Identification of QTL for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese wheat landrace Pingyuan 50
Muhmmd Azeem Asd,Bin Bi,Cixi Ln,Jun Yn,Xinhun Xi,Yong Zhng,Zhonghu He,d,*
aInstitute of Crop Science,National Wheat Improvement Center/The National Key Facility for Crop Gene Resources and Genetic Improvement,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(CAAS),Beijing 100081,China
bWheat Research Institute,Gansu Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Lanzhou 730070,China
cCotton Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(CAAS),Anyang 455000,China
dInternational Maize and Wheat Improvement Center(CIMMYT),China Office,c/o CAAS,Beijing 100081,China
1.Introduction
Powdery mildew,caused by Blumeria graminis f.sp.tritici(Bgt),is an important disease of wheat worldwide [1],causing significant reductions in both grain quality and yield in susceptible wheat cultivars [2,3],and leading to substantial economic losses in wheat production annually on a global scale[4].The use of powdery mildew resistance genes in elite cultivars is the most cost-effective and sustainable strategy to control this disease[5].
Over the last three decades,most disease resistance studies have focused on major genes,which are known as qualitative or race specific resistance genes.These genes are simply inherited and easy to manipulate in breeding programs,as they express complete resistance and are usually associated with hypersensitive responses that limit pathogen growth [6].Race specific resistance is often transient due to the occurrence of new pathogen races arising from mutation or increased frequencies of previously rare variants[7,8].More than 70 powdery mildew resistance genes have been cataloged in wheat[9].Most named powdery mildew resistance genes are currently ineffective in China.
One of the principal challenges in wheat breeding is to develop cultivars with durable disease resistance.Adult-plant resistance (APR) often appears to offer race non-specific and therefore durable resistance based on the additive effects of several genes that delay infection,and reduce growth and reproduction of the pathogen at the adult-plant stage [1].This type of resistance however may not be adequate under all growth conditions,but their additive nature offers opportunities to increase resistance levels to almost immunity[10].Molecular markers made it easier to locate APR genes on chromosomes,and to estimate the additive effect of each gene[11].So far,more than 100 quantitative trait loci (QTL) for powdery mildew resistance have been identified and mapped on almost all wheat chromosomes in a range of different genetic backgrounds(Z.F.Li,pers.comm.),including the Swiss winter wheat cv.Forno[12],French winter wheat lines RE714,Festin,Courtot,and RE9001 [13–16],North American winter wheats Massey and USG3209 [10,17],Japanese wheat cultivar Fukuho-komugi [18],Israeli wheat cultivar Oligoculm[18],CIMMYT wheat lines Opata 85,W7984,and Saar [19,20],Australian wheat cultivar Avocet[20],and Chinese wheat cultivars Bainong 64[21]and Lumai 21[11].Unfortunately,only a few of these genotypes have good adaptability and associated agronomic traits in Chinese environments[22].Wheat landraces are valuable genetic resources;they sometimes carry multiple genes for resistance to several diseases and are more adaptable to local environments[5].It is,therefore,important to explore APR to powdery mildew in wheat landraces.Moreover,closely linked molecular markers to the resistance genes would play an important role in incorporation of APR genes in wheat breeding programs.
The Chinese wheat landrace Pingyuan 50 was a leading cultivar in the Yellow and Huai Valley Autumn-sown Wheat Zone of China in the 1950s,and has shown APR to stripe rust and powdery mildew in the field for over 60 years.Previously,we mapped QTL for APR to stripe rust in Pingyuan 50[22].The main objectives of the present study were to locate powdery mildew resistance QTL in Pingyan 50 and to determine whether there are pleiotropic or closely linked APR loci involved in stripe rust response.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Plant materials
A doubled haploid(DH)population of 137 lines from Pingyuan 50/Mingxian 169 was used for QTL analysis.Pingyuan 50 showed APR to powdery mildew in field trials.Mingxian 169,a landrace from Shanxi province,is highly susceptible to all races of Puccinia striiformis f.sp.tritici at the seedling stage [22],whereas it is moderately resistant at the adult plant stage.Both parents were susceptible to Bgt isolate E20 at the seedling stage.Jingshuang 16 was highly susceptible to powdery mildew,and used as a susceptible check in all tests.
2.2.Evaluation of powdery mildew response
The DH population was evaluated for powdery mildew response over the 2009–2010 and 2010–2011 wheat seasons at two locations,viz.the CAAS Experimental Station,Beijing,and CAAS Cotton Research Institute,Anyang,Henan province (herein referred to as Beijing 2010,Beijing 2011,and Anyang 2010).Hill plots (50 seeds/hill) were used and genotypes were sown in randomized complete blocks with three replicates.The highly susceptible cv.Jingshuang 16 was planted in every tenth row as a check and around the experimental block as an inoculum spreader.In Beijing,inoculation with Bgt isolate E20 was performed before stem elongation.Disease severities were assessed as percentage cover on penultimate leaves at five and six weeks after inoculation[23]when disease levels reached their maxima around May 20.In Anyang under natural infection,powdery mildew severities were recorded once,when cv.Jingshuang 16 expressed a maximum severity during the third week of May.Attempts to obtain a further site year of data in Anyang in 2011 were abandoned due to dry conditions and lack of disease development.
