Impacts of Power Density on Heavy Metal Release During Ultrasonic Sludge Treatment Process*
Impacts of Power Density on Heavy Metal Release During Ultrasonic Sludge Treatment Process*
ZHANG Guangming (張光明)1,**, WAN Tian (萬甜)2, GAO Feng (高峰)2and DONG Shan (董姍)2
1School of Environment & Natural Resource, Renmin University of China, Beijing 100872, China
2State Key Lab of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150090, China
The impact of ultrasonic power density on changes of heavy metals during sludge sonication was investigated. Results showed that ultrasound could release heavy metals from sludge into the supernatant. There existed an effective power density range of 0.8-1.6 W·ml?1for the release of the total heavy metal; there was little release below 0.8 W·ml?1and too high power density was adverse to the release. Furthermore, sonication showed selective release of heavy metal from sludge to the supernatant; copper, cadmium and lead were not released by sonication, while arsenic and nickel were released easily and their release ratio could reach 40%. The effective energy range for each heavy metal was also different that 0.8-1.2 W·ml?1for arsenic, 0.5-1.6 W·ml?1for nickel, and 0.8-1.6 W·ml?1for mercury and chrome. The differences among heavy metal release during sonication might be explained by the different distribution of chemical fractions of each metal in sludge. Such selectivity could be used to control heavy metal release during sludge treatment.
activated sludge, sonication, metals, power density, chemical fractions
1 INTRODUCTION
Large content of excess sludge are generated during biological wastewater treatment processes. The presence of contaminants such as organics, heavy metals and pathogens in excess sludge poses serious environmental risks, and considerably hampers the final sludge disposal, especially in the agricultural use [1, 2]. Over the past decades, many techniques have been developed for sludge treatment and disposal [3]. Among these techniques, ultrasound is of great values [4].
During ultrasonic sludge treatment process, violent cavitation occurs, which quickly disrupts sludge flocs, breaks cells of sludge bacteria, and thus releases the intracellular and extracellular substances, and inorganic and organic materials trapped in the sludge flocs into the supernatant. Therefore, sludge characteristics such as floc size, viscosity, capillary suction time and soluble organic contents are changed by ultrasound [5, 6]. Those changes are beneficial for improving sludge biodegradability, enhancing the aerobic digestion rate, and cutting down the sludge dewatering time and sludge volume [5-8]. Therefore, sonication can serve as pretreatment of sludge before anaerobic digestion, aerobic fermentation, and mechanical dewatering [7-10]. Alternatively, the sonicated sludge may be recycled into an aeration tank as substances for microorganisms to achieve 60%-100% of sludge reduction in low-sludge wastewater treatment processes [7, 9]. The sonicated sludge may also be used as carbon source for biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal processes [6, 8]. Detailed changes of organic matters and floc morphology during sonication have been reported [7, 9], and change of heavy metals during sonication has also been reported but the details are still unclear [11].
Heavy metals in sludge are of great concerns due to their health and environment impacts. Sludge heavy metals are most of transition elements, which are easily affected by the environmental conditions, such as pH, oxidation reduction potential, temperatures, organic matters and so on [12, 13]. As sonication effectively changes the physical, chemical and morphological properties of sludge, it is reasonable to suppose significant changes of sludge heavy metals during sonication. Such changes of heavy metals might impact the following processes when sonication was used as sludge pretreatment before anaerobic digestion, aerobic fermentation, sludge recycling in low-sludge wastewater treatment processes, and carbon source provision for nitrogen and phosphorous removal processes. Therefore, it is very important to understand the detailed changes of heavy metals during sludge sonication for safe and efficient sludge treatment.
This study investigated the detailed changes of heavy metals during sludge sonication. Since ultrasonic power density was the most significant factor for sonication efficiency [14], the impact of ultrasonic power density was examined.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Sludge and reagents
The studied sludge was collected from a local wastewater treatment plant in Harbin, China. Tables 1 and 2 show the basic properties of the sludge used. Ultra-pure water was used for all experiments andanalysis. All reagents used were of analytical-reagent grade or higher.

