Association of nutrients intake during pregnancy with the risk of allergic disease in offspring: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies
Hua Feng, Yan Chen, Xiujuan Xiong, Qunying Xu, Zhongwei Zhang,Qinghua Xi, Yongning Wua,,*, Yuanan Lu*
a State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, China
b School of Public Health, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, China
c Research Unit of Food Safety (2019RU014), Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences; NHC Key Laboratory of Food Safety Risk Assessment,China National Center for Food Safety Risk Assessment (CFSA), Beijing 100022, China
d Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, China
e Environmental Health Laboratory, Department of Public Health Sciences, University of Hawaii, Honolulu 96822, US
Keywords:Nutrients Pregnancy Offspring Allergy Immune disease
A B S T R A C T To investigate the role of nutrients intake during pregnancy with longitudinal development of rhinitis, asthma,eczema, wheeze, and food allergy in offspring. The PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane library were searched for articles published throughout May 2022. The pooled effect estimate were presented using relative risk and calculated by the random-effects model. Twenty-three prospective cohort studies enrolling 210 817 individuals were included. The risk of wheeze in offspring were lowered when high vitamin D, vitamin E, zinc, and milk intakes during pregnancy, whereas high meat intake during pregnancy could induce additional risk of wheeze in offspring. Moreover, high β-carotene and magnesium intakes during pregnancy were related to lower eczema risk in offspring, whereas eczema risk in offspring was increased for pregnant women with high intake of butter and margarine. Finally, the asthma risk in offspring could protect against for pregnant women with high intake of vitamin D and apple, whereas high folic acid during pregnancy could produce excess asthma risk in offspring. This study provides the summary evidences regarding the role of nutrients intake during pregnancy and subsequent risk of rhinitis, asthma, eczema, wheeze, and food allergy, and further effective intervention strategies should be employed to improve childhood allergic diseases.
1. Introduction
Allergic diseases are widely occurred in children and adolescents and contributed public health concerns [1]. There is an increasing evidence which investigated the development of fetal immune regulation and the disorders in later life induced by infancy and pregnancy nutrition exposures [2]. Currently, the aetiology for allergic disease was multifactorial, and exposures during infancy and pregnancy have been suggested to affect the development of allergic disease [3,4]. The prevalence of rhinitis, asthma, eczema, wheeze, and food allergy are increasing before adolescence owing to sensitization to inhalant allergens [5-8]. Therefore, it is important to explore whether nutrients intake during pregnancy can affect the subsequent risk of allergic disease.
Systematic reviews have already addressed the potential role of nutrients and allergic disease risk in children, including Mediterranean diet, fish or fish oil, probiotic, fruits and vegetables, zinc, vitamins A, D, or E, and folate [9-19]. However, previous studies mostly included both prospective and retrospective observational studies,which might induce uncontrolled confounders. Moreover, several prospective studies have been already completed regarding the role of nutrients intake during pregnancy with the risk of allergic disease in offspring. Therefore, this study was performed to comprehensive summarizes the rhinitis, asthma, eczema, wheeze, and food allergy risk in offspring and explore the potential role of nutrients intake during pregnancy.
2. Methods
2.1 Literature search and inclusion criteria
The current study was performed following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Statement [20]. Studies designed as prospective cohort and investigating the role of nutrients intake during pregnancy with the rhinitis, asthma, eczema, wheeze or food allergy risk in offspring were eligible in our meta-analysis, and no other restrictions. We searched PubMed, EmBase and Cochrane Library for articles published through May 2022 and Supplemental 1 listed the search strategy in PubMed.New potential eligible studies were identified through manual search the reference lists of original articles.
Two reviewers performed literature search and study selection,and conflicts was resolved by mutually discussion. Study was included if: (1) prospective cohort design; (2) the study evaluated nutrients intake during pregnancy with the subsequent rhinitis,asthma, eczema, wheeze, and food allergy risk in offspring; and(3) the risk ratio (RR), hazard ratio (HR), or odds ratio (OR) and 95%confidence interval (CI) should be reported or can be obtained by calculation. Study designed as retrospective observational study was excluded because uncontrolled confounding factors could bias the pooled results.