2.3.Statistical analysis
The frequency distribution of powdery mildew responses and correlation coefficients(r)based on maximum disease severities(MDS) in different environments were calculated in Microsoft Excel 2007.The area under the disease progress curve (AUDPC)was calculated according to Bjarko and Line [24].Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using the PROC GLM in the statistical analysis system(SAS Institute 1997).ANOVA information was then used to calculate broad-sense heritability (h2) as:h2= σg2/ (σg2+ σge2/ e + σε2/ re),where σg2,σge2,and σε2are estimates of genotypic,genotype × environment interaction and error variances,respectively,and e and r are the numbers of environments and replicates per environment,respectively.
2.4.SSR analysis
A total of 1528 pairs of simple sequence repeat(SSR)primers from published sources including the WMC[25],BARC[26],GWM[27],CFA [28],and CFD [29] series (http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/) were used to scan the parents.Bulked segregant analysis [30]was conducted,using equal amounts of ten resistant and ten susceptible lines based on MDS.Amplification of DNA,electrophoresis of PCR products on polyacrylamide gels and gel staining procedures were performed as described by Bryan et al.[31] and Bassam et al.[32].Five hundred and forty polymorphic SSR markers were used to genotype the entire population for linkage map construction and QTL analysis.
2.5.Map construction and QTL detection
Genetic linkage groups were constructed with the software Map Manager QTXb20 [33],and map distances between markers were estimated by the Kosambi mapping function[34].Linkage groups were assigned to each chromosome according to published wheat consensus maps[35].QTL analysis was performed with QTL Cartographer 2.5 software by composite interval mapping [36].A logarithm of odds (LOD) was calculated from 2000 permutations for each trait to declare significance of QTL at P = 0.01.Estimates of phenotypic variance (R2) explained by individual QTL and additive effects at LOD peaks were obtained by QTL Cartographer 2.5.Two QTL on the same chromosome in different environments,having curve peaks within a distance of 20 cM,were considered as a single QTL,and different QTL when distances exceeded 20 cM.
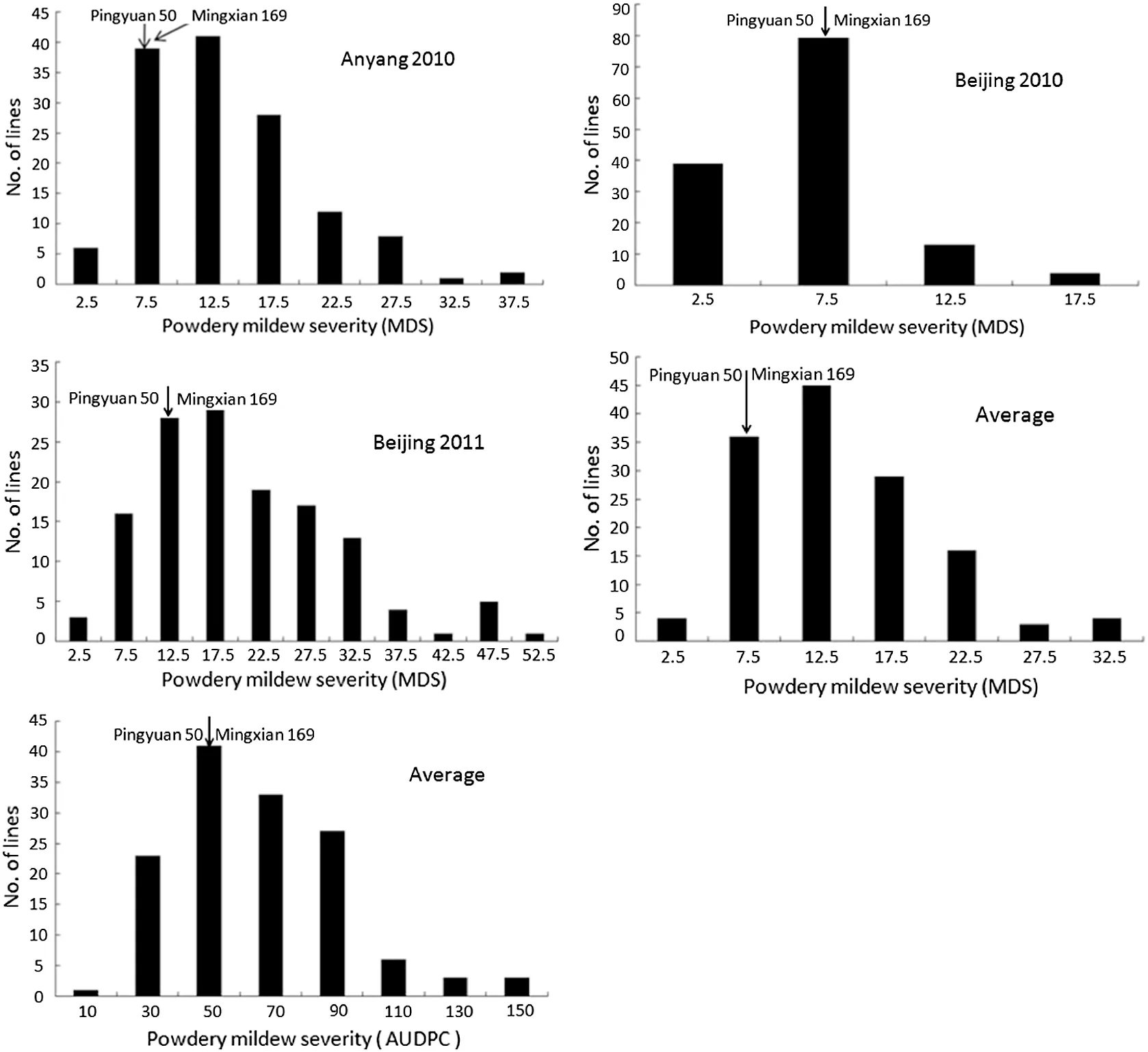
