Five-CpG-based prognostic signature for predicting survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
Feng Fang, Xiaoqing Wang, Tianqiang Song
Department of Hepatobiliary Cancer, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin, Tianjin’s Clinical Research Center for Cancer,Tianjin 300060, China
ABSTRACT Objective: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignancy associated with high morbidity and mortality rates worldwide. Early diagnosis plays an important role in the improvement of HCC prognosis.Methods: In this study, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of HCC DNA methylation and gene expression datasets in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), to identify a prognostic signature for HCC diagnosis and survival prediction. First, we identified differential methylation CpG (dmCpG) sites in HCC samples and compared them with those in adjacent normal liver tissues; this was followed by univariate analysis and Sure Independence Screening (SIS) in the training set. The robustness of the identified prognostic signature was evaluated using the testing set. To explore the biological processes involved in HCC progression, we also performed functional enrichment analysis for overlapping genes between genes containing dmCpG sites (DMGs) and differential expression genes (DEGs) in HCC patients, using data from the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery(DAVID).Results: As a result, we identified five CpG sites that were significantly associated with HCC survival through univariate analysis and SIS. Univariate analysis of clinical characteristics identified age and risk factors (including alcohol consumption and smoking)as independent factors that indicated HCC survival. Multivariate analysis indicated that the integrated prognostic signature(weighted combination of the five CpG sites) that took age and risk factors into consideration resulted in more accurate survival prediction.Conclusions: This study provides a novel signature for predicting HCC survival, and should be helpful for early HCC diagnosis and personalized treatment.
KEYWORDS Hepatocellular carcinoma; methylation; prognosis; prognostic signature; TCGA
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third cause of death from cancer, and one of the few cancers for which upward trends are observed in both sexes worldwide1. Several risk factors have been identified to induce HCC, including chronic infections with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV), alcohol abuse, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome2,3. Clinical statistical analysis showed that earlystage HCC patients have a relatively favorable prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate of 75%4. However, after resection,recurrence would be observed in half of these patients,causing the 5-year survival rate to decrease to 30%. In essence, hepatocarcinogenesis is essentially a slow process,accompanied by genomic and epigenetic changes that produce cellular intermediates; this eventually evolves into hepatocellular carcinoma5. Recent studies have explored genomic alterations occurring during HCC using highthroughput analysis of gene microarrays, and have identified frequently mutated genes as molecular markers for tumor detection6-8. However, the knowledge regarding the association between the genomic phenotype and clinical outcome of HCC prediction remains extremely limited.
Genomic DNA has relatively few CpG dinucleotides(5%–10%) in which a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its 5'→ 3' direction. In addition, methylating the cytosine of CpG di-nucleotides within a gene can cause heritable genomic changes without altering the DNA sequence, which is an important epigenetic pattern9,10. Moreover, DNA hypermethylation in CpG sites can lead to the repression of tumor-suppressor genes and inactivation of tumor-repair genes, resulting in a loss of tumor suppression and increased genetic damage11,12. Recent reports have indicated that DNA hypermethylation in promoter CpG islands was related to epidemiological characteristics, histological features,precancerous lesions, molecular characteristics, and HCC prognosis, in RASSF1A, p16, p53, DLC-1, and GSTP113-17.However, further molecular investigations are still needed to obtain more information for predicting recurrence and HCC patient classification.
In the present study, DNA methylation profiles of HCC patients (n = 317) in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)database were analyzed, to determine the relationship between the aberrant methylation of cancer-specific methylation sites and clinicopathologic features. Five differential methylation CpG (dmCpG) sites that were associated with HCC prognosis were distinctly identified by a combination of univariate Cox analysis and Sure Independence Screening (SIS). Furthermore, the integration of specific clinical features with the prognostic signature(weighted combination of the five dmCpG sites) resulted in a more accurate prediction of survival. This study provides more insights about HCC survival prediction.
