Singular Boundary Method:Three Regularization Approaches and Exterior Wave Applications
Zhuo-Jia Fu,Wen Chen,2,Jeng-Tzong Chenand Wen-Zhen Qu
1 Introduction
During the past decades we have witnessed a research boom on the boundary-type meshless techniques[Atluri and Zhu(2000);Chen et al.(2013)],since the con-struction of a mesh in the standard BEM is non trivial.They can be classified into weak and strong form categories.Among them,weak-form category includes the local boundary integral equation method[Zhu et al.(1998)],the meshless local Petrov-Galerkin method[Atluri and Zhu(1998);Zhang et al.(2013)],the boundary node method.[Mukherjee and Mukherjee(1997);Zhang et al.(2002)],the boundary face method.[Zhang et al.(2009)],the null- field boundary integral equation method[Chen et al.(2007);Lee and Chen(2013a);Lee and Chen(2013b)]and so on.Strong-form category includes the boundary point interpolation method[Gu and Liu(2002)],the method of fundamental solutions[Chen et al.(2008);Fairweather and Karageorghis(1998);Lin et al.(2011);Tsai(2008)],the boundary knot method[Chen and Tanaka(2002);Fu et al.(2011)],the boundary particle method[Fu et al.(2013);Fu et al.(2012)],the Trefftz method[Dong and Atluri(2012a);Dong and Atluri(2012b);Liu(2008)],the regularized meshless method[Chen et al.(2006);Young et al.(2005)],the modified method of fundamental solutions[Sarler(2009)],the singular boundary method[Chen(2009)]and the boundary distributed source method[Kim(2013);Liu(2010)]and so on.
This study focuses on a recent meshless boundary collocation method,the singular boundary method(SBM)[Chen(2009)],which introduces the concept of source intensity factor to regularize the singularities of fundamental solutions,in some literatures it also named as origin intensity factor.Therefore,it avoids singular numerical integrals in the boundary element method and circumvents the troublesome placement of the fictitious boundary in the method of fundamental solutions.
At first,an inverse interpolation technique(IIT)has been proposed to determine the above-mentioned source intensity factors of fundamental solutions.This SBM formulation has been successfully applied to interior and exterior Laplace[Chen and Fu(2010);Chen et al.(2009);Chen and Wang(2010)],Poisson[Wei et al.(2013)],Helmholtz[Fu and Chen(2010)]and elastostatic[Gu et al.(2011)]problems.Later,Chen and Gu[Gu et al.(2012b)]introduced the desingularization of subtracting and adding-back technique and proposed an improved singular boundary method(ISBM)for interior and exterior potential problems.Its main improvement is developing a semi-analytical technique(SAT1)to determine the source intensity factors without any inner sample nodes.The approach employs the null- field or full- field integral equations to evaluate analytically the source intensity factors on Neumann boundary conditions for Laplace equation.After that it uses the inverse interpolation technique with boundary source points to determine the source intensity factors on Dirichlet boundary conditions for Laplace equation.Then Fu and Chen used the relationships between Laplace and Helmholtz-type fundamental solutions to extend the ISBM to solve interior and exterior Helmholtz-type problems[Chen et al.(2014);Fu et al.(2014);Fu and Chen(2013)].Recently,another semi-analytical technique(SAT2)has been proposed[Gu et al.(2012a)],whose difference with the SAT1 is implementing the integral mean value approach to determine the source intensity factors on Dirichlet boundary conditions for Laplace equation.
This study will extend the SAT2 to determine the source intensity factors of the Helmholtz fundamental solutions,and then compares numerical accuracy and stability of these three approaches(IIT,SAT1 and SAT2)on exterior wave problems.A brief outline of the paper is as follows.Section 2 describes the singular boundary method with three regularization treatments for Helmholtz problems.In Section 3,the efficiency and accuracy of these three approaches are examined in 2D and 3D benchmark examples.Section 4 presents the singular boundary method to two exterior wave scattering applications.Finally,Section 5 concludes this paper with some remarks.
2 Three regularization treatments in the SBM
The problem under consideration is the propagation of time-harmonic waves in a homogeneous isotropic mediumDexterior to a closed bounded curve Γ,which is described by the Helmholtz equation

subjected to the boundary conditions:

wherek=ω/cthe wavenumber,ω the angular frequency,cthe wave speed in the exterior mediumD,and n the unit outward normal on physical boundary.ΓDand ΓNrepresent the essential boundary(Dirichlet)and the natural boundary(Neumann)conditions,respectively,which construct the whole closed bounded curve Γ=ΓD+ΓN,anduis complex-valued amplitude of radiated and/or scattered wave(velocity potential or pressure):

where the subscriptsT,RandIdenote the total,radiation and incidence wave,respectively.For the exterior wave problems,it requires guaranteeing the physical requirement that all scattered and radiated waves are outgoing.This is accomplished by imposing an appropriate radiation condition at infinity,which is termed as the Sommerfeld radiation condition:

wheredimis the problem dimension,andBy utilizing single layer fundamental solutions,the SBM approximate solutionsu(x)andq(x)of exterior Hemholtz problem(Eqs.(1)and(2))can be expressed as follows
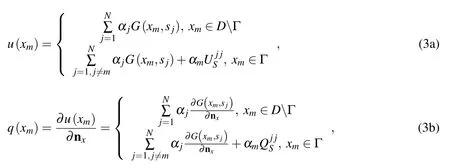
whereNdenotes the number of source pointssj,αjthejth unknown coefficient,nxthe outward normal unit vector on the collocation pointsxm,2D fundamental solutionsand 3D fundamental solutions G(xm,sj)=in whichis thenth order Hankel function of the first kind,the Euclidean distanceIf the collocation points and source points coincide,i.e.,xm=sj,the well-known singularities are encountered.The SBM introduces the concept of the source intensity factorsandto avoid these singularities.The key issue of the SBM is how to determine these source intensity factorsand.Fortunately,it is of interest to point out that the fundamental solutions of Helmholtz equation have the similar order of the singularities as the related fundamental solutions of Laplace equation[Kirkup(1998)].The corresponding relationships can be represented by the following asymptotic expressions
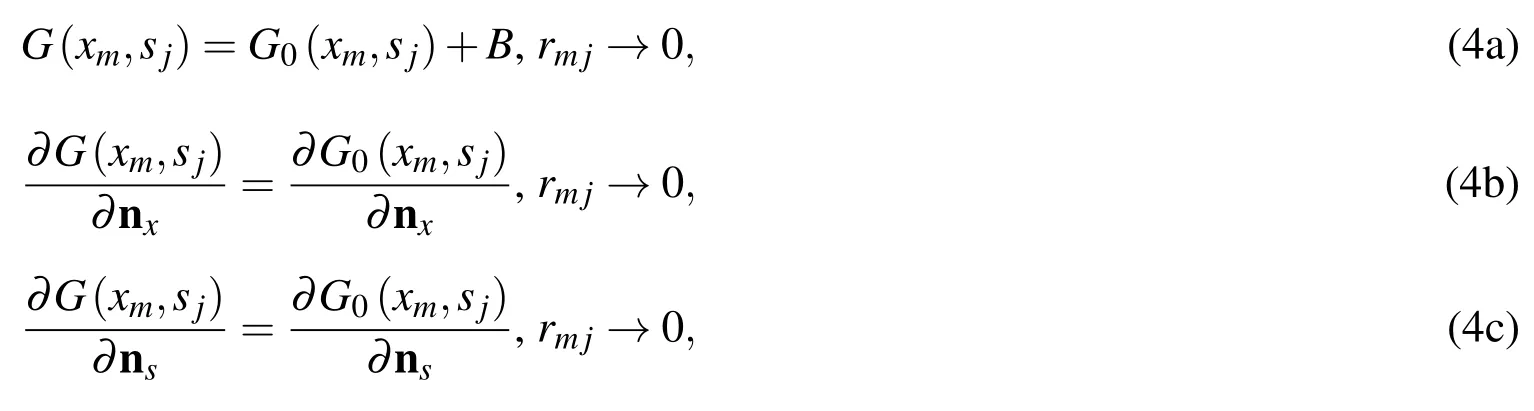
where Euler constant γ=0.57721566490153286···,nsthe outward normal unit vector on the source pointssj,For 2D problem,Laplace fundamental solutionandFor 3D problem,Laplace fundamental solutionHence we can introduce the existing approaches to determine the source intensity factors for Laplace equation,and then implement the above-mentioned relationship to calculate the source intensity factors for Helmholtz equation.In the next section,we will introduce three approaches to determine the source intensity factors for removing the singularities of Helmholtz fundamental solutions at origin.
