Olive oil ameliorate allergic response in ovalbumin-induced food allergy mouse by promoting intestinal mucosal immunity
Yu M, Ming Liu, Donghui Li, Jie Li, Zixin Guo, Yunjun Liu, Shengnn Wn, Yixing Liu,c,*
a College of Ocean Food and Biological Engineering, Jimei University, Xiamen 361021, China
b National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration, Beijing 100083, China
c Collaborative Innovation Center of Provincial and Ministerial Co-Construction for Marine Food Deep Processing, Dalian Polytechnic University, Dalian 116034, China
Keywords:Olive oil Ovalbumin-induced food allergy Anti-food allergy Intestinal mucosal immunization
A B S T R A C T The numerous health benefits of olive oil are widely known, however, it also provides anti-allergic properties that have not yet been fully defined. In this study, the anti-allergic activity of olive oil was evaluated by analyzing the clinical symptoms and immune-related factors in BALB/c mice that had ingested 600 mg/(kg·day) olive oil for two weeks prior to the evaluation. An allergy model was subsequently constructed for analysis, the results of which showed that the olive oil reduced the scores of allergic symptoms in the mice, and up-regulated the hypothermia and the decline in the immune organ index. Moreover, fewer allergy-related cytokines and reduced intestinal inf lammation was discovered in the olive oil-treated group.In addition, analysis of intestinal mucosal immune-related factors revealed that the olive oil promoted the expression of intestinal tight junction proteins (Claudin-1, Occludin, and ZO-1) and IL-22, and helped maintain the integrity of the intestinal epithelial physical barrier. Increased levels of mucin 2 and β-defensin were also found in the intestinal mucus of the olive oil-treated mice. These findings suggest that the oral administration of olive oil effectively attenuated the ovalbumin-induced allergic immune response in the mice,and had a positive effect on intestinal epithelial mucosal immunity.
1. Introduction
Since the start of the 21stcentury, food allergies have increased dramatically, introducing a ‘second wave’ of the allergy epidemic and replacing the ‘first wave’ that began in the 1950s, which was dominated by asthma and allergic rhinitis [1]. Adverse immune reactions to foods reportedly affect approximately 6% of young children and 3%-4% of adults in Western countries [2]. Studies have found that immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated food allergies can trigger responses ranging from incessant scratching to those more life-threatening such as diarrhea, vomiting and even restriction of the airway [3,4]. Egg allergy is one of the most common food allergies,with an estimated prevalence of 1%-9% worldwide, occurring especially in infants and young children [5]. Ovalbumin (OVA),which is derived from egg white, is thermally unstable and is digested and absorbed in the intestines, is the main egg allergen [6,7].
There is growing evidence that food allergies are closely related to the gut microbiome and gut health [8]. The gastrointestinal tract is the main route of exposure to food allergens, however an intact intestinal epithelial layer isolates the invasion of pathogens through the mucosal immune system and keeps the commensal microbiota compartmentalized [9]. A single layer of enterocytes and tight junctions (TJ, intercellular multiprotein complexes) form the core of the mucosal immune system [10]. Columnar intestinal epithelial cells(IECs) secrete a number of factors that contribute to barrier function,including antimicrobial peptides, mucins and trefoil factors [11].In addition, the intestinal epithelium is covered by a thick mucus layer,which is mainly secreted by goblet cells [12]. The large number of mucin glycoproteins in this mucus provide an important physical and biochemical barrier that prevents microbial contact with the epithelial surface by trapping noxious molecules as well as pathogens [13].The incidence of food allergies is, thus, mitigated by an intact and healthy intestinal mucosal immune system.
In addition to genetics, environment and drugs, diet is the most important factor affecting the mucosal immune system [14].Indeed, many studies have confirmed that dietary structure affects the occurrence and development of food hypersensitivity by regulating the health of the intestinal tract. For example, a high-fat diet has been shown to disrupt the intestinal microbial composition in normal mice, and to potentiate food anaphylaxis associated with dysregulated intestinal effector mast cell responses and increased intestinal permeability [15]. A high-salt diet drives the differentiation of regulatory T (Treg) cells into pro-inflammatory T helper 17 (Th17) cells in mouse intestines, as well as promoting the production of interleukin(IL)-17 and IL-23, and causing intestinal inflammation [16,17].Furthermore, the abundance of the mucus-degrading bacteriaAkkermansia muciniphilaandBacteroides fragilisincreases with high sugar consumption, and the enrichment of bacteria-derived mucolytic enzymes leads to the erosion of the colonic mucus layer [18].In contrast, high-fiber feeding in mice was found to enhance oral tolerance and protect against food allergy by improving retinal dehydrogenase activity in CD103-expressing dendritic cells (CD103+DC)and increasing the release of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) [19].Findings such as these support the understanding that diets or dietary ingredients influence food allergies by regulating intestinal immunity.
