無旋波近似下的二能級開放系統(tǒng)非馬爾科夫動力學
徐甜甜 , 唐 寧, 鄭艷萍, 曾浩生
(湖南師范大學 物理系, 教育部低維量子結構與調控重點實驗室, 湖南 長沙, 410081)
無旋波近似下的二能級開放系統(tǒng)非馬爾科夫動力學
徐甜甜 , 唐 寧, 鄭艷萍, 曾浩生
(湖南師范大學 物理系, 教育部低維量子結構與調控重點實驗室, 湖南 長沙, 410081)
在無旋波近似下, 研究了一個二能級系統(tǒng)與零溫結構庫的相互作用. 當系統(tǒng)與環(huán)境為弱耦合時, 推導出描述系統(tǒng)狀態(tài)演化的主方程. 解析與數(shù)值結果均表明, 反旋轉波項對系統(tǒng)的非馬可夫動力學起著重要作用. 同時也分析了最近提出的兩種非馬可夫度量之間的差別.
開放量子系統(tǒng); 旋波近似; 非馬爾科夫性
1 Introduction
Realistic quantum systems cannot avoid interactions with their environments, thus the study of open quantum systems is very important. It is not only relevant for better understanding of quantum theory, but also fundamental for various modern applications of quantum mechanics, especially for quantum communication, cryptography and computation[1]. The early study of dynamics of open quantum systems usually consists in the application of an appropriate Born-Markov approximation, that is, neglects all the memory effects, leading to a master equation which can be cast in the so-called Lindblad form[2]. Masterequations in Lindblad form can be characterized by the fact that the dynamics of the system satisfies both the semi-group property and the complete positivity, thus ensuring the preservation of positivity of the density matrix during the time evolution. We usually attribute the dynamical processes with these evolutional properties to the well-known Markovian ones.
However, people recently find that many relevant physical systems, such as quantum optical system[3], quantum dot[4], superconductor system[5], could not be described simply by Markovian dynamics. Similarly, quantum chemistry[6]and excitation transfer of biological system[7]also need to be treated as non-Markovian processes. Quantum non-Markovian processes can lead to distinctly different effects on decoherence and disentanglement[8-9]of open systems compared to Markovian processes. These dynamical traits are important for the enriching of the basic theory of quantum mechanics, as well as for quantum information processing. Because of these distinct properties and extensive applications, more and more attention and interest have been devoted to the study of non-Markovian processes of open systems, including the measures of non-Markovianity[10-16], the positivity[17-18], and some other dynamical properties[19-23]and approaches[24-25]of non-Markovian processes. Experimentally, the simulation[26-27]of non-Markovian environment has been realized.
The measure of non-Markovianity of quantum evolution is a fundamental problem which aims to detect whether a quantum process is non-Markovian and how much degrees it deviates from a Markovian one. Although several measures of non-Markovianity have been presented already, it is noted that these measures do not agree exactly. Therefore, the problem for measuring the non-Markovianity of quantum processes still remains elusive and, in some sense, controversial. Based on the distinguishability of quantum states, Breuer, Laine and Piilo (BLP)[10]proposed a measure to detect the non-Markovianity of quantum processes which is linked to the flow of information between system and environment. Alternatively, Rivas, Huelga and Plenio (RHP)[11]also presented a measure of non-Markovianity by exploiting the dynamical divisibility of a trace-preserving completely positive map. It is clear that the BLP measure is based on the physical features of the system-reservoir interactions, while the RHP definition is based on the mathematical property of the dynamical maps. It has been found that these two measures do not agree actually[28]. In this paper, we will use both the two measures to describe the non-Markovianity of the dynamics of the system of interest and find that there exists distinct difference between the two kinds of measuring results.
The study of the dynamics of non-Markovian open quantum systems is typically very involved and often requires some approximations. Almost all the previous treatments are based on the rotating wave approximation, that is, neglect the counter-rotating terms in the microscopic system-reservoir interaction Hamiltonian. However, the counter-rotating terms which are responsible for the virtual exchanges of energy between the system and the environment not always can be neglected. For example, when the effective frequency-band of the reservoir spectra is wide enough or when the main value of the frequency-spectrum distribution of the structured environment is detuned large enough from the transition of the system, the rotating wave approximation is invalid. The main motivation of this paper is to demonstrate the limitations of the commonly-used rotating wave approximation and to see how the counter-rotating terms affect the non-Markovian dynamics of the open quantum system.
The article is organized as follows. In Sec. 2 we introduce the microscopic Hamiltonian model and derive the non-Markovian time-local master equation for a two-level system weakly coupled to a vacuum reservoir, without rotating-wave approximation. In Sec. 3, we calculate the non-Markovianity of the system dynamics in terms of both the RHP and BLP measures, and show their difference visibly in measuring the non-Markovianity. And in sec. 4, we choose the Lorentzian spectra reservoir as an exemplary example, giving the analytic expressions of the time-dependant transition rate and demonstrating quantitatively theeffect of the counter-rotating wave terms on the non-Markovian dynamics. Finally, the conclusion is arranged in Sec.5.
2 The microscopic model
Consider a two-level atom with Bohr frequency ω0interacting with a zero-temperature bosonic reservoir modeled by an infinite chain of quantum harmonic oscillators. The total Hamiltonian for this system in the Schrodinger picture is given by

