Finite Element Multi-mode Approach to Thermal Postbuckling of Functionally Graded Plates
W.Xia,Y.P.Fengand D.W.Zhao
Finite Element Multi-mode Approach to Thermal Postbuckling of Functionally Graded Plates
W.Xia1,Y.P.Feng2and D.W.Zhao3
Postbuckling analysis of functionally graded ceramic-metal plates under temperature field is presented using finite element multi-mode method.The three-node triangular element based on the Mindlin plate theory is employed to account for the transverse shear strains, and the von-Karman nonlinear strain-displacement relation is utilized considering the geometric nonlinearity.The effective material properties are assumed to vary through the thickness direction according to the power law distribution of the volume fraction of constituents.The temperature distribution along the thickness is determined by one dimensional Fourier equations of heat conduction.The buckling mode shape solved from eigen-buckling analysis is adopted as the assumed mode function to reduce the degrees of freedom of nonlinear postbuckling equilibrium equations.The postbuckling response is obtained by solving the nonlinear equilibrium equations,and compared with the Newton-Raphson numerical results.The effects of boundary conditions,material gradient index and temperature distribution on postbuckling behavior are examined.
Functionally graded plates,thermal postbuckling,geometric nonlinearity,finite element method.
1 Introduction
Functionally graded materials(FGMs)are believed to be ideal high-heat-resistant composites because the continuous varied material composition eliminates the sharp local thermal stress concentration which is often encountered in the interface between two constitutive materials.The most common FGM structures are ceramic-metal plates(or shells)with the through-the-thickness material distribution,where the ceramic-rich top has good thermal resistance and the metallic-rich bottom has superior fracture toughness.Functionally graded(FG)plates are easy to deflect when subjected to thermal load because the plate is asymmetric about the middle plane.Therefore,the thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded plates,including thermal stresses,stabilities,buckling and postbuckling,becomes an essential problem in FGMs applications.
A survey on the modeling and analysis of FGM structures was given by Birman and Byrd(2007),and the literature on homogenization theories and the thermomechanical analysis of FG plates was recently reviewed by Jha,Kant and Singh(2013).The classical plate theory(CPT)and Sander’s assumption were adopted to derive equilibrium and stability equations for rectangular simply supported FG plates,and the closed-form solution of critical buckling temperature was presented by Javaheri and Eslami(2002).The first-order shear deformation theory(FSDT)and the third-order shear deformation theory(TSDT)accounting for the transverse shear strain and rotary inertia were also used to analyze the thermo-elastic bending of FG plates[Reddy and Chin(1998);Reddy(2000)].The mechanical models of circular FG plates based on CPT,FSDT and TSDT were compared,and the FSDT was proved to be suitable in buckling analysis for the axisymmetric bending of FG plates[Ma and Wang(2004)].The FSDT was utilized in stability analysis for simply supported rectangular FG plates under thermal load[Wu(2004)].The thermal post buckling behavior of FG skew plates was investigated utilizing nonlinear von Karman strain-displacement relations[Prakash,Singha,and Ganapathi(2008)].The shear deformable finite element approach was further developed to analyze the influence of neutral surface position on the postbuckling deformation of FG plates[Prakash,Singha,and Ganapathi(2009a)].The strain energy equations considering non-uniform shear stresses were established to derive the shear correction factor for FSDT of FG plates[Singha,Prakash,and Ganapathi(2011)].Many computational methods developed for the linear and nonlinear analysis of plate/shell structures are applicable in FG plates.For example,Tessler and Hughes(1985),Ibrahim,Tawfik and Al-Ajmi(2008)developed displacement plate elements based on Kirchhoff or Mindlin theories.Dong,El-Gizawy,Juhany and Atluri(2014)proposed a mixed-collocation C0finite element for modeling the thick-section FG plates instead of higher-order or layer-wise zig-zag plate theory.Cai and Atluri(2012)employed the drilling degrees of freedom in plate/shell elements to avoid the problem of singularity in the stiffness matrix,and proposed a triangular plate element using co-rotational frames and the von Karman nonlinear theories.The static and dynamic stability of FG panels in supersonic airflow were studied using finite element method[Sohn and Kim(2008)].The finite element model for FG panels under thermal and aerodynamic loads was established on the base of FSDT,von-Karman strain-displacement relations and the first-order piston theory aerodynamics.The thermal postbuckling and aeroelastic flutter of damped FG panels were investigated by Lee and Kim(2010).A three-dimensional finite element method was developed to determine the thermal buckling boundary of clamped FG plates.In the three-dimensional method,an 18-node solid element was employed to simulate the material distribution and non-uniform temperature field[Na and Kim(2004)].The thermal postbuckling behavior of FG plates considering initial geometric imperfection was further studied by many investigators[Shen(2007);Li,Zhang,and Zhao(2007);Yang,Liew,and Kitipornchai(2006)].
The studies on the nonlinear postbuckling behavior of FG plates revealed that the postbuckling deformation of FG plates is similar to that of asymmetric laminates,because the neutral surface does not coincide with the geometric mid-plane for both structures.The influence of bending-extension coupling on the instability of bifurcation type was examined for FG plates under in-plane load[Aydogdu(2008)],and for FG plates with initial geometric imperfection[Yang,Liew and Kitipornchai(2006)].The eigen-buckling analysis was proved to be inaccurate because the bending-extension coupling does not properly take into account.The nonlinear method based on the Newton-Raphson iterative technique was widely used but only the postbuckling deflection amplitude was obtained.Due to the geometric nonlinearity and bending-extension coupling,the postbuckling of FG plates may exhibit more than one equilibrium states which are asymmetry about the mid-plane.The snap-through phenomenon between two of the equilibriums was recently reported in theoretical analysis and numerical simulations[Prakash,Singha,and Ganapathi(2009b);Singha,Prakash, and Ganapathi(2011)],but to the authors’knowledge,the thorough analysis of asymmetrical postbuckling equilibriums of FG plates has not been reported in any major international journal.
The present work proposes a finite element multi-mode approach to investigate nonlinear postbuckling equilibriums of FG plates.The material properties are assumed to vary continuously and smoothly through the thickness according to the power law distribution of the constituent volume fraction.A three-node triangular Mindlin plate element based on the first-order shear deformation theory and the von-Karman nonlinear strain-displacement relation is utilized to establish the finite element model accounting for transverse shear strains,moderate rotations and geometric nonlinearities.The temperature field is considered to vary through the thickness direction alone and determined by nonlinear Fourier equations of heat conduction.The Euler type thermal buckling is analyzed by eigen-buckling analysis.The postbuckling response is obtained by the Newton-Raphson numerical procedure and the multi-mode method.In the multi-mode method,the buckling mode shapes solved from eigen-buckling analysis are adopted as the assumed mode functions.The current formulation is verified by comparison between present results and available solutions,and the influence of plate boundary condition,plate length-to-thickness ratio,material gradient index and non-uniform temperature distribution on the postbuckling response of FG plates is discussed.
2 Formulations
Fig.1 shows a ceramic-metal FG plate measuring with length l,width b and thickness h.A coordinate system(x,y,z)is established on the middle plane of the plate.We will consider the nonlinear postbuckling behavior of the FG plate subject to thermal load,which involves the structure stretching and bending coupling.Based on two-dimensional plate theory,the displacement field includes three displacements(u,v,w in x,y,z directions,respectively)and two rotations(?xand ?yaround the x and y axes,respectively).
The material constitution is assumed to vary continuously through the plate thickness according to the following simple power law distribution.
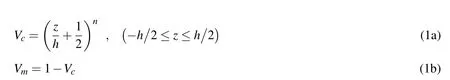
where n is the gradient index(n≥0),Vcand Vmdenote the volume fractions of ceramic and metal,respectively.Applying the linear rule of mixture,the effective material property distribution is determined as follows:
where P represents the effective material properties,including Young’s modulus E,Poisson’s ratio υ,thermal expansion α and heat conductivity κ;Pcand Pmdenote the properties of ceramic and metal,respectively.
