Electroacupuncture improves neuropathic pain Adenosine, adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium and their receptors perhaps change simultaneously☆
Wen Ren, Wenzhan Tu, Songhe Jiang, Ruidong Cheng, Yaping Du
1 Institute of Social & Family Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, Zhejiang Province, China
2 Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical College, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China
Electroacupuncture improves neuropathic painAdenosine, adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium and their receptors perhaps change simultaneously☆
Wen Ren1, Wenzhan Tu2, Songhe Jiang2, Ruidong Cheng2, Yaping Du1
1Institute of Social & Family Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, Zhejiang Province, China
2Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical College, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China
Applying a stimulating current to acupoints through acupuncture needles - known as electroacupuncture - has the potential to produce analgesic effects in human subjects and experimental animals. When acupuncture was applied in a rat model, adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium in the extracellular space was broken down into adenosine, which in turn inhibited pain transmission by means of an adenosine A1 receptor-dependent process. Direct injection of an adenosine A1 receptor agonist enhanced the analgesic effect of acupuncture. The analgesic effect of acupuncture appears to be mediated by activation of A1 receptors located on ascending nerves. In neuropathic pain, there is upregulation of P2X purinoceptor 3 (P2X3) receptor expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Conversely, the onset of mechanical hyperalgesia was diminished and established hyperalgesia was significantly reversed when P2X3 receptor expression was downregulated. The pathways upon which electroacupuncture appear to act are interwoven with pain pathways, and electroacupuncture stimuli converge with impulses originating from painful areas. Electroacupuncture may actviapurinergic A1 and P2X3 receptors simultaneously to induce an analgesic effect on neuropathic pain.
electroacupuncture; analgesia; adenosine; adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium; A1 receptors; P2X purinoceptor 3 receptors; neuropathic pain; peripheral nervous system; central nervous system; regeneration; neural regeneration.
Research Highlights
(1) Previous studies addressing the analgesic effect of acupuncture mainly focused on purine and a single purine receptor; no studies have examined the possible influence of synergism or antagonism with other receptors.
(2) Electroacupuncture may induce an analgesic effect in neuropathic pain by influencing both purinergic A1 and P2X purinoceptor 3 (P2X3) receptors simultaneously.
(3) Electroacupuncture analgesia may also involve adenosine and adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium receptors in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Electroacupuncture can inhibit purinergic A1 and P2X3 receptors and exert an analgesic effect on neuropathic pain.
Abbreviations
ATP, adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium; P2X3, P2X purinoceptor 3
INTRODUCTION
Electroacupuncture is a procedure in which fine needles are inserted into an individual at discrete points and then electrical stimulation is applied, with the aim of relieving chronic pain[1-3]. Electroacupuncture analgesia is essentially a manifestation of integrative processes between afferent impulses from painful areas and impulses from acupoints within the peripheral nervous system and at different levels of the central nervous system. A complex network of numerous brain structures is involved in the mechanisms that mediate electroacupuncture analgesia[1]. Acupuncture triggers an increase in the extracellular concentration of adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium (ATP), adenosine diphosphate, adenosine monophosphate and adenosine. Electroacupuncture also triggers an increase in the extracellular concentration of ATP and related nucleotides[4]. P2X purinoceptor 3 (P2X3) and P2X2/3 receptors are located in the central and peripheral nervous system. ATP plays a crucial role in facilitating pain transmission by acting at P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors especially in acute, inflammatory, neuropathic and visceral pains[5-6]. Noxious or injurious stimuli damage cells, which release ATP. ATP then acts at P2X3 homomeric and P2X2/3 heteromeric receptors situated on the peripheral terminals of sensory neurons, such as those of dorsal root ganglia, to induce painful sensations[7-8]. ATP cannot be transported back into the cell but is rapidly degraded to adenosine by several ectonucleotidases before reuptake[9].
Adenosine plays a complex role in mediating pain that is highly dependent on the site of administration and the receptor subtype activated[8]. Whereas the stimulation of A1 receptors results in analgesic effects in a wide range of animal models, in rats lacking the A1 receptor there is an enhanced response to nociceptive stimuli[10]. The actions of adenosine may be antagonistic or synergistic with ATP.
