Effect of moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) on airway inflammation in asthma model rats
Zhang Guo-shan (張國山), Qiu Ran-ran (邱冉冉), Pan Jiang (潘江), Zhang Jian (張建), Zhang Chi (張馳), Wang Cheng-xi (王誠喜), Liu Mi (劉密)
1 School of Acupuncture, Moxibustion & Tuina, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
2 The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410007, China
3 Hengyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hengyang 421001, China
Abstract
Keywords: Moxibustion Therapy; Moxa Stick Moxibustion; Point, Feishu (BL 13); Asthma; Inflammation; Cytokines; Rats
Bronchial asthma (asthma for short) is a chronic airway inflammation involving multiple cells and cellular components, often accompanied by increased airway responsiveness, recurrent wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and/or cough. It is a common disease of the respiratory system[1]. There are approximately 300 million children with asthma worldwide. The prevalence of asthma is still rising and it tends to affect younger children, especially in developing countries[2]. Disastrous weather such as smog is increasing with the expanding industrialization and urbanization, which results in the rapidly increased incidence of asthma. The repeated asthma attacks not only bring suffering to patients, but also bring a heavy financial burden to their families and the society.
Moxibustion is an external therapy in Chinese medicine. With the thermal stimulation effect on the points, moxibustion causes moderate stress response in the local skin tissues, thus to activate the local skin immune function around the points to produce a preventive effect on the immune-related diseases. Many clinical trials have confirmed that moxibustion not only reduces the airway resistance, increases the effective lung volume, and improves the pulmonary compliance of the asthma patients, but also suppresses the inflammatory response of the respiratory tract by improving various immune indicators of asthma patients, and eventually relieves asthma attack-caused airway spasm[3-7]. By analyzing the clinical literatures on moxibustion treating asthma, Feishu (BL 13) was found to be one of the most commonpoints[8-11]. To reveal the mechanism of moxibustion in treating asthma, in our current work, the effects of moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) on the airway responsiveness, the inflammatory cells and inflammatory cytokines in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of the asthma model rats were investigated, thus to provide an experimental basis for the clinical application and promotion of moxibustion to treat asthma.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental animals and groups
A total of 48 SPF grade male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats, weighing (200±20) g, were provided by Hunan Slake Jingda Experimental Animal Co., Ltd. [License No.: SCXK (Xiang) 2016-0002], and reared in separated cages at the Experimental Animal Center of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, with the temperature of 20-25 ℃ and the humidity of 50%-70%. After 1 week of adaptive feeding, rats were randomly divided into a normal group, a model group, a moxibustion group and a medication group, with 12 rats in each group.
All treatments of animals throughout the experiment were in accordance with theGuiding Opinions on the Treatment of Experimental Animalsissued by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China in 2006[12].
1.2 Main reagents and instruments
1.2.1 Main reagents
Ovalbumin (Batch No.: A5253, Sigma, USA); 10% aluminum hydroxide gel (Batch No.: BF040, Xi'an Hutt Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China); dexamethasone tablets (Batch No.: 131220, Zhejiang Xianju Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China); hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining solution (Batch No.: 20160607, Nanjing Jiancheng Technology Co., Ltd., China); interleukin (IL)-12 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Batch No.: 201404, Beijing Chenglin Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China); IL-4 ELISA kit (Batch No.: 20140331, Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute, China); IL-5 ELISA kit (Batch No.: P03032893, Wuhan Huamei Biological Engineering Co., Ltd., China); IL-10 ELISA kit (Batch No.: 12/2016, Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute, China); tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α ELISA kit (Batch No.: P26032895, Wuhan Huamei Biological Engineering Co., Ltd., China); interferon (IFN)-γ ELISA kit (Batch No.: 20140321, Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute, China).
1.2.2 Main instruments
SPECTRAMAX M5 multifunctional microplate reader (Molecular Devices, USA); PFT Pulmonary Maneuvers animal lung function tester (Buxco, USA); YP10002 small animal electronic scale (Shanghai Youke Instrument Co., Ltd., China); EG1160 histopathology embedding instrument and RM2135 histopathology slicer (Leica, Germany); 2 mm diameter moxa stick (Li Shizhen Qiai Group Hubei Co., Ltd., China); DYY-6C thermostat (Beijing Liuyi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China); -20 ℃/4 ℃ refrigerator (Panasonic Corporation, Japan).