Material and methods
HCC dataset preprocessing
We downloaded HCC datasets from TCGA containing genome-wide scale DNA methylation and gene expression profiling data for 317 samples. Fifty patients had DNA methylation data in both HCC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. For DNA methylation datasets, we filtered out CpG sites with a detection P value > 0.05 in more than 75%samples. Samples were also excluded from analysis if more than 75% CpG sites were unreliably detected (i.e. detection P value < 1 × 10–5). Then, the quantile normalization method was applied for correcting background noises before conducting a comparison analysis between the rest of the normal and HCC samples. The dmCpG sites in HCC samples that were compared with those in adjacent normal tissues were identified via the Illumina Methylation Analyzer(IMA)18bioconductor package, which has been specifically designed for exploratory analysis and summarization of siteand region-level methylation changes based on the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip, using the criteria: absolute delta beta > 0.3 and adjusted P value < 0.001.
For gene expression datasets, we first conducted the quartile normalization of raw read count data, followed by logarithmic transformation, to obtain normal distribution expression values. Differential expression genes (DEGs) in HCC samples that were compared with those in adjacent normal tissues were obtained through the DESeq219bioconductor package, with a thresholds of absolute log2-based fold change > 1 and adjusted P value < 0.01.
Prognostic signature construction
To construct a methylation profile-based prognostic signature for HCC survival prediction, we conducted a combination analysis of univariate and SIS. First, the samples were randomly divided into two groups, i.e. training set (158 samples) and testing set (159 samples); their clinicopathologic characteristics have been shown in Table 1.Second, univariate survival analysis was conducted for dmCpG sites in the training set to identify CpG sites that were significantly associated with HCC survival, which have been abbreviated as SurvCG hereafter. Thirdly, we performed SIS, which is a variable selection technique for model selection and estimation in high-dimensional statistical models, for SurvCG identification using LASSO regression analysis via the SIS R package, to identify a reliable CpG combination for HCC survival prediction. The prognostic signature is a weighted combination of SIS identified CpG sites.
Multivariate survival analysis
Clinicopathologic features might also prove to be important indicators for HCC survival. We have studied four features,i.e. age, sex, risk factors (including alcohol consumption,smoking, and HBV infection), and stage, to analyze their associations with HCC survival in the training and testing sets. Prognostic score, which was based on the prognostic signature for every sample, was calculated through the distinct values for every CpG site included in the prognostic signature, and its association with HCC survival was evaluated through univariate survival analysis in the training and testing sets. Besides, we also conducted multivariate survival analysis for clinicopathologic features and prognostic scores to obtain the most robust combination of features for HCC survival prediction.
Functional enrichment analysis
We intersected DEGs in HCC patients with genes containing dmCpG sites (DMGs), to obtain genes whose dysregulation might be affected by aberrant DNA methylation. Thefunctions of the involved overlapping genes should represent biological processes involved in HCC progression. Hence, we conducted a functional enrichment analysis for overlapping genes using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID)20. Gene Ontology (GO) terms and KEGG pathways with P values < 0.05 were identified,and biological process (BP) terms were further clustered through the Enrichment Map Plugin of Cytoscape21,22.

Table 1 Clinical characteristics of samples used as training and testing sets.
Results
Differential methylation analysis
Preprocessing the DNA methylation dataset retained 479,036 of 485,577 CpG sites and samples for the following analysis.Figure 1A illustrated the average beta value for every CpG site in adjacent normal tissues (X-axis) and HCC samples (Y-axis). Differential methylation analysis identified 10,803 dmCpG sites in HCC samples, as compared with those in adjacent normal tissues; of which 9,373 and 1,430 sites were hypomethylation and hypermethylation sites, respectively.Figure 1B showed the heatmap of beta values of dmCpG sites(row) in HCC and adjacent normal samples (column), in which green and red colors represent low and high methylation values, respectively. We then explored the location-wise distribution of hypermethylation and hypomethylation CpG sites relative to the CpG island and gene. As a result, hypermethylation CpG sites tend to be located in a CpG island (80.13%) and regulatory elements,such as TSS200 (200bp upstream/downstream of transcription start site) and TSS1500 (Figure 1C).Hypomethylated CpG sites tend to be located in the OpenSea(70.15%, i.e. area far away from CpG island, and usually 4,000 bp or more) and gene body area (62.09%) (Figure 1D).This was consistent with the fact that the cancer methylome is characterized by hypermethylation in CpG islands of the promoter region and hypomethylation in diffuse CpG sites.