Fig.1-Frequency distribution of powdery mildew maximum disease severities (MDS) and area under the disease progress curve(AUDPC)values in the DH lines derived from Pingyuan 50/Mingxian 169.Results include average,mean MDS across three environments,and AUDPC in Beijing for more than 2 years.Mean values for parents,Pingyuan 50 and Mingxian 169,are indicated by arrows.
3.Results
3.1.Phenotypic analysis
The MDS of the susceptible check Jingshuang 16 ranged from 80%to 100%,60%to 90%,and 90%to 100%,whereas Pingyuan 50 and Mingxian 169 were 8.5%and 7.1%,7.7%and 6.0%,and 12.3 and 14.5%in Anyang 2010,Beijing 2010,and Beijing 2011,respectively.Both parents showed mean MDS of less than 10% across the three environments.Frequency distributions of MDS and AUDPC for DH lines showed continuous variation in all environments with clear transgressive segregation,indicating quantitative resistance to powdery mildew(Fig.1).In addition,the MDS scores were significantly correlated across three environments (r = 0.63 to 0.85).Analyses of variance of MDS and AUDPC showed significant variation among the DH lines (Table 1).The broad-sense heritabilities of MDS and AUDPC were 0.80 and 0.62,respectively,across the three environments.
3.2.QTL analysis
Based on MDS,three QTL from Pingyuan 50 on chromosomes 2BS,3BS,and 5AL,and one from Mingxian 169 on chromosome 3BL,respectively,were detected across environments(Table 2 and Fig.2).They were designated QPm.caas-2BS.2,QPm.caas-3BS,QPm.caas-3BL,and QPm.caas-5AL,respectively.
The QTL on chromosome 2BS,detected in Beijing 2010,Beijing 2011,and the averaged MDS across all three environments,was located in the marker interval Xbarc13–Xgwm374 and explained 4.0–9.1% of the phenotypic variance across environments(Table 2).
QPm.caas-3BS was mapped on chromosome 3BS,flanked by SSR markers Xwmc366 and Xgwm77,and accounted for 9.1% of the phenotypic variance with an additive effect of-2.17.The third QTL,QPm.caas-3BL,was close to the centromere on chromosome 3BL linked to markers Xwmc527 and Xwmc418 with a LOD value of 4.4.This QTL identified only in Anyang 2010 explained 18.1% of the phenotypic variation with an additive effect of 2.83.
QPm.caas-5AL in marker interval Xwmc410–Xbarc261 on chromosome 5AL explained 10.2%of the phenotypic variance with an additive effect-1.04.The total phenotypic variance explained by the detected QTL for MDS ranged from 9.3 to 27.2% in single environments and was 17.7% for the mean across environments.Pingyuan 50 carries three QTL,where as Mingxian 169 carries one(QPm.caas-3BL).