2.2 Data abstracted and methodological quality
The data abstracted and methodological quality assessed were independently undertaken by 2 reviewers, and any inconsistencies were checked by a third author reviewing the original article. The collected data items included first author and study groups’ name,publication year, country, sample size, exposures, age at outcome,outcomes reported, and adjusted factors. The quality assessment was conducted using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), and the staring system for individual study ranged 0-9 [21]. High quality study was defined as 7 or more stars.
2.3 Statistical analysis
The association of nutrients intake during pregnancy with the rhinitis, asthma, eczema, wheeze, and food allergy risk in offspring were assessed on the basis of RR, HR, OR and its 95% CI in individual study. The pooled RRs and 95% CI for the high versus low nutrients intake during pregnancy were analyzed using the randomeffects model [22,23]. TheI2andQstatistic were used to assess heterogeneity, and significant heterogeneity defined asI2> 50.0%orPvalue < 0.10 was regarded as significant heterogeneity [24-26].The stability of pooled results for outcomes reported ≥ 5 cohorts were evaluated using the sensitivity analysis [27]. Moreover,subgroup analyses were also performed for outcomes reported ≥ 5 cohorts based on age at outcome, and the ratio between RR with specific 95% CI was calculated [28]. Publication biases for outcomes reported ≥ 5 cohorts were assessed using the Funnel plot, which were the test results of Egger et al. [29], and Begg et al. [30]. The trim and fill method was employed to adjusted the pooled results if potential publication bias was detected [31]. The inspection level for pooled results was 2-sided, and statistically significant defined asP< 0.05. The analyses in our study were performed using software STATA, with the version of 12.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station,TX, USA).
3. Results
3.1 Study selection
The initial electronic searches produced 11 793 records after duplicate citations were excluded. A further 11 600 studies were removed due to irrelevant topics by initially. One hundred and ninetythree studies were retrieved for detailed evaluations, and 170 studies were removed because of: retrospective studies (n= 69), no sufficient data (n= 34), affiliate study (n= 30), review or meta-analysis(n= 24), and nutrition intake in infancy (n= 13). Finally, 23 prospective cohort studies were included, and no additional new eligible study was found [32-54] (Fig. 1).
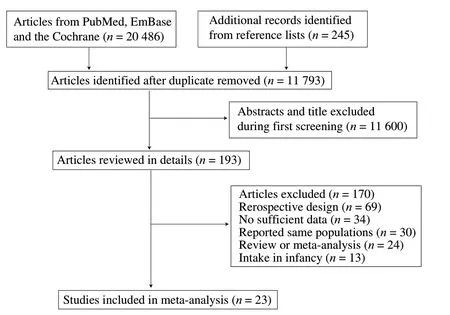
Fig. 1 Flow diagram of the literature search and studies selection process.
3.2 Study characteristics
Of 23 included studies, 20 studies were performed in Western countries (UK, US, Spain, the Netherlands, Finland, Germany,Australia, France, Denmark, Greece, Canada, Norway, and Ireland),and 3 studies were performed in Eastern countries (Japan). These studies recruited a total of 210 817 individuals, and 420 to 80 270 samples were included in individual study. The age at outcomes across included studies ranged 1.0-10.0 years. Following the NOS staring system, 7 studies with 8 stars, 10 studies with 7 stars, and 6 studies with 6 stars (Table 1).