Prognostic signature
Univariate analysis showed that 100 CpG sites were significantly associated with HCC survival. SIS identified 5 CpG sites, whose combination could robustly predict HCC survival. Figure 2A illustrated the beta value in adjacent normal tissues and HCC samples and regression coefficients of the 5 CpG sites. Four of the five CpG sites were hypermethylated in HCC samples compared to those in adjacent normal tissues. Prognostic score = 1.10 ×cg05971966 – 0.61 × cg08833577 + 1.23 × cg14826425 + 1.92 ×cg20980783 + 1.17 × cg24085930. Kaplan-Meier plots were prepared and compared using the log-rank test. Hence, we found that a higher prognostic score is significantly associated with poor HCC survival in the training (P = 3.60 ×10–4) and testing sets (P = 7.62 × 10–3) (Figure 2B). To evaluate the robustness of our prognostic signature further,we assigned the samples in the testing set into four groups with the same sample size in an increasing order of prognostic score. It was found that HCC survival became poorer with an increase in the prognostic score (Figure 2C,P = 0.017).
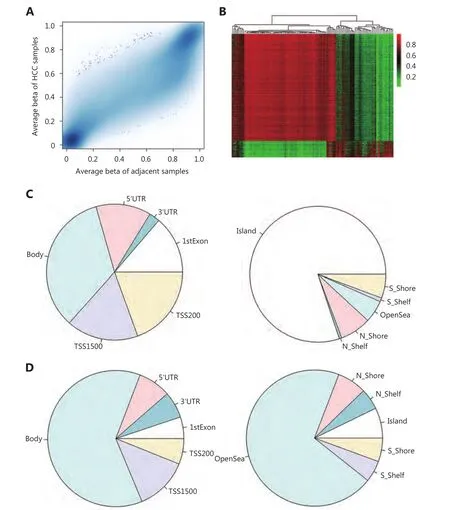
Figure 1 Differential methylation analysis. (A) Average beta value of all CpG sites in HCC (Y-axis) and adjacent normal samples (X-axis). (B)Heatmap of beta values of dmCpG sites in HCC patients and their corresponding adjacent normal samples. Rows represent dmCpG sites and columns represent samples; green and red colors represent the low and high beta values, respectively. (C) Distribution of hypermethylation CpG site locations relative to the gene (left panel) and CpG island (right panel). (D) Distribution of hypomethylation CpG site locations relative to the gene (left panel) and CpG island (right panel).
Multivariate survival analysis
As shown in Table 2, age (> 60 and < 60) and risk factors(with and without) were identified as independent survival factors in training and testing sets. Combining the prognostic score and all the four clinicopathologic features could further separate samples with better survival from those with poorer survival in training (P = 0.023) and testing sets (P = 0.042)(Figure 3). Multivariate survival analysis indicates that a combination of prognostic scores and ages could provide the most robust prediction method for HCC survival.
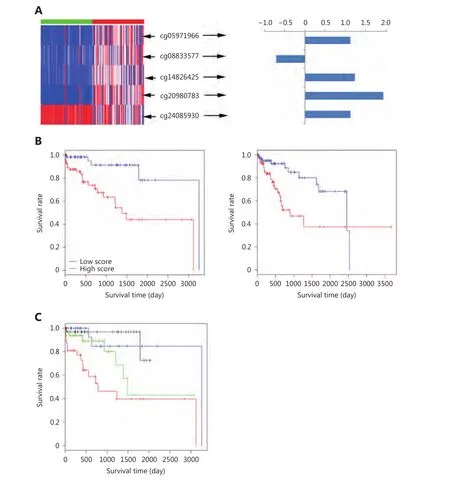
Figure 2 Prognostic signature and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. (A) Beta value (left panel) and the regression coefficients (right panel) of the five CpG sites, identified through a combination of univariate survival analysis and SIS. Blue and red bars at the top of the heatmap (left panel) represent adjacent normal and HCC samples. (B) Kaplan-Meier plot of samples with lower (green line) and higher (red line)prognostic scores (divided by the median prognostic score) in the training set (left panel) and testing set (right panel). Plus signs are censored values. (C) Kaplan-Meier plot of samples with different prognostic scores in the testing set. Prognostic scores were sorted in the decreasing order. The red line represents the first quarter samples; blue line represents the second quarter samples; green line represents the third quarter samples and black line represents the last quarter samples. Plus signs are censored values.
