Reliability Assessment of a New General Matching Composed Network
Zhengyuan Liang ,Junbin Liang,* ,Guoxuan Zhong
1 Guangxi Key Laboratory of Multimedia Communications and Network Technology,School of Computer,Electronics and Information,Guangxi University,Nanning 530004,China
2 Jiangxi Engineering Laboratory of IoT Technologies for Crop Growth,Ji’an 343000,China
Abstract: The reliability of a network is an important indicator for maintaining communication and ensuring its stable operation.Therefore,the assessment of reliability in underlying interconnection networks has become an increasingly important research issue.However,at present,the reliability assessment of many interconnected networks is not yet accurate,which inevitably weakens their fault tolerance and diagnostic capabilities.To improve network reliability,researchers have proposed various methods and strategies for precise assessment.This paper introduces a novel family of interconnection networks called general matching composed networks(gMCNs),which is based on the common characteristics of network topology structure.After analyzing the topological properties of gMCNs,we establish a relationship between super connectivity and conditional diagnosability of gMCNs.Furthermore,we assess the reliability of gMCNs,and determine the conditional diagnosability of many interconnection networks.
Keywords: conditional diagnosability;interconnection networks;network reliability;super connectivity
I.INTRODUCTION
Nowadays,a multiprocessor system might contain thousands of processors,and its high complexity may adversely affect its reliability.Therefore,more accurate measures of reliability are needed.
All kinds of connectivities and diagnosabilities play important roles in measuring the reliability of interconnection networks.Among them,connectivity can correctly reflect the fault tolerance of small networks,but it does not reflect the real resilience of large networks[1,2].Motivated by this,many kinds of connectivities have been introduced,such as conditional connectivity[3],restricted connectivity[4],Rgconnectivity[1]and super connectivity[5].
The diagnosability of a system refers to the maximum number of faults that it can guarantee to diagnose[6].To further improve the diagnostic ability,in 2005,Lai et al.[7] proposed conditional diagnosability by assuming that each vertex has at least one good neighbor.The conditional diagnosability under the PMC model[6] and the comparison model[8]of many well-known interconnection networks have been studied [7,9-29].In 2012,Peng et al.proposed g-good-neighbor conditional diagnosability inspired by Rg connectivity[30].In a g-good-neighbor conditionally t-diagnosable system,each good vertex has at least g good neighbors.In 2016,Zhang et al.introduced g-extra conditional diagnosability inspired by extra connectivity[31].G-extra conditionally t-diagnosable systems require that each fault-free connected component has at least g+1 vertices[31].The definition of g-extra conditional diagnosability is highly consistent with the definition of g-extra vertex connectivity.In 2020,Guo et al.further generalized the conditional diagnosability by combining the advantages of g-good-neighbor conditional diagnosability,and proposed the Rg conditional diagnosability theory[32].Rg conditionally t-diagnosable systems require that every vertex has at least g good neighbors[32].Then,Yuan et al.studied the relationship between Rg connectivity and Rg conditional diagnosability,and obtained the Rg conditional diagnosability for some interconnection networks[33,34].
In this paper,we propose a new family of interconnection networks named general matching composed networks(gMCNs)which includes many well-known interconnection networks such as hypercube,M¨obius cube,locally twisted cubes,crossed cube,exchanged hypercube and exchanged crossed cube.In addition,we analyze the topological properties and fault tolerance of gMCNs and built an relationship between their super connectivity and conditional diagnosability under the PMC model.Using the newly-found relationship,the conditional diagnosability of gMCNs can be easily derived.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section II introduces the preliminaries.Section III introduces a new family of interconnection networks.Then we build the relationship between their super connectivity and conditional diagnosability.Section IV contains some concluding remarks.
II.PRELIMINARIES
LetG(V,E) be the graph of an interconnection network with the vertex setV(G)and the edge setE(G).Forx ∈V(G),N(x) is the neighborhood ofxandN[x]=N(x)∪{x}.ForS ? V(G),N(S)=x∈SN(x) -S,N[S]=N(S)∪SandNS(x)=N(x)∩S.The degree ofxis deg(x)=|N(x)| andδ(G) is the minimum degree of any vertex inG.ForF ?V(G),Fis a vertex-cut ofGifG-Fis disconnected.Connectivityk(G)is the size of the minimum vertex cut ofG.Forx,y ∈V(G),the number of common neighbors ofxandyis denoted bycn(x,y)=|N(x)∩N(y)|.Letcn(G)=max(cn(x,y)|x,y ∈V(G),x=y).A vertex-cutVcofGis a super vertexcut ofGif every component ofG-Vchas at least two vertices.The super connectivityk′(G)ofGis the minimum size of all the super vertex-cuts ofG.Clearly,k′(G)≤k(G)≤δ(G).
In order to diagnose faults,a number of tests between vertices are required.A collection of all test results inGis called a syndrome,denoted byσ(G).For a given syndromeσ(G),a fault setFis consistent with the syndrome ifFcan produceσ(G).The diagnosability ofG,written ast(G),is the maximum value of t such thatGis t-diagnosable[6].The notion of conditional faulty setF ?V(G)is a fault set andN(x)Ffor anyx ∈V(G).The conditional diagnosabilitytc(G) ofGis the maximum value of t such thatGis conditionally t-diagnosable.The following lemmas provide three important characterizations of conditionally t-diagnosable systems and conditional fault sets[7].
Definition 1.Two distinct sets F1and F2in V(G)are said to be indistinguishable if σ(F1)∩σ(F2)=?,otherwise,F1and F2are said to be distinguishable.
Besides,we say(F1,F2)is an indistinguishable pair if σ(F1)∩σ(F2)=?;else,(F1,F2)is a distinguishable pair.
Lemma 1.A system is conditionally t-diagnosable if each pair of distinct conditional faulty sets(F0,F1)is distinguishable,such that|F0|,|F1|≤t[7].
Lemma 2.Under the PMC model,a pair of conditional faulty set(F0,F1)is distinguishable if there exists an edge from F0ΔF1to V(G)-(F0∪F1),where F0ΔF1=(F0-F1)∪(F1-F0)[35](see Figure 1).
Lemma 3.For G(V,E),if(F0,F1)is a pair of distinct distinguishable conditional faulty sets,then[7]:
(1)Each vertex in V(G)-(F0∪F1)has at least one neighbor in V(G)-(F0∪F1).
