Morphology, histology and ultrastructure of the alimentary canal of the adult mute cicada,Karenia caelatata(Hemiptera: Cicadidae)
ZHONG Hai-Ying, ZHANG Ya-Lin, WEI Cong,*
(1. Key Laboratory of Plant Protection Resources and Pest Management, Ministry of Education, Entomological Museum,Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi 712100, China; 2. Institute of Plant Protection and Microbiology,Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, China)
Abstract: 【Aim】In order to better understand the morphology and function of alimentary canal of insects in Cicadidae, the alimentary canal of the mute cicada, Karenia caelatata, was investigated at the morphological, histological and ultrastructural levels. 【Methods】 The gross morphology of alimentary canal, ultrastructure of associated organs including oesophagus, filter chamber (including anterior and posterior extremities of the midgut, internal proximal extremity of the ileum, and internal proximal extremities of the Malpighian tubules), conical segment, a midgut loop, and hindgut (ileum and rectum), and histology of filter chamber of male adult of K. caelatata were observed using light and transmission electron microscopy. 【Results】 The results showed that the alimentary canal of K. caelatata consists of the oesophagus, filter chamber, external midgut section and hindgut. The elongated oesophagus is lined with a cuticle containing an epicuticle and an endocuticle. The filter chamber is enveloped by a thin filter chamber sheath, which contains the anterior and posterior extremities of the midgut, internal proximal extremity of the ileum and internal proximal extremities of the Malpighian tubules. Cells of the anterior and posterior extremities of the midgut possess well-developed basal infoldings and densely-packed apical microvilli. Numerous mitochondria and electron-dense secretory granules were observed in the posterior extremity of the midgut. The external midgut section contains a conical segment and a midgut loop. The conical segment is dilated, and consists of two types of cells: the first is featured by the well-developed basal infoldings, and the second lacks basal infoldings. The midgut loop is divided into three distinct regions, i.e., the anterior segment containing numerous secretory granules, mitochondria, rough endoplasmic reticulum and lysosomes in the cytoplasm, the mid-segment containing secretory granules in the cytoplasm, and the posterior segment with cells possessing numerous electron-lucent secretory granules and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Ferritin-like granules scatter in the cells of the anterior segment and mid-segment of the midgut loop. Filamentous materials coat the microvilli of the cells of the conical and anterior segments of the midgut loop. The hindgut is lined by a layer of cuticle. Microorganisms reside in the oesophagus, mid-segment of the midgut loop and rectum cells. 【Conclusion】 Findings of the morphological, histological and ultrastructural characteristics of the gut alimentary canal of K.caelatata in this study improve our understanding of the functional differentiation of alimentary canal in this species. The discovery of microorganisms in the alimentary canal is formative to future study of coevolution between the Cicadoidea and related bacteria.
Key words: Auchenorrhyncha; Cicadidae; Karenia caelatata; digestive tract; morphology; histology; light microscopy; transmission electron microscopy
1 INTRODUCTION
Auchenorrhyncha including Fulgoromorpha (planthoppers) and Cicadomorpha (cicadas, leafhoppers, treehoppers, and spittlebugs) is regarded as a suborder of the Hemiptera, with approximately 42 000 described species worldwide (Larivièreetal., 2010). The phylogeny of this suborder has been controversial for decades: it was treated as a paraphyletic group in some studies (Cuietal., 2013; Songetal., 2016), whereas it was treated as a monophyletic group based on 3 102 gene data or various subsets (Wangetal., 2017), combined mitochondrial and/or nuclear genes (Cryan and Urban, 2012), and morphological characteristics (Ossiannilsson, 1949; Yoshizawa and Saigusa, 2001).
As the least species-rich superfamily in Auchenorrhyncha, Cicadoidea has approximately 3 000 extent species classified into two families, Tettigarctidae and Cicadidae (Sanborn, 2013; Marshalletal., 2018). This group is well known for their loud sound produced by timbals of male adults during the hot summer (Yound and Bennet-Clark, 1995). However, a few species, such as these in the genusKareniawith currently five known species worldwide, cannot generate noise due to the absence of timbals (Weietal., 2009; Thai and Yang, 2012). The taxonomic status ofKareniahad long been controversial (Chouetal., 1997; Moulds, 2005; Weietal., 2009; Thai and Yang, 2012), and recently it was transferred together with its tribe Sinosenini from Cicadettinae to Cicadinae (Marshalletal., 2018).
Morphology of the alimentary canal has been used to supply information for evolution or taxonomical study in many insect lineages, such as the Hemiptera, Coleoptera, Orthoptera and the Hymenoptera (Goodchild, 1966; Yahiro, 1990; Elzinga, 1996; Serr?o, 2001). In Auchenorrhyncha, especially in Cicadoidea, however, only a few studies documented the alimentary canal (Licent, 1912; Hargitt, 1923; Hickernell, 1923; Marshall and Cheung, 1973, 1974; Cheung and Marshall, 1973; Zhongetal., 2014). With respect to the genusKarenia, little research has dealt with the internal anatomy and ultrastructure of the alimentary canal. In the present study, we illustrate the alimentary canal of the mute cicada,K.caelatata, using light and transmission electron microscopy, so as to supply detailed morphological and ultrastructural information of the alimentary canal for this species. The results may be informative to further taxonomic, phylogenetic and physiological analysis of Cicadoidea.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Insects
There is a great similarity in layout and morphology of alimentary canal betweenK.caelatatamales and females. However, the reproductive organs of females occupy most of the abdominal cavity, making it very difficult to dissect out the alimentary canal efficiently. Thus, 15 male adults ofK.caelatatawere used in this study, which were obtained from the Huoditang Forest Farm in the Qinling Mountains, Shaanxi, northwestern China, during August 2010 and 2012, respectively.
2.2 Observation of the general structure of alimentary canal under light microscopy
The alimentary canals ofK.caelatatawere dissected out in phosphate buffered saline (0.2 mol/L PBS, pH 7.2) under a Motic SMZ168 Stereoscopic Zoom Microscope. Photographs were taken with a scientific digital micrography system equipped with an Auto-Montage Imaging system and a Qimaging Retiga 2000R digital camera (CCD).
