Recovery rates of combination antibiotic therapy using in vitro microdialysis simulating in vivo conditions
Jysh A.Dhnni,Suznn L.Prkr,Jry Lipmn,b,c,Stvn C.Wllis,Jrmy Cohn,b,John Frsr,Arin Brntt,Michll Chw,Json A.Robrts,b,g,h
aBurns,Trauma and Critical Care Research Centre,The University of Queensland,UQ Centre for Clinical Research,Herston,Brisbane,QLD 4029,Australia
bDepartment of Intensive Care Medicine,Royal Brisbane&Women's Hospital,Brisbane,Australia
cFaculty of Health,Queensland University of Technology,Brisbane,Australia
dCritical Care Research Group,The University of Queensland,Brisbane,Australia
eInstitute of Health and Biomedical Innovation&School of Public Health and Social Work,Queensland University of Technology,Kelvin Grove,Brisbane,Australia
fDepartment of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care,and Department of Medical and Health Sciences,Link?ping University,Link?ping,Sweden
gSchool of Pharmacy,The University of Queensland,Brisbane,Australia
hDepartment of Pharmacy,Royal Brisbane&Women's Hospital,Brisbane,Australia
Keywords:Microdialysis Combination antibiotic therapy Relative recovery rate Pharmacokinetics Anti-infectives Protein binding
A B S T R A C T Microdialysis is a technique used to measure the unbound antibiotic concentration in the interstitial spaces,the target site of action.In vitro recovery studies are essential to calibrating the microdialysis system for in vivo studies.The effect of a combination of antibiotics on recovery into microdialysate requires investigation.In vitro microdialysis recovery studies were conducted on a combination of vancomycin and tobramycin,in a simulated in vivo model.Comparison was made between recoveries for three different concentrations and three different perfusate flow rates.The overall relative recovery for vancomycin was lower than that of tobramycin.For tobramycin,a concentration of 20μg/mL and flow rate of 1.0μL/min had the best recovery.A concentration of 5.0μg/mL and flow rate of 1.0μL/min yielded maximal recovery for vancomycin.Large molecular size and higher protein binding resulted in lower relative recoveries for vancomycin.Perfusate flow rates and drug concentrations affected the relative recovery when a combination of vancomycin and tobramycin was tested.Low perfusate flow rates were associated with higher recovery rates.For combination antibiotic measurement which includes agents that are highly protein bound,in vitro studies performed prior to in vivo studies may ensure the reliable measurement of unbound concentrations.
1.Introduction
Combination antibiotic therapy is commonly used in clinical practice due to an increase in multidrug resistant bacterial infections[1,2].Consequently,antibiotic pharmacokinetic data is essential to developing accurate dosing regimens which can achieve effective antibiotic concentrations at the site of infection which is mostly the interstitial fluid of tissue[3,4].This principle is fundamental for not only optimal microbiological and clinical outcome,but also for minimizing the risk of microbial resistance[5–9].Moreover,it is the free(unbound)drug concentrations at the site of infection that are relevant with dosing challenges prominent because tissue interstitial space fluid penetration can differ substantially for some drugs[10].
Microdialysis is a minimally invasive sampling technique used to measure unbound drug concentrations in the interstitial space fluid of different tissues[11,12],both in animals and humans[13].The pharmacokinetic data from in vivo microdialysis studies can be used to design antibiotic dosing guidelines[14].The details of the microdialysis technique have been described else where[15–18].Brie fly,the probe has a semipermeable membrane tip,which is perfused with a physiological solution(perfusate)at a slow flow rate.According to the concentration gradient,molecules with a size less than that of the membrane pore size will diffuse from the tissue interstitial space fluid(Ctissue)into the perfusate and collect as the microdialysate(Cdialysate).
For most substances,the full equilibrium cannot be achieved i.e.Ctissue>Cdialysate.The term ‘recovery’is used to describe the relationship between Ctissueand Cdialysate.The ratio of Cdialysateto Ctissueis termed ‘relative recovery’.This factor is then used to calculate the actual drug concentration in the tissue interstitial space fluid.Knowing the drug concentration in the solution,in vitro recovery studies could be used to investigate the effect of parameters such as perfusate flow rate,membrane characteristics,membrane length and drug characteristics on recovery[19].Furthermore,data from these studies could inform subsequent in vivo studies.