(2)Each vertex in F0ΔF1has at least one neighbor in F0-F1and has at least one neighbor in F1-F0.
III.GMCN’S
In this section,we introduce a new family of interconnection networks.
Definition 2.Let r be a positive integer with r ≥1,and let Gi be graphs where1≤i ≤2r,such that Gi is triangle-free and cn(Gi)≤2. The 2-dimensional gMCNs,denoted by X2,is a cycle of length 4. The ndimensional gMCNs Xn=(G1,Gr,...,G2r,M)(n ≥3)is a graph with|V(Xn)|=2n and|V(Gi)|=|V(Xn)|/2r > δ(Xn). The set of edges of Xn is E(Xn)=E(G1)∪E(G2)∪...∪E(G2r)∪M with1≤i ≤2r-1,and Mi,i+1is a perfect matching between V(Gi)and V(Gi+1),while M=M1,2∪M2,3∪···∪M2r-1,2r(see Figure 2).

Figure 2.The illustration of gMCN Xn.

Figure 3.The topology of hypercube-like networks.

Figure 4.Interconnection networks included in gMCNS and HLs.
Let the path x1-x2-· · · -x2r of length2r-1be a horizontal path where xj ∈V(Gj)and1≤j ≤2r.Then,Xn satisfies the following conditions:
(1)There exists a cycle a-b-c-d-a of length 4,where a,b ∈V(Gr)and c,d ∈V(Gr+1)(see Figure 2).
(2)Xn can be decomposed into two copies of Xn-1,denoted by L and R.
(3)δ(Xn)=δ(Xn-1)+1.
(4)Gi is k-regular,where1≤i ≤2r.
(5)For any x,y ∈V(L) (or x,y ∈V(R))with x ∈V(Gi),y ∈V(Gj)and i=j,there is at most one horizontal path which contains a vertex of N[x]and contains a vertex of N[y].
gMCNs is not a new kind of interconnection network topologies,but a new class of them.This class of interconnection network has several properties about horizontal path and perfect matching.By Definition 2,several well-known interconnection networks belong to the family of gMCNs,such as hypercube(see Figure 5),M¨obius cube(see Figure 6),locally twisted cubes(see Figure 7),crossed cubes(see Figure 8),exchanged hypercube(see Figure 9),and exchanged crossed cube(see Figure 10).Figures 5(a)-8(a)are the most commonly used topologies and Figures 5(b)-8(b)are their isomorphic copies.
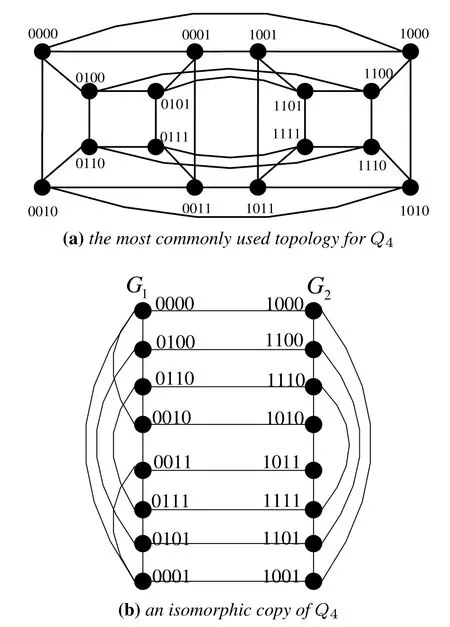
Figure 5.The structures of Q4.

Figure 6.The structures of MQ4.
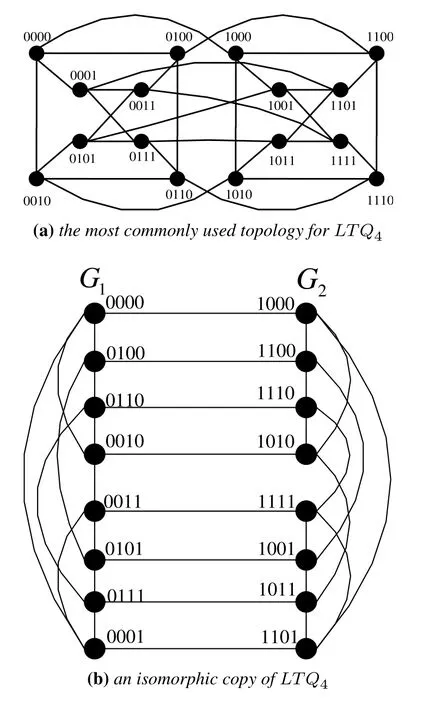
Figure 7.The structures of LTQ4.

Figure 8.The structures of CQ4.
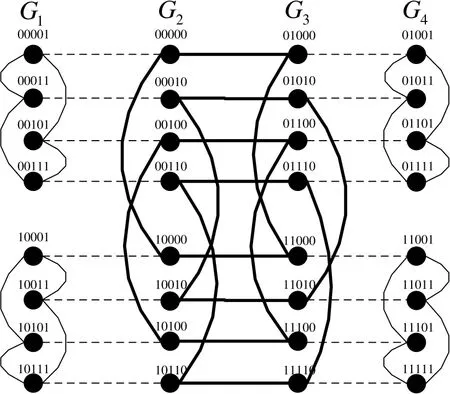
Figure 9.The structures of EH(2,2).

Figure 10.The structures of ECQ(2,2).
On the other hand,hypercube-like networks (HLs for short) are also a class of interconnection network topologies.HLs are a class of networks including several well-known interconnection networks like hypercubes and its variants,such as twisted cubes,crossed cubes,locally twisted cubes,generalized twisted cube,and M¨obius cubes,defined as:
where‘⊕’indicates a perfect matching.
By definition,there is a perfect matching in HLs betweenG0(denoted byL)andG1(denoted byR).That is,every node inLhas exactly a neighbor inR,and vice versa(see Figure 3).
Although both gMCNs and HLs emphasize perfect matching,gMCNs only requires perfect matching betweenGiandGi+1,and does not require perfect matching betweenLandR.As we have seen from Figure 2,the red node (blue node) does not have a perfect matching neighbor node inR(L).Therefore,HLs are included in gMCNs,some wellknown interconnection networks such as exchanged crossed cubes,exchanged hypercubes,locally exchanged twisted cubes and exchanged folded crossed cubes belong to gMCNs,but do not belong to HLs(see Figure 4).That is to say,gMCNs is not a special case of the HLs.On the contrary,HLs is a special case of gMCNs.