Table 1 Physical-chemical characteristics of the untreated sludge

Table 2 Heavy metal content in the untreated sludge (mg·kg?1)
2.2 Experiments
The sonication equipment was a horn-system (JY90-II, Ningbo Haishu Kesheng Ultrasonic Equipment Co., China) that emitted 25 kHz ultrasound waves through a tip with a surface area of 2.12 cm2. The range of ultrasonic power was from 0 to 250 W. Each time 100 ml sludge was put into a 150 ml beaker for sonication, and the probe was dipped 1 cm below the sludge surface in the center of the beaker. The beaker was then put in a water-bath to prevent over heating of sludge. Sonication duration of 15 min was used according to the previous work [9].
The sonicated sludge was centrifuged at 4000 r·min?1using a TCL-16G desk centrifuge (Anting Scientific Apparatus plant in Shanghai, China) in order to separate the solid phase and the liquid phase (supernatant). The supernatant was used for the measurement of supernatant chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) and aqueous heavy metal concentrations, and the solid phase was for the analysis of heavy metal and chemical fractions in sludge.
2.3 Analytical methods
The SCOD, suspended solid content (TSS), and volatile solid content (VSS) were measured according to APHA standard methods [15]. The pH of samples was monitored with a PHS-3C pH meter (Shanghai Precision Scientific Instrument Co., China). The heavy metal concentrations in the supernatant were directly measured by a PerkinElmer Optima 5300 DV ICP (Perkin Elmer Inc., America) [16]. The chemical fraction of heavy metals in the solid phase was analyzed by a five-step sequential extraction procedure [17].
All reported values of each index were average values calculated from duplicate samples.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Ultrasonic release of sludge organics and total heavy metals
The shear force generated in sonication breaks down the bacterial cell wall and releases the intracellular and extracellular substances into the aqueous phase including inorganic and organic materials. Fig. 1 shows the release of organic matters and heavy metals during sonication. Organic matters are largely released by sonication (high released SCOD), which might be contributed by the release of extracellular polymeric substances during floc disintegration and the release of cell components during cells lysis. Heavy metals could also be released, but their concentrations in the aqueous phase are thousands times lower than that of organic matters.
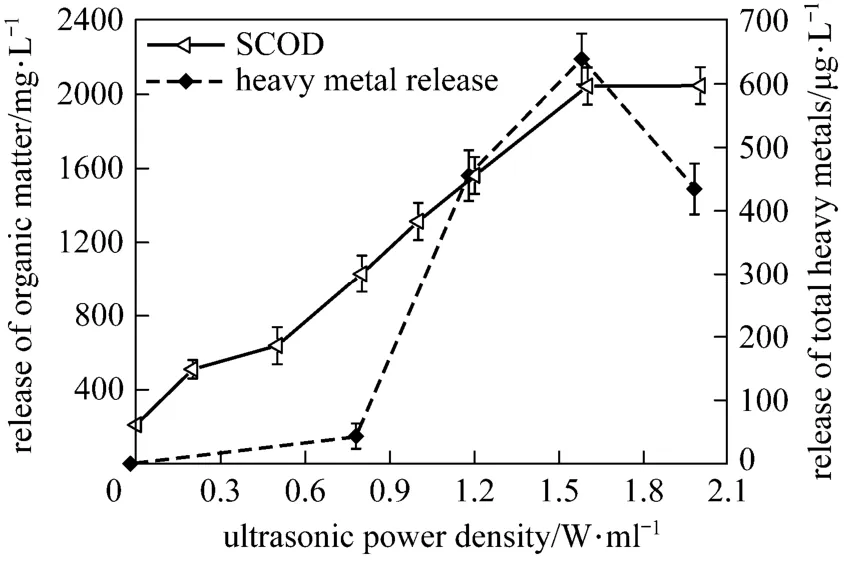
Figure 1 Effect of ultrasonic power density on the release of sludge matters (15 min)
Ultrasonic power density significantly affects the release of both organic matters and heavy metals during sludge sonication. For organic matters, low power density input could cause their release. SCOD concentration increases steadily till the power density reaches 1.6 W·ml?1, and do not change with further increasing power density. For the total heavy metals, the release by sonication is fall-after-rise with the increase of ultrasonic power density. A certain level of ultrasonic power density is needed for heavy metal release and significant increase of metal concentration is observed beyond 0.8 W·ml?1. However, the concentration of total heavy metal in the aqueous phase descends when the power density increases to 2.0 W·ml?1. Therefore, the effective energy range is 0-1.6 W·ml?1for organics release and 0.8-1.6 W·ml?1for total heavy metal release. Energy increase beyond the range is useless or even adverse.
