Structural, Electronic, Optical and Thermodynamic Properties of Nanolaminated Boride Cr4AlB6①
ZHANG Rui-Zhou CUI Hong-Ling LI Xio-Hong, ② (College of Physics nd Engineering, Henn University of Science nd Technology, Luoyng 471003, Chin) (Henn Key Lortory of Photoelectric Energy Storge Mterils nd Applictions, Luoyng 471023, Chin)
The structural, electronic, optical and thermal properties of Cr4AlB6were investigated by density functional theory.The investigated results confirm the metallic nature of Cr4AlB6and the maximum optical conductivity occurs at about 8.12 eV.Thermodynamic properties such as thermal expansion, bulk modulus, and heat capacity were further investigated with increasing the temperature and pressure.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, a family of ternary nano-layered compounds known as MAX alloys or MAX phases[1-3]was investigated.The general formula for MAX phases is Mn+1AXn, where M is an early transition metal, A is an A-group (mostly IIIA and IVA) element, X is either C or N, and n is an integer,commonly equal to 1, 2 or 3[4,5].Such a nanolaminated structure endows the unique property combination of metals and ceramics because of a hard carbide or nitride part (MX)nand a ductile intermetallic part MA[1-3,6].The MAX phases have the properties such as: good electrical and thermal conductivity, machinability, low thermal expansion, and reversible plasticity[7].Furthermore, they are the only polycrystalline solids in which single grains can deform by a combination of slip, kink band formation and delamination[8,9].The MAX phases have been applied into the defense, high temperature reactor, automobile, protective coatings, etc[10-12].The remarkable property collection of the MAX phases makes them open the door to viable commercial applications from catalysis to aerospace in future[13].
In the 1960s, the metallic ceramics MAX phases were discovered[14]and became the research focus in recent years[1-3].Now, about 70 MAX compounds are discovered[15].In the MAX phases, the oxidation of alumina can make materials used at extended high temperature[16], and this is observed only in the Al-containing MAX carbides such as Ti3AlC2[17]and Cr2AlC[18].So, it is reasonable to assume that other Al-containing MAX phases would also exhibit a similar oxidation resistance.Ade et al.[19]thought that inserting Al layer to form nanolaminated, ternary transition-metal borides (called MAB phases) can improve the intrinsic brittleness and poor oxidation resistance of binary borides.The general formula for MAB phases is (MB)2Alm(MB2)n(n = 1, 2, ···; m = 1,2, 3, ···).Bai et al.[20]investigated the electronic structure, elastic properties of ternary layered boride MoAlB and thought that there exhibit similarities in properties between MAB and MAX.Li et al.[21]investigated the electrical and mechanical properties of polycrystalline Fe2AlB2bulk from element powders.They thought that Fe2AlB2is quite damage tolerant and the energy-absorbing mechanisms are delamination and pullout of Fe2AlB2grains.Li et al.[22]investigated the mechanical, electronic and bonding properties of MAB phases (CrB2)nCrAl (n =1,2 3), Dai et al.[23]further calculated the shear response of nanonaminated (CrB2)nCrAl and thought that dislocations tend to nucleate in basal planes and may result from the local open structure around Al layers.
The structure of CrB was determined[24]and the combination of the polygons beyond hexagons appears such as YCrB4[25].The crystal structure of Cr3AlB4was determined in 1972[26].By insertion of additional boron atoms in the surrounding of Cr in Cr3AlB4, Martin et al.[19]synthesized the ternary borides Cr4AlB6, a new MAB phase, and its structure is similar to the MAX phases with two Al layers interleaving the transition metal boride sublattice.To the best of our knowledge, little experimental and theoretical information about the electronic, optical and thermodynamic information is available for Cr4AlB6.Thus, investigating these properties theoretically can help Cr4AlB6to be used in industrial applications.
The all-electron projector augmented wave (PAW)method was reported to investigate the structural and electronic properties of MnB4-type structure[27].This method has also been used by Wang et al.[28]to investigate the elastic constants of B4CO4.Using the PAW method, we calculated the structural, optical,and thermal properties of Cr4AlB6.Density functional theory (DFT) within the quasi harmonic approximation (QHA) was used to investigate the thermal properties of bulk materials[13,29].
2 COMPUTATIONAL DETAILS
Cr4AlB6has orthorhombic crystal structure and belongs to Cmmm space group[19].The calculations about energy and electronic structure were carried out within the generalized gradient approximation(GGA), as implemented in the Vienna ab-initio simulation package (VASP)[30].The PAW[31]and GGA[32]were used.Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE)functional[33]was also used.Geometry optimizations were performed without any restriction.The plane wave cut-off energy is 800 eV.And the Monkhorst-Pack k-point mesh is set to 7 ′ 7 ′ 7 to ensure the energy differences of less than 10-6eV/atom.The k-point of 9 ′ 9 ′ 9 mesh was used to calculate the band structure.In the calculation of DOS, the tetrahedron method[34]was used for the Brillouinzone integration and a dense 15 ′ 15 ′ 15 k-points was used.