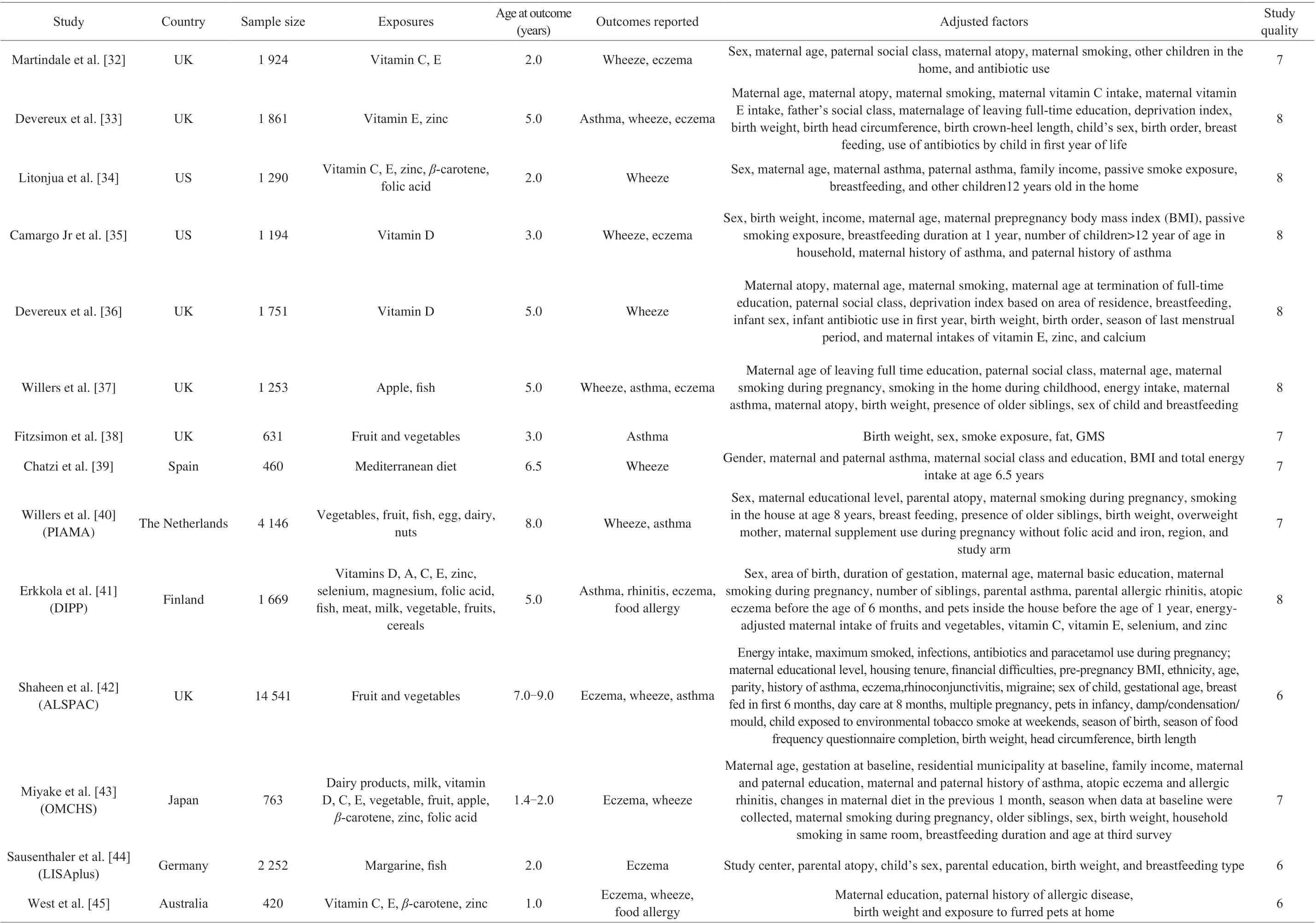
Table 1 The baseline characteristics of included studies.