Supplementary Figure S1 showed the prediction performance of prognostic score in the testing set after adjustment for age (A), stage (B), gender (C), and risk factors(D), respectively, from which we conclude that the prognosis score could effectively predict HCC prognosis independent of the main clinicopathologic features. Additionally, receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis was conducted to compare differences in predicting HCC prognosis using a combination of the prognostic score and different clinicopathologic features. As shown in Supplementary Figure S2, a combination of prognostic score and agedistinctly outperformed other combinations, as well as the prognostic score alone.
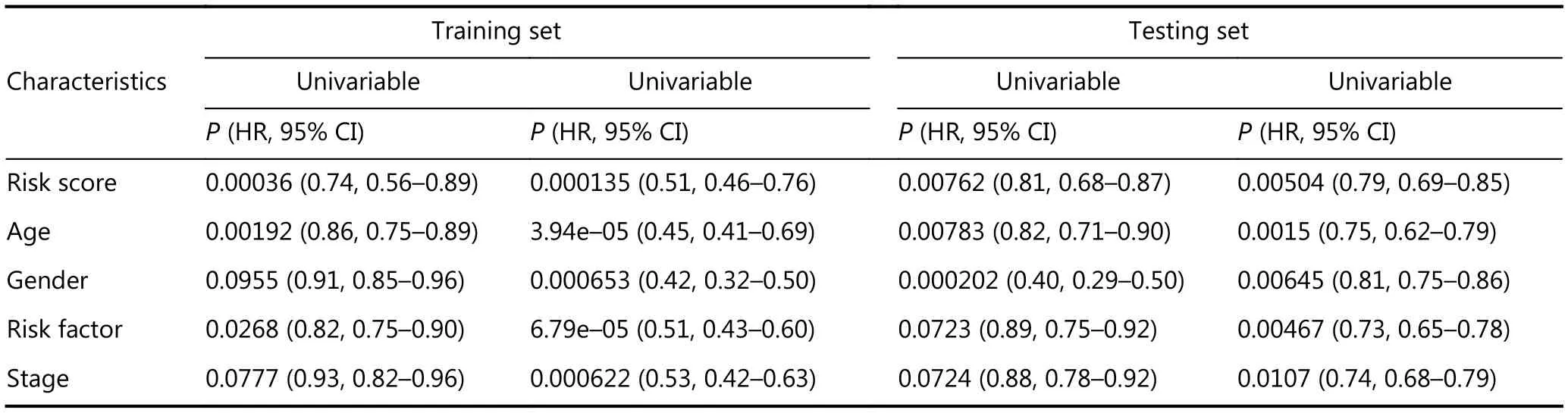
Table 2 Cox regression analysis of clinical characteristics and risk scores.