The optical properties are determined by the complex dielectric function e(w) = e1(w) + ie2(w).The real part e1(w) and imaginary part e2(w) can be obtained by calculating the wave function matrix.Based on the dielectric function, the other optical properties such as the refraction index n(w), the extinction coefficient k(w), the optical reflectivity R(w), the absorption coefficient a(w), and the energyloss spectrum L(w) can be obtained[35].A dense sampling grid of 15 ′ 15 ′ 15 k-points was used for the calculation of optical properties.The related theoretical formulas of optical properties are as follows[36]:
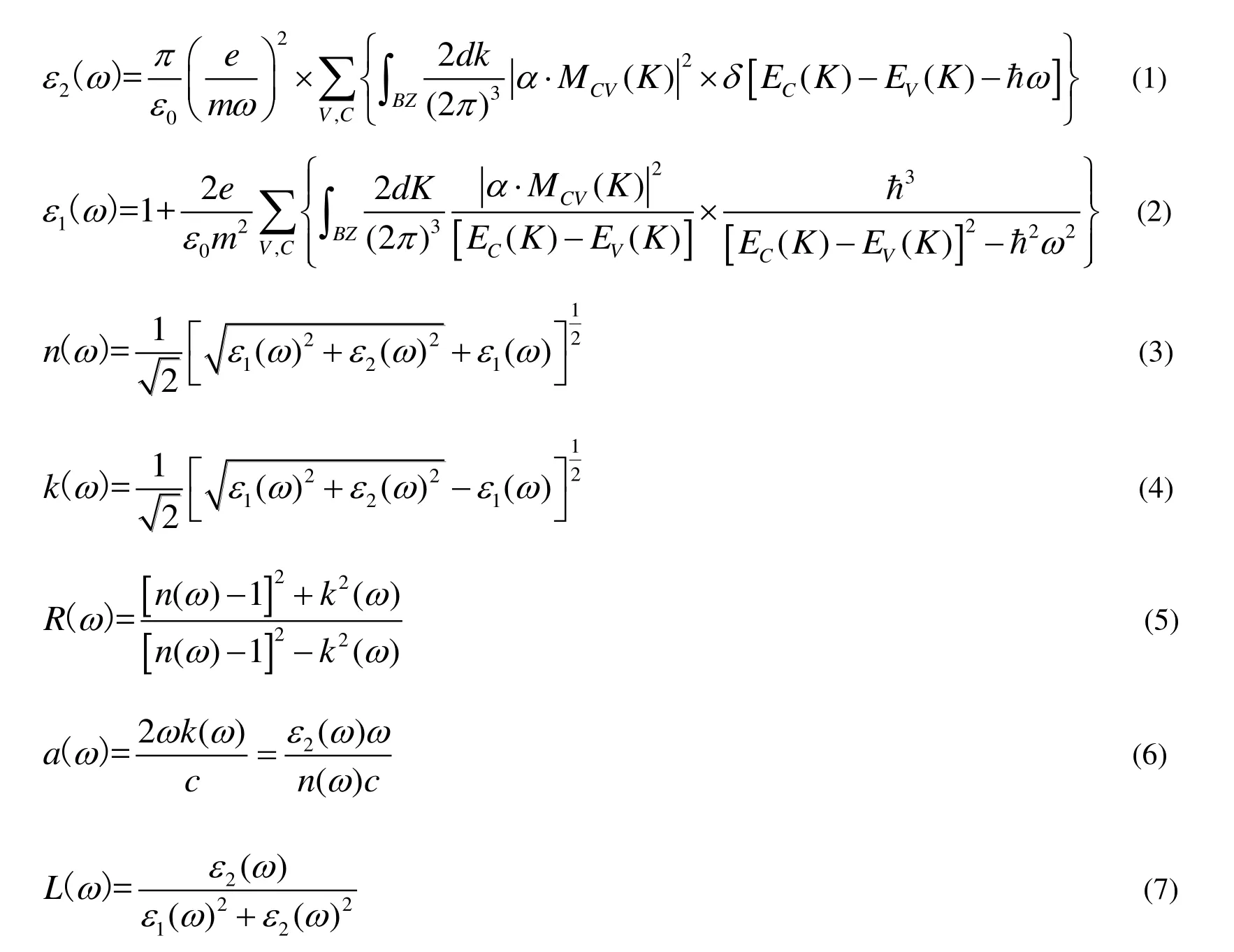
where C and V represent the conduction band and valence band, respectively.BZ means the first Brillouin zone, K is the reciprocal lattice, EC(K) and E(K) are the intrinsic energy levels of conduction and valence bands, respectively.the matrix element of momentum transition, e0is the vacuum permittivity, a is the unit direction vector, wis the angular frequency, n(w) is the refractive index,k(w) is the extinction coefficient, R(w) is the reflectivity, a(w) is the absorption coefficient, and L(w) is the energy loss function.
For metal, the intraband transition is more important than the interband transition in the low energy (< 1 eV).So the intraband transition affects mainly the low-energy infrared part of the spectra and can be expressed using empirical Drude term,which can be expressed as

where wpand gDare the plasma frequency and damping parameter, respectively and can be obtained from the experiment.
The quasi-harmonic Debye model is applied to investigate the thermodynamic properties.In the quasi-harmonic Debye model, the non-equilibrium Gibbs function G*(V; P, T) can be expressed as
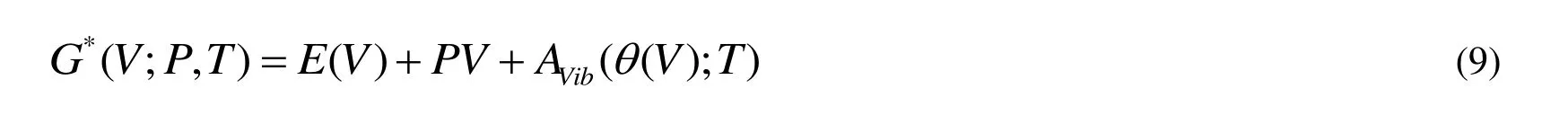
where E(V) represents the total energy per unit cell of the crystal and can be obtained from the electronic structure calculations.PV represents the constant hydrostatic pressure condition.q (V) corresponds to the Debye temperature.AVibcorresponds to the vibrational Helmholtz free energy and can be obtained by the following equation[37,38]:
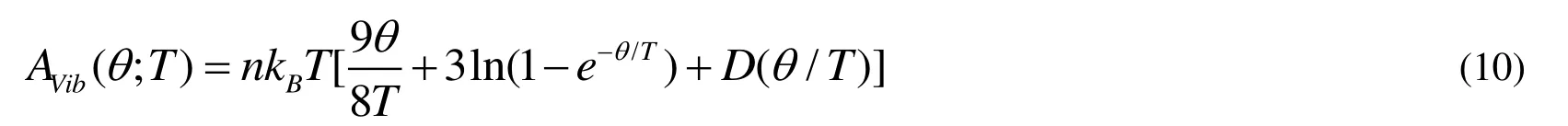
where D(q/T) is the Debye integral, n is the number of atoms per formula unit, and q is the Debye temperature and related to an average sound velocity.For an isotropic solid, q can be computed as

where M corresponds to the molecular mass per formula, Bsis the adiabatic bulk modulus, and f(s)and Bs are given by the following equations[39]:
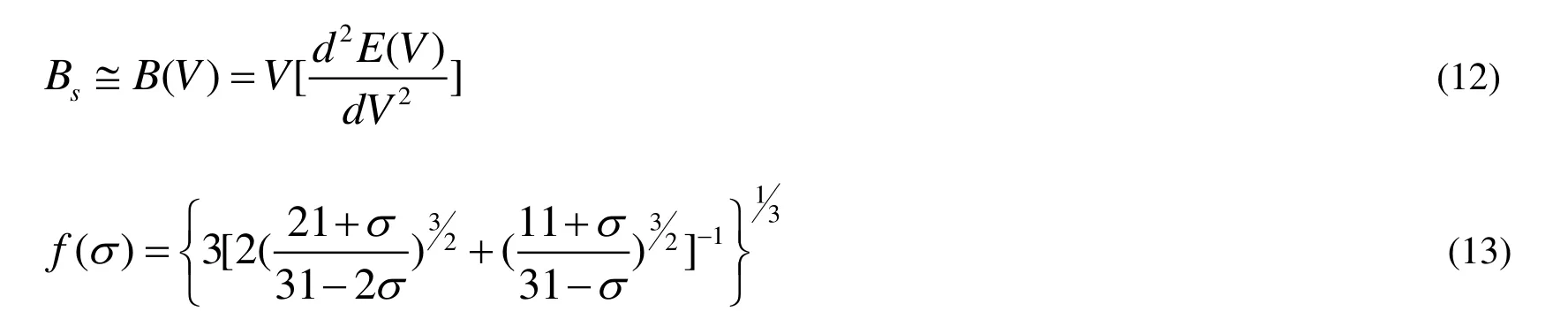
Therefore, the non-equilibrium Gibbs function G*(V; P, T) can be minimized with respect to volume V.