According to the Mindlin plate theory,the displacement field can be determined by mid-plane displacements and rotations as follows:

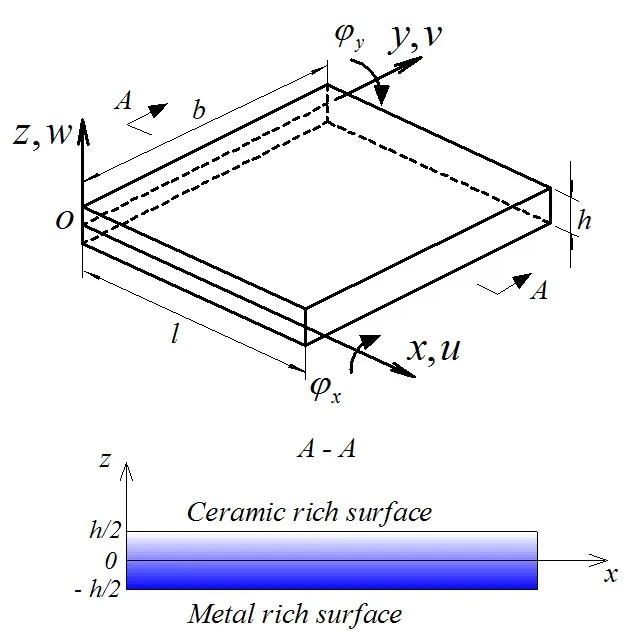
Figure 1:Schematic of a functionally graded plate.
where u0,v0and w0denote the mid-plane displacements in x,y and z directions,respectively;while ?xand ?ydenote the transverse normal rotations around the x and y axes,respectively.Because the rotations ?xand ?yare independent of displacements(u,v,w)in the Mindlin plate theory,the finite element model requires only C0-continuity.The displacement field is then approximated as a polynomial which is a function of the element degrees of freedom(DOFs)by applying a threenode triangular Mindlin(MIN3)plate element[Tessler and Hughes(1985)].
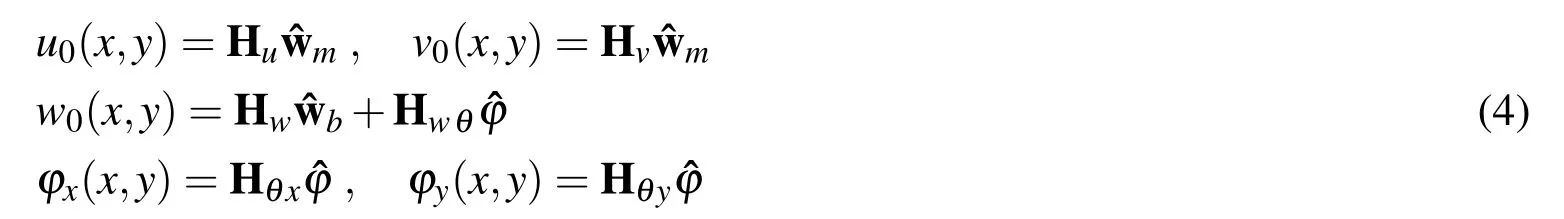
where?wm,?wband?? denote the membrane,bending and rotation element DOFs,respectively;while Hu,Hv,Hw,Hwθ,Hθx,Hθyare element interpolation functions.The detailed derivation of MIN3 element interpolation functions are given by Tessler and Hughes(1985).The geometric nonlinearity is considered by applying von Karman strain-displacement relations.The in-plane strains are then expressed in terms of mid-plane displacements as

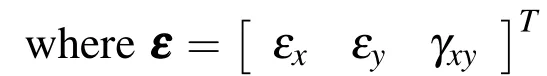

The constitutive relations are expressed as
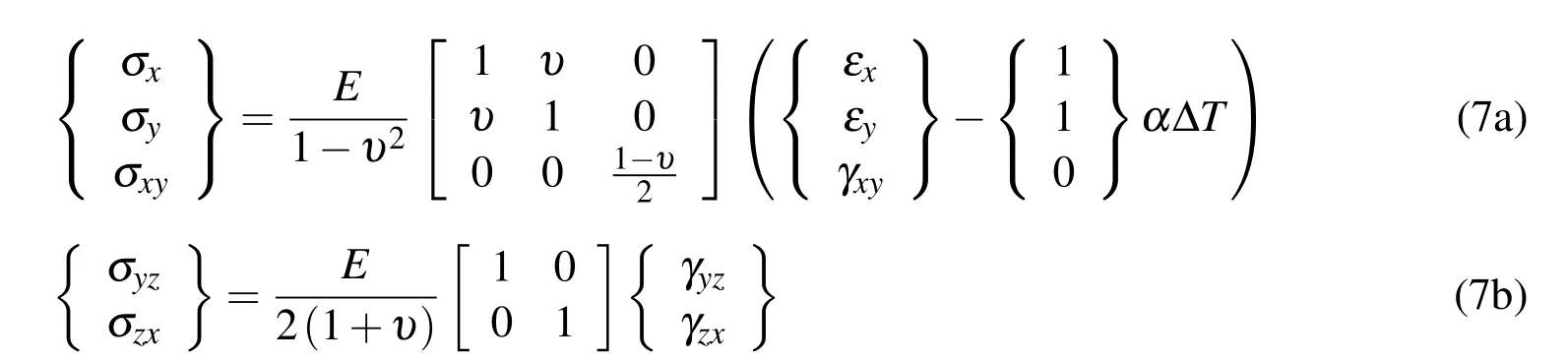
where?T is the temperature change from a stress-free state(room temperature).The material properties vary along the thickness direction for the FG plate,and the effective properties(E,υ and α)are functions of z according to Eq.2.The in-plane force,moment and transverse shear force resultants are defined,respectively,by
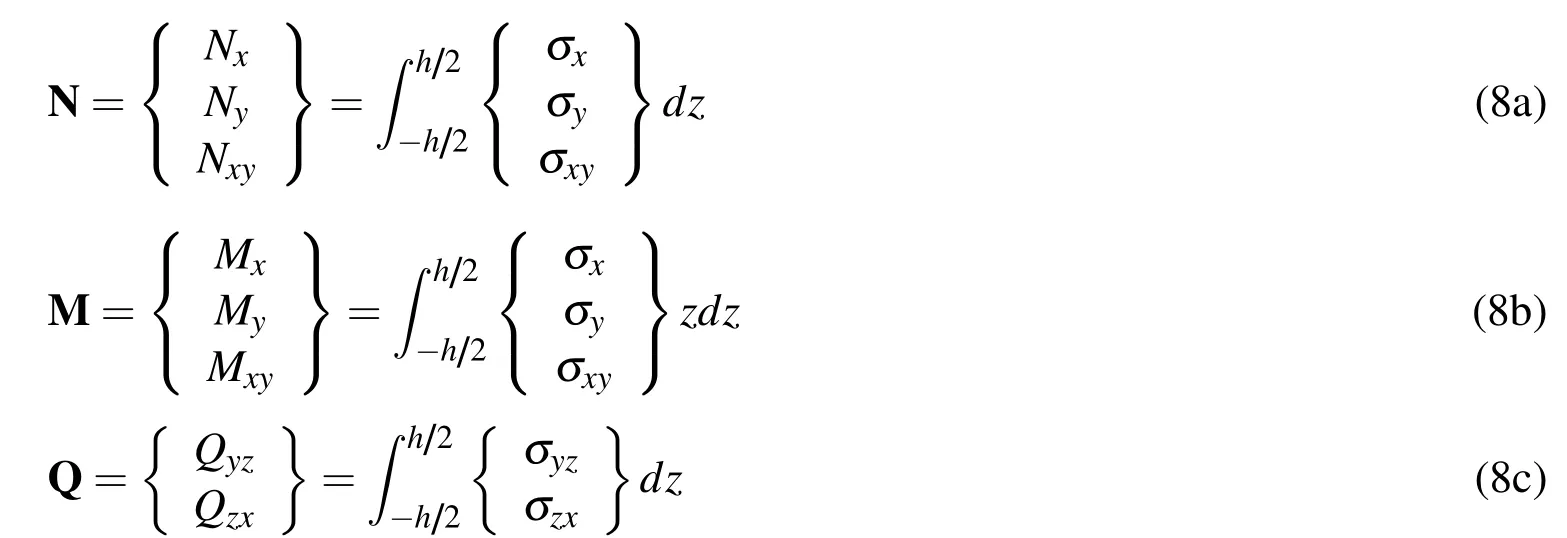
In matrix form,the relation between the stress resultants and the strains is written as
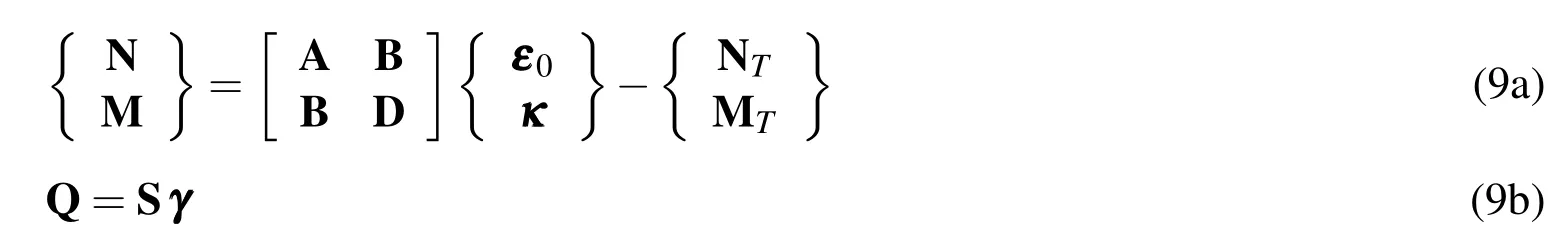
