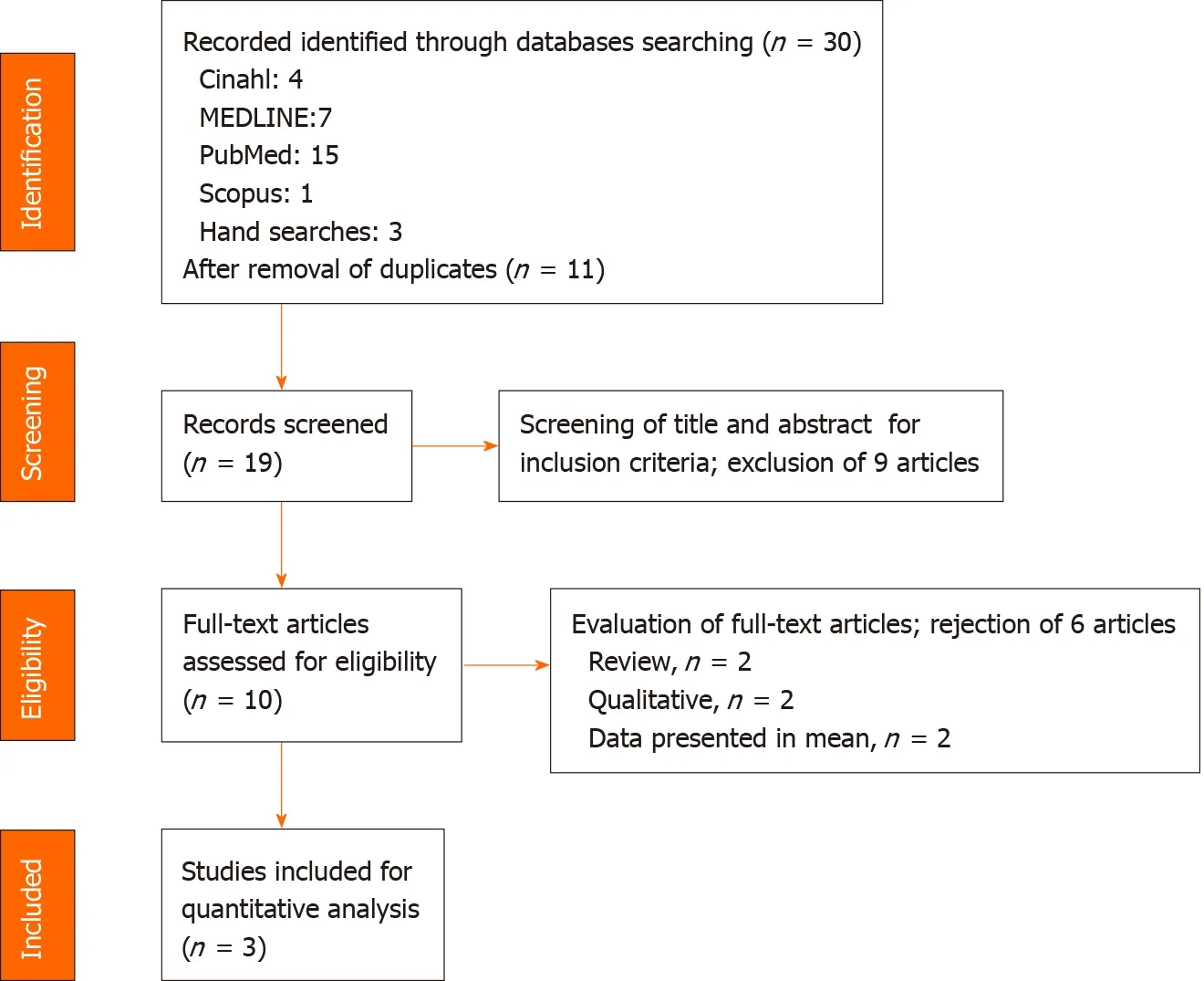
Figure 1 Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols flow diagram of the literature screening process.
