Structure of Mitochondrial DNA Control Region of Pholis fangi and Its Phylogenetic Implication
LI Lin, ZHANG Hui, SUN Dianrong, and GAO Tianxiang,
1) Institute of Evolution and Marine Biodiversity, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, P. R. China
2) South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Guangzhou 510300, P. R. China
Structure of Mitochondrial DNA Control Region of Pholis fangi and Its Phylogenetic Implication
LI Lin1), ZHANG Hui1), SUN Dianrong2),*, and GAO Tianxiang1),*
1) Institute of Evolution and Marine Biodiversity, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, P. R. China
2) South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Guangzhou 510300, P. R. China
In this study, the entire mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) control region (CR) ofPholis fangiwas amplified via polymerase chain reaction followed by direct sequencing. The length of the mtDNA CR consensus sequence ofP. fangiwas 853 bp in length. In accordance with the recognition sites as were previously reported in fish species, the mtDNA CR sequence ofP. fangican be divided into 3 domains,i.e., the extended terminal associated sequence (ETAS), the central conserved sequence block (CSB), and the CSB domain. In addition, the following structures were identified in the mtDNA CR sequence ofP. fangi: 2 ETASs in the ETAS domain (TAS and cTAS), 6 CSBs in the central CSB domain (CSB-F to CSB-A), and 3 CSBs in the CSB domain (CSB-1 to CSB-3). These demonstrated that the structure of the mtDNA CR ofP. fangiwas substantially different from those of most other fish species. The mtDNA CR sequence ofP. fangicontained one conserved region from 656 bp to 815 bp. Similar to most other fish species,P. fangihas no tandem repeat sequences in its mtDNA CR sequence. Phylogenetic analysis based on the complete mtDNA CR sequences showed that there were no genetic differences withinP. fangipopulations of the same geographical origin and betweenP. fangipopulations of different geographical origins.
Pholis fangi; mitochondrial DNA; control region; structure; phylogenetic relationship
1 Introduction
Pholis fangi, formerlyEnedrias fangi, belongs to order Perciformes, family Pholidae.P. fangiis an offshore cold temperate species of demersal fish, which mainly inhabits Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea (Chenget al., 1987; Yamadaet al., 2007) and spawns from September to November offshore (Yamadaet al., 2007). The pelagic larvae ofP. fangimove into inshore waters and grow there until they return to offshore waters in June. While migrating offshore, the pelagic larvae transformed into demersal juveniles.P. fangiis supposed to stay offshore in summer; few are caught inshore from July to September (Bi, 2005; Hwanget al., 2008). When used as the feed of large-scale commercial fish,P. fangiplays a role in the transfer of energy and matter within fish food chain. In recent years,P. fangihas become one of the most commercially and ecologically important fish species in Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea due to the decline of offshore fishery resources (Liet al., 2011; Bi, 2005). At different life stages, larvae are the most commercially important form ofP. fangi(Bi, 2005; Hwanget al., 2008). In order to prevent its overexploitation, the basic genetic information ofP. fangineeds to be interpreted.
The mitochondrial genome has been widely used as a marker for evolutionary and population studies because of its compact size, fast evolutionary rate, and exclusive maternal mode of inheritance (Brownet al., 1979; Harrison, 1989). The mitochondrial genome of vertebrates is a small, closed circular molecule, which contains 2 rRNAs, 22 tRNAs, 13 enzymes encoding genes and a control region (CR) that regulates the replication of H strand and transcription of all mitochondrial (mtDNA) genes (Clayton, 1992). The mtDNA CR, also known as displacement-loop (D-loop) region, located between the tRNAPheand the tRNAProin the mtDNA. The mtDNA CR is the major non-coding segment in the vertebrate mitochondrial genome (Shuiet al., 2008). Some portions of the mtDNA CR evolve much faster than the average because of the reduced functional constraints (Brown, 1985). The segments are directly adjacent to the flanking tRNAs commonly show the highest rates of base substitutions and insertion/deletion events (Sacconeet al., 1987). The mtDNA CR contains several conserved domains, structurally, the extended termination associated sequence (ETAS), the central conserved sequence block (CSB or CD), and the CSB domain (Sbisaet al., 1997; Southernet al., 1988; Liu, 2002). In some animals, tandemly repeated sequences exist near the 5’ and 3’ ends of the mtDNA CR, ranging from 4 to hundreds of nucleotides insize and 2 to over 100 copies in abundance (Luntet al., 1998). The length of the mtDNA CR changes in correspondence with the variations in the number of tandem repeats.