With combination antibiotic therapy,a number of issues can affect drug recovery with in vivo studies[15].In vitro microdialysis recovery studies using combination drugs can provide preliminary data on drug recovery and likely in vivo calibration[15].Despite this there are very few microdialysis studies investigating relative recovery of antibiotics,let alone a combination of antibiotics,despite how commonly they are used clinically[20].Furthermore,for combination antibiotics therapy,previous in vitro microdialysis recovery studies have not fully accounted for in vivo conditions[20].
Microdialysis catheters may have individual variation in membrane permeability. Diffusion through the microdialysis membrane follows Fick's law.Hence,factors such as partition coefficient,particle size and surface area of the substance will affect the drug permeability through the membrane[21].This necessitates individual probe calibration[22].
The feasibility of using microdialysis for different drugs depends on the physico-chemical characteristics of the substance,e.g.lipophilic and high molecular weight compounds are less likely to diffuse through the microdialysis catheter membrane and may be less feasible for microdialysis[23].High molecular weight is associated with lower diffusion coefficients through the microdialysis membrane,thus resulting in decreased recovery[23].
Vancomycin has protein binding of approximately 55%[24]and a molecular weight of~1.5 Da.The molecular weight of tobramycin is 467Da with low serum protein binding(<30%)[25].Both drugs are also hydrophilic and suitable for microdialysis studies.
Therefore,the aim of this study was to assess the relative recovery of concomitant vancomycin and tobramycin in an in vitro model simulating in vivo conditions.The study assessed the effect of different perfusate flow rates and the concentrations of the antibiotic solutions on the relative recoveries.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Chemicals and standards
Vancomycin hydrochloride was obtained from Aspen Pharmacare(St Leonards,Australia),tobramycin sulphate was obtained from P fizer(Perth,Australia),and compound sodium lactate IV solution was obtained from Baxter(Old Toongabbie,Australia).The chemical structures for vancomycin and tobramycin are shown in Fig.1.
Acetonitrile was of HPLC-gradient grade(Merck,Darmstadt,Germany),while dichloromethane(Merck,Darmstadt,Germany),formic acid(Ajax,Taren Point,Australia),hepta fluorobutyric acid(HFBA,Fluka,Castle Hill,Australia)and trichloroacetic acid(Sigma-Aldrich,Castle Hill,Australia)were of analytical grade.Ultrapure water was obtained using a Permutit system(resistivity at 25°C at least 18 ΩM.cm).Drug-free human plasma was obtained from the Royal Brisbane and Women's Hospital blood bank(Brisbane,Australia).
Fig.1.Structures of vancomycin(A)and tobramycin(B).
2.2.Microdialysis in vitro model
Commercially available microdialysis probes CMA 63(CMA Microdialysis AB,Stockholm,Sweden)with a molecular weight cut-off of 20 kDa,an outer diameter of 0.6 mm and a membrane length of 30 mm were used.Probes were perfused with lactated Ringer's solution at flow rates of 1 and 2μL/min by using a precision microinfusion pump CMA 107(CMA Microdialysis AB,Stockholm,Sweden).To enable perfusion at 1.5 μL/min,a Cole-Parmer two-syringe infusion pump 230 VAC CE(John Morris Group,Chatswood,Australia),was used.
2.3.Stock and standard solution preparation
A stock solution was freshly prepared by dissolving tobramycin in compound sodium lactate IV solution at 2 mg/mL and stored at-80°C.A stock solution was freshly prepared by dissolving vancomycin in compound sodium lactate IV solution at 2 mg/mL and stored at-80°C.These stock solutions were serially diluted with compound sodium lactate IV solution to produce a standard solution containing 200 μg/mL of both vancomycin and tobramycin,and a standard solution containing 20 μg/mL of both vancomycin and tobramycin.
2.4.Plasma sample solutions
The study plasma solutions were prepared using the stock solutions containing both vancomycin and tobramycin and drug-free plasma,to yield plasma sample solutions containing vancomycin and tobramycin of 0.5,5.0 and 20 μg/mL.
2.5.Recovery experiments
Microdialysis probes were fully immersed in four separate 100 mL beakers.The beakers contained either 0.5,5 or 20 μg/mL of vancomycin and tobramycin plasma sample solution,or drug-free plasma.A magnetic stirrer was used to simulate in vivo conditions as previously described[26].Temperature and pH of each of the study solutions were recorded to ensure consistency of these variables.
The microdialysis probe was connected to the precision pump and perfused at 5 μL/min with compound sodium lactate IV solution for 10min to flush the air out of the system.Following this,the probe was perfused at 1 μL/min for 1h to enable equilibration.At the end of the equilibration period the following perfusate flow rates were used for 100 min each,with sampling occurring at 20-min intervals(n=5 sampling points):1.0,1.5 and 2μL/min.Samples were then stored at-80°C for analysis.