where NTand MTdenote the thermal force and moment resultants,respectively,and are given by
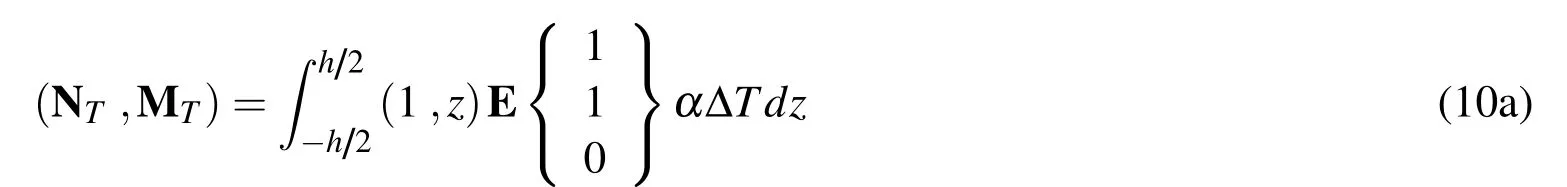

The matrices A,B,D,and S denote the in-plane,bending-stretching coupling,bending,and transverse shear stiffness,respectively,which are defined by

where κsis the shear correction coefficient of MIN3 element.The strain energy stored in the plate is
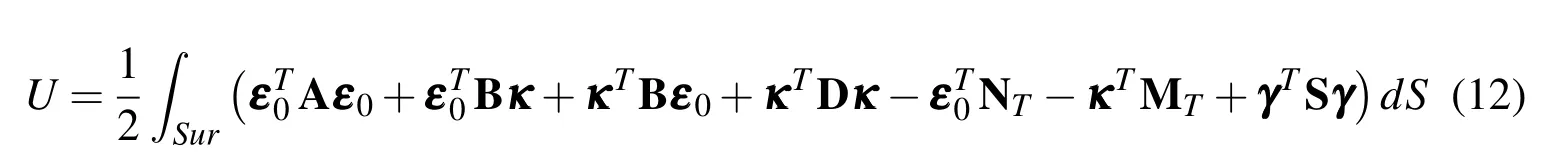
By applying the finite element discretization using MIN3 element,the potential energy is expressed in terms of the structural DOFs as
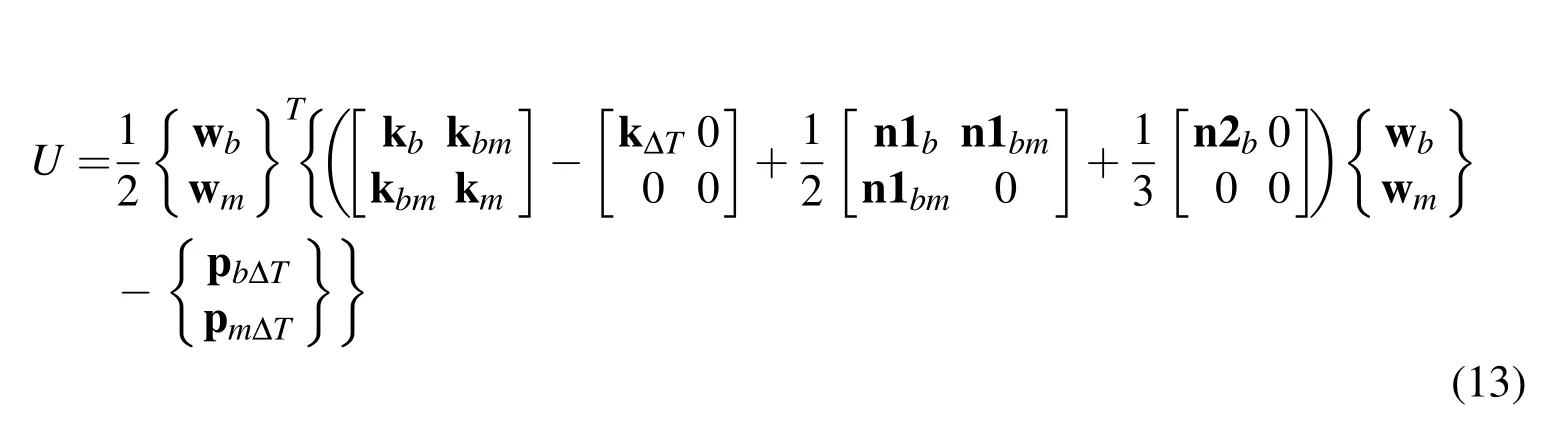
where wmand wbdenote the membrane and bending structural DOFs,respectively;pm?Tand pb?Tdenote the membrane and bending thermal loads,respectively;km,kbm,kbdenote the linear membrane,bending-stretching coupling,and bending stiffness matrices,respectively;k?Tis the thermal stiffness matrix;n1b,n1bmdenote the first-order nonlinear bending and bending-stretching coupling stiffness matrices,respectively;n2bis the second-order nonlinear bending stiffness matrix.The equilibrium equations are then derived by minimization of total potential energy as
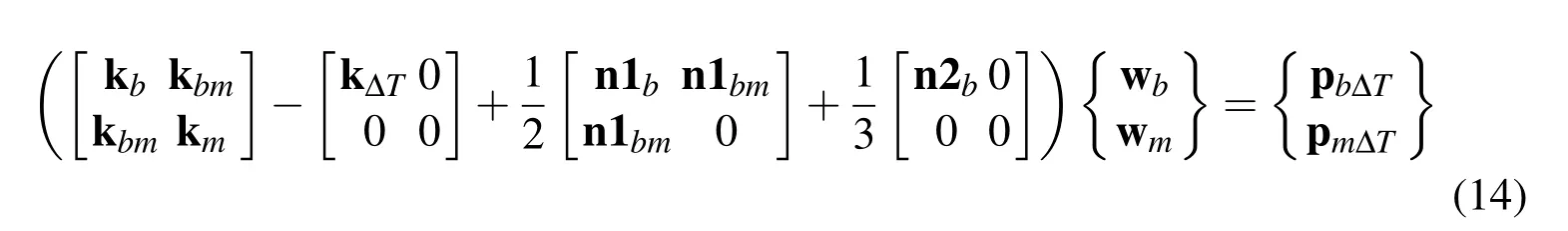
3 Solution procedure
3.1 Thermal analysis
The temperature field in the plate is assumed to vary only along the thickness direction,and the temperature distribution is governed by one dimensional Fourier equation of heat conduction as follows.

where T is the temperature distribution in the plate.If we define room temperature as T0,the temperature change in Eq.?7i/s e?xpressed? as?/T?=T?T0.Considering thermal boundary conditions as Th2=Tc,T?h2=Tm,the solution of Eq.15 gives the temperature distribution function as
where
3.2 Buckling analysis
The thermal buckling equations are derived from Eq.14 by solving the partitioned equations for wm,and reducing the equilibrium equations in terms of the bending deflection wbas follows.
