GILL MEDIATES IMMUNE RESPONSES AFTER GRASS CARP REOVIRUS CHALLENGE IN GRASS CARP (CTENOPHARYNGODON IDELLA)
LI Qing-Mei , CHEN Li-Jun, RAO You-Liang, FU Xiao-Zhe and SU Jian-Guo
(1. Key Laboratory of Fishery Drug Development, Ministry of Agriculture, and Key Laboratory of Aquatic Animal Immune Technology, Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510380, China; 2. College of Veterinary Medicine, Northwest A&F University,Yangling 712100, China; 3. College of Animal Science and Technology, Northwest A&F University, Yangling 712100, China)
Abstract: Gill plays an important physical barrier role in defending environmental microbes. How are immune responses to endogenous viruses in gill? In the present study, mRNA expressions of 12 antiviral immune-related genes were examined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) gill after grass carp reovirus (GCRV) challenge. The relative values of CiTLR3, CiTLR7,CiTLR22, CiRIG-I, CiMDA5, CiLGP2, CiNOD1, CiNOD2 and CiIFN-I were almost up-regulated at 12h, 24h,48h and 72h. Additionally, the mRNA expression of CiIgM was triggered at 72h. However, relative expressions of CiMyD88 and CiIPS-1 were down-regulated at 6h, and subsequently increased. To further verify the reliability of viral infection, VP4 gene (outer capsid protein of GCRV, segment 6) was checked by RT-PCR amplification. The results indicate that gill serves as an important immune organ, and plays crucial roles in triggering antiviral immune responses in grass carp.
Key words: Immune responses; Grass carp; Grass carp reovirus; Gill
Grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella, a member of the family Cyprinidae, is one of the most important farmed fish species in global aquaculture, mainly in China. Production of grass carp constitutes the largest aquaculture industry in China. However, it is susceptible to several epidemics, thereinto hemorrhage disease, caused by the grass carp reovirus (GCRV), is a viral disease resulting in tremendous losses.
The innate immune system serves as the first line of protection against invading microbial pathogens through a limited number of germ line-encoded pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). PRRs recognize different pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), then trigger innate immunity and subsequently adaptive immune response[1]. Recently, three major classes of PRRs related-recognition of viral PAMPs have been identified, including toll-like receptors (TLRs), retinoic acid-inducible gene I-like receptors (RLRs) and nucleotide-oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs)[2].
To date, more than 13 TLR members have been found in mammals. TLRs are implicated in the detection of a vast range of pathogens including viruses,bacteria, protozoa and fungi[3]. Various viruses are perceived by intracellular TLRs (TLR3, TLR7/TLR8 and TLR9). TLR3 senses dsRNA, TLR7/ TLR8 mainly recognizes single-stranded RNA (ssRNA), and TLR9 is triggered by CpG DNA[4]. Upon viral activation,TLR7/TLR8 and TLR9 recruit the adaptor molecule MyD88 (myeloid differentiation factor 88) that initiates the induction of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and interferon regulatory factors-3/7 (IRF-3/7), both of them contribute to type I interferon (IFN-I) and pro-inflammatory cytokines productions[4]. Additionally,TLR22 occurs exclusively in aquatic animals (teleosts and amphibians) and recognizes long-sized dsRNA[5,6].TLR3 and TLR22 rely on TIR domain-containing adaptor-inducing IFN-β (TRIF) to trigger downstream signaling cascades of IFN-I and pro-inflammatory cytokines[5].
RLRs consist of RIG-I (retinoic acid-induced protein I),MDA5 (melanoma-differentiation-associated gene 5) and LGP2 (laboratory of genetics and physiology 2)[7].RIG-I and MDA5 contain two N-terminal caspase recruitment domains (CARDs), a DExD/H box RNA helicase domain and a C-terminal repressor domain(RD), whereas LGP2 lacks the CARDs domain. The CARDs mediate downstream signaling cascades and induce the activation of interferon-β promoter stimulator 1 (IPS-1; also known as MAVS, CARDIF, or VISA)[8]. IPS-1 functions as an adaptor molecule mediating the activation of TBK1 (TANK-binding kinase 1) and IKK-ε (inhibitor of nuclear factor Iκ kinase-ε), which phosphorylate IRF-3/7. Then, IRF-3/7 translocates into the nucleus, and subsequently induces IFN-I and ISGs (IFN-stimulated genes)expressions[7].