2.3 Observation of distinct regions of alimentary canal under transmission electron microscopy
Different parts of the alimentary canal were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde (0.1 mol/L PBS, pH 7.2) for 12 h, and rinsed four times with PBS (0.1 mol/L, pH 7.2). The samples were post-fixed in 1% osmium tetroxide for 1.5 h. After the same rinse, the tissues were dehydrated in ethanol series and 100% (v/v) acetone, and infiltrated with araldite and embedded in Epon 812. Ultra-thin sections were stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and examined and photographed under a JEOL JEM-1230 TEM at 80 kV.
Morphological terminology of the alimentary canal follows Cheung and Marshall (1973) and Marshall and Cheung (1974).
3 RESULTS
3.1 Gross morphology of the alimentary canal of adult K. caelatata
Alimentary canal ofK.caelatatais morphologically differentiated into four distinct regions: the foregut (oesophagus), filter chamber, external midgut section (conical segment, midgut loop) and hindgut (ileum and rectum) (Fig. 1). The oesophagus (Oe) is a slender, elongated tube, which expands posteriorly and enters into the filter chamber (Fig. 1). The filter chamber (Fc) is a complex structure, fawn and rod-shaped, containing a filter chamber sheath (Fcs) and a filter organ. The filter chamber sheath is very thin, externally surrounded by thick muscle layers (Mu), and envelopes the filter organ inwards (Fig. 2). The filter chamber is composed of four portions: the anterior extremity of the midgut [i.e., filter chamber proper (Fcp)], posterior extremity of the midgut [i.e., internal midgut (Img)], internal proximal extremities of the Malpighian tubules (Imt), and internal proximal extremity of the ileum (Ihg) (Fig. 2). The anterior extremity of the midgut expands to be a sac-like structure; coils around which are the posterior extremity of the midgut and internal extremities of the Malpighian tubules (Fig. 2). The conical segment (Cs) follows the filter chamber and connects posteriorly with the midgut loop. It is red brown and inflates to become an extremely developed sac. The conical segment is about three times the diameter and 1.5 times the length of the filter chamber (Fig. 1). The midgut loop is divided into three regions based on their morphological and ultrastructural characteristics: a tawny and very thick anterior segment (Amg), a fawn and thick mid-segment (Mmg), and a red brown and thin posterior segment (Pmg) (Fig. 1). The anterior segment descends backwards and connects with the mid-segment. The mid-segment ascends and connects with the posterior segment which enters into the filter chamber, forming a “U-shaped” midgut loop (Fig. 1). The ileum (Il) is long, narrow and uniform, which emerges from the apex of the filter chamber and runs in a zigzag path backward, and finally enters into the peritoneal sheath (Ps). The peritoneal sheath is translucent, situated at the base of the fusiform rectum (Rc) (Fig. 1).
3.2 Ultrastructure of the alimentary canal of adult K. caelatata
The oesophagus is lined with a highly convoluted cuticle (Fig. 3: A), which contains an electron-dense epicuticle and an electron-lucent endocuticle (Fig. 3: B). Oesophagal cells have irregular nuclei resting on a thin basal lamina. The basal lamina is externally surrounded by well-developed muscles (Figs. 3: A). The nuclei are enlarged, vary in shape, and possess hyperchromatic chromatin and irregular nucleoli. Microorganisms (about 0.5 μm in diameter) are visible at the apical region of the oesophagal cells (Fig. 3: A, B).
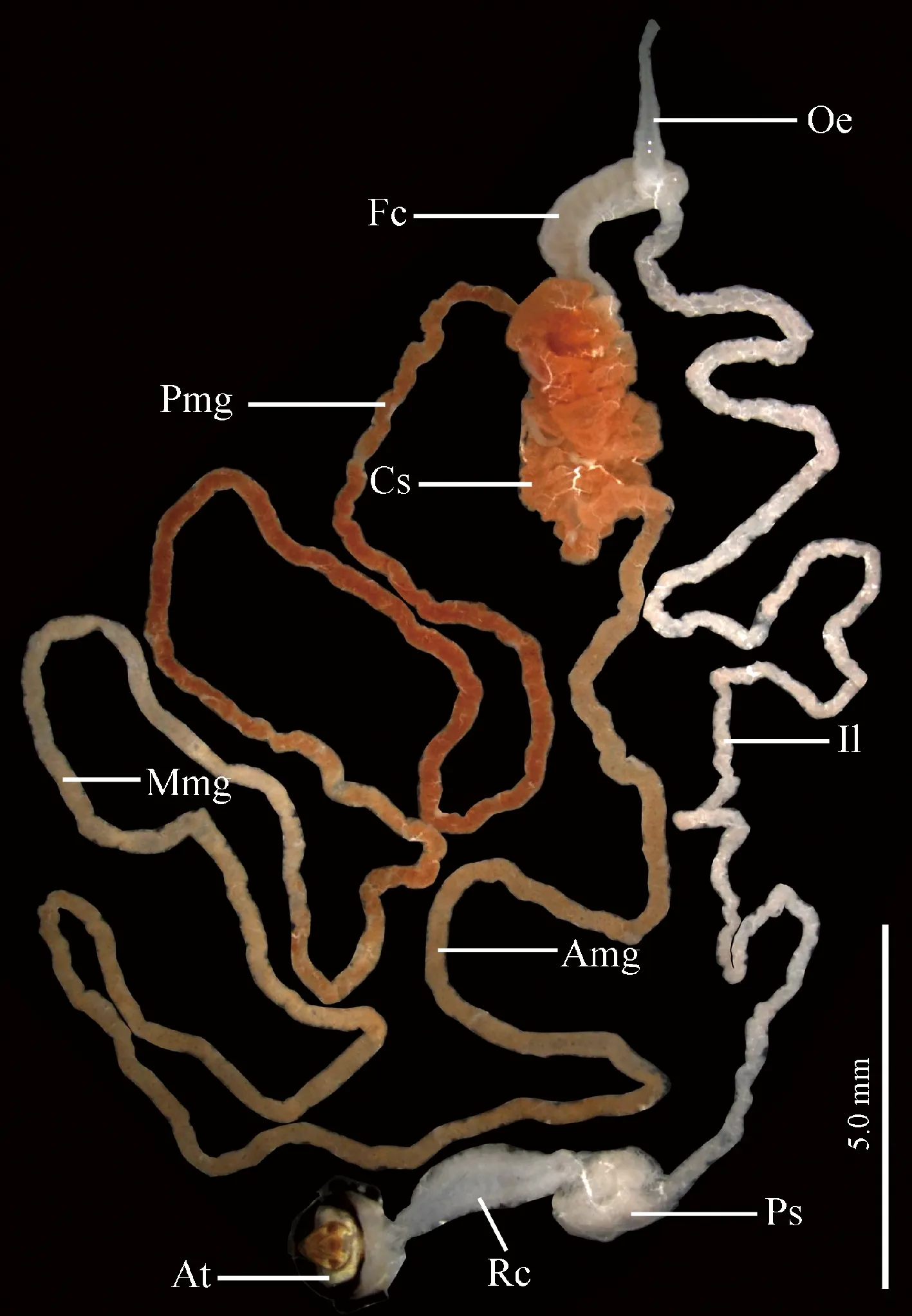
Fig. 1 Gross morphology of the alimentary canalof male adult of Karenia caelatata Amg: Anterior segment of midgut loop; At: Anal tube; Cs: Conical segment; Fc: Filter chamber; Il: Ileum; Mmg: Mid-segment of midgut loop; Oe: Oesophagus; Pmg: Posterior segment of midgut loop; Ps: Peritoneal sheath; Rc: Rectum.