4.Discussion
In the present study,the QTL on chromosome 2BS detected in different environments was within a genetic distance of less than 20 cM.We therefore considered them as a single QTL designated QPm.caas-2BS.2.Previously,a QTL was mapped on chromosome 2BS in the Italian wheat cultivar Strampelli [37] and located around SSR marker Xwmc25,which is about 32 cM from QPm.caas-2BS.2 based on a wheat consensus map[35].In addition,previously mapped QTL QPm.crag-2BS[14]and QPm.caas-2BS[11],detected in Festin and Lumai 21,respectively,were located about 12 cM distal and proximal to QPm.caas-2BS.2 [35],which were assumed to be different based on their origins.Large-effect powdery mildew resistance genes Pm26 and Pm42,derived from wild emmer(Triticum turgidum var.dicoccoides),were also mapped in the same vicinity of less than 20 cM from QPm.caas-2BS.2[38,39].Stripe rust resistance QTL QYr.caas-2BS was mapped in the same region as QPm.caas-2BS.2 in this population [22].QTL for stripe rust resistance were also identified at the same position in cv.Louise,Luke and Kariega[40–42].This region of chromosome 2BS has a pleiotropic effect on both powdery mildew and stripe rust responses and therefore could be useful in breeding for resistance to both diseases by marker assisted selection.
QPm.caas-3BS,identified in marker interval Xwmc366–Xgwm77 on chromosome 3BS and contributed by Pingyuan 50,explained 9.1% of the phenotypic variation.Chen et al.[43]reported a QTL linked with Xwms533 on the short arm of chromosome 3B in Line 2174 with a genetic distance of about 56 cM from QPm.caas-3BS [35].Donini et al.[44] mapped Pm13,derived from Ae.longissimum,to a similar region on 3BS using RFLP markers.QPm.caas-3BS,however,seems to be a new QTL for powdery mildew resistance based on chromosomal location and origin.
QPm.caas-3BL was mapped to the centromeric region of chromosome 3BL between SSR markers Xwmc527 and Xwmc418,explaining 18.1% of the phenotypic variance.It was contributed by Mingxian 169.Race specific resistance gene Pm41 in wild emmer was mapped to chromosome 3BL,but at a genetic distance of about 34 cM from QPm.caas-3BL[45].Although the genetic distance between QPm.caas-3BS and QPm.caas-3BL is less than 10 cM [35],we considered them as two QTL due to their locations on different chromosome 3B arms.No other QTL for powdery mildew resistance have been reported on chromosome 3BL.
QPm.caas-5AL in marker interval Xwmc410–Xbarc261 explained 10.2% of the phenotypic variance.Sources of previously mapped QTL in this chromosome include Folke[1],Saar[20],Triticum militinae [46],and Forno [12] with genetic distances of 80,80,77,and 68 cM,respectively,from QPm.caas-5AL based on the wheat consensus map [35].This appears to be a new locus for powdery mildew APR.In addition,the QTL QYr.caas-5AL [22] was mapped in the same
region of this Pingyuan 50/Mingxian 169 population,suggesting the possibility of a pleiotropic APR locus conferring resistance to both powdery mildew and stripe rust.Yr48,for partial resistance to stripe rust was mapped to the same position[47].This locus needs further investigation to determine whether it confers pleiotropic powdery mildew and stripe rust resistances.
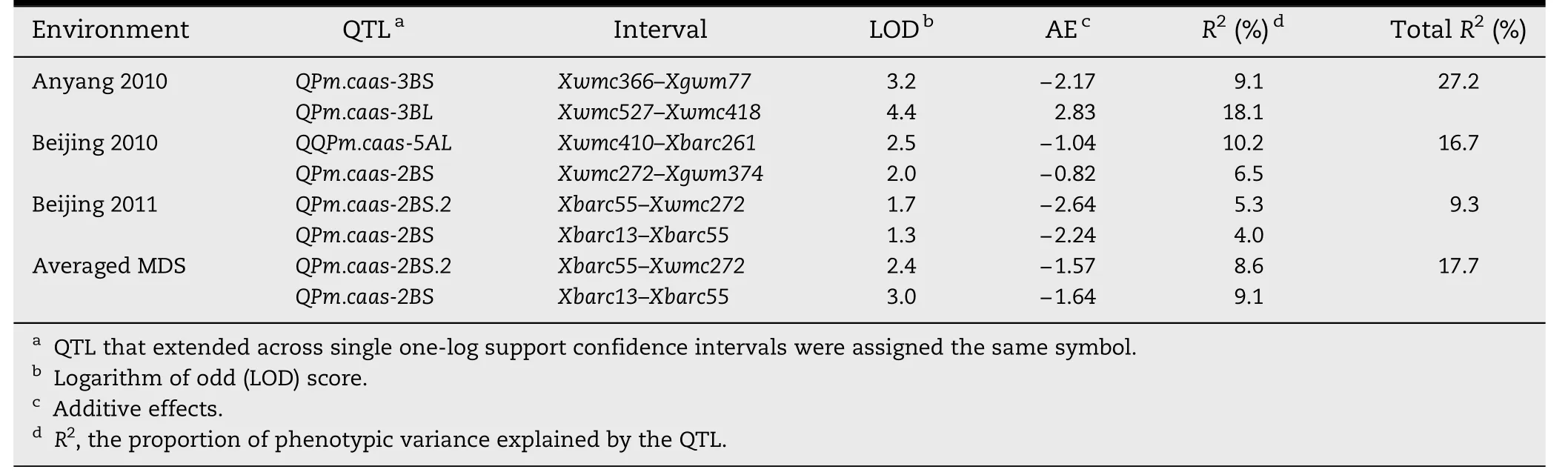
Table 2-Quantitative trait loci(QTL)detected for APR to powdery mildew in the DH population derived from the Pingyuan 50/Mingxian 169 cross.