1.3 Preparation of asthma model
According to the relevant literatures, rats in the model, moxibustion and medication groups were used to prepare the asthma models by sensitization and stimulation with ovalbumin[13-14]. Preparation of ovalbumin antigen solution: 5 g ovalbumin and 50 g aluminum hydroxide gel were dissolved in normal saline to a final volume of 500 mL. On the first day of the experiment, ovalbumin antigen solution was injected subcutaneously into the back and groin (0.5 mL) on both sides, and intraperitoneally (1 mL) for each rat. On the 8th day of the experiment, sensitization was repeated with the same dose and method. Starting on the 15th day of the experiment, rats were challenged daily with nasal drop of 1% ovalbumin, 40 μL for each nasal cavity and 80 μL for both sides, once a day for 14 d. The restlessness, shortness of breath, nodding, abdominal muscle twitching, wheezing, and cyanosis of the lips or extremities of rats indicated the successful modeling.
1.4 Intervention methods
1.4.1 Normal group
According to the method of preparing asthma rat model, rats in the normal group were given the same dose of normal saline on the first day and the 8th day of the experiment. Beginning on the 14th day of the experiment, after nasally dripping the same dose of normal saline, rats were fixed in a prone position on the rat board for 15 min every day followed by intragastric administration of normal saline at 10 mL/(kg·bw), once a day, for 14 d.
1.4.2 Model group
To replicate the asthma rat models, from the 14th day of the experiment, after daily stimulation with ovalbumin, rats were fixed in a prone position on the rat plate for 15 min followed by intragastric administration of normal saline at 10 mL/(kg·bw), once a day for 14 d. 1.4.3 Moxibustion Group
Points: Bilateral Feishu (BL 13).
Methods: Points were positioned according to the
ExperimentalAcupunctureScience[15]and the anthropomorphic comparison method. Feishu (BL 13) is located beneath the spinous process of the 3rd thoracic vertebra, laterally away 1.5 cun. From the 14th day of the experiment, the replicated asthma model rats were subjected to daily nasal challenge with ovalbumin, followed by moxibustion at bilateral Feishu (BL 13) and intragastric administration of normal saline at 10 mL/(kg·bw), once a day, for 14 consecutive days. When receiving moxibustion, rats were fixed on the rat board in a prone position to expose the bilateral Feishu (BL 13); the customized fine moxa sticks (2 mm in diameter) were then lighted and placed at 3-5 cm above the bilateral Feishu (BL 13) for 15 min (a self-made body surface temperature sensor was fixed to the moxibustion site for determination of the moxibustion distance to keep the skin temperature between 45 ℃ and 55 ℃ during moxibustion for the first time). 1.4.4 Medication group
From the 14th day of the experiment, the replicated asthma model rats were subjected to daily nasal challenge with ovalbumin, followed by being fixed on the rat board for 15 min in a prone position, and then intragastric administration of dexamethasone, once a day, for 14 consecutive days. Dexamethasone was prepared as a solution with distilled water (the final concentration of 0.2 mg/mL) for intragastric administration at 10 mL/(kg·bw).
1.5 Test items and methods
1.5.1 General behavior
The demeanor, activity, breathing status, urinary status, and other general behaviors of rats were observed, and special attention should be paid to the secretions of the mouth, nose and other parts. Possible abnormal changes mainly included restlessness or curling up, sneezing, coughing, shortness of breath, abdominal muscle twitching, wheezing, cyanosis of lips or extremities, increased secretions in the mouth and nose.
1.5.2 Airway responsiveness
After the last challenge with ovalbumin, the rats were fasted for 24 h, and then anesthetized with 10% urethane by intraperitoneal injection. The rats were fixed in a supine position on the rat board to expose the trachea and perform tracheal intubation. Then the inspiratory resistance, expiratory resistance, and pulmonary compliance of the rats were determined using a small animal lung function tester.