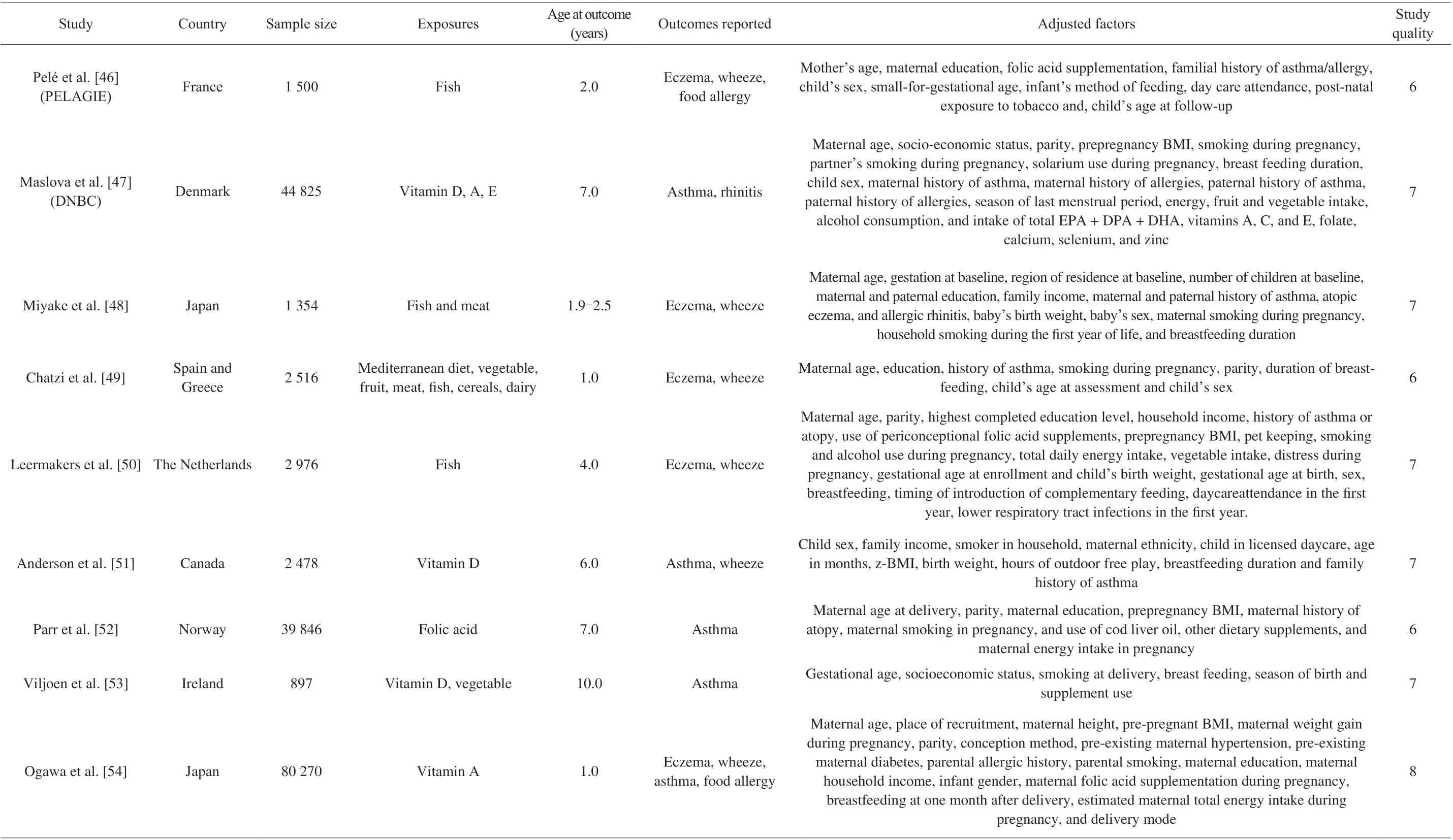
Table 1 (Continued)
3.3 Meta-analysis
The summary results for pregnant women’s nutrients intake with the wheeze risk are presented in Fig. 2A. The summary RR indicated pregnant women with high intake of vitamin D (RR: 0.55; 95% CI:0.40-0.75;P< 0.001), vitamin E (RR: 0.61; 95% CI: 0.48-0.77;P< 0.001), zinc (RR: 0.60; 95% CI: 0.45-0.81;P= 0.001), and milk (RR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.68-0.97;P= 0.022) was related to lower wheeze risk in offspring, whereas high meat intake during pregnancy could induce greater risk of wheeze in offspring (RR: 1.23; 95%CI: 1.04-1.46;P= 0.018). The heterogeneity for these results was not significant. However, no significant associations of vitamin A,vitamin C,β-carotene, folic acid, fruit and vegetables, fish, cereals,mediterranean diet, apple, eggs, and nuts with the wheeze risk in offspring were observed.