In the present study, the variable sequences and basic structural characteristics of the mtDNA CR ofP. fangiwere investigated. The phylogenetic relationship ofP. fangipopulations was evaluated based on the complete mtDNA CR sequences obtained. The results will provide useful information for understanding the genetic diversity ofP. fangi.
2 Materials and Methods
2.1 Sample Information
Forty-fiveP. fangispecimens were collected from 9 different populations, Northern Yellow Sea (NYS), Dalian (DL), Laizhou Bay (LZB), Yantai (YT), Rushan (RS), Qingdao (QD), and Rizhao (RZ1, RZ2, and RZ3), 5 each (Fig.1). Muscle was preserved in 95% ethanol.

Fig.1 Sample distribution of Pholis fangi in Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea, China.
2.2 DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
The muscle tissue was minced and then digested with proteinase K. Total genomic DNA was isolated using the standard phenol-chloroform extraction method (Sambrook, 1989). The complete mtDNA CR sequences were amplifiedviatwo-step PCR reactions using the primer sets Dl-S/D1-R (Hanet al., 2008) and LL-CR/CR (Chenet al., 2012). The LL-CR was newly designed as 5’-GTAAACATCCCCATAACTTA-3’. The 50 μL PCR reactions contained 20–50 ng template DNA, 5 μL of 10×PCR buffer, 2 μL of dNTP (10mmol L-1each), 2 μL of each primer (10 μmol L-1), 1 μL ofTaqDNA polymerase, and 36 μL of H2O. PCR amplification was carried out on an Eppendorf Mastercycler (Eppendorf 5533, Hamburg, Germany) under the following conditions: initial denaturation at 94℃ for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 94℃ for 45 s, annealing at 52℃ for 45 s, and extension at 72℃ for 45 s, and a final extension at 72℃for 10 min (Zhanget al., 2011). PCR products were separated through 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. Purified PCR products were used as the template for cycle sequencing reactions performed with the BigDye terminator cycle sequencing kit v2.0 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA). Sequencing was conducted on an ABI Prism 3730 automatic sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA) using both forward and reverse primers for PCR amplification.
2.3 Sequence Analysis
Sequences were edited and aligned using the DNAStar software (DNASTAR, Inc., Madison, USA) and then manually refined. The nucleotide compositions were calculated in MEGA 4.0 (Tamuraet al., 2007). The gamma distribution shape parameters for the rates sites of heterogeneity were calculated using Modeltest 3.7 (Posadaet al., 1998).
2.4 Phylogenetic Analysis
The phylogenetic relationship ofP. fangiwas evaluated based on complete mtDNA CR sequences. Phylogenetic trees were constructed with MEGA 4.0 using neighbor joining (NJ) and Bayesian method withP. crassispina(GenBank accession no. AP004449) as outgroup. The optimized parameters and the optimal bases substitution model for NJ analysis were estimated by Modeltest 3.7 (Posadaet al., 1998) using the hierarchical likelihood ratio tests (hLRTs). The best model for the complete mtDNA CR sequences was HKY+I+G (I = 0.6743, G = 0.8821). NJ tree was reconstructed using PAUP* (Swofford, 2002). Bayesian analysis was conducted using MrBayes 3.1.2 (Huelsenbecket al., 2001; Ronquistet al., 2003).