NLRs, consisting of more than 20 members, are present in the cytosol and recognize intracellular microorganisms. NOD1 and NOD2 were significantly induced by GCRV in grass carp spleen[9]. NOD2 can interact with the IPS-1, leading to the activation of NF-κB and IRF-3, then induce the productions of cytokines and IFN-I in mammals[10].
In contrast to innate immunity, adaptive immunity employs antigen receptors that generate highly specific immune responses. Immunoglobulins (Igs) bind antigens with high specificity, and they are important molecules in adaptive immunity. IgM is evidenced to link innate immunity and adaptive immunity in mammals[11].Additionally, teleosts produce IgM as a primary antibody response during the infection process.
Gill is an important tissue for processing of pathogens in environmental water[12]. Some reports about tissue expressions have indicated that gill plays important immune functions in teleosts[13,14], however,expression patterns of immune-related genes are scattered. Therefore, systematic expression profiles of classical immune-related genes can contribute to clarify immune functions of fish gill. Furthermore, better understanding immune defense mechanisms may be conducive to the development of management strategies for disease control in teleosts.
In the present study, we investigated mRNA expression profiles of twelve representative immunerelated genes in grass carp gill after GCRV challenge.The results will outline immune responses to virus infection in gill.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Fish, virus challenge, sample collection, RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
Grass carp (15—20 g) from a fish farm were used as a source of mRNA expression analysis. Fish were acclimatized to laboratory conditions for one week in a quarantine area by maintaining in 300 L aerated aquaria at 28and fed twice a day.
For viral challenge, 100 μL of GCRV (097 strain,3.63×107TCID50/mL) per gram body weight, suspended in PBS, were injected intraperitoneally. The control animals were injected with PBS. Five individuals were sacrificed and their gills were harvested at 0h, 6h, 12h, 24h, 48h and 72h post injection.
The samples were homogenized in TRIZOL reagent (Invitrogen) and total RNAs were isolated according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Total RNAs were incubated with RNase-free DNase I(Roche) to eliminate contaminated genomic DNA before being reversely transcribed into cDNA using random hexamer primers and M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase (Promega).
1.2 Virus detection
All the cDNA samples were examined for the virus by RT-PCR. The gene specific primers were designed according to the VP4 gene of GCRV 097 strain. The forward primer was S131, and reverse primer was S132 (Tab. 1).
1.3 The temporal expression profiles of TLRs,RLRs, NLRs, MyD88, CiIPS-1, CiIFN-I and CiIgM genes in grass carp gill post GCRV challenge
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) method was established to quantify mRNA expressions of TLRs (CiTLR3, CiTLR7 and CiTLR22), RLRs(CiRIG-I, CiMDA5 and CiLGP2), NLRs (CiNOD1 and CiNOD2), adaptor molecules (CiMyD88 and CiIPS-1),CiIFN-I and CiIgM genes post GCRV injection in grass carp gill using CFX96 Multicolor Real-time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad). The primers were listed in Tab. 1. All cDNA concentrations were adjusted to 200 ng/μL. 18S rRNA was utilized as an internal control for cDNA normalization[15]. The qRT-PCR mixture consisted of 2 μL of cDNA sample,7.6 μL nuclease-free water, 10 μL of 2 × SYBR Green PCR master mix (TaKaRa), and 0.2 μL of each gene specific primers (10 mmol/L). The PCR cycling conditions were following: 1 cycle of 95 ℃ for 30s, 40 cycles of 95 ℃ for 5s, 60 ℃ for 30s, 1 cycle of 95 ℃ for 15s, 60 ℃ for 30s, 95 ℃ for 15s, followed by dissoci ation curve analysis to verify the amplification of a single product. The threshold cycle (CT) value was determined by using the manual setting on the CFX96 Sequence Detection System and exported into a Microsoft Excel Sheet for subsequent data analyses. The relative expression ratios of target gene in treated group versus those in control group were calculated by 2–ΔΔctmethod. Each sample was run in triplicate. The data from five independent biological replicates were subjected to one-way analysis of variance (One-way ANOVA), followed by an unpaired, two-tailed t-test. A value of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.