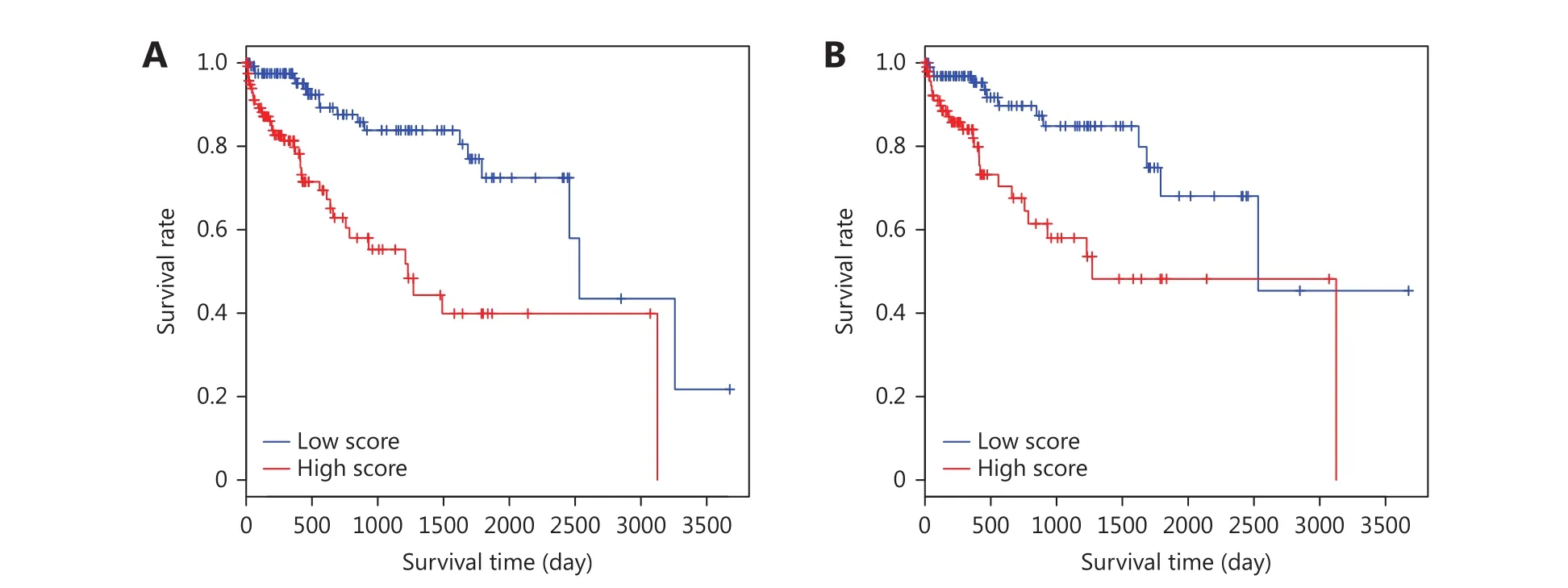
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier plot of multivariate survival analysis of prognostic score and clinicopathologic features. (A) Kaplan-Meier plot of samples with lower (green line) and higher (red line) combined scores (divided by the median combined score) in the training set. Plus signs are censored values. (B) Kaplan-Meier plot of samples with lower (green line) and higher (red line) combined score (divided by the median combined score) in the testing set. Plus signs are censored values.
Functional enrichment analysis
A total of 2,538 DEGs were identified in HCC samples compared with adjacent normal tissues. The dmCpG sites were found to be located in 3,618 genes, i.e. DMGs. We identified 580 overlaps between DEGs and DMGs, and those overlapping genes were significantly associated with biological processes and pathways of cancer progression and neurodegenerative diseases. Figure 4 top-right panel shows the cluster analysis of significantly enriched BP terms. A main cluster that was associated with extracellular matrix and vasculature development was obtained. Figure 4 bottomright panel shows the significantly enriched pathways with gene number shown. Strikingly, we found a significantly enrichment of nervous system disease-related pathways,which indicated the potential associations between cancer and nervous system diseases. Consistent with this result,many studies have previously proven associations between cancer and nervous system disorders23,24.
Discussion
The value of clinical characteristics and initial performance status as prognostic factors for HCC survival has long been recognized25,26. However, due to the great individual differences and complicated influential factors, the traditional analytic strategies are often unable to predict the prognosis of HCC patients. DNA methylation is a type of covalent chemical modification and a stable (replicationcoupled) epigenetic marker. It can be detected in biological fluids and fresh-frozen and paraffin-embedded tissue samples, by methylome profiling in the clinical setting27.Thus, the high-throughput detection of genetic alterations has been widely used in the early diagnosis, individual treatment, and prognosis prediction of various cancers28.CpG island methylation, a common molecular tumor marker, has already been confirmed as a prognostic indicator in lung, prostate, and esophageal cancers, and acute leukemia12.