HYPOTHESIS AND SUPPORTING EVIDENCE
In clinical practice, acupuncture in itself is not painful, but traditional acupuncturists stress that it can elicit the
‘De-Qi’ feeling, a constellation of unique sensations that are essential for its clinical efficacy[1].
In the model of neuropathic pain described above, ATP is released from damaged peripheral nerve tissue and plays an important role in the initiation of pain by sensitizing primary afferents. Neuropathic pain results in upregulation of P2X3 receptor expression on dorsal root ganglion neurons and causes primary sensory neurons to become hyperexcitable to ATP-evoked inward currents[11-12]. The increased amplitude of the currents evoked by ATP and its analogs has been shown to sensitize sensory afferents. After electroacupuncture treatment, pathological pain was relieved, previously upregulated expression of P2X3 receptors was reversed and the amplitudes of ATP-evoked inward currents at P2X3 receptors were suppressed[13-14]. This suggests that P2X3 receptors are critical in the development of neuropathic pain and that electroacupuncture treatment could likely cause analgesia by decreasing expression and sensitization of P2X3 receptors[13-14].
Electroacupuncture treatment produces a long-lasting analgesic effect on neuropathic pain and increases expression of P2X3 receptors in the midbrain periaqueductal gray matter, which potentiates the function of the purinergic signaling system at the supraspinal level and provides a rational basis for explaining the analgesic effect of electroacupuncture[15].
Similar to acupuncture, electroacupuncture can trigger a general increase in the extracellular concentration of ATP and its breakdown product adenosine near the acupuncture point[4]. As in electroacupuncture, adenosine may accumulate during these treatments and dampen pain in part by the activation of A1 receptors on the sensory afferents in ascending tracts. It is possible that ATP release from keratinocytes in response to skin stimulation results in an accumulation of adenosine that transiently reduces pain, as A1 receptors are likely to be expressed by nociceptive axon terminals in the epidermis[16-17]. However, this effect differs from the anti-nociceptive effect of acupuncture, which is independent of the afferent innervation of the skin[1-18]. In electroacupuncture, needles are typically applied to deeper tissues, including muscle and connective tissue, and these acupoints may be closer to ascending nerve tracts than the dense cutaneous afferents. The analgesic effects of peripheral, spinal and supraspinal A1 receptors are well established, and an A1 receptor agonist has been found to substantially reduce inflammatory and neurogenic pain; also, the suppression of pain mediated by electroacupuncture requires adenosine A1 receptor expression. These findings suggest that A1 receptor activation is both necessary and sufficient for the clinical benefits of electroacupuncture[4]. A1 receptors are widely distributed throughout the brain at synaptic and extrasynaptic sites, with high densities present in the hippocampus, cerebellum and cerebral cortex[19].
Electroacupuncture preconditioning involves a mechanism related to the actions of an A1 receptorrelated pathway in the brain[20].
Extracellular adenosine concentration rose following the release of ATP, which was dephosphorylated to adenosine diphosphate, adenosine monophosphate and adenosine by potent ectonucleotidases. Adenosine is only present in the extracellular space for a short time because of facilitated uptake by nucleoside transporters. After reuptake, adenosine is quickly converted back to ATP[21].
Interaction between the adenosine receptor and P2 receptor systems has been shown to occur in neuronal and non-neuronal cells[22]. Both adenosine and ATP induce astroglial cell proliferation and formation of reactive astrocytes. In the hippocampus, adenosine and ATP are released on stimulation and are potent inhibitors of neuronal action potential transmission[23]. ATP must be converted to adenosine outside the cell to exert its inhibitory effects on hippocampal synaptic transmission[4].
In summary, the analgesic role of electroacupuncture in neuropathic pain may involve purinergic A1 and P2X3 receptors simultaneously.