2.1 Inverse interpolation technique
This section will introduce a simple numerical technique,called the inverse interpolation technique(IIT)[Chen and Fu(2010);Fu and Chen(2010)],to determine the source intensity factors for Laplace equation.Then we can use the relationships between Helmholtz and Laplace fundamental solutions to determine the source intensity factors for Helmholtz equation.In the first step,the IIT requires choosing a known sample solutionuS0of Laplace equation and placing some sample pointsykinside the physical domain.It is noted that the sample pointsykdo not coincide with the source pointssj,and the number of sample pointsNKshould not be fewer than the source node numberNon physical boundary.By using the interpolation formula(3),we can then determine the influence coefficients βjandˉβjby solving the following linear equations
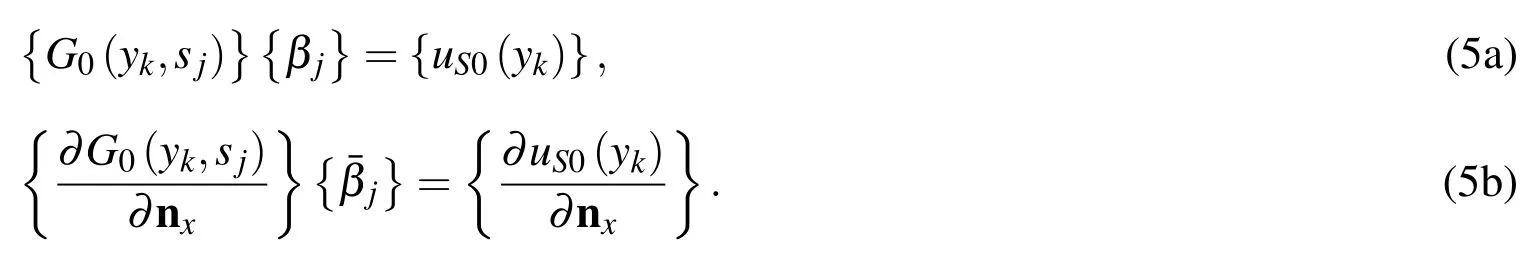
Replacing the sample pointykwith the boundary collocation pointxm,the SBM interpolation matrix(Eqs.(1)and(2))can be written as
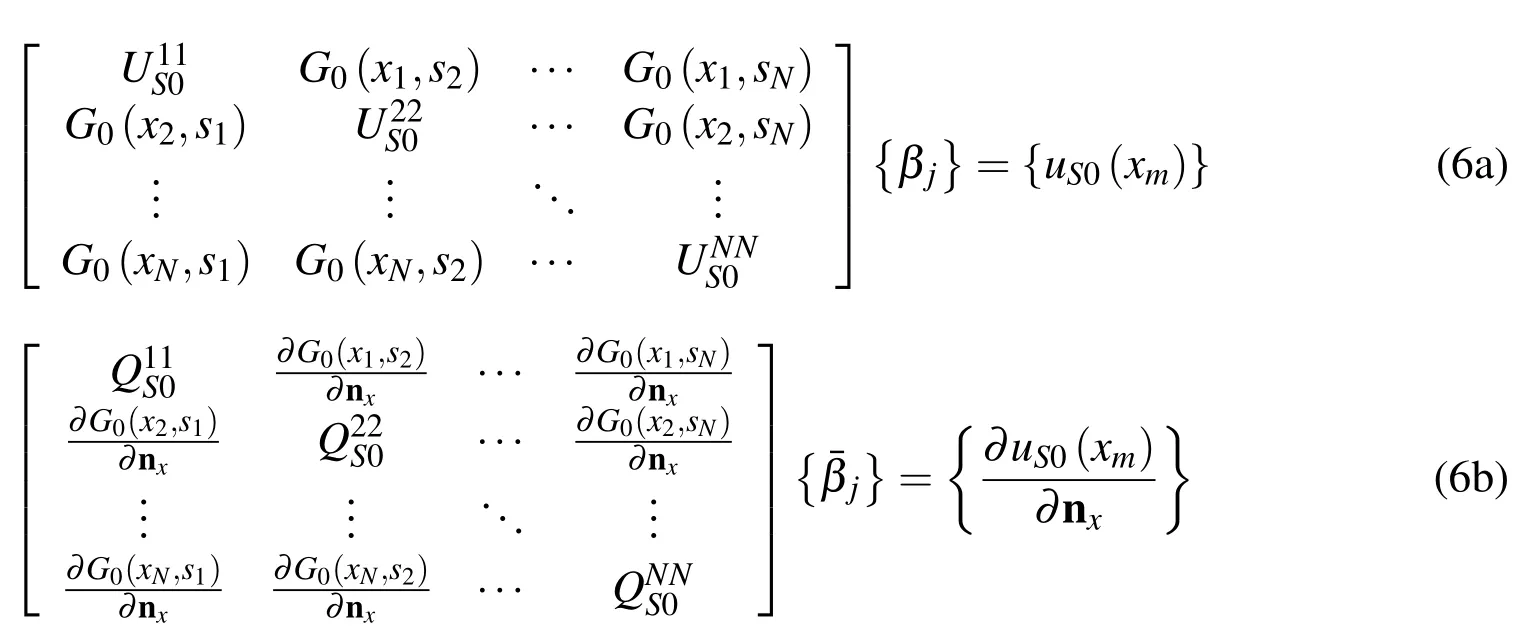
The source intensity factors for Laplace equation can be calculated by:
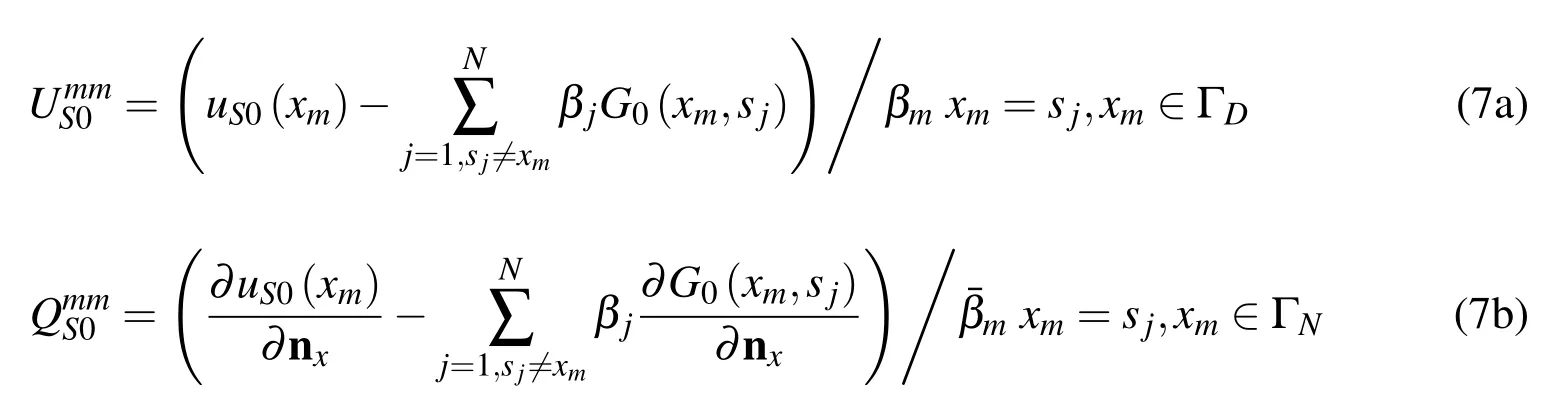
Then the source intensity factors for the Helmholtz equation can be represented as

2.2 Semi-analytical technique with boundary IIT(SAT1)
This section will introduce a semi-analytical technique[Chenetal.(2014);Guetal.(2012b)]to calculate the source intensity factors,it does not require the additional inner sample nodes.
2.2.1 Source intensity factors on Neumann boundary conditions

Figure 1:Schematic con figuration of(a)source points sjand the related curve on 2D problems and(b)source points sjand the related infinitesimal area Ljon 3D problems.
By adopting the subtracting and adding-back technique in Eq.(3b)atxm=sj,we obtain
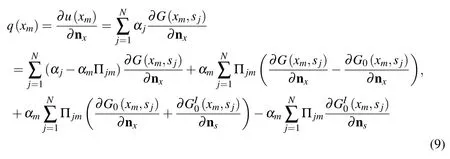
According to the dependency of the outward normal vectors on the fundamental solutions of interior and exterior Laplace equations[Gu et al.(2012b);Young et al.(2005)],we have the following relationships
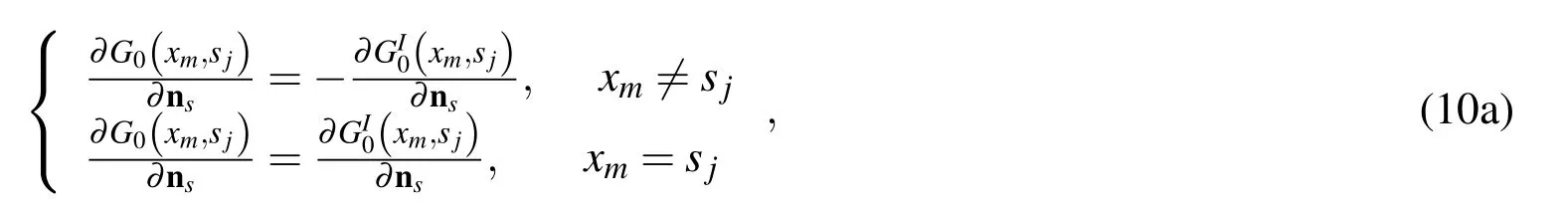
and
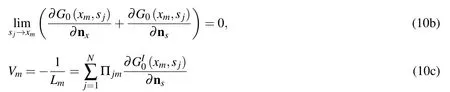
when the boundary shape is of a straight line,Eq.(10b)is explicitly equal to zero since nx(xm)=ns(sj)at all boundary knots.For an arbitrarily shaped smooth boundary,herein we assume that the source pointsjapproaches inchmeal to the collocation pointxmalong a line segment,then Eq.(10b)is tenable.Eq.(10c)can be derived based on the discretization of the reduced full- fields equations[Ochmann(1999)].With the help of Eqs.(4)and(10),Eq.(9)can be regularized as follows
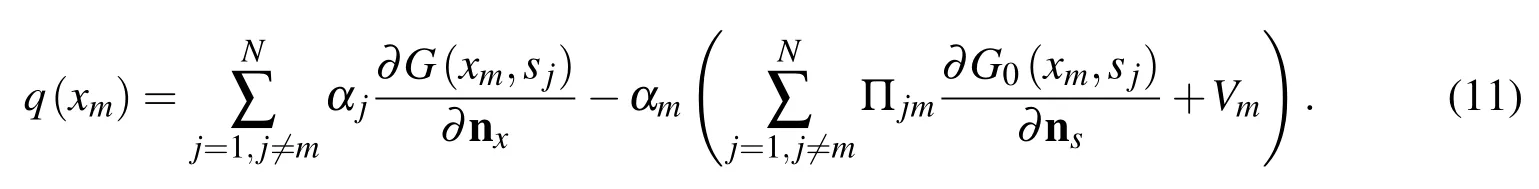
By contrast with Eq.(3b)atxm=sj,we can obtain
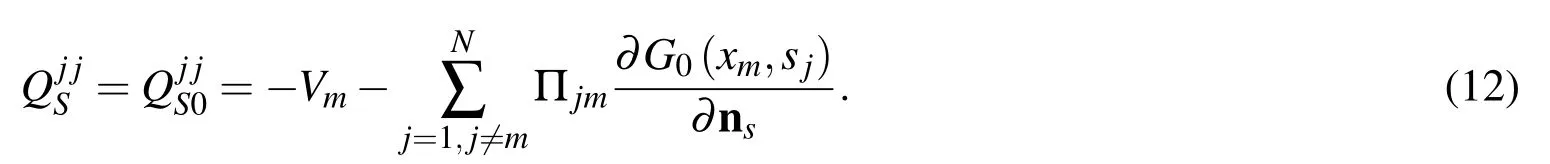
which is the source intensity factors for Neumann boundary conditions in Eq.(3b).
