Statistical Second-order Two-scale Method for Nonstationary Coupled Conduction-Radiation Heat Transfer Problem of Random Porous Materials
Zhiqiang Yang,Yufeng Nie,Yatao Wu,Zihao Yangand Yi Sun
1 Introduction
Porous materials are widely used in high technology engineering as well as ordinary industrial products owing to their high temperature resistance,high radiation attenuation coefficient and light weight.Especially,with rapid development of space aircraft,porous materials have attracted tremendous attention and wide research interests in thermal engineering.Therefore,the accurate determination of thermal properties of porous materials has been an important issue.Some scientists and engineers investigated the physical properties of porous materials by physical tests,various empirical and semi-empirical numerical methods[Zhou,Qi and Shao(2006);Glicksman,Schuetz and Sinofsky(1987);Liang and Qu(1999);Contento,Oliviero,Bianco and Naso(2014)].Later,Dong et al.proposed a novel method"Computational Grains",which enables a direct numerical simulation of a large number of heterogeneous materials[Dong,Gamal and Atluri(2013);Dong and Atluri(2012a);Dong and Atluri(2012b)].The literatures mentioned above have just predicted effective macroscopic properties of thermal conduction and thermal radiation,respectively,and can not be employed to calculate the temperature and heat flux fields at mesoscopic level.Meanwhile,other researchers were interested in the modeling of the heat transfer at high temperatures,taking into account both conductive and radiative contributions[Zhao,Lu and Hodson(2004);Zhao,Tassou and Lu(2008);Loretz,Coquard,Baillis and Maire(2008);Coquard,Rochais and Baillis(2009);Coquard,Rochais and Baillis(2012)].It can be seen that the literature on experimental and theoretical models of radiation or conduction in porous materials are abundant,but the number of numerical studies remain relatively limited.Moreover,these experimental investigations generally concern the radiation or the conduction alone,requiring expensive equipments,especially for measurements at high temperatures[Coquard,Rochais and Baillis(2009)].Actually,in many practical thermal engineering problems,coupled conduction and radiation problem should be considered in order to give more accurate results.Moreover,the random porous materials have better physical properties and agree with the real working environment of materials more.Thus it is significant and meaningful to study the coupled conduction-radiation heat transfer problem of porous materials with random distribution.
The ways of heat transfer in porous materials contains conduction,convection and radiation.Convection occurs by flow,and can be neglected at low pressures or in closed-cell porous materials[Liu and Zhang(2006);Daryabeigi(1999)].Radiation is a way of heat transmission and sometimes plays an important role in heat transfer at high temperature.Considering the surface radiation of porous materials,some interesting works were reported in recent years.Liu and Zhang(2006)predicted the effective macroscopic properties of heat conduction-radiation problem.Bakhvalov(1981)obtained the formal expansions for the solution of those problems,but had no theoretical justification.On this basis,Allaire and El Ganaoui(2009)studied a linear heat conduction equation with ε?1-order radiation boundary conditions by two-scale asymptotic expansion.Yang[Yang,Cui,Nie and Ma(2012);Yang,Cui and Li(2013)]proposed a second-order two-scale method to solve the coupled conduction and radiation equation with a classical radiation model in physics.In addition,for the optically thick materials at high temperature with high porosity,scientists considered the radiation problem approximated by Rosseland equation in the fields of experimental and theoretical studies[Coquard,Rochais and Baillis(2009);Daryabeigi(1999);Doermann and Sacadura(1996);Yan(2006)].Experimental studies and theoretical prediction models can be just applied to the predicting of the macroscopic effective properties of porous materials,and no model has taken into account random porous materials with all random parameters together,including the shape,orientation,spatial location,volume fraction and so on.So this paper will lay a strong emphasis on the investigation of the Rosseland problem for the porous materials with random distribution.
Based on the asymptotic expansion homogenization approach[Bensoussan,Lions and Papanicolaou(1978);Oleinik,Shamaev and Yosi fian(1992)],Cui proposed a multi-scale analysis method for different types of composites[Yang,Cui,Nie and Ma(2012);Yang,Cui and Li(2013);Cui,Shin and Wang(1999);He and Cui(2006);Li and Cui(2005);Yu,Cui and Han(2008);Yang,Cui,Nie,Wu,Yang and Wu(2013);Yu,Cui and Han(2009)].They established a second-order two scale analysis method to predict physical and mechanical properties of composites with periodic configuration[Yang,Cui,Nie and Ma(2012);Cui,Shin and Wang(1999);He and Cui(2006)].Meanwhile,for the physics field problems of random composites,Jikov,Kozlov and Oleinik(1994)proved the existences of the homogenized coefficients and the homogenized solution.On the basis of the Monte Carlo method,Cui[Yang,Cui and Li(2013);Li and Cui(2005);Yu,Cui and Han(2008);Yang,Cui,Nie,Wu,Yang and Wu(2013);Yu,Cui and Han(2009)]established a statistical second-order two-scale analysis method by introducing a random sample model to predict physical and mechanical properties of the composite structure with random distribution.This method is able not only to show the macro characteristic of composite material with random configurations,but also greatly decrease the computation time required for numerical simulations.
However,the previous second-order two-scale asymptotic expansion cannot be employed to the coupled conduction-radiation heat transfer problem because of the nonlinearity of the coupled problem.In this paper,we introduce higher-order correction terms into the asymptotic expansion of the temperature field,and derive a family of cell problems.A new SSOTS method is developed by a constructive way to predict heat transfer properties,and calculate temperature and heat flux fields at mesoscopic level of random porous materials.
The remainder of this paper is outlined as follows.In the following section,the mesoscopic configurations for porous materials with random distribution are represented.Section 3 is devoted to the formulations of the SSOTS method and the algorithm procedure for the maximum heat flux density.Finally,numerical results for the performance analysis of coupled conduction-radiation heat transfer are shown,which strongly support our method.
Throughout the paper the Einstein summation convention on repeated indices is adopted.
2 Representation of porous materials with random distribution
Referring to Ref.[Li and Cui(2005);Yu,Cui and Han(2008)],we suppose that all the pores in the geometry are considered as ellipsoids,which are randomly distributed in the matrix.In this paper,all of the ellipsoid pores are also considered as“same scale”,which means all of their long axes satisfyr1<a<r2,wherer1andr2are given upper and lower bounds.Then,the microstructures of random porous materials are represented as follows:
1)In the investigated structure ?ε,there exists a constant ε satisfying 0 < ε<<L,whereLdenotes the macro scale of ?ε.Thus,?εis composed of all the cells of size ε,as shown in Figure 1(a).
2)Each ellipsoid in the three-dimensional space is denoted by nine random parameters,describing the shape,size,orientation and spatial distribution of ellipsoid pores:a1,a2,a3,β1,β2,β3,x01,x02,x03,wherea1,a2anda3denote length of three axes;β1,β2and β3three Euler angles of the rotations;x01,x02andx03the coordinates of the center.Let the random vector ξ =(a1,a2,a3,β1,β2,β3,x01,x02,x03),it includes all the information of an ellipsoid.
3)Based on the above random parameters defining the ellipsoid in a cell εYs,letKdenote the maximum number of ellipsoids located inside the cell,Ysrepresents a normalized cell,and its random sample is defined as ωs,wheres=1,2,3...denote the index of samples.Then we can define a sample ωsof ellipsoidal pores distribution in a normalized statistic screen as follows:
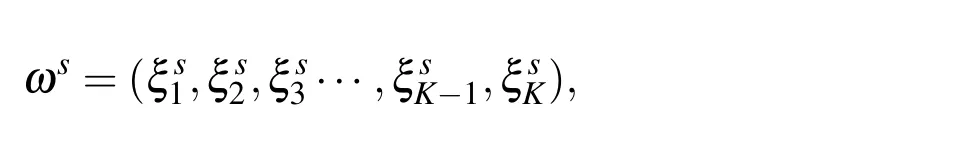
for sample ωsshown in Figure 1(b).Therefore,the investigated structure ?εis logically composed of ε-size cells subjected to identical probability distribution modelP,part of which is shown in Figure 1(a).
In this work,the following material parameters of porous materials with random distribution can be considered
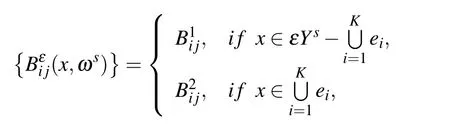