One could get the thermal equation of state (EOS)V(P, T) by solving Eq.(14).The thermodynamic function was fitted to the integral form of Vinet's equation of state (EOS) at zero pressure[40].The heat capacity Cpwas determined by a numerical differentiationand by polynomial fitting for both Cvand S.The phonon modes were calculated from the force constants using the PHONOPY package[41].A 2 ′ 1 ′ 2 supercell including 88 atoms with 11 ′ 11 ′ 11 k-mesh was used to ensure the convergence.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Structural and elastic properties
Cr4AlB6crystal is in orthogonal system with space group Cmmm and Fig.1 shows its crystal structure.Its unit cell contains two unit formulas.Table 1 lists the lattice constants, structural parameters and available experimental values[19]of Cr4AlB6.Obviously, the calculated results are in good agreement with the experimental values, which confirms the reliability of our computation.
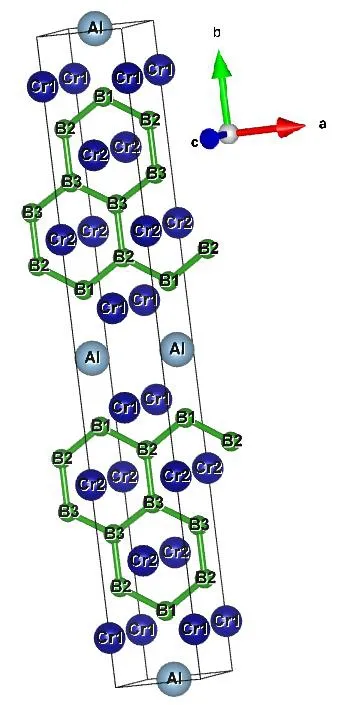
Fig.1.Crystal structure and molecular numbering of Cmmm-Cr4AlB6
In Table 1, the calculated lattice constants agree well with the experimental values of 2.9517,21.2803, and 3.0130 ? for a, b and c, respectively.For the lattice constants, the maximum differences between the calculated and experimental values are 0.17%, 0.19% and 0.82% for a, b, and c,respectively.The B6–B10bond length is 1.7396 ?,which is close to the experimental value of 1.7384 ?[19].The B6–B10and B10–B11bonds form a zigzag chain with B6–B10–B11bond angle of 120.19°, close to the experimental value of 120.23°.The B10–B11distance is 1.761 ? for the Cr2AlB2crystal, 1.739 ? for Cr3AlB4and 1.708 ? for Cr4AlB6[19].This shows that the B–B bond length shortens with increasing the boron content.Thereby, the stronger B–B covalent interactions and shorter B–B bond in Cr4AlB6may play an important role in resisting the plastic deformation and make Cr4AlB6tougher than Cr2AlB2and Cr3AlB4.In addition, it is noted that the other bond lengths and bond angles are all close to the corresponding experimental values[19].

Table 1.Experimental and Calculated Lattice Constants, Atomic Position,Bond Lengths and Bond Angles of the Cmmm-Cr4AlB6 Crystal at Standard Pressure
From Fig.1, all B atoms form the planar hexagons and the hardness of materials can be improved by adding metal binder[42], so we think that Cr4AlB6is a hard material.We further investigated the elastic constants of Cr4AlB6by CASTEP program[43].For orthorhombic system, nine independent components of the elastic constants must satisfy the necessary conditions for mechanical stability[44]:
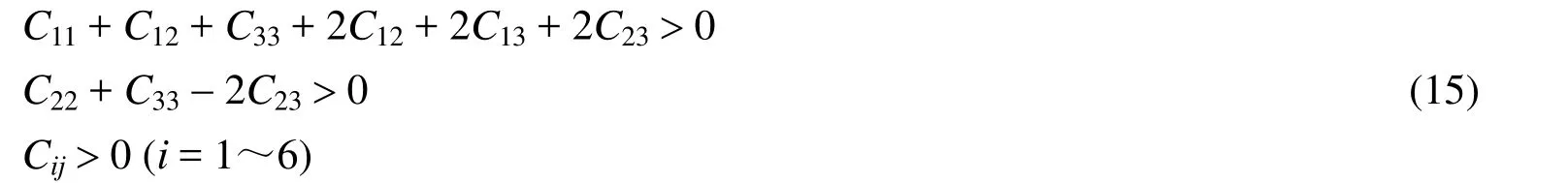
Table 2 lists the calculated elastic constants Cij(GPa), bulk modulus B (GPa), shear modulus G(GPa), Young's modulus Y (GPa), the G/B ratio,Poisson's ratio v and Vicher's hardnesss Hv(GPa) at ambient pressure.The available experimental values[45]were also included.From Table 2, the whole set of elastic constants matrix Cijsatisfies the mechanical stability criteria[46], which shows that Cr4AlB6is mechanically stable at ambient pressure.
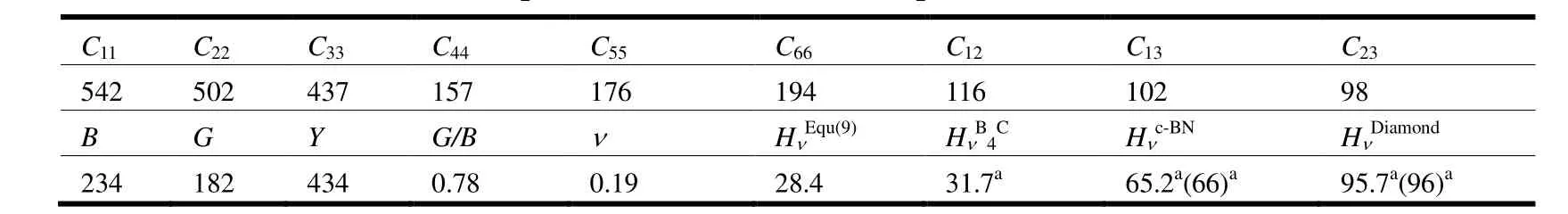
Table 2.Calculated Elastic Constants, Cij (GPa), Bulk Moduli, B (GPa), Shear Moduli, G (GPa),Young's Moduli, Y (GPa), the G/B Ratio, Poisson's Ratio n and Vicker's Hardness, Hn (GPa) at Ambient Pressure, Compared with the Available Experimental and Theoretical Results
Fig.2 presents the graph of the total energy (E)versus the volume (V).By fitting the E-V data to Birch-Murnaghan's equation of state[46], we can obtain the equilibrium lattice volume, the bulk modulus B0and the pressure derivative of the bulk modulus
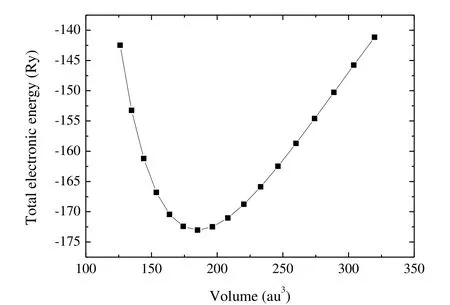
Fig.2.Graph of the total energy versus volume
From Table 2, the calculated bulk modulus is 234 GPa, which is close to the fitted value (237 GPa)from the Birch-Murnaghan equation of state.The shear modulus and Pugh's ratio[47](k = G/B) are two important elastic properties which are related with the hardness according to the empirical formulation of Chen et al.[48], and the hardness can be written as

where K = G/B.