DISCUSSION
Although the analgesic effect of electroacupuncture is well documented, little is understood about its biological basis. Insertion of the acupuncture needles in itself is not sufficient to relieve pain. An acupuncture session typically lasts for 30 minutes, during which the needles may be electrically stimulated or, in some cases, heated. The patient’s pain threshold is reported to slowly increase, an observation that outlasts the treatment[1]. The primary mechanism implicated in the analgesic effect of electroacupuncture involves release of endogenous opioid peptides in response to the long-lasting activation of ascending sensory tracts during stimulation[24-25].
Neuropathic pain typically occurs after nerve damage that can be induced by physical injury, nerve compression by tumors or intervertebral discs, diabetes, infection or autoimmune disease[26-29]. Evidence accumulated from neuropathic pain models suggests that neuropathic pain might involve abnormal excitability of the nervous system. Notably, in primary sensory ganglia and in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, many functional and anatomical alterations occur in neurons after peripheral nerve injury[30]. Besides these changes in neurons, emerging lines of evidence suggest that they also occur in glial cells, especially microglia[31-32]. Also, it has been suggested that the analgesic effects of electroacupuncture are associated with its ability to counter-regulate spinal glial activation[31-33]. Tactile allodynia induced by nerve injury depends upon a unique pattern of activation of purinergic P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors in damaged primary sensory neurons[31].
The analgesic effect of electroacupuncture has been used widely to alleviate diverse pains in clinical practice, particularly chronic pain. Following the application of acupuncture, the pain threshold gradually increases in both humans and animals, indicating a delayed development of acupuncture analgesia. Moreover, there is a long-lasting analgesic effect after acupuncture stimulation has been completed[34-35]. Increasing attention has been paid to exploring the physiological and biochemical mechanisms that underlie electroacupuncture analgesia. The complex acupuncture-induced sensations of soreness, numbness, heaviness and distension in the tissue deep beneath the acupoint is essential to acupuncture analgesia[36-37]. The meridians are considered as a network system that transmits and relays electroacupuncture signalsviasensory nerves, through ganglia to the spinal cord and then onward to the brain stem, hypothalamus and higher centers[1]. Sensory nerve activity initiated by acupuncture has an inhibitory modulating effect on higher pain centers in the brain[38].
Previous studies have shown that the P2X signaling system is associated with various pain mediators including opioid peptides, glutamate, γ-amino butyric acid and substance P in peripheral primary afferent terminals and areas of the central nervous system related to nociception and pain, while it is well documented that electroacupuncture analgesia is a complex physiological process modulated by the same mediators[14]. Therefore, electroacupuncture may influence these transmitters and modulators, which in turn act upon purinergic receptors to alleviate the symptoms of allodynia.
Although ATP is released during electroacupuncture, extracellular ATP does not reach sufficiently high concentrations to activate P2X3 because of its rapid degradation, which explains the lack of direct pain during electroacupuncture[4]. Therefore, the ATP release induced by electroacupuncture does not activate P2X3 receptors and so does not exert an anti-analgesic effect. However, it has been demonstrated that ATP and adenosine mediate the analgesic role of electroacupuncture[4-14]. In neuropathic pain model, changes in the expression levels of A1 and P2X3 receptors can be observed before and after electroacupuncture treatment, an observation that can be used as a paradigm to explore the importance of the balance between each receptor system in the peripheral and central nervous systems[39-42]. For example, rats with deleted A1 receptors can be used to evaluate whether electroacupuncture treatment alters mechanical and thermal pain thresholds, and the influence of selective A1 and P2X3 receptor antagonists can be explored in rat models of neuropathic pain. Furthermore, new techniques allow the influence of ATP and adenosine upon electroacupuncture to be observed in the central nervous system.
Adenosine and ATP have been shown to have a wide spectrum of unique pain-relieving properties in various clinical situations. In patients with chronic neuropathic pain, adenosine compounds appear to mediate their analgesic effects through A1 receptor-related modulation of central sensitization at spinal or supraspinal levels. Intravenous adenosine and ATP, intrathecal adenosine, or longer-acting analogs of these molecules may offer novel therapeutic interventions for the treatment of pain in the future[43].