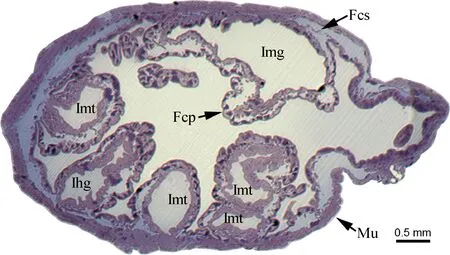
Fig. 2 Transverse section of filter chamber of male adult of Karenia caelatataA light micrograph of semithin section showing the epithelium of the filter chamber and anterior and posterior extremities of the midgut. Fcs: Filter chamber sheath; Fcp: Filter chamber proper; Ihg: Internal proximal extremity of the ileum; Img: Posterior extremity of the midgut; Imt: Internal proximal extremities of the Malpighian tubules; Mu: Externally enveloped muscles.
Cells of the thin filter chamber sheath consist of rod or round nuclei and a small number of cytoplasm strands. The strands envelope the nuclei, and are joined at intervals by loose junctions. Tracheoles penetrate the muscles and even reach to the cells of the filter chamber sheath (Fig. 3: C).
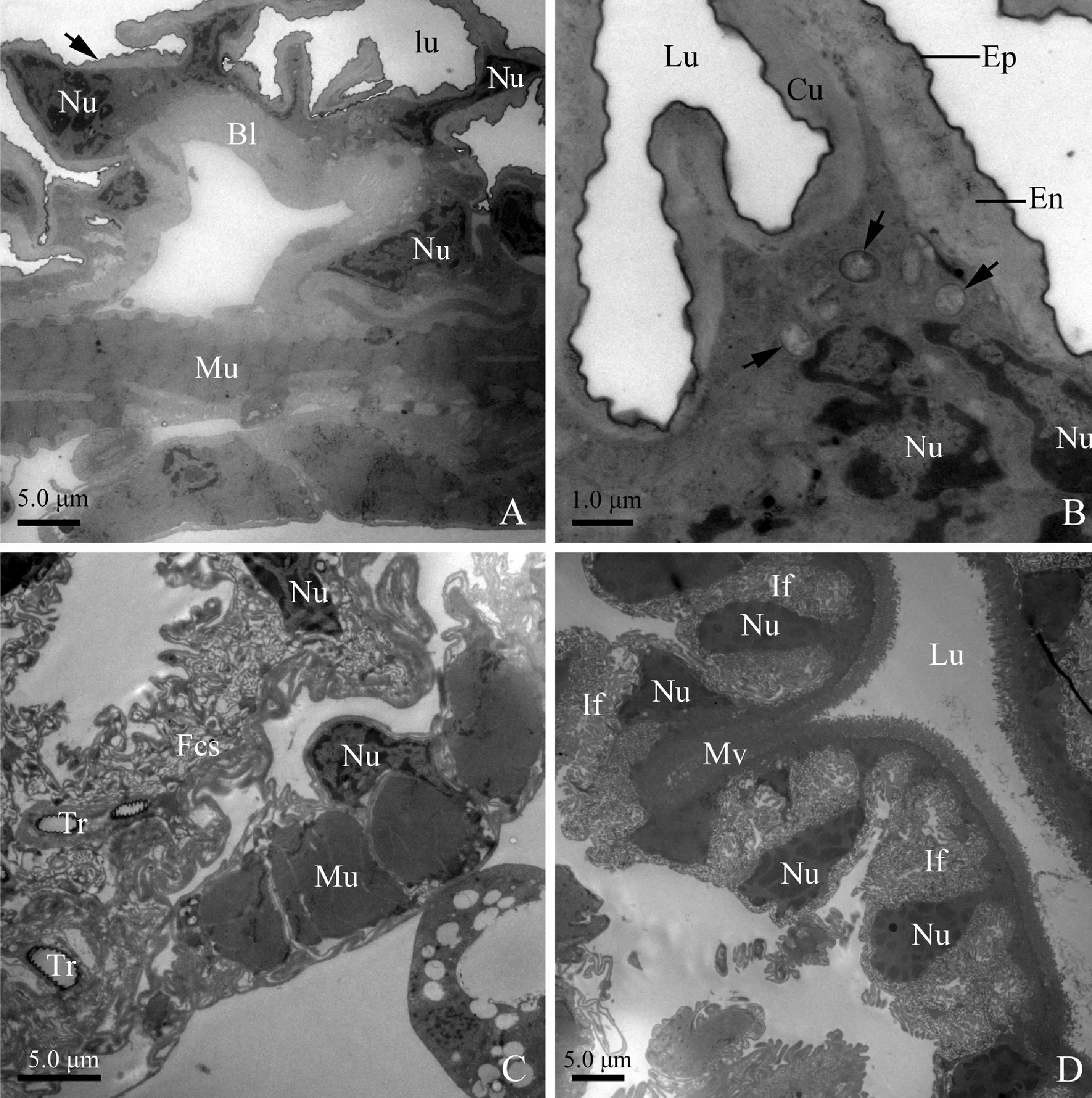
Fig. 3 Transverse section of oesophagus, filter chamber sheath and anterior extremity ofmidgut (filter chamber proper) of male adult of Karenia caelatataA: A cuticle lining lumen of the oesophagus is highly convoluted (as black arrow indicated). The oesophagus epithelia are externally surrounded by well-developed circular muscles. B: The oesophagus cuticle consists of an inner epicuticle and an overlying endocuticle, which envelopes and invaginates into lumen. The cytoplasm contains microorganisms (as black arrows indicated) and large nuclei. C: Transverse section of the filter chamber sheath with evident nuclei. Tracheoles penetrate the muscles and reach to the filter chamber sheath. The filter chamber sheath is externally surrounded by well-developed longitudinal muscles. D: Transverse section of the anterior extremity of the midgut, showing well-developed basal infoldings, apical microvilli, and numerous nuclei. Epithelia are externally surrounded by longitudinal muscles. Bl: Basal lamina; Cu: Cuticle; En: Endocuticle; Ep: Inner epicuticle; Fcs: Filter chamber sheath; If: Basal infoldings; Lu: Lumen; Mu: Circular muscles; Mv: Microvilli; Nu: Nuclei; Tr: Tracheoles.