The Mediterranean diet is globally considered to provide one of the most healthy dietary patterns, thanks to its combination of foods that are rich in antioxidants and various anti-inflammatory nutrients [20].Olive oil, which is an important element in the Mediterranean diet,has been shown to reduce the risk of a variety of diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes and cancer [21]. However, the effect of olive oil on food allergies is rarely reported. In this work, the ameliorative effect of olive oil on OVA-induced food allergy was evaluated based on a mouse model, and the impact of olive oil on the intestinal mucosa of allergic mice subsequently examined.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Mueloliva extra virgin olive oil was used in this research (Córdoba,Andalusia, Spain). It was stored at 15 °C, with avoidance to light.Imject Alum was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham,MA, USA). The allergen, OVA, was obtained from Aladdin (Shanghai,China), while anti-OVA-specific IgE was purchased from Mskbio Limited (Wuhan, China). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA) kits of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and mouse mast cell protease (mMCP)-1 were purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis,MN, USA), and other kits were from Enzyme Link Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Enhanced RIPA lysate and tissue fixative were obtained from Boster Biological Technology Co., Ltd.(Wuhan, China).
2.2 Animals and experimental design
Male BALB/c mice of 3-5 weeks were obtained from the Shanghai Laboratory Animal Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China) and acclimated to their new environment for one week. They were maintained in a specific pathogen free (SPF)environment with a relatively stable temperature ((22 ± 1) °C) and relative humidity ranging from 55% to 60%. They were freely provided with drinking water and were fed a standard breeding diet (SLAC).All experiments in this study were performed in strict accordance with the NIH guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals (NIH Publication No. 85-23 Rev. 1985). Protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Animal Laboratory Center of Jimei University (Xiamen, China, No. SCXK 2016-0006).
The food allergy model was monitored as previously described [22],with some modifications. Briefly, mice in the olive oil group received additional doses of 600 mg/(kg·day) olive oil for 2 weeks prior to sensitization. For the sensitization, the mice in both the model group and the olive oil group were immunized with 100 μg OVA in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) emulsified with aluminum adjuvant(OVA:aluminum adjuvant:PBS = 1:1:1) by intraperitoneal (i.p.)injection on days 0 and 14, and were subsequently challenged 5 times with 50 μg of OVA in 200 μL of PBS by oral administration every 3 d, between days 28 to 40, to establish the food allergy model.Anaphylactic symptoms and diarrhea were scored for 1 h after the last challenge, rectal temperatures were measured for 1 h after the last challenge, and sera were collected the following day. As a native control, the mice were immunized and gavaged with the same volume of PBS, and 5 mice were included in each group. The specific animal experiment treatment is based on Fig. 1.
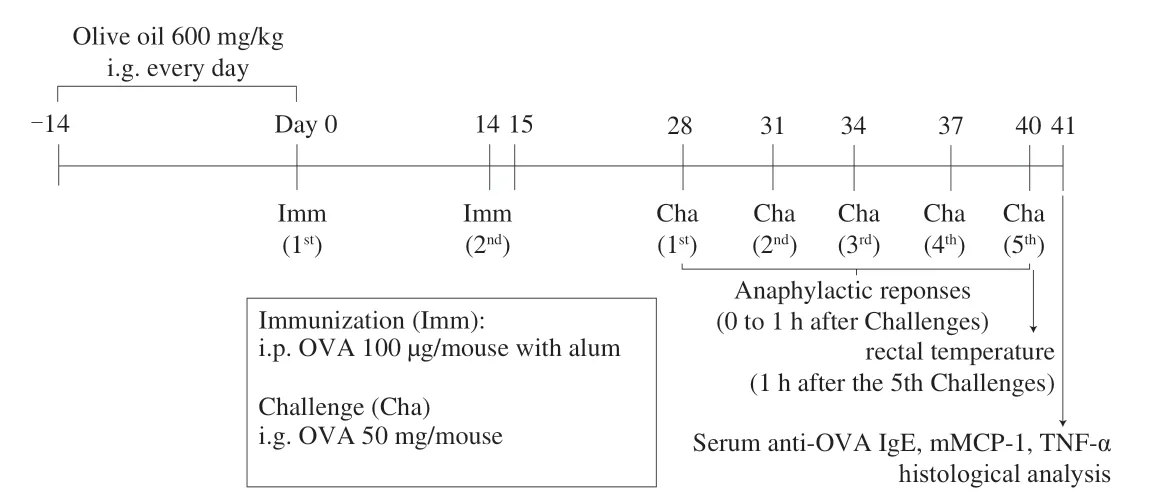
Fig. 1 Experimental study design.