where σzand σ±are the Pauli and inversion operators of the atom, ωk, bkand bk+are respectively the frequency, annihilation and creation operators for the k-th harmonic oscillator of the reservoir. The coupling strength gkis assumed to be real for simplicity. The distinct feature of this Hamiltonian is the reservation of the counter-rotating wave terms, σ+bk+and σ-bk.
The time-convolutionless (TCL) projection operator technique is most effective in dealing with the dynamics of open quantum systems. In the limit of weak coupling between the system and the environment, by expanding the TCL generator to the second order with respect to coupling strength, the non-Markovian master equation describing the evolution of the reduced system, in the interaction picture, can be written as

where

is the Lamb shift Hamiltonian which describes a small shift in the energy of the eigenstates of the two-level atom. This term has no qualitative effect on the dynamics of the system and therefore is neglected usually. The dissipator D[ρ(t)] that describes the secular motion of the system has the form
where the first term describes the dissipation of the atom to the vacuum environment with time-dependent decay rate γ-(t), and the second term denotes the heating of the atom in the vacuum environment with time-dependent heating rate γ+(t). This heating is related to the dissipation, for a ground-state atom in a zero-temperature environment, there is no heating effect. Note that the heating term completely originates from the counter-rotating terms present in the system-reservoir interaction Hamiltonian, as it would not exist under rotating wave approximation[3]. In the following, we will show that this heating term in some cases may play an important role, in particular to the non-Markovian behaviors of the system's dynamics. The dissipater D′[ρ(t)], which also originates from the counter-rotating terms in the coupling Hamiltonian, represents the contribution of the so-called nonsecular terms, that is, terms oscillating rapidly with atomic transition frequency ω0,

here h.c. denotes the Hermitian conjugation. In what follows, we will neglect the effect of these nonsecular terms, that is, perform the so-called secular approximation. Just as pointed out in reference [29], this kind of secular approximation that used after tracing over the bath degrees of freedom is different from the rotating wave approximation before the tracing. It is a more precise approximation that consists in an average over rapidly oscillating terms, but does not wash out the effect of the counter-rotating terms present in the coupling Hamiltonian. The time-dependent coefficients in the above equations are respectively


where the spectral density function is defined as.
3 Measures of Non-Markovianity
In this section, we employ two measures to describe the non-Markovianity of the dynamics of the considered system so as to explicitly show the difference of the two measures. The first measure was proposed by RHP[11]which is based on the divisibility of the dynamical map: a trace-preserving completely positive map ε(t2, 0) that describes the evolution from times zero to t2is divisible if it satisfies composition law,