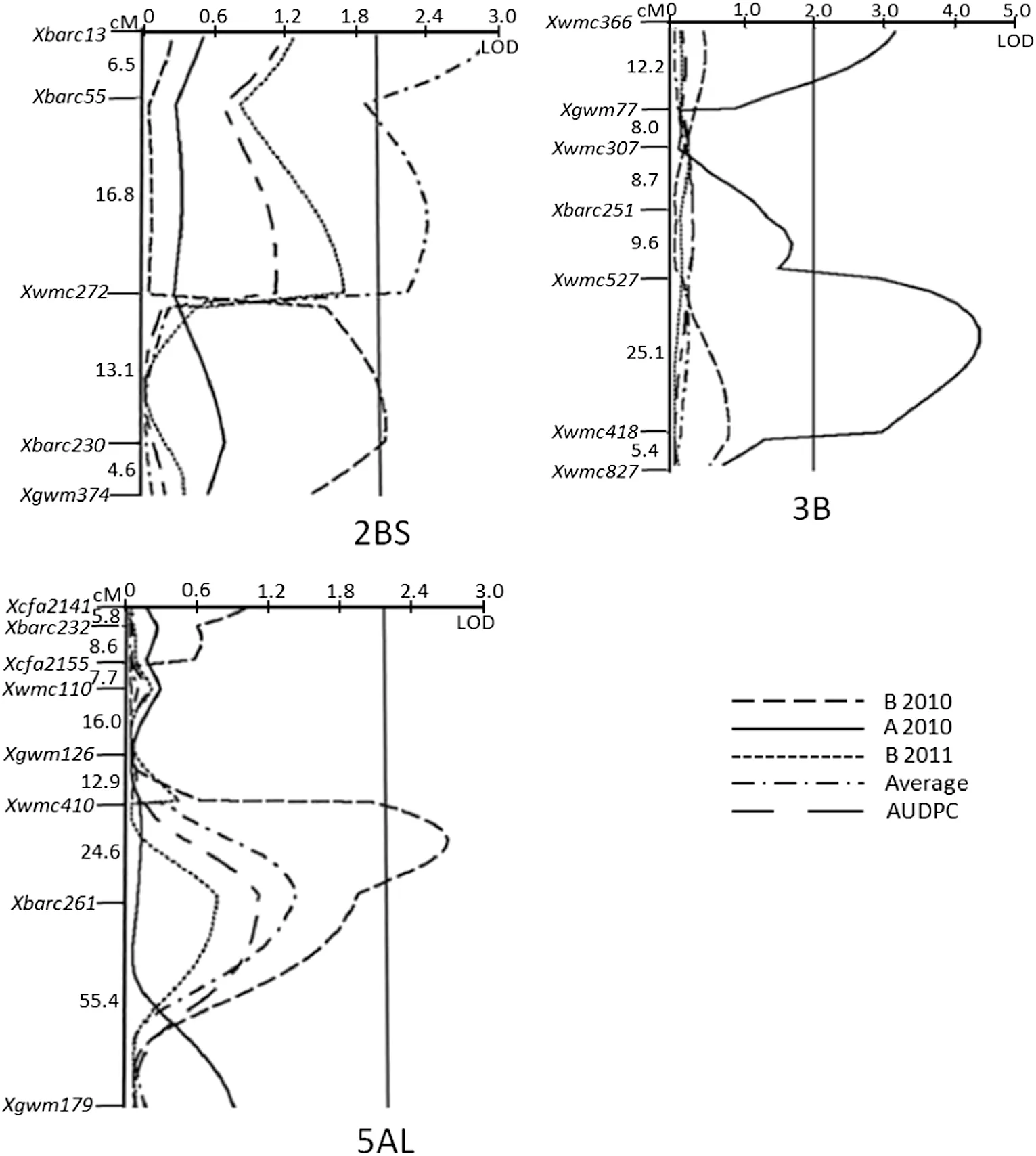
Fig.2-Logarithm of odd(LOD)contours identified by composite interval mapping of powdery mildew APR QTL on chromosomes 2BS,3B and 5AL in the Pingyuan 50/Mingxian 169 DH population.A2010:maximum disease severities (MDS),Anyang 2010;B2010 and B2011,maximum disease severities,Beijing 2010 and 2011,respectively;average:mean MDS across three environments;AUDPC:averaged area under the disease progress curve in Beijing for more than two years.The LOD threshold for significance is 2.0.