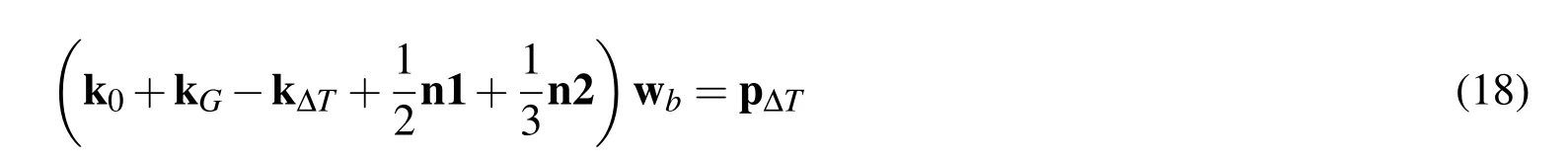
where
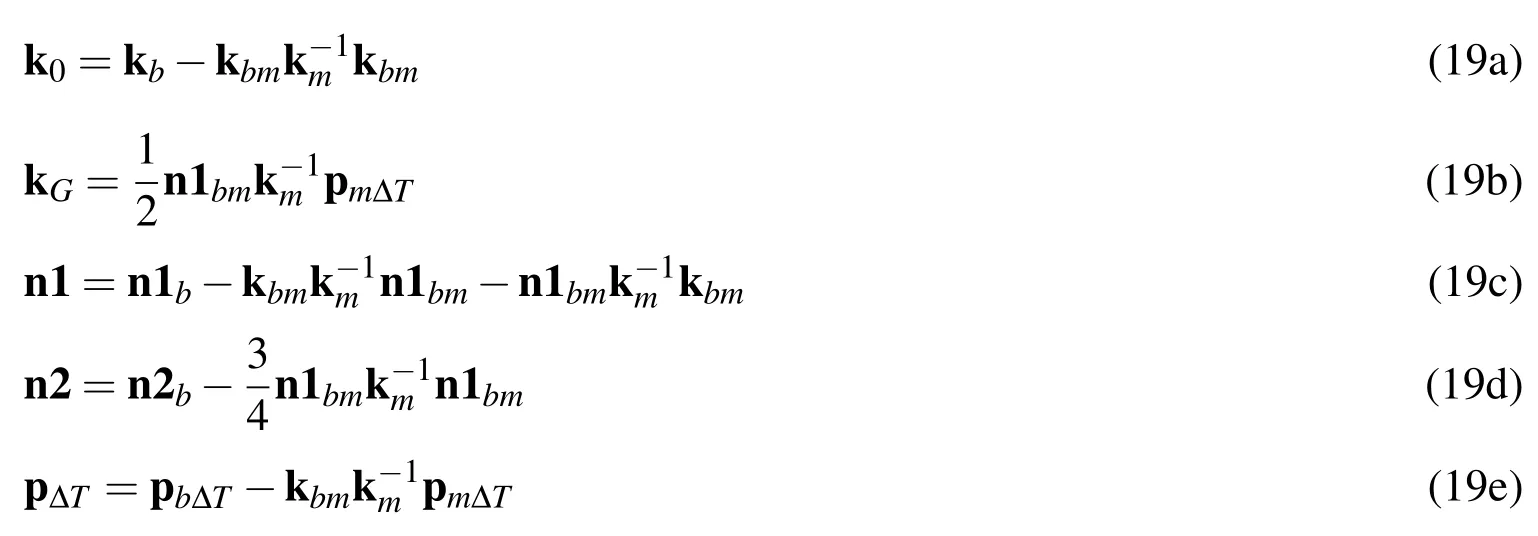
The equilibrium equations in Eq.18 can be rewritten in a residual form as
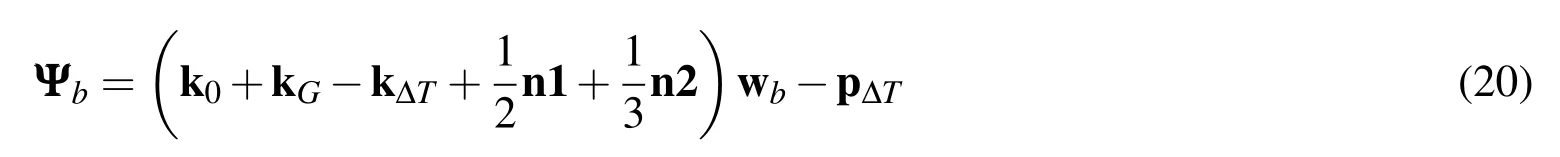
For the linear Euler type buckling problem,the nonlinear terms in Eq.20 can be neglected.The critical buckling temperature is obtained by solving the following eigenvalue problem.
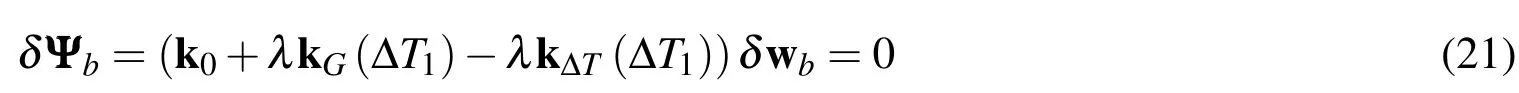
where?T1is the unit temperature rise,denote the positive real eigenvalues solved by Eq.21,and λ1is the minimal one of eigenvalues.The critical buckling temperature rise is defined by

3.3 Postbuckling analysis
For the postbuckling problem,the nonlinear equilibrium equation in Eq.18 can be solved numerically by applying either a conventional Newton-Raphson procedure,or a modified Newton’s procedure in conjunction with various iterative strategies that permit the load parameter to vary during equilibrium iterations.Because the incremental-iterative solution represents only one of the equilibrium states of the plate for a given initial condition,it cannot show the asymmetrical postbuckling behavior of the FG plate.But it is difficult to give analytical solutions to Eq.18.Therefore,the current work will introduce a multi-mode approximated method to analyze the asymmetrical postbuckling equilibriums of the FG plate based on the finite element model.
Since the number of structural node DOFs of wbis usually very large,this turns out to be computationally costly.An efficient solution procedure is to transfer Eq.18 into modal coordinates with a modal reduction.Firstly,the structural deflection is assumed to be expressed as a linear combination of known functions as


where the linearized matrices n1(i)and n2(i,j)have the same forms as n1 and n2 except they use normalized eigenvectors ?iand ?jin evaluating the corresponding element matrices.Thirdly,the finite element equilibrium equation is transformed into modal coordinates as
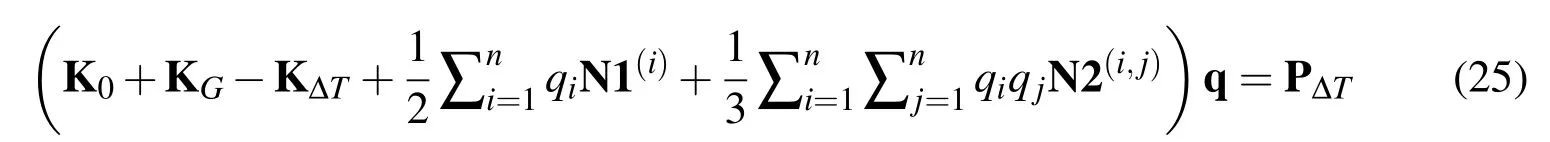
where the modal stiffness K,N1 and N2,and the modal force P?Tare defined,respectively,by
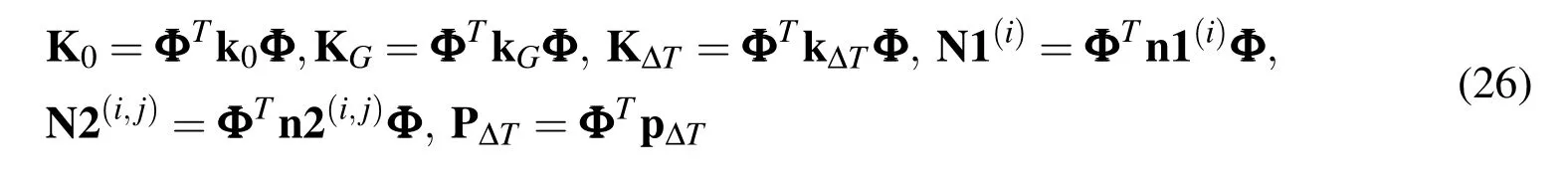
The DOFs of the finite element equation are reduced by the use of modal coordinate transformation.Therefore,the nonlinear equation can be studied by analytical approach.Meanwhile a class of problems involving material behavior,temperature distribution,plate geometry and boundary condition are convenient to take into account in this multi-mode approach because the actual buckling mode shapes are employed as the assumed mode functions.