By the definition of gMCNs,we have the following lemmas.
Lemma 4.cn(Xn)≤2.
Lemma 5.Xn is triangle-free.
Lemma 6.Each vertex in Xn is in exactly one horizontal path.
A horizontal segment is a part of horizontal path.By Definition 2,several basic properties of gMCNs are listed below:
Lemma 7.deg(u)=δ(Xn)for u ∈ V(Gr)∪V(Gr+1).
Proof.Without loss of generality,letu ∈V(Gr),we have deg(u)=degL(u)+1.Letxbe arbitrary vertex ofV(L)-V(Gr).Then,degL(x)=deg(x)≥δ(Xn).If deg(u)≥δ(Xn)+1,degL(u)≥δ(Xn).Since degL(x)≥ δ(Xn) and degL(u)≥ δ(Xn),we haveδ(Xn-1)≥ δ(Xn) which contradicts thatδ(Xn-1)=δ(Xn) -1.Hence,deg(u)≤δ(Xn).Since deg(u)≥δ(Xn),deg(u)=δ(Xn).
Lemma 8.Let x ∈V(Gi)and y ∈V(Gj)where i ∈{1,2r}and j ∈{2,3,...,2r-1}. Then,there are at leastdeg(x)horizontal paths where each horizontal path contains a vertex of N(x). And there are at leastdeg(y)-1horizontal paths where each horizontal path contains a vertex of N(y).
Proof.Without loss of generality,leti=1.Since each vertex inXnis in exactly one horizontal path,xhas deg(x)-1 neighbors inV(Gi)and has exactly one neighbor inV(Gi+1).Then,there are at least deg(x)horizontal paths where each path has a vertex ofN(x).
Similarly,as shown in Figure 2,yhas deg(y) -2 neighbors inV(Gj),has exactly one neighbor inV(Gj-1) and has exactly one neighbor inV(Gj+1).Therefore,there are at least deg(y)-1 horizontal paths where each path has a vertex ofN(y).
Lemma 9.Let(u,v)∈E(Gi). If i ∈{1,2r},then there are at leastdeg(u)+deg(v)-2horizontal paths where each path contains a vertex of N(u,v). Otherwise,if i ∈{2,3,...,2r-1},then there are at leastdeg(u)+deg(v)-4horizontal paths where each path contains a vertex of N(u,v).
Proof.Without loss of generality,leti=1.SinceXnis triangle-free,|N(u,v)∩V(Gi)|=deg(u)+deg(v)-4 and|N(u,v)∩V(Gi+1)|=2.Then,there are at least deg(u)+deg(v)-2 horizontal paths,and each path contains a vertex ofN(u,v).Similarly,ifi ∈{2,3,...,2r-1},we have|N(u,v)∩V(Gi)|=deg(u)+deg(v)-6 and |N(u,v)∩V(Gi-1)|=2 and|N(u,v)∩V(Gi+1)|=2.Therefore,there are at least deg(u)+deg(v)-4 horizontal paths,and each path contains a vertex ofN(u,v).
Lemma 10.Let x1,x2,x3,x4∈ V(L)where(x1,x2)∈E(Gi),(x3,x4)∈V(Gj)and i=j.There are at most four horizontal paths,and each path contains a vertex of N[x1,x2]and contains a vertex of N[x3,x4].
Proof.By the definition of gMCNs,there is at most one horizontal path which contains a vertex ofN[x1]and a vertex ofN[x3].And there is at most one horizontal path which contains a vertex ofN[x1] and a vertex ofN[x4].Similarly,there is at most one horizontal path which contains a vertex ofN[x2] and a vertex ofN[x3].And there is at most one horizontal path which contains a vertex ofN[x2]and a vertex ofN[x4].
Therefore,there are at most 4 horizontal paths where each path contains a vertex ofN[x1,x2],as well as a vertex ofN[x3,x4].
Furthermore,we introduce some theorems about gMCNs.
Theorem 1.Let F ?V(Xn)with n ≥3. Suppose that any vertex u ∈V(L)-F is disconnected from R-F. Then there exist at least δ(Xn)horizontal paths and each path contains a vertex of F,further denoted by|F|≥δ(Xn).
Proof.Without loss of generality,there are two scenarios.
Case 1.u ∈V(G1).
By the definition of gMCNs,u hasdeg(u)-1neighbors in V(G1)and has exactly one neighbor in V(G2)(see Figure 11). Since u is disconnected from R-F,then each horizontal path in subgraph P has at least one vertex in F.There aredeg(u)horizontal segments in P.Hence,|F|≥deg(u)≥δ(Xn).
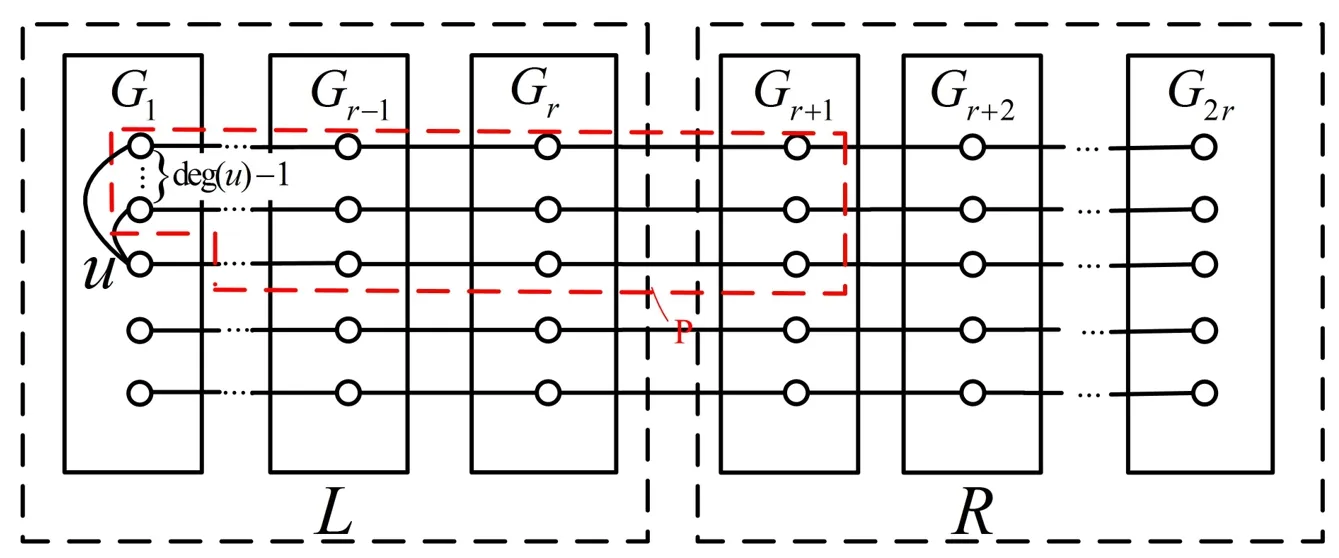
Figure 11.Illustration of case 1 in the proof of Theorem 1.