Pingyuan 50 is considered a valuable source of APR to both stripe rust and powdery mildew in local wheat breeding programs,and three QTL for APR to stripe rust were mapped in Pingyuan 50 [20].In the present study,four QTL for APR to powdery mildew were mapped in the same population,and three of them were in Pingyuan 50.Although these QTL were not detected across all environments,QPm.caas-2BS.2 and QPm.caas-5AL were mapped to the same chromosome regions as QYr.caas-2BS and QYr.caas-5AL,respectively,for APR to stripe rust,indicating possible pleiotropic genes for APR to both powdery mildew and stripe rust in Pingyuan 50.Gene pyramiding is a useful approach to enhance disease resistance and a number of genes can be accumulated in a single line.We have pyramided QTL for powdery mildew resistance derived from Bainong 64 and Lumai 21 through marker assisted selection [48].The QTL detected in Pingyuan 50,particularly QPm.caas-2BS.2 and QPm.caas-5AL in combination with three previously identified QTL,including Pm38 from cv.Strampelli and Libellula,should be useful in developing cultivars with potentially durable resistance to both powdery mildew and stripe rust.
This study was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2013CB127700),National Natural Science Foundation of China (31261140370 and 31260319),International Collaboration Projects from the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology (2011DFG32990) and the Ministry of Agriculture(2011-G3),the National High Technology Research Program of China (2012AA101105),and the China Agriculture Research System(CARS-3-1-3).M.A.Asad gratefully acknowledges full scholarship support for Ph.D.studies from the China Scholarship Council(2008GXZA85).
[1] M.Lillemo,A.Bj?rnstad,H.Skinnes,Molecular mapping of partial resistance to powdery mildew in winter wheat cultivar Folke,Euphytica 185 (2012) 47–59.
[2] K.L.Everts,S.Leath,P.L.Finney,Impact of powdery mildew and leaf rust on milling and baking quality of soft red winter wheat,Plant Dis.85(2001) 423–429.
[3] R.L.Conner,A.D.Kuzyk,H.Su,Impact of powdery mildew on the yield of soft white spring wheat cultivars,Can.J.Plant Sci.83 (2003) 725–728.
[4] A.Morgounov,H.A.Tufan,R.Sharma,B.Akin,A.Bagci,H.J.Braun,Y.Kaya,M.Keser,T.S.Payne,K.Sonder,R.McIntosh,Global incidence of wheat rusts and powdery mildew during 1969–2010 and durability of resistance of winter wheat variety Bezostaya 1,Eur.J.Plant Pathol.132(2012) 323–340.
[5] J.M.Wang,H.Y.Liu,H.M.Xu,M.Li,Z.S.Kang,Analysis of differential transcriptional profiling in wheat infected by Blumeria graminis f.sp tritici using gene chip,Mol.Biol.Rep.39(2012) 381–387.
[6] G.Gustafson,G.Shaner,Influence of plant age on the expression of slow-mildewing resistance in wheat,Phytopathology 72(1982) 746–749.
[7] S.L.K.Hsam,F.J.Zeller,Breeding for powdery mildew resistance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.),in: R.R.Belanger,W.R.Bushnell,A.J.Dik,T.L.W.Carver(Eds.),The Powdery Mildews,a Comprehensive Treatise,The American Phytopathological Society,St.Paul,MN,2002,pp.219–238.
[8] D.Z.Yu,X.J.Yang,L.J.Yang,M.J.Jeger,J.K.M.Brown,Assessment of partial resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese wheat varieties,Plant Breed.120 (2001) 279–284.
[9] R.A.McIntosh,W.J.Rogers,C.F.Morris,R.Appels,X.C.Xia,Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat: 2011 supplement,http://www.shigen.nig.ac.jp/wheat/komugi/genes/macgene/supplement2011.pdf.
[10] S.X.Liu,C.A.Griffey,M.A.S.Maroof,Identification of molecular markers associated with adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat cultivar Massey,Crop Sci.41(2001) 1268–1275.
[11] C.X.Lan,X.W.Ni,J.Yan,Y.Zhang,X.C.Xia,X.M.Chen,Z.H.He,Quantitative trait loci mapping for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese wheat cultivar Lumai 21,Mol.Breed.25(2010) 615–622.
[12] M.Keller,B.Keller,G.Schachermayr,M.Winzeler,J.E.Schmid,P.Stamp,M.M.Messmer,Quantitative trait loci for resistance against powdery mildew in a segregating wheat × spelt population,Theor.Appl.Genet.98 (1999)903–912.
[13] N.Chantret,D.Mingeot,P.Sourdille,M.Bernard,J.M.Jacquemin,G.Doussinault,A major QTL for powdery mildew resistance is stable over time and at two development stages in winter wheat,Theor.Appl.Genet.103 (2001) 962–971.
