Fractions of Compact Object Binaries in Star Clusters: Theoretical Predictions
Zhong-Mu Li ,Bhusan Kayastha ,Albrecht Kamlah ,Peter Berczik ,Yang-Yang Deng,3,8 ,and Rainer Spurzem,9
1Institute for Astronomy,Dali University,Dali 671003,China;zhongmuli@126.com
2 National Astronomical Observatories &Key Laboratory of Computational Astrophysics,Chinese Academy of Sciences NAOC/CAS,Beijing 100101,China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
4 Zentrum für Astronomie—Astronomisches Rechen-Institut,M?nchhofstr.12-14,Heidelberg D-69120,Germany
5 Max-Planck-Institut fr Astronomie,K?nigstuhl 17,D-69117 Heidelberg,Germany
6 Main Astronomical Observatory,National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine,27 Akademika Zabolotnoho St.,03143,Kyiv,Ukraine
7 Konkoly Observatory,Research Centre for Astronomy and Earth Sciences,E?tv?s Loránd Research Network(ELKH),MTA Centre of Excellence,Konkoly Thege Miklós út 15-17,1121 Budapest,Hungary
8 Yunnan Observatories,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Kunming 650216,China
9 Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics,Peking University,Beijing 100871,China
Abstract The binary population in field stars and star clusters contributes to the formation of gravitational wave (GW)sources.However,the fraction of compact-object binaries(CBs),which is an important feature parameter of binary populations,is still difficult to measure and very uncertain.This paper predicts the fractions of important CBs and semi-compact object binaries (SCBs) making use of an advanced stellar population synthesis technique.A comparison with the result of N-body simulation is also presented.It is found that most CBs are formed within about 500 Myr after the starburst.The fractions of CBs and SCBs are demonstrated to correlate with stellar metallicity.The higher the metallicity becomes,the smaller the fraction of black hole binaries(BHBs),neutron star binaries (NSBs) and SCBs.This suggests that the GW sources of BHBs and NSBs are more likely to form in metal-poor environments.However,the fraction of black hole-neutron star binaries is shown to be larger for metalrich populations on average.
Key words: (stars:) binaries: visual–gravitational waves–(Galaxy:) globular clusters: general–methods:numerical
1.Introduction
Binary stars and their properties are central in a number of astrophysical studies.For example,the sources of progenitors of some type I supernovae are thought to be binary stars (Whelan &Iben 1973;Nomoto et al.1995).Furthermore,on the observational side,binary stars have significant effects on the determination of stellar age and star formation histories of star clusters and galaxies (Han et al.2007;Li &Han 2008;Li et al.2013b,2016).Populations of binary stars are also important in gravitational wave (GW)source studies (Blanchet 2014;Abbott et al.2016,2017;Wysocki et al.2018),and stellar population studies (Zhang et al.2004;Li &Han 2008).From the former we know that tight compact-object binaries (CBs) are sources of GWs that have been detected up to date (see e.g.,Abbott et al.2019).Note that both of the two members of each CB cannot be observed in the optical band.Thus it is of statistical importance to constrain the compact binary fraction with population synthesis (e.g.,Breivik et al.2020b) andN-body simulations (e.g.,Kamlah et al.2022).
In general,binary populations,which we observe today,have undergone significant dynamical interaction with surrounding gas and other stars from birth until the time of observation.However,some works did not consider the combination of binary stellar population synthesis andN-body simulations (e.g.,Fregeau et al.2009;Li et al.2013b),which has been widely used for studying the formation of GW sources in star clusters(e.g.,Di Carlo et al.2019,2020a,2020b,2021;Rizzuto et al.2021).This makes it difficult to have a complete image of the binary population features.In particular,the poor understanding impedes an accurate study of such objects and many related targets (e.g.,GW sources).
The fractions of normal binary populations,which have at least one member that can be observed in the optical band,can be estimated from the observations of,e.g.,fractions of pulsars and X-ray binaries,or the spectra or color–magnitude diagrams(see the review of Kalogera et al.2007;Sana et al.2008;Abadie et al.2010;Hu et al.2010;Li et al.2013a).However,such methods can only work for a handful of star clusters and galaxies,and are generally not useful for studying the fraction of CBs.Therefore,we need more methods to estimate the fractions of binary populations.A useful way is the evolution of fraction of binary populations based on some well-known inputs,and then determining the binary fractions from the age of stellar systems.Some researches were done in this way and different trends for the evolution of binary fraction have been revealed(Ivanova et al.2005;Hurley et al.2007;Sollima 2008;Fregeau et al.2009;Li &Mao 2018).In the studies of normal binary stars,the binary fraction seems to decrease with time in stellar evolution (Ivanova et al.2005;Li &Mao 2018),but increases with time in dynamical evolution(Hurley et al.2007;Fregeau et al.2009) when implementing one of the two processes.The reason is that compact objects such as black holes (BHs)and neutron stars (NSs)cannot be observed in the optical band and new binaries can form when stars are moving toward the mass center of a stellar system.The case for CBs is very complicated because CBs can evolve from not only massive binary stars but also dynamical processes.Binary fractions also depend on rotation of the star cluster and the general tidal field.Therefore,the techniques of stellar population synthesis andN-body simulation are usually used to study the fraction of CBs.