2.2.2 Source intensity factors on Dirichlet boundary conditions
Next the source intensity factorscan be calculated by the inverse interpolation technique[Chen et al.(2014);Gu et al.(2012b)].This strategy chooses a sample solutionof Laplace equation,e.g.=x+y+cfor 2D problems and=x+y+z+cfor 3D problems.Then 2N+1 linear equations are obtained with 2N+1 unknowns(,βj,c)onNboundary source points and one inner pointxI.
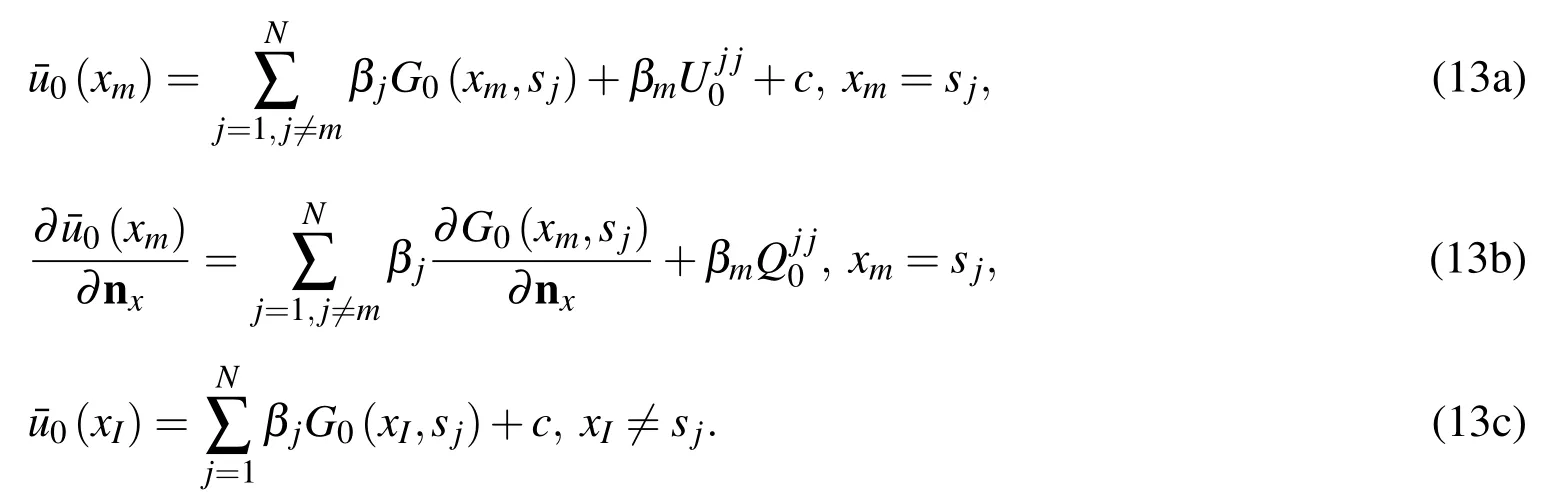
Therefore,the source intensity factorsin Eq.(3a)can now be determined indirectly by calculating the source intensity factorsof Laplace equation by using the expression(8a).
2.3 Semi-analytical technique with integral mean value(SAT2)
This section will introduce a recently developed semi-analytical technique[Gu et al.(2012a)],which do not require the inverse interpolation technique.As with Section 2.2.1,the regularized SBM formulation for the Neumann boundary condition(3b)can be expressed as follows

and
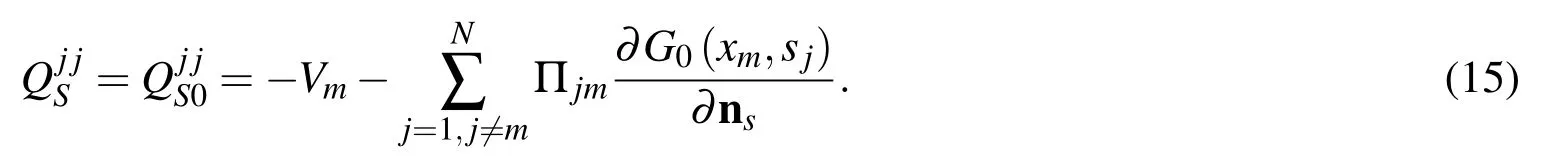
is the aforementioned source intensity factors for the Neumann boundary condition.Next the regularized expression for the Dirichlet boundary equation(3a)can be performed using the strategy proposed in the reference[Sarler(2009)],where the corresponding source intensity factors are directly set as an average value of the Laplace fundamental solution over a line segments.This can be formulated as
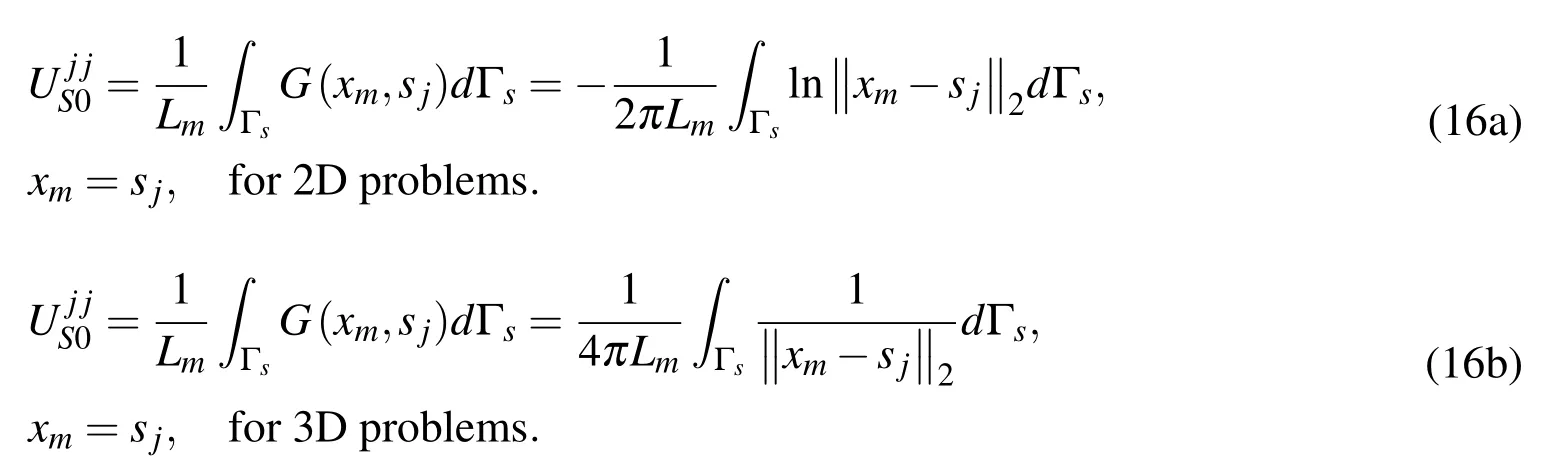
Then the source intensity factorsfor the Dirichlet boundary condition can be calculated by using the expression(8a).
3 Numerical investigations and discussions
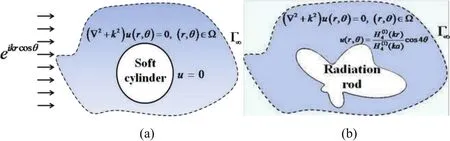
Figure 2:Sketch of(a)the scattering problem for an in finite soft cylinder and(b)the radiation problem of an in finite irregular-shaped rod.