4 Results and Discussion
In this section,the buckling stabilities and postbuckling responses of a ceramicmetal FG plate under thermal loads are investigated.The FG plate considered here comprises silicon nitride(Si3N4)and stainless steel(SUS304).The properties of each constituent,including the Young’s modulus E,thermal expansion coefficient α and heat conductivity κ,are given in Tab.1.The reference room temperature is assumed to be 300K(27?),and the Poisson’s ratio is chosen as 0.3 for simplicity.The geometryof the plate is l×b=0.3m×0.3m,and the length-to-thickness ratio is chosen if not specially defined.A 288-element full-plate mesh is utilized to model the plate.When uniform temperature distribution is considered,the critical buckling temperature rise is=29.72K for the clamped FG plate and=11.15K for the simply supported FG plate.The corresponding buckling mode shapes of clamped and simply supported FG plates are shown as contour plots in Fig.2.
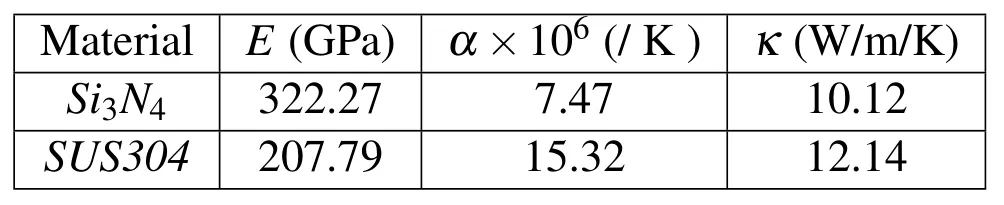
Table 1:Properties of the functionally graded material constitution.
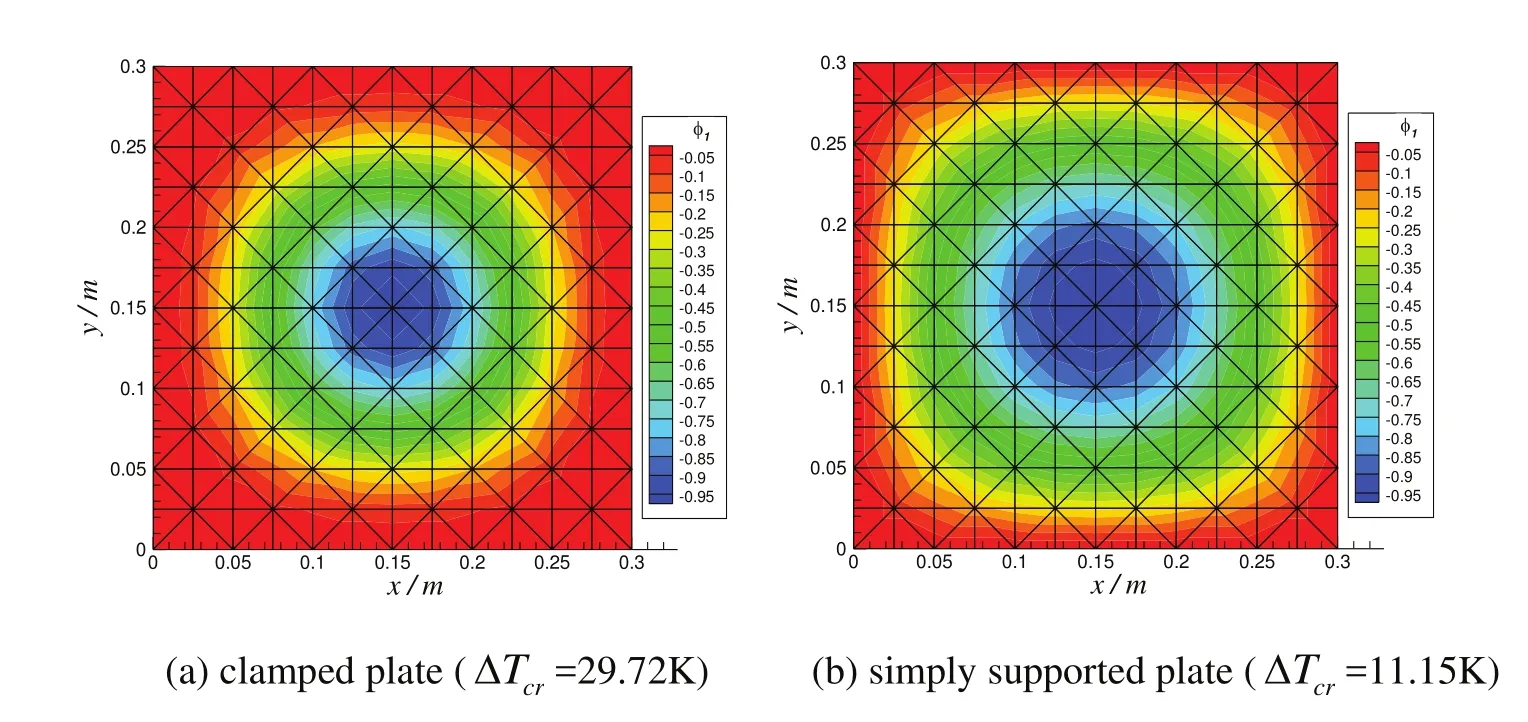
Figure 2:Thermal buckling mode shapes of FG plates.
4.1 Clamped FG plates
Before proceeding for the detailed study,the formulation developed herein is validated against the thermal-mechanical analysis of clamped FG plates with various values of length-to-thickness ratioThe Si3N4/SUS304 FG plates with gradient index n=1 are clamped at the edges with the assumption that thedisplacements are immovable.The length-to-thickness ratios are chosen as80 and 100.Tab.2 presents the resulting buckling temperature rise obtained by the finite element eigen-buckling analysis with different mesh sizes,along with results from present multi-mode method.
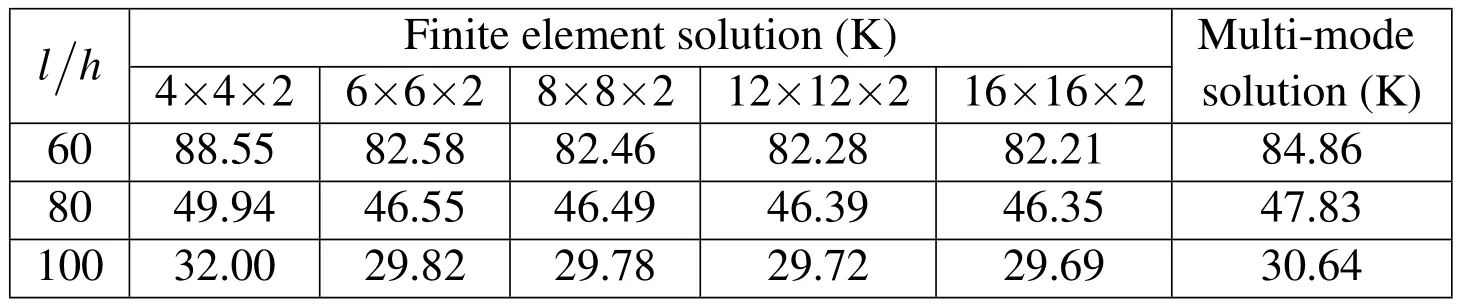
Table 2:Resulting buckling temperature rise compared with finite element solutions.