with ε(t2, t1) being completely positive for any t2≥ t1≥ 0 RHP defined all the divisible maps to be Markovian exactly. Therefore, the indivisibility of a map advocates its dynamical non-Markovianity. It was shown that all the evolutions governed by Lindblad-type master equation with positive transition rates (timeindependent or time-dependent) are divisible and thus Markovian[30]. RHP further proved that the indivisibility of map ε(t, 0) is equivalent to the positivity of the quantity,
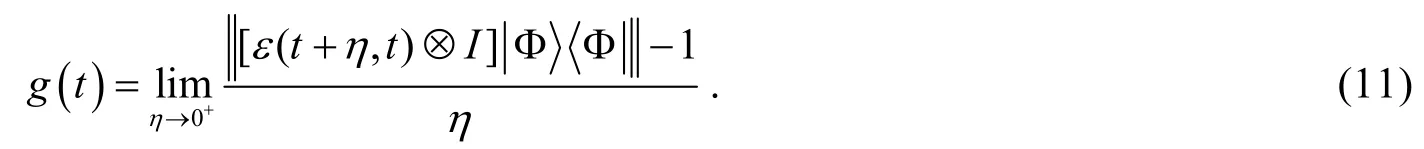

According RHP measure, for Markovian processes, g(t) = 0 at any time t; and if g(t) > 0 for some times, the dynamical evolution takes on non-Markovianity. The distinct advantage of this non-Markovian measure is that its calculation can be processed only by knowledge of time-local master equation, not requiring the exact form of the map ε(t, 0).
For the open two-level system considered in this paper, suppose that, a straightforward deduction combined with equations (2) and (12) gives

where γ±(t) are given by Eq.(7). In the deduction, we neglect the contribution of the nonsecular term D′[ρ(t)], but the consideration of the Lamb shift HLS(t) does not alter the result of g(t), i.e., Lamb shift does not affect the divisibility of the system's dynamics. Eq.(13) shows that γ+(t) not only affects, but in the same way as γ-(t), affects the non-Markovianity of the system's dynamics. As long as one of them is negative, g(t) > 0 and the evolution takes on non-Markovianity.
The second measure of non-Markovianity for quantum processes of open systems we employ is proposed by BLP[10]which is based on the consideration in purely physics. Note that Markovian processes always tend to continuously reduce the trace distance between any two states of a quantum system, thus anincrease of the trace distance during any time intervals implies the emergence of non-Markovianity. The authors further linked the changes of the trace distance to the flow of information between system and its environment, and concluded that the back flow of information from environment to the system is the key feature of a non-Markovian dynamics. In quantum information science, the trace distance for quantum states ρ1and ρ2is defined as[1]


where ρ1,2(t) are the dynamical states of the system corresponding to the initial states ρ1,2(0). For Markovian processes, the monotonically reduction of the trace-distance implies σ(t, ρ1,2(0)) ≤ 0 for any initial states ρ1,2(0) and at any timet. If there exists a pair of initial states of the system such that for some evolutional time t the trace-distance increases, that is, σ(t, ρ1,2(0)) > 0, the process must be non-Markovian.
In order to calculate BLP measure, we must solve the dynamics of the system. Thus, we write the alternative Bloch equation corresponding to Eq.(2) as

where we neglect the Lamb shift HLS(t) and the nonsecular term D′[ρ(t)], and the Bloch vector is defined as bj(t) = tr[ρ(t)σj]. This set of decoupled equations can be easily solved which gives


where the positive function G(t) is defined as G(t) = e-Λ(t)/2{Δt + [Δbz(0)]2e-Λ(t)/Δ(t)} > 0, Δ(t) = {[Δbx(0)]2+ [Δby(0)]2+ [Δbz(0)]2e-Λ(t)}1/2and Δbj(0) = b1j(0) - b2j(0) with j = x, y, z are the difference of the initial Bloch components. This result implies that the RHP and BLP criteria of non-Markovianity have distinct differences: According to BLP criterion, the condition for the system's dynamics to reveal non-Markovianity is γ-(t) + γ+(t) < 0; While RHP criterion only requires γ-(t) < 0 or γ+(t) < 0. Eqs.(13) and (20) also shows that when one of the transition rates, γ-(t) or γ+(t), is zero, then the two criteria agree qualitatively. This further approves the previous conclusion: For Lindblad-form master equation with single time-dependant transition rate, the RHP and BLP criteria are equivalent to each other[31]. But for Lindblad-form master equation with multiple time-dependant transition rates, the two measures are in general not in agreement according to above results.
4 Non-M arkovian dynamics for Lorentzian spectrum
In order to demonstrate quantitatively the effects of counter-rotating wave terms, we specify our study to a particular reservoir spectra, Lorentzian spectra,