There have been a number of evolutionary population synthesis andN-body simulation studies on CBs.For example,Eldridge&Stanway(2016)calculated the rates,timescales and mass distributions for black hole binary (BHB) mergers as a function of metallicity,using the Binary Population and Spectral Synthesis (BPASS)code (Eldridge &Stanway 2016).They found that BHB mergers are rare for initial metallicity aboveZ=0.010.Giacobbo &Mapelli (2018) used an upgraded version of BSE (Hurley et al.2002),MOBSE(Giacobbo&Mapelli 2018),to study the effects of metallicity,mass loss,core-collapse supernovae and common envelope on merging BHBs.They found that most merging BHBs have gone through a common envelope phase.Kruckow et al.(2018)performed a binary population synthesis at different metallicities using a grid-based binary population synthesis code,ComBinE (Kruckow et al.2018).They demonstrated that all the BHB mergers,GW150914,LVT151012,GW151226,GW170104,GW170608 and GW170814,as well as the neutron star binary(NSB)merger GW170817,were accounted for in their models.Di Carlo et al.(2019) investigated the possibility that BHs with mass in the pair instability gap form via stellar mergers and multiple stellar mergers facilitated by dynamical encounters in young star clusters.They took the directN-body code NBODY6++GPU coupled with MOBSE to find that up to 5%of all simulated BHs have mass in the pair instability gap,depending on the progenitor’s metallicity.Spera et al.(2019)investigated the statistics of BHBs that form from isolated binaries,by the upgraded SEVN population synthesis code,in which the mass-transfer prescription described in Hurley et al.(2002) has been updated.They found that the mass distribution of BHs which are members of CBs is quite similar to the one obtained considering only single stellar evolution calculations.Di Carlo et al.(2019) performed NBODY6++GPU simulations of young star clusters withZ=0.002,using a population-synthesis approach based on the MOBSE code,and found that cluster dynamics do not affect the merger rate significantly,but they change the properties of merging BHBs.More than 50% of merging BHBs in young clusters formed by dynamical exchanges in the first few Myr.Kumamoto et al.(2019)studied the formation rate of BHBs in stellar clusters using NBODY6++GPU with an updated mass loss model of Belczynski et al.(2010) and concluded that the contribution of BHBs originating from open clusters is not negligible.
However,no work compares the fraction of CBs in populations with different metallicities and compares the results with dynamical simulations in detail.Aiming to clarify the evolution of fractions of CBs in globular clusters,this work presents and compares the results from stellar population synthesis andN-body simulation.The structure of this paper is as follows: the model inputs and calculations are described in Section 2.The main results are presented in Section 3.Section 4 provides a comparison between advanced stellar population synthesis (ASPS) andN-body simulation.Finally,Section 5 concludes and discusses future aspects of this research.
2.Model Inputs and Calculations
This work models a stellar population with 100,000 objects.The star sample is similar to small clusters.We generate the initial cluster model with McLuster (Küpper et al.2011).An initial mass function (IMF) of Kroupa (2001) is taken to generate the masses of stars,and the lower and upper mass limits are set to 0.08 and 100M⊙,respectively.We use a primordial hard binary fraction of 10%,which corresponds to 8180 binaries with orbital periods shorter than 108days within 100,000 stars.This is a physical choice,because most soft binaries will be disrupted in a few dynamical timescales in dense stellar environments.Thus the initial binary fraction does not affect the global dynamics andN-body simulation results very much,and it does not affect the results of evolutionary population synthesis.In fact,there are different choices for binary fraction (e.g.,Kroupa 1995a;Sana et al.2012 and Moe&Di Stefano 2017) but the fraction of hard binaries is not different by a lot.From the work of Marks et al.(2011),we can safely assume that most binaries are already disrupted in 5 Myr if we assume a period distribution by Kroupa (1995a,1995b).Figure 1 shows the mass distribution of components of initial binaries.The separations of binary stars are generated according to a simple distribution,which is flat in the logarithm of semimajor axis (a) from 0.005 to 50 au.The square of eccentricities (e2) of pairs follows a uniform distribution(thermal distribution),but it is restricted by the eigen-evolution according to Kroupa (1995b),such that highly eccentric binaries,if the stars overlap at the pericenter,are omitted.The results can be used for estimating the formation and merger rates of various CBs,combining with the models of cosmology and star formation rate.After building the star sample,we evolve the stellar population using the ASPS model (Li et al.2012,2016).An upgraded version of the rapid stellar evolution code of Hurley et al.(2002),i.e.,MOBSE (Giacobbo et al.2018;Giacobbo &Mapelli 2018),is used to calculate the evolutionary parameters of stars,because this code includes advanced prescriptions for mass loss by stellar winds and a formalism for core-collapse,electron-capture and pair instability supernovae.CE parameters of α=1.0 and λ=0.5,Reimers mass loss rates η=0.5,momentum-conserving kick of Belczynski et al.(2008)and compact remnant mass description by Fryer et al.(2012) are incorporated in our simulations.In order to check the evolution of CB fraction in a large age range,an age step of 100 Myr is set for the ASPS simulation.