1.5.3 Classification and counting of inflammatory cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
The lung tissues were quickly separated, the right main bronchus was ligated, and 2.5 mL of normal saline was slowly injected into the left lung through the tracheal intubation when the airway responsiveness measurement was completed. After a short while, the normal saline was slowly drawn back and then slowly injected into the left lung again. The first bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was obtained after this procedure was repeated three times. By the same way, the second and the third bronchoalveolar lavage fluids were obtained. The bronchoalveolar lavage fluids from 3 procedures were mixed, and centrifuged at 2 000 r/min for 10 min to collect the supernatant for detecting the cytokines to be tested; the cell sediment for sorting and counting the inflammatory cells after Wright staining.
1.5.4 Cytokine level in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
The supernatant of the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was collected by centrifuging. The levels of IL-12, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, TNF-α and IFN-γ in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were detected by ELISA strictly following the instruction of the kit.
1.5.5 Pulmonary histopathology
The right upper lobes of the rat lung tissues in each group were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, stained with HE staining, and the pathological and the morphological changes of lung tissues were observed under the light microscope.
1.6 Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using SPSS version 20.0 statistical software. The measurement data were first tested for normal distribution and homogeneity of variance. The data meeting the normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s). One-Way ANOVA was used for comparison between groups. The least significant difference (LSD) method was used for comparing the data with homogeneity of variance. Dunnett T3 method was used for comparing the data with heterogeneity of variance. The rank-sum test was used when the normal distribution was not satisfied.P<0.05 indicated statistical significance.
2 Results
2.1 General behavioral observations
Throughout the experiment, the rats in the normal group were in good mental state and responsive, with neat and shiny hair, strong body, regular and uniform breathing rhythm, normal defecation and urine, without abnormal secretions in the mouth, nose and other parts. After the nasal dripping stimulation with the ovalbumin, rats in the model group gradually started to scratch the nose and mouth, frequently nod, together with breathlessness, sneezing and other reactions; white viscous secretions in the mouth and nose, and occasional wheezing. With the increased challenge time, the rats showed lassitude or restlessness, and dull hair; rats in the moxibustion and the medication groups also showed the above- mentioned reactions after nasal challenge with ovalbumin, but the overall symptoms were milder than in the model group.
2.2 Airway responsiveness comparison
Compared with the normal group, the inspiratory resistance and the expiratory resistance of the model group were significantly increased (bothP<0.01), and the pulmonary compliance was significantly decreased (P<0.01); compared with the model group, the inspiratory resistance and the expiratory resistance of the moxibustion and the medication groups were significantly reduced (allP<0.01), and the pulmonary compliance was significantly increased (bothP<0.01); there was no statistically significant difference between the moxibustion and the medication groups (allP>0.05). These results indicated that ovalbumin stimulation increased the inspiratory resistance and expiratory resistance, and reduced the pulmonary compliance of rats; moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) and dexamethasone administered by gavage showed a certain preventive effect on this process (Table 1).