which describes the interaction of an atom with an imperfect cavity and is widely used in literatures. Where ω0denotes the transition frequency of the atom, Δ = ω0-ωcis the frequency detuning between the atom and the cavity mode. λ is the width of Lorentzian distribution and is connected to the reservoir correlation time TR= λ-1. The parameter γ0can be regarded as the decay rate for the excited atom in the Markovian limit of flat spectrum which is related to the relaxation time TS= γ0-1. For the Lorentzian spectra, the time-dependent transition rates γ±(t) can be analytically written as

with Δ-= Δ = ω0-ωcand Δ+= 2ω0- Δ = ω0+ ωc. The other time-dependent coefficients S±(t), α(t) and β(t) related to Lamb shift and nonsecular terms also can be calculated analytically, but we have neglected them already. For different spectral widths and different frequency detunings between the atom and the cavity mode, we plot the rescaled transition rates γ±(t)/γ0as functions of dimensionless time γ0t in Figs.1 and 2. Where we choose the atomic transition frequency to be ω0= 100γ0.
Fig.1 shows that with the increasing of Δ, the relative amplitude (relative to γ-(t)) for the oscillation of γ+(t) increases, implying that the role of γ+(t) increases. Thus for large frequency detuning between the atom and the cavity mode, the rotating wave approximation would be incorrect. In addition, according to RHP criterion, γ+(t) plays an important role to the non-Markovian dynamics of the system. For small detunig (see Fig.1 (a)), γ-(t) has no oscillation and always positive, thus the non-Markovianity completely arises by γ+(t). However, when the detuning augments (see Fig.1 (b) and (c)), γ-(t) oscillates and appears negative values for some time intervals, leading that both γ±(t) have contributions to the non-Markovianity of the system's dynamics.

Fig.1 The time-dependent tr ansition r ates(t)/γ0(dot line ) and γ+(t)/γ0(solid lin e ) as functions of dimensionless time γ0t. Where ω0= 100γ0, λ = 2γ0and Δ = γ0, 10γ0, 30γ0for (a), (b), (c) respectively.

Fig.2 The time-dependent transition rates γ-(t)/γ0(dot line ) and γ+(t)/γ0(solid line ) as fun ctions of dimensionless time γ0t. Where ω0= 100γ0, Δ = 10γ0, and λ = 5γ0, 50γ0, 200γ0for (a), (b), (c) respectively.
From Fig.2, we see that, firstly, with the increasing of the spectral width, the value of γ+(t) becomeslarger, implying that the role of γ+(t) becomes more and more important. In particular when λ→∞, it has γ+(t) = γ-(t) = γ0, leading to the same degrees of significance of γ±(t). Thus for a broad and smooth spectral distribution, the rotating wave approximation is invalid. Next, when the width λ of the reservoir spectra is narrower (Fig.2 (a)), the memory time of the reservoir is longer, thus γ+(t) oscillates for a relatively longer time. But with the increasing of the spectral width, the oscillation time of γ+(t) becomes shorter (see Fig.2 (b) and (c)), implying that the non-Markovian time scale imposed by γ+(t) becomes shorter.
In Fig.3, we plot the time evolution of the rescaled RHP non-Markovian measure g(t)/γ0where the parameters are chosen to be in agreement with that in Fig.1. From this figure, we can see clearly the contributions of γ±(t) to the non-Markovianity of the system's dynamics. In Fig.3 (a), all the positive-value intervals of g(t) stem from the negative values of γ+(t) shown in Fig.1. While in Fig.3 (b) and (c), only the series of minor positive-value intervals of g(t) stem from the negative values of γ+(t), and the major positive-value intervals stem from mainly the contributions of the negative values of γ-(t). Clearly, according to RHP measure, the dynamics that corresponds to all the three situations of (a), (b) and (c) is non-Markovian.

Fig.3 The rescaled RHP non-Markovian measure g(t)/γ0as function of dimensionless time γ0t, Where ω0= 100γ0, λ = 2γ0and Δ = γ0, 10γ0, 30γ0for (a), (b), (c) respectively.