As described earlier, endogenous and exogenous ATP essentially acts as an algogenic substance. Local increases in ATP concentration may lead to the upregulation of an enzyme cascade that hydrolyzes the ATP and thus reduces its levels[44]. When administered intravenously or intrathecally, however, ATP may act like adenosine at sites in the peripheral and central nervous systems[45]. It has been suggested that in neuropathic pain there are disturbances in the endogenous adenosine system that lead to a deficiency of adenosine in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid, which may explain the potential therapeutic anti-neuropathic effects of adenosine or its analogs[46].
Although adenosine, following ecto-enzymatic breakdown of ATP, is the predominant presynaptic modulator of neurotransmitter release in the central nervous system, ATP can also act presynaptically[8-46]. Coordinated purinergic regulatory systems in the central nervous system control the behavior of local networks by regulating the balance between the effects of ATP, adenosine and ectonucleotidases on synaptic transmission[8-47]. In addition, electroacupuncture signals combined with suppression of adenosine monophosphate deaminase activity[4], and promotion of the degradation of ATP to adenosine could increase the availability of adenosine in the peripheral and central nervous systems[48-50]. Although generally adenosine is produced by ecto-enzymatic breakdown of released ATP, there may be subpopulations of brain neurons and/or astrocytes that release adenosine directly[8].
Chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve promotes the expression of P2X3 receptors[37]. Furthermore, the elevated expression of the P2X3 receptor is accompanied by an increase in receptor sensitivity. It has been shown that electroacupuncture treatment can decrease the expression of the P2X3 receptors and inhibit the sensitization of the P2X3 receptors in dorsal root ganglion neurons. The analgesic effect of adenosine and ATP is slow in onset and long-lasting. It may be possible to potentiate electroacupuncture treatment to prolong its pain-relieving effects.
In the peripheral nervous system, electroacupuncture signals decrease the expression of P2X3 receptors, inhibit their activation and suppress their sensitization. On the other hand, electroacupuncture signals promote the degradation of ATP to adenosine, which may accumulate during electroacupuncture treatment and dampen pain in part by the activation of A1 receptors on the sensory afferents in ascending nerve tracts. At the same time, electroacupuncture signals promote trafficking of the A1 receptor to the cell surface and elevate the sensitization of A1 receptors to adenosine. In the central nervous system, electroacupuncture signals may modulate the release of adenosine and ATP, and increase the expression of the A1 receptor. Meanwhile, the activation of A1 receptors by adenosine may be enhanced by electroacupuncture treatment (Figure 1). Furthermore, if the synergistic effect of purinergic A1 and P2X3 receptors in electroacupuncture analgesia can be demonstrated experimentally, this may help to elucidate the possible molecular mechanisms that underpin adenosine and ATP receptors.
Author contributions: Wen Ren and Wenzhan Tu had full access to the study conception and design, and wrote the manuscript. Ruidong Cheng was responsible for producing the figure. Yaping Du and Songhe Jiang validated the article, and supervised the study. All authors participated in manuscript development, oversight and instruction.
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Author statements: The manuscript is original, has not been submitted to or is not under consideration by another publication, has not been previously published in any language or any form, including electronic, and contains no disclosure of confidential information or authorship/patent application disputations.