In this section,the efficiency,accuracy and convergence of the above-mentioned three treatments(IIT,SAT1 and SAT2)in the SBM are implemented to solve 2D and 3D exterior wave problems.The numerical accuracy is calculated by the relative root mean square errors(RMSE)Lerr(u)which is defined as
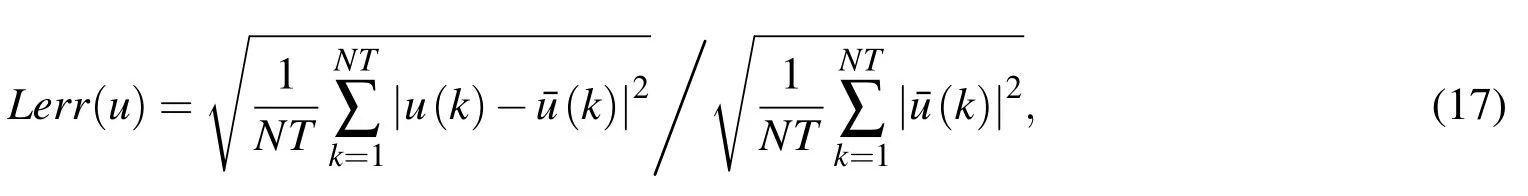
Example 1:Scattering problem of a soft in finite circular cylinder(Dirichlet boundary condition)
We consider a plane waveeikrcosθscattered by a soft in finite circular cylinder as shown in Fig.2a.The analytical solution of the scattering fielduS[Chen et al.(2007)]is
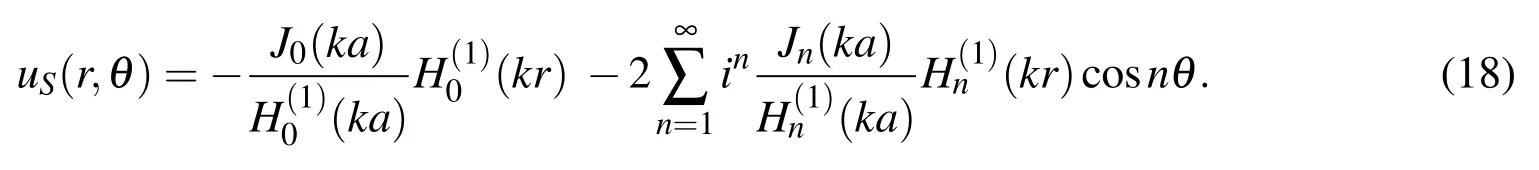
Fig.3 shows the error analysis of the SBM with three treatments for 2D scattering problem withka=40.The analytical solutions in this case are calculated by using the first 100 terms in the above series representation(18).The test points(NT=101)are uniform angular distribution on the circle with radius 1.2.It can be found that all of these three methods converge with the increasing boundary node numberN.In this case,the SBM with SAT1 provides better results than the SBM with IIT and SAT2 under the same number of boundary knots,the slope of the convergence curve is about-3.The SBM with SAT2 has the slowest convergence rate and the slope of the convergence curve is about-1.While the SBM with IIT has the same convergence rate to the SAT1 with modestly increasing boundary node number(N=10000),but it converges slowly with further increasing boundary node number.This may result from the non-optimal source intensity factors calculated by the IIT.Consider the radiation problem of an in finite soft irregular-shaped rod as shown in Fig.2b.The analytical solution of the radiation fielduRis

Fig.4 shows the error analysis of the SBM with three treatments for 2D radiation problem of a soft in finite irregular-shaped rod withka=1.The test points(NT=101)are uniform angular distribution on the circle with radius 1.5?0.425.
Similar to the conclusion in Example 1,the SBM with SAT1 has the best performance among these three treatments,the SBM with SAT2 converges very slowly.
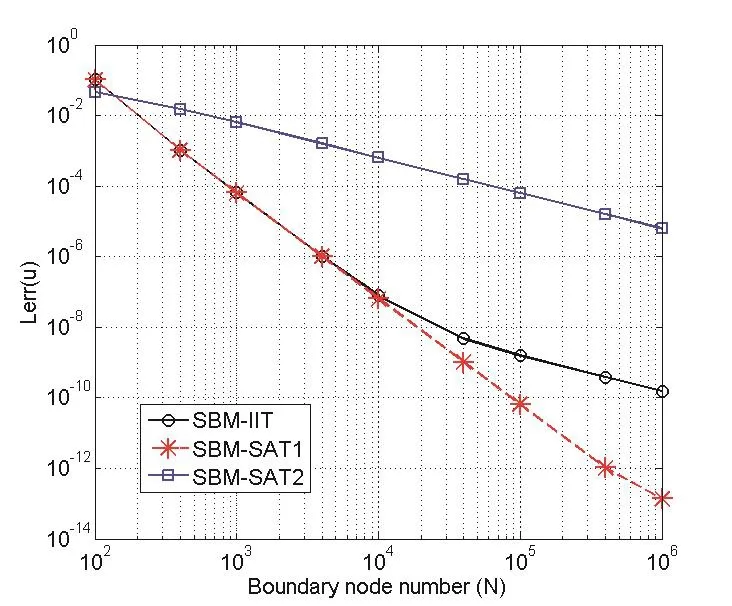
Figure 3:Convergence analysis Lerr(u)of the SBM with IIT,SAT1 and SAT2 for the scattering problem of a soft in finite cylinder with ka=40
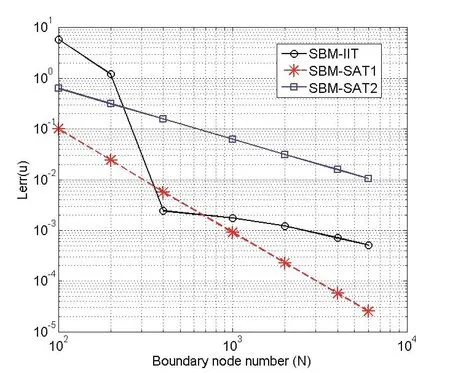
Figure 4:Convergence analysis Lerr(u)of the SBM with IIT,SAT1 and SAT2 for the radiation problem of an soft in finite irregular-shaped rod with ka=1.
Numerical stability is very sensitive to the placement of sample nodes in the SBM with IIT.
Example 3:Scattering problem of a soft sphere(Dirichlet boundary condition)

Figure 5:Sketch of a soft spherical scatterer with the incident wave uI.
Consider the scattering problem of a soft sphere with the incident plane waveuI=where(θ0,?0)denotes the angle of the incident plane wave in the spherical coordinates as shown in Fig.5.The analytical solution of the scattering fielduS[Chen et al.(2010)]is
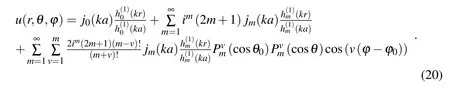
Fig.6 shows the error analysis of the SBM with three treatments for 3D scattering problem withka=1.The analytical solutions in this case are calculated by using the first 30 terms in the above series representation(20).The test points(NT=100)are uniform angular distribution on the surface of the sphere with radius 1.25.It can be found that all of these three methods converge with the increasing boundary node numberN.In this case,the SBM with SAT1 provides better results than the SBM with IIT and SAT2 under the same number of boundary knots,the slope of the convergence curve is about-1.5.The SBM with SAT2 has the slowest convergence rate and the slope of the convergence curve is about-0.5.While the SBM with IIT has the same convergence rate to the SAT1 with modestly increasing boundary node number(N=10000),but it converges slowly with further increasing boundary node number.This may result from the non-optimal source intensity factors calculated by the IIT.
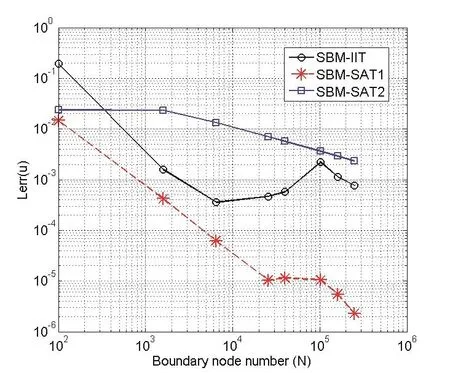
Figure 6:Convergence analysis Lerr(u)of the SBM with IIT,SAT1 and SAT2 for the scattering problem of an soft sphere with ka=1.
Example 4:Radiation model for a soft ellipsoid(Dirichlet boundary condition)Consider the radiation problem of a soft ellipsoidas shown in Fig.7.The analytical solution of the radiation fielduRis

Fig.8 shows the error analysis of the SBM with three treatments for 3D radiation problem of a soft ellipsoid withka=1.The test points(NT=100)are uniform angular distribution on the surface of the ellipsoidSimilar to the conclusion in Example 3,the SBM with SAT1 has the best performance among these three treatments,the SBM with SAT2 converges very slowly.Numerical accuracy has a heavy oscillation with further increasing boundary node number(N>10000)by using the SBM with IIT.Generally speaking,the above-mentioned numerical results show that SAT1>IIT>SAT2 in numercial accuracy and SAT2>SAT1>IIT in numerical stability for solving 2D and 3D exterior wave radiation and scattering problems.
Figure 7:Sketch of the radiation problem of a soft ellipsoid.