The difference between the release of organic matters and the release of heavy metals might be thatthe combination of heavy metals with the sludge was different from that of organic matters. Large quantity of organic matters exited in the extracellular polymeric substances [5, 8, 18], and even low energy input could loose the sludge floc and release them [9]. High ultrasonic power density was needed to cause acoustic cavitation, which then caused the sludge floc disintegration and cell breakage. Therefore, the released organic matters increased stably with power density increased from 0 to 1.6 W·ml?1. However, it was reported that when ultrasound power density increased beyond the most efficient level, the cavitation decreased with the increased power density, and the sludge disintegration thereby became weak [8, 18].
Heavy metals combined with sludge more complexly [19]. Chemical fractions of heavy metals in the untreated sludge were examined, namely exchangeable (F1), carbonated-bound (F2), Fe/Mn oxides-bound fraction (F3), organically-bound (F4) and residual (F5). According to the determination of the five chemical fractions [17], F1, F2 and F3 are considered to be unsteady forms, while F4 and F5 are considered as stable ones [20]. The results are reported in Fig. 2. The most unsteady fractions (sum of F1 and F2) account for only about 10% in the untreated sludge, and therefore the release of heavy metals by sonication is not obvious at a low power density. With powerful energy inputting, the biting forces between heavy metals and sludge are weakened and more heavy metals could be released. However, sonication with higher power density might greatly disintegrate sludge matrix, and the floc size became smaller, which could supply large surface areas. The released heavy metals in the aqueous phase are then re-adsorbed by the small flocs with huge surface areas. Therefore, beyond 1.6 W·ml?1, the re-adsorption of heavy metal onto flocs exceeds the release of heavy metals from sludge, and the aqueous total heavy metals finally decreases.

Figure 2 Chemical fractions of total heavy metals in the untreated sludge
3.2 Ultrasonic release of individual heavy metals from sludge
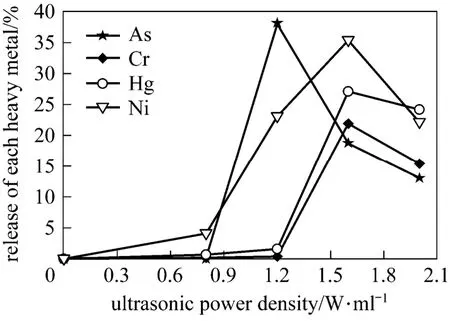
Figure 3 Release of each heavy metal by sonication (15 min)
Ultrasonic power density greatly affects the release of each heavy metal during sonication (Fig. 3). Seven typical heavy metals are detected in the untreated sludge, namely copper, nickel, chrome, mercury, lead, arsenic and cadmium. After sonication, arsenic, nickel, chrome and mercury can be released, and all their release curves show fall-after-rise pattern. Other metals such as copper, lead and cadmium are released little during sonication with power density of 0-2.0 W·ml?1. Therefore, sonication can selectively release heavy metal from the sludge.
Furthermore, for the four heavy metals that could be released by sonication, the effective energy range of each metal release is also different. For arsenic, low power density (lower than 0.8 W·ml?1) sonication has no effect on the release from sludge, and the release is naught. Power density of 1.2 W·ml?1is the most efficient for the release of arsenic and about 40% of arsenic is released from sludge. Therefore, the effective energy range for arsenic release is 0.8-1.2 W·ml?1.
For nickel, it can be released at low power density (0.5 W·ml?1) in spite that vary low concentration is detected. With increased power density, the released concentration increases sharply. When power density reaches 1.6 W·ml?1, the release of nickel increases to 38%. The energy work range for nickel release is 0.5-1.6 W·ml?1.