3 Statistical second-order two-scale method
3.1 Statistical second-order two-scale formulation
In this section,a novel SSOTS formulation is derived by using a constructive way for calculating the thermal properties of the heat transfer problem,including effective thermal conductivity parameters,temperature field and heat flux densities.
When the optical thickness of porous materials is sufficiently large,the local radiation heat transfer is mainly controlled by the gradient of the fourth power of the temperature.Under such conditions,one can define a radiation-based thermal conductivityby the Rosseland equation[Daryabeigi(1999);Doermann and Sacadura(1996);Yan(2006);Modest(2003);Zhang and Cui(2012);Zhang(2012);Yang,Cui and Zhang(2013)].Then,we consider the coupled conductionradiation heat transfer problem for a given structure as follows:

whereTε(x,ω,t)denotes the temperature,are the coefficients of the thermal conductivity and thermal radiation,respectively. ρε(x,ω)andcε(x,ω)denote,respectively,the densities and the specific heat of porous materials,and ε> 0 is a small parameter which represents the relative size of a cell.(x,t)is the temperature on the boundary??,andf(x,t)is the internal heat source.ω ={ωs,x∈εYs??ε}.
In order to avoid the arguments on the mathematical properties of investigated functions below,we suppose that:


Figure 1:Porous materials with random distribution of pores[Li and Cui(2005)].
By supposition(ii)and(iii),for any fixed given sample ω,Zhang[Zhang and Cui(2012);Zhang(2012)]proved the existence and uniqueness of Eq.(1).
It is well known that the temperature increments of porous material with random distribution depend not only on its global behaviors,but also on random mesoscopic configurations.It hence can be expressed asTε(x,ω,t)=T(x,y,ω,t),wherey=,xdenotes the macroscopic coordinate andyis the local one.And then material parameters can be expressed as ρε(x,ω)= ρ(y,ω),cε(x,ω)=c(y,ω),(x,ω)=kij(y,ω)and(x,ω)=bij(y,ω).
In order to obtain the two-scale expression of the temperature field,it is assumed thatTε(x,ω,t)can be expanded into the series of the following form:

whereT0(x,t)only reflects the macroscopic behaviors of the structure,and is called the homogenization solution.P1(x,y,ω,t)is the asymptotic expansion function depending the two-scale variablesxandy.Nα1(x,y,ωs),Mα1α2(x,y,ωs),Nα1α2(x,y,ωs),Rα1(x,y,ωs),Cα1(x,y,ωs)and θ(x,y,ωs)are the local solutions,respectively.They will be determined below.For simplicity,letT0=T0(x,t)andf=f(x,t).
It is worth noting that the expansion(2)is different from the traditional form given by[Li and Cui(2005)],the differences are that the correction termsNα1α2(x,y,ωs),Rα1(x,y,ωs)andCα1(x,y,ωs)are constructed into the asymptotic expansion and all of the correction terms depend on the macroscopic variablexowing to the thermal radiation.
Taking into account

and substituting(2)into(1)yield the equalities


Supposing that the equality(4)holds for any ε> 0,then from the coefficients of ε?1in both sides of equality(4),the following equality is obtained:
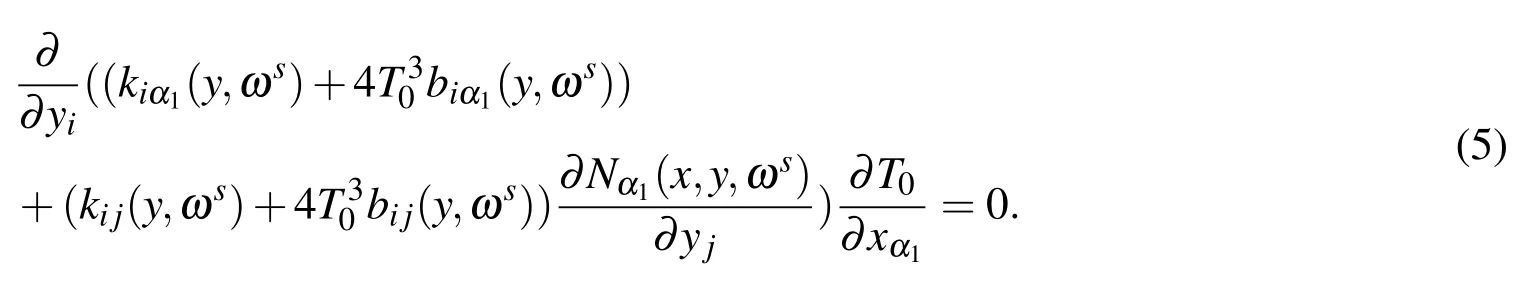
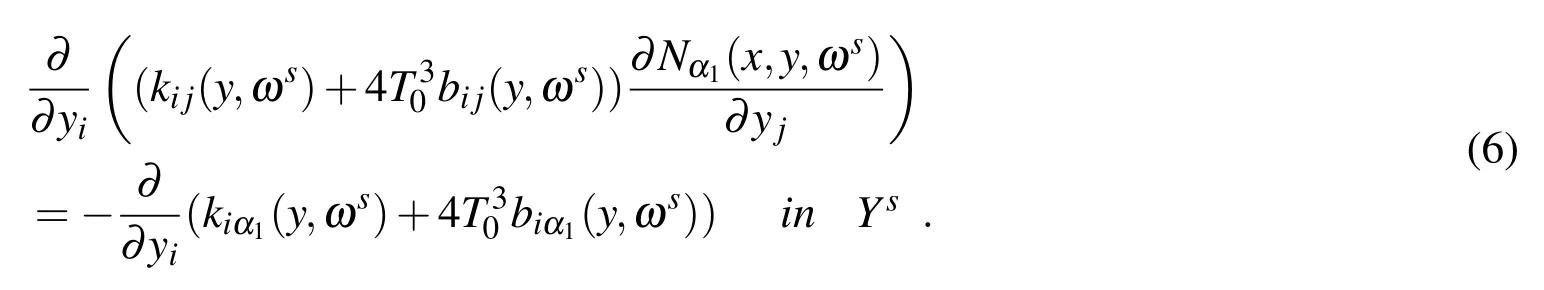
To attach the following boundary condition on?Ys