The percent relative recovery was calculated using the recovery-by-gain formula as follows:
Relative recovery(%)=(Cdialysate/Csolution)×100
Where Cdialysateis the mean concentration in the microdialysate(n=5);Csolutionis the mean concentration in the study solution(n=5).
2.6.Instrument and analytical method
Vancomycin and tobramycin in plasma and microdialysate matrices were measured using validated liquid chromatographytandem massspectrometry(LC-MS/MS)methods.Drug-free compound sodium lactate IV solution and drug-free plasma solution were used to prepare calibration standards used in the assay.
The LC-MS/MS used two Perkin Elmer LC-200 micro-pumps and a CTC PAL autosampler equipped with an Applied Biosystems API2000 mass spectrometer detector.An electro-spray ionization(ESI)source interface operating in positive-ion mode was used for the multiple reaction monitoring(MRM)LC-MS/MS analysis.The interface settings consisted of the nebulizing gas flow of 40 L/min,turbo gas of 50 L/min,curtain gas of 30 L/min,ion-spray voltage of 4500 V,a turbo-gas temperature of 400°C,and the interface heater on.Two MRMs were monitored and summed for vancomycin,m/z of 725–144 and 725–99,whilst tobramycin was monitored at m/z of 468–163.
Chromatographic separation of vancomycin,tobramycin and the internal standard(teicoplanin)was achieved using a Waters Xterra C18column(2.1mm × 150 mm,5 μm)using a gradient of mobile phases consisting of(a)0.1%formic acid with 10 mM HFBA and(b)80%methanol in 0.1%formic acid with 10mM HFBA.The mobile phase was operated using a concentration gradient for methanol,ranging from 5%to 80%.The analytical method for tobramycin was similar to that used in other studies[27–29].
Vancomycin and tobramycin in plasma were assayed separately.For the extraction of vancomycin from plasma,100 μL of plasma was treated with 400 μL of acetonitrile to precipitate proteins,with 600 μL of dichloromethane subsequently added to remove both the acetonitrile and lipids.For the extraction of tobramycin from plasma,200μL of plasma was treated with the addition of 50 μL of 30%trichloroacetic acid.Both vancomycin and tobramycin were assayed simultaneously in microdiaysate,with 10 μL of sample being diluted with 40 μL of internal standard(teicoplanin,100 μg/mL)for direct injection onto the instrumental analysis.
Calibration standards were prepared using sequential dilution to obtain concentrations of 0.1,0.2,0.5,1,2,5,10,20 and 50 μg/mL.The chromatographic calibration was linear for vancomycin from 0.1 to 50 μg/mL in plasma(LLOQ 0.0917±0.011(mean±SD))and 0.2–50 μg/mL in microdialysate(LLOQ 0.196±0.010,)and for tobramycin from 0.2 to 50 μg/mL in plasma(LLOQ 0.205±0.012),and 0.1–20 μg/mL in microdialysate(LLOQ 0.111±0.004).Quality control samples were prepared at three concentrations 0.6,2 and 16 μg/mL with precision and accuracy within 15%for all analyses.All analyses passed the batch acceptance criteria.The assay was validated according to an international FDA guideline[30]in terms of stability,specificity,linearity,precision and accuracy.
2.7.Statistical analysis
A linear regression model was used,with recovery as the dependent variable and flow rate and concentration as independent variables.This allowed us to examine if the recovery changed when the flow rate or concentration was altered.To estimate the variation in recovery we fitted the linear regression model using a Bayesian paradigm and modelled the result of a new test,using the 95%credible interval to estimate the likely range in percent recovery for a new test.As we assume a constant variance across dose, flow rate,and sample number,this credible interval will apply to any mean.We used 10,000 Markov chain Monte Carlo iterations with a burn-in of 10,000 thinned by 3.All analyses were made using R version 3.0.2(www.r-project.org)with the Bayesian analysis in WinBUGS version 3.1.4[31].
3.Results
The temperature of all the study solutions was constant at room temperature(24.0°C±0.5).The pH of all the study solutions was 7.40±0.04.The mean(±SD)concentrations of vancomycin and tobramycin are summarized in Table 1.Table 2 presents the mean(±SD)relative recoveries of vancomycin and tobramycin,respectively.