Using Eq.(9), the hardness of Cr4AlB6is estimated to 28.4 GPa, which is smaller than the hardness' of B4C, c-BN, and diamond[36]listed in Table 2.Compared to other materials with similar structures, such as WAlB (Hv: ~21.7 GB)[19]and W45.6Re30.4B24(Hv= 23.5 GPa)[49], the hardness of Cr4AlB6is moderate.In Table 2, the C11value is larger than the C22and C33values, which implies the strong resistances to deformation along the a-direction when compared with that along the c- and b-directions.
3.2 Electronic and dynamic properties
In our previous paper[22], we have confirmed the dynamical stability of Cr4AlB6and Fig.S1 in Supporting Information shows the phonon dispersion.Fig.3 illustrates the density of states (DOS) and partial density of states (PDOS) of Cr4AlB6.There is a large finite DOS of 11.67 states/eV at the Fermi energy level for Cr4AlB6, which confirms the metallic characteristic of Cr4AlB6.The DOS near Fermi level are mainly from the Cr-3d orbital electrons, with some of the B-2p orbital electrons and negligible contributions from Al-2p states.Few electrons are available from the s orbital near the Fermi energy level.From –7.8 to –3.7 eV, the PDOS for Cr-d and B-p orbitals are similar, indicating the strong hybridization between Cr-d and B-p states.
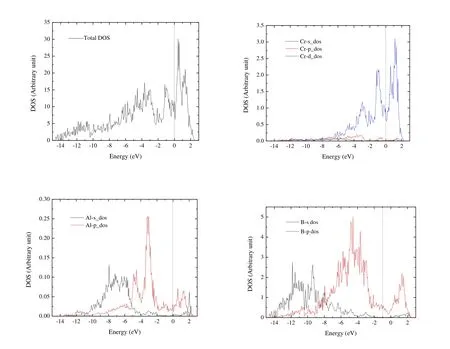
Fig.3.Total electronic density of states and the projected atomic orbital density of states of Cr4AlB6
Fig.4 shows the normalized total phonons density of states and the total atomic projected density of states of Cr4AlB6.From Figs.S1 and 4, there are two distinct peaks of bands of frequency.The first peak of frequencies ranges from 0 to 11.48 THz and characterized as the optical and acoustic bands of the Cr and Al atoms.The second peak of frequency ranges from 11.48 to 30 THz and corresponds to the optical mode of B atoms.In addition, from Fig.4, the intensity of Cr and B compositions is much stronger than that of the Al bands.And the frequency compositions of Cr and B atoms form the relative broad peak of bands, when compared with the Al atom.
Fig.5 presents the calculated band structure of Cr4AlB6along the high-symmetry directions of the Brillouin zone.The overlap between the conduction and valence bands confirmed its metallic nature once again.This suggests that Cr4AlB6would exhibit metallic conductivity like other MAX phases.From Fig.5, the Fermi energy (EF) is crossed by several different bands along the G-X, S-Y, G-Z and Z-U directions, indicating metallic behavior along the directions parallel to the a- and c-directions.While the buckling along the b- direction opens band gaps of 0.86 and 0.12 eV along X-S and Y-G, respectively.Thus Cr4AlB6behaves as a metal with strong anisotropy.And the electrical conductivity is confined along the b-direction.
3.3 Optical properties
The dielectric function was investigated and Fig.6(a)presents the real part e1(w) and imaginary part e2(w)of dielectric functions of Cr4AlB6as a function of photon energy.The investigation of e1(w) can make us understand the electronic polarizability of the material[50].For Cr4AlB6, e1(w) decreases drasticcally when the photon energy ranges from 0 to 2 eV.When the photon energy varies between 7.87 and 23.48 eV, e1(w) 0, indicating the metallic behavior of Cr4AlB6.When the photon energy is above 23.48 eV, e1(w) increases with increasing the photon energy and is nearly a constant at higher energy.This shows that Cr4AlB6becomes a transparent material at higher energy radiation.When the photon energy is zero, the static dielectric constant e1(0) is about 128.0,much larger than those of BaTiO3, BiInO3and Ti3N4[51-53].Thereby, Cr4AlB6may be useful for manufacturing the high value capacitors[54].