Cells of the anterior extremity of the midgut are also featured by extremely developed basal infoldings and densely-packed apical microvilli (Fig. 3: D). However, the basal infoldings are wide and bulb-shaped, associated with many mitochondria (Fig. 4: A). Pear-shaped nuclei with oval nucleoli and clumps of heterochromatin insert deeply into the infoldings (Fig. 3: D; Fig. 4: A). The reduced cytoplasm contains clusters of elongated mitochondria near the microvilli (Fig. 4: B).
Cells of the posterior extremity of the midgut are characterized by well-developed basal infoldings and regularly-arranged microvilli. The basal infoldings are narrow and distally devoid of bulb-shaped structure. The microvilli are long (about 1.8 μm) and densely packed. Numerous mitochondria are distributed through the cytoplasm. Electron-dense secretory granules (approximately 0.5 μm in diameter) scatter in the cytoplasm. Well-developed longitudinal muscles externally surround the cells of the internal midgut (Fig. 4: C).
Cells of the conical segment are marked by well-developed microvilli at the apical region and numerous ferritin-like granules in the cytoplasm (Fig. 4: D). The microvilli are straight, densely packed and regularly arranged, with their surface being coated by filamentous materials (Fig. 5: A, B). Two types of cells are recognized in this segment: the first is characterized by well-developed basal infoldings (Fig. 5: C), and the second is devoid of basal infoldings (Fig. 5: D). However, the cytoplasm of the latter is packed with abundant secretory granules which are different in size, shape and electron-density, and some granules are electron-dense in the center and electron-lucent in the periphery (Fig. 5: D).
The basal plasma membrane of anterior segment of the midgut loop deeply infolds to form well-developed labyrinths (Fig. 5: E). The cells bear regularly-arranged apical microvilli which are covered by a large amount of filamentous materials (Fig. 6: A, B). Many ferritin-like granules are visible in the cytoplasm and the basal infoldings (Fig. 5: E; Fig. 6: A). Oval mitochondria, sparse rough endoplasmic reticulum and many irregularly-shaped lysosomes were observed in the cytoplasm (Fig. 6: B). Spherical secretory granules of different size are found among the scattered elements of rough endoplasmic reticulum (Fig. 6: C).
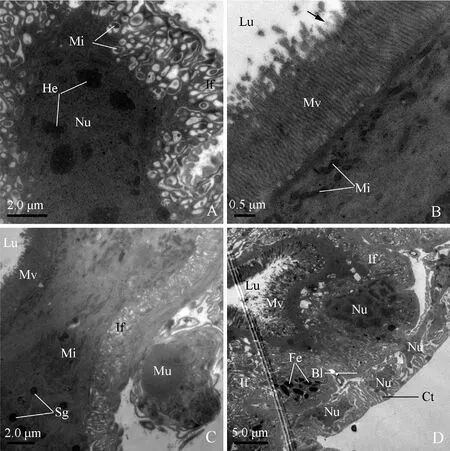
Fig. 4 Transverse section of the anterior extremity of midgut (filter chamber proper), posterior extremityof midgut and conical segment of male adult of Karenia caelatataA: Transverse section of the anterior extremity of the midgut. Basal infoldings are well-developed and their apex is bulb-shaped and contains mitochondria. Nuclei with oval nucleoli and clumps of heterochromatin are visible. B: Transverse section of the anterior extremity of the midgut, showing regularly-arranged microvilli and elongated mitochondria adjacent to the base of the microvilli. Arrow indicates filamentous materials coating the microvilli. C: Many secretory granules and mitochondria exist in the cytoplasm of the posterior extremity of the midgut. Microvilli are densely packed. Basal plasma membrane invaginates into infoldings. Epithelia are externally surrounded by longitudinal muscles. D: Transverse section of the conical segment, showing nuclei, well-developed microvilli facing the lumen, basal infoldings, thick basal lamina, and numerous ferritin-like granules. Well-developed connective tissue with irregular nuclei externally surrounds the conical segment. Bl: Basal lamina; Ct: Connective tissue; Fe: Ferritin-like granules; He: Heterochromatin; If: Infoldings; Lu: Lumen; Mi: Mitochondria; Mv: Microvilli; Nu: Nuclei; Sg: Secretory granules.
Fig. 5 Transverse section of conical segment and anterior segment of midgut loop of male adult of Karenia caelatataA: Transverse section of the conical segment. Note big nucleus and densely-packed and regularly-arranged apical microvilli. Arrow indicates filamentous materials coating the microvilli. B: Transverse section of microvilli. C: Transverse section of the conical segment. Cytoplasm of type I cell with well-developed basal infoldings. D: Transverse section of the conical segment. Cytoplasm of type II cell is filled with secretory granules. Ferritin-like granules exist near the secretory granules. E: Transverse section of the anterior segment of the midgut loop, showing well-developed basal infoldings and apical microvilli. Bl: Basal lamina; Fe: Ferritin-like granules; If: Basal infoldings; Mv: Microvilli; Nu: Nuclei; Sg: Secretory granules.