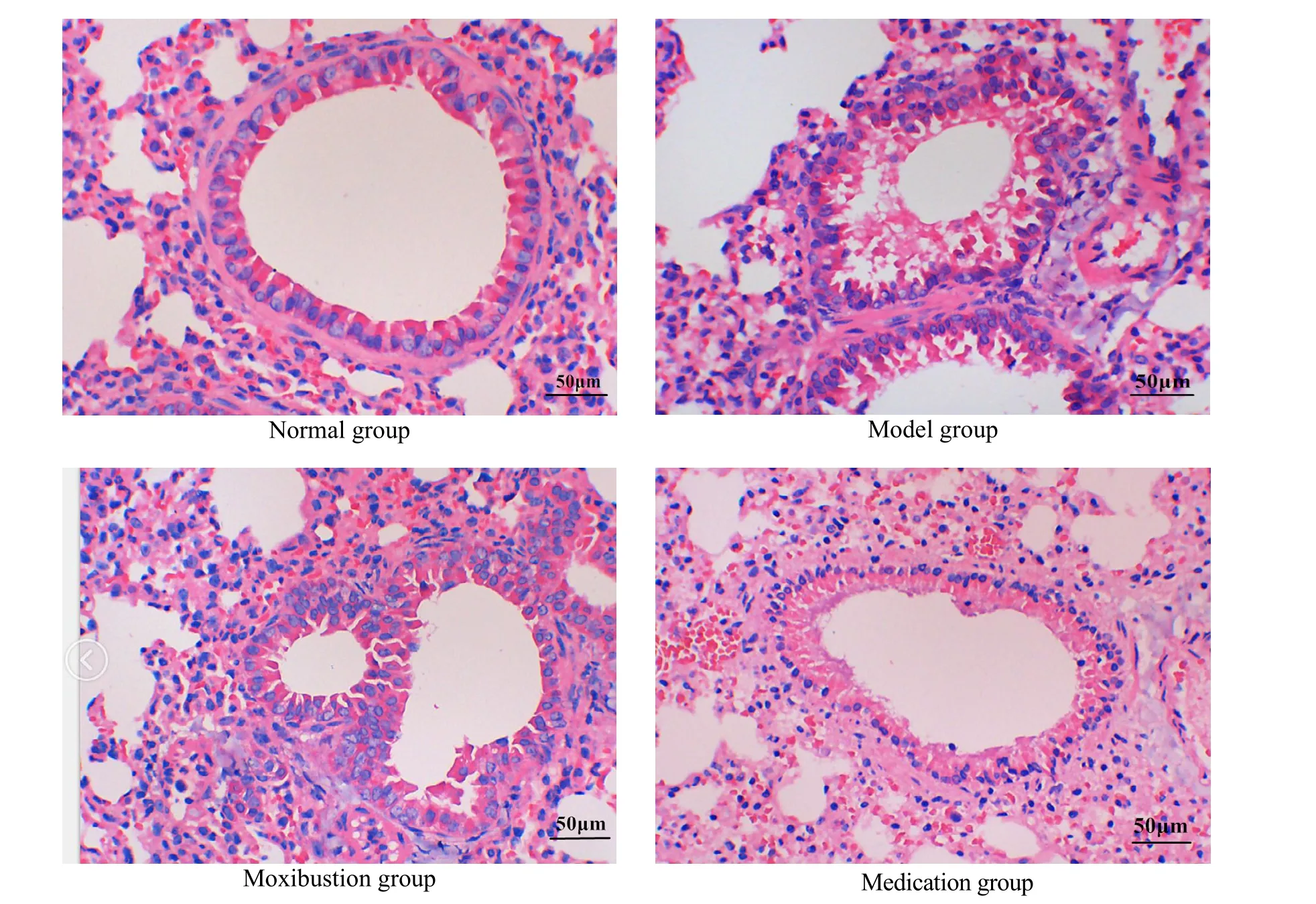
2.3 Effects on the pathological morphology
The alveoli and bronchioles were normal in the shape and structure; the bronchial lumen was smooth and regular, and the cilia were arranged neatly; there was no inflammatory secretion in the vascular cavity, bronchoalveolar cavity, and interstitial lung of rats in the normal group.
Rats in the model group showed thickened tracheal wall, narrowed lumen, inflammatory cell infiltration and increased eosinophils in and around the tracheal wall; compared with the model group, the bronchoalveolar wall structure was complete, the bronchiole morphology was regular, and there was no mucus plug formation and epithelial cell shedding in the lumen of rats in the moxibustion and the medication groups; there was no significant difference between the moxibustion and the medication groups (Figure 1).