3.1.Stability of relative recovery during in vitro microdialysis
There was no significant inter-experiment variation in relative recovery.Relative recovery appeared stable for each microdialysis probe over the 100-min sampling period.The variations were±11%for tobramycin and±14%for vancomycin(using the Bayesian 95%credible intervals(CI)).
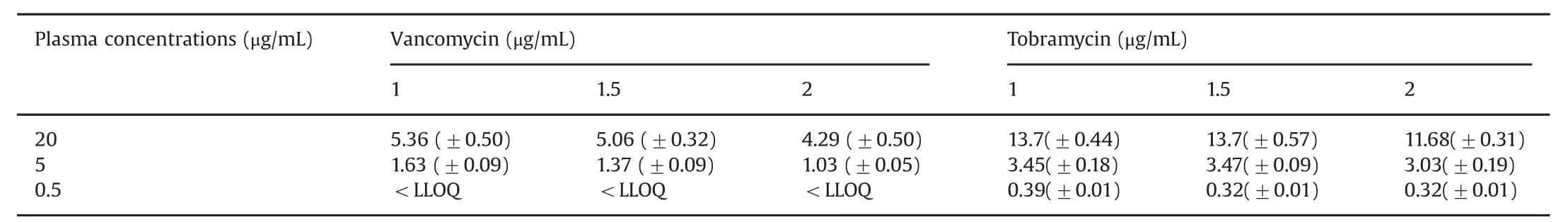
Table 1 Mean(±SD)vancomycin and tobramycin concentrations(μg/mL)in microdialysate at different microdialysis flow rates(1,1.5,and 2 μL/min).
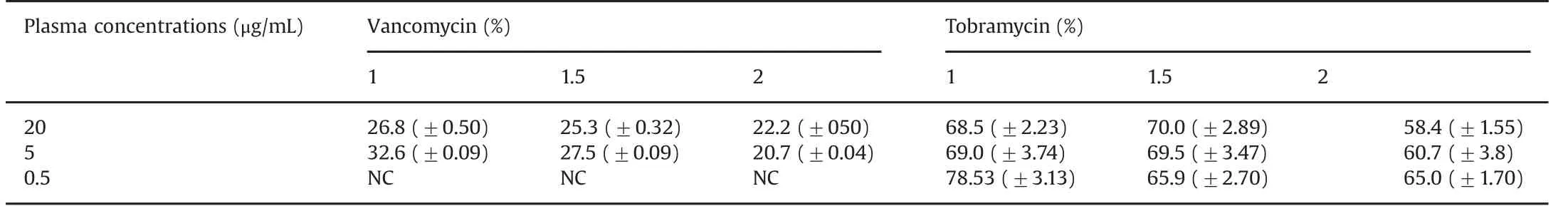
Table 2 Mean(±SD)vancomycin and tobramycin relative recovery(%)at different microdialysis flow rates(1,1.5,and 2 μL/min).
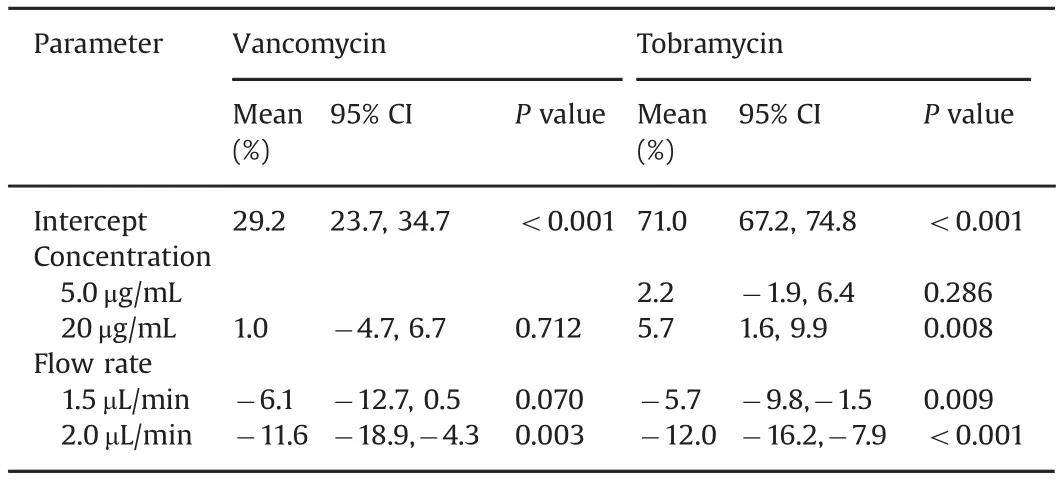
Table 3 Multiple regression analysis for relative recovery rates(mean(%)and 95%confidence interval(CI))of vancomycin and tobramycin for different concentrations and perfusate flow rates(For vancomycin,reference level is 1.0 μL/min flow rate and concentration 5.0 mg/mL.For tobramycin,reference level is 1.0μL/min flow rate and concentration 0.5μg/mL).