The summary results for pregnant women’s nutrients intake with the eczema risk are presented in Fig. 2B. We noted pregnant women with high intake ofβ-carotene (RR: 0.57; 95% CI: 0.36-0.88;P= 0.012) and magnesium (RR: 0.78; 95% CI: 0.62-0.97;P= 0.030)is related to lower eczema risk in offspring, whereas high butter and margarine intake during pregnancy could produce additional eczema risk in offspring (RR: 1.49; 95% CI: 1.08-2.04;P= 0.014). Moreover,we noted vitamin A, C, D, or E, folic acid, selenium, zinc, fruit and vegetables, milk, fish, meat, apple, cereals, and mediterranean diet did not affect the eczema risk in offspring.
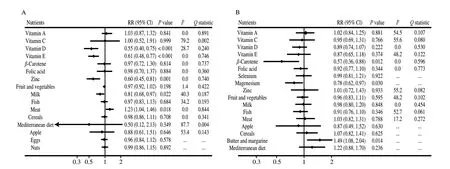
Fig. 2 The summary effect estimates for the associations of nutrients intake in pregnancy with the risk of (A) wheeze and (B) eczema.
The summary results for pregnant women’s nutrients intake with the asthma risk are presented in Fig. 3A. The summary RR indicated pregnant women with high intake of vitamin D (RR: 0.93; 95% CI:0.89-0.98;P= 0.002) and apple (RR: 0.47; 95% CI: 0.27-0.82;P= 0.008) were related to lower asthma risk in offspring, whereas high folic acid intake was related to elevated asthma risk in offspring(RR: 1.20; 95% CI: 1.04-1.39;P= 0.011). We noted vitamin A, C, or E, selenium, magnesium, zinc, fruit and vegetables, milk, fish, meat,eggs, nuts, cereals, or butter and margarine did not affect asthma risk in offspring.
The summary results for pregnant women’s nutrients intake with rhinitis risk are presented in Fig. 3B. The investigated nutrients including vitamin A, C, D, or E, folic acid, selenium, magnesium,zinc, fruit and vegetables, and cereals were not associated with rhinitis risk in offspring. No significant heterogeneity was seen for these nutrients on rhinitis risk in offspring across included studies.
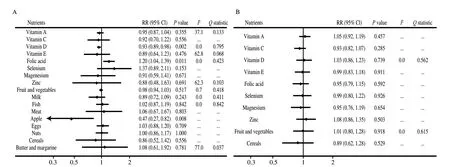
Fig. 3 The summary effect estimates for the associations of nutrients intake in pregnancy with the risk of (A) asthma and (B) rhinitis.
The summary results for pregnant women’s nutrients intake with food allergy risk are presented in Fig. 4. We noted vitamin A, C, D,or E,β-carotene, folic acid, zinc, and fish were not associated with food allergy risk in offspring, and no significant heterogeneity was observed in included studies.