For any sample ωs(s=1,2,3,...),we obtain the auxiliary functionNα1(x,y,ωs).Nα1(x,y,ωs)is the solution of the following elliptic partial differential equation
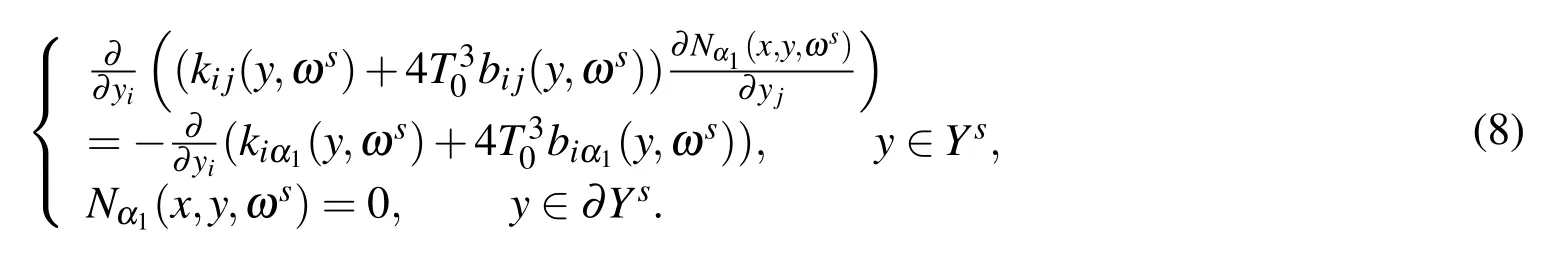
It is proved that problems Eq.(8)have a unique solution for any specified sample.Referring to[Li and Cui(2005);Yu,Cui,Han and Chen(2008);Yu,Cui and Han(2009)],for any sample ωs(s=1,2,3,...),the homogeneous parameters are defined as
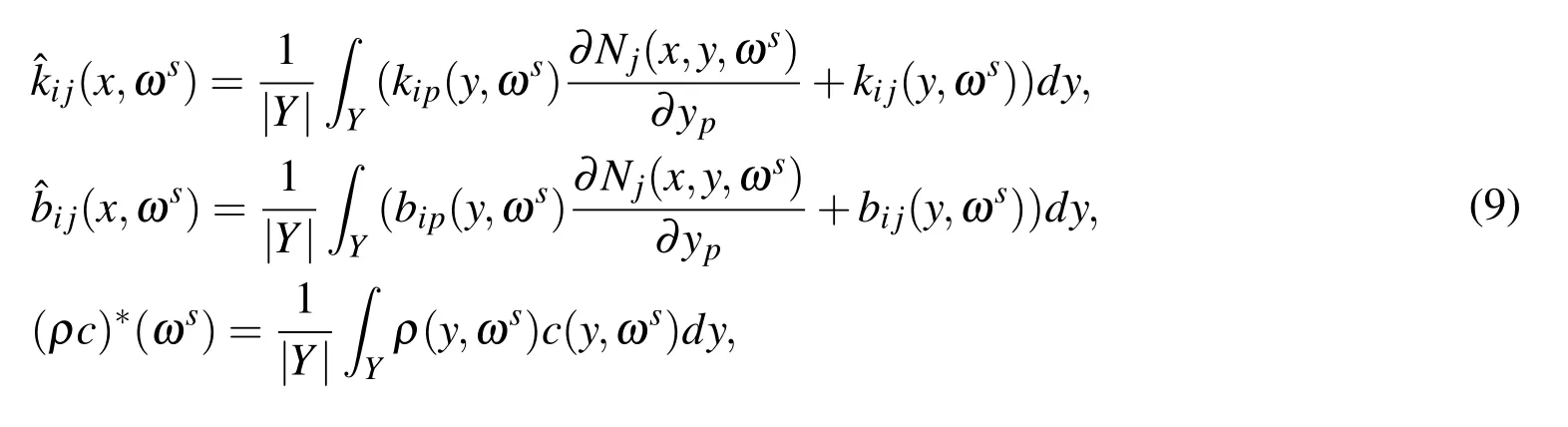
where|Y|denotes the Lebesgue measure ofY.
From the finiteness ofkij(y,ωs),bij(y,ωs),ρ(y,ωs),c(y,ωs)and Lemma 3.2 in[Li and Cui(2005)],it follows that(x,ωs),(x,ωs)and(ρc)?(ωs)are bounded random functions and exist uniquely.Then applying Kolmogorov’s strong law of large numbers,the expected homogenization coefficients can be calculated by

whereMis the maximum number of samples.
After the expected homogenized coefficients are obtained in the structure ?,the homogenized equation associated with Eq.(1)is defined as follows

Similar to[Oleinik,Shamaev and Yosi fian(1992)]and[Li and Cui(2005)],it is proved that(x)and(x)are symmetrical and positive define.Thus the homogenization problem(11)has the unique solution,see[Zhang and Cui(2012);Zhang(2012)].

Nα1α2(x,y,ωs)is the solution of the following problem:

Rα1(x,y,ωs)is the solution of the following problem:
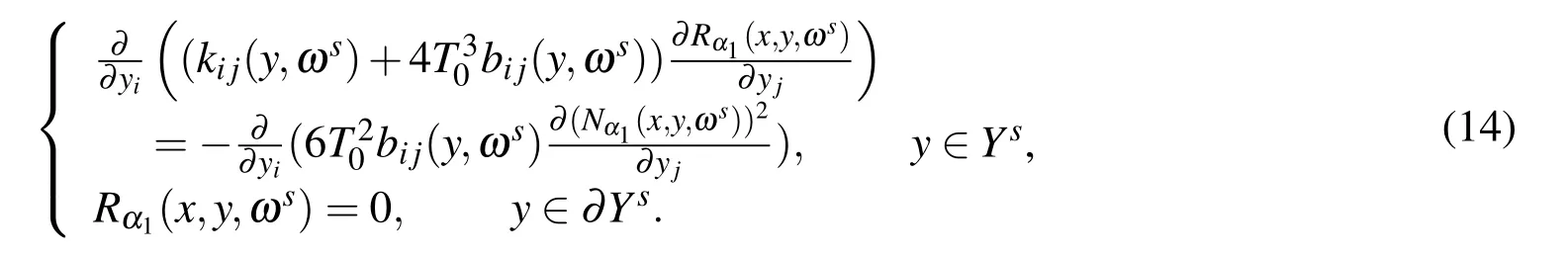
Cα1(x,y,ωs)is the solution of the following problem:
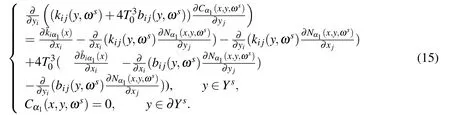
θ(x,y,ωs)is the solution of the following problem
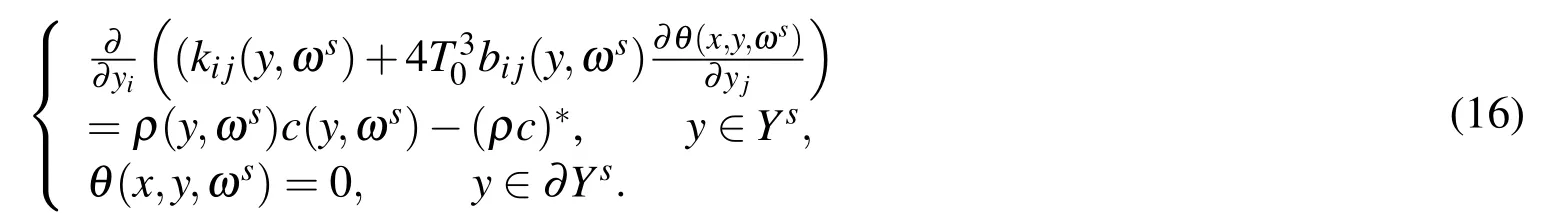
For any fixed given sample ωs(s=1,2,3,...),by Lax-Milgram theorem,Poincare’s inequality and supposition(ii),(12)-(16)are determined uniquely.
To sum up,one acquires the following theorem:
TheoremThe coupled conduction-radiation heat transfer problem(1)for porous materials with random distribution formally has a SSOTS asymptotic expansion given by