Tab. 1 Primers used in this study
2 Results
2.1 The verification of GCRV challenge by PCR
The electrophoresis profile was exhibited at 0h, 6h,12h, 24h, 48h and 72h post GCRV injection in both the control group and the injected group (Fig. 1). GCRV was not detected at all check points in the control group.In contrast, viral mRNA was examined in the injected group from 24h.

Fig. 1 Agarose gel electrophoresis profile of the PCR products was shown for virus detection at 0, 6h, 12h, 24h, 48h and 72h post GCRV injection. The fragment length was 312 bp
2.2 Expression profiles of TLRs and CiMyD88 in gill
The mRNA expression profiles of TLRs (CiTLR3,CiTLR7 and CiTLR22) and the adaptor molecule Ci-MyD88 were measured post GCRV injection (Fig. 2A).The mRNA expressions of target genes in the control group were no significant differences among tested time points (P>0.05) (data not shown). The relative expressions of CiTLR3 were no significant differences at 6h, and largely increased from 12h (2.42 folds,P<0.05) to 72h (7. 98 folds, P<0.05). No significant change was detected in CiTLR7 gene expression during the course of GCRV injection at 6h (P>0.05). At 12h after GCRV treatment, the expression level was slightly increased (1.53 folds, P<0.05). As time progressed, the expression level of CiTLR7 mRNA was enhanced at 24h (2.09 folds, P<0.05). After that,mRNA expressions were rapidly increased at 48h(8.03 folds, P<0.05) and 72h (12.21 folds, P<0.05).The expression level of CiTLR22 transcript was no significant difference at 6h. Then, the relative values were gradually increased from 12h (2.97 folds, P<0.05)to 72h (7.31 folds, P<0.05).
The relative expression of CiMyD88 was decreased at 6h (0.43 fold, P<0.05), then increased at 24h (1.55 folds, P<0.05) and reached the peak at 48h (5.12 folds,P<0.05). After that, the mRNA expression was still high at 72h (2.71 folds, P<0.05) although lower than that at 48h.
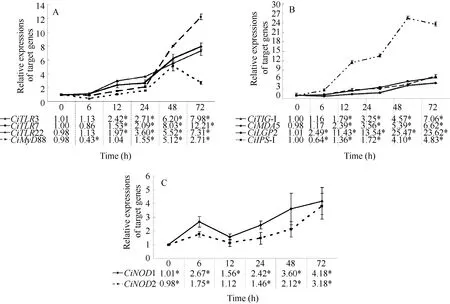
Fig. 2 mRNA expression profiles of three PRR families and their adaptors at different time points post GCRV injection in gill
2.3 Expression patterns of RLRs and CiIPS-1 in gill
The mRNA expressions of RLRs (CiRIG-I, CiMDA5 and CiLGP2) and CiIPS-1 were examined in gill post viral challenge (Fig. 2B). The expression levels of CiRIG-I were gradually increased from 12h (2.79 folds,P<0.05) to 72h (7.06 folds, P<0.05). Similarly, the relative quantities of CiMDA5 were increased between 12h(2.39 folds, P<0.05) and 72h (6.62 folds, P<0.05). The relative values of CiLGP2 were up-regulated at 6h (2.49 folds, P<0.05), and sharply increased from 12h (11.43 folds, P<0.05) to 72h (23.62 folds, P<0.05).
Interestingly, the relative value of CiIPS-1 was down-regulated to 0.64-fold (P<0.05) at 6h. After that,the expression levels were slightly increased at 12h(1.36 folds, P<0.05) and 24h (1.72 folds, P<0.05),then rapidly enhanced at 48h (4.10 folds, P<0.05) and 72h (4.83 folds, P<0.05).
2.4 Expression tendencies of NLRs in gill
The time-dependent expression patterns of CiNOD1 were shown in Fig. 2C. After GCRV challenge, the mRNA expression of CiNOD1 began to increase at 6h(2.67 folds, P<0.05). The relative expressions were slightly enhanced at 12h (1.56 folds, P<0.05). After that, the relative levels of CiNOD1 were up-regulated at 24h (2.42 folds, P<0.05), 48h (3.60 folds, P<0.05)and 72h (4.18 folds, P<0.05). Similarly, mRNA expressions of CiNOD2 were shown in Fig. 2C. The relative value was slightly increased at 6h (1.75 folds,P<0.05). Afterwards, the mRNA expression of Ci-NOD2 was decreased to the control level at 12h. Then,the relative quantities were gradually enhanced from 24h (1.46 folds, P<0.05) to 72h (3.81 folds, P<0.05).