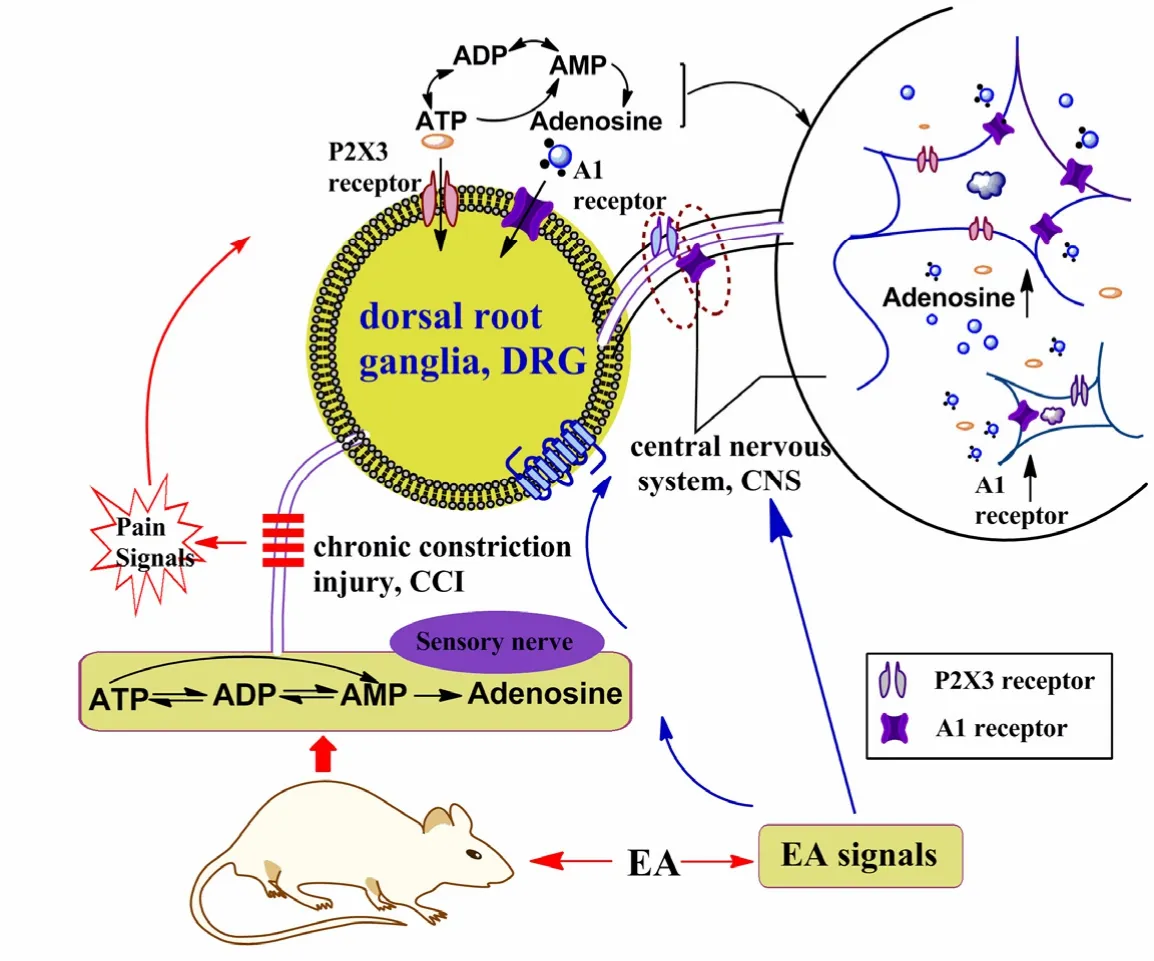
Figure 1 Effect of electroacupuncture (EA) signals on adenosine and adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium (ATP) receptors within the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system (CNS) in rats with neuropathic pain.
[1] Zhao ZQ. Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol. 2008;85(4):355-375.
[2] Kim JH, Min BI, Schmidt D, et al. The difference between electroacupuncture only and electroacupuncture with manipulation on analgesia in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2000;279 (3):149-152.
[3] Lao L, Zhang RX, Zhang G, et al. A parametric study of electroacupuncture on persistent hyperalgesia and Fos protein expression in rats. Brain Res. 2004;1020(1-2):18-29.
[4] Goldman N, Chen M, Fujita T, et al. Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13(7):883-888.
[5] Burnstock G. Historical review: ATP as a neurotransmitter. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27(3):166-176.
[6] Burnstock G. Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;110(3):433-454.
[7] Burnstock G, Verkhratsky A. Evolutionary origins of the purinergic signalling system. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2009; 195(4):415-447.
[8] Burnstock G, Krügel U, Abbracchio MP, et al. Purinergic signalling: from normal behaviour to pathological brain function. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;95(2):229-274.