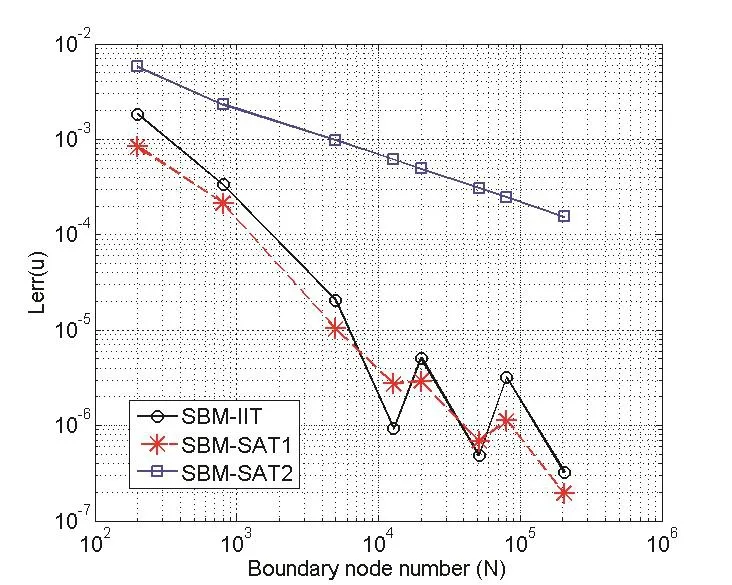
Figure 8:Convergence analysis Lerr(u)of the SBM with IIT,SAT1 and SAT2 for the radiation problem of an soft ellipsoid with ka=1.
4 Exterior wave scattering applications
In this section,the SBM with SAT1 is implemented to two exterior wave scattering applications.First we consider water wave scattering problem.Under the assumptions of the potential flow and linear wave theory,3D water wave-structure interaction problem shown in Fig.9a can be reduced to 2D water wave scattering problem shown in Fig.9b by removing the depth dependence[Chen et al.(2011b);Chen et al.(2012);Evans and Porter(1997)].Then the mathematical model can be represented as
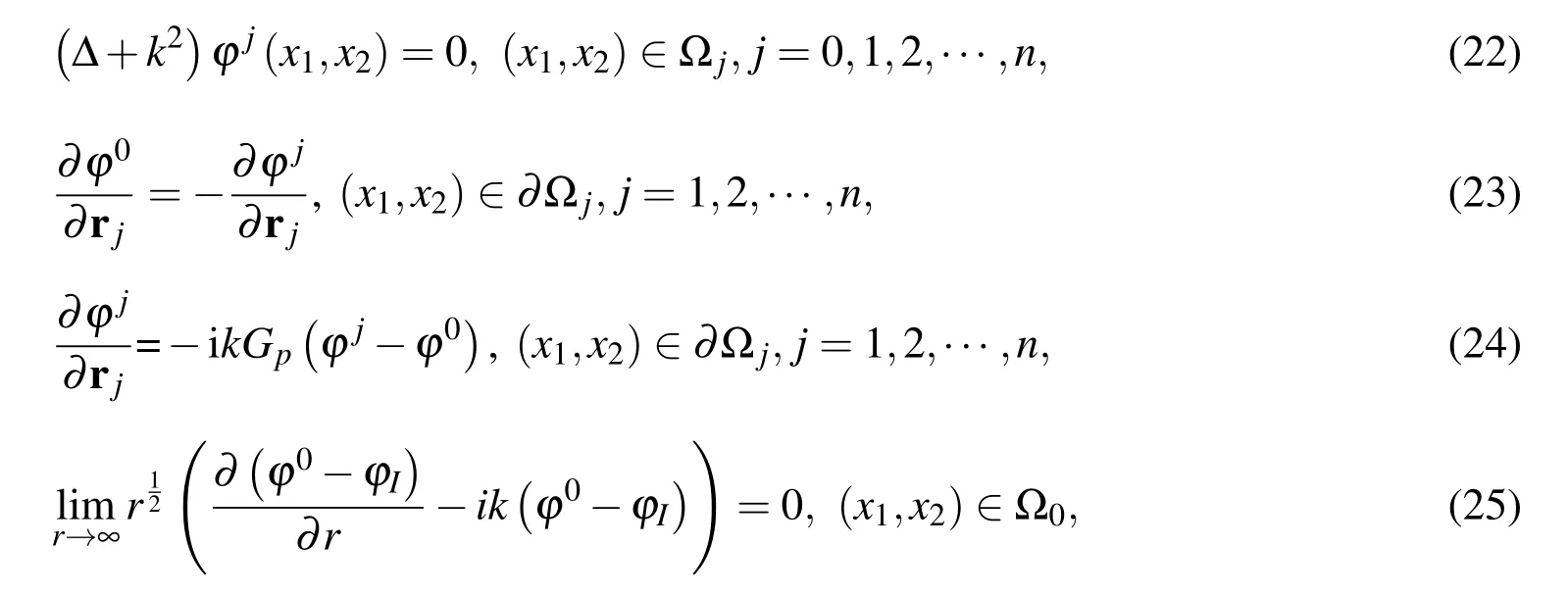
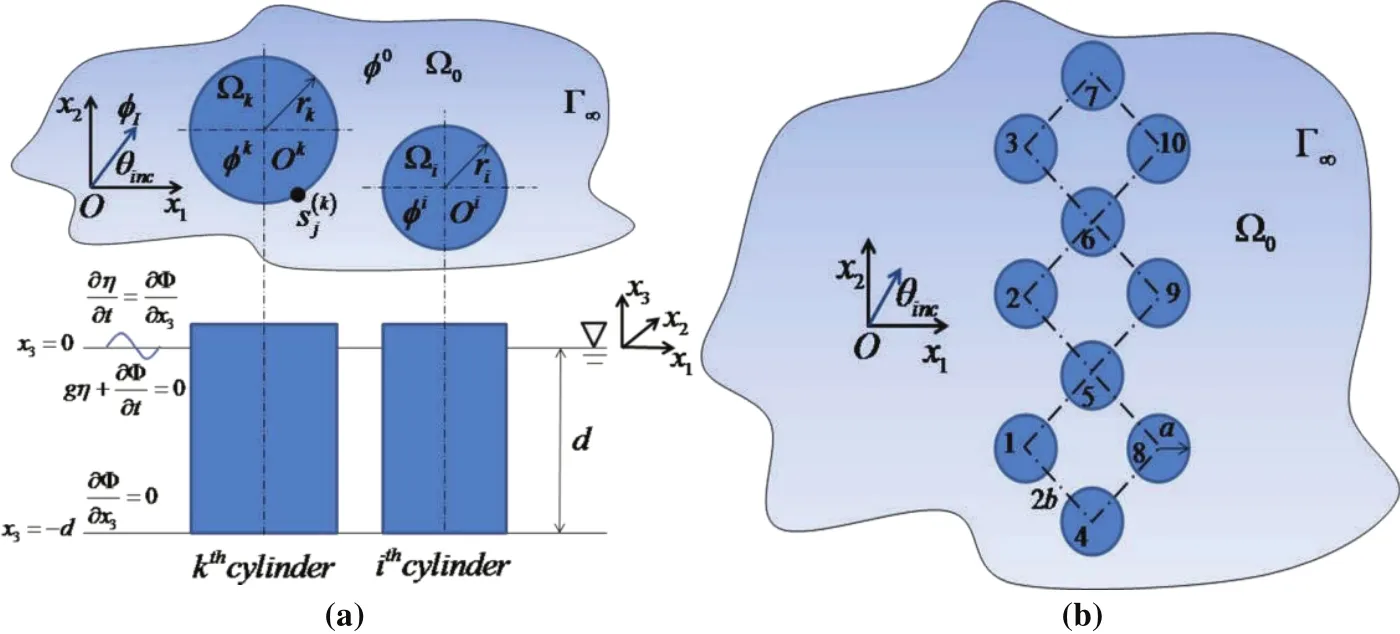
Figure 9:Problem statement of(a)3D water wave-structure interaction and(b)the related 2D water wave problem.
where rjdenotes the unit normal vector on thejth cylinder surface,?I(x1,x2)=eik(x1cosθinc+x2sinθinc)is the incident water wave and its amplitude isA,|η|=|A?(x1,x2)|the free-surface elevation,and the wavenumberkis the real root of the dispersion relationship ω2=gktanhkd,ω the angular frequency,gthe gravitational acceleration,dthe water depth andGp=γρω(μk)the dimensionless porosity[Chen et al. (2011b)],in which μ the dynamic viscosity coefficient,γ a material constant having the dimension of length and ρ the fluid density.Gp=0 means the impermeable cylinder. The entire plane potential- field regionR2is divided inton+1 sub-regions,nfinite circular regions,j=1,2,···,nand an in finite
region ?0= ?e,whererepresents the coordinate of the center of thejth circular cylinder andrjis the radius of the related cylinder.Therefore,?j(x1,x2)denotes the horizontal velocity potential in the sub-region ?j,andwhereis the horizontal velocity potential of the scattering wave by thejth circular cylinder.
In the SBM simulation,we set some parameters asa=0.4,b=0.5,d=2,θinc=0,ka=4.08482,and place 100 boundary nodes on the boundary of each cylinder.Fig.10 shows the free-surface elevation in the vicinity of ten-cylinder array with different dimensionless porosity(Gp=0,0.0001,1)and different disorder parameters(τ=0,0.1).As shown in Fig.11,the disorder displacement of each cylinder center away from its original regular position can be calculated by?xj=γj(b?a)τcos(2πγj),?yj= γj(b?a)τsin(2πγj),where the random number γjcan be generated by using Matlab function “rand”.