For chrome and mercury, the released concentration increases slowly at low power density, then increases sharply and finally decreases when power density reaches 1.6 W·ml?1. The work range for release of these two metals is 0.8-1.6 W·ml?1. The highest release ratio for chrome and mercury is 21% and 26%, respectively.
The possible explanation for the different changes of heavy metals is that each metal showed different characteristics and chemical forms. The five chemical fractions of each heavy metal in the untreated sludge are examined and the distributions are reported in Fig. 4. For arsenic and nickel, unsteady fractions are high, resulting in the high release ratio from sludge and the wide energy work range as well. For chrome, fractions of F3 and F4 are the main forms with 55% and 42%, respectively. Therefore, the energy work range for release of chrome is narrower than nickel and arsenic. For mercury, fraction of F5 is the major fraction, however, mercury is a metalloid and its characteristics are relatively unstable [11]. The combination between mercury and sludge may be torn apart by the shear force during sonication. Besides,strong stirring during sonication also increased the sludge temperature by 10-20 °C [18], which may also contribute to mercury release. For cadmium, copper and lead, the stable fractions are high, and the combination force of these metals with sludge may be stronger than other metals. Therefore, little change can be observed during sonication.
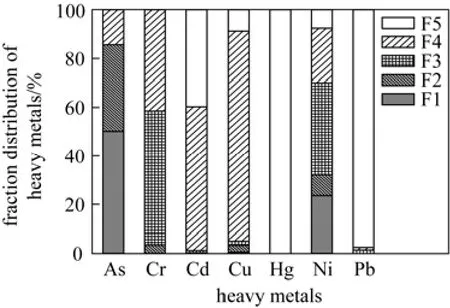
Figure 4 Heavy metals chemical fraction distributions in the untreated sludge
3.3 Potential applications
According to the investigation of heavy metal release during sonication, an energy work range of heavy metal release by sonication with power density of 0.8-1.6 W·ml?1was found. Too low or too high power density was not effective for heavy metal release. This new finding that the heavy metals can be removed from sludge within an energy range is useful for sludge treatment. For example, carbon source is normally insufficient in the biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal processes. As a counter measure, sonicated sludge can be put into the aeration tank as carbon source supplement. If the power density is controlled lower than the energy work range of heavy metal release, the sonicated sludge would supplement carbon source without heavy metals.
Furthermore, as it was shown in the results, different heavy metals could be selectively released by sonication. Therefore, the power density of ultrasound could be adjusted for separating metals in a multi-metal system, which is beneficial for heavy metals recovery.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study investigated the impact of ultrasonic power density on release of heavy metals in sludge during ultrasonic treatment. Several conclusions could be obtained as follows:
Sonication released the organic matter and heavy metals. The released amount of the total heavy metals was far less than that of organic matter within power density range of 0-2.0 W·ml?1. The release of total heavy metals showed a pattern of fall-after-rise with the increased power density.
There was an effective energy range of 0.8-1.6 W·ml?1for heavy metals release. The heavy metals in sludge could be effectively removed if power density was adjusted in the work range. Beyond the work range, more energy inputs were not good. Besides, the sonicated sludge could be safely recycled to wastewater treatment process as carbon source if the power density was adjusted lower than the work range.
The release of each heavy metal had its individual energy work range, and the mechanism might be determined by the chemical fractions of each heavy metal in sludge. Nickel and arsenic had a wide energy work range since their unsteady fractions were high. Mercury and chrome could be released but the energy range was narrow. Other metals could not be released during sonication.
REFERENCES
1 Brisolara, K.F., Qi, Y.N., “Biosolids and sludge management”, Water Environ. Res., 82 (10), 1311-1326 (2010).
2 Mungray, A.K., Murthy, Z.V.P., Tirpude, A.J., “Post treatment of up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket based sewage treatment plant effluents: A review”, Desal. Wat. Treat., 22 (1-3), 220-237 (2010).
3 Dogan, I., Sanin, F.D., “Alkaline solubilization and microwave irradiation as a combined sludge disintegration and minimization method”, Water Res., 43, 2139-2148 (2009).
4 Bougrier, C., Albasi, C., Delgenès, J.P., Carrère, H., “Effect of ultrasonic, thermal and ozone pretreatments on waste activated sludge solubilization and anaerobic biodegradability”, Chem. Eng. Process., 45 (8), 711-718 (2006).