[9] Burnstock G. Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev. 2007;87(2):659-797.
[10] Johansson B, Halldner L, Dunwiddie TV, et al. Hyperalgesia, anxiety, and decreased hypoxic neuroprotection in mice lacking the adenosine A1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(16):9407-9412.
[11] Burnstock G. Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;110(3):433-454.
[12] Ou S, Zhao YD, Xiao Z, et al. Effect of lappaconitine on neuropathic pain mediated by P2X3 receptor in rat dorsal root ganglion. Neurochem Int. 2011;58(5):564-573.
[13] Zhang A, Xu C, Liang S, et al. Role of sodium ferulate in the nociceptive sensory facilitation of neuropathic pain injury mediated by P2X(3) receptor. Neurochem Int. 2008; 53(6-8):278-282.
[14] Tu WZ, Cheng RD, Cheng B, et al. Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on chronic neuropathic pain mediated by P2X3 receptors in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurochem Int. 2012;60(4):379-386.
[15] Xiao Z, Ou S, He WJ, et al. Role of midbrain periaqueductal gray P2X3 receptors in electroacupuncture-mediated endogenous pain modulatory systems. Brain Res. 2010;1330:31-44.
[16] Sawynok J. Adenosine receptor activation and nociception. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;347(1):1-11.
[17] Takakura N, Yajima H. Analgesic effect of acupuncture needle penetration: a double-blind crossover study. Open Med. 2009;3(2):e54-61.
[18] Salter MW, Henry JL. Evidence that adenosine mediates the depression of spinal dorsal horn neurons induced by peripheral vibration in the cat. Neuroscience. 1987;22(2):631-650.
[19] Fredholm BB, Arslan G, Halldner L, et al. Structure and function of adenosine receptors and their genes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000;362(4-5):364-374.
[20] Wang Q, Xiong L, Chen S, et al. Rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia in rats is induced by preconditioning with electroacupuncture: window of protection and the role of adenosine. Neurosci Lett. 2005;381(1-2):158-162.
[21] Fredholm BB. Adenosine, an endogenous distress signal, modulates tissue damage and repair. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14(7):1315-1323.
[22] Sebasti?o AM, Ribeiro JA. Fine-tuning neuromodulation by adenosine. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2000;21(9):341-346.
[23] Sichardt K, Nieber K. Adenosine A1 receptor: Functional receptor-receptor interactions in the brain. Purinergic Signal. 2007;3(4):285-298.
[24] Han JS. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci Lett. 2004;361(1-3):258-261.
[25] Huang C, Wang Y, Han JS, et al. Characteristics of electroacupuncture-induced analgesia in mice: variation with strain, frequency, intensity and opioid involvement. Brain Res. 2002;945(1):20-25.
[26] Scholz J, Woolf CJ. Can we conquer pain? Nat Neurosci. 2002;5 Suppl:1062-1067.
[27] Zimmermann M. Pathobiology of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;429(1-3):23-37.
[28] Gwak YS, Hulsebosch CE. Remote astrocytic and microglial activation modulates neuronal hyperexcitability and below-level neuropathic pain after spinal injury in rat. Neuroscience. 2009;161(3):895-903.
[29] Trang T, Beggs S, Salter MW. ATP receptors gate microglia signaling in neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol. 2012; 234(2):354-361.
[30] Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ. Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2009;32:1-32.
[31] Inoue K, Tsuda M. Purinergic systems, neuropathic pain and the role of microglia. Exp Neurol. 2012;234(2):293-301.
[32] Tsuda M, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K. Purinergic system, microglia and neuropathic pain. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2012;12(1):74-79.
[33] Kang JM, Park HJ, Choi YG, et al. Acupuncture inhibits microglial activation and inflammatory events in the MPTP-induced mouse model. Brain Res. 2007;1131(1):211-219.
[34] Cui KM, Li WM, Gao X, et al. Electro-acupuncture relieves chronic visceral hyperalgesia in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2005; 376(1):20-23.
[35] Han JS, Zhou Z, Xuan Y. Acupuncture has an analgesic effect in rabbits. Pain. 1983;15(1-4):83-91.