whereT0is the solution of the homogenized Eq.(11)with the parameters(10).P1(x,y,ωs,t)is the asymptotic expansion function depending the two-scale variablesxandy.Nα1(x,y,ωs),Mα1α2(x,y,ωs),Nα1α2(x,y,ωs),Rα1(x,y,ωs),Cα1(x,y,ωs)and θ (x,y,ωs)are the local solutions satisfying(8),(12),(13),(14),(15)and(16),respectively.
In practical computation of engineering only the sum of fore three terms in(17)are evaluated.Furthermore,the expansion formulation of the temperature gradients and heat flux densities are approximately given as follows
3.2 Algorithm procedure
1.Generate a sample ωsfor a unit cellYsaccording to the probability distribution modelsPand the volume fraction.Further,partitionYsinto finite element(FE)mesh.
2.Choose different pointsxi(i=1,2,···,)??εand solveNα1(xi,y,ωs)according to the problem(8)by FE method for a range of macroscopic temperature[Ta,Tb].And then homogenization coefficients?(xi,ωs)?and?(xi,ωs)?are evaluated by using the formula(9).
3.Repeat the step 1)and 2)forMsamples ωs∈P(s=1,···,M),andMhomogenized coefficients are obtained,respectively.The expected thermal conduc-parameters are given by the formula(10).
5.With the same meshes to 2),we evaluateMα1α2(x,y,ωs),Nα1α2(x,y,ωs),Rα1(x,y,ωs),Cα1(x,y,ωs)and θ(x,y,ωs)corresponding to a sample ωs∈Pby solving the cell problems(12),(13),(14),(15)and(16),respectively.
6.From(18)and(19),the temperature and heat flux densities distributions corresponding to the sample ωs∈Pare evaluated.
7.Suppose the value of the heat flux densities atx∈csisq(x,ωs,t).One obtains the following maximum heat flux density for a cellcscorresponding to the sample ωs∈P

8.Repeating the steps 6)and 7)forMsamples ωs∈P(s=1,···,M),one obtainsMthe maximum heat flux densityqextr(ωs,t).By analogizing the expected homogenization parameters,the expected maximum heat flux density is given by

4 Numerical experiments and results
In order to verify that the presented algorithm is feasible and effective to predict the thermal properties of the porous materials,we have developed computer programs and performed some numerical experiments.
4.1 Algorithm validation
Consider the mixed boundary value problem(1)and study the validity of the SSOTS method,a macrostructure ?ε,which is the union of entire periodic cells as illustrated in Figure 2(a),is chosen,and the unit cellY=[0,1]is as shown in Figure 2(b).The boundary temperatures in the z-direction are set asˉT1andˉT2,and the time step is taken as Δt=0.02.
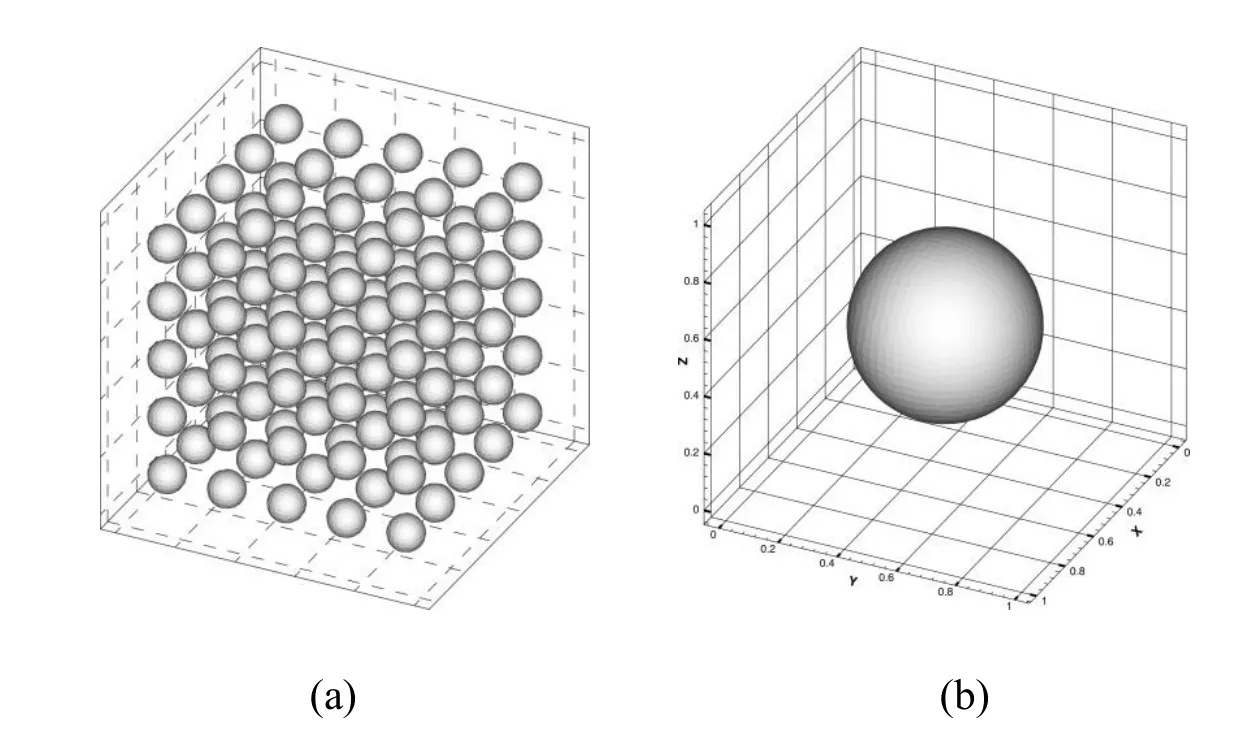
Figure 2:(a)Domain ?ε=[0,0.25]3(b)Unit cellY=[0,1]3.
Since it is difficult to find the analytical solution of(1),we have to replaceTε(x,ωs,t)with its FE solutionT?FEin a very refined mesh,and implement the tetrahedron partition for ?ε.The number of elements and nodes used in the numerical simulations are listed in Table 1.
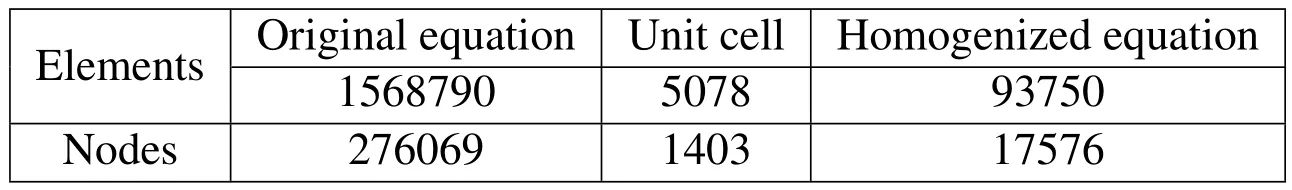
Table 1:Comparison of computational cost.
The following two cases are investigated:

The relative numerical errors of the homogenization, first-order,and second-order two-scale methods in theL2-norm andH1-norm for examples are listed in Tables 2 and 3.

Table 2:Comparison with computing results of norm L2.

Table 3:Comparison with computing results of semi-norm H1.