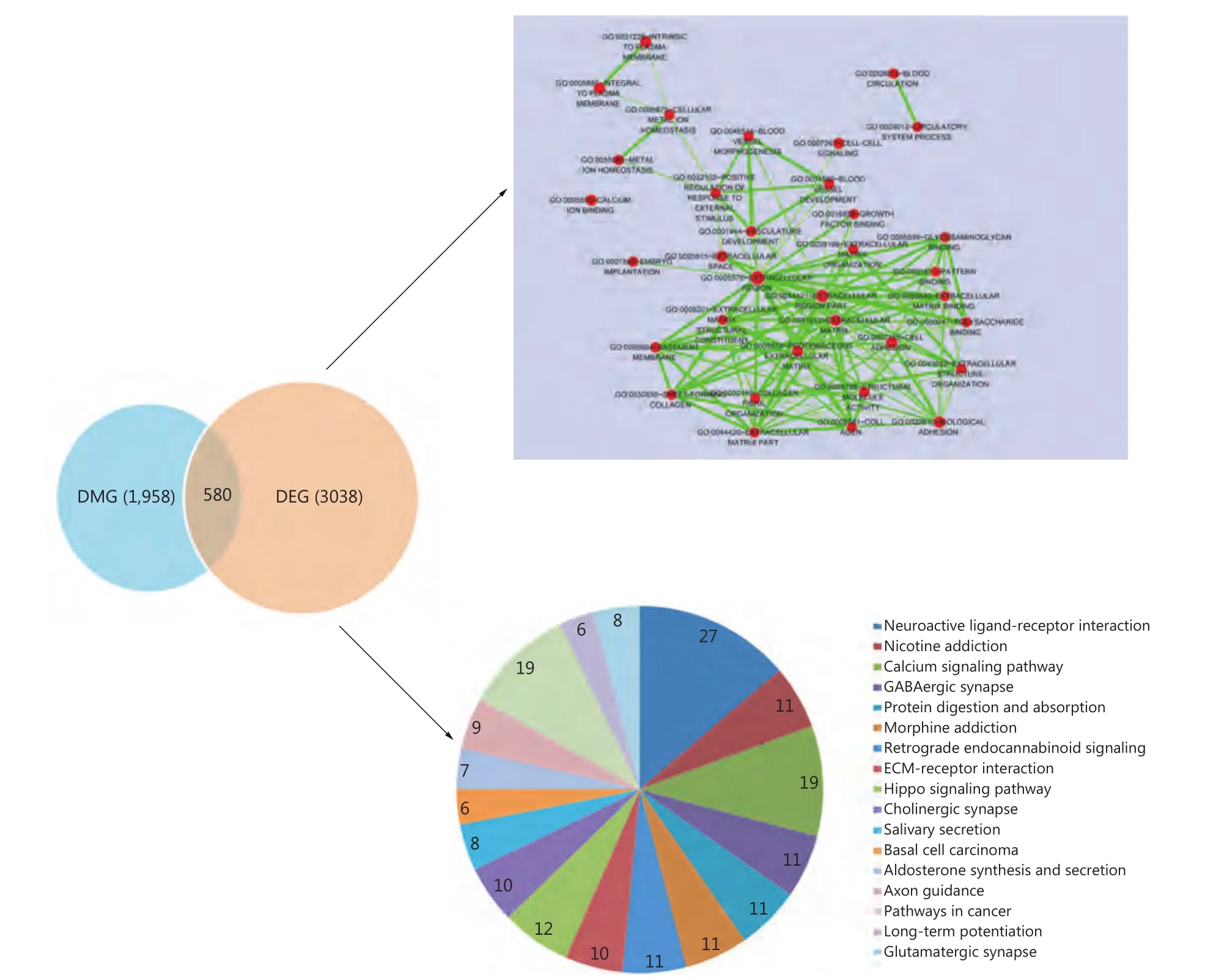
Figure 4 Cross-analysis of DEGs and DMGs. A total of 580 overlaps were identified between DEGs and DMGs (left panel). The top-right panel shows the cluster analysis of significantly enriched BP terms of overlapping genes. Nodes are BP terms and lines are interactions among them. The larger node represents more genes contained in the terms and darker color i.e. smaller P value is more significant. Line thickness represents the number of overlapping genes between two terms. The bottom-right panel represents the significantly enriched KEGG pathways of overlapping genes. The gene number involved in each pathway is also shown in the pie chart.