2.3 Allergy symptom score and immune organ index
To assess the severity of shock symptoms 1 h after the intragastric(i.g.) challenge, a validated anaphylaxis symptom scoring table was used [23] as follows: 0 = no signs; 1 = repeated scratching/rubbing around snout and mouth; 2 = swelling around eyes and snout/piloerection/reduced activity with increased respiratory rate; 3 =wheezing/activity after stimulation; 4 = no activity after stimulation/tremor and convulsions; and 5 = death by shock. Total scores for each animal were obtained by adding the average scores for individual clinical signs. The immune organ index was calculated according to a previously reported method [24]. Twenty-four hours after the last drug administration, the animals were weighed and then sacrificed via cervical dislocation. The spleen and thymus were removed and weighed immediately. The thymus and spleen indices were calculated according to the following formula:

2.4 Allergy-related inflammatory factors in serum
On the 41stday, vitreous blood was collected to obtain serum for determining the allergy-related inflammatory factors. The OVAspecific IgE, mMCP-1 and TNF-α were determined by ELISA kits,according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5 Scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis
The integrity of the ileum villi was determined using SEM, as described in a previous report [25]. Transverse slices of each intestinal segment (2 mm × 2 mm) were prepared and the contents and intestinal mucus that had adhered to the surface were washed away by PBS(0.1 mol/L). The ileum was immersed in 2.5% (V/V) glutaraldehyde for fixation overnight, after which the samples were rinsed with PBS 3 times for 5 min each. Thereafter, they were immersed in ethanol for 15 min per concentrations of 30%, 50%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 95%and 100% for dehydration. The samples were subsequently soaked in a mixture of ethanol-isoamyl acetate (1:1,V/V) for 30 min. They were then treated with 100% isoamyl acetate for 1 h to replace the ethanol, after which they were dried in a critical point dryer. The dried jejunum tissue was glued onto conductive tape with the villi facing upward, then placed in a gold steaming chamber, sealed and vacuumed. The sputtering instrument was gold-plated for 90 s under a predetermined vacuum degree and kept at a constant current value.After the gold spraying was completed, the sample was placed in a SEM (Phenom-World PW-100-016, Eindhoven, Netherlands) for observation, photography and recording.
2.6 Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining
Pathological analysis of the ileum tissue was performed using a previously described method [26]. In brief, the proximal ilea of the sacrificed mice were fixed in 4% (V/V) formaldehyde solution, and the sections were embedded in paraffin for H&E staining. Subsequently,evaluation was performed using a light microscope (Olympus BX41,Tokyo, Japan). The heights of 5 villi and the depths of 5 crypts were measured for each sample and data analysis. Villus length was measured from the crypt opening to the villus tip, while crypt depth was measured as the depth of the invagination between the adjacent villus [27], and the ratios of villus heights to crypt depths (V/C) were also calculated.
2.7 Analysis of related intestinal factors
Dissected ileum tissue was rinsed with saline, dried with filter paper and weighed. Subsequently, the intestinal tissue was cut into pieces, and 10% tissue homogenate (intestinal tissue (g):cell lysate(mL) = 1:9) was made with the cell lysate in an ice bath. After centrifugation at 8 000 r/min for 10 min at 4 °C, the supernatant was collected and stored at -80 °C for later use. The ELISA method was used to detect the level of tight junction proteins (Claudin-1,Occludin, and ZO-1), IL-22, MUC-2,β-defensin and secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) in the intestine, according to the kit manufacturer’s instructions.
2.8 Statistical analysis
All data were expressed as mean ± SD of at least 3 individual experiments. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s test using SPSS Statistical 24 Software (IBM,USA).P< 0.05 (two-sided) was regard as significant (* &#,P< 0.05;** &##,P< 0.01).
3. Results
3.1 Improvement effect of olive oil on clinical allergic symptoms in mice
As shown in Fig. 2A, there was no significant difference between the body weights of the olive oil-treated mice and the normal group. On the final experimental day, mice were challenged with OVA by oral gavage and were observed for 1 h for rectal temperature changes and clinical scoring (Fig. 2B-C). The average body temperature of the sensitized mice dropped from 35.27 °C to 32.58 °C within 30 min of the oral administration of OVA, however, the average body temperature of mice in the olive oil group then rose to 33.55 °C, and their anaphylactic symptom scores were also reduced in comparison to those of the model group (from 3.84 to 2.76). Spleen and thymus indices can reflect the immune function and prognosis of an organism. As shown in Fig. 2D, the spleen and thymus indices of the model group remarkably decreased compared with those of the normal group (from 2.36 to 2.05 and from 1.36 to 1.28, respectively). Olive oil significantly increased the spleen index of the model group (P< 0.05), and the thymus index also increased although no significant difference was observed. These results, thus, suggest that olive oil can reverse the OVA-induced atrophy of immune organs.