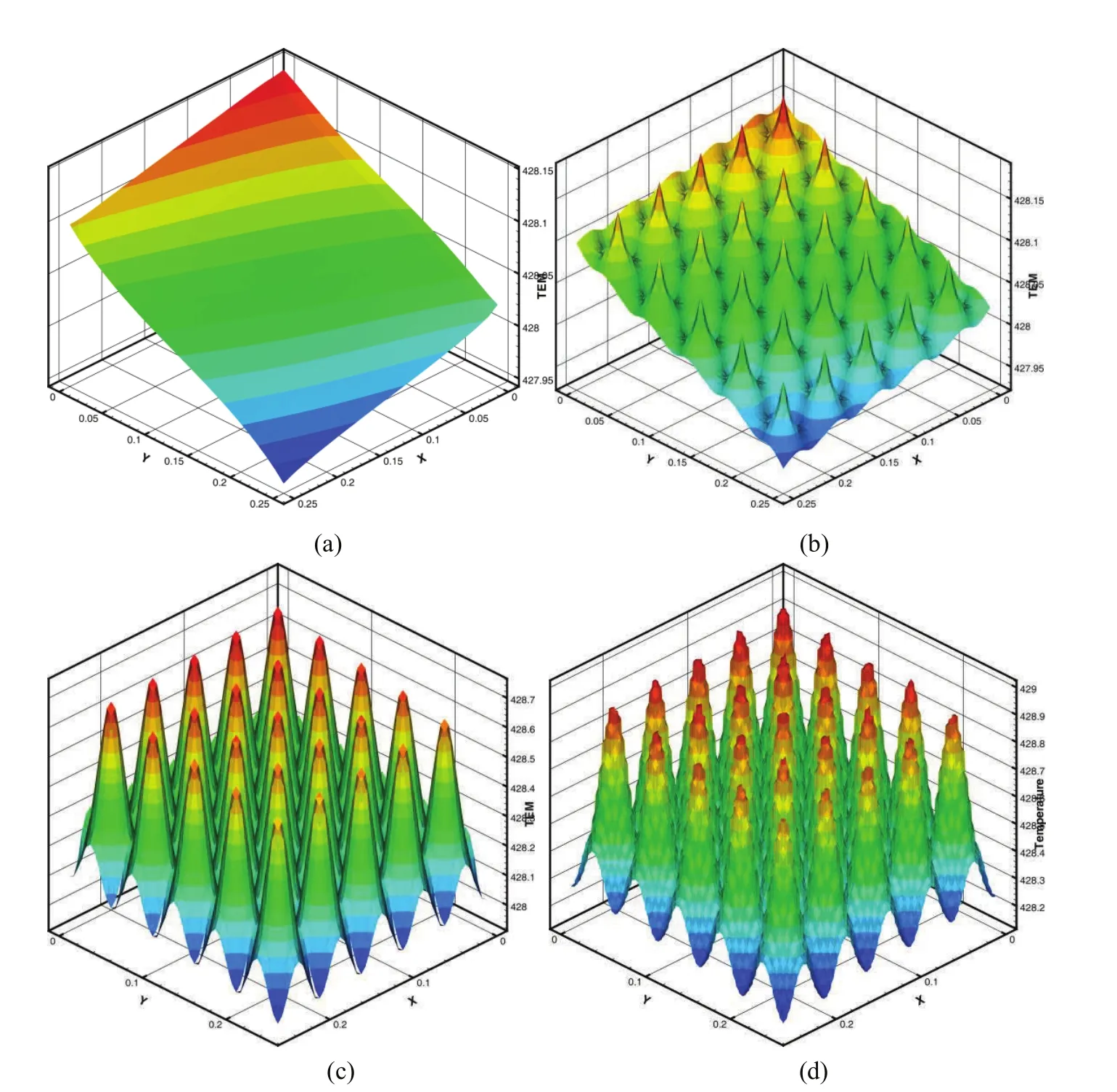
Figure 3:t=0.2;Case 1(a)T0(x,t);(b)(x,ωs,t);(c)(x,ωs,t);(d)T?FE.
In practical engineering,porous materials generally consist of a large number of pores.A porous system depicted in Figure 5 is used to demonstrate the effectiveness of the SSOTS computational method,consisting of 27000 pores with a diameter of d=4.1667mm.The thermal conductivity of the matrix isk=150WK?1m?1.The boundary temperatures in the z-direction are set as=100K and=500K.The internal heat sourcef=1000MWm?3.Other materials parameters are the same as example listed in Case 1.
Figures 6(a)–(c)illustrate the numerical results forT0(x,t),(x,ωs,t)and(x,ωs,t)at the intersectionz=0.13333 at timet=0.2.
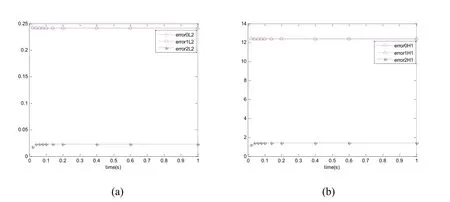
Figure 4:Case 1;(a)the evolution of L2relative errors with t;(b)the evolution of H1relative errors with t.

Figure 5:Porous materials with a large number of pores.?ε=[0,0.25]3.
Both the SSOTS method and the direct numerical simulations are performed on the same computer(which has memory of 96GB and 24 processors with CPU=2.33GHz).On the aspect of the SSOTS method,it is very cheap to solve the simulation(it takes about 40 seconds to finish solving the cell problem,and about 60 seconds for the homogenized problem),which takes the majority of the computational efforts.On the other hand,we cannot easily obtainT?FEby classical numerical methods because it would require very fine meshes and a great amount of computation.Moreover,the convergence of FE method is not easy.
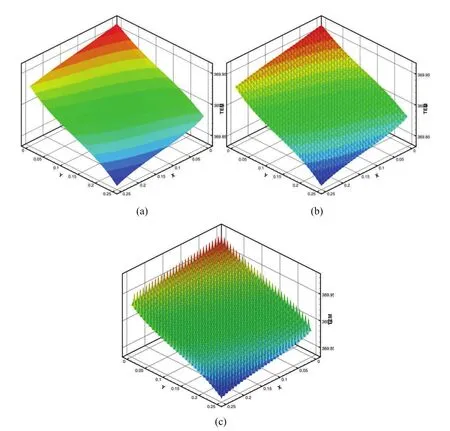
Figure 6:t=0.2;(a)T0(x,t);(b)(x,ωs,t);(c)(x,ωs,t).
From the results presented in Tables 2-3 and Figures 3-6,we can see that the statistical second-order two-scale approximate solution is in a good agreement with the FE solution in a refined mesh,and can effectively capture the local fluctuations caused by 3-D microstructures well.But the statistical first-order two-scale approximate solution and the homogenized solution are not capable of providing satisfactory results,especially when the thermal conduction coefficients in different parts of unit cell are large or the source term varies with large amplitude.The statistical second-order two-scale method is clearly the best among the computation schemes studied in this paper,and it gives the accurate numerical solutions.Furthermore,the proposed method is suitable for a very small periodic parameter ε;i.e.,there are a great number of cells in porous materials.
From Table 1,it is seen that the mesh partition numbers of statistical second-order two-scale approximate solution are much less than that of refined FE solution,especially for small ε.It means the new approximate solution can greatly save computer memory and CPU time,which is very important in engineering computations.
4.2 Thermal properties of randomly distributed porous material
In order to investigate thermal properties of porous materials with random distribution,we consider three different types of microscopic distributions and their effective computer generation algorithm has been developed by authors[Yu,Cui and Han(2008)]based on the probability distribution model of pores:spherical pores subject to uniformly stochastic distribution in a ε-cell;spherical pores subject to normal distribution around the centric point of ε-cell;orientations of ellipsoidal pores,whose long axes is about two times that of the middle axes and short axes,which are subjected to normal distribution alongx1-axis,and subjected to uniformly stochastic distribution in ε-cell.Figure 7 depicts the three samples corresponding to those.The effect of locations,orientations and shapes of pores on material properties is investigated by the SSOTS method,and due to pores random dispersion,the numerical results of the different samples will vary even for the same distribution models of pores.Therefore,to obtain more accurate prediction values a numbers of samples are required.It should be noted that the following computation results are averaged from 50 random samples.