Case 2.u ∈V(Gi),2≤i ≤r.
By the definition of gMCNs,u hasdeg(u)-2neighbors in V(Gi),has exactly one neighbor in V(Gi-1),and has exactly one neighbor in V(Gi+1)(see Figure 12). Since u is disconnected from R-F,then each horizontal path in subgraph P has at least one vertex in F. There aredeg(u)-1horizontal segments in subgraph P.Hence,|F|≥deg(u)-1.

Figure 12.Illustration of case 2 in the proof of Theorem 1.
Case 2.1deg(u)≥δ(Xn)+1.
Since|F|≥deg(u)-1anddeg(u)≥δ(Xn)+1,|F|≥δ(Xn).
Case 2.2deg(u)=δ(Xn).
Let ui-1=N(u)∩V(Gi-1)and let the horizontal segment l be u1-u2-···-ui-1where uj ∈V(Gj)for1≤j ≤i-1(see Figure 12). If there is at least one vertex in l that belongs to F,then there are at leastdeg(u)horizontal segments where each segment contains a vertex of F. Therefore,|F|≥deg(u)≥δ(Xn). Otherwise,all vertices in l are not in F. Since u is disconnected from R-F,u1is also disconnected from R-F. Similar to that of Case 1,if u1is disconnected from R-F,there are at least δ(Xn)horizontal paths where each path contains a vertex of F. Then,|F|≥δ(Xn).
Theorem 2.k(Xn)=δ(Xn)for n ≥2.
Proof.Sincek(Xn)≤δ(Xn),we only need to prove thatk(Xn)≥δ(Xn).The result is proved by induction onn.SinceX2is a cycle of length 4,k(X2)=δ(X2)=2.Hence,the result holds forn=2.Suppose the result is true forn-1.Then,consider the case ofn.
LetFbe an arbitrary vertex subset ofXn,such that|F|≤δ(Xn) -1.IfXn-Fis connected,thenk(Xn)≥δ(Xn).The theorem follows.Otherwise,letFL=F ∩V(L)andFR=F ∩V(R).Since|F|≤δ(Xn)-1,we have|FL|≤δ(Xn)-2=δ(Xn-1)-1 or |FR|≤ δ(Xn) -2=δ(Xn-1) -1.Without loss of generality,assume that |FR|≤δ(Xn)-2=δ(Xn-1)-1.By the induction hypothesis,we havek(Xn-1)≥δ(Xn-1).Hence,R-F1is connected.By Theorem 1,if any vertex inL-F0is disconnected fromR-F1,then |F|≥δ(Xn) which contradicts|F|≤δ(Xn)-1.Therefore,L-F0is connected toR-F1.Xn-Fis connected.Then,k(Xn)≥δ(Xn).Sincek(Xn)≤δ(Xn),we havek(Xn)=δ(Xn).
Theorem 3.If edge(a,b)∈E(Xn),then N(a,b)is a super vertex-cut of Xn and|N(a,b)|≥k′(Xn)where n ≥2and δ(Xn)≥5.
Proof.Clearly,Xn-N(a,b)is disconnected.Letube an arbitrary vertex ofV(Xn)-N[a,b](see Figure 13).Sincecn(Xn)≤2,in the worst case,we have|N(u)∩N(a,b)|=4.Sinceδ(Xn)≥5,there exists at least one neighbor ofuwhich is not inN(a,b).Therefore,N(a,b) is a super vertex-cut ofXn.Then,we have|N(a,b)|≥k′(Xn).
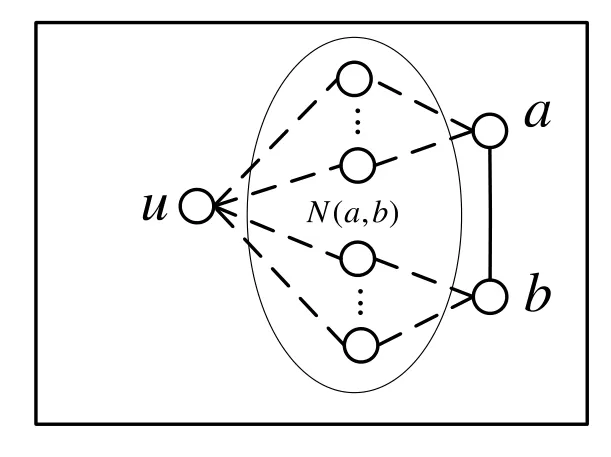
Figure 13.Illustration of Theorem 3.
Then,we have the following corollaries.
Corollary 1.Let x and y be two arbitrary vertices of Xn with n ≥2and δ(Xn)≥5. Then2δ(Xn)-2≥k′(Xn),and|N(x,y)|≥k′(Xn).
Proof.Let (a,b)∈E(Gr).By Lemma 7,deg(a)=deg(b)=δ(Xn).Then,we have |N(a,b)|=2δ(Xn)-2.Sincecn(Xn)≤2,|N(x,y)≥2δ(Xn)-2=|N(a,b)|.By Theorem 3,2δ(Xn) -2=|N(a,b)|≥k′(Xn).
Therefore,|N(x,y)|≥k′(Xn).