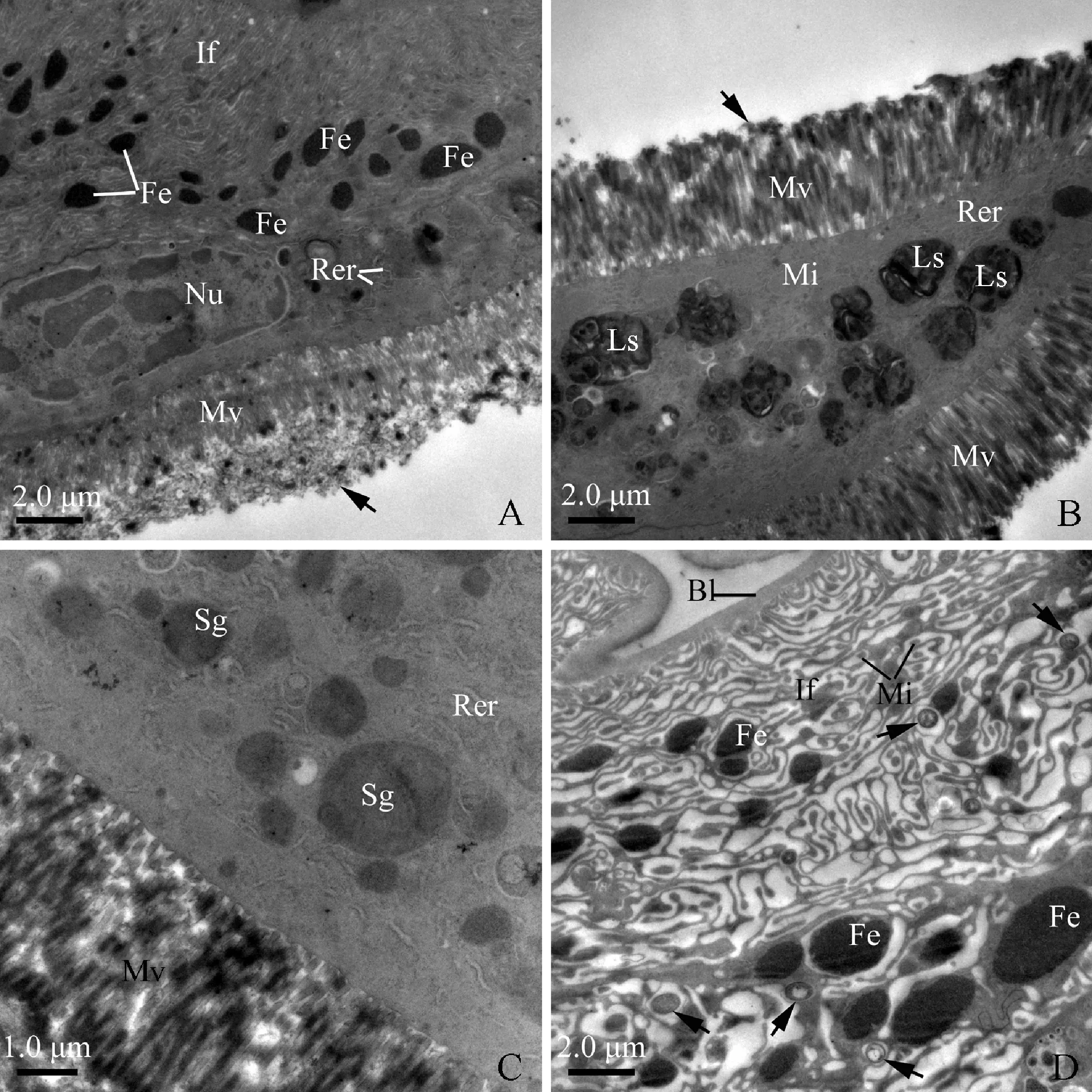
Fig. 6 Transverse section of anterior segment and mid-segment of midgut loop of male adult of Karenia caelatataA: Apical region of a cell of the anterior segment of the midgut loop, showing well-developed basal infoldings and apical microvilli. Arrow indicates filamentous materials coating on the microvilli. The cytoplasm contains numerous ferritin-like granules, rod-shaped nuclei, and scattered elements of rough endoplasmic reticulum. B: Apical area of an epithelium of the anterior segment of the midgut loop, showing regularly-arranged microvilli, extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and lysosomes. Filamentous materials (as arrow indicated) coat the microvilli. C: Cytoplasm of the anterior segment of the midgut loop cell, showing numerous secretory granules and scattered elements of rough endoplasmic reticulum. D: Transverse section of the mid-segment of the midgut loop. Basal infoldings containing mitochondria are extremely developed. Numerous ferritin-like granules exist among the infoldings. Microorganisms (as arrows indicated) also scatter among the infoldings. Bl: Basal lamina; Fe: Ferritin-like granules; If: Basal infoldings; Ls: Lysosomes; Mi: Mitochondria; Mv: Microvilli; Nu: Nuclei; Rer: Rough endoplasmic reticulum; Sg: Secretory granules.
Cells of the mid-segment of the midgut loop are featured by shallow, extensive basal infoldings, which form well-developed labyrinths associated with mitochondria (Fig. 6: D). Among these labyrinths, many ferritin-like granules and microorganisms are found (Fig. 6: D; Fig. 7: A). The apical border of these cells is densely packed with well-developed microvilli (about 2.3 μm in length) (Fig. 7: B).
The posterior segment of the midgut loop is externally surrounded by well-developed muscles (Fig. 7: C). Cells of this segment possess well-developed basal infoldings and regularly-arranged apical microvilli (Fig. 7: C, D; Fig. 8: A). However, their cytoplasm contains numerous electron-lucent secretory granules in different size and shape. It appears that some smaller granules fuse to become larger ones (Fig. 7: C). Adjacent to the secretory granules, many ferritin-like granules were observed (Fig. 7: C). Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is visible through the cytoplasm and even reaches to the base of microvilli (Fig. 7: D).