Figure 7:(a)uniform distribution(b)location-normal distribution(c)orientationnormal distribution.
Figure 8 depicts the geometry structure of the plate studied which is of the length is 10mm,width is 10mm,and the thickness is 5mm,respectively.The internal heat sourcef=10MWm?3,and the boundary temperatures in the z-direction are set as(x,t)=100K,(x,t)=500K.The materials parameters of porous materials are listed in Table 4,and we choose the effective radiative thermal conductivity calculated by genetic algorithm in Yan(2006).The radii are both taken as 0.05 for the spherical pores subjected to uniform distribution and spherical pores subjected to normal distribution.As for the orientations of spherical pores are normal distribution,the sizes of their long axes are taken as 0.1,middle axes and short axes are both 0.05.
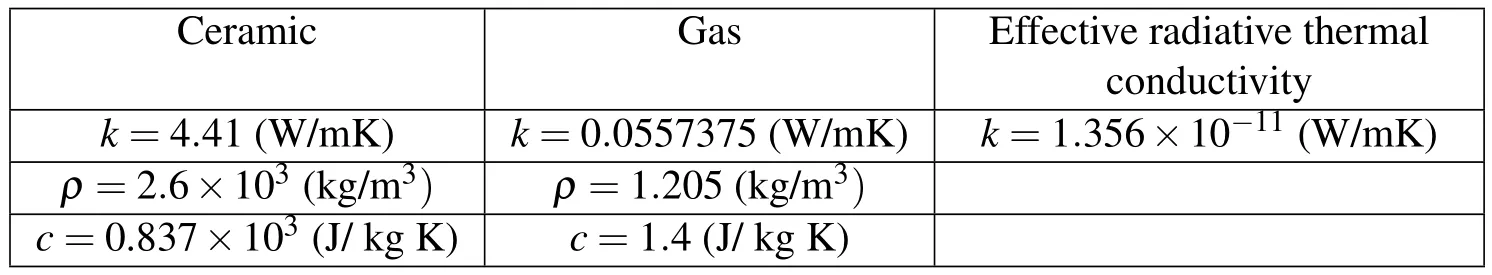
Table 4:Material parameters of porous materials[Yan(2006)].
Figure 8:Schematic of porous materials plate.
From the discussion in Section 3 it follows that the effective thermal conductivity and effective radiative thermal conductivity of the porous materials are dependent of temperature because of the nonlinearity of Rosseland equation.In order to investigate thermal properties of the porous materials,the effective thermal conductivity coefficients are obtained,and compared to Hashin-shtrikman bounds and Voigt-Reuss bounds[Jikov,Kozlov and Oleinik(1994);Hashin and Shtrikman(1963)]for different temperatures.The results are listed in Table 5 as temperatures are 50K and 1250K for different volume fractions with normal distribution of pores.Table 6 shows that the effective thermal conductivity at 1000K and the spherical pores are orientation-normal distribution around the centric point of ε-cell.From Tables 5 and 6,it can be seen that the effective thermal conductivity decrease with the increment of volume fraction,and SSOTS method show the effective thermal conductivity which satisfy Hashin-shtrikman bounds and Voigt-Reuss bounds,between super and low bounds.
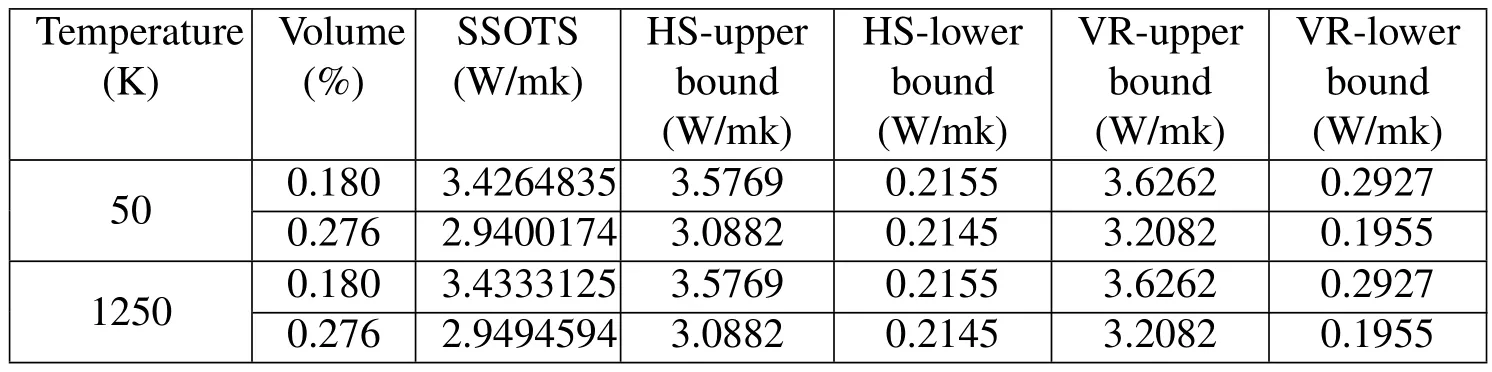
Table 5:Effective thermal conductivity of porous materials for different volume fractions at 50K and 1250K with normal distribution of pores.
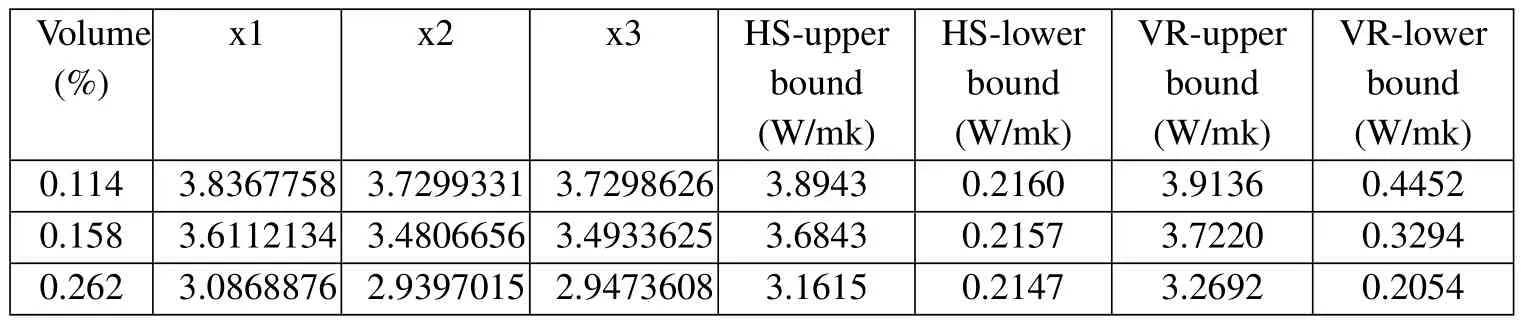
Table 6:Effective thermal conductivity of porous materials for different volume fractions at 1000K with orientation-normal distribution of spherical pores.
In Figure 9 we plot K11 and K22 of the homogenized conductivities of porous material with volume fraction are 38%in terms of the macroscopic temperature from 100K to 1500K,and pores subject to uniform random distribution.As a result,we note that these diagonal components are different at high temperature because of the effect of radiation.
We have studied the limit of the cell problems and the homogenized coefficients when the macroscopic temperature goes to infinity.In Figs.10 we plot the three different values of the homogenized conductivities with volume fraction of pores is 38%,and find that,at extremely high temperatures,they reach the limit value,which has the similar changing trends to the results showed in Allaire and Ganaoui(2009)owing to the importance of heat radiation at the high temperature.