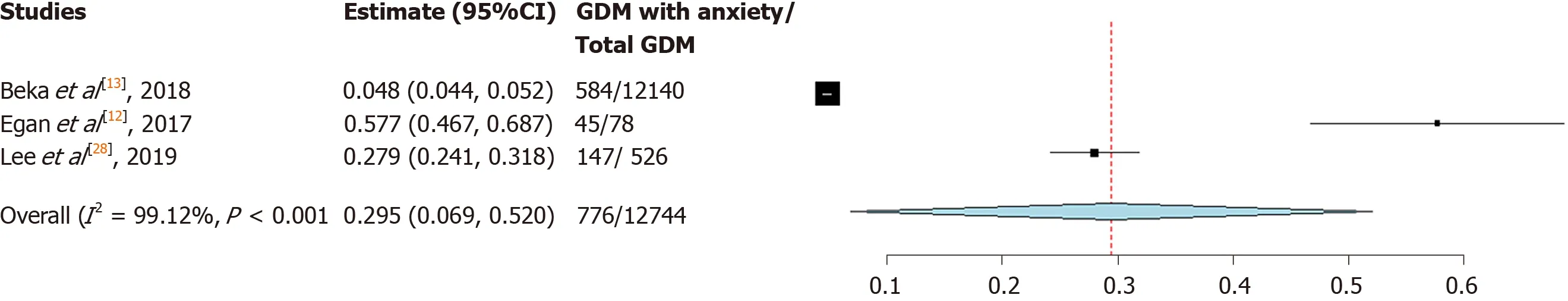
Figure 2 The forest plot of the pooled prevalence of anxiety among gestational diabetes mellitus patients.GDM: Gestational diabetes mellitus.
The vast disparity of anxiety prevalence between study population may be one of the reasons for the discrepancy.Study by Beka et al[13](2018) was a population-based study, while studies by Egan et al[12](2017) and Lee et al[28](2019) were hospital-based study.In the study by Bekaet al[13](2018), there was no sample size calculation, and the patients’ medical information were obtained via health services databases.The weakness of health services databases is that it contains information about formal diagnosis and healthcare services provided for patients, yet it didn’t provide results of mental health screening, therefore the prevalence of anxiety (4.8%) reported by Bekaet al[13](2018) may not reflect the prevalence of clinically significant anxiety faced by GDM patients.We noted that two studies which conducted in hospital (Eganet al[12], 2017 and Leeet al[28], 2019) had sample size calculation; these two studies achieved sufficient sample number.However, Eganet al[12](2017) had a sample size of less than 100 for GDM patients.Hence, the prevalence of clinically significant anxiety symptoms in Eganet al[12](2017) (57.7%) was higher compared to Leeet al[28](2019) (27.9%).Sample size remains an important criteria when determining the prevalence of anxiety, as studies have shown the positive correlation between sample size and prevalence[31,32].Hence, all these reasons might have contributed to the high heterogeneity in the prevalence of anxiety in our study.
More than half of pregnant women showed moderate anxiety during their pregnancy[33,34].Anxiety during pregnancy could be due to worries about health and well-being of the babies and the mothers themselves.The worries also extend to the concern of parenting and the transition to maternal role after birth[28].A meta-analysis reported that antenatal anxiety could increase the risk for adverse birth outcomes such as preterm delivery (relative risk = 1.50, 95%CI: 1.33, 1.70) and low birth weight (relative risk = 1.76, 95%CI: 1.32, 2.33)[35].
Around 11.5% of pregnant women in Asia are affected by GDM[36].Recent metaanalysis reported that hyperglycaemia in pregnancy increases the risk for adverse outcomes such as caesarean section (OR = 1.59, 95%CI: 1.49, 1.70), large for gestational age (OR = 2.11, 95%CI: 1.73, 2.58), macrosomia (OR = 2.06, 95%CI: 1.86, 2.28), neonatal hypoglycaemia (OR = 1.37, 95%CI: 1.20, 1.57), gestational hypertension (OR = 1.91, 95%CI: 1.49, 2.43) and pre-eclampsia (OR = 2.15, 95%CI: 1.45, 3.19)[5].GDM patients are at higher risk for experiencing anxiety as compared to pregnant women without medical complications[20].Similarly, the adverse birth outcomes could be exacerbated if women with GDM experiences anxiety during pregnancy.
Antenatal anxiety is an evolving field, and unlike depression, only a few studies have been conducted among GDM patients.However, studies have reported that antenatal anxiety is more prevalent than antenatal depression[28,34], and this study reports anxiety symptoms are prevalent in GDM patients.In order to promote the detection of antenatal anxiety, several screening tools have been recently recommended by National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, which include Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale, GAD-2[37].GAD-2 can be used as an ultra-brief screening scale for antenatal anxiety.Even so, other screening scales are more commonly used in clinical setting as compared to GAD-2, such as DASS-21[29], Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale[38], Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale – Anxiety subscale[39], State-Trait Anxiety Inventory[40], GAD-7[41], Brief Measure of Worry Severity[42], Cambridge Worry Scale[43]and Wijma Delivery Expectancy/Experience Questionnaire –Version A[44].