3.2 Olive oil intake reduces serum levels of allergy-related inflammatory factors
After the 5thOVA oral challenge, sera were collected from both untreated and olive oil-treated mice on day 41, to determine allergic response. Analysis clearly showed that the OVA challenge had resulted in significant increases in OVA-specific antibody IgE, allergic mediator mMCP-1, and inflammatory cytokine TNF-α (P< 0.01)(Fig. 3). However, compared with the model group, the levels of IgE, mMCP-1 and TNF-α in the olive oil group were significantly reduced by 37.99%, 35.59% and 30.44% (P< 0.01), respectively. The above results provide further evidence that olive oil might enhance oral tolerance to OVA in mice.
3.3 Olive oil ameliorates intestinal injury caused by allergies

Fig. 2 The improvement effect of olive oil intake on the allergic responses of mice. (A) Body weight changes within 5 weeks after sensitization;(B) Rectal temperature changes within 1 h after final oral administration of OVA; (C) Anaphylactic symptom scores of mice groups; (D) Immune organ indices,including spleen index and thymus index. #P < 0.05 vs PBS; ##P < 0.01 vs PBS; *P < 0.05 vs model; **P < 0.01 vs model.
In this work, SEM was used to observe the integrity of ileum villi and histopathological sections of the ileum, in order to examine the extent of intestinal inflammation in the OVA-induced food allergy mice. As seen in Fig. 4A, the SEM observations showed the intestinal villi in the PBS group to be neatly arranged, and in plump, round shapes without cracks or defects. In contrast, the ileum villi in the model group displayed ruptured surfaces and partial damage, however,the ileum fluff of the mice that received an extra 600 mg/(kg·day)olive oil more closely resembled that of the normal group. Although there were a few visible breaks, the surfaces of the villi were intact and without the cracks evident in the model group.
The pathological observation results of the jejunum tissue are shown in Fig. 4B. In the PBS group, the intestinal villi were slender and closely arranged, with an intact intestinal mucosal structure. In addition, the columnar cells and goblet cells in the lamina propria were abundant and no apparent signs of inflammation were observed.In contrast, the villi of the model group were atrophied and broken,and the IECs were reduced, providing evidence of prominent inflammation. When the mice were treated with 600 mg/(kg·day) olive oil, a slight widening of the spacing between intestinal glands was still evident, however, the villus morphology was similar to that observed in the normal group and inflammation had been alleviated. The villus length and crypt depth of the ileum slices were further measured and their ratios were calculated. Villus height reflects the status of the absorptive surface, whereas crypt depth is closely associated with tissue turnover [28]. A tall villus, a short crypt or a highV/Cratio generally reflect a healthy digestive system [29]. As seen in Fig. 4C-E,compared with the model group, significantly (P< 0.01) increased villus height and decreased crypt depth were detected in the olive oil group, while theV/Cvalue had increased from 2.16 to 4.63. These results imply that olive oil can effectively inhibit intestinal epithelial injury during the development of food allergy.
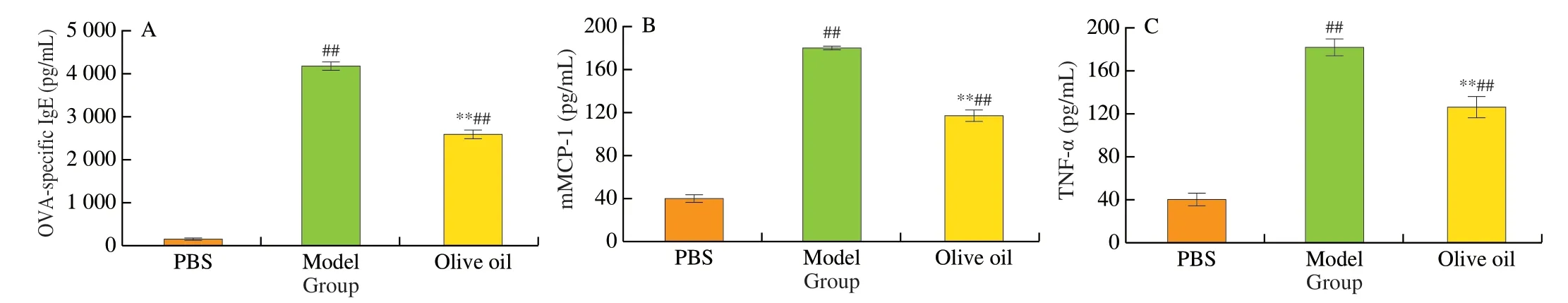
Fig. 3 Serological analyses of the levels of allergy-related inflammatory factors in mouse groups. (A) OVA-specific IgE; (B) mMCP-1; (C) TNF-α.##P < 0.01 vs PBS; **P < 0.01 vs model.