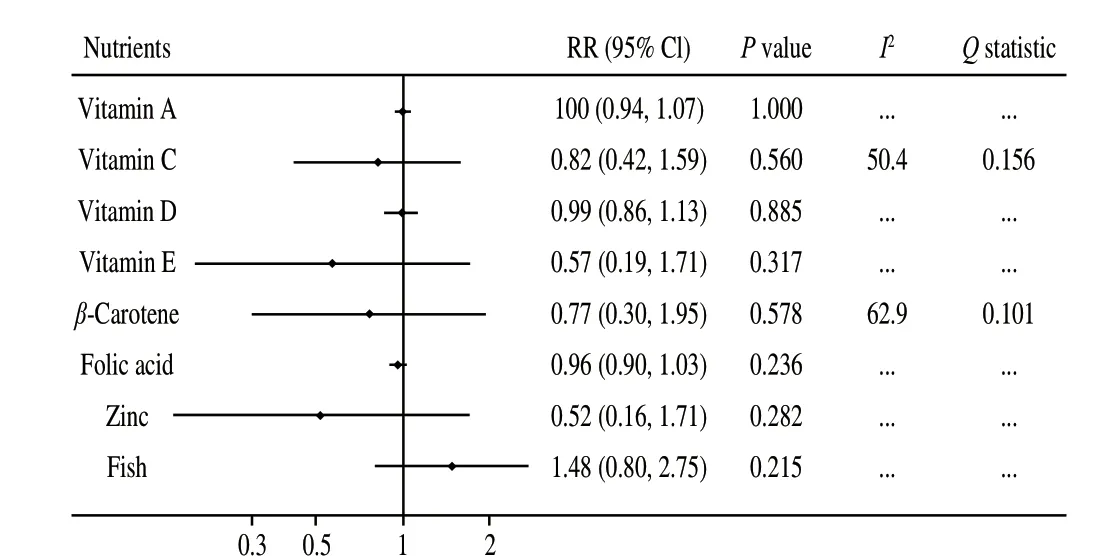
Fig. 4 The summary effect estimates for the associations of nutrients intake in pregnancy with the risk of food allergy.
3.4 Sensitivity and subgroup analysis
Sensitivity analyses were conducted for outcomes reported ≥ 5 cohorts and the results were presented in Supplemental 2. We noted the associations of fish intakes during pregnancy with the wheeze, and eczema risk were not altered by sequential excluding individual study.Moreover, the pooled conclusions for pregnant women with intake of fruit and vegetables with the wheeze and asthma risk were not changed through sequential excluding individual study. Furthermore,the pregnant women with intake of vitamin E with the wheeze risk was stable by sequential excluding each study. In addition, subgroup analyses for these results were also conducted based on the age at outcome: (1) we noted pregnant women with intake of fish, fruit or vegetables were not affect the wheeze risk irrespective of age of outcome; (2) pregnant women with intake of vitamin E is related to lower wheeze risk in all subgroups; (3) there were no significant association of fish intake with eczema risk in all subgroups; and(4) fruit and vegetables intake during pregnancy did not affect asthma risk when age of outcome measured ≥ 3.0 years (Table 2). Finally,the associations of fish intake with wheeze risk (RR: 0.95; 95% CI:0.66-1.36), fruit and vegetables intake with wheeze risk (RR:0.98; 95% CI: 0.83-1.15), vitamin E with wheeze risk (RR: 1.37;95% CI: 0.68-2.77), and fish intake with eczema (RR: 1.26; 95% CI:0.72-2.20) were not affected by follow-up duration (Table 2).
3.5 Publication bias
Supplemental 3 presented the results of publication biases. No significant publication biases were detected for fish intake during pregnancy with wheeze (PEgger: 0.109;PBegg: 0.221), and eczema risk(PEgger: 0.504;PBegg: 0.707). No significant publication bias for fruit and vegetables intake during pregnancy and wheeze risk was detected(PEgger: 0.619;PBegg: 0.602). No significant publication bias was noted for vitamin E intake during pregnancy and wheeze risk (PEgger: 0.488;PBegg: 0.806). Although the result of Begg test indicated no significant publication bias for fruit and vegetables intake during pregnancy and asthma risk (P= 0.230), whereas potential publication bias was observed from the result of Egger test (P= 0.075). The pooled conclusions were stability after adjusted using the trim and fill method [31].