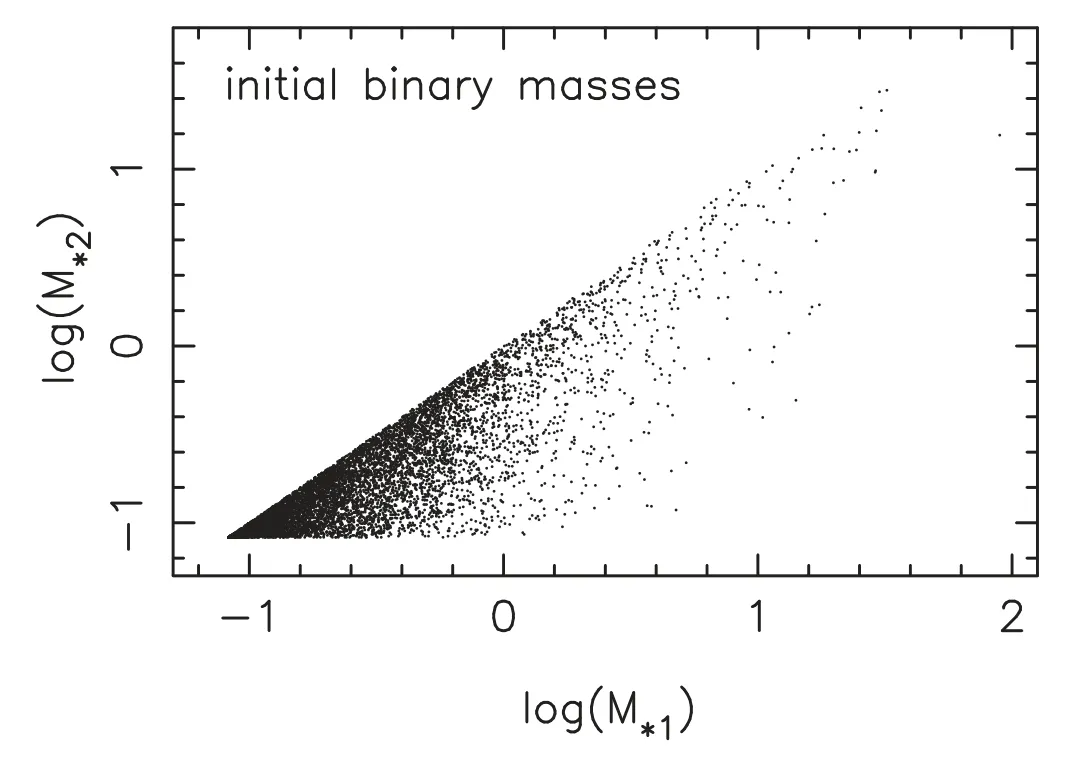
Figure 1.Initial masses of binaries in a mimic star cluster.M*1 and M*2 are for the masses of the primary and secondary,respectively.Masses are in solar mass.
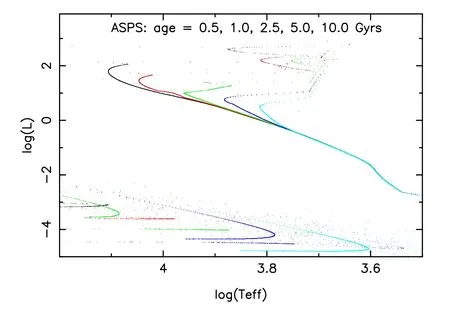
Figure 2.Some normal stars in the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram.Stars have the same metallicity (Z=0.000 51) but different ages.Effective temperature (Teff) is in K and luminosity (L) is in solar luminosity.
3.Results of ASPS Simulation
Stars excluding BHs and NSs are treated as normal stars(see Figure 2 for examples),and they can be observed in the optical band.Because normal stars are not as important as BHs and NSs in present GW observational studies(Breivik et al.2020a),they are not studied in this paper.Therefore,the compact objects in this paper ignore a well-known compact object,a white dwarf (WD),which has been included in normal stars.Figures 3–7 depict the evolution of fraction of CBs in the ASPS simulation and the fractions of different kinds of binaries at 10 Gyr are presented in Table 1.Because tight CBs are important GW sources,these results are useful for many GW studies.Note that these results are computed from an initial hard binary fraction of 10%.If all stars are hard binaries,the results will be 10 times the values shown here.Figure 3 displays the evolution of fraction of BHBs,which is a kind of important GW source candidate.It is clear that the fraction of BHBs increases steeply in the first 0.5 Gyr and then it remains almost the same for the ASPS simulation after that time.The reason is that a time step of 0.5 Gyr was taken here and most single stars and binaries form BHs within about 0.2 Gyr.The fraction of BHBs is obviously larger in metal-poor(Z≤0.004)populations.The BHB fraction of metal-rich populations is less than half that of metal-poor populations,because of the metallicity-dependent stellar wind.The results imply that only a few BHBs can be observed in a cluster of 100,000 stars.Figure 4 plots the evolution of fraction of another important GW source candidate,NSB.We see that the fraction of NSBs has a similar trend as that of BHBs.This suggests that the BHB and NSB systems including potential GW sources are more likely to form in metal-poor environments.
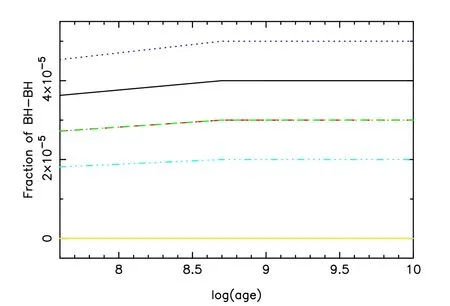
Figure 3.Evolution of fraction of BHBs with various metallicities.Different lines signify metallicities.Age is in yr.Black,red,green,blue,cyan,purple and yellow lines are for Z=0.0001,0.0003,0.001,0.004,0.01,0.02 and 0.03,respectively.
Figure 4.Similar to Figure 3,but for the fraction of NSBs.