3.4 Olive oil promotes the expression of tight junctionrelated factors in the intestines of allergic mice
TJ is integral to the intestinal physical barrier, and TJ proteins play a critical role in regulating the invasion of allergens and pathogenic bacteria [30]. In this study, subsequent to sensitization,the levels of the three intestinal TJ proteins (Claudin-1, Occludin,and ZO-1) were found to be significantly decreased (P< 0.01) in the model group (Fig. 5A-C), however, the levels of the three TJ proteins in the olive oil group were comparatively 18.67%, 18.43%and 41.63% higher, respectively. Meanwhile, IL-22, which is known to exert a positive effect on the intestinal epithelial barrier function [31],had also increased significantly (P< 0.01) (Fig. 5D). These results, thus,provide evidence that lesions to the intestinal epithelial barrier function caused by food allergies can be restored by the ingestion of olive oil.
3.5 Olive oil affects the chemical composition of intestinal mucus
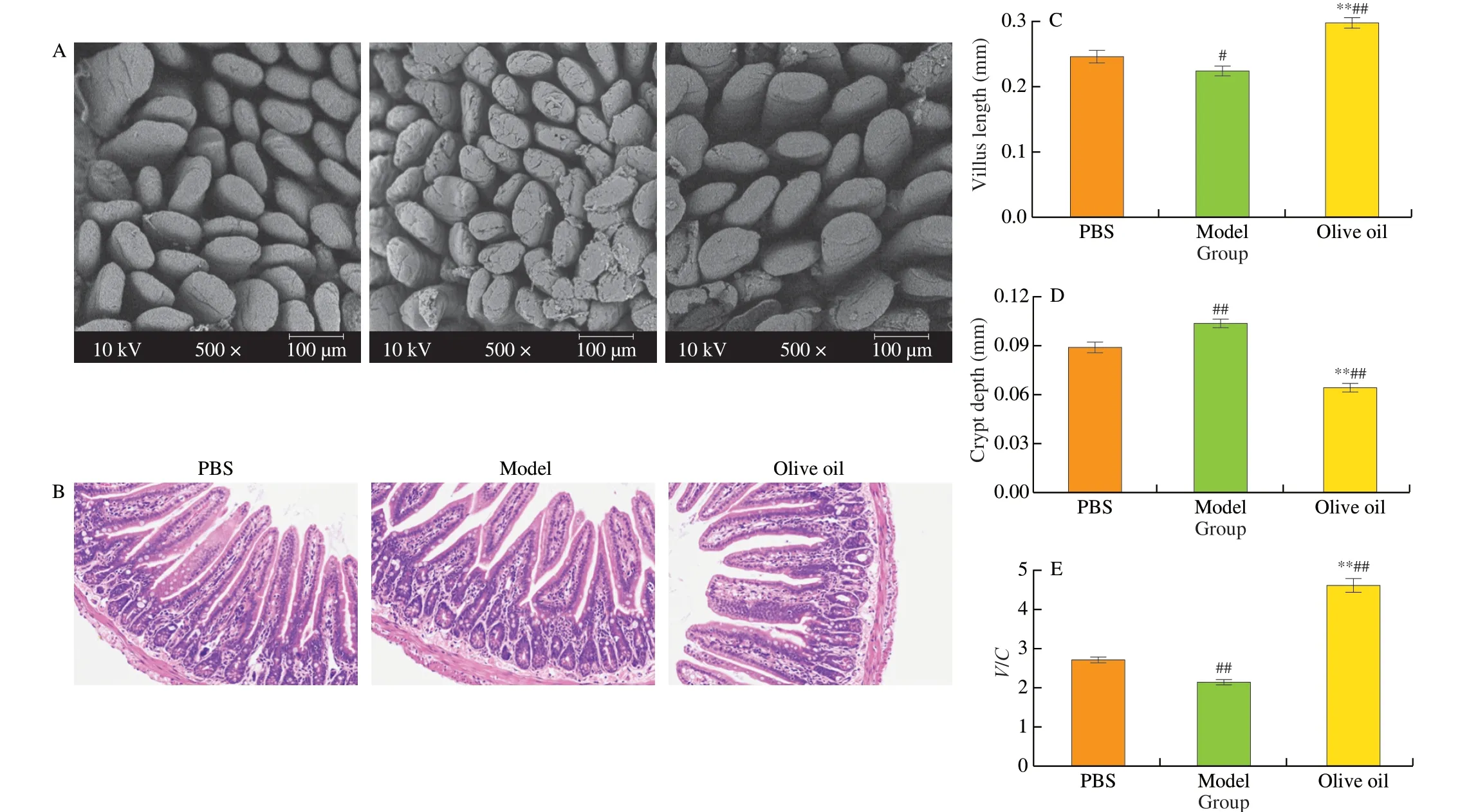
Fig. 4 The effect of olive oil intake on intestinal inflammation in allergic mice based on morphological and histological observations. (A) SEM observation of the integrity of jejunum villi, original magnification 500×; (B) Optical microscope observation of the jejunum tissue after H&E staining; Effect of olive oil on intestinal villus length (C), crypt depth (D), and their ratio (E) in mice. #P < 0.05 vs PBS; ##P < 0.01 vs PBS; **P < 0.01 vs model.
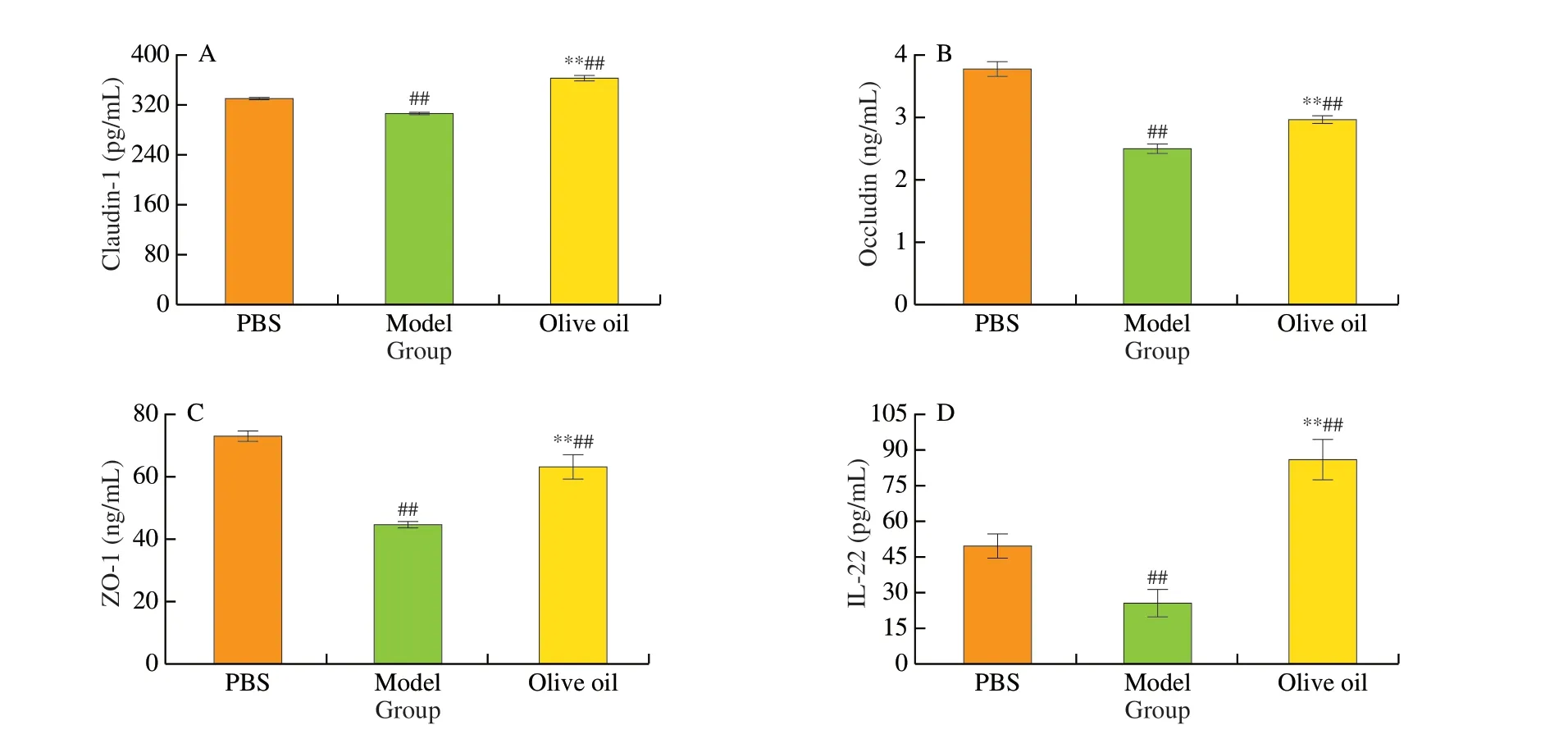
Fig. 5 Analysis of tight junction-related factors in the intestines of different groups of mice. (A) Claudin-1; (B) Occludin; (C) ZO-1; (D) IL-22.##P < 0.01 vs PBS; **P < 0.01 vs model.