Figure 9:K11 and K22 of the homogenized conductivities as a function of the macroscopic temperature with uniform distribution of pores.
Figure 11 demonstrates that the statistically maximum heat flux density increases with the increment of time for different volume fraction,and the(t)of orientation normal distribution is larger than the(t)of uniform distribution in a unit cell,and they all reach a steady state at last.So the curves of Fig.11 indicate that the statistically maximum heat flux density of the porous materials is concurrently affected not only by macroscopic properties,but also by the microscopic structure of random distribution of pores.
Figures 12 and 13 illustrate heat flux densities distribution for different random distributions with different volume fractions of pores at timet=1.0.One can see that the heat flux densities in the two local cells are different for different distribution with a marked fluctuation,and local heat flux densities with high volume fraction are relatively high.Moreover,the statistically heat flux densities with orientation normal distribution of pores are larger than that with uniform distribution of pores for the same volume fraction.
All the results from above examples demonstrate that the thermal properties of coupled conduction-radiation heat transfer problem for porous materials with random distribution can be effectively predicted by the SSOTS method.
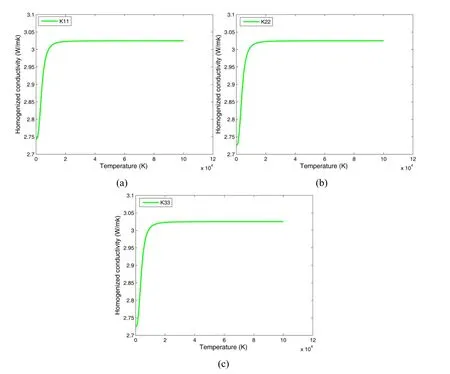
Figure 10:Homogenized conductivities as a function of the macroscopic temperature with uniform distribution of pores.(a)K11;(b)K22;(c)K33.
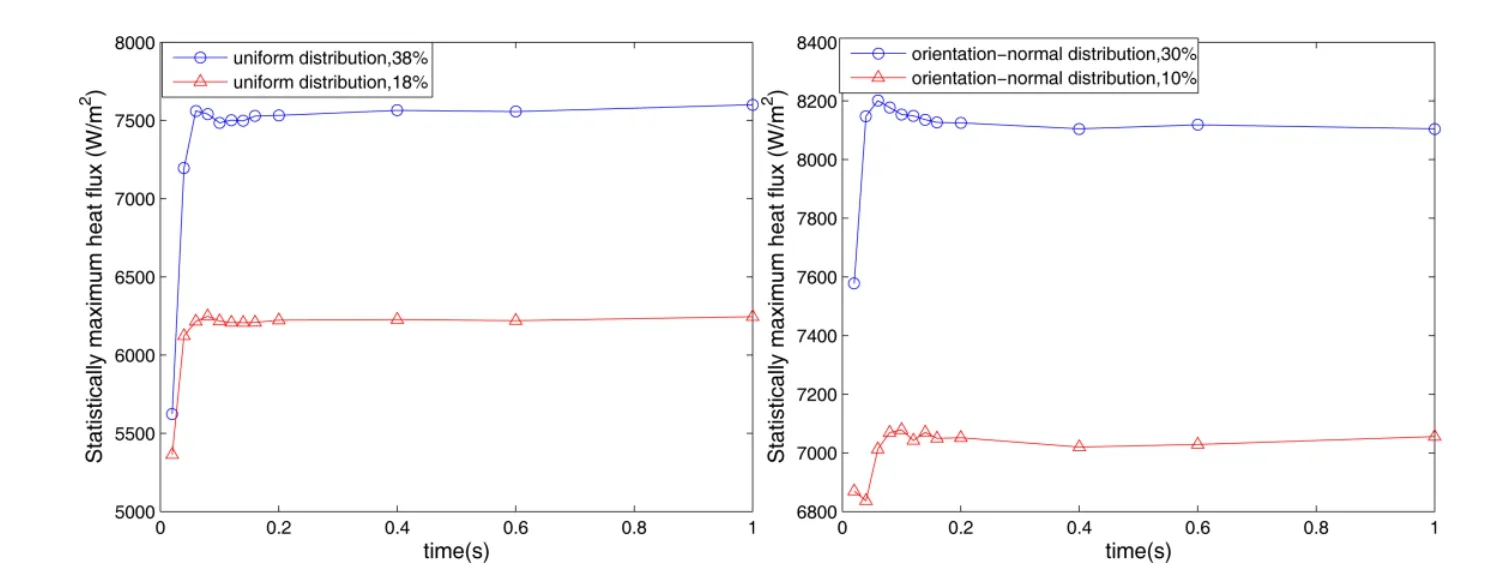
Figure 11:Statistically maximum heat flux density as time for different distributions of pores locations.