2.5 Expression patterns of CiIFN-I in gill
The time-dependent expression patterns of CiIFN-I were examined (Fig. 3A). The expression levels of CiIFN-I were slightly increased at 6h (1.44 folds,P<0.05), then rapidly enhanced from 12h (2.81 folds,P<0.05) to 72h (8.30 folds, P<0.05).
2.6 Expression profiles of CiIgM in gill
The mRNA expression profiles of CiIgM were tested (Fig. 3B). There were no significant differences of CiIgM expressions from 0h to 48h. Then, the mRNA expression of CiIgM was enhanced at 72h(2.85 folds, P<0.05).
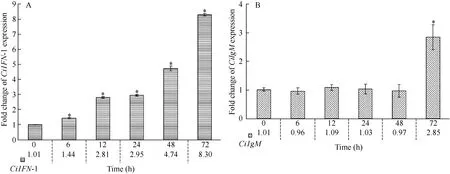
Fig. 3 The mRNA expression patterns of CiIFN-I and CiIgM at different time points after GCRV injection in gill. A: CiIFN-I; B: CiIgM.Other captions are same as those in Fig. 2
3 Discussion
Fish gill contacts with external water environment,and it is a vital organ to defense the invasion of different pathogens[12]. GCRV is endogenic virus, and intraperitoneal injection is superior to immersion or co-habitation challenge for virus invasion[16]. According to the profile of agarose electrophoresis (Fig. 1), it showed that GCRV successfully infected grass carp.
mRNA expression of TLR3 is significantly up-regulated by GCRV challenge in spleen at day 1 in grass carp[17]and in gill at 12h in rare minnow[18].The relative expressions of CiTLR3 in gill were increased from 12h to 72h post GCRV injection (Fig. 2A)and the data implied that TLR3 played a role in inducing the innate immune response against virus in grass carp gill. mRNA expressions of CiTLR22 are significantly increased at 6h, then rapidly drop to control levels from 12h to 48h post GCRV injection in spleen[6].In the present study, the expression of CiTLR22 was increased at 12h post GCRV challenge in gill (Fig. 2A).The relative value in gill was lower than that in spleen at 6h, however, the mRNA expression showed a more persistent up-regulation in gill. Taken together, the results indicated that CiTLR22 displayed different expression profiles in different tissues post GCRV challenge. The tendencies of CiTLR3 and CiTLR22 were nearly the same at examined time points in gill (Fig.2A). Therefore, TLR22 might serve as a surveillance coupled with TLR3 for dsRNA virus recognition in grass carp. TLR7 recognizes viral ssRNA inducing the production of IFN-I and inflammatory cytokines in mammals[4]. Additionally, TLR7 expression level in rainbow trout anterior kidney leukocytes is not affected by poly(I:C) treatment[19]. Interestingly, the expression of TLR7 was significantly up-regulated after GCRV injection in grass carp gill (Fig. 2A). The previous study has implied that TLR7 is involved in response to dsRNA virus in grass carp[20,21]. The results further evidenced that TLR7 might participate in the recognition of dsRNA virus in grass carp, which provided a new sight for systematic research of immune signaling pathways in teleosts. The mRNA expressions of CiMyD88 were decreased at 6h post GCRV challenge, and gradually increased from 12h to 72h (Fig. 2A). The down-regulation of MyD88 at the early stage might be explained that the expression of MyD88 was suppressed by GCRV injection. Therefore,MyD88 was an important regulator in response to GCRV challenge in grass carp gill.