[14] D.Mingeot,N.Chantret,P.V.Baret,A.Dekeyser,N.Boukhatem,P.Sourdille,G.Doussinault,J.M.Jacquemin,Mapping QTL involved in adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in the winter wheat line RE714 in two susceptible genetic backgrounds,Plant Breed.121 (2002) 133–140.
[15] Y.Bougot,J.Lemoine,M.T.Pavoine,H.Guyomar'ch,V.Gautier,H.Muranty,D.Barloy,A major QTL effect controlling resistance to powdery mildew in winter wheat at the adult plant stage,Plant Breed.125 (2006) 550–556.
[16] H.Muranty,M.T.Pavoine,B.Jaudeau,W.Radek,G.Doussinault,D.Barloy,Two stable QTL involved in adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in the winter wheat line RE714 are expressed at different times along the growing season,Mol.Breed.23(2009) 445–461.
[17] D.M.Tucker,C.A.Griffey,S.Liu,G.Brown-Guedira,D.S.Marshall,M.A.S.Maroof,Confirmation of three quantitative trait loci conferring adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in two winter wheat populations,Euphytica 155(2007)1–13.
[18] S.S.Liang,K.Suenaga,Z.H.He,Z.L.Wang,H.Y.Liu,D.S.Wang,R.P.Singh,P.Sourdille,X.C.Xia,Quantitative trait loci mapping for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in bread wheat,Phytopathology 96(2006) 784–789.
[19] A.B?rner,E.Schumann,A.Furste,H.Coster,B.Leithold,M.S.Roder,W.E.Weber,Mapping of quantitative trait loci determining agronomic important characters in hexaploid wheat(Triticum aestivum L.),Theor.Appl.Genet.105(2002)921–936.
[20] M.Lillemo,B.Asalf,R.P.Singh,J.Huerta-Espino,X.M.Chen,Z.H.He,A.Bj?rnstad,The adult plant rust resistance loci Lr34/Yr18 and Lr46/Yr29 are important determinants of partial resistance to powdery mildew in bread wheat line Saar,Theor.Appl.Genet.116(2008)1155–1166.
[21] C.X.Lan,S.S.Liang,Z.L.Wang,J.Yan,Y.Zhang,X.C.Xia,Z.H.He,Quantitative trait loci mapping for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese wheat cultivar Bainong 64,Phytopathology 99 (2009) 1121–1126.
[22] C.X.Lan,S.S.Liang,X.C.Zhou,G.Zhou,Q.L.Lu,X.C.Xia,Z.H.He,Identification of genomic regions controlling adult-plant stripe rust resistance in Chinese landrace Pingyuan 50 through bulked segregant analysis,Phytopathology 100(2010) 313–318.
[23] R.F.Peterson,A.B.Campbell,A.E.Hannah,A diagrammatic scale for estimating rust intensity of leaves and stems of cereals,Can.J.Res.26(1948) 496–500.
[24] M.E.Bjarko,R.F.Line,Heritability and number of genes controlling leaf rust resistance on four cultivars of wheat,Phytopathology 78 (1988) 457–461.
[25] P.K.Gupta,S.Rustgi,S.Sharma,R.Singh,N.Kumar,H.S.Balyan,Transferable EST-SSR markers for the study of polymorphism and genetic diversity in bread wheat,Mol.Gen.Genomics.270 (2003) 315–323.
[26] Q.J.Song,E.W.Fickus,P.B.Cregan,Characterization of trinucleotide SSR motifs in wheat,Theor.Appl.Genet.104(2000) 286–293.
[27] M.S.R?der,V.Korzun,K.Wendehake,J.Plaschke,M.H.Tixier,P.Leroy,M.W.Ganal,A microsatellite map of wheat,Genetics 149 (1998) 2007–2023.
[28] P.Sourdille,S.Singh,T.Cadalen,G.L.Brown-Guedira,G.Gay,L.Qi,Microsatellite based deletion bin system for the establishment of genetic physical map relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.),Funct.Integr.Genomics 4 (2004)12–25.
[29] H.Guyomarc'h,P.Sourdille,K.J.Edwards,M.Bernard,Studies of the transferability of microsatellites derived from Triticum tauschii to hexaploid wheat and to diploid related species using amplification,hybridization and sequence comparisons,Theor.Appl.Genet.105 (2002) 736–744.
[30] R.W.Michelmore,I.Paran,R.V.Kesseli,Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations,Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A.88(1991) 9828–9832.
[31] G.J.Bryan,A.J.Collins,P.Stephenson,A.Orry,J.B.Smith,M.D.Gale,Isolation and characterization of microsatellites from hexaploid bread wheat,Theor.Appl.Genet.94(1997)557–563.