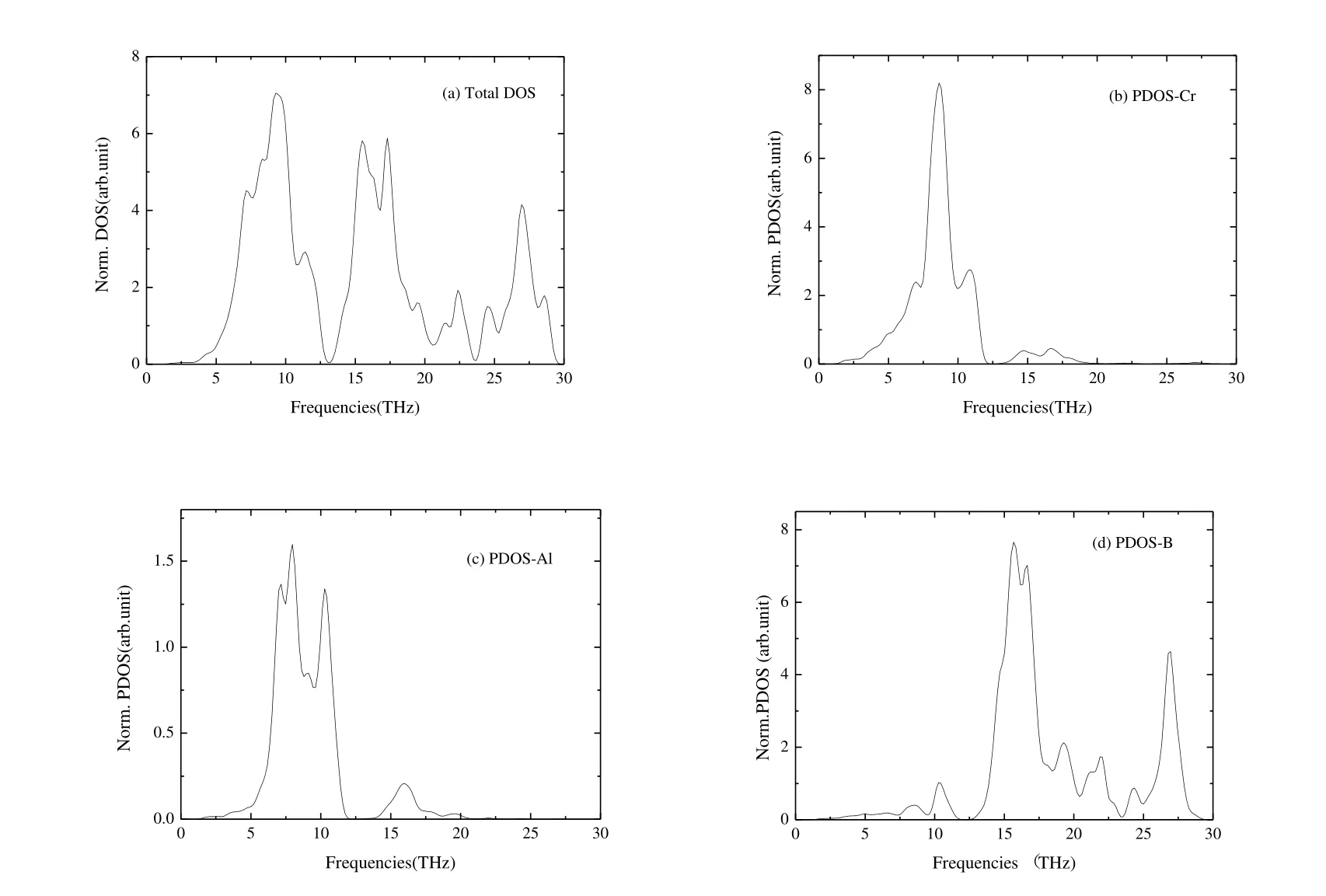
Fig.4.(a) Normalized total phonons density of states and (b~d)heir total atomic projected density of states of Cr4AlB6
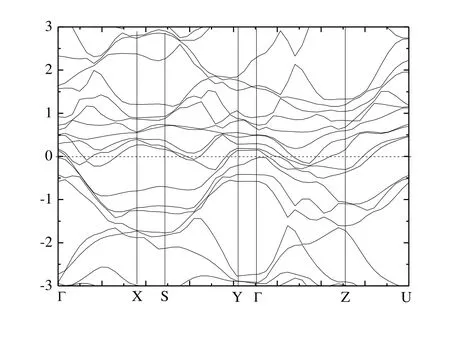
Fig.5.Electronic band structures of Cr4AlB6
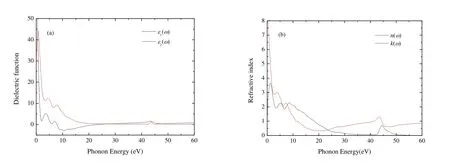
Fig.6.Dielectric functions and refractive index of Cr4AlB6
The peak of e2(w) is related to the electron excitation.From Fig.6(a), the metallic behavior of Cr4AlB6is observed once again, since for small frequencies, w ? 0, e2(w) is much larger compared with the rest of the spectrum.e2(w) has three main peaks for Cr4AlB6.At low energy, where intraband transitions occur, an abrupt rise appears below 1 eV,and e2(w) reaches the first minimum at about 2.04 eV,which confirms the low energy divergence for metallic materials.e2(w) reaches the first dielectric peak at 3.63 eV and the second and third peaks at 6.95 and 9.47 eV, respectively.The first and second peaks are derived from the transition between Cr-d and B-p states, while B-s and Al-s states contribute to the third peaks.For Cr4AlB6, e2(w) is zero at about 55 eV.This indicates that Cr4AlB6becomes transparent above 55 eV.
The refractive index exhibits the fundamental optical and electronic properties.The refractive index n(w) and extinction coefficient k(w) are illustrated in Fig.6(b).From Fig.6(b), the static refractive index n(0) is 11.3, which satisfies the condi-When the photon energy ranges from 0 to 11.25 eV, refractive index n(w) is greater than 1, which indicates that the interactions with the electrons make the photons slow down.According tothe valley of e1(w)corresponds to the peak of k(w) in this frequency range.The extinction coefficient k first increases, and reaches the first peak at 1.24 eV.Then k fluctuates and reaches the second and third peaks at 5.23 and 8.55 eV, respectively.k decreases to zero at about 55 eV, so the intrinsic oscillation frequency of Cr4AlB6is about 55 eV and Cr4AlB6possesses the characteristics of transparent ultraviolet.k is bigger than n when the photon energy varied between 7.87 and 23.48 eV, and Cr4AlB6shows a metal reflective property.
Fig.7 presents the absorption, energy loss function,reflectivity, and the optical conductivity of Cr4AlB6as a function of photon energy.Fig.7(a) presents the absorption coefficient spectrum of Cr4AlB6, which begins at zero photon energy due to the metallic nature.The absorption coefficient of Cr4AlB6has two main peaks.The first peak of 3.60058 ′ 105cm-1is at 14.2 eV and the second peak of 4.95160 ′ 105cm-1at 44.5 eV.Then the absorption coefficient decreases to zero at about 60 eV, which indicates that Cr4AlB6is colorless and transparent above 60 eV.Meanwhile, the absorption coefficient is greater than 105cm-1, indicating that Cr4AlB6is a promising candidate for optical applications.
Fig.7(b) presents the energy loss function with the increasing photon energy.And the plasma resonance frequency wpis the highest peak.From Fig.7(b), wpof Cr4AlB6is at 23.85 eV.If the frequencies of incident light are larger than the plasma frequencies of Cr4AlB6, Cr4AlB6will change from metal to dielectric material.
Fig.7(c) presents the variation of reflectivity of Cr4AlB6with incident photon energy.The average reflectivity is more than 40% for Cr4AlB6in the infrared-visible -UV range up to ~20.1 eV.When the photon energy is bigger than 20.1 eV, the reflectivity sharply decreases to very low reflectivity (high transparency) for short wavelength.According to Li et al.[55], a MAX-phase compound can reduce solar heating if it has a reflectivity of ~44% in the visible light region, so we think that Cr4AlB6is a candidate material for coating to reduce solar heating.