Generally, RIG-I and MDA5 discriminate different PAMPs against RNA viruses in mammals[7]. mRNA expressions of channel catfish RIG-I and MDA5 are increased in channel catfish ovarian cells post channel catfish virus (CCV) challenge[22]. In the present research, both RIG-I and MDA5 were also up-regulated post GCRV injection in grass carp gill (Fig. 2B).Similarly, common carp RIG-I is up-regulated in spleen, head kidney and intestine tissues after SVCV(spring viraemia of carp virus) infection[23]. It has been reported that the expression of RIG-I is dramatically enhanced in EPC cell post VHSV (viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus) infection[24]. Collectively,CiRIG-I and CiMDA5 were critical for the activation of antiviral innate immunity. Mammalian LGP2 acts as a negative regulator of IFN-I production and antiviral signaling[25], but Japanese flounder LGP2 exhibits positive function in response to both ssRNA and dsRNA viruses[26]. In addition, LGP2 shows a positive role post VHSV infection in rainbow trout[27]. In the present study, LGP2 exhibited a powerful up-regulation,especially at 48h and 72h in grass carp gill (Fig. 2B).The expression patterns of IPS-1 were discrepant after virus challenge in teleosts. IPS-1 is down-regulated post poly(I:C) stimulation or ISKNV (infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus) challenge in spotted green pufferfish spleen . Whereas, common carp IPS-1 are up-regulated in spleen, head kidney and intestine tissues post SVCV challenge[23]. In accord with EPC cells and common carp, the expression of IPS-1 was mainly enhanced from 12h to 72h post GCRV challenge in grass carp (Fig. 2B). Interestingly,the relative value of IPS-1 was slightly reduced at 6h(Fig. 2B), which was the similar to the expression of MyD88 in grass carp gill (Fig. 2A). The data further implied that IPS-1 played a vital role in antiviral immune response against GCRV in grass carp gill.
NLRs and RLRs are two major classes of cytoplasmic PRRs in innate immune system. In general,RLRs mediate antiviral defense, whereas NLRs primarily elicit antibacterial function. However, the mRNA expressions of NOD1 and NOD2 are significantly increased upon GCRV infection in grass carp spleen[9]. In the present study, GCRV also could induce the expression of NOD1 and NOD2 in grass carp gill (Fig. 2C). Furthermore, the relative quantities of CiNOD1 were higher than those of CiNOD2 at corresponding time points (Fig. 2C), which was opposite to that in spleen[9]. Collectively, NOD1 and NOD2 had a role in immune protection in response to viral invasion in grass carp.
During virus infection, multiple signaling cascades are activated, leading to the production of IFN-I to inhibit viral replication. To data, a variety of IFN genes have been identified in teleosts[29,30]. The expression of CiIFN-I mRNA was gradually increased by GCRV challenge in gill (Fig. 3A), which provided the evidence that IFN-I played a critical role in innate immunity against viral invasion in grass carp gill.
Teleosts have both innate and adaptive immune systems to combat viral infection. IgM is mainly detected in gill, head kidney, intestine, liver, trunk kidney and spleen by semi-qRT-PCR in grass carp[31].The expression levels of CiIgM were no differences at examined time points except at 72h (Fig. 3B), which indicated that the adaptive immunity was initiated at three days after GCRV injection in grass carp gill.
In summary, mRNA expression patterns of 12 immune-related genes were checked in grass carp gill post GCRV challenge. The results indicated that gill is an important immune organ to resist virus in grass carp. The findings contribute to comprehensive clarification of antiviral immunity in teleosts and lay a foundation for development of management strategies in disease control.
Acknowledgements:
The authors thank Peng Li-Min, Wan Quan-Yuan,Wang Lan, Chen Xiao-Hui, Zhang Yi-Xuan and other laboratory members for fish husbandry and technical assistance.
- 水生生物學(xué)報(bào)的其它文章
- GILL MEDIATES IMMUNE RESPONSES AFTER GRASS CARP REOVIRUS CHALLENGE IN GRASS CARP (CTENOPHARYNGODON IDELLA)
- MORPHOLOGICAL OBSERVATION AND RBCL SEQUENCE ANALYSIS OF A NEW SPECIES FROM CHINA, GRATELOUPIA BOAOENSIS WANG ET LUAN SP. NOV.(HALYMENIACEAE, RHODOPHYTA)
- 養(yǎng)殖密度對(duì)俄羅斯鱘幼魚的生長、生理和免疫指標(biāo)的影響
- 一種快速構(gòu)建集胞藻6803 petBD必需基因定點(diǎn)突變株的方法
- 大通湖環(huán)棱螺的次級(jí)生產(chǎn)力
- 黃鯽線粒體DNA控制區(qū)結(jié)構(gòu)及長度多態(tài)性分析