Theorem 4.Let F be an arbitrary vertex set of Xn where n ≥2and let a,b ∈V(L) -F such that(a,b)∈E(Gi)and1≤i ≤r.If edge(a,b)is disconnected from R-F,then there are at least2δ(Xn)-2horizontal paths where each path has at least one vertex in F,denoted by|F|≥2δ(Xn)-2.Proof.Consider the following two cases.
Case 1.(a,b)∈E(G1).
By Theorem 1 and Xn is triangle-free,there aredeg(a)+deg(b)-2horizontal paths where each path contains a vertex in N[a,b](see Figure 14(a)). Then,we havedeg(a)+deg(b)-2≥2δ(Xn)-2. If edge(a,b)is disconnected from R-F,then there exist at least2δ(Xn)-2horizontal paths in subgraph P where each horizontal path contains at least one vertex in F.Hence,|F|≥2δ(Xn)-2.
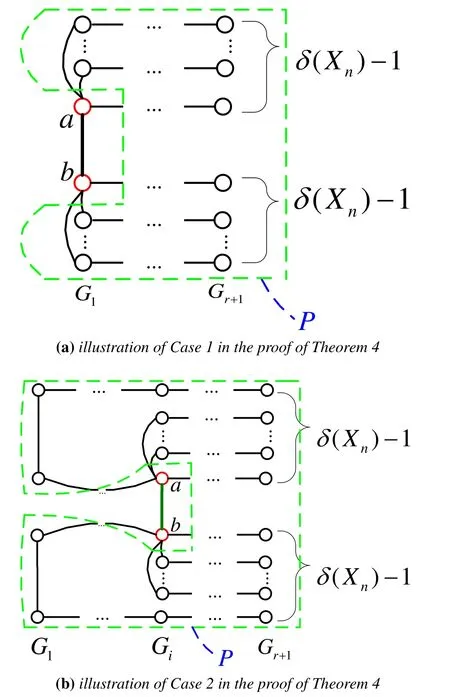
Figure 14.Illustration of Theorem 4.
Case 2.(a,b)∈E(Gi),2≤i ≤r.
By Theorem 1,if a is disconnected from R-F,then there are at least δ(Xn)horizontal paths where each path contains at least one vertex in F. Similarly,if b is disconnected from R-F,then there are at least δ(Xn)horizontal paths where each path contains at least one vertex in F. Since Xn is triangle-free and cn(Xn)≤2,if(a,b)is disconnected from R-F,then there are at least2δ(Xn)-2horizontal paths in subgraph P and each contains at least one vertex in F(see Figure 14(b)). Hence,|F|≥2δ(Xn)-2.
Corollary 2.Let F ? V(Xn)with n ≥2and δ(Xn)≥5. Let a,b ∈V(L)-F with(a,b)∈E(Gi)and1≤i ≤r. If edge(a,b)is disconnected from R-F,then there are at least k′(Xn-1)+2horizontal paths where each path has at least one vertex in F,further denoted by|F|≥k′(Xn-1)+2.
Proof.Theorem 4,if(a,b)is disconnected fromRF,there are at least 2δ(Xn)-2 horizontal paths where each path has at least one vertex inF.Then we have|F|≥2δ(Xn) -2.By the definition of gMCNs and Corollary 1,|F|≥2δ(Xn)-2=2δ(Xn-1)=k′(Xn-1)+2.
Theorem 5.Let F ?V(Xn)with δ(Xn)≥4. Let(a,b)∈E(Xn)where a,b ∈V(L)-F,a ∈V(Gi)and b ∈V(Gi+1)with1≤i ≤r-1. If edge(a,b)is disconnected from R-F,then|F|≥2δ(Xn)-2.
Proof.LetHbe the connected components ofXn-Fwherea,b ∈V(H).We complete the proof by considering the following two cases.
Case 1.There are two vertices x,y ∈V(H)where x,y ∈V(Gj)and1≤j ≤r.
By Theorem 4,|F|≥2δ(Xn)-2.
Case 2.There does not exist x,y ∈V(H)where x,y ∈V(Gj)and1≤j ≤r.
Then,H is a horizontal segment.
Case 2.1H is edge(a,b).
Then,we have N(a,b)? F. Hence,|F|≥|N(a,b)|≥|N(a)|+|N(b)|-2≥2δ(Xn)-2.
Case 2.2H is not edge(a,b).
Without loss of generality,let c ∈V(H)(see Figure 15).Then,N(a)∩V(Gi)?F,N(b)∩V(Gi+1)?F and N(c)∩V(Gi+2)?F.Since|N(a)∩V(Gi)|≥δ(Xn) -2,|N(b)∩V(Gi+1)|≥ δ(Xn) -2and|N(c)∩V(Gi+2)|≥ δ(Xn) -2,we have|F|≥3δ(Xn)-6.

Figure 15.Illustration of Theorem 5.
Since δ(Xn)≥4,|F|≥2δ(Xn)-2.
Theorem 6.k′(Xn)=2δ(Xn)-2for δ(Xn)≥6.Proof.By Corollary 1,we have 2δ(Xn)-2≥k′(Xn).If we can prove thatk′(Xn)≥2δ(Xn)-2,then the theorem holds.By contradiction,assume there is a super vertex cutFofXnwhere |F|≤2δ(Xn)-3.LetFL=F ∩V(L) andFR=F ∩V(R).Then,|FL|≤δ(Xn)-2 or|FR|≤δ(Xn)-2.
Without loss of generality,let|FR|≤δ(Xn)-2.By Theorem 2,we havek(R)=δ(Xn-1)=δ(Xn)-1.Hence,R-FRis connected.SinceFis a super vertex cut ofXn,Xn-Fis disconnected.Then,there is a vertexu ∈V(L) -FLwhereN(u)Fanduis disconnected fromR-FR.Letu ∈V(Gi) with 1≤i ≤r.We consider two cases.
Case 1.(N(u)-F)∩V(Gi)=?.
Let v ∈(N(u) -F)∩V(Gi). Since u is disconnected from R-FR,(u,v)is disconnected from R-FR. By Theorem 4,|F|≥2δ(Xn)-2,which contradicts with|F|≤2δ(Xn)-3.
Case 2.(N(u)-F)∩V(Gi)=?.