The ileum is externally enveloped by well-developed longitudinal muscles, and internally lined with a convoluted, thin cuticle (approximately 0.02 μm in thickness) (Fig. 8: B, C). Numerous rod-shaped or oval mitochondria occupy the most area of the cytoplasm (Fig. 8: B, C). Tracheole cells are elongated, which possess a highly convoluted chitinous citucle along the luminal edge (Fig. 8: B). The tracheole cells penetrate the longitudinal muscles and even reach to the basal plasma membrane (Fig. 8: B).
The rectum is lined with a cuticle containing an electron-dense epicuticle and electron-lucent endocuticle (Fig. 8: D). There are two types of rectum cells resting on a multilayered basal lamina. However, the multilayered basal lamina on which the first type of cells laid is very thick (approximately 0.5-0.6 μm in thickness) (Fig. 8: D). The multilayered basal lamina on which the second type of cells stood is very thin (about 0.05-0.1 μm in thickness) (Fig. 9: A, B). The first type of cells contains extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum and elongated nuclei (Fig. 8: D). The second possesses the following characteristics: (1) abundant oval or rod-like mitochondria are visible throughout the cytoplasm (Fig. 9: B); (2) the apical plasma membrane is elaborated into well-developed leaflets associated with mitochondria; (3) the leaflets extend deeply into the cytoplasm (Fig. 9: C); and (4) numerous microorganisms (about 1.0-1.5 μm in length and 0.4-1.0 μm in diameter) are visible at the basal region of the cells (Fig. 9: D).
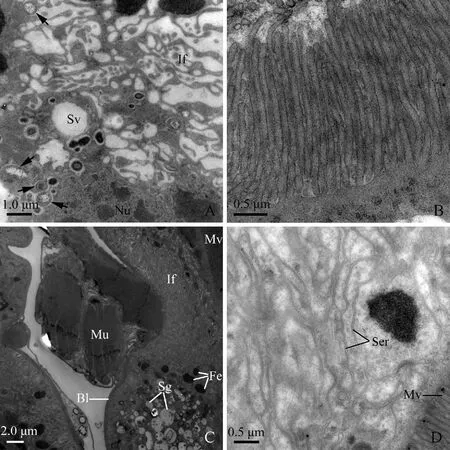
Fig. 7 Transverse section of mid-segment and posterior segment of midgut loop of male adult of Karenia caelatataA: Transverse section of the mid-segment of the midgut loop. Basal infoldings are very wide and shallow. Secretory vesicles and microorganisms (black arrows) intersperse in the cytoplasm. B: Cross-section of the regularly-arranged microvilli of mid-segment of the midgut loop. C: Cell of the posterior segment of the midgut loop possesses well-developed basal infoldings and apical microvilli. The cytoplasm is packed with secretory granules. Numerous ferritin-like granules are visible near the secretory granules. Well-developed muscles externally surround the posterior midgut. D: Transverse section of the posterior segment of the midgut loop. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum present through the cytoplasm. The apical microvilli are regularly arranged. Bl: Basal lamina; Fe: Ferritin-like granules; If: Basal infoldings; Mu: Muscles; Mv: Microvilli; Nu: Nuclei; Sg: Secretory granules; Ser: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum; Sv: Secretory vesicles.
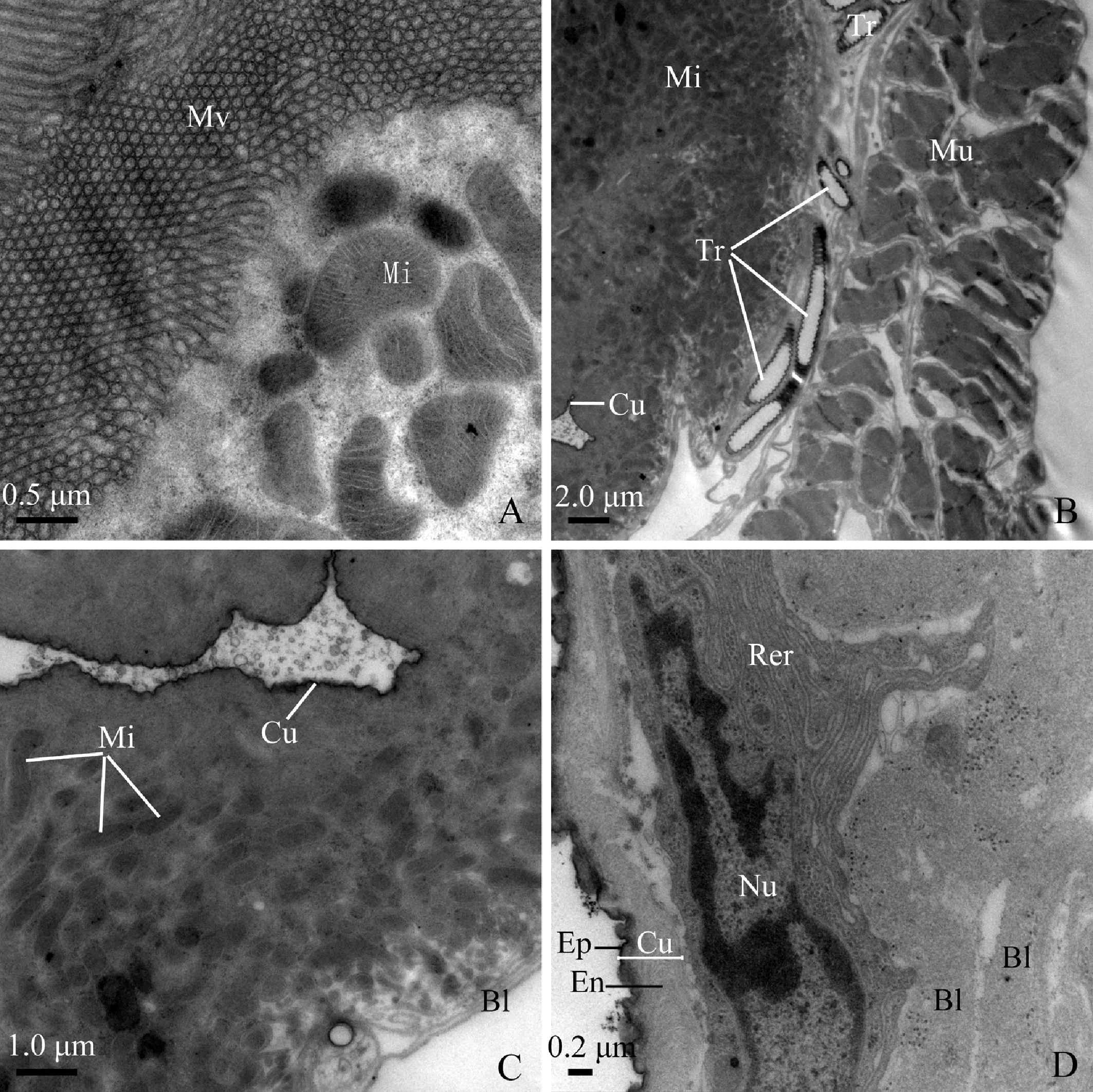
Fig. 8 Transverse section of posterior segment of midgut loop and hindgut of male adult of Karenia caelatataA: Apical region of a cell of the posterior-segment of the midgut loop, showing well-developed microvilli and abundant mitochondria. B: Transverse section of the ileum. The ileum is lined with a layer of cuticle. Extremely well-developed longitudinal muscles externally envelope the ileum. Tracheoles penetrate the muscles and reach to the cells of the ileum. C: Transverse section of the ileum. The cytoplasm filled with mitochondria. Basal lamina is multilayered. D: Transverse section of the rectum, showing that the cuticle lining the lumen contains inner epicuticle and overlying endocuticle. The basal lamina is multilayered. The cytoplasm of the type I cell contains extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum and elongated nuclei. Bl: Basal lamina; Cu: Cuticle; En: Endocuticle; Ep: Epicuticle; Mi: Mitochondria; Mu: Longitudinal muscles; Mv: Microvilli; Nu: Nuclei; Rer: Rough endoplasmic reticulum; Tr: Tracheoles.
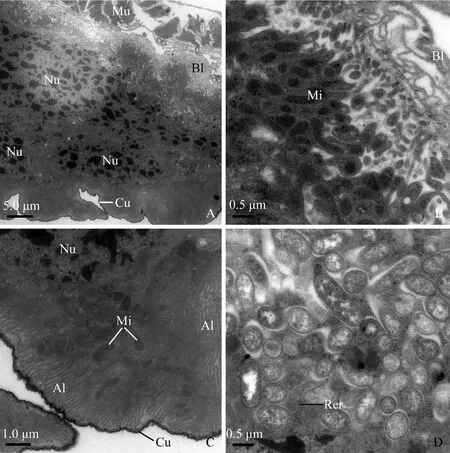