Table 1. Comparison of airway responsiveness among groups (±s)
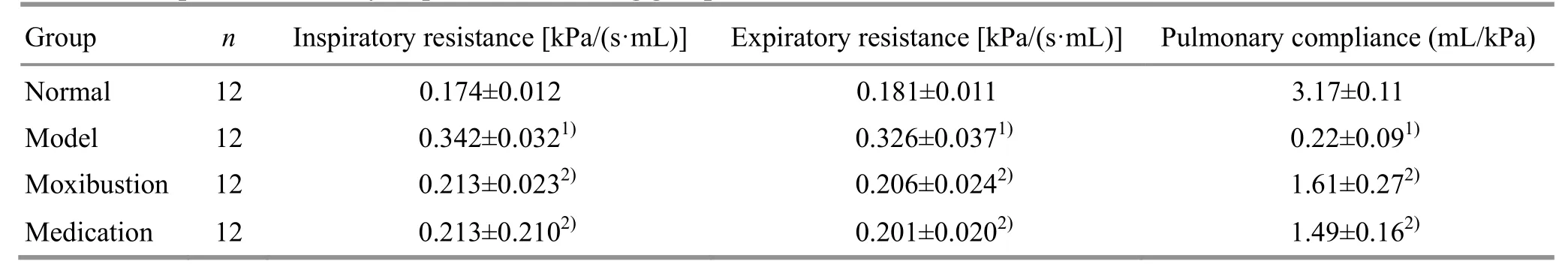
Table 1. Comparison of airway responsiveness among groups (±s)
Note: Compared with the normal group, 1) P<0.01; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.01
Group n Inspiratory resistance [kPa/(s·mL)] Expiratory resistance [kPa/(s·mL)] Pulmonary compliance (mL/kPa)Normal 12 0.174±0.012 0.181±0.011 3.17±0.11 Model 12 0.342±0.0321) 0.326±0.0371) 0.22±0.091) Moxibustion 12 0.213±0.0232) 0.206±0.0242) 1.61±0.272) Medication 12 0.213±0.2102) 0.201±0.0202) 1.49±0.162)
2.4 Effects on the inflammatory cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
Compared with the normal group, the total number of inflammatory cells and the proportion of eosinophils in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of the model group were significantly increased (bothP<0.01). Compared with the model group, the total number of inflammatory cells and the proportion of eosinophils in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of the moxibustion and the medication groups were significantly reduced (P<0.05 orP<0.01); there was no significant difference between the moxibustion and the medication groups (bothP>0.05). These results indicated that ovalbumin challenge stimulated the inflammatory response in rat lung tissues, while moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) and intragastric administration of dexamethasone showed a certain anti-inflammatory effect (Table 2).
2.5 Effect on the inflammatory cytokines in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
Compared with the normal group, the levels of IL-10, IL-12 and IFN-γ were significantly reduced (allP<0.01), and the levels of IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α were significantly increased in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of the model group (allP<0.01). Compared with the model group, the IL-12 and IFN-γ levels were significantly increased, while the IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α levels were significantly reduced in the rat bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of both the moxibustion and the medication groups (P<0.05 orP<0.01); and the IL-10 level was significantly decreased in the medication group (P<0.01); there were no significant differences between the moxibustion and the medication groups (allP>0.05). These results indicated that ovalbumin challenge reduced the levels of IL-10, IL-12 and IFN-γ, and increased the levels of IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α in rat lung tissues. Moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) or intragastric administration of dexamethasone increased the levels of IL-12 and IFN-γ, and reduced the levels of IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α in the lung tissues of the experimental rats (Table 3).