When food allergens invade the intestines, the immune system is stimulated to produce more mucus to maintain host defenses [32].As shown in Fig. 6A, compared with the PBS group, the expression of mucin 2 (MUC2) in the mucus of the model group increased, while that of the olive oil group was 20.37% higher than that of the model group.β-defensins are small, cationic, antibacterial peptides produced mainly by epithelial and Paneth cells, and constitutive or induced by microorganisms or cytokines that contribute to the broad spectrum innate immunity [33]. Food allergies reduce the level ofβ-defensin in the intestines, however, in this study, olive oil intake was found to promote the expression ofβ-defensin to a level 23.16% higher than that in the model group (Fig. 6B). In addition, the release of sIgA in the intestinal tracts of the sensitized mice was restricted, even in the olive oil group (Fig. 6C).

Fig. 6 The secretion levels of cytokines in the intestines of mice: (A) MUC-2; (B) β-defensin; (C) sIgA. #P <0.05 vs PBS; ##P < 0.01 vs PBS; *P < 0.05 vs model; **P < 0.01 vs model.
4. Discussion
The prevalence of food allergies has risen continuously in recent decades to become a significant global health problem. Food allergies develop as a consequence of immune dysregulation and a failure in oral tolerance [34]. Normally, the remaining intact food proteins and peptides are transported from the lumen to the mucosa through IECs and by specialized IECs called microfold cells (M cells), which are localized above Peyer patches [35]. CD103+DCs in the mucosa internalize and process these proteins and peptides, after which they move to the mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), where they interact with naive T cells and present antigens on MHC class II molecules [36].The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and retinoic acid produced by CD103+DCs induce naive T cells to differentiate into antigenspecific forkhead box P3 (FOXP3)+Treg cells [37]. Antigenspecific FOXP3+Treg inhibits adverse reactions to food in the intestinal lamina propria by producing cytokines TGF-β, IL-10, and IL-35 [38]. Conversely, epithelial damage or inflammation in the gut, skin or airways enables increased antigen entry and promotes the secretion of the epithelium-derived cytokines interleukin-25(IL-25), IL-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), which act on DCs and other cells to deviate the immune response towards Th2 cell-related allergic responses, rather than tolerogenic responses [39].Therefore, the prevention of allergen invasion into the intestinal epithelium and maintenance of the Th1/Th2 balance have become important strategies to combat food allergies.
Numerous studies have revealed the influence of certain fats and fatty acids on food allergies. In observational research of Icelandic children from birth to 2.5 years of age, it was found that regular supplementation of fish oil in postpartum infants can greatly reduce the incidence of food allergies in children [40]. In another study,a DHA-rich tuna oil diet significantly relieved acute allergic skin reactions and allergic symptoms in both PE- and whey-allergic mice,including the decline of IgE, IgG1 and IgG2a levels and the generation of Treg, and the restraint of Th2 and Th1 activity [41,42]. In contrast, a 10% soybean diet, rich inn-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), was reported to enhance anaphylaxis to cow’s milk by enhancing Th2 cell polarization and the allergic effector response [43]. This could be reduced by increasing the amount ofn-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids(LCPUFAs) [44], indicating that the dietary ratio ofn-3:n-6 PUFAs is important in immune system modulation.
Olive oil has a high nutritional value due to its rich monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA)-oleic acid, a reasonable ratio ofn-3 andn-6 fatty acids, and the presence of a variety of phenolic compounds and carotenoids [45]. The therapeutic effect of olive oil in OVA-sensitized mice was assessed in this study, with results verifying that mice exposed to olive oil for 5 weeks presented lower clinical scores as well as lower concentrations of allergy biomarkers. These findings suggest the potential use of olive oil in hyposensitization therapy. More specifically, we demonstrated that olive oil supplementation significantly decreased clinical symptoms of allergy, such as scratching, hypothermia and gastrointestinal response, and improved the production of allergic mediators (OVAspecific IgE, mMCP-1 and TNF-α) and the atrophy of immune organs. However, this study did not ascertain the effects of different doses of olive oil on food allergies, and further research is required to further standardize the dosage range for optimal effects.