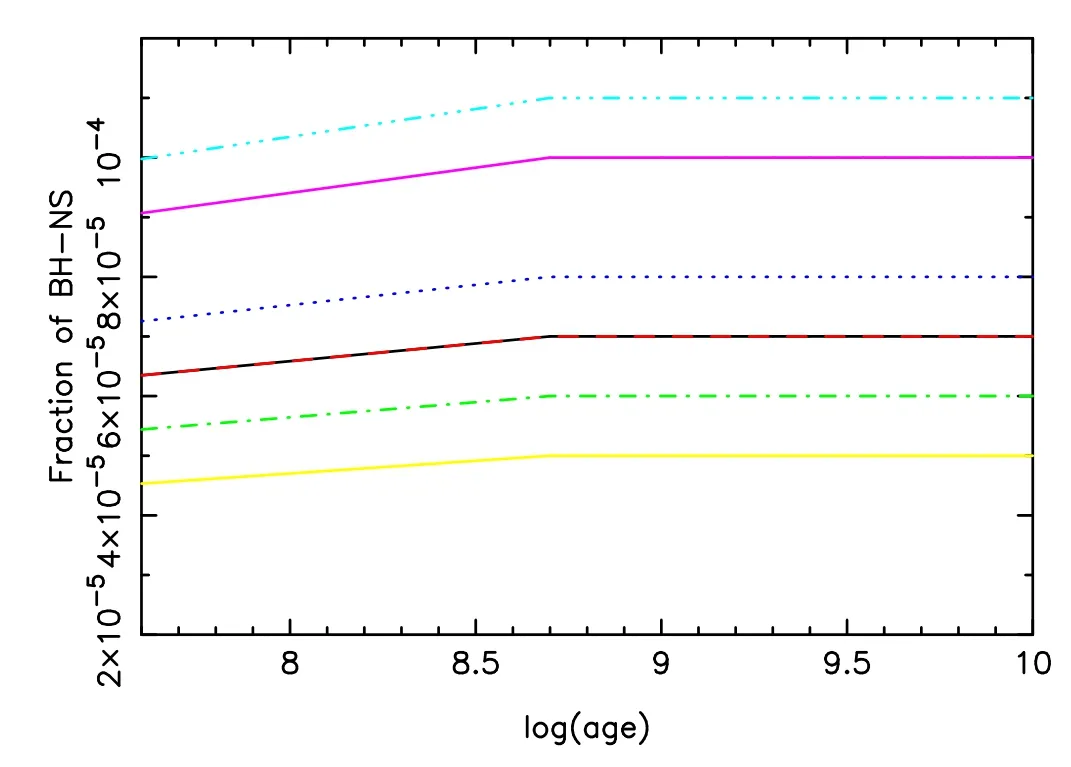
Figure 5.Similar to Figure 3,but for the fraction of BH-NS binaries.
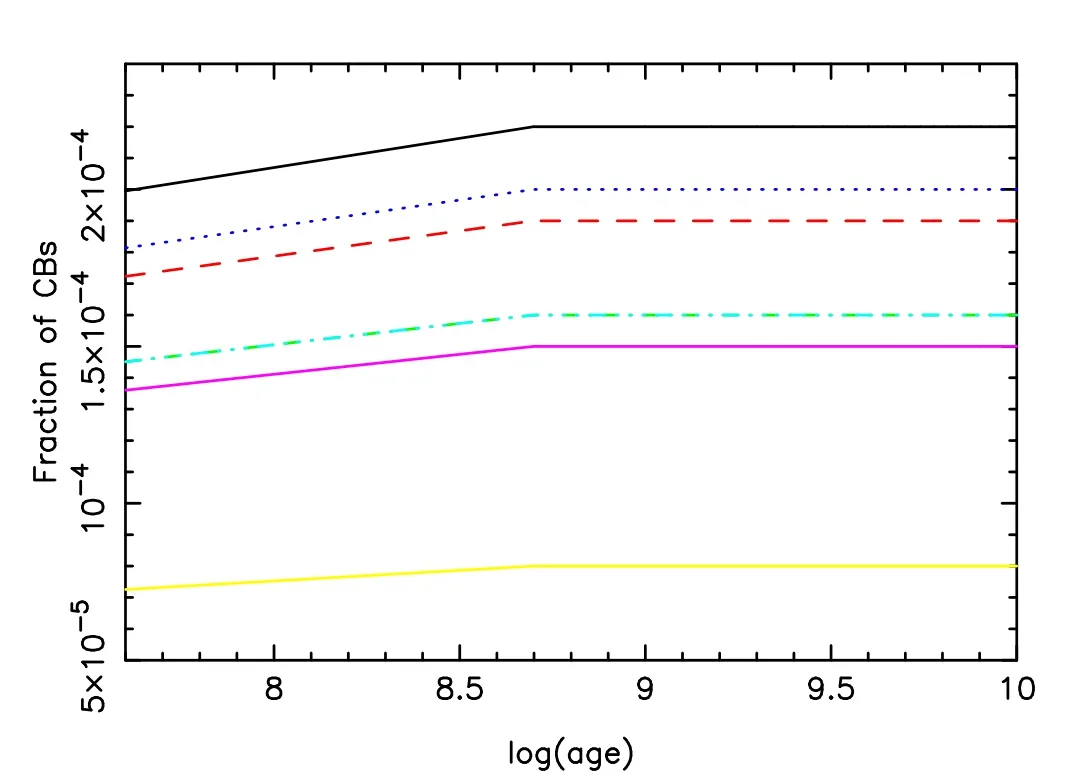
Figure 6.Evolution of fraction of CBs.Each CB consists of two BH or NS objects.Lines have the same meaning as in Figure 3.