Table 2. Comparing the inflammatory cell counts in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of rats among groups (±s)
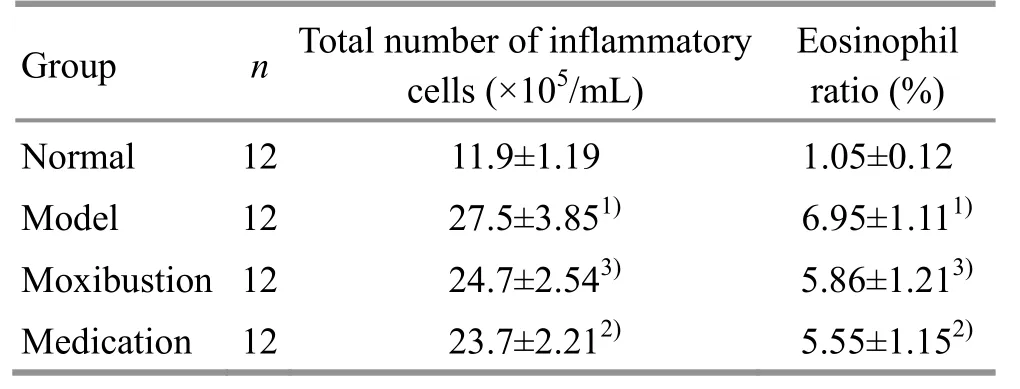
Table 2. Comparing the inflammatory cell counts in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of rats among groups (±s)
Note: Compared with the normal group, 1) P<0.01; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.01, 3) P<0.05
Group n Total number of inflammatory cells (×105/mL) Eosinophil ratio (%) Normal 12 11.9±1.19 1.05±0.12 Model 12 27.5±3.851) 6.95±1.111)Moxibustion 12 24.7±2.543) 5.86±1.213)Medication 12 23.7±2.212) 5.55±1.152)
Table 3. Comparing IL-10, IL-12, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α levels in the rat bronchoalveolar lavage fluid among groups (±s, ng/L)
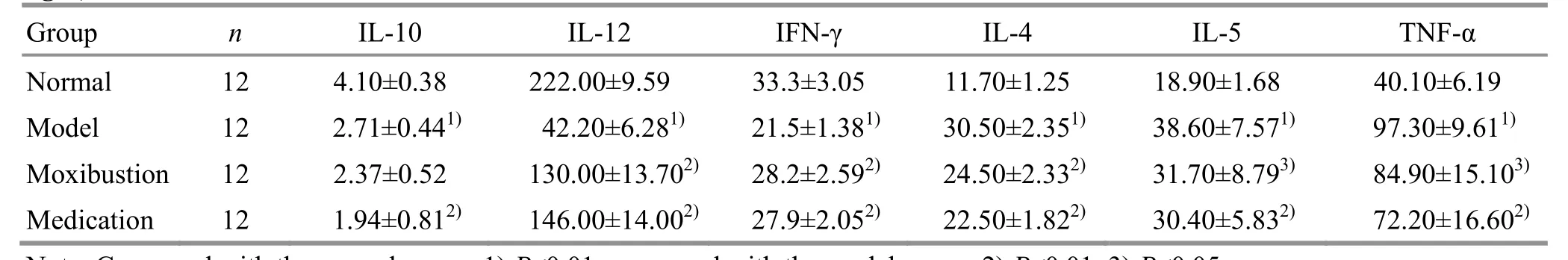
Table 3. Comparing IL-10, IL-12, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α levels in the rat bronchoalveolar lavage fluid among groups (±s, ng/L)
Note: Compared with the normal group, 1) P<0.01; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.01, 3) P<0.05
Group n IL-10 IL-12 IFN-γ IL-4 IL-5 TNF-α Normal 12 4.10±0.38 222.00±9.59 33.3±3.05 11.70±1.25 18.90±1.68 40.10±6.19 Model 12 2.71±0.441) 42.20±6.281) 21.5±1.381) 30.50±2.351) 38.60±7.571) 97.30±9.611) Moxibustion 12 2.37±0.52 130.00±13.702) 28.2±2.592) 24.50±2.332) 31.70±8.793) 84.90±15.103)Medication 12 1.94±0.812) 146.00±14.002) 27.9±2.052) 22.50±1.822) 30.40±5.832) 72.20±16.602)
3 Discussion
3.1 Effects of moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) on the asthmatic symptoms in the experimental rats
Moxibustion produces warm stimulation to patients through the heat generated by moxa burning, which in turn can warm meridians, remove cold, activate blood, warm yang and prevent collapse. It is a common method to treat asthma[16]. Feishu (BL 13) is located where the qi and blood of the lung transfuses on the back. This point can relieve cough and asthma, is an important point for the treatment of lung diseases and often used to treat respiratory diseases such as cough, asthma, hemoptysis, pulmonary dystrophy, tidal fever due to lung atrophy, and allergic rhinitis. Wen X,et al[17]found that ginger cake-partitioned moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) combined with acupuncture had a significant effect in treating acute exacerbation of bronchial asthma. Chen JS,et al[18]found that Qi Ai Tian Jiu Gao plus suspended moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) could prevent and control asthma in kids, reduce and control the asthma exacerbation.