From Fig.10a,it can be observed that the near-trapped mode phenomenon[Chen et al.(2011b);Evans and Porter(1997)]is revisited in the wave structure with impermeable regular cylinders(Gp=0,τ=0),and the maximum amplitude appearing on the inner sides of the cylinders is about 150 times over the incident wave amplitude.Numerical results demonstrate that both the porosity of the cylinder sidewall and the disorder arrangement have a great effect on the free-surface elevations in the vicinity of the wave structure.We can see from Fig.10 that the increase of the porosity leads to the decrease of the maximum free-surface amplitude,and small disorder arrangement can also reduce the maximum free-surface amplitude remarkably.When the porosity parameter is relatively large(Gp=1),the porosity of the structure has more influence to avoid the occurrence of near-trapped mode phenomenon than the disorder arrangement of the structure.When the porosity parameter is relatively small(Gp=0.0001),the disorder arrangement of the structure has more influence to avoid the occurrence of near-trapped mode phenomenon than the porosity of the structure.
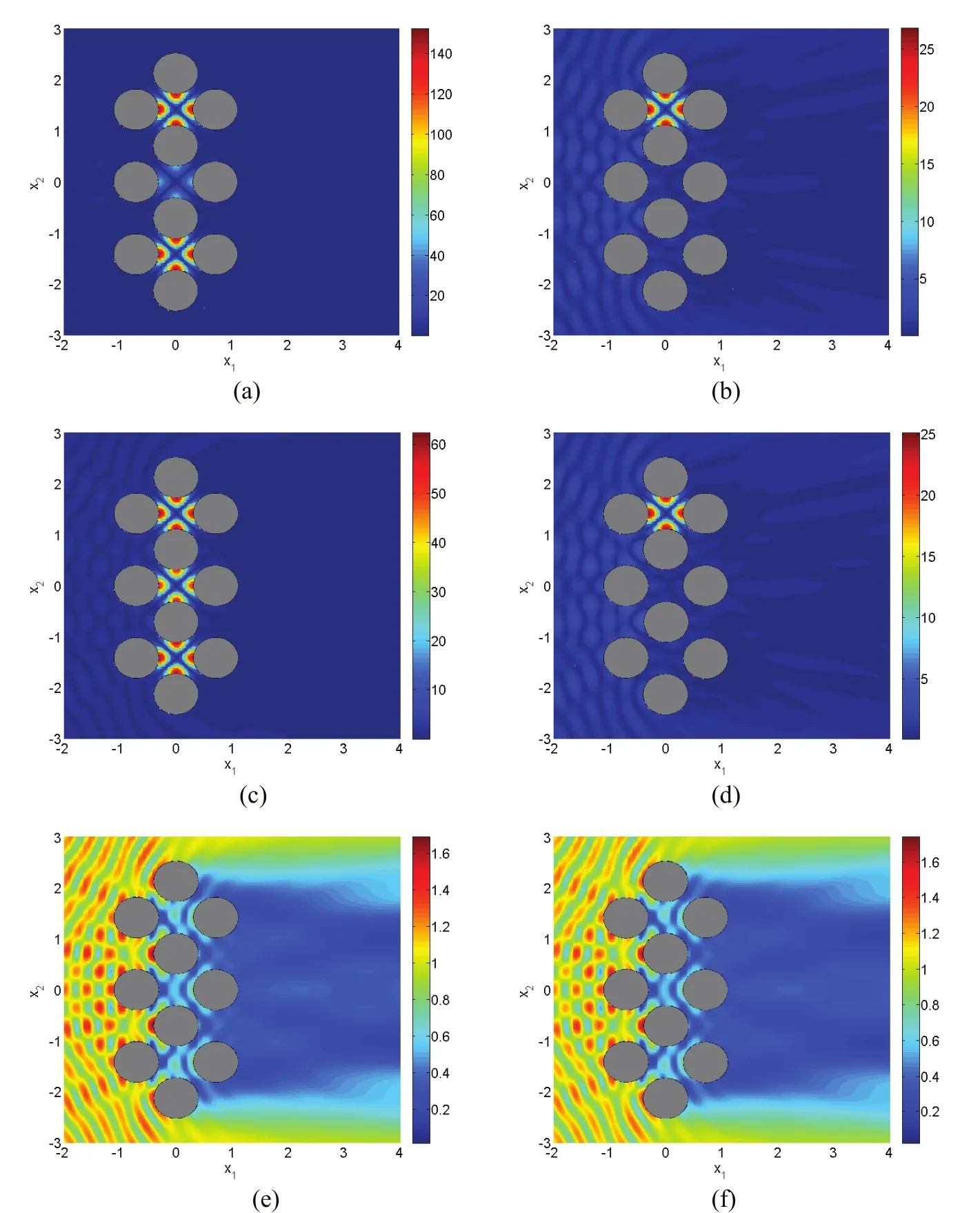
Figure 10:SBM results of the free-surface elevation in the vicinity of tency-linder array with different porosity and disorder parameters:(a)Gp=0,τ=0;(b)Gp=0,τ=0.1;(c)Gp=0.0001,τ=0;(d)Gp=0.0001,τ=0.1;(e)Gp=1,τ=0;(f)Gp=1,τ=0.1.
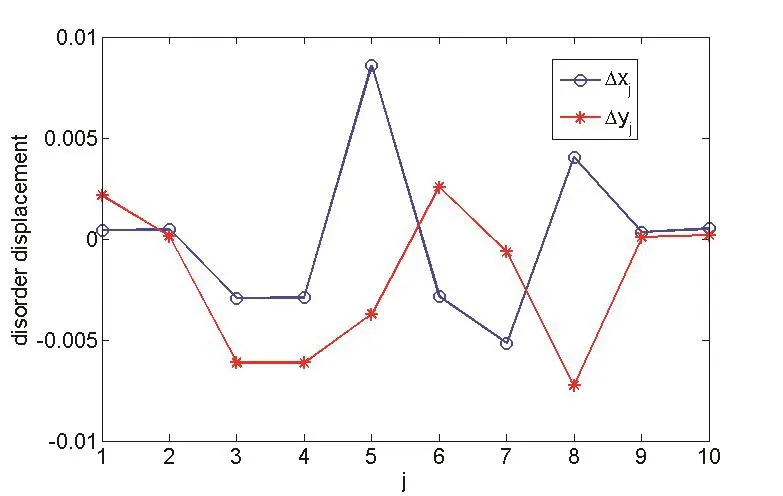
Figure 11:Disorder displacement(?xj,?yj)of jth cylinder center with disorder parameter τ=0.1.
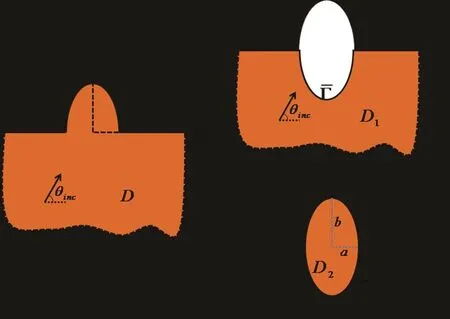
Figure 12:Decomposition and conjunction technique for SH wave scattering problem.(a)Original region D,(b)a semi-in finite region D1and(c)an interior region D2.
Then SH wave scattering problem with a semi-circular hill(a=b=1)is considered[Tsaur and Chang(2009)]as shown in Fig.12. ?I(x1,x2)=eik(x1cosθinc+x2sinθinc)is incident SH wave expression,where θincis the incident wave angle,kdenote the wavenumber.For easy comparison with the other reference results,the dimensionless frequency η is defined as η =.The mathematical model of SH wave scattering problem is
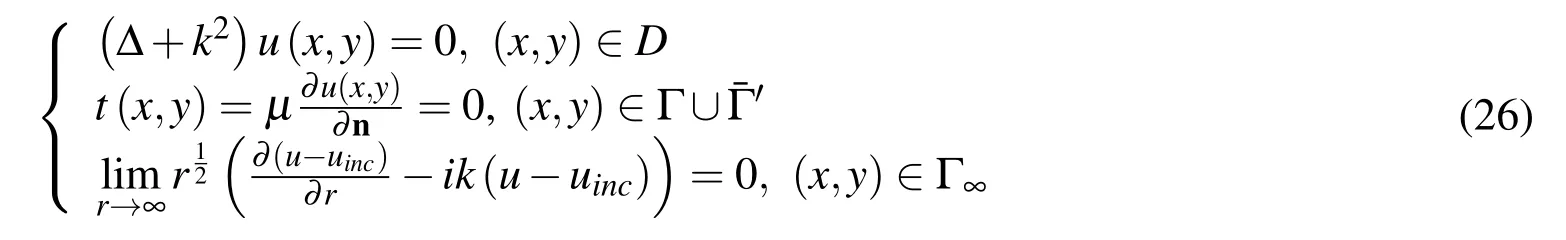
By implementing decomposition and conjunction technique[Yuan and Liao(1996)],the mathematical model can be represented as
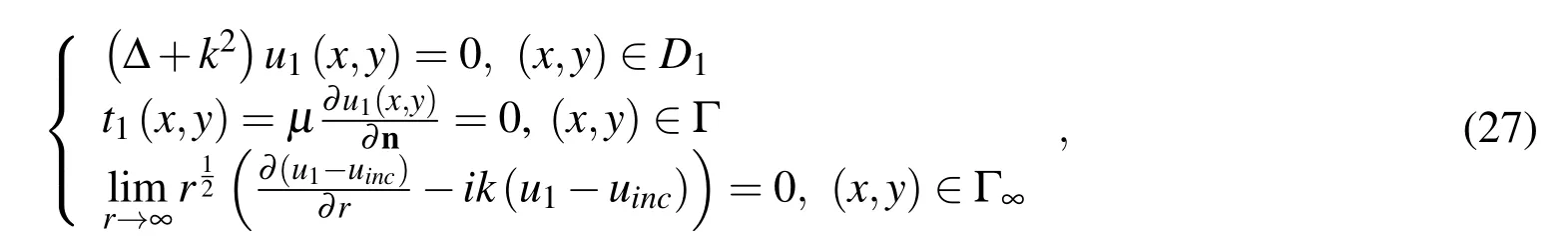
and

with the continuity condition on fictitious boundary

For the interior problem,we chooseas the basis function,whereY0is zero-order Bessel functions of the second kind.The related source intensity factors can be calculated by Eq.(8)withIn the SBM simulation,we place 100 boundary nodes on the boundaryand 50 auxiliary nodes on the boundary Γ.