3.2.Flow rate dependence on relative recovery
As shown in Table 2,the relative recoveries for vancomycin were higher at the 1.0 μL/min and 1.5 μL/min flow rates(mean 29.7%and 26.4%,respectively),compared with the 2.0 μL/min flow rate group(mean 21.4%).The regression model in Table 3 shows that a flow rate of 2.0 μL/min had a significantly lower relative recovery than the reference flow rate of 1.0 μL/min.The relative recoveries remained stable for the duration of sampling,i.e.100 min.
In Table 2,relative recoveries for tobramycin were seen to be comparable at the 1.0 μL/min and 1.5 μL/min flow rates(means 72.0%and 68.5%,respectively),but decreased at 2.0μL/min(61.4%).There were no significant variations in the results over the duration of the study.Table 3 shows the regression model demonstrating the differences in the effect of flow rate on the relative recoveries,with a significantly lower relative recovery for flow rates of 1.5 and 2.0 μL/min compared with 1.0 μL/min.
3.3.Concentration dependence relative recovery
As shown in Table 2,the relative recoveries for vancomycin were higher for the 5.0μg/mL concentration(range 20.664%–32.69%)compared with the 20 μg/mL concentration(range 21.7%–27.3%).Importantly,the microdialysate in the 0.5 μg/mL group did not yield any results,as the concentrations were less than the lower limit of quantification of the assay(0.2 μg/mL).For tobramycin,the range of relative recoveries is shown in Table 2 and was the highest for concentration of 0.5μg/mL(range 63.3%–81.66%).
3.4.Combined effect of drug concentration and flow rate
For vancomycin(Table 3)there was no statistical difference between the concentrations,but there was a lower relative recovery for flow rate of 2.0 μL/min compared with flow rate of 1.0 μL/min(mean difference-11.6%,95%CI:-18.9 to-4.3%,P value=0.003).The highest relative recovery was for the concentration of 5.0 μg/mL and flow rate of 1.0 μL/min(mean recovery 32.6%,95%CI:24.8%–35.7%).
For tobramycin(Table 3),there was a higher relative recovery for the concentration of 20μg/mL compared with 0.5μg/mL,with a mean increase of 5.7%(95%CI 1.6%–9.9%,P value=0.008).Flow rates of 1.5μL/min and 2.0μL/min had lower relative recoveries than the flow rate of 1.0μL/min,with P value 0.009 and<0.001,respectively.The highest relative recovery was for a concentration of 0.5μg/mL and flow rate 1.0μL/min(mean 78.53%,95%CI:73.0%–80.6%).
4.Discussion
Though in vitro microdialysis studies have been performed previously to examine probe recovery,to the best of our knowledge,this is the first study simulating in vivo conditions and examining the relative recoveries for a combination of antibiotics in plasma.Knowledge of potential drug effects on microdialysis recovery is essential as combination antibiotic therapy is commonly used clinically and if not accounted for in relative recovery,may have the risk of under-or over-estimating drug concentrations in interstitial space fluid in in vivo studies.In vitro studies provide an ideal platform to study this effect and thus allow useful calibration for in vivo studies.Although there were inter-experiment differences in the relative recovery,its practical relevance is negligible.In general,for a drug,inter-experiment relative recovery variations of 20%are acceptable under in vivo conditions[12].
Nosocomial infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA)and Pseudomonas spp are prevalent[32]and hence most therapies,both empirical and specific,would include vancomycin and tobramycin as part of the regimen[33].Hence,for our study,we chose these two antibiotics.Interstitial space fluid concentrations of antibiotics could be affected by a number of factors during in vivo microdialysis.For vancomycin,the reported values in the microdialysis samples have been variable with a wide range[34–36].For tobramycin,there is dearth of data in the microdialysis samples but Bernardi et al.[37]report a lung microdialysis study using tobramycin and Rodvold et al.[38]report a range of lung penetration ratio for tobramycin.Hence,the three concentrations chosen for the study would encompass a wide range of possible values.