Figure 12:Heat flux densities in a local cells with different volume fraction and pores subjected to uniform distribution(a)0.09(b)0.26.
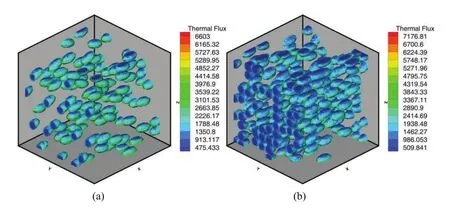
Figure 13:Heat flux densities in a local cells with different volume fraction and pores subjected to orientation-normal distribution(a)0.09(b)0.20.
5 Conclusions
In this paper,the SSOTS method is presented to predict the heat transfer performance of nonstationary coupled conduction-radiation problem for porous materials with random distribution.The validity of this two-scale model and the effectiveness of the developed SSOTS method have been verified by comparing with FE methods in a very fine mesh.As a result,the statistical second-order two-scale method is effective to numerically solve the coupled conduction-radiation equation.Besides,the convergence of the SSOTS numerical results is much better than FE method,especially at a high temperature.
The macroscopic thermal properties for the structures with varying probability distribution models,including volume fraction,location,orientation and spatial distribution of pores,are shown.Numerical results demonstrate that the microstructure has a marked effect on the macroscopic thermal properties.specifically,these properties vary with the probability model of random inclusion dispersions.And the local behaviors caused by microstructures inside porous materials can be captured exactly by the SSTOS method.Therefore,the SSOTS method proposed in this paper can be practically employed to predict thermal properties of the random porous materials.
Furthermore,the SSOTS method and related numerical approximation techniques developed in this work is helpful to the design and optimization of the porous materials with random distribution.
Acknowledgement:This work is supported by the Special Funds for National Basic Research Program of China(973 Program 2010CB832702),and also supported by the State Key Laboratory of Science and Engineering Computing,and Center for High Performance Computing of Northwestern Polytechnical University.
Allaire,G.;El Ganaoui,K.(2009):Homogenization of a conductive and radiative heat transfer problem.Multiscale Model.Sim.,vol.7,pp.1148-1170.
Bakhvalov,N.S.(1981):Averaging of the heat-transfer process in periodic media with radiative.Differ.Uraun.,vol.17,no.10,pp.1774-1778.
Bensoussan,A.;Lions,J.L.;Papanicolaou,G.(1978):Asymptotic Analysis for Periodic Structure,North-Holland,Amsterdam.
Cui,J.Z.;Shin,T.M.;Wang,Y.L.(1999):Two-scale analysis method for bodies with small period configuration.Struct.Eng.Mech.,vol.7,pp.601–614.
Contento,G.;Oliviero,M.;Bianco,N.;Naso,V.(2014):Prediction of radiative heat transfer in metallic foams.Int.J.Therm.Sci.,vol.76,pp.147-154.
Coquard,R.;Rochais,D.;Baillis,D.(2009):Experimental investigations of the coupled conductive and radiative heat transfer in metallic/ceramic foams.Int.J.Heat Mass Tran.,vol.52,pp.4907-4918.
Coquard,R.;Rochais,D.;Baillis,D.(2012):Conductive and Radiative Heat Transfer in Ceramic and Metal Foams at Fire Temperatures.Fire Technol.,vol.48,no.3,pp.699-732.
Doermann,D.;Sacadura,J.F.(1996):Heat transfer in open cell foam insulation.J.Heat Trans.-T Asme,vol.118,pp.88-93.
Daryabeigi,K.(1999):Analysis and testing of high temperature fibrous insulation for reusable launch vehicles.37th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit,January 11-14,Reno,NV.
Dong,L.T.;Atluri,S.N.(2012):Development of 3D Trefftz Voronoi Cells with Ellipsoidal Voids&/or Elastic/Rigid Inclusions for Micromechanical Modeling of Heterogeneous Materials.CMC-Comput.Mater.Con.,vol.30,no.1,pp.39-81.
Dong,L.T.;Atluri,S.N.(2012):T-Trefftz Voronoi cell finite elements with elastic/rigid inclusions or voids for micromechanical analysis of composite and porous materials.CMES:Comp.Model.Eng.,vol.83,no.2,pp.183-219.
Dong,L.T.;Gamal,S.H.;Atluri,S.N.(2013):Stochastic Macro Material Properties,Through Direct Stochastic Modeling of Heterogeneous Microstructures with Randomness of Constituent Properties and Topologies,by Using Trefftz Computational Grains(TCG).CMC-Comput.Mater.Con.,vol.37,no.1,pp.1-21.
Glicksman,L.R.;Schuetz,M.;Sinofsky,M.(1987):Radiation heat transfer in foam insulation.Int.J.Heat Mass Tran.,vol.30,pp.187-197.
Hashin,Z.;Shtrikman,S.(1963):A variational approach to the theory of the elastic behavior of multiphase materials.J.Mech.Phys.Solids,vol.11,pp.127-140.
He,W.M.;Cui,J.Z.(2006):A finite element method for elliptic problems with rapidly oscillating coefficients.Bit Numer.Math.,vol.22,pp.581-594.
Jikov,V.V.;Kozlov,S.M.;Oleinik,O.A.(1994):Homogenization of Differential Operators and Integral Functions,Springer:Berlin.
Liang,X.G.;Qu,W.(1999):Effective thermal conductivity of gas-solid composite materials and the temperature difference effect at high temperature.Int.J.Heat Mass Tran.,vol.42,pp.1885-1893.
Loretz,M.;Coquard,R.;Baillis,D.;Maire,E.(2008):Metallic foams:Radiative properties/comparison between different models.J.Quant.Spectrosc.Radiat.Trans.,vol.109,no.1,pp.16-27.
Liu,S.T.;Zhang,Y.C.(2006):Multi-scale analysis method for thermal conductivity of composite material with radiation.Multidiscipline Modeling in Mat.and Str.,vol.2,no.3,pp.327-344.
Li,Y.Y.;Cui,J.Z.(2005):The multi-scale computational method for mechanics parameters of the materials with random distribution of multi-scale grains.Compos.Sci.Technol.,vol.65,pp.1447-1458.
Modest,M.F.(2003):Radiative Heat Transfer,second ed.,New York.
Oleinik,O.A.;Shamaev,A.S.;Yosi fian,G.A.(1992):Mathematical Problems in Elasticity and Homogenization,North-Holland,Amsterdam.
Su,F.;Xu,Z.;Dong,Q.L.;Li,H.S.(2011):A second-order and two-scale computation method for heat conduction equation with rapidly oscillatory coefficients.Finite Elem.Anal.Des.,vol.47,pp.276-280.
Yang,Z.Q.;Cui,J.Z.;Nie,Y.F.;Ma,Q.(2012):The second-order two-scale method for heat transfer performances of periodic porous materials with interior surface radiation.CMES:Comp.Model.Eng.,vol.88,no.5,pp.419-442.
Yang,Z.Q.;Cui,J.Z.;Li,Y.Q.(2013):The statistical second-order two-scale method for heat transfer performances of random porous materials with interior surface radiation.Int.J.Numer.Anal Mod.Ser.B,vol.4,no.2,pp.151-166.
Yan,C.H.(2006):Thermal insulating mechanism and research on thermal insulating efficiency of thermal insulations of metallic thermal protection system,PhD Thesis,Harbin Institute of Technology,(in Chinese).
Yu,Y.;Cui,J.Z.;Han,F.(2008):An effective computer generation method for the composites with random distribution of large numbers of heterogeneous grains.Compos.Sci.Technol.,vol.68,pp.2543-2550.
Yang,Z.H.;Cui,J.Z.;Nie,Y.F.;Wu,Y.T.;Yang,B.;Wu,B.(2013):Microstructural modeling and second-order two-scale computation for mechanical properties of 3D 4-directional braided composites.CMC-Comput.Mater.Con.,vol.38,no.3,pp.175-194.
Yu,Y.;Cui,J.Z.;Han,F.(2009):The statistical second-order two-scale analysis method for heat conduction performances of the composite structure with inconsistent random distribution.Comp.Mater.Sci.,vol.46,pp.151-161.
Yang,Z.Q.;Cui,J.Z.;Zhang,Q.F.(2013):The statistical second-order twoscale analysis method for conduction-radiation coupled heat transfer of porous materials.Acta Mater.Compos.Sin.,vol.30,no.2,pp.173-182.
Zhou,W.Y.;Qi,S.H.;Li,H.D.;Shao,S.Y.(2006):Study on insulating thermal conductive BN/HDPE composites.Thermochim.Acta,vol.452,pp.36-42.
Zhao,C.Y.;Lu,T.J.;Hodson,H.P.(2004):Thermal radiation in ultralight metal foams with open cells.Int.J.Heat Mass Tran.,vol.47,pp.2927-2939.
Zhao,C.Y.;Tassou,S.A.;Lu,T.J.(2008):Analytical considerations of thermal radiation in cellular metal foams with open cells.Int.J.Heat Mass Tran.,vol.47,pp.929-940.
Zhang,Q.F.;Cui,J.Z.(2012):Existence theory for Rosseland equation and its homogenized equation.Appl.Math.Mech-Engl.,vol.33,no.12,pp.1595-1612.
Zhang,Q.F.(2012):Multi-scale analysis method for Rosseland-type equation of periodic composites,PhD Thesis,Chinese Academy of Sciences,(in Chinese).