3 Results
3.1 Structure of the mtDNA CR
The length of the entire mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangiwas 853 bp in length, showing no obvious variability among the 45 individuals. The average content of A+T was 31.7+29.8, higher than G+C content (17.6+20.9). In accordance with the recognition sites previously reported in fish species, we divided the obtained mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangiinto 3 domains, ETAS, central CSB or CD, and CSB. No tandem repeat sequence was found in the mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangi.
One ETAS domain was recognized in the mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangi(Fig.2). A termination associated sequence (TAS) motif (GACAT) was found in the 5’ end of mtDNA CR sequences, and a complementary TAS (cTAS) motif (ATGTA) was observed downstream of the TAS motif. The third motif (ACAT) detected in the mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangihad four copies, being distinctively different from the reported in other marine fish species.
In central CSB, all of the 6 CSBs, A to F, were found. The central CSB domain was distinguished from the ETAS domain in the CSB-F. In the present study, the key identical sequence of CSB-F was ATGTAGTAAGAACCGACCA (Fig.2). CSB-E characterized by the box GTGGGG located downstream CSB-F. The key consensus sequence of CSB-E was AGGGACAAGTATTGTGGGGGT, in which the ‘-’ indicated nucleotide variations such as transitions, transversions and indels (Fig.2). The CSB-D located downstream CSB-E had the consensus sequence TATTCCTGGCATTTGGTTCCTA (Fig.2). The CSB-C, CSB-B and CSB-A following CSB-D had the key sequences CTTTCATCGACGCTT-CATAAGTTA, CGAGATGACCCAGCATGCCG- and ATCGGGCAAG GGGTTCTCTTTTT, respectively. These sequences were highly conserved and easily recognized in the central CSB domain.
Three CSBs, 1 to 3, were detected in CSB domain. Their consensus sequences were ATTACATAAGAATGCATA, TAAAACCCCCCTACCCCCC and TGAAAA CCCCCGGAAACA, respectively (Fig.2). CSB1 was the first part of the CSB domain. Compared to the sequence of CSB1, the sequences of CSB2 and CSB3 were more conservative. One conserved region (conservation = 1.000; homozygosity = 1.000;P= 0.035) existed in the mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangifrom 656 bp to 815 bp (Fig.2).

Fig.2 Structure of the mitochondrial DNA control region of Pholis fangi. The longer bars above the base indicate the consensus strength of 45 sequences obtained in this study; and the short ones indicate the nucleotide variations among the obtained sequences.
3.2 Phylogenetic Implication of the Complete mtDNA CR Sequences
The genetic differentiation and phylogenetic relationship of the 45P.fangiindividuals were evaluated based on the complete mtDNA CR sequences obtained in this study (total length = 853 bp).
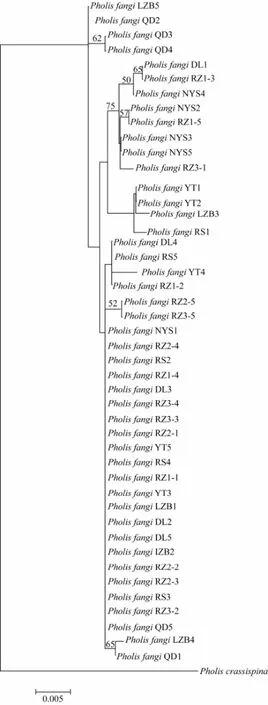
Fig.3 Neighbor-joining tree of 45 Pholis fangi individuals based on the complete mitochondrial DNA CR sequences. Bootstrap values were calculated based on 1000 replicates.
The NJ and Bayesian trees reconstructed based on the complete mtDNA CR sequences are highly similar, showing that all the 45P. fangiindividuals were grouped regardless of their geographic origin (Fig.3).