The results of this study showed that after the nasal dripping challenge with ovalbumin, the experimental rats gradually appeared asthma-like reactions such as scratching the nose and mouth, frequent nodding, breathlessness, and sneezing; significantly increased inspiratory resistance and expiratory resistance, along with significantly decreased pulmonary compliance. These findings are basically consistent with what has been reported[13-14]. This study also found that moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) significantly alleviated ovalbumin-sensitized asthma-like symptoms.
3.2 Effects of moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) on the inflammatory cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthma model rats
Bronchial asthma is a chronic airway inflammatory reaction involving multiple cells and cellular components. It is a common chronic respiratory diseases characterized by airway inflammation, hyperresponsiveness and remodeling. The airway inflammation is the basis of airway hyperresponsiveness and airway remodeling. Infiltration and increase of inflammatory cells in the airway are the important features of asthma, and the degree is significantly positively correlated with the severity of bronchial asthma[19]. The immune response during the asthma exacerbation activates the inflammatory cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes, and eosinophils, and the activated inflammatory cells are chemotactically and aggregated to the inflammation site, and release the inflammatory factors, which indirectly or directly damage the epithelial cells in the airway, causing airway inflammation[20]. Therefore, eosinophils, neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes are considered to be the main inflammatory effector cells in asthma exacerbation, and the most important indicators for the clinical diagnosis of asthma. It is also an important index to evaluate the therapeutic effect in treating of asthma. Acute asthma exacerbation and chronic airway inflammation are accompanied by substantial infiltration and accumulation of inflammatory cells[21-23]. Effective control of airway inflammatory response is the key to treating asthma. Therefore, the current treatment of asthma is mainly to regulate the immune function and control the airway inflammatory response.
Many experiments have confirmed that the inflammatory cell levels such as eosinophils, neutrophils, macrophages and lymphocytes in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthma model animals are significantly increased[24-25]. The results of this study also confirmed that sensitization and stimulation with ovalbumin increased the total inflammatory cell numbers and the eosinophil level in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of experimental rats; moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) reduced the total numbers of inflammatory cells and eosinophil level in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, indicating that moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) inhibited the activation, prevented the chemotaxis and accumulation of the inflammatory cells to lung in the asthma model rats, and reduced the release of inflammatory mediators in the lungs, thereby protecting airway epithelial cells, reducing airway inflammation, and ultimately relieving or inhibiting asthma exacerbation.
3.3 Effects of moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) on the inflammatory cytokines in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of the asthmatic model rats
At present, it is generally believed that immune dysfunction is an important mechanism of asthma. T cells, as the most important effector cells in the immune system, plays central role in the cellular immune response. Previous studies have suggested that the ratio and function imbalances of T helper (Th) 1/Th2 cells are the key factors in asthma exacerbation. In recent years, the important role of Th17/Treg imbalance in the pathogenesis of asthma has also received increasing attention[26-31]. Activated T cells mainly release specific cytokines to regulate the immune function, and the functions of different cytokines are antagonistic to each other, thereby ensuring the immune homeostasis of the body[32].
IL-10 is an important cytokine with immune- regulatory effects and significantly reduced when asthma occurs to limit the inflammatory response and autoimmune response, and inhibit airway hyperresponsiveness, thus to play complex biological role in asthma effector cells[33]. Studies have shown that the deficiency of IL-10 and IL-12 leads to asthma aggravation; IL-10 and IL-12 are positively correlated in the course of asthma; treatment with IL-10 and IL-12 alone or together significantly reduces the incidence of asthma[34]. IFN-γ is mainly derived from CD8+cells to antagonize IL-4 by inhibiting the transcription level of IL-4 mRNA, thereby inhibiting the production of immunoglobulin E (IgE)in vivo[35]. Ma L,et al[36]found that vaccine can be used to treat allergic asthma by increasing the IFN-γ level, thus to reduce the serum IgE level. Mitchell C,et al[37]found that IFN-γ significantly inhibited IL-4-induced proliferation of B lymphocytes, and reduced airway inflammatory response, thus to reduce the degree of airway obstruction.