Aberrant DNA methylation changes in CpG islands as well as hypermethylation and diffuse genomic hypomethylation are common phenomena in multiple human cancers, and there is a good chance that these two changes are mechanically linked29,30. In this study, differential methylation CpG sites (dmCpG) in HCC samples were compared to those in adjacent normal tissues and were screened using DNA methylation microarrays in TCGA samples. The probes have been annotated based on their relationship with the nearest gene and the probes might belong to any of the following genomic elements: TSS1500,TSS200, 5’UTR, 1stexon, gene body, 3’UTR, or intergenic regions. Genomic regions close to the transcription start site showed a relatively high level of methylation (TSS1500,TSS200, 5’UTR and 1stexon), and 80% of the hypermethylation sites were located in the CpG island, which indicated that CpG islands in promoters tend to be hypermethylated in HCC patients. Most of the hypomethylation dmCpG sites were located in regions further away from the transcription start site (gene body and 3’UTR) and CpG islands (OpenSea). This is consistent with the reported associations between DNA methylation and cancer development.
Promoter CpG island hypermethylation has been reported to occur in chronic liver diseases31,32, whereas genome-wide hypomethylation takes place at the HCC stage33. As shown in the previous study, p16 hypermethylation in HCC was found to be more frequently caused by cirrhotic than non-cirrhotic inducements, suggesting that the epigenetic modulations of HCC may be influenced by the disease state of the background liver34. However, the underlying mechanism between CpG island hypermethylation and the background liver condition remains unclear. The GO term and KEGG analysis results of overlapping genes between DMG and DEG in HCC samples were compared to those in para-carcinoma tissues, and they indicated a significant enrichment of molecule activity, extracellular matrix formation, cell-matrix and cell-cell interactions, cell secretion, cell adhesion, and vessel morphogenesis, suggesting the main signal transduction pathway regulated by DNA methylation during the development of HCC. Tumor cells need to grow in the appropriate target organ microenvironment, and cancer progression depends on the interplay between transformed cells and their microenvironment, particularly the surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM)35. In human livers,fibro genes underlie the development of HCC in at least 90%of cases36, and the overexpression of matrix components and MMP2 activity were strikingly associated in HCCs37.Microenvironment of the background liver is undoubtedly a decisive factor that influences tumor recurrence and metastasis38.
Considering all these factors, we identified five dmCpG sites that exhibited a significant association between their aberrant methylation and patient prognosis using a combination of univariate analysis and sure independence screening. A prognostic signature of the combination of the five dmCpG sites was obtained and the prognostic score was negatively correlated with HCC prognosis. Furthermore,multivariate analysis revealed that the prognostic score showed significant relevance together with clinical characteristics such as age and risk factors, which affected the overall survival of HCC patients. It has been proven that CpG island hypermethylation in HCC tumors was closely associated with the condition of the background liver and sex39. In addition, our study indicates that the combination of age, risk factors, and the prognostic score provides a more robust prediction for HCC prognosis than any one of these alone.
Conclusions
In this study, we performed a comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression datasets of HCC data obtained from TCGA and identified an important prognostic signature. This should be helpful for HCC survival prediction and personalized treatment.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81201644 and 81572858)and National Key Clinical Specialist Construction Programs of China (Grant No. 2013-544).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
 Cancer Biology & Medicine2018年4期
Cancer Biology & Medicine2018年4期
- Cancer Biology & Medicine的其它文章
- 2017 Chinese expert consensus on the clinical application of serum marker for thyroid cancer
- Multidisciplinary team for the diagnosis and treatment of 2 cases of primary intestinal yolk sac tumor
- Comparison of sentinel lymph node detection performances using blue dye in conjunction with indocyanine green or radioisotope in breast cancer patients: a prospective singlecenter randomized study
- Prognostic factors of refractory NSCLC patients receiving anlotinib hydrochloride as the third- or further-line treatment
- PD-L1 expression and its effect on clinical outcomes of EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients treated with EGFR-TKIs
- A new tumor-associated antigen prognostic scoring system for spontaneous ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma after partial hepatectomy