4 Discussion
The mtDNA CR is a unique and highly variable region characterized by fast evolution and non-protein coding function (Sbisaet al., 1997). Our findings in the present study demonstrated that the length of the complete consensus mtDNA CR sequence ofP. fangiwas 853 bp in length without any deletion/insertion or repeat. Similar to that of other vertebrates, the complete mtDNA CR ofP. fangicontained 3 domains, ETAS, central CSB and CSB. As the first reported by Dodaet al. (1981), the ETAS domain contains TAS elements, which are closely related to the termination of the nascent H strand during replication. In addition, Sbisaet al. (1997) recognized two conservative blocks, ETAS1 and ETAS2, putatively playing an important role in regulation of replication and transcription. In the present study, only one ETAS domain was found in the mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangi. A TAS motif (GACAT) which was proposed to act as a sequence-specific signal for the termination of the control region synthesis was found at the 5’ end of the mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangi. There was a transversion compared to the putative TAS elements with the motif of other fish species (Liu, 2002). In addition, we detected a cTAS motif (ATGTA) downstream TAS motif, which was common among marine fish species (Zhanget al., 2011). Of note, a third motif (ACAT) was found to have four copies, which was a special characteristic of the complete mtDNA CR ofP.fangi.
Despite of being highly conservative in fish, the function of central CSB domain remains largely unclear (Sbisaet al., 1997). Southernet al. (1988) first identified the conserved sequences CSB-F, CSB-E, CSB-D, CSB-C and CSB-B in the central CSB domain of mammals. Generally, only CSB-F, CSB-E and CSB-D are recognizable among most fish species (Broughton and Dowling, 1994). However, in the present study, we detected all of the 6 CSBs in the mtDNA CR ofP. fangias were reported in 15 fish species of Pleuronectiformes (Heet al., 2007, Zhanget al., 2011). The central CSB domain is likely more conservative in Pleuronectiformes andP. fangi; only CSB-C, CSB-B and CSB-A existed (Heet al., 2007; Zhanget al., 2011). Similar to other fish species, CSB-F is the key feature which distinguishes the ETAS from the central CSB domain. In addition, the 6 CSBs (A to F) were highly conservative in the mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangi, and the consensus sequences of CSB-F, CSB-E, CSB-D, CSB-C, and CSB-A were consistent with those described in other fish species (Liu, 2002; Heet al., 2007). An exception was that the sequence of CSB-B was slightly different from that of other fish species (Heet al., 2007).
In the CSB domain, CSB1 is associated with the initiation of mtDNA duplication. CSB1 is highly conservativein mammals (Sbisaet al., 1997) but variable in fish species (Liu, 2002; Zhanget al., 2003; Guoet al., 2003). In the present study, however, the sequence of CSB-1 was found to be almost identical among 45P. fangiindividuals. The sequences of CSB-2 and CSB-3 were completely conservative, which was consistent with those of other fish species (Liu, 2002). One conserved region existed in the mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangi(656 to 815 bp). These conserved structures are the characteristics of the CSBs in the mtDNA CR ofP.fangi.
Ubiquitous CSB-2 and CSB-3 can be used to examine potential existence of repeat sequences in the mtDNA CR of vertebrates (Zhanget al., 2012). Previously, tandem repeats were found in the mtDNA CR and mostly between the ETAS region and the central conserved region in some reptiles, such asPhoca vitulina(Arnason and Johnsson, 1992) andAcipenser sinensis(Zhanget al., 2000). In the present study, CSB-2 and CSB-3 were found to be nearly identical among 45P.fangiindividuals. No tandem repeat sequences were detected in the mtDNA CR inP. fangi, which was consistent with most other marine fish species.