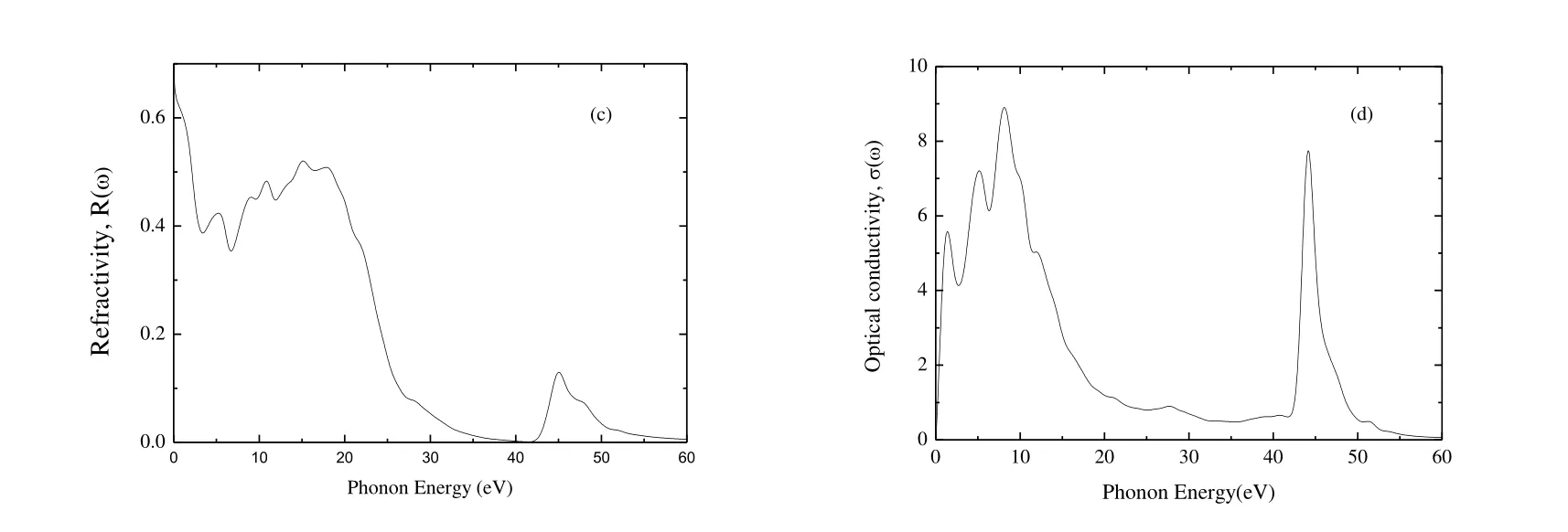
Fig.7.Absorption (a), energy loss function (b), refractivity (c) and optical conductivity (d) of Cr4AlB6
Fig.7(d) presents the optical conductivity of Cr4AlB6.The photoconductivities start with zero photon energy, which indicates that Cr4AlB6has no band gap and has metallic nature.The maximum optical conductivity occurs at the photon energy about 8.12 eV.
3.4 Thermodynamic properties
The quasi-harmonic Debye approximation is applied to investigate the thermodynamic properties of Cr4AlB6.The thermodynamic properties are determined in the temperature range from 0 to 2000 K and pressure range from 0 to 100 GPa.
Fig.8 presents the dependence of the primitive cell volume and thermal expansion coefficient as the function of T and P.From Fig.8(a), the volume increases nearly linearly with increasing T for a given P, and decreases with increasing P for a given T.The rate of increase is nearly zero from 0 to 250 K and becomes very moderate for T > 250 K.At T =300 K and P = 0 GPa, the calculated equilibrium primitive cell volume V is 187.28 ?3, which is close to the experimental values of 189.26 ?3[19].From Fig.8(b), the thermal expansion coefficient a firstly increases quickly with increasing T up to 500 K for a given P.When T > 500 K, a tends to a linear increase and the propensity of increment becomes very moderate, which means that the effect of T on ais very small at high T.In addition, a decreases quickly with increasing P for a given T.At T = 300 K and P = 0 GPa, a is 2.16 ′ 10-5K-1.
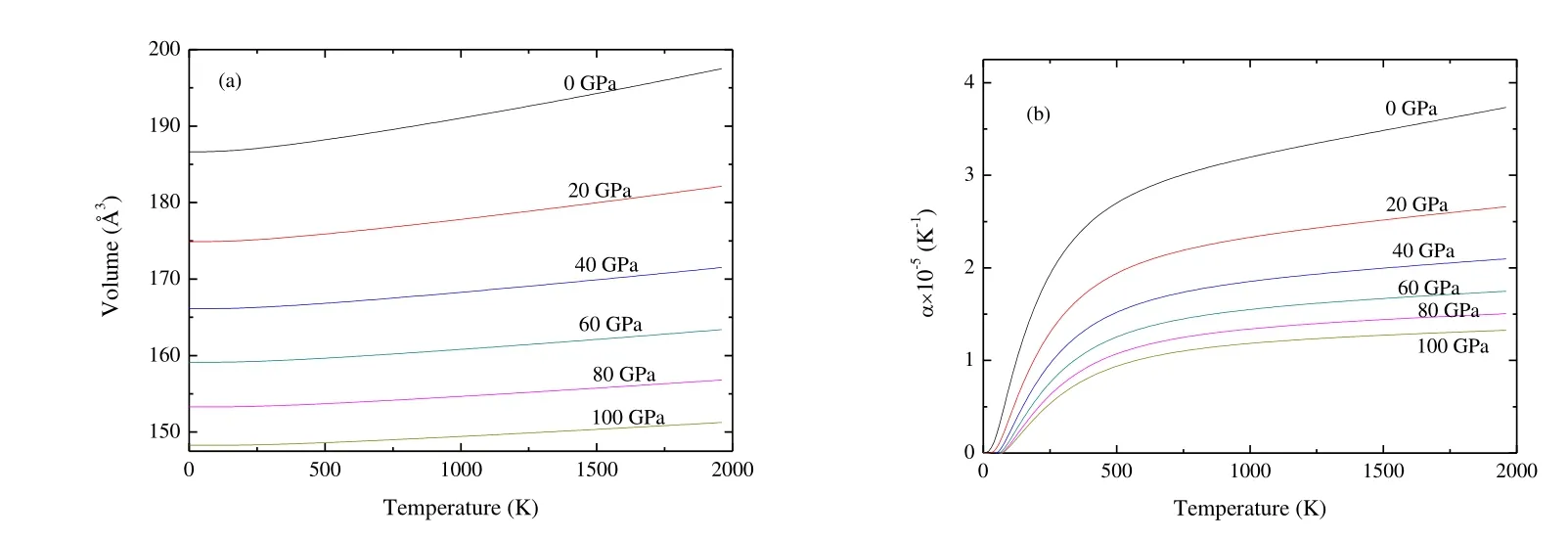
Fig.8.Dependence of the primitive cell volume (a) and thermal expansion (b) as a function of temperature and pressure
Fig.9 shows the variations of bulk modulus and heat capacity Cvas a function of T and P.From Fig.9(a),the compressibility is nearly a constant when T 150 K, then decreases linearly with increasing T for a given P.The bulk modulus increases with increasing P for a given T.This indicates that the ability to resist the volume change becomes weaker with increasing T and stronger with increasing P.Heat capacity Cvcan provide the information about the vibrational properties.Two famous limiting cases are correctly predicted by the standard elastic continuum theory[56].Cvis proportional to T3at very low temperature[53]and tends to the Dulong-Petit limits[57]at high T.From Fig.9(b), Cvincreases exponentially from 0 to 500 K and tends to the Dulong-Petit limits(548.7 J×mol-1×K-1).The interactions between ions in Cr4AlB6have great effect on Cv, especially at low T.In addition, Cvdecreases gradually with the increasing P for a given T.And the effect of T on Cvis more significant than that of P.At T = 300 K and P= 0 GPa, Cvis 243.94 J×mol-1×K-1.