Fig.4 The z component of t he Bloch ve ctor a s a function of dimensionless time γ0t for initial value of bz(0) = 1. Where ω0= 100γ0, λ = 2γ0and Δ = γ0, 10γ0, 30γ0for (a), (b), (c) respectively.
However, the BLP measure gives inconsistent results. According to the expression of Eq.(20) combined with the evolution of γ±(t) in Fig.1, one can easily conclude that only the dynamics corresponding to the situations of Fig.1 (b) and (c) is non-Markovian, while the dynamics related to Fig.1 (a) is Markovian. In order to further demonstrate the physical features of BLP measure, we plot under the same parameters as in Fig.1 the time evolution of the Bloch component bz(t) as in Fig.4, for the initial state (bx(0), by(0), bz(0)) = (0, 0, 1). We see that in case (a) it decreases monotonically, implying that there is no visible exchange of energy or information between the system and the environment. While in cases of (b) and (c), the oscillations of bz(t) occurring in times of the order of the reservoir memory time advocates the exchange of energy or information, which is the indication of non-Markovian dynamics according BLP measure.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, we have studied the non-Markovianity for a two-level system interacting with a zero-temperature structured environment without rotating wave approximation. In the limit of weak coupling between the system and the reservoir, we have derived the time-local non-Markovian master equation for the reduced state of the system. For the case of Lorentzian reservoir, the analytic expressions for the time-dependent coefficients were obtained. It was found that when the width of the reservoir spectra is large enough or when the cavity frequency is detuned large enough from the transition of the system, the rotating wave approximation is invalid. We have investigated the non-Markovian dynamical behavior of the system in terms of both the RHP and BLP measures. It was found on the one hand that the counter-rotating wave terms have important contributions to the non-Markovianity of the system's dynamics. And on the other hand there is explicit difference for the two measures to describe the non-Markovianity of the system: when the Lindblad-form master equation has only a single time-dependant transition rate, the RHP and BLP measures are equivalent to each other. While for the case of the master equation with multiple time-dependant transition rates, the two measures are in general not agreement. This difference alerts people that the research on the essence of non-Markovian dynamics for open quantum systems is still necessary.
[1] Nielsen M A, Chuang I L. Quantum computation and quantum information [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
[2] Lindblad G. On the generator of quantum dynamical semigroups [J]. Commun. Math. Phys, 1976, 48: 119-130.
[3] Breuer H P,Petruccione F. The theory of open quantum systems [M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007.
[4] Kubota Y, Nobusada K. Applicability of site-basis time-evolution equation for thermalization of exciton states in a quantum dot array [J]. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn, 2009, 78: 114603.
[5] Ji Y H, Hu J J. Entanglement and decoherence of coupled superconductor qubits in a non-Markovian environment [J]. Chin. Phys. B, 2010, 19: 060304.
[6] Shao J. Decoupling quantum dissipation interaction via stochastic fields [J]. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120: 5053-5056.
[7] Chin A W, Datta A, Caruso F, et al. Noise-assisted energy transfer in quantum networks and light-harvesting complexes [J]. New J. Phys. 2010, 12: 065002.
[8] Dijkstra A G, Tanimura Y. Non-Markovian entanglement dynamics in the presence of system-bath coherence [J]. Phys. Rev. Lett, 2010, 104: 250401.
[9] Huang L Y, Fang M F. Protecting entanglement by detuning: in Markovian environments vs in non-Markovian environments [J]. Chin. Phys. B, 2010, 19: 090318.
[10] Breuer H P, Laine E M,Piilo J. Measure for the degree of non-Markovian behavior of quantum processes in open systems [J]. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2009, 103: 210401.
[11] Rivas ?, Huelga S F, Plenio M B. Entanglement and non-Markovianity of quantum evolutions [J]. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2010, 105: 050403.
[12] Usha Devi A R, Rajagopal A K, Sudha. Open-system quantum dynamics with correlated initial states, not completely positive maps, and non-Markovianity [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2011, 83: 022109.