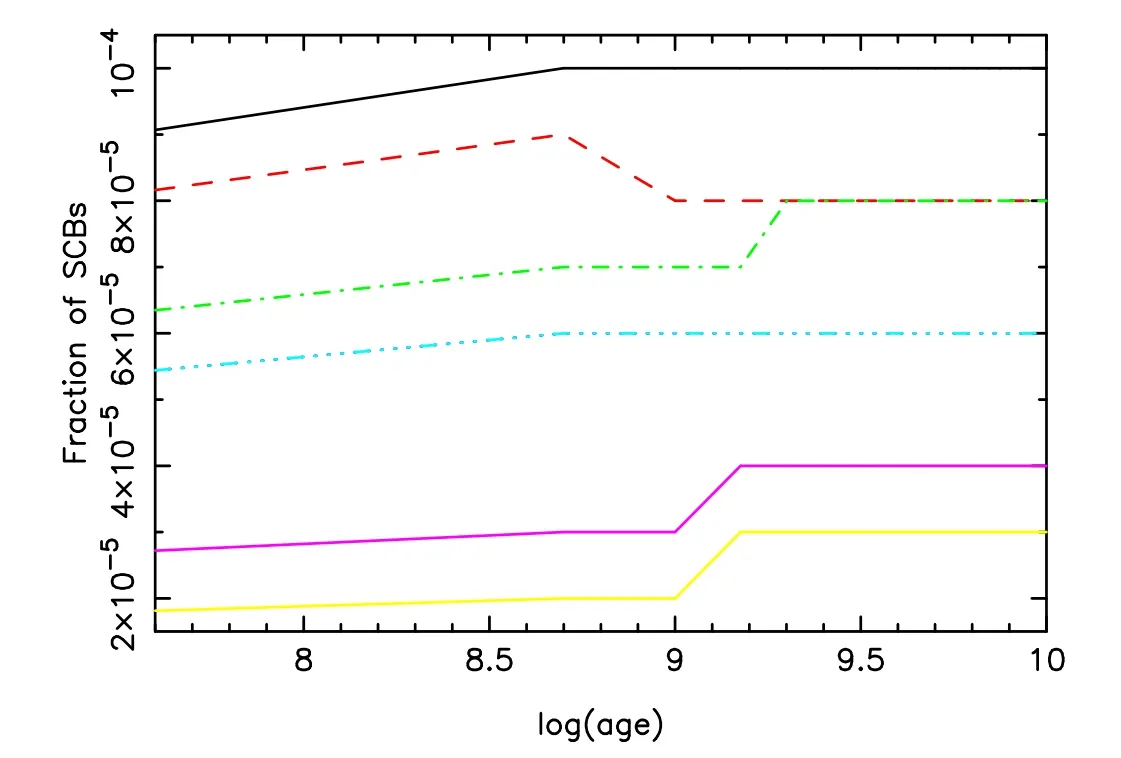
Figure 7.Evolution of fraction of SCBs.Each SCB consists of a BH or NS,and a normal star.Lines have the same meaning as in Figure 3.

Table 1 Fractions of Different Kinds of Binaries at 10 Gyr in ASPS Simulation
Figure 5 shows the evolution of fraction of BH-NSs.We observe that the fraction of BH-NSs increases quickly with time when age is younger than 0.5 Gyr and it remains unchanged after that,for all metallicities.Metallicity affects the fraction of BH-NSs in a way different from the case of BHBs and NSBs.In detail,the fraction of BH-NSs is highest when metallicityZis 0.01 and 0.02,but the fraction is the lowest forZ=0.03.The BH-NS fraction is medium for poorer metallicities.Note that we exclude ultra-stripping in binary stars (e.g.,Kamlah et al.2022),which supposedly greatly decreases the expected BHB and NS-BH merger rates and only slightly increases the expected NS-NS merger rate (Schneider et al.2021).
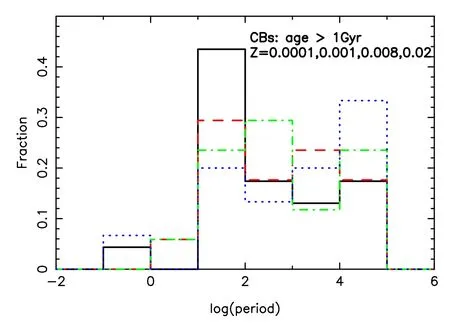
Figure 8.Period distribution of CBs at ages older than 1 Gyr.Period is in days.Black solid,red dashed,green dash–dotted and blue dotted lines are for Z=0.0001,0.001,0.008 and 0.02,respectively.
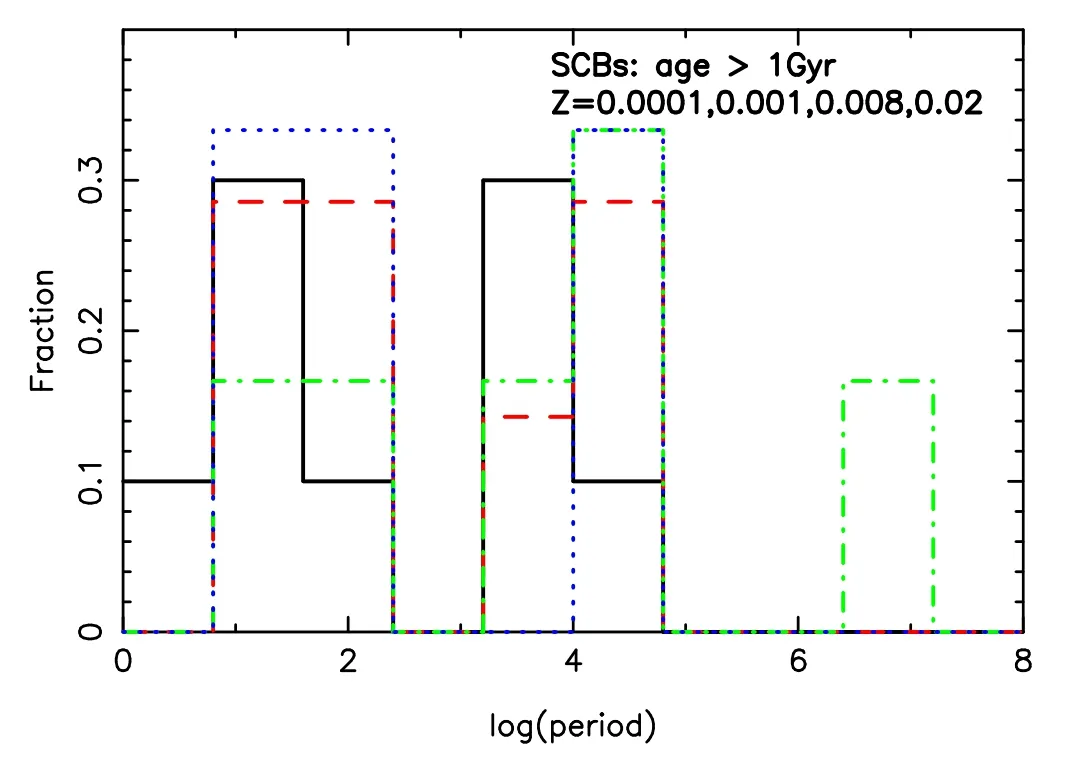
Figure 9.Similar to Figure 8,but for SCBs.