Impacts of anxiety after delivery period
Mental illness is a leading cause of maternal morbidity and even endangers maternal life especially in high -income countries[45].Indirectly it also impacts new-born babies, causing perinatal morbidity and mortality as well as the impact on the long-term child development[46,47].The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has emphasised that perinatal mental illness is one of the most important issues in women’s health that need to be highlighted, especially in the postpartum period[48,49].
The prevalence of postpartum anxiety disorders varies.Recket al[50](2008) and Milleret al[51](2006) found a comparable percentage of postpartum women having anxiety disorder, at 11.1 % and 10 % respectively.Mattheyet al[52]documented that 16.2% of mothers were diagnosed with a pure anxiety disorder while Wenzelet al[53](2005) noted a prevalence rate of 8.2% for generalized anxiety disorder.
There were many reviews confined to maternal depression in postpartum period but there were scarcity of data on anxiety disorder despite of the high health risks for both mother and child associated with postpartum disorders[50].Maternal anxiety disorder is part of a broad spectrum condition comprising of mild to severe mental illnesses such as bipolar disorder and psychotic disorder.It is common that both anxiety and depression co-exist in postpartum women[51,54].
Socio-demographic factors and socioeconomically deprived status have important impacts on maternal mental illness.The most common risk factors include age of more than 35 year old, single parent, lower educational level and low -income family[47,55].Women with greater socioeconomic deprivation are more likely to have maternal mental illness than those with lesser degree of socioeconomic deprivation[56,57].An early recognition of women at risk and implementation of effective intervention are essential as preventive measures to treat maternal mental illness accordingly, aiming to reduce the complications related to maternal mental illness.
Strength and limitations
To date, this is the first systematic and meta-analysis on anxiety among patient with GDM.This study clearly indicates that anxiety is prevalent among GDM patients.The finding of this review is consistent with the previous literature pertaining to anxiety among pregnant women experiencing medical complications.However, there are several limitations.Strict inclusion/exclusion criteria and a paucity of literature on the topic of interest have resulted in the inclusion of only three papers.However, according to Valentineet al[58], 2010, the minimum number of studies needed to conduct a meta-analysis is two.On top of that, we did sensitivity analysis and funnel plot to show the publication bias.Nevertheless, due care is necessary when interpreting the results as at least 5 studies or more are needed to reasonably and consistently achieve powers from the random-effects meta-analyses that are greater than the studies that contribute to them[59].Second, the pooled sample size is not large enough to reflect the anxiety prevalence in clinical setting, therefore limiting the generalizability of our study findings.
In conclusion, our study provides an estimation of the prevalence of anxiety among patients with GDM.Our study showed that the pooled prevalence was high at 29.5%.We recommend that more epidemiological studies on anxiety during pregnancy to be conducted in this particular population.In addition, it is important to identify factors associated with anxiety during pregnancy so that early detection and intervention can be implemented to improve various obstetric and mental health outcomes.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
There is lack of systematic review and meta-analysis on prevalence of anxiety among GDM women.
Research motivation
The systematic review and meta-analysis reporting the pooled prevalence of anxiety among GDM patients is high (29.5%).
Research objectives
Authors aimed to pool data from existing literature to determine the pool estimates for the prevalence of anxiety among women diagnosed with GDM.
Research methods
Multiple databases including MEDLINE, Cinahl, PubMed and Scopus were searched to identify studies published up to 31 October 2019 with data on the prevalence of anxiety among women diagnosed with GDM.
Research results
Total 19 abstracts, retrieved 10 articles and included three studies incorporating 12744 GDM women from three countries were reviewed.The pooled prevalence of anxiety was 29.5% among GDM women.
Research conclusions
The results suggest that epidemiological studies on anxiety should be conducted urgently as it merits clinical attention.In addition, it is important to identify factors associated with anxiety among women diagnosed with GDM.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the Director General of Health Malaysia for his permission to publish this article.
 World Journal of Meta-Analysis2020年3期
World Journal of Meta-Analysis2020年3期
- World Journal of Meta-Analysis的其它文章
- Hydatidosis and the duodenum: A systematic review of the literature
- Exclusive cigar smoking in the United States and smoking-related diseases: A systematic review
- Role of non-coding RNAs in pathogenesis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- Thrombopoietin-receptor agonists in perioperative treatment of patients with chronic liver disease
- Combined endoscopy/laparoscopy/percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage, hybrid techniques in gastrointestinal and biliary diseases
- Immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Combination strategies