Fig. 9 The second type of rectum cells of male adult of Karenia caelatataA: Cytoplasm possesses well-developed basal infoldings, numerous rod or elongated nuclei. The rectum is externally enveloped by longitudinal muscles. B: Cells rest on a multilayer of basal lamina. Abundant mitochondria exist adjacent to the basal infoldings. C: Numerous mitochondria are visible at the apical region of the cell. Apical leaflets are well-developed, which even reach to the middle area of the cytoplasm. D: Clusters of microorganisms reside in the cytoplasm. Very sparse rough endoplasmic reticulum exists among the microorganisms. Al: Apical leaflets; Bl: Basal lamina; Cu: Cuticle; If: Basal infoldings; Mi: Mitochondria; Mu: Longitudinal muscles; Nu: Nuclei; Rer: Rough endoplasmic reticulum.
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Morphology of the alimentary canal in Auchenorrhyncha
To date, the alimentary canal in cicadas has been studied only in very limited species,i.e.,Tibicenseptendecim(Hargitt, 1923; Hickernell, 1923),Gaeanamaculata,Cryptotympanamimica(Cheung and Marshall, 1973; Marshall and Cheung, 1973, 1974), andPlatypleurakaempferi(Zhongetal., 2014). Here we add one species of the genusKarenia. Based on the previous and present investigations, we conclude that the alimentary canal of cicadas share the following features: (1) the alimentary canal consists of the oesophagus, filter chamber (filter chamber sheath and filter organ), external midgut section (conical segment and midgut loop), and hindgut (long ileum and dilated rectum); (2) the oesophagus is slender and elongated; (3) the filter chamber is composed of the anterior extremity of the midgut, posterior extremity of the midgut, internal proximal extremities of the Malpighian tubules and internal proximal extremity of the ileum, or only consists of the former three elements; (4) the conical segment is a dilated sac, more developed than the filter chamber; (5) the midgut loop displays a “U-shaped” path; (6) the ileum is narrow, long and uniform, whereas the rectum is short and inflated; and (7) the peritoneal sheath is translucent, which is positioned at the base of rectum and encloses part of the distal ends of Malpighian tubules and ileum. However, regarding the alimentary canal ofT.septendecim, previous studies noted that the junction of the filter chamber and the conical segment are very narrow, and no peritoneal sheath was observed (Hargitt, 1923; Hickernell, 1923). These differences probably attribute to the careless observation of the authors, which needs to be confirmed in the future.
Within Auchenorrhyncha, although the general structure and layout of the alimentary canal of cicadas are similar to those of other previously reported taxa (Smith and Littau, 1960; Wiesenborn, 2004; Zhangetal., 2012; Zhongetal., 2013, 2014), differences also exist. In Cercopoidea, the hindgut emerges from halfway along the filter chamber (Marshall and Cheung, 1973; Zhongetal., 2013). In Membracoidea, the filter chamber is round-shaped; the midgut loop is relatively short; and no peritoneal sheath is noted (Smith and Littau, 1960; Wiesenborn, 2004; Zhangetal., 2012). In Fulgoroidea, such as the lantern bugsPyropscandelariaandP.tenebrosusand the corn delphacidPeregrinusmaidis, tubular or lobulate bubbles filled anterior diverticulum opens into the anterior extremity of the midgut (Goodchild, 1966; Cheung, 1981; Ammaretal., 1985; Tsai and Perrier, 1993); the midgut is coiled and enclosed in a membranous sheath inP.candelaria(Cheung, 1981; Ammaretal., 1985), but no such a sheath was observed in Delphacidae (e.g.,Perkinsiellasaccharicida,Oliarussp. andP.maidis) (Kershaw, 1913; Ammaretal., 1985; Tsai and Perrier, 1993); and the ileum is very short. Goodchild (1966) suggested that the alimentary canal is closely associated with the feeding habits. Therefore, the morphological and functional differentiation of alimentary canal supports the sister-group relationship of “(Cicadoidea +Cercopoidea)+Membracoidea” and the monophyly of Auchenorrhyncha.