Since N(u)F,there exists a vertex v ∈N(u)-F,such that v ∈V(Gi±1). Since u is disconnected from R-FR,v ∈V(L).Hence,(u,v)is disconnected from R-FR. By Theorem 5,|F|≥2δ(Xn) -2,which contradicts with|F|≤2δ(Xn)-3. Therefore,there does not exist a super vertex cut F with|F|≤2δ(Xn) -3. Then,k′(Xn)≥2δ(Xn) -2. Since k′(Xn)≤2δ(Xn)-2,k′(Xn)=2δ(Xn)-2.
Theorem 7.Let F ?V(Xn)and δ(Xn)≥7. Suppose that every component of Xn-F is nontrivial and there exists a component H of Xn-F such that H ?V(L)(or H ?V(R))and|NH(x)|≥2for any vertex x ∈V(H). Then,|F|≥2k′(Xn-1).
Proof.Since |NH(x)|≥2 for anyx ∈V(H),there exists at least one cycle inH.We assume thatCHis the shortest cycle inH.SinceXnis triangle-free,|V(CH)|≥4.
Case 1.V(CH)?V(Gi),1≤i ≤r.
Case 1.1|V(CH)|=4.
Let CH be a-b-c-d-a(see Figure 16).By Theorem 4,if(a,b)is disconnected from R-F,there are at least2δ(Xn) -2horizontal paths,and each one of them contains at least one vertex in F. Similarly,if(c,d)is disconnected from R-F,there are at least2δ(Xn) -2horizontal paths,and each path contains at least one vertex in F. Since2δ(Xn)-2=2δ(Xn-1)=k′(Xn-1)+2,by removing the duplicated horizontal paths,if CH is disconnected from R-F,there exist at least2k′(Xn-1)horizontal paths in subgraph P(see Figure 16). Therefore,|F|≥2k′(Xn-1).

Figure 16.Case 1.1 of Theorem 7.
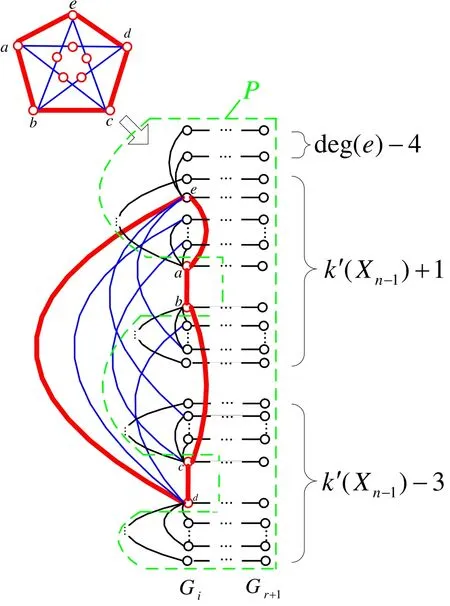
Figure 17.Case 1.2 of Theorem 7.
Case 1.2|CH|=5.
Let CH be a-b-c-d-e-a. By Corollary 2,if(a,b)is disconnected from R-F,then there are at least k′(Xn-1)+2horizontal paths where each has at least one vertex in F. Similarly,if(c,d)is disconnected from R-F,there exist at least k′(Xn-1)+2horizontal paths where each has at least one vertex in F. Since cn(Xn)≤2,if CH is disconnected from R-F,in the worst case,by removing the duplicated horizontal paths,subgraph S has at least2k′(Xn-1)+deg(e)-6horizontal segments(see Figure 17)where each segment has at least one vertex inF. Since δ(Xn)≥7,deg(e)≥δ(Xn)≥7. Then,|F|≥2k′(Xn-1)+deg(e)-6≥2k′(Xn-1).
Case 1.3|CH|≥6.
There exists a path a-b-c-d-e of CH where(a,e)/∈E(Xn). By Corollary 2,if(a,b)is disconnected from R-F,then there exist at least k′(Xn-1)+2horizontal paths where each has at least one vertex in F. Similarly,if(c,d)is disconnected from R-F,then there exist at least k′(Xn-1)+2horizontal paths where each has at least one vertex in F. Since cn(Xn)≤2,in the worst case,if the path a-b-c-d-e is disconnected from R-F,by removing the duplicated horizontal paths,the subgraph S has at least2k′(Xn-1)+deg(e) -7horizontal segments where each segment has at least one vertex in F(see Figure 18). Since δ(Xn)≥7,we havedeg(e)≥δ(Xn)≥7. Then,|F|≥2k′(Xn-1) +deg(e)-7≥2k′(Xn-1).
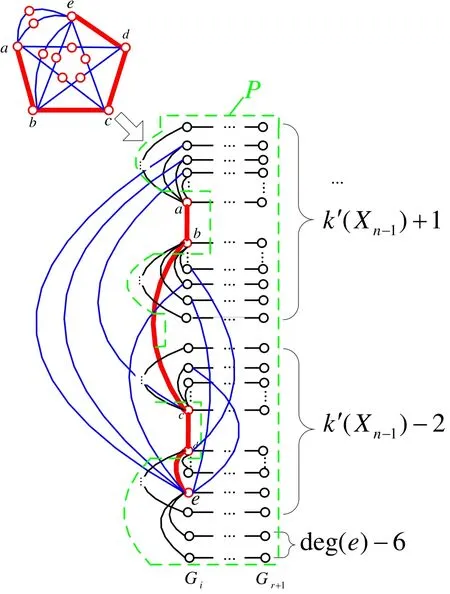
Figure 18.Case 1.3 of Theorem 7.
Case 2.V(CH)V(Gi).
Since CH is a cycle and CH V(Gi),there are(a,b)∈E(Gj)and(c,d)∈E(Gk)with j=k.By Corollary 2,if(a,b)is disconnected from R-F,then there exist at least k′(Xn-1)+2horizontal paths where each has at least one vertex in F. Similarly,if(c,d)is disconnected from R-F,then there exist at least k′(Xn-1)+2horizontal paths where each has at least one vertex in F. By Lemma 10,there are at most 4 horizontal paths where each path contains a vertex of N[a,b]and each passes through a vertex of N[c,d]. Therefore,if both(a,b)and(c,d)are disconnected from R-F,by removing the duplicated horizontal paths,there are at least2k′(Xn-1)horizontal paths and each has at least one vertex in F. Hence,|F|≥2k′(Xn-1).