4. Discussion
This study included prospective cohort studies and explored any potential role of nutrients intake during pregnancy with rhinitis, asthma, eczema, wheeze, and food allergy risk in offspring.The current comprehensive, quantitative study enrolled 210 817 participants from 23 studies with broad individuals’ characteristics range. This study indicated increased vitamins D and E, zinc, and milk intakes during pregnancy could protect against wheeze risk.Highβ-carotene and magnesium intakes during pregnancy could prevent the development of eczema. In addition, the risk of asthma was significantly reduced when pregnant women with high intake of vitamin D and apple. Finally, high meat, butter and margarine, and folic acid intakes during pregnancy could induce additional risk of wheeze, eczema, and asthma, respectively. These conclusions are stability, and stratified by age of outcome measured in childhood. As compared with previous studies [9-19], the current study provides comprehensive results for pregnant women nutrients intake and subsequent rhinitis, asthma, eczema, wheeze, and food allergy risk in offspring, and the conclusions with high reliable since retrospective studies were excluded.
The summary results indicated that pregnant women’s vitamin D or E, zinc, and milk intakes could prevent the risk of wheeze in offspring, whereas high meat intake was associated with an increased risk of wheeze in offspring. The reasons for above results included:(1) vitamin D could modulate the antigen-presenting cells, includingmacrophages and regulatory T cells [55-57]; (2) vitamin E intake could accelerate growth in hypoplastic lung, increase lung complexity,surface area, and bud count [58]; (3) the function of transcription factor, antioxidant defense, and DNA repair could be affected by zinc, which could affect Th1 cytokine secretion and Th2 cytokine responses [59-61]; (4) the protective effect of milk intake could be caused by calcium, vitamin A, and other microbial agents, which needed further detailed analysis [62,63]. Moreover, the maternal microbiome could affect the fetal immune system, mainly focused on the regulatory immune status between maternal and infant, or microbial metabolites and immunoglobulin G through transplacental passage [64]; and (5) meat including meat products and processed meat, which contained rich trans-fatty acids, which are significantly correlated with inflammation status [65,66]. Moreover, we noted increasedβ-carotene and magnesium intakes during pregnancy could protect against eczema risk in offspring, whereas pregnant women’s intake of butter and margarine induce excess eczema risk in offspring. The potential reasons included: (1) the antioxidant effect ofβ-carotene could adjust immune tolerance, which could affect the progression of allergic disease in children; (2) magnesium might play a beneficial effect on hyperactivity and pulmonary functions,which associated with lower risk of asthma and allergies [67,68]; and(3) the potential harmful effects of butter and margarine could be due to high content of proinflammatoryn-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in them [69]. Finally, increasing vitamin D and apple intakes during pregnancy played beneficial effects on asthma risk in offspring,whereas increasing folic acid during pregnancy induced additional risk of asthma in offspring. The reasons for the above results could be due to: (1) the association of vitamin D and asthma could regulate to T helper 2 cell differentiation; (2) the potential beneficial effect of apple could due to the phytochemical content; and (3) there was potential difference for women with intake of folic acid and women presented unknown causes of asthma. Finally, the risk of food allergy in offspring were not affected by the intakes of vitamin A, C, or E,β-carotene, folic acid, zinc, and fish in pregnancy, which could explain by smaller number of studies reported the risk of food allergy related to nutrients intake during pregnancy.