In this study, the complete mtDNA CR sequences ofP. fangiwere obtained and then used to evaluate the phylogenetic relationship of 45P.fangiindividuals with the NJ and Bayesian methods. The 45 individuals were grouped into differed clusters regardless of their geographic origins. Being an offshore fish species,P. fangispends a considerable part of their life migrating between offshore and inshore waters (Bi, 2005; Hwanget al., 2008). As a result, they are less affected by inshore hydrological conditions which restrict the dispersal. This may be the main reason for the lack of genetic heterogeneity in the 45 individuals ofP.fangi. Considering the small sample size in the present study, future investigation is needed to analyze the population genetic structure ofP.fangi. Since the present work provided baseline information on genetic background ofP.fangi, it contributes to population conservation and fisheries management of this fish species as well as its relatives.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean (Nos. 201305043 and 201405010).
Arnason, U., and Johnsson, E., 1992. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the harbor seal, Phoca vitulina. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 34 (6): 493-505.
Bi, Y. B., 2005. Biology and its fishery of Fang’s blenny Enedrias fangi Wang et Wang in offshore in Liaoning Province. Fisheries Science, 24 (9): 27-28 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Broughton, R. E., and Dowling, T. E., 1994. Length variation in mitochondrial DNA of the minnow Cyprinella spiloptera. Genetics, 138 (1): 179-190.
Brown, W. M., 1985. The mitochondrial genome of animals. In: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. MacIntyre, R. J., ed., Plenum Press, New York, 95-130.
Brown, W. M., George, M., and Wilson, A. C., 1979. Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 76 (4): 1967-1974.
Chen, C., Li, Y. L., Wang, L., and Gong, G. Y., 2012. Structure of mitochondrial DNA control region of Argyrosomus amoyensis and molecular phylogenetic relationship among six species of Sciaenidae. African Journal of Biotechnology, 11 (26): 6904-6909.
Cheng, Q. T., and Zheng, B. S., 1987. Chinese Fish System Retrieval. Science Press, Beijing, 394-399 (in Chinese).
Clayton, D. A., 1992. Transcription and replication of animal mitochondrial DNAs. In: International Review of Cytology, Vol 141, Mitochondrial Genomes. Wolstenholme, D. R., and Jeon, K. W., eds., Academic Press, San Diego, 217-323.
Doda, J. N., Wright, C. T., and Clayton, D. A., 1981. Elongation of displacement-loop strands in human and mouse mitochondrial DNA is arrested near specific template sequences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 78 (10): 6116-6120.
Guo, X. H., Liu, S. J., and Liu, Y., 2003. Comparative analysis of the mitochondrial DNA control region in cyprinids with different ploidy level. Aquaculture, 224 (1-4): 25-38.
Han, Z. Q., Gao, T. X., Yanagimato, T., and Sakurai, Y., 2008. Genetic population structure of Nibea albiflora in Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Fisheries Science, 74 (3): 44-552.
Harrison, R. G., 1989. Animal mitochondrial DNA as a genetic marker in population and evolutionary biology. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 4 (1): 6-11.
He, C. B., Cao, J., Liu, W. D., Zhou, Z. C., Ge, L. L., Gao, X. G., and Wang, X. M., 2007. Structure analysis of mtDNA control region of spotted halibut (Verasper variegatus) and its related species. Hereditas, 29 (7): 829-836 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Huelsenbeck, J. P., and Ronquist, F., 2001. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogeny. Bioinformatics, 17 (8): 754-755.
Hwang, S. D., Lee, T. W., and Hwang, S. W., 2008. Age, growth and life history of gunnel, Pholis fangi, in the Yellow Sea. Fisheries Research, 93 (1-2): 72-76.
Li, T., Zhang, X. M., Zhang, P. D., and Huang, G. Q., 2011. Seasonal variation on community structure of fishery resources in the coastal waters of Southern Shangdong Peninsular. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 41 (1/2): 41-50.
Liu, H. Z., 2002. The structure and evolution of the mtDNA control region in fish: Taking example for Acheilognathinae. Progress in Natural Science, 12 (3): 266-270 (in Chinese).
Lunt, D. H., Whipple, L. E., and Hyman, B. C., 1998. Mitochondrial DNA variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs): Utility and problems in molecular ecology. Molecular Ecology, 7 (11): 1441-1455.