Fig.13 shows the surface displacement amplitude versusxwith different incident wave angles and different dimensionless frequenciesη=3).From Fig.13,one can find that the present SBM performs well with the reference results[Chen et al.(2011a);Tsaur and Chang(2009)].
Then the focusing phenomenon of vertical SH wave scattering(θinc=)by a semicircular hill is revisited.Fig.14 plots the spectral variation of surface displacement amplitudes along the central axis of the semi-circular hill,ranging from the top of the hill(y=1)to the bottom of the fictitious boundaryˉΓ(y=-1)with the dimensionless frequency η from 0 to 12.It should be mentioned that the present SBM results are in good accordance with the reference results[Tsaur and Chang(2009)].From Fig.14,it can be observed that the focusing of wave energy mostly occurs at the depth between y=0.5 and 0.75.However,the maximum surface displacement amplitudes may take place on the top of the semi-circular hill(y=1)at some frequencies(η=5.0-5.3 and 8.5-9.5).
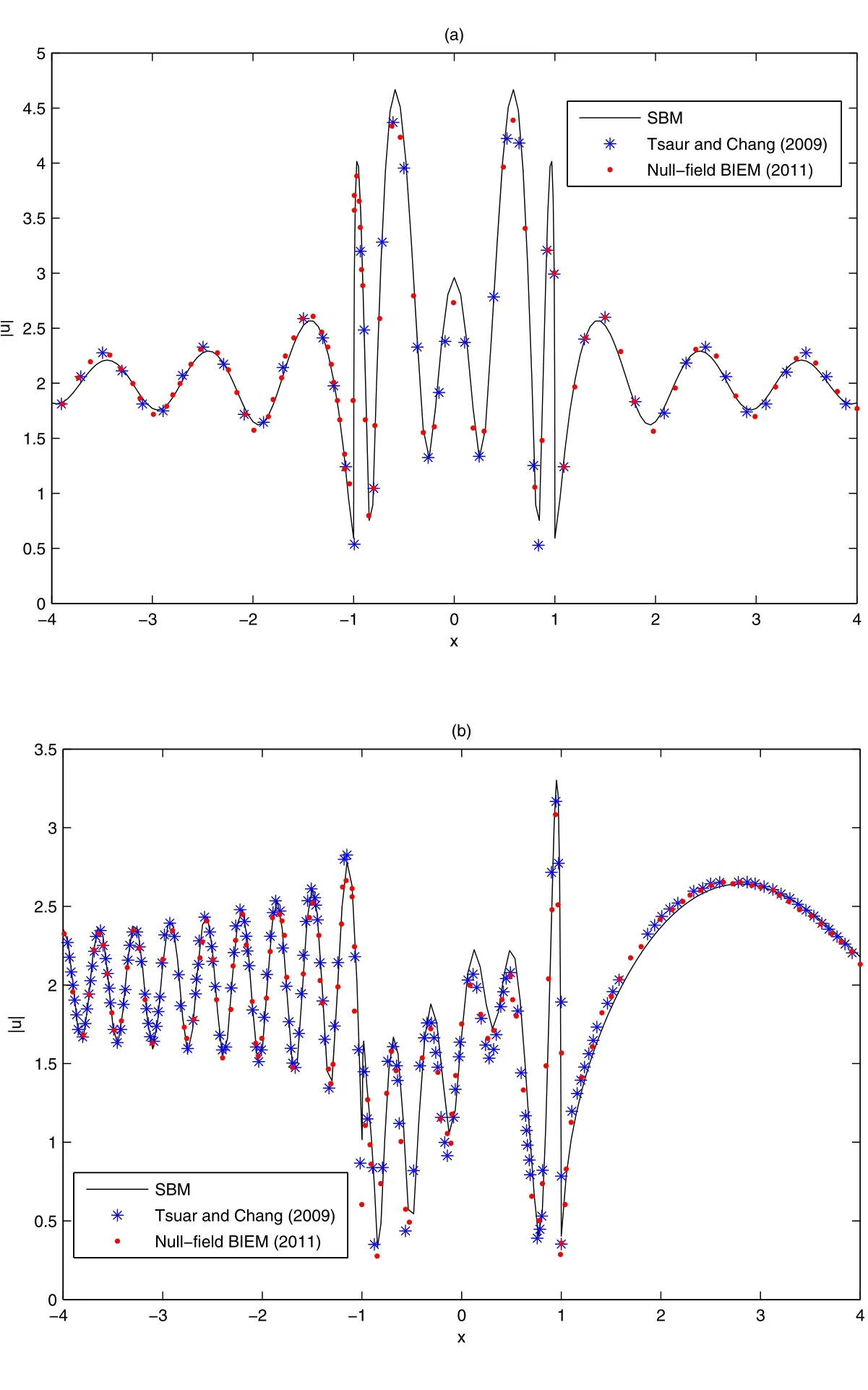
Figure 13:Surface displacement amplitudes|u|versus x with(a)incident wave angleand the dimensionless frequency η =2;(b)and η=3.
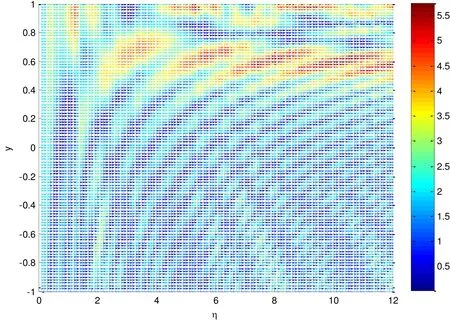
Figure 14:Spectral variation of displacement amplitudes|u|along the central axis of the semi-circular hill for the incident SH wave angle of θinc=
Figure 15:Synthetic seismograms of SH wave scattering by a semi-circular hill with the incident wave angle of θinc=

wherefcdenotes the characteristic frequency of Ricker wavelet.In the SBM simulation,we setfc=1.5Hzand compute the surface displacement amplitudes|u|with 96 dimensionless frequencies(η=0.0625(Nf?1),Nf=1,2,···,96)as the frequency-domain solutions,and then introduce the Fast Fourier Transform to obtain the time-domain synthetic seismic response from the frequency-domain solutions.Fig.15 displays the synthetic seismograms of SH wave scattering by a semi-circular hill with the incident wave angleThe present SBM results are in good agreement with the reference results[Tsaur and Chang(2009)].
5 Conclusions
This study makes the numerical comparison on three treatments for calculating the source intensity factors in the singular boundary method.Numerical results shows that the SBM with SAT1 provides the best performance among these three methods,the SBM with SAT2 converges very slowly.By employing the SBM with IIT,numerical stability is very sensitive to the placement of sample nodes.In this study,we propose a strategy to select the appropriate sample nodes,however,this strategy still needs further verification and improvement.Generally speaking,numerical investigations show that SAT1>IIT>SAT2 in numercial accuracy and SAT2>SAT1>IIT in numerical stability for solving 2D and 3D exterior wave radiation and scattering problems.
Then the SBM with SAT1 is implemented to two exterior wave applications.Numerical results demonstrate that the present SBM results are in good agreement with the reference results.For water wave-structure interaction,numerical investigations show that both the porosity of the cylinder sidewall and the disorder arrangement have a great effect on the free-surface elevations in the vicinity of the wave structure.For SH wave scattering by a semi-circular hill,the focusing phenomenon is revisited,and the related synthetic seismograms are plotted by introducing the Fast Fourier Transform.Further study is to introduce fast matrix algorithms[Bebendorf and Rjasanow(2003);Liu(2009);Yan et al.(2010)]to accelerate the SBM simulation for large-scale exterior wave applications.
Acknowledgement:The work described in this paper was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China(973 Project No.2010CB832702),the National Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars of China(Grant No.11125208),the National Science Funds of China(Grant No. 11302069,11372097),the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(Grant No.2013B32814)and the 111 Project(Grant No.B12032).
Atluri,S.N.;Zhu,T.(1998):A new Meshless Local Petrov-Galerkin(MLPG)approach in computational mechanics.Computational Mechanics,vol.22,no.2,pp.117-127.
Atluri,S.N.;Zhu,T.(2000):New concepts in meshless methods.International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,vol.47,no.1-3,pp.537-556.
Bebendorf,M.;Rjasanow,S.(2003):Adaptive Low-Rank Approximation of Collocation Matrices.Computing,vol.70,no.1,pp.1-24.
Chen,C.S.;Karageorghis,A.;Smyrlis,Y.S.(2008):The Method of Fundamental Solutions–A Meshless Method.Dynamic Publishers.