[13] Lu X M, Wang X G, Sun C P. Quantum Fisher information flow and non-Markovian processes of open systems [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2010, 82: 042103.
[14] Hou S C, Yi X X, Yu S X, et al. Alternative non-Markovianity measure by divisibility of dynamical maps [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2011, 83: 062115.
[15] Xu Z Y, Yang W L, Feng M. Proposed method for direct measurement of non-Markovian character of the qubitscoupled to bosonic reservoirs [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2010, 81: 044105.
[16] He Z, Zou J, Li L et al. Effective method of calculating the non-Markovianity N for single-channel open systems [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2011, 83: 012108.
[17] Shabani A, Lidar D A. Vanishing quantum discord is necessary and sufficient for completely positive maps [J]. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2009, 102: 100402.
[18] Breuer H P, Vacchini B. Structure of completely positive quantum master equations with memory kernel [J]. Phys. Rev. E, 2009, 79: 041147.
[19] Haikka P, Maniscalco S. Non-Markovian dynamics of a damped driven two-state system [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2010, 81:052103.
[20] Chang K W, Law C K. Non-Markovian master equation for a damped oscillator with time-varying parameters [J], Phys. Rev. A, 2010, 81: 052105.
[21] Chru?ciński D, Kossakowski A, Pascazio S. Long-time memory in non-Markovian evolutions [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2010, 81: 032101.
[22] Haikka P, Cresser J D, Maniscalco S. Comparing different non-Markovianity measures in a driven qubit system [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2011, 83: 012112.
[23] Ding B F, Wang X Y, Tang Y F, et al. Non-Markovian dynamics of a qubit in a reservoir: different solutions of non-Markovian master equation [J]. Chin. Phys. B, 2011, 20: 060304.
[24] Jing J, Yu T. Non-Markovian relaxation of a three-level system: Quantum trajectory approach [J]. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2010, 105: 240403.
[25] Wu C, Li Y, Zhu M, et al. Non-Markovian dynamics without using a quantum trajectory [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2011, 83:052116.
[26] Xu J S, Li C F, Gong M, et al. Experimental demonstration of photonic entanglement collapse and revival [J]. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2010, 104: 100502.
[27] Xu J S, Li C F, Zhang C J, et al. Experimental investigation of the non-Markovian dynamics of classical and quantum correlations [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2010, 82: 042328.
[28] Chru?ciński D, Kossakowski A, Rivas ?. Measures of non-Markovianity: Divisibility versus backflow of information [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2011, 83: 052128.
[29] Maniscalco S, Piilo J, Intravaia F, et al. Lindblad- and non-Lindblad-type dynamics of a quantum Brownian particle[J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2004, 70: 032113.
[30] Alicki R, Lendi K. Quantum dynamical semigroups and applications [M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2007.
[31] Zeng H S, Tang Ning, Zheng Y P, et al. Equivalence of the measures of non-Markovianity for open two-level systems [J]. Phys. Rev. A, 2011, 84: 032118.
(責任編校: 江 河)
Non-Markovian dynamics for an open two-level system without rotating wave approximation
XU Tian-tian, TANG Ning, ZHENG Yan-ping, ZENG Hao-Sheng
(Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Quantum Structures and Quantum Control of Ministry of Education, Department of Physics, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, china)
The non-Markovianity for a two-level system interacting is studied with a zero-temperature structured environment without rotating wave approximation. In the limit of weak coupling between the system and the reservoir, the time-local non-Markovian master equation for the reduced state of the system is derived. Both the analytic and numerical results show that the counter-rotating wave terms play an important role for the non-Markovian dynamics of the system. And the difference of the two non-Markovian measures is proposed recently.
open quantum system; rotating wave approximation; non-Markovianity
O 431.2
1672-6146(2012)02-0012-09
10.3969/j.issn.1672-6146.2012.02.005
2012-05-06
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.11075050), the National Fundamental Research Program of China (Grant No.2007CB925204), and the Construct Program of the National Key Discipline.
徐甜甜(1986-), 女, 碩士研究生, 研究方向為量子光學. E-mail: liweitian930924@163.com
曾浩生(1965-), 男, 教授, 博士生導師, 主要研究方向為量子光學與量子信息.
E-mail: hszeng@hunnu.edu.cn