Figure 6 features the evolution of fraction of CBs.BHBs,NSBs and BH-NSs are counted in CBs here.We see that CB fraction increases with age in the first 0.5 Gyr and metal-poor(Z≤0.004) stellar populations have higher CB fractions.
Figure 7 depicts the evolution of fraction of semi-compact object binaries (SCBs).Note that besides a BH or NS,each SCB contains a normal star.We have shown that the fraction of SCBs changes from 0 to 2 Gyr,and then it does not change.It is clear that metal-poor (Z≤0.001) populations have higher SCB fractions compared to their metal-rich counterparts.Although the fraction of SCBs changes when age is younger than 2 Gyr for all metallicities,the trend is different for various metallicities.
Figures 8 and 9 present the period distributions of CBs and SCBs respectively.The results are for ages older than 1 Gyr.We observe that a small fraction of CBs has periods shorter than 1 day,which may be detected by Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) (see e.g.,Shao &Li 2021).This means that a few of them can possibly be observed by LISA,according to the work of Lamberts et al.(2018).It is also clear that SCBs are distributed more widely than CBs.A few SCBs have periods longer than a million days.Figures 10–12 show the mass distributions of CBs and SCBs;as a whole,the larger the total mass,the less the number of CBs (Figure 10).The fraction of SCBs peaks at about 3.16M⊙at 1 Gyr,but some lighter ones are generated at 6 Gyr (Figures 11 and 12).When we count the number of X-ray binaries after 0.5 Gyr,the results forZ=0.00001,0.0003,0.001,0.004,0.008,0.01,0.02 and 0.03 are 10,8,8,6,6,6,4 and 3,respectively.These results can possibly be compared to some observations.
Because this work adopts a default value of λ=0.5,but most other works take values of 0.01–0.1,we test the effect of λ.The results show that similar results of CBs will be obtained if λ=0.05 is applied.However,the results of SCBs for metallicities ofZ=0.0003,0.001,0.02 and 0.03 are different.Figures 13 and 14 feature the results of λ=0.05.
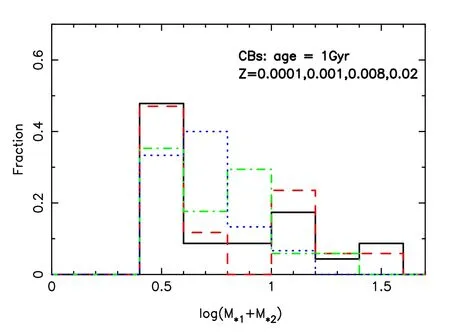
Figure 10.Mass distribution of CBs at 1 Gyr.M*1 and M*2 are masses of the primary and secondary components of a binary respectively.The case of older ages is similar.
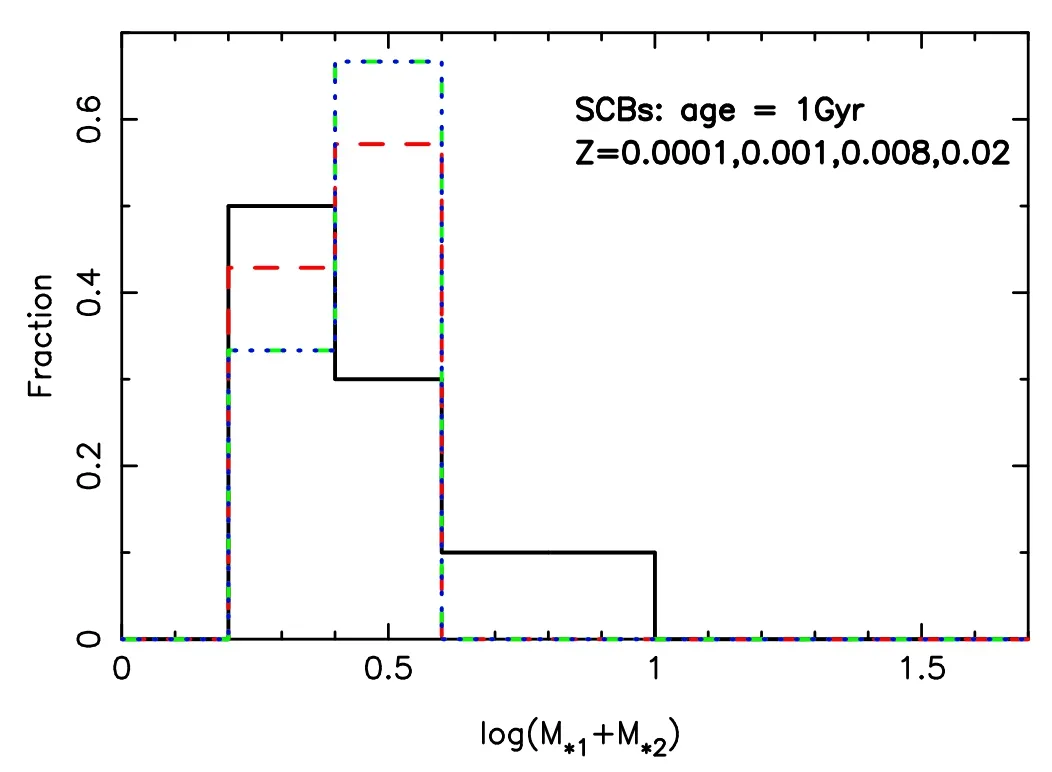
Figure 11.Similar to Figure 10,but for SCBs.The case of 1–6 Gyr is similar.