4.2 Ultrastructure and function of the alimentary canal
In the present study, three different types of basal infoldings were observed in the alimentary canal ofK.caelatata: (1) developed and very narrow infoldings devoid of mitochondria; (2) bulb-like infoldings which are associated with oval mitochondria; and (3) extensive shallow infoldings. Given that the basal infoldings and apical microvilli can increase the cell surface, the existence of these basal infoldings and the apical microvilli in the alimentary canal may greatly increase the effective absorption of nutrients or ions in related regions. The differences of the infoldings in shape and density probably indicate different degrees of ion transport across the interface.
A lipoprotein membrane (viz, perimicrovillar membrane) coating the microvilli and extending into the gut lumen was detected in some hemipterans,e.g., the spittlebugMahanarvaposticata, the cicadaQuesadagigasand the bugEurygasterintegriceps(Terra, 1988; Silvaetal., 1995, 1996, 2004; Fonsecaetal., 2010; Mehrabadi and Bandani, 2011). This membrane is functionally similar to peritrophic matrix of the midgut in insects with chewing mouthparts (Terra, 1988). In the present study, we observed abundant filamentous materials coating the apical microvilli in the alimentary canal ofK.caelatata. Similar filamentous materials have been reported in some other species of Cicadomorpha (e.g., the spittlebugsPhilagraparvaandLepyroniacoleopterata, the cicadaG.maculata, and the leafhopperE.distincta), which cover the apical microvilli of the filter chamber proper and the midgut (Cheung and Marshall, 1973; Marshall and Cheung, 1974; Lindsay and Marshall, 1980; Zhongetal., 2013). These filamentous materials appear to be formed in the Golgi bodies and are likely to bind cations (especially potassium) in the ingested sap (Marshall and Cheung, 1974). Based on the derivation and function, we infer that the filamentous materials found in our investigated species and other related sap-sucking hemipterans are the perimicrovillar membrane, which may be closely related to nutrient absorption.
The secretory granules present in the cells of the conical segment, anterior and posterior segments of the midgut loop and the posterior extremity of the midgut ofK.caelatata. These secretory granules are different in electron density and size, suggesting that different substances are synthesized in the secretory cells, as has been indicated by Nunes and Camargo-Mathias (2006). The existence of endoplasmic reticulum in the anterior and posterior segments of the midgut loop ofK.caelatatasuggests that proteinic substances such as enzymes are synthesized there, and that these regions are related to nutrient absorption.
Apical leaflets in the rectum ofK.caelatataare similar to those found in the hindguts of the spittlebugPhilaenusspumarius, the stinkbugCenocorixabifida, and the antFormicanigricans(Jarial and Scudder, 1970, Marshall and Cheung, 1973; Garayoaetal., 1999). The presence of apical leaflets and mitochondria in the rectum ofK.caelatatasuggests that effective water transport and ion reabsorption occur in this region. Since the xylem fluid ingested by sap-sucking insects is very poor in nutrients but contains large amounts of water (Terra, 1990), in order to filter and discharge the excessive water, the rectum equipped with apical leaflets in these insects could perform a vital role in the ions reabsorption and water transport.
Lysosomes observed inK.caelatata, are similar to those noted in the alimentary canal of the cicadaG.maculata, the spittlebugCosmoscartaabdominalis, the cockroachPeriplanetaamericanaand the stinkbugBrontocoristabidus(Cheung and Marshall, 1973; Marshall and Cheung, 1974; Fialhoetal., 2009; Parketal., 2009). The lysosomes are supposed to be engaged in the ultrastructure change of aging cells (de Priester, 1972). The presence of many lysosomes in the anterior segment of the midgut loop ofK.caelatataindicates that these cells were probably undergoing an ultrastructural change.
Many ferritin-like granules were observed in the cytoplasm and basal infoldings of the conical segment and anterior, mid- and posterior-segments of the midgut loop inK.caelatata. Similar granules have been reported in the midgut of the cicadaG.maculata, the spittlebugChaetophyescompactaand the leafhopperCicadulinambila(Cheung and Marshall, 1973; Kimuraetal., 1975). Collinetal. (1988) and Harrison and Arosio (1996) indicated that such kind of granules are ion-containing protein and play a vital role in the storage and detoxification of iron.
4.3 Microorganisms in the alimentary canal
Microorganisms frequently reside in the alimentary canal of many insects,e.g., in the oesophageal bulb of the medflyCeratitiscapitata(Marchinietal., 2002), the midgut of the fire antSolenopsisinvicta(Lietal., 2005), the ileum of termiteReticulitermesflavipes, and ockroachesPeriplanetaamericanaandEublaberusposticus(Cruden and Markovetz, 1984; Gijzenetal., 1991). In our study, microorganisms were observed in the cells of oesophagus, mid-segment of the midgut loop and rectum ofK.caelatata. The mid-segment of midgut loop has been indicated to be involved in storage excretion of ions such as calcium, magnesium and phosphates (Cheung and Marshall, 1973); the rectum is the region for reabsorbing ions (Phillips, 1964; Ramsay, 1964). All eukaryotic microorganisms can uptake metal ions, manganese, zinc and copper as their essential nutrients (Eide, 2000). The microorganisms found in the oesophagus, the mid-segment of the midgut loop and the rectum ofK.caelatatamight be beneficial to the cicada host,e.g., being helpful to take in ions for nutrients. However, further work is needed to isolate the microorganisms and to clarify their identity, which is helpful to supply data on the interaction betweenK.caelatataand related microorganisms.