[32] B.J.Bassam,G.Caetano-Anolles,P.M.Gresshoff,Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels,Anal.Biochem.196 (1991) 80–83.
[33] K.F.Manly,R.H.Cudmore Jr.,J.M.Meer,Map Manager QTX,cross-platform software for genetic mapping,Mamm.Genome 12(2001) 930–932.
[34] D.D.Kosambi,The estimation of map distance from recombination values,Ann.Eugen.12(1943) 172–175.
[35] D.J.Somers,P.Isaac,K.Edwards,A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat(Triticum aestivum L.),Theor.Appl.Genet.109(2004)1105–1114.
[36] S.Wang,C.J.Basten,Z.B.Zeng,Windows QTL Cartographer v2.5,Statistical Genetics,North Carolina State University,2005.
[37] M.A.Asad,B.Bai,C.X.Lan,J.Yan,X.C.Xia,Y.Zhang,Z.H.He,QTL mapping for adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in Italian wheat cv.Strampelli,J.Integr.Agric.5(2013) 756–764.
[38] J.K.Rong,E.Millet,J.Manisterski,M.Feldman,A new powdery mildew resistance gene:introgression from wild emmer into common wheat and RFLP-based mapping,Euphytica 115 (2000) 121–126.
[39] W.Hua,Z.Liu,J.Zhu,C.Xie,T.Yang,Y.Zhou,X.Duan,Q.Sun,Identification and genetic mapping of Pm42,a new recessive wheat powdery mildew resistance gene derived from wild emmer (Triticum turgidum var.dicoccoides),Theor.Appl.Genet.119 (2009) 223–230.
[40] A.H.Carter,X.M.Chen,K.Garland-Campbell,K.K.Kidwell,Identifying QTL for high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f.sp tritici) in the spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivar ‘Louise',Theor.Appl.Genet.119 (2009) 1119–1128.
[41] Q.Guo,Z.J.Zhang,Y.B.Xu,G.H.Li,J.Feng,Y.Zhou,Quantitative trait loci for high-temperature adult-plant and slow-rusting resistance to Puccinia striiformis f.sp tritici in wheat cultivars,Phytopathology 98(2008) 803–809.
[42] V.P.Ramburan,Z.A.Pretorius,J.H.Louw,L.A.Boyd,P.H.Smith,W.H.P.Boshoff,R.Prins,A genetic analysis of adult plant resistance to stripe rust in the wheat cultivar Kariega,Theor.Appl.Genet.108 (2004) 1426–1433.
[43] Y.H.Chen,R.M.Hunger,B.F.Carver,H.L.Zhang,L.L.Yan,Genetic characterization of powdery mildew resistance in U.S.hard winter wheat,Mol.Breed.24 (2009) 141–152.
[44] P.Donini,R.M.D.Koebner,C.Ceoloni,Cytogenetic and molecular mapping of the wheat Aegilops longissima chromatin breakpoints in powdery mildew-resistant introgression lines,Theor.Appl.Genet.91(1995)738–743.
[45] G.Q.Li,T.L.Fang,H.T.Zhang,C.J.Xie,H.J.Li,T.M.Yang,E.Nevo,T.Fahima,Q.X.Sun,Z.Y.Liu,Molecular identification of a new powdery mildew resistance gene Pm41 on chromosome 3BL derived from wild emmer(Triticum turgidum var.dicoccoides),Theor.Appl.Genet.119(2009)531–539.
[46] I.Jakobson,H.Peusha,L.Timofejeva,K.Jarve,Adult plant and seedling resistance to powdery mildew in a Triticum aestivum × Triticum militinae hybrid line,Theor.Appl.Genet.112 (2006) 760–769.
[47] I.Lowe,L.Jankuloski,S.Chao,X.Chen,D.See,J.Dubcovsky,Mapping and validation of QTL which confer partial resistance to broadly virulent post-2000 North American races of stripe rust in hexaploid wheat,Theor.Appl.Genet.123(2011)143–157.
[48] B.Bai,Z.H.He,M.A.Asad,C.X.Lan,Y.Zhang,X.C.Xia,J.Yan,X.M.Chen,C.S.Wang,Pyramiding adult-plant powdery mildew resistance QTLs in bread wheat,Crop Pasture Sci.63(2012) 606–611.
- The Crop Journal的其它文章
- Productivity,quality and soil health as influenced by lime in ricebean cultivars in foothills of northeastern India
- Genotype × environment interaction effects on early fresh storage root yield and related traits in cassava
- Effect of subsoil tillage depth on nutrient accumulation,root distribution,and grain yield in spring maize
- Isolation and characterization of a novel wall-associated kinase gene TaWAK5 in wheat(Triticum aestivum)
- Exp2 polymorphisms associated with variation for fiber quality properties in cotton(Gossypium spp.)
- The impacts of conservation agriculture on crop yield in China depend on specific practices,crops and cropping regions