It is seen from Tab.2 that MIN3 element employed here has a good convergence property,and the 288-element mesh(12×12×2 elements)is found to be adequate to model the FG plate.Thus,the mesh size of 12×12×2 elements is utilized in constructing the multi-mode model. Furthermore, the nonlinear postbuckling equations in modal coordinates are utilized to investigate the critical buckling temperature by solving a linearized eigenvalue problem.The multi-mode solutions are obtained using the first buckling mode as assumed mode function,and verified by comparing with the finite element results(3%error with 288-element mesh results).Fig.3 shows the resulting thermal buckling mode shapes obtained by the finite element eigen-buckling analysis and the present multi-mode method.By comparing the thermal buckling mode shapes along the center line of the FG plate,the multi-mode solution shows good agreement with the finite element results.
The thermal postbuckling paths of a typical clamped FG plate with gradient index n=1 under uniform temperature elevation are further analyzed using the multi-mode method.Fig.4 shows the variation in non-dimensional central plate deflection w/h against temperature change for clamped FG plates with length-to-thickness ratios as l/h=60,80 and 100.The solid,dashed and dashdot lines denote the results for three deformed configurations solved from the multi-mode equilibrium equations.It is seen from Fig.4 that no transverse deflection(only zero solution P0)occurs at low temperature rise(?T ≤ ?Tcr),while two non-zero values of postbuckling deflection(positive solution P1and negative solution P2)occur after?T>?Tcr.It proves to be a typical bifurcation buckling in this case.Because the non-zero values of postbuckling deflection(P1and P2)are almost symmetric about the mid-plane of the plate,either of the two deflection branches can represent the postbuckling amplitude of the clamped FG plate.The numerical results obtained by Lee and Kim(2010)are also depicted in Fig.4,and good agreement with present multi-mode solutions is discovered,regardless of the length-to-thickness ratios.Fig.5 shows the variation in non-dimensional central plate deflection w/h against temperature change for clamped FG plates with gradient indexes as n=0,0.2,1,5 and∞.As defined in Eq.1,the plate with gradient index n=0 corresponding to the pure ceramic plate,while gradient index n=∞refer to the pure metal plate.The solid and dashed lines inFig.5 denote the non-zero and zero results solved from the multi-mode equilibrium equations,respectively.The non-zero solutions represent the thermal postbuckling deflections.Typical bifurcation buckling is observed in Fig.5 for clamped FG plates,regardless of the gradient indexes.With the gradient index of FG plates decreasing the critical buckling temperature increases,while the postbuckling deflection decreases.As depicted in Eq.1,the volume fraction of the ceramic increases with the gradient index decreasing.Also considering the elastic modulus of the ceramic is larger than that of the metal,but the thermal expansion coefficient of the ceramic is smaller than that of the metal.It is concluded that the ceramic-metal FG plate with more ceramic constituent is more stiffen and not ease to buckle with temperature elevation.
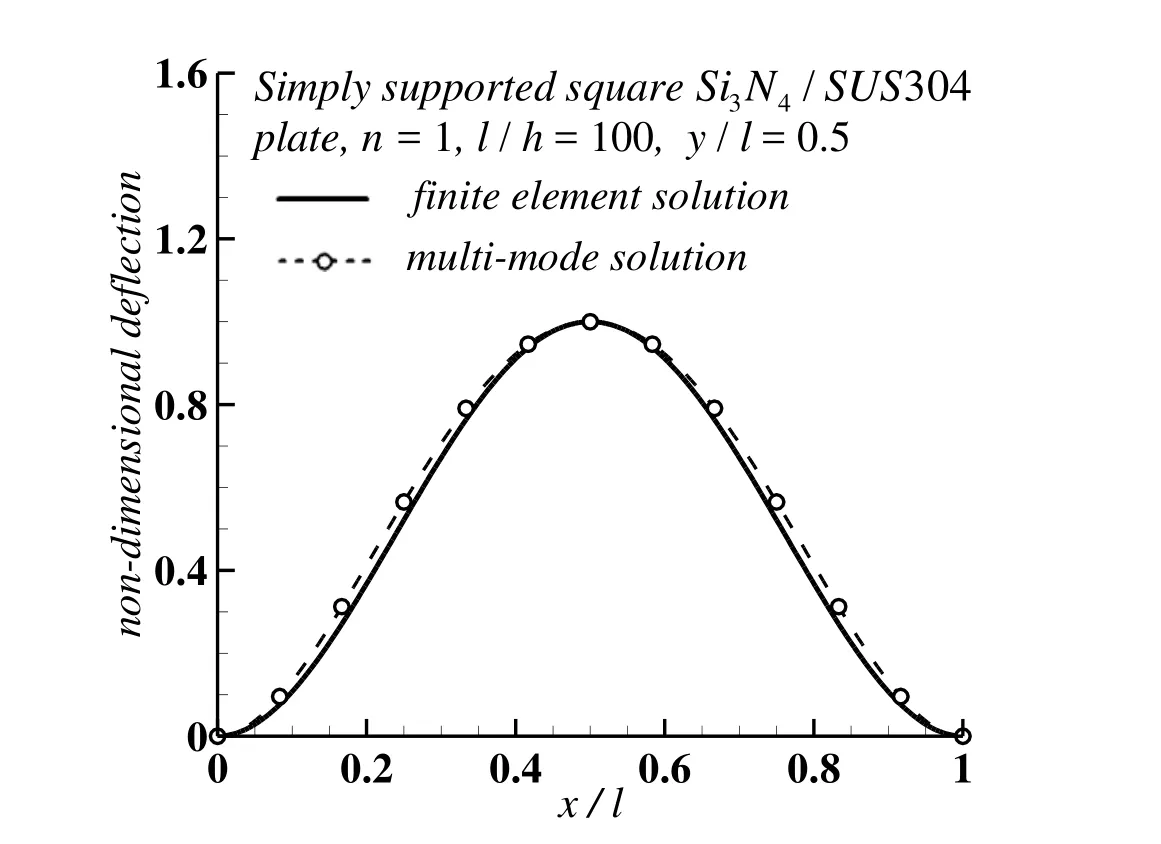
Figure 3:Thermal bucking mode shapes along plate center line of the clamped FG plate.
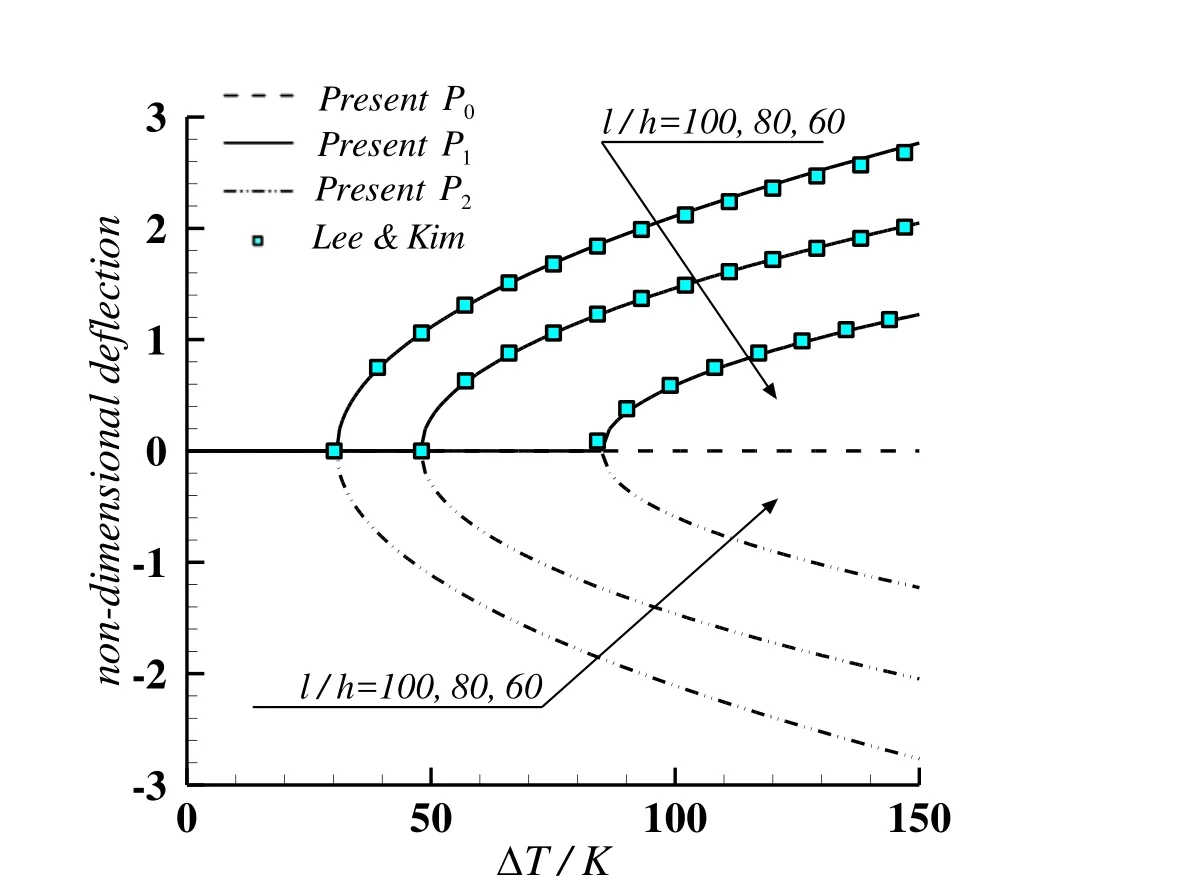
Figure 4:Thermal postbuckling paths of clamped FG plates with various lengthto-thickness ratios.