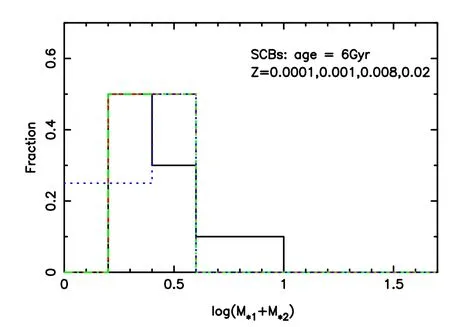
Figure 12.Similar to Figure 11,but for the case of 6 Gyr.The case of older ages is similar.
4.Comparison of ASPS and N-body Simulations
As the ASPS simulation does not take into account the dynamical processes as well as the internal evolution of binary stars which affect the formation of CBs,this section tests the effect ofN-body dynamical processes.In this test,the star sample is generated by the same method as the above ASPS simulation,and metallicities ofZ=0.001 and 0.00051 are taken.An updated version of NBODY6++GPU code(Spurzem 1999;Wang et al.2016) is utilized for theN-body simulation.This code enables calculating large stellar systems with more than one million particles as it implements a GPU parallel calculation technique.The code has included different dynamical processes,and it was widely employed in astrophysical studies (e.g.,Hong et al.2017 &Rodriguez et al.2016).
Figure 15 shows the evolution of fractions of BHBs in theNbody simulation.We observe that the BHB fraction of theNbody simulation is similar to that of the ASPS simulation,although there is a small difference.Because there is large fluctuation in the fraction of BHBs in theN-body simulation,the average value of nine simulations is calculated to test the random uncertainties.The average result is plotted by the solid line in Figure 15 together with the root mean square (r.m.s.)standard deviations.The star samples of nine simulations are generated by the same method,but taking different random seeds to generate the initial positions,velocities,stellar masses,binary separations and orbital eccentricities.We see that although the average fraction of nine simulations is taken,there is still obvious fluctuation.However,the fluctuation in the average fraction is much less than any one of the nine simulations.The fluctuation decreases with increasing number of simulations.This suggests that the main fluctuation is possibly caused by random uncertainties in theN-body simulation.Thereby,the evolution of BHB fraction has a similar trend in theN-body and ASPS simulations(see the cyan line in Figure 3).
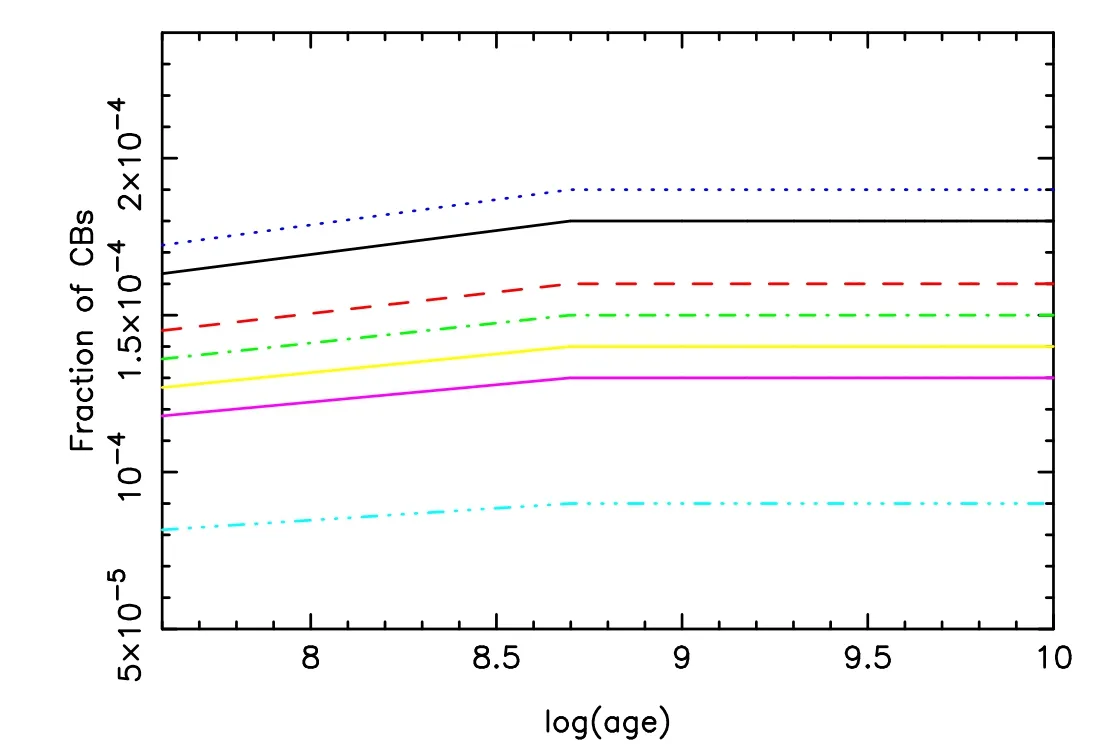
Figure 13.Similar to Figure 6,but for the case of λ=0.05.
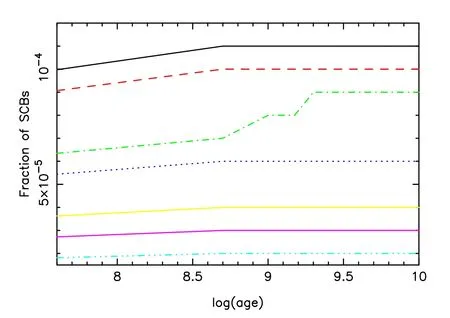
Figure 14.Similar to Figure 7,but for the case of λ=0.05.