Meyer, A., 1993. Evolution of mitochondrial DNA in fish. In: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Fish. Hochachka, P. W., and Mommsen, P., eds., Elsevier Press, New York, 1-38.
Posada, D., and Crandall, K. A., 1998. Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14 (9): 817-818.
Ronquist, F., and Huelsenbeck, J. P., 2003. MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed model. Bioinformatics, 19 (12): 1572-1574.
Saccone, C., Attimonelli, M., and Sbisa, E., 1987. Structural elements highly preserved during the evolution of the D-loop containing region in vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 26 (3): 205-211.
Sambrook, J., 1989. Molecular Cloning: A laboratory manual. 3rd edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 2344pp.
Sbisa, E., Tanzariello, F., Reyes, F., Pesole, G., and Saccone, C., 1997. Mammalian mitochondrial D-loop region structure analysis: Identification of new conserved sequences and the functional and evolutional implications. Gene, 205 (1-2): 125-140.
Shui, B. N., Han, Z. Q., Gao, T. X., and Miao, Z. Q., 2008. Tandemly repeated sequence in 5’ end of mtDNA control region of Japanese Spanish mackerel Scomberomorus niphonius. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7 (24): 4415-4422.
Southern, S. O., Southern, P. J., and Dizon, A. E., 1988. Molecular characterization of a cloned dolphin mitochondrial genome. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 28 (1-2): 32-42.
Swofford, D. L., 2002. PAUP*, Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and Other Methods). Sinauer Associates, Sunderland MA.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., and Kumar, S., 2007. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24 (8): 1596-1599.
Yamada, U., Tokimura, M., Horikawa, H., and Nakabo, T., 2007. Fishes and Fisheries of the East China and Yellow Seas. Tokai University Press, Kanagawa, 890pp (in Japanese).
Zhang, H., Li, P. F., Gao, T. X., Zhuang, Z. M., and Jin, X. S., 2012. Structure of mitochondrial DNA control region of Fenneropenaeus chinensis and phylogenetic relationship among different populations. Mitochondrial DNA, 23 (3): 216-222.
Zhang, H., Zhang, Y., Gao, T. X., Li, P. F., and Xu, H. X., 2011. Genetic identification of two species of Pleuronichthys by DNA barcoding. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 29 (5): 967-972.
Zhang, S. M., Wu, Q. J., and Zhang, Y. P., 2000. Tandem repeats of Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) and related species and its significance in evolution. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 16 (4): 458-461 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Y., Zhang, E., and He, S. P., 2003. Studies on the structure of the control region of the Bagridae in China and its phylogenetic significance. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 27 (5): 463-467 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Gao, T. X., and Miao, Z. Q., 2011. Structure of mitochondrial DNA control region and molecular phylogenetic relationship among three flounders of genus Pleuronectes. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 39 (4-6): 627-634.
(Edited by Qiu Yantao)
(Received September 6, 2012; revised November 29, 2012; accepted September 22, 2013)
? Ocean University of China, Science Press and Spring-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2014
* Corresponding authors. E-mail: Drsun73@163.com
E-mail: gaozhang@ouc.edu.cn
 Journal of Ocean University of China2014年3期
Journal of Ocean University of China2014年3期
- Journal of Ocean University of China的其它文章
- Effects of Sulfate Chitosan Derivatives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Variation of Bioaccumulation Ability of 2,2’,4,4’-Tetrabromodiphenyl Ether by Marine Diatom Skeletonema costatum Under Different N:P Ratios
- Preference of the Herbivorous Marine Teleost Siganus canaliculatus for Different Macroalgae
- Effect of Temperature on Gene Expression in the Pearl Oyster Pinctada fucata
- Nitrogen and Phosphorus Budget of a Polyculture System of Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus), Jellyfish (Rhopilema esculenta) and Shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis)
- Fishery Biology of Jumbo Flying Squid Dosidicus gigas off Costa Rica Dome