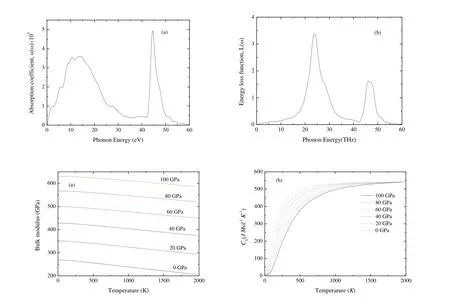
Fig.9.Dependence of the bulk modulus (a) and heat capacity Cv (b) as a function of temperature and pressure
4 CONCLUSION
Using PAW method based on the DFT within GGA, the electronic, optical and thermodynamic properties of Cr4AlB6were investigated.The obtained conclusions are as follows:
(1) The stronger B-B covalent interactions in Cr4AlB6play an important role in resisting the plastic deformation.(2) Like other MAX phases, Cr4AlB6exhibits metallic nature from the analysis of band structure and DOS.(3) The analysis of optical properties shows that Cr4AlB6is a promising dielectric material with e1(0) of 128.0.In the photon energy range from 7.87 to 23.48 eV, Cr4AlB6presents a metal reflective property.(4) The obtained thermal properties under different T and P show that the heat capacity Cvis proportional to T3at very low T for a given P and tends to the Dulong-Petit limits (541.1 J×mol-1×K-1).The effect of T on Cvis more significant than that of P, while the effect of T on the thermal expansion coefficient a is very small at high T.
REFERENCES
(1) Hadi, M.A.; Naqib, S.H.; Christopoulos, S.R.; Isiam, A.K.M.A.Mechanical behavior, bonding nature and defect processes of Mo2ScAlC2: a new ordered MAX phase.J.Alloys.Comp.2017, 724, 1167-1175.
(2) Zapata-Solvas, E.; Hadi, M.A.; Horlait, D.; Parfitt, D.C.; Thibaud, A.; Chroneos, A.; Lee, W.E.Synthesis and physical properties of(Zr1?x,Tix)3AlC2MAX phases.J.Am.Ceram.Soc.2017, 100, 3393-3401.
(3) Hadi, M.A.; Rohnuzzaman, M.; Chroneos, A.; Naqib, S.H.; Islam, A.K.M.A.; Vovk, R.V.; Ostrikov, K.Elastic and thermodynamic properties of new (Zr3?xTix)AlC2MAX-phase solid solutions.Comp.Mater.Sci.2017, 137, 318-326.
(4) Barsoum, M.W.; El-Raghy, T.Synthesis and characterization of a remarkable ceramic: Ti3SiC2.J.Am.Ceram.Soc.1996, 79, 1953-1956.
(5) Wang, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.C.Recent progress in theoretical prediction, preparation, and characterization of layered ternary transition-metal carbides.Annu.Rev.Mater.Res.2009, 39, 1-29.
(6) Eklund, P.; Beckers, M.; Jansson, U.The Mn+1AXnphases: materials science and thin-film processing.Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 1851-1878.
(7) Radovic, M.; Barsoum, M.W.MAX phases: bridging the gap between metals and ceramics.Am.Ceram.Soc.Bull.2013, 92, 20-27.
(8) Barsoum, M.W.; Ei-Raghy, T.Room-temperature ductile carbides.Met.Mater.Trans.1999, 30A, 363-369.
(9) Barsoum, M.W.; Farber, L.; Ei-Raghy, T.Dislocations, kink bands, and room-temperature plasticity of Ti3SiC2.Mater.Trans.1999, 30A,1727-1738.
(10) Guilera, G.; Gorges, B.; Pascarelli, S.; Hara, N.Novel high-temperature reactors for in situ studies of three-way catalysts using turbo-XAS.J.Synchrotron Radiat.2009, 16, 628-634.
(11) Yin, K.D.; Zhang, X.T.; Huang, Q.; Xue, J.M.Theoretical investigation on radiation tolerance of Mn+1AXnphase.Thin Solid Films 2017, 26,060703-8.
(12) Sun, Z.M.Progress in research and development on MAX phases: a family of layered ternary compounds.Int.Mater.Rev.2011, 56, 143-166.
(13) Lofland, S.E.; Hettinger, J.D.; Harrell, K.; Finkel, P.; Gupta, S.; Barsoum, M.W.; Hug, G.Elastic and electronic properties of select M2AX phase.Appl.Phys.Lett.2004, 84, 508-510.
(14) Nowotny, V.H.Strukturchemie einiger verbindungen der ü bergangsmetalle mit den elementen C, Si, Ge, Sn.Prog.Solid State Chem.1970, 2,27-70.
(15) Hu, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Huang, Q.; Bao, Y.New phases’ discovery in MAX family.Int.J.Refract.Met.Hard Mater.2013, 36, 300-312.
(16) Barsoum, M.W.MAX Phases.Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.KGaA: Weinheim, Germany 2013, p89-92.
(17) Bai, Y.L.; He, X.D.; Zhu, C.C.; Chen, G.Microstructures, electrical, thermal and mechanical properties of bulk Ti2AlC synthesized by self-propagating high temperature combustion synthesis with pseudo hot isostatic pressing.J.Am.Ceram.Soc.2012, 95, 358-364.
(18) Lin, Z.J.; Li, M.S.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.C.High-temperature oxidation and hot corrosion of Cr2AlC.Acta Mater.2007, 55, 6182-6191.
(19) Ade, M.; Harald, H.Ternary borides Cr2AlB2, Cr3AlB4, and Cr4AlB6: the first members of the series (CrB2)nCrAl with n = 1, 2, 3 and a unifying concept for ternary borides as MAX-phases.Inorg.Chem.2015, 54, 6122-6135.
(20) Bai, Y.; Qi, X.; Duff, A.; Li, N.; Kong, F.; He, X.; Wang, R.; Lee, W.E.Density functional theory insights into ternary layered boride MoAlB.Acta Mater.2017, 132, 69-81.
(21) Li, N.; Bai, Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Kong, F.; Qi, X.; Wang, R.; He, X.; Duff, A.I.Rapid synthesis, electrical, and mechanical properties of polycrystalline Fe2AlB2bulk from elemental powders.J.Am.Ceram.Soc.2017, 100, 4407-4411.
(22) Li, X.H.; Chagas, da Silva, M.; Salahub, D.R.First-principles calculations of the structural, mechanical, electronic and bonding properties of(CrB2)nCrAl with n = 1, 2, 3.J.Alloys.Comp.2017, 698, 291-303.
(23) Dai, F.Z.; Feng, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.C.Easily tiltable B_Al_B linear chain: the origin of unusual mechanical properties of nanolaminated MAB phases(CrB2)nCrAl.J.Alloys.Comp.2017, 723, 462-466.
(24) Bertaut, F.; Blum, P.Existence et structure d'une nouvelle phase dans le systè me Mo–B.Acta Crystallogr.1951, 4, 72-72.
(25) Kuz’ma, Y.B.Crystal structure of the compound YCrB4and its analogs.Sov.Phys.Crystallogr.1970, 15, 312-314.
(26) Kuz’ma, Y.B.; Krypyakevich, P.I.; Chaban, N.F.Crystal structure of Cr3AlB4.Dopov.Akad.Nauk Ukr.RSR, Ser.A: Fiz.-Mat.Tekh.Nauki.1972,34, 1118-1125.