The development of asthma is mediated by proinflammatory cytokines, mainly including IL-4 and IL-5 secreted by Th2 cells, and TNF-α secreted by Th1 cells[27]. It was reported that sensitization with ovalbumin increased IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of the experimental rats[25]. IL-4 is an inflammation promoting factor secreted by Th1/Th2, which can not only switch Th0 to Th2, but also promote the secretion of IL-5 and IL-12 by Th2, and indirectly inhibit the secretion of inflammatory inhibitory factors of IFN-γ and IL-12[31]. Clinical studies by Gao ZG,et al[38]suggested that the high level of serum IL-4 promoted the formation of airway hyperresponsiveness in children with asthma. During the onset of asthma, the Th1/Th2 balance is broken, and the immune response tends to Th2, which reduces the Th1-type cytokine IFN-γ and increases the Th2-type cytokine IL-4[30].
Study by Zhao YZ,et al[23]found that the levels of IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 were significantly increased, and the IFN-γ level was significantly reduced in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthma model rats, and imperatorin regulated the above factors. The study by Zhu YT,et al[25]found that the levels of IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthma model rats were significantly increased, and verbenaside regulated these factors. Ke LQ,et al[39]found that the IL-10 concentration in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthma model rats was significantly lower than that of normal rats, and vasoactive intestinal peptide had a certain regulatory effect on it. The study by Li Y,et al[40]found that the IL-12 expression levels in the plasma and the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of the asthma model rats were lower than those of the normal rats, and smoke exposure further reduced the IL-12 levels in the plasma and the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthmatic rats. The results of this study also showed that the levels of IL-10, IL-12 and IFN-γ were significantly reduced, and the levels of IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α were significantly increased in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthma model rats. Moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) significantly regulated IL-12, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-5 and TNF-α, but had no significant regulatory effect on IL-10.
In summary, the results of this study suggested that moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) significantly improved the asthma-like symptoms, reduced the airway resistance, improved the lung ventilation function, and reduced the pathological and morphological damage of lung tissues in the experimental asthma rats; at the same time, moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) had a beneficial regulatory effect on the total number of inflammatory cells, eosinophil level, IL-12, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-5, TNF-α and other inflammatory cytokines, indicating that moxibustion at Feishu (BL 13) may regulate the immune response of the lungs in asthmatic rats, thereby preventing asthma.

Conflict of Interest There is no potential conflict of interest in this article. Acknowledgments This work was sponsored by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 國家重點基礎研究發(fā)展計劃項目, No. 2015CB554502); National Natural Science Foundation of China (國家自然科學基金項目, No. 81603705, No. 81774438); the 61st Batch Project of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (中國博士后科學基金第 61 批面上資助項目, No. 2107M612567); Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (湖南省自然科學基金項目, No. 2017JJ3245, No. 2017JJ3243); The Key Project of Hunan Province Education Office (湖南省教育廳重點項目, No. 18A223). Statement of Human and Animal Rights The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria.
Received: 8 October 2019/Accepted: 8 November 2019
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年3期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年3期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Analysis of clinical application patterns in acupuncture-moxibustion treatment of Alzheimer disease
- Therapeutic observation of manipulation plus exercise therapy in treating upper crossed syndrome postures of primary school students
- Therapeutic observation on lung-clearing and spleen-strengthening tuina in children with exogenous cough
- Clinical observation on heat-sensitive moxibustion plus lactulose for postoperative constipation of mixed hemorrhoid due to spleen deficiency
- Therapeutic effect of heat-sensitive moxibustion plus medications for senile osteoporosis and its effect on serum BMP-2 and OPG levels
- Effects of electroacupuncture plus drug anesthesia on pain and stress response in patients after radical surgery for stomach cancer