When comparing the fractions of SCBs in the ASPS andNbody simulations,the results seem similar.In the first 1 Gyr,the fraction increases quickly then it changes slightly.One can see Figure 16 for the detailed comparison.Note that the compact objects in SCBs include only BHs and NSs,rather than WDs.The SCBs in this paper are actually part of X-ray binaries.

Figure 15.Evolution of average fraction of BHBs from nine N-body simulations and the associated r.m.s.standard deviation.Age is in yr.A metallicity of Z=0.001,star number of 100,000 and hard binary fraction of 10% are taken for the simulation.Solid line signifies the average fraction and dashed lines mean the r.m.s.
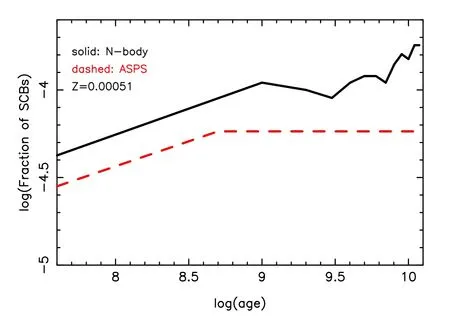
Figure 16.Evolution of SCB fraction for a pair of N-body and ASPS simulations.Age is in yr.A metallicity of Z=0.000 51,star number of 100,000 and hard binary fraction of 10% are taken.
5.Conclusion and Discussion
We investigated the evolution of fractions of compact object binaries in star clusters,via ASPS andN-body simulations.As a result,two kinds of simulations reveal similar results for the evolution of fraction of CBs and SCBs.This is the first work to demonstrate the evolution of fraction of SCBs with the two methods.Our results are more comprehensive than previous studies,e.g.,Giacobbo &Mapelli (2018),because seven metallicities rather than one are examined by this work.The results are also shown to be different.The fraction of BHBs does not decrease with increasing metallicity in this work,and it is different from the monotonic decline trend of the previous work.The combined effects of dynamics and stellar evolution seem very complicated and the previous results of,e.g.,Di Carlo et al.(2019),should be confirmed from different works.In addition,theN-body simulations result in lower fractions of CBs than stellar population synthesis.This means that the effect of dynamics remains very uncertain,which may depend on the model inputs.
As a whole,the results of this work suggest that evolutionary population synthesis such as ASPS can be used to estimate the fraction of CBs and SCBs,in particular the BHBs of star clusters.This will provide a good opportunity to combine stellar population synthesis and GW progenitor studies (see e.g.,Belczynski et al.2016).Note that an increasing initial hard binary fraction may not change the results,as the simulations with 10% hard binary fraction compare very well in terms of binary fraction at 10 Gyr with a Monte-Carlo simulation with a Kroupa (1995a) period distribution.In this research,some widely used inputs are applied,but there are still some uncertainties in the results.It is necessary to simulate the binary populations of more realistic star clusters,by taking their known metallicity,stellar mass,binary fraction,chemical enhancement and star formation history into account.Now we present simulations from a relatively small star sample (N=100,000).In order to decrease the stochastic variations in our results,we have calculated nine of these models in total,with statistically independent initial conditions.We are currently calculating larger models,with one million stars,which will be the subject of future work and take much more computing time.In addition,it is possible to get a different result if we use another population synthesis code,e.g.,SEVN,instead of the MOBSE code.Some comparisons to other works,e.g.,Eldridge &Stanway (2016)and Kruckow et al.(2018),are also needed to give better constraints on the CB fractions of star clusters in the future.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the reviewer for constructive comments on this paper,and thank Jarrod Hurley,Sambaran Banerjee and Manuel Arca Sedda for cooperation,help and assistance in developing and using the NBODY6++GPU code.This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC,Grant Nos.11863002 and 11673032),Yunnan Academician Workstation of Wang Jingxiu (202005AF150025),China Manned Space Project with No.CMS-CSST-2021-A08,and Sino-German Cooperation Project (No.GZ 1284).
B.K.would like to thank the CAS-TWAS President’s PhD Fellowship Programme of the Chinese Academy of Sciences&The World Academy of Sciences.The work of P.B.was supported by the Volkswagen Foundation under the special stipend No.9B870 (2022).P.B.acknowledges the support within the grant No.AP14869395 of the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science,Higher Education of Kazakhstan(“Triune model of Galactic center dynamical evolution on cosmological timescale”),Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine under the collaborative grant M/32-23.05.2022 and the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine under the Main Astronomical Observatory GPU computing cluster project No.13.2021.MM.
This work was also supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG,German Research Foundation) -Project-ID 138713538—SFB 881 (“The Milky Way System”),and by the Volkswagen Foundation under the Trilateral Partnerships grant Nos.90411 and 97778.
Data Availability
The data on fractions of CBs and SCBs from ASPS simulations are available at the Zenodo repository.
ORCID iDs
 Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics2023年2期
Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics2023年2期
- Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics的其它文章
- Formation and Destiny of White Dwarf and Be Star Binaries
- Determination of Distance,Extinction,Mass,and Age for Stars in LAMOST DR7
- A Two-limb Explanation for the Optical-to-infrared Transmission Spectrum of the Hot Jupiter HAT-P-32Ab
- The First Photometric and Spectroscopic Study of Contact Binary V2840 Cygni
- Galaxy Interactions in Filaments and Sheets: Effects of the Large-scale Structures Versus the Local Density
- Influence and Correction of Wavefront Primary Aberrations for Radio Telescopes using Aberration Theory