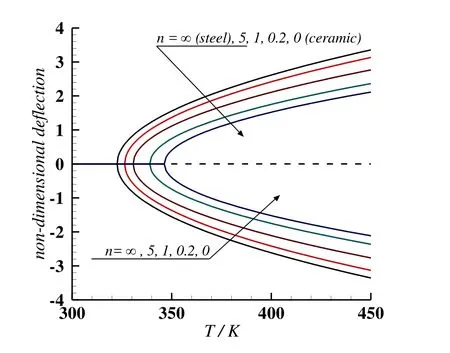
Figure 5:Thermal postbuckling paths of clamped FG plates with various gradient indexes.
4.2 Simply supported FG plates
The thermal buckling and postbuckling behavior of simply supported FG plates are further discussed.Fig.6 shows the variation in critical buckling temperature rise?Tcragainst the gradient index n for simply supported Si3N4/SUS304 FG plates with length-to-thickness ratios as60 and 100.It proves that the critical buckling temperature increases with the decrease of the gradient index(more ceramic constituent)and the length-to-thickness ratio(thicker plate).For a given length-to-thickness ratio,the critical buckling temperature of the pure ceramic plate(n=0)is the highest,while the critical buckling temperature of the pure metal plate(n=∞)is the lowest.

Figure 6:Variation of critical buckling temperature with gradient index.
Fig.7 shows the variation in non-dimensional central plate deflection w/h against temperature change for a simply supported Si3N4/SUS304 FG plate based on the multi-mode method.The uniform temperature elevation is assumed and the gradient index is chosen as n=1.The solid and dashed lines in Fig.7 denote the nonzero and zero results solved from the multi-mode equilibrium equations,respectively.By contrasting Fig.7 and Fig.4,it is discovered that the simply supported FG plate under thermal load exhibits quite different prebuckling and postbuckling behavior from that of the clamped FG plate.For the simply supported FG plate,the transverse deflection occurs no matter how small the temperature rise.Therefore,there is no bifurcation buckling in this case.It is also seen in Fig.7 that two different non-zero solution branches of the temperature-deflection curve(P1and P2)exist for the simply supported FG plate,which appear quite similar to the behavior corresponding to imperfect structures[Iooss and Joseph(1980)].Then the simply supported FG plate may have three different values of deflection(P0,P1and P2)corresponding to a given temperature,that is,three deformed configurations may exist for a simply supported FG plate for a given thermal load.The numerical results using Newton-Raphson iteration based on the finite element model are also depicted in Fig.7 with symbol‘◆’.For a given temperature and initial condition,the Newton-Raphson iteration gives only one solution of plate deflection,but good agreement between the numerical iterative result and the multi-mode solution is discovered.
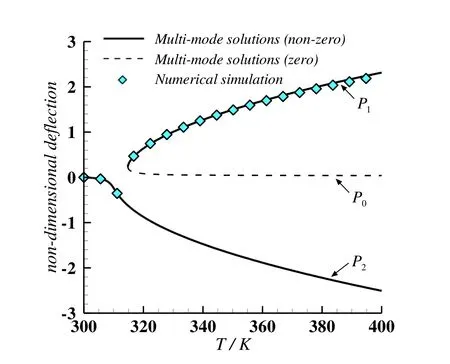
Figure 7:Asymmetrical postbuckling paths of a simply supported FG plate.
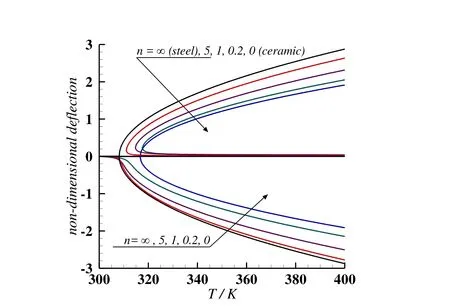
Figure 8:Thermal postbuckling paths of simply supported FG plates with various gradient indexes.
Fig.8 shows the variation in non-dimensional central plate deflection w/h against temperature change for simply supported FG plates with gradient indexes as n=0,0.2,1,5 and∞.It is seen that asymmetrical postbuckling branches of the temperature-deflection curve exist for most simply supported FG plates.But bifurcation buckling behavior reappears for FG plates with gradient indexes as n=0 and∞,which refer to the pure ceramic and pure metal plate,respectively.It is also shown in Fig.8 that the postbuckling deflection decreases with the gradient index of FG plates decreasing(more ceramic constituent).
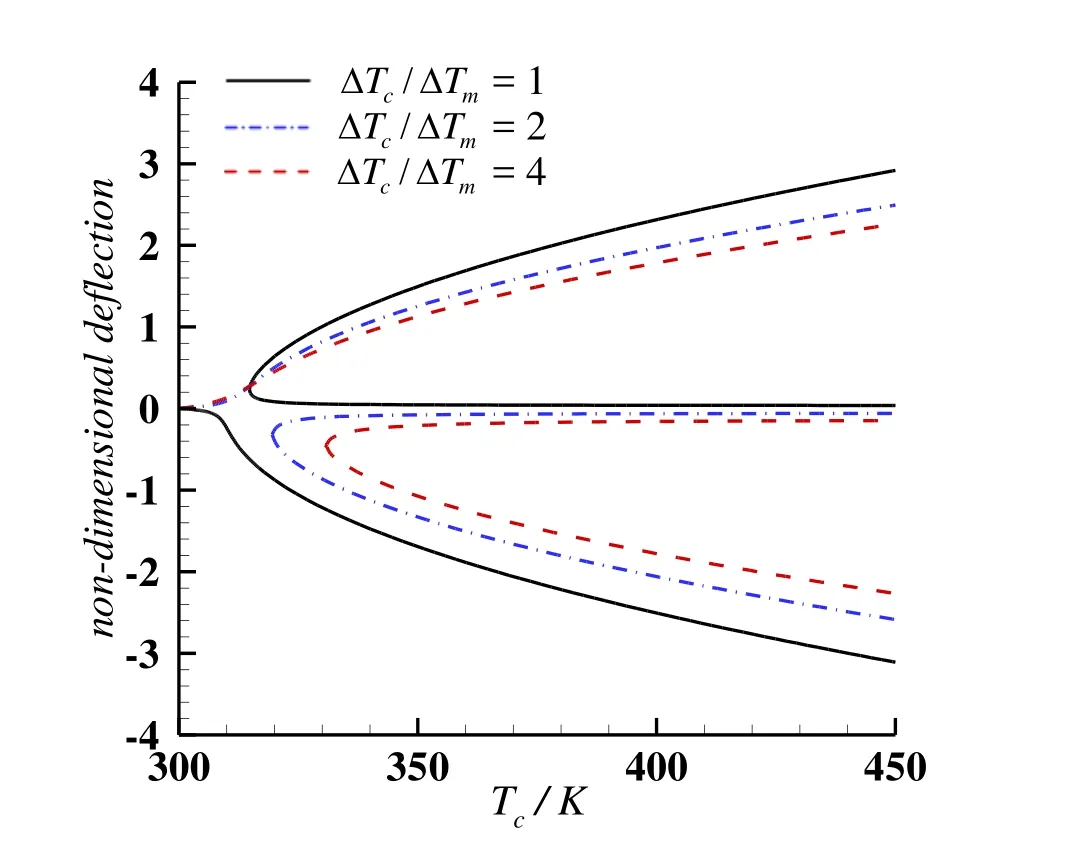
Figure 9:Thermal postbuckling paths of a simply supported FG plate under different temperature distribution.