The gastrointestinal mucosa provides the main route for exposure and uptake of allergens and, thus, maintaining a complete intestinal barrier function has become a new tactic for allergy prevention and treatment [11]. Children are more likely to have food anaphylaxis than adults, possibly due to the relative immaturity of the intestinal mucosa barrier and mucosal immunity [46]. In this study of OVA-challenged mice, intestinal epithelium injury was observed, including the destruction of the jejunal villi, widened intestinal glands, decreasedV/Cratio and increased levels of inflammation. However, following the administration of olive oil, these intestinal epithelial injuries were found to have been effectively ameliorated, thus concurring with the results of previous studies [22,47]. In addition, a decrease of intestinal TJ proteins after sensitization was also observed in this work. It has been reported that peanut allergens damage the barrier integrity of Caco-2 by modifying the co-localisation of the transmembrane TJ proteins occludin, JAM-A and Claudin-1 with the intracellular adhesion protein ZO-1, which leads to an increase in peanut allergens and induces immune responses [48]. OVA has been proven to have the same effect [49]. These findings indicate that promoting the expression of intestinal TJ proteins and avoiding the increase in intestinal mucosal permeability can effectively control food allergies and, as hypothesized,olive oil was found in this study to perform this function.
In addition to the static epithelial barrier, composed of IECs and paracellular pathways, the dynamic part of the intestinal barrier is composed of the luminal microbiota and mucus, as well as epithelial and immune cell products secreted into the lumen, which cannot be ignored [13]. In sterile mice, the absence of microorganisms was reported to result in a very thin intestinal mucosa, displaying reduced IEC proliferation as well as the impaired production of mucins and other IEC-derived mediators [50]. IECs express pattern-recognition receptors for direct interaction with the microbial environment, enabling them to participate in specific mucosal immune responses [13].Moreover, for the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis, secreted antimicrobial products such asβ-defensin, lysozyme C and RegIIIα(or RegIIIγ in mice) released by IECs and Paneth cells, as well as sIgA produced by plasma cells, prevent pathogens’ adhesion and colonization [51]. All of these antimicrobial products are essential for the spatial segregation of luminal commensals and pathogens from the intestinal epithelium. In the present results, increases were observed in the secreted MUC2 andβ-defensin levels after ingestion of olive oil, however, the level of intestinal sIgA had decreased, the specific reasons for which have yet to be investigated.
5. Conclusion
This study evaluated the anti-allergic effect of olive oil on OVAinduced food allergy in mice. The results showed that, in addition to typical allergic symptoms, OVA-sensitized mice also experienced an increase in allergen-specific factors and a decrease in intestinal immunity, however, after olive oil administration, these allergic symptoms were ameliorated. Specifically, olive oil reduced the scores of allergic symptoms in mice, and up-regulated the hypothermia and the decline in immune organ indices. Moreover, a reduction in allergyrelated cytokines, along with decreased intestinal inflammation was discovered in the olive oil-treated group. In addition, the analysis of intestinal mucosal immune-related factors revealed that olive oil promoted the expression of intestinal tight junction proteins(Claudin-1, Occludin, and ZO-1) and IL-22, and helped to maintain the integrity of the intestinal epithelial physical barrier. At the same time, increased levels of MUC2 andβ-defensin in the intestinal mucus were found in the olive oil-treated group. In conclusion, it is evident that olive oil can effectively ameliorate food allergies and maintain intestinal mucosal immunity.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The present work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFC1605003-3) and the Science and Technology Projects of Xiamen Science and Technology Bureau (3502Z20183034).
- 食品科學與人類健康(英文)的其它文章
- Maternal obesity exacerbates the responsiveness of offspring BALB/c mice to cow’s milk protein-induced food allergy
- Au@Ag-labeled SERS lateral f low assay for highly sensitive detection of allergens in milk
- Impact of three different processing methods on the digestibility and allergenicity of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) tropomyosin
- Effect of lipid peroxidation on the allergenicity and functional properties of soybean β-conglycinin (7S) and glycinin (11S)
- Comparative acetylome analysis reveals the potential mechanism of high fat diet function in allergic disease
- Therapeutic effects of epigallocatechin and epigallocatechin gallate on the allergic reaction of αs1-casein sensitized mice