Theorem 8.tc(Xn)≤2k′(Xn-1)+1for δ(Xn)≥6.Proof.By the definition of gMCNs,there exists a cyclea-b-c-d-a,such thata,b ∈ V(Gr)andc,d ∈V(Gr+1)(see Figure 19).We setF1=N(a,b,c,d)∪{a,b}andF2=N(a,b,c,d)∪{c,d}.Then,F1andF2are two distinct conditional fault sets ofXnand(F1,F2)is indistinguishable under the PMC model.By Theorem 3,|F1|=|F2|=|NL(a,b)|+|NR(c,d)|+2≥2k′(Xn-1)+2.Then,by Lemma 1,Xnis not conditionally(2k′(Xn-1)+2)-diagnosable.Therefore,tc(Xn)≤2k′(Xn-1)+1.

Figure 19.Illustration of Theorem 8.
Theorem 9.Let S ?V(Xn)with δ(Xn)≥6and k(Xn)≤|S|≤k′(Xn)-1.If Xn-S is disconnected,then Xn-S has exactly two components,one is trivialthe other is nontrivial.
Proof.Suppose thatXn-Shas at least two trivial components.Let{u}and{v}be two trivial components ofXn-S.Then,N(u)?SandN(v)?S.We have |S|≥|N(u,v)|.By Corollary 1,we have|S|≥|N(u,v)|≥ k′(Xn) which contradicts tok(Xn)≤|S|≤k′(Xn)-1.Therefore,Xn-Shas no more than one trivial component.Suppose thatXn-Sdoesn’t have any trivial component,thenSis a super vertex-cut ofXn.We have|S|≥k′(Xn),which contradicts tok(Xn)≤|S|≤k′(Xn)-1.Therefore,Xn-Shas exactly one trivial component.Let{u}be the trivial component ofXn-S.Without loss of generality,assume that{u}∈V(L).LetSL=S ∩V(L)andSR=S ∩V(R).
Since{u} ∈V(L),|SL|≥|NL(u)|≥δ(Xn-1)=δ(Xn)-1.By Corollary 1,k′(Xn)≤2δ(Xn)-2.Sincek(Xn)≤|S|≤k′(Xn)-1,we havek(Xn)≤|S|≤2δ(Xn)-3.Since|SL|≥δ(Xn)-1,|SR|=|S|-|SL|≤δ(Xn)-2.By Theorem 2,k(SR)=δ(Xn-1)=δ(Xn)-1.Hence,R-SRis connected.
For anyv ∈V(L) -SL-{u},since{u}is the unique trivial component ofXn-S,{v}is not a trivial component ofXn-S.ThenN(v).If(N(v) -S)∩V(R)=?,thenvis connected toR-SR.Otherwise,(N(v)-S)∩V(R)=?.There exists (v,w)∈E(L) withwSL.By Theorems 4 and 5,|S|≥2δ(Xn)-2=k′(Xn) which contradicts tok(Xn)≤|S|≤k′(Xn)-1.Therefore,vis connected toR-SR.L-SL-{u}is connected toR-SR.Then,Xn-Shas exactly two components,one is{u},and the other isXn-S-{u}.
Theorem 10.Let Xn be an n-dimensional gMCN with δ(Xn)≥7,|V(Xn-1)|≥3k′(Xn-1)-3and k′(Xn-1)≥3. Let S ?V(Xn)such that Xn-S is disconnected and each component of Xn-S is nontrivial. If there exists a component C of Xn-S such thatdegC(x)≥2for any vertex x in C,then one of the following conditions holds:
(1)|S|≥2k′(Xn-1).
(2)|V(C)|≥2k′(Xn-1)-1.
Proof.LetCL=C ∩V(L),CR=C ∩V(R),SL=S ∩V(L)andSR=S ∩V(R).Without loss of generality,there are two cases to consider.
Case 1.CL=?and CR=?.
SincedegC(x)≥2for any vertex x in C and each vertex in L has at most one neighbor in R(and vice versa),we have|CL|≥2and|CR|≥2. Since Xn-S is disconnected,without loss of generality,we consider the following two subcases.
Case 1.1L-SL is connected and R-SR is disconnected.
Since|CR|≥2and R-SR is disconnected,CR is a nontrivial components of R-SR. Let C′be another arbitrary nontrivial component of Xn-S besides C.Then,we have V(L)=SL ∪CL and V(C′)?V(R).Hence,C′is also a nontrivial components of R-SR.Since CR and C′are two nontrivial components of RSR,SR is a super vertex-cut of R. Therefore,|SR|≥k′(Xn-1).
If|SL|≥ k′(Xn-1),then|S|=|SL|+|SR|≥2k′(Xn-1). The condition(1)holds. Otherwise,|SL|≤k′(Xn-1)-1. Then|CL|=|V(Xn-1)|-|SL|≥|V(Xn-1)| -k′(Xn-1)+1. Since|V(Xn-1)|≥3k′(Xn-1) -3,|V(C)|=|V(CL)|+|V(CR)|≥(|V(Xn-1)| -k′(Xn-1)+1)+2≥2k′(Xn-1).Condition(2)holds.
Case 1.2L-SL is disconnected and R-SR is disconnected.
Case 1.2.1|SL|≥k′(Xn-1)and|SR|≥k′(Xn-1).
Then,|S|=|SL|+|SR|≥2k′(Xn-1). Condition(1)holds.
Case 1.2.2k(Xn-1)≤|SL|≤k′(Xn-1)-1and k(Xn-1)≤|SR|≤k′(Xn-1)-1.
By Theorem 9,L-SL has exactly 2 components,one is trivial the other is nontrivial. Hence,we have|V(CL)|≥|V(L)| -|SL| -1≥|V(Xn-1)| -k′(Xn-1)≥2k′(Xn-1) -3. Similarly,we have|V(CR)|≥|V(R)| -|SR| -1≥|V(Xn-1)| -k′(Xn-1)≥2k′(Xn-1) -3. Then,|V(C)|=|V(CL)|+|V(CR)|≥4k′(Xn-1) -6=2k′(Xn-1)-1+(2k′(Xn-1)-5).Since k′(Xn-1)≥3,|V(C)|≥2k′(Xn-1) -1. Therefore,condition(2)holds.
Case 1.2.3(|SL|≥ k′(Xn-1)and k(Xn-1)≤|SR|≤ k′(Xn-1) -1)or(k(Xn-1)≤|SL|≤k′(Xn-1)-1and|SR|≥k′(Xn-1)).