5 Erden, G., Filibeli, A., “Ultrasonic pre-treatment of biological sludge: consequences for disintegration, anaerobic biodegradability, and filterability”, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 85, 145-150 (2010).
6 Na, S., Kim, Y.U., Khim, J., “Physiochemical properties of digested sewage sludge with ultrasonic treatment”, Ultrason. Sonochem. 14 (3), 281-285 (2007).
7 Yoon, S., Kim, H., Lee, S., “Incorporation of ultrasonic cell disintegration into a membrane bioreactor for zero sludge production”, Process Biochem., 39 (12), 1923-1929 (2004).
8 Wang, F., Lu, S., Ji, M., “Components of released liquid from ultrasonic waste activated sludge disintegration”, Ultrason. Sonochem., 13, 334-338 (2006).
9 Zhang, G., Zhang, P., Yang, J., Chen, Y., “Ultrasonic reduction of excess sludge from the activated sludge system”, J. Hazard. Mater., 145 (3), 515-519 (2007).
10 Muller, C.D., Abu-Orf, M., Blumenschein, C.D., Novak, J.T., “A comparative study of ultrasonic pretreatment and an internal recycle for the enhancement of mesophilic anaerobic digestion”, Water Environ. Res., 81 (12), 2398-2410 (2009).
11 Laurent, J., Pierra, M., Casellas, M., Dagot, C., “The fate of heavy metals during thermal and ultrasound treatment of activated sludge”, Environ. Prot. Eng., 35 (3), 5-15 (2009).
12 Sauvé, S., Hendershot, H., Allen, H.E., “Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: dependence on pH total metal burden and organic matter”, Environ. Sci. Technol., 34 (7), 1125-1131 (2000).
13 Masood, F., Malik, A., “Biosorption of metal ions from aqueous solution and tannery effluent by Bacillus sp. FM1”, J. Environ. Sci. Health. Part A: Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng., 46 (14),1667-1674 (2011).
14 Zhang, G., Zhang, P., Yang, J., Liu, H., “Energy-efficient sludge sonication: Power and sludge characteristics”, Bioresour. Technol., 99, 9029-9031 (2008).
15 Clesceri, L., Greenberg, A., Eaton, A., Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C. (1998).
16 Dewil, R., Baeyens, J., Roelandt, F., Peereman, M., “The analysis of the total sulphur content of wastewater treatment sludge by ICP-OES”, Environ. Sci. Tech., 23, 904-907 (2007).
17 Tessier, A., Compbell, P.G., Bisson, M., “Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals”, Anal. Chem., 51 (7), 844-850 (1979).
18 Dewil, R., Baeyens, J., Goutvrind, R. “The use of ultrasonics in the treatment of waste activated sludge”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 14 (1), 105-113 (2006).
19 Fuents, A., Llorens, M., Saez, J., Aguilar, M.I., Ortuno, J.F., Meseguer, V.F., “Comparative study of six different sludges by sequential speciation of heavy metals”, Bioresour. Technol., 99, 517-525 (2008).
20 Zorpas, A.A., Inglezakis, V.J., Loizidou, M., “Heavy metals fractionation before, during and after composting of sewage sludge with natural zeolite”, Waste Manage., 28, 2054-2060 (2008).
2012-08-25, accepted 2013-01-25.
* Supported by the Basic Research Funds in Renmin University of China from the center government (12XNL101).
** To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: zgm200@126.com
 Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2014年4期
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2014年4期
- Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- PVC Membrane Selective Electrode for Determination of Cadmium(II) Ion in Chocolate Samples
- Determination and Correlation of Solubilities of Four Novel Benzothiazolium Ionic Liquids with6PF?in Six Alcohols*
- An Approach to Formulation of FNLP with Complex Piecewise Linear Membership Functions
- One Step Preparation of Sulfonated Solid Catalyst and Its Effect in Esterification Reaction*
- Determination and Correlation of Solubility for D-Xylose in Volatile Fatty Acid Solvents*
- Effects of Assistant Solvents and Mixing Intensity on the Bromination Process of Butyl Rubber*