In comparison to a previous study[20],our study showed that relative recoveries for vancomycin were lower(26%vs.50%)across all flow rates and concentrations.Considering that MacVane et al.[20]performed their study in a non-protein medium,our results could be explained by the protein binding of vancomycin.However,perfusate composition,membrane characteristics and other factors may also play a role in this phenomenon.
For both drugs and all concentrations,we found improved relative recovery at lower flow rates.Hence,where possible,lower microdialysis flow rates should be preferred for optimal recovery.However,decreasing the flow rate could reduce the ability to sample frequently,due to the increased time required to collect the sample volume required for the assay.Less frequent sampling may adversely affect the temporal resolution of the data.Studies using drugs with narrow therapeutic index or in conditions with temporal fluctuations of drug concentration are likely to produce significant differences.Therefore,choosing a flow rate appropriate for the desired sampling frequency is an important consideration of all studies.In future and with improved analytic techniques,where measurement in a low volume is possible,this may not be an issue.
Careful consideration of the expected interstitial space fluid concentration should be taken into account when performing studies.Here,the lower recovery rates caused the microdialysate concentration to fall below the lower limit of the assay,as we encountered in the group of low vancomycin concentrations.Therefore,in vitro calibration can help prevent loss of clinical samples from the same issue.
5.Limitations
The exact composition of the interstitial space fluid is likely to be different between individual tissues and could be different in illness[39].Moreover,in critical illness the increased inflammation could lead to changes in the interstitial space fluid protein content[39].We were unable to obtain interstitial fluid,hence plasma was used for the study as the surrogate medium.Plasma offers a reasonable surrogate for this experiment,while the protein concentrations are higher at around 60–80g/L in a healthy adult,compared to interstitial fluid with protein content 24–32g/L(interstitial fluid to serum protein ratio~0.4)[40],this offers an insight into the conditions of a patient during critical illness where capillary leak syndrome may elevate the protein content in the interstitial fluid.Although we have attempted to mimic in vivo conditions,our study focussed on only two factors,drug concentration and perfusate flow rate,which affects relative recovery.There is currently no data on the effect of different concentrations of one antibiotic on the recovery rate of another antibiotic during combined antibiotic therapy.Our study did not investigate this effect,but it remains a worthy subject for better characterisation of relative recoveries in this context.Processes such as pressure gradients,extracellular–microvascular exchange,metabolism,and tissue diffusion of the drug can affect the relative recovery of the drugs.In vivo recovery may be affected by experimental and/or disease conditions[19].Besides these,microdialysis probe related factors such as membrane length,material and surface area,perfusate composition and temperature;tissue factors such as blood flow and temperature;the tissue-drugprobe material interactions could affect the drug concentrations,resulting in even lower concentrations of the drug in the microdialysate[19].With this study,we have attempted to establish a minimum set of conditions to be fulfilled for microdialysis-based studies.When possible,future studies should include in vivo calibration for recovery calculations.
6.Conclusion
In this simulated in vivo model,the in vitro relative recoveries for vancomycin and tobramycin varied with the perfusate flow rate and drug concentration.We suggest that a low perfusate flow rate≤ 1 μL/min should be used to achieve optimal relative recovery.
Furthermore,we recommend performing in vitro recovery studies simulating in vivo conditions to accurately calibrate the microdialysis system prior to in vivo studies,to establish the most accurate combination of flow rate and drug concentration.Performing studies in plasma for moderate-to-highly protein bound drugs may better replicate in vivo conditions.Based on our study results,vancomycin and potentially other molecules of larger size and/or high protein binding need additional consideration for improving the relative recovery.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the TPCH foundation grant(MS2011-40)and the RBWH foundation grant 2012.We wish to recognize funding from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council for a Centre of Research Excellence(APP1099452).JAR is funded in part by a Practitioner Fellowship(APP1117065)from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
 Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis2018年6期
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis2018年6期
- Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis的其它文章
- Novel ligand-based docking;molecular dynamic simulations;and absorption,distribution,metabolism,and excretion approach to analyzing potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease
- Evaluation of naproxen-induced oxidative stress,hepatotoxicity and in-vivo genotoxicity in male Wistar rats
- Cytotoxic effect of Rosa canina extract on human colon cancer cells through repression of telomerase expression
- Long-term stability of gentamicin sulfate-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt(EDTA-Na2)solution for catheter locks
- Highly sensitive LC–MS/MS method to estimate doxepin and its metabolite nordoxepin in human plasma for a bioequivalence study
- Detection and determination of undeclared synthetic caffeine in weight loss formulations using HPLC-DAD and UHPLC-MS/MS