[36] Dibaj P, Steffens H, Nadrigny F, et al. Purinergic activation of dorsal root ganglion neurones in vivo. Neurosci Lett. 2011;487(1):107-109.
[37] Zhuo M. Neuronal mechanism for neuropathic pain. Mol Pain. 2007;3:14.
[38] Burnstock G. Acupuncture: a novel hypothesis for the involvement of purinergic signalling. Med Hypotheses. 2009;73(4):470-472.
[39] Zylka MJ. Needling adenosine receptors for pain relief. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13(7):783-784.
[40] Zylka MJ. Pain-relieving prospects for adenosine receptors and ectonucleotidases. Trends Mol Med. 2011; 17(4):188-196.
[41] Wirkner K, Sperlagh B, Illes P. P2X3 receptor involvement in pain states. Mol Neurobiol. 2007;36(2):165-183.
[42] Gu JG, Heft MW. P2X receptor-mediated purinergic sensory pathways to the spinal cord dorsal horn. Purinergic Signal. 2004;1(1):11-16.
[43] Hayashida M, Fukuda K, Fukunaga A. Clinical application of adenosine and ATP for pain control. J Anesth. 2005; 19(3):225-235.
[44] Braun N, Zhu Y, Krieglstein J, et al. Upregulation of the enzyme chain hydrolyzing extracellular ATP after transient forebrain ischemia in the rat. J Neurosci. 1998;18(13):4891-4900.
[45] Hayashida M, Fukuda K, Fukunaga A, et al. Analgesic effect of intravenous ATP on postherpetic neuralgia in comparison with responses to intravenous ketamine and lidocaine. J Anesth. 2005;19(1):31-35.
[46] Cunha RA, Ribeiro JA. ATP as a presynaptic modulator. Life Sci. 2000;68(2):119-137.
[47] Matsuoka I, Ohkubo S. ATP- and adenosine-mediated signaling in the central nervous system: adenosine receptor activation by ATP through rapid and localized generation of adenosine by ecto-nucleotidases. J Pharmacol Sci. 2004;94(2):95-99.
[48] Inoue K. P2 receptors and chronic pain. Purinergic Signal. 2007;3(1-2):135-144.
[49] Jarvis MF, Burgard EC, McGaraughty S, et al. A-317491, a novel potent and selective non-nucleotide antagonist of P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors, reduces chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(26):17179-17184.
[50] Burrell HE, Wlodarski B, Foster BJ, et al. Human keratinocytes release ATP and utilize three mechanisms for nucleotide interconversion at the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(33):29667-29676.
10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.33.007 [http://www.crter.org/nrr-2012-qkquanwen.html]
Ren W, Tu WZ, Jiang SH, Cheng RD, Du YP. Electroacupuncture improves neuropathic pain: adenosine, adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium and their receptors perhaps change simultaneously. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(33):2618-2623.
Wen Ren☆, M.D., Institute of Social & Family Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, Zhejiang Province, China
Wen Ren and Wenzhan Tu contributed equally to this article.
Yaping Du, Ph.D., Professor, Institute of Social & Family Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, Zhejiang Province, China
duyp@zju.edu.cn
2012-08-20
2012-10-15
(N20120615005/YJ)
We thank Bo Cheng from the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical College for his advice in this paper.
(Edited by Bai WZ, Song XG/Qiu Y/Wang L)
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Underlying mechanism of protection from hypoxic injury seen with n-butanol extract of Potentilla anserine L. in hippocampal neurons***☆
- Shuanghuanglian injection downregulates nuclear factor-kappa B expression in mice with viral encephalitis*★
- Antioxidant effects of the orientin and vitexin in Trollius chinensis Bunge in D-galactose-aged mice**★
- Acupuncture inhibits cue-induced heroin craving and brain activation**★
- Puerarin prevents high glucose-induced apoptosis of Schwann cells by inhibiting oxidative stress*★
- Heat-sensitive moxibustion attenuates the inflammation after focal cerebral ischemia/ reperfusion injury*☆