The thermal postbuckling paths of the simply supported FG plate with non-uniform temperature distributions are further investigated.The temperature distribution along the plate thickness i/s governed by Eq.16,and the top/bottom temperature rise ratio is chosen as?Tc?Tm=1,2 /and 4.Fig.9 shows the variation in nondimensional central plate deflection wh against temperature change for simply supported FG plates with the gradient index as n=1 under different temperaturefield.It is seen in Fig.9 that postbuckling branches of the temperature-deflection curve under n/on-uniform temperature distribution with top/bottom temperature rise ratios as?Tc?Tm=2 and 4 are quite d/ifferent from the postbuckling branch under uniform temperature distribution(?Tc?Tm=1).Because the negative value of deflection is larger than the positive value of deflection for FG plate under uniform temperature distribution,the negative deflection branch(bending to the metal-rich side)represents the postbuckling amplitude o/f the simply supported plate.But for non-uniform temperature distribution of?Tc?Tm=2 and 4,the positive value of deflection is larger than the negative value.Thus the positive deflection branch(bending to the ceramic-rich side)represents the postbuckling amplitude of the FG plate.For a given temperature at the top side of the plate(Tc),the value of postbuckling deflection decreases with the top/bottom temperature rise ratio increasing.
5 Conclusions
Thermal buckling and postbuckling behavior of FG plates has been investigated using an approximated multi-mode method.Numerical studies are conducted to examine the effect of boundary condition,material distribution and temperature distribution on the postbuckling response of ceramic-metal FG plates.The following conclusions are reached:(1)MIN3 element has good convergence property in modeling the FG plate and performing the thermal buckling analysis.The multimode method based on the finite element model provides an efficient and accurate approach to study the asymmetrical postbuckling behavior of the FG plate.(2)Typical bifurcation buckling phenomenon is found in the clamped FG plate,regardless of the length-to-thickness ratio and the gradient index variation.The ceramic-metal FG plate with more ceramic constituent is more stiffen and not ease to buckle(higher critical buckling temperature and lower postbuckling deflection)with temperature elevation.(3)Three deformed configurations may exist for a simply supported FG plate under given thermal load,and the transverse deflection occurs no matter how small the temperature rise.Then no bifurcation buckling occurs for the simply supported FG plate.For uniform temperature distribution,the bending deflection branch to the metal-rich side represents the postbuckling amplitude of the simply supported FG plate.While for non-uniform temperature distribution,the bending deflection branch to the ceramic-rich side represents the postbuckling amplitude of the simply supported ceramic-metal FG plate.
Acknowledgement: The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant no.11302162),Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Grant no. 201102011 20023),and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(Xi’an Jiao-tong University).This research was also supported in part by Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China(Program no.2013JQ1005).
Aydogdu,M.(2008):Conditions for functionally graded plates to remain flat under in-plane loads by classical plate theory.Composite Structures,vol.82,no.1,pp.155-157.
Birman,V.;Byrd,L.W.(2007):Modeling and analysis of functionally graded materials and structures.Applied Mechanics Reviews,vol.60,pp.195-216.
Cai,Y.C.;Atluri,S.N.(2012):Large rotation analyses of plate/shell structures based on the primal variational principle and a fully nonlinear theory in the updated Lagrangian co-rotational reference frame.CMES:Computer Modeling in Engineering&Sciences,vol.83,no.3,pp.249-273.
Dong,L.;El-Gizawy,A.S.;Juhany,K.A.;Atluri,S.N.(2014):A simple locking-alleviated3D 8-node mixed-collocation C0 finite element with over-integration for functionally-graded and laminated thick-section plates and shells,with&without Z-pins.CMC:Computers,Materials&Continua,vol.41,no.3,pp.163-192.
Ibrahim,H.H.;Tawfik,M.;Al-Ajmi,M.(2008):Non-linear panel flutter for temperature-dependent functionally graded material panels.Computational Mechanics,vol.41,no.2,pp.325-334.
Iooss,G.;Joseph,D.D.(1980):Elementary Stability and Bifurcation Theory.Springer.
Javaheri,R.;Eslami,M.R.(2002):Thermal buckling of functionally graded plates.AIAA Journal,vol.40,no.1,pp.162-169.
Jha,D.K.;Kant,T.;Singh,R.K.(2013):A critical review of recent research on functionally graded plates.Composite Structures,vol.96,pp.833-849.
Lee,S.L.;Kim,J.H.(2010):Thermal post-buckling and the stability boundaries of structurally damped functionally graded panels in supersonic airflows.Composite Structures,vol.92,no.2,pp.422-429.
Li,S.R.;Zhang,J.H.;Zhao,Y.G.(2007):Nonlinear thermomechanical postbuckling of circular FGM plate with geometric imperfection.Thin-Walled Structures,vol.45,no.5,pp.528-536.
Ma,L.S.;Wang,T.J.(2004):Relationships between axisymmetric bending and buckling solutions of FGM circular plates based on third-order plate theory and classical plate theory.International Journal of Solids and Structures,vol.41,pp.85-101.
Na,K.S.;Kim,J.H.(2004):Three-dimensional thermal buckling analysis of functionally graded materials.Composites Part B:Engineering,vol.35,no.5,pp.429-437.
Prakash,T.;Singha,M.K.;Ganapathi,M.(2008):Thermal postbuckling analysis of FGM skew plates.Engineering Structures,vol.30,no.1,pp.22-32.
Prakash,T.;Singha,M.K.;Ganapathi,M.(2009a):Influence of neutral surface position on the nonlinear stability behavior of functionally graded plates.Computational Mechanics,vol.43,no.3,pp.341-350.
Prakash,T.;Singha,M.K.;Ganapathi,M.(2009b):Thermal snapping of functionally graded materials plates.Materials and Design,vol.30,no.10,pp.4532-4536.
Reddy,J.N.;Chin,C.D.(1998):Thermomechanical analysis of functionally graded cylinders and plates.Journal of Thermal Stresses,vol.21,no.6,pp.593-626.
Reddy,J.N.(2000):Analysis of functionally graded plates.International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,vol.47,no.1-3,pp.663-684.
Shen,H.S.(2007):Thermal postbuckling behavior of shear deformable FGM plates with temperature-dependent properties.International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,vol.49,no.4,pp.466-478.
Singha,M.K.;Prakash,T.;Ganapathi,M.(2011):Finite element analysis of functionally graded plates under transverse load.Finite Elements in Analysis and Design,vol.47,no.4,pp.453-460.
Sohn,K.J.;Kim,J.H.(2008):Structural stability of functionally graded panels subjected to aero-thermal loads.Composite Structures,vol.82,no.3,pp.317-325.
Tessler,A.;Hughes,T.(1985):A three-node Mindlin plate element with improved transverse shear.Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,vol.50,pp.71-101.
Wu,L.(2004):Thermal buckling of a simply supported moderately thick rectangular FGM plate.Composite Structures,vol.64,no.2,pp.211-218.
Yang,J.;Liew,K.M.;Kitipornchai,S.(2006):Imperfection sensitivity of the post-buckling behavior of higher-order shear deformable functionally graded plates.International Journal of Solids and Structures,vol.43,no.17,pp.5247-5266.
1Corresponding author.State Key Laboratory for Strength and Vibration of Mechanical Structures,School of Aerospace,Xi’an Jiaotong University,28 Xianning West Road,Xi’an 710049,P.R.China.Tel:86-29-82668754;E-mail:xwei@mail.xjtu.edu.cn
2State Key Laboratory for Strength and Vibration of Mechanical Structures,School of Aerospace,Xi’an Jiaotong University,Xi’an 710049,P.R.China.
3State Key Laboratory for Strength and Vibration of Mechanical Structures,School of Aerospace,Xi’an Jiaotong University,Xi’an 710049,P.R.China.