(27) Zhao, W.J.; Xu, B.First-principles calculations of MnB4, TcB4, and ReB4with the MnB4-type structure.Comp.Mater.Sci.2012, 65, 372-376.
(28) Wang, S.; Oganov, A.R.; Qian, G.; Zhu, Q.; Dong, H.; Dong, X.; Mahdi Davari Esfahani, M.Novel superhard B-C-O phases predicted from first principles.Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.2016, 18, 1859-1863.
(29) Magnuson, M.; Mattesini, M.; Wilhelmsson, O.; Emmerlich, J.; Palmquist, J.P.; Li, S.; Ahuja, R.; Hultman, L.; Eriksson, O.; Jansson, U.Electronic structure and chemical bonding in Ti4SiC3investigated by soft X-ray emission spectroscopy and first-principles theory.Phys.Rev.B 2006, 74,205102-12.
(30) Kresse, G.; Furthmuller, J.Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set.Phys.Rev.B 1996, 54,11169-11186.
(31) Kresse, G.; Joubert, D.From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method.Phys.Rev.B 1999, 59, 1758-1775.
(32) Perdew, J.P.; Wang, Y.Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy.Phys.Rev.B 1992, 45, 13244-13249.
(33) Perdew, J.P.; Bruke, K.; Ernzerhof, M.Generalized gradient approximation made simple.Phys.Rev.Lett.1996, 77, 3865-3868.
(34) Jepsen, O.; Anderson, O.K.The electronic structure of h.c.p.ytterbium.Solid State Commun.1971, 9, 1763-1757.
(35) Pan, L.; Lu, T.C.; Su, R.Study of electronic structure and optical properties of g-AlON crystal.Acta Phys Sin.2012, 61, 027101-6.
(36) Shen, X.C.The Spectrum and Optical Property of Semiconductor.Science Press: Beijing 1992, p121-130.
(37) Blanco, M.A.; Pendá s, A.M.; Francisco, E.; Recio, J.M.; Franco, R.Thermodynamical properties of solids from microscopic theory: applications to MgF2and Al2O3.J.Mol.Struct.1996, 368, 245-255.
(38) Fló rez, M.; Recio, J.M.; Francisco, E.; Blanco, M.A.; Pendas, A.M.First-principles study of the rocksalt-cesium chloride relative phase stability in alkali halides.Phys.Rev.B 2002, 66, 144112-7.
(39) Wang, Y.; Tan, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.First-principles calculations of structural and thermodynamic properties of BeB2compound.Chin.Phys.2007,16, 3046-3051.
(40) Vinet, P.; Rose, J.H.; Ferrante, J.; Smith, J.R.Universal features of the equation of state of solids.J.Phys.: Condens.Matter.1989, 1,1941-1963.
(41) Togo, A.; Oba, F.; Tanaka, I.First-principles calculations of the ferroelastic transition between rutile-type and CaCl2-type SiO2at high pressures.Phy.Rev.B 2008, 78, 134106-9.
(42) Ezzat Elshazly, S.; Abdelrahman, A.A.M.; Elmasry, M.A.A.Mechanical properties of Cr3B4cermets cemented by different metallic binders.Inter.J.Mater.Eng.2012, 2, 57-60.
(43) Segall, M.D.; Lindan, P.J.D.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.C.First-principles simulation: ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code.J.Phys.: Condens.Matter.2002, 14, 2717-2744.
(44) Patil, S.K.R.; Khare, S.V.; Tuttle, B.R.; Bording, J.K.; Kodambaka, S.Mechanical stability of possible structures of PtN investigated using first-principles calculations.Phys.Rev.B 2006, 73, 104118-8.
(45) Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Leinenweber, K.; Xu, H.; Popov, D.; Park, C.; Yang, W.; He, D.; Zhao, Y.Crystal structures, elastic properties,and hardness of high-pressure synthesized CrB2and CrB4.J.Superhard Mater.2014, 36, 279-287.
(46) Murnaghan, F.D.On the theory of the tension of an elastic cylinder.Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.1944, 30, 382-384.
(47) Pugh, S.F.XCII.Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals.Philos.Mag.Ser.1954, 45,823-842.
(48) Chen, X.Q.; Niu, H.Y.; Li, D.Z.; Li, Y.Modeling hardness of polycrystalline materials and bulk metallic glasses.Intermetallics 2011, 19,1275-1281.
(49) Thakoor, A.P.; Lamb, J.L.; Khanna, S.K.; Mehra, M.; Johnson, W.L.Refractory amorphous metallic (W0.6Re0.4)76B24coatings on steel substrates.J Appl.Phys.1985, 58, 3409-3414.
(50) Lokman Ali, M.; Zahidur Rahaman, M.The structural, elastic, electronic and optical properties of cubic perovskite SrVO3compound: an ab initio study.Inter.J.Mater.Sci.App.2016, 5, 202-206.
(51) Li, C.L.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, R.First-principles study of the structure, electronic, and optical properties of orthorhombic BiInO3.Appl.Phys.Lett.2007, 91, 071902-3.
(52) Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Li, Q.K.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Wang, R.; Woo, C.H.First-principles study of cubic perovskites BiMO3(M = Al, Ga, In and Sc).Phys.Rev.B 2007, 75, 245209-9.
(53) Xu, M.; Wang, S.Y.; Yin, G.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Jia, Y.Optical properties of cubic Ti3N4, Zr3N4, and Hf3N4.Appl.Phys.Lett.2009, 89,151908-151910.
(54) Rahman, M.; Rahaman, M.The structural, elastic, electronic and optical properties of MgCu under pressure: a first-principles study.Inter.J.Modern Phys.B 2016, 30, 1650199-13.
(55) Li, S.; Ahuja, R.; Barsoum, M.W.; Jena, P.; Johansson, B.Optical properties of Ti3SiC2and Ti4AlN3.Appl.Phys.Lett.2008, 92, 221907-3.
(56) Debye, P.Zur Theorie der spezifischen W? rmen.Ann.Phys.1912, 39, 789-839.
(57) Petit, A.T.; Dulong, P.L.Recherches sur quelques points importants de la theoreie de la chaleur.Ann.Chim.Phys.1819, 10, 395-413.
- 結構化學的其它文章
- Synthesis and Characterization of a Palladium Complex Supported by Bidentate Ligand and Catalysis of the Vinyl Polymerization of Norbornene①
- Synthesis, Structure and Photochromism of a New Diarylethene and Its Ag(I) Complex①
- Ionothermal Synthesis, Structure and Luminescent Properties of a New 2-D Bismuth(III) Coordination Polymer with (6,5)-Connected Topological Sheet①
- Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Properties of a 1D Heteronuclear Cobalt-sodium Polymer with Bridging Ligand 2-(2-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)Hydrazinecarbothioamide①
- Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Photoluminescence of a Dinulear Copper Complex①
- Iodoplumbate(II)-based Hybrid Templated by 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane Derivative: Structure,Photocurrent Response Behavior and Photocatalytic Activity for the Degradation of Organic Dye①