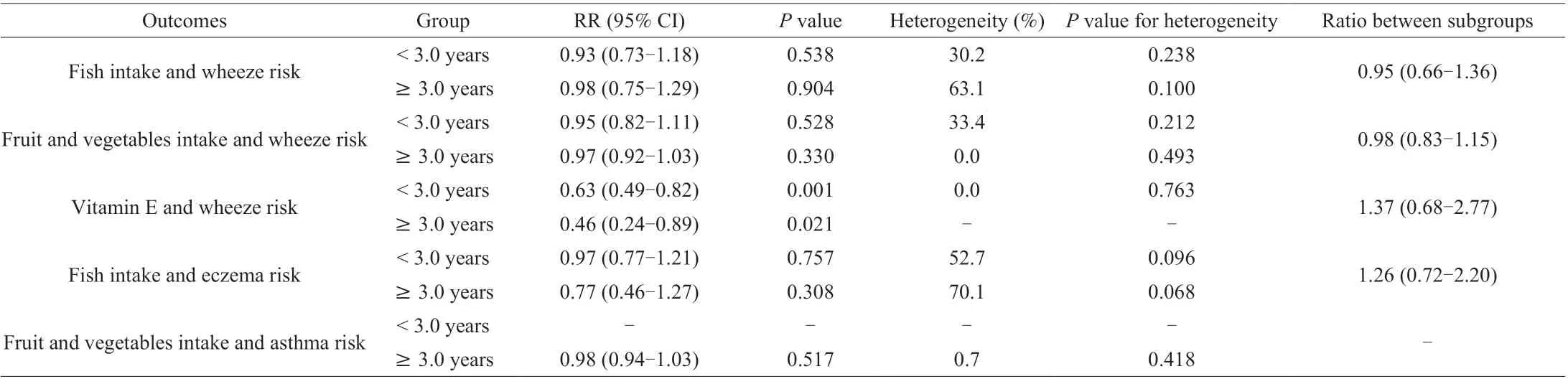
Table 2 Subgroup analyses for outcomes reported ≥ 5 cohorts based on age at outcomes.
The strengths in our study included: (1) this study only included prospective cohort studies, which could eliminate selection and recall biases that may be concerned in retrospective observational or crosssectional studies; (2) a comprehensive results regarding the nutrients intake during pregnancy on rhinitis, asthma, eczema, wheeze,and food allergy risk in offspring was summarized; (3) the large number of enrolled individuals allowed us quantitatively evaluated pregnant women nutrients intake with the risk of rhinitis, asthma,eczema, wheeze, and food allergy in offspring, and the conclusions were robustness. The shortcomings of this study included: (1) the associations for several specific nutrients are available in smaller number of studies, and these conclusions were variable; (2) the adjusted factors are different in the studies, which might affect the results; (3) the analysis focused on rhinitis, asthma, eczema, wheeze,and food allergy, while several other allergic diseases should be explored in further studies; and (4) the analyze using published data,and publication bias was inevitable.
In conclusions, the intakes of vitamins D and E, magnesium,β-carotene, zinc, milk, and apple in pregnancy could prevent the risk of childhood allergic disease, whereas increasing meat, butter and margarine, and folic acid intakes during pregnancy could induce additional risk of allergic disease in offspring. Further large-scale prospective cohort study and randomized controlled trial should be performed to explore the effective nutrition intervention strategy for preventing allergic diseases in childhood.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Science (CIFMS 2019-I2M-5-024).
Availability of data and materials
Since it is a meta-analysis study, all data from published literatures, so all data were available.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was waived by the institutional review board because this is a meta-analysis.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at http://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2022.09.004.
- 食品科學(xué)與人類健康(英文)的其它文章
- Maternal obesity exacerbates the responsiveness of offspring BALB/c mice to cow’s milk protein-induced food allergy
- Au@Ag-labeled SERS lateral f low assay for highly sensitive detection of allergens in milk
- Impact of three different processing methods on the digestibility and allergenicity of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) tropomyosin
- Effect of lipid peroxidation on the allergenicity and functional properties of soybean β-conglycinin (7S) and glycinin (11S)
- Comparative acetylome analysis reveals the potential mechanism of high fat diet function in allergic disease
- Therapeutic effects of epigallocatechin and epigallocatechin gallate on the allergic reaction of αs1-casein sensitized mice