Chen,J.T.;Chen,C.T.;Chen,P.Y.;Chen,I.L.(2007):A semi-analytical approach for radiation and scattering problems with circular boundaries.Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,vol.196,no.25-28,pp.2751-2764.
Chen,J.T.;Lee,J.W.;Wu,C.F.;Chen,I.L.(2011a):SH-wave diffraction by a semi-circular hill revisited:A null- field boundary integral equation method using degenerate kernels.Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,vol.31,no.5-6,pp.729-736.
Chen,J.T.;Lee,Y.T.;Lin,Y.J.(2010):Analysis of multiple-spheres radiation and scattering problems by using a null- field integral equation approach.Applied Acoustics,vol.71,pp.690-700.
Chen,J.T.;Lin,Y.J.;Lee,Y.T.;Wu,C.F.(2011b):Water wave interaction with surface-piercing porous cylinders using the null- field integral equations.Ocean Engineering,vol.38,no.2-3,pp.409-418.
Chen,J.T.;Wu,C.F.;Chen,I.L.;Lee,J.W.(2012):On near-trapped modes and fictitious frequencies for water wave problems containing an array of circular cylinders using a null- field boundary integral equation.European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids,vol.32,pp.32-44.
Chen,K.H.;Chen,J.T.;Kao,J.H.(2006):Regularized meshless method for solving acoustic eigenproblem with multiply-connected domain.CMES:Computer Modeling in Engineering&Sciences,vol.16,no.1,pp.27-39.
Chen,W.(2009):Singular boundary method:A novel,simple,meshfree,boundary collocation numerical method.(in Chinese).Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica,vol.30,no.6,pp.592-599.
Chen,W.;Fu,Z.;Chen,C.S.(2013):Recent Advances on Radial Basis Function Collocation Methods.Springer Berlin.
Chen,W.;Fu,Z.J.(2010):A novel numerical method for in finite domain potential problems.Chinese Science Bulletin,vol.55,vol.16,pp.1598-1603.
Chen,W.;Fu,Z.J.;Wei,X.(2009):Potential Problems by Singular Boundary Method Satisfying Moment Condition.Cmes-Computer Modeling in Engineering&Sciences,vol.54,no.1,pp.65-85.
Chen,W.;Tanaka,M.(2002):A meshless,integration-free,and boundary-only RBF technique.Computers&Mathematics with Applications,vol.43,no.3-5,pp.379-391.
Chen,W.;Wang,F.Z.(2010):A method of fundamental solutions without fictitious boundary.Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,vol.34,no.5,pp.530-532.
Chen,W.;Zhang,J.Y.;Fu,Z.J.(2014):Singular boundary method for modified Helmholtz equations.Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,vol.44,pp.112-119.
Dong,L.;Atluri,S.N.(2012a):Development of 3 D Trefftz Voronoi Cells with Ellipsoidal Voids&/or Elastic/Rigid Inclusions for Micromechanical Modeling of Heterogeneous Materials.CMC:Computers Materials and Continua,vol.30,no.1,pp.39.
Dong,L.;Atluri,S.N.(2012b):A Simple Multi-Source-Point Trefftz Method for Solving Direct/Inverse SHM Problems of Plane Elasticity in Arbitrary Multiply-Connected Domains.CMES:Computer Modeling in Engineering&Sciences,vol.85,no.1,pp.1-43.
Evans,D.V.;Porter,R.(1997):Near-trapping of waves by circular arrays of vertical cylinders.Applied Ocean Research,vol.19,no.2,pp.83-99.
Fairweather,G.;Karageorghis,A.(1998):The method of fundamental solutions for elliptic boundary value problems.Advances in Computational Mathematics,vol.9,no.1-2,pp.69-95.
Fu,Z.J.;Chen,W.;Gu,Y.(2014):Burton-Miller-type singular boundary method for acoustic radiation and scattering.Journal of Sound and Vibration,vol.333,no.16,pp.3776-3793.
Fu,Z.J.;Chen,W.;Yang,H.T.(2013):Boundary particle method for Laplace transformed time fractional diffusion equations.Journal of Computational Physics,vol.235,pp.52-66.
Fu,Z.J.;Chen,W.A novel boundary meshless method for radiation and scattering problems.Advances in Boundary Element Techniques XI,Berlin,Germany,pp.83-90.
Fu,Z.J.;Chen,W.Water wave interaction with multiple surface-piercing porous cylinders by singular boundary method.11TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS 2013:ICNAAM 2013,pp.928-931.
Fu,Z.J.;Chen,W.;Qin,Q.H.(2011):Boundary knot method for heat conduction in nonlinear functionally graded material.Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,vol.35,no.5,pp.729-734.
Fu,Z.J.;Chen,W.;Zhang,C.Z.(2012):Boundary particle method for Cauchy inhomogeneous potential problems.Inverse Problems in Science and Engineering,vol.20,no.2,pp.189-207.
Gu,Y.;Chen,W.;He,X.Q.(2012a):Domain-decomposition singular boundary method for stress analysis in multi-layered elastic materials.CMC:Computers Materials&Continua,vol.29,no.2,pp.129-154.
Gu,Y.;Chen,W.;Zhang,C.Z.(2011):Singular boundary method for solving plane strain elastostatic problems.International Journal of Solids and Structures,vol.48,no.32,pp.2549-2556.
Gu,Y.;Chen,W.;Zhang,J.(2012b):Investigation on near-boundary solutions by singular boundary method.Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,vol.36,no.8,pp.1173-1182.
Gu,Y.T.;Liu,G.R.(2002):A boundary point interpolation method for stress analysis of solids.Computational Mechanics,vol.28,no.1,pp.47-54.
Kim,S.(2013):An improved boundary distributed source method for two dimensional Laplace equations.Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,vol.37,no.7,pp.997-1003.
Kirkup,S.(1998):The boundary element method in acoustics.Integrated Sound Software.
Lee,J.W;Chen,J.T.(2013a):A Semianalytical Approach for a Nonconfocal Suspended Strip in an Elliptical Waveguide.Microwave Theory and Techniques,IEEE Transactions on,vol.60,no.12,pp.3642-3655.
Lee,Y.T.;Chen,J.T.(2013b):Null- field approach for the antiplane problem with elliptical holes and/or inclusions.Composites Part B:Engineering,vol.44,no.1,pp.283-294.
Lin,J.;Chen,W.;Wang,F.(2011):A new investigation into regularization techniques for the method of fundamental solutions.Mathematics and Computers in Simulation,vol.81,no.6,pp.1144-1152.
Liu,C.S.(2008):A highly accurate MCTM for inverse Cauchy problems of Laplace equation in arbitrary plane domains.CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering&Sciences,vol.35,pp.91-111.
Liu,Y.J.(2009):Fast Multipole Boundary Element Method-Theory and Applications in Engineering.Cambridge University Press,Cambridge.
Liu,Y.J.(2010):A new boundary meshfree method with distributed sources.Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,vol.34,no.11,pp.914-919.
Mukherjee,Y.X.;Mukherjee,S.(1997):The boundary node method for potential problems.International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,vol.40,no.5,pp.797-815.
Ochmann,M.(1999):The full- field equations for acoustic radiation and scattering.The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,vol.105,no.5,pp.2574-2584.
Sarler,B.(2009):Solution of potential flow problems by the modified method of fundamental solutions:Formulations with the single layer and the double layer fundamental solutions.Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,vol.33,no.12,pp.1374-1382.
Tsai,C.C.(2008):The method of fundamental solutions with dual reciprocity for thin plates on Winkler foundations with arbitrary loadings.Journal of Mechanics,vol.24,no.2,pp.163-171.
Tsaur,D.H.;Chang,K.H.(2009):Scattering and focusing of SH waves by a convex circular-arc topography.Geophysical Journal International,vol.177,no.1,pp.222-234.
Wei,X.;Chen,W.;Fu,Z.J.(2013):Solving inhomogeneous problems by singular boundary method.Journal of Marine Science and Technology-Taiwan,vol.21,no.1,pp.8-14.
Yan,Z.Y.;Zhang,J.;Ye,W.;Yu,T.X.(2010):Numerical characterization of porous solids and performance evaluation of theoretical models via the precorrected-FFT accelerated BEM.CMES:Computer Modeling in Engineering&Sciences,vol.55,no.1,pp.33.
Young,D.L.;Chen,K.H.;Lee,C.W.(2005):Novel meshless method for solving the potential problems with arbitrary domain.Journal of Computational Physics,vol.209,no.1,pp.290-321.
Yuan,X.;Liao,Z.P.(1996):Surface motion of a cylindrical hill of circulararc cross-section for incident plane SH waves.Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,vol.15,no.3,pp.189-199.
Zhang,J.;Qin,X.;Han,X.;Li,G.(2009):A boundary face method for potential problems in three dimensions.International Journal for Numerical Methods inEngineering,vol.80,no.3,pp.320-337.
Zhang,J.;Yao,Z.;Li,H.(2002):A hybrid boundary node method.International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,vol.53,no.4,pp.751-763.
Zhang,T.;Dong,L.;Alotaibi,A.;Atluri,S.N.(2013):Application of the MLPG Mixed Collocation Method for Solving Inverse Problems of Linear Isotropic/Anisotropic Elasticity with Simply/Multiply-Connected Domains.CMES:Computer Modeling in Engineering&Sciences,vol.94,no.1,pp.1-28.
Zhu,T.;Zhang,J.D;Atluri,S.N.(1998):A local boundary integral equation(LBIE)method in computational mechanics,and a meshless discretization approach.Computational Mechanics,vol.21,no.3,pp.223-235.