Without loss of generality,let|SL|≥k′(Xn-1)and k(Xn-1)≤|SR|≤k′(Xn-1)-1. By Theorem 9,RSR has exactly two components,one is trivial the other is nontrivial. Then,|V(CR)|=|V(R)|-|SR|-1≥|V(Xn-1)|-k′(Xn-1)≥2k′(Xn-1)-3. Since|CL|≥2,|V(C)|=|V(CL)|+|V(CR)|≥2+2k′(Xn-1)-3≥2k′(Xn-1)-1. Condition(2)holds.
Case 2.CL=?and CR=?
By Theorem 7,|S|≥2k′(Xn-1). Conditional(1)holds.
Theorem 11.Let F0and F1be two arbitrary indistinguishable conditional fault sets of Xn where δ(Xn)≥7,|V(Xn-1)|≥3k′(Xn-1) -3and k′(Xn-1)≥6. Then,either|F0|≥2k′(Xn-1)+2or|F1|≥2k′(Xn-1)+2.
Proof.We consider two cases.
Case 1.Xn-(F0∩F1)is connected.
Since|V(Xn-1)|≥3k′(Xn-1) -3,|V(Xn)|=2|V(Xn-1)|≥6k′(Xn-1)-6≥4k′(Xn-1)+4+(2k′(Xn-1)-10)>4k′(Xn-1)+4. By Lemma 2,F0ΔF1is disconnected from V(G)-(F0∪F1). Since V(Xn)-(F0∩F1)is connected,V(G)-(F0∪F1)=?. Then,we have F0ΔF1=V(Xn)-(F0∩F1)and V(Xn)=(F0∪F1). If|F0|≤2k′(Xn-1)+2 and|F1|≤2k′(Xn-1)+2,then|V(Xn)|=|F0|+|F1|-|F0∩F1|≤|F0|+|F1|≤4k′(Xn-1)+4which contradicts to|V(Xn)|>4k′(Xn)+4. Therefore,either|F0|≥2k′(Xn-1)+2or|F1|≥2k′(Xn-1)+2.
Case 2.Xn-(F0∩F1)is disconnected.
By Lemmas 1 and 3,each vertex of V(Xn)-(F0∪F1)has at least one neighbor in V(Xn)-(F0∪F1)and each vertex in F0ΔF1has at least one neighbor in F0and has at least one neighbor in F1. Therefore,every component of Xn-(F0∩F1)is nontrivial and there exists a component C of Xn-(F0∩F1)in F0ΔF1where NC(x)≥2for any vertex x ∈C. Hence,F0∩F1is a super vertex-cut of Xn. By Theorem 10,either|F0∩F1|≥2k′(Xn-1)or|V(C)|≥2k′(Xn-1)-1.
Case 2.1|F0∩F1|≥2k′(Xn-1).
Since NC(x)≥2for any x ∈C and Xn is trianglefree,|V(C)|≥4. Therefore,either|F0-F1|≥|V(C)|/2≥2or|F1-F0|≥|V(C)|/2≥2. Then,either|F0|=|F0-F1|+|F0∩F1|≥2k′(Xn-1)+2or|F1|=|F1-F0|+|F0∩F1|≥2k′(Xn-1)+2.
Case 2.2|V(C)|≥2k′(Xn-1)-1
Either|F0-F1|≥|V(C)|/2≥k′(Xn-1)or|F1-F0|≥|V(C)|/2≥k′(Xn-1). Since F0∩F1is a super vertex-cut of Xn,we have|F0∩F1|≥k′(Xn). By Theorem 6,|F0∩F1|≥k′(Xn)=2δ(Xn) -2=2δ(Xn-1)≥k′(Xn-1)+2. Therefore,either|F0|=|F0-F1|+|F0∩F1|≥2k′(Xn-1)+2or|F1|=|F1-F0|+|F0∩F1|≥2k′(Xn-1)+2.
Theorem 12.If|V(Xn)|≥3k′(Xn)-3,k′(Xn-1)≥6and δ(Xn)≥7,then tc(Xn)=2k′(Xn-1)+1.
Proof.By Theorem 11 and Lemma 1,we havetc(Xn)≥2k′(Xn-1)+1.By Theorem 8,tc(Xn)≤2k′(Xn-1)+1.
Therefore,tc(Xn)=2k′(Xn-1)+1.
By Theorem 12,we can directly obtain the conditional diagnosability of gMCNs under the PMC model by their known super connectivity.Then,we summarize all the results in Table 1.

Table 1.Conditional diagnosability of gMCNs.
IV.CONCLUSION
Connectivity and diagnosability are two important measures for assessing the reliability of interconnected networks,and they are closely related to each other.In this paper,we discussed the relationship between super connectivity and conditional diagnosability for a new family of interconnection networks,called general matching composed network,within the framework of the PMC model.With this newly discovered relationship,we can obtain the conditional diagnosability for a family of well-known networks.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.62362005).
ABBREVIATIONS AND ACRONYMS
gMCNs: General Matching Composed Networks.
PMC model: Preparata,Metze and Chien model.
NOTATIONS
G(V,E): A multi-processor system.
V(G): The vertex set ofG.
deg(u): The degree of vertexuinG.
N(x): The neighbors of vertexx.
N(S):All the neighbors of vertices inS(except any vertices inS).
NS(x):N(x)∩S.
σ(G): A collection of all test results ofG.
cn(x,y): The number of common neighbors ofxandy.
k(G): The vertex connectivity ofG.
k′(G): The super connectivityG.
t(G): The diagnosability ofG.
tc(G): The conditional diagnosability ofG.
F1ΔF2: (F1-F2)∪(F2-F1).
- China Communications的其它文章
- An Efficient Approach to Escalate the Speed of Training Convolution Neural Networks
- Cooperative User-Scheduling and Resource Allocation Optimization for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Enhanced LEO Satellite Communication
- Flight Time Minimization of UAV for Cooperative Data Collection in Probabilistic LoS Channel
- Joint Optimization of Resource Allocation and Trajectory Based on User Trajectory for UAV-Assisted Backscatter Communication System
- Cooperative Anti-Jamming and Interference Mitigation for UAV Networks: A Local Altruistic Game Approach
- A Novel Multi-Stream Fusion Network for Underwater Image Enhancement

