Molecular Modulation of Structure and Ferroelectric Performance of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Free Standing Films from Aspects of Molecular Weight and Crystallization Temperature
MENG Nan(孟 楠), LIAO Yaozu(廖耀祖)*
1 State Key Laboratory for Modification of Chemical Fibers and Polymer Materials, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China2 College of Materials Science and Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
Abstract: Ferroelectric polymer poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) has received great research interest because of its special electroactive properties which are strongly dependent on the crystalline structures and in turn processing conditions. The effect of molecular weight and crystallization temperature on the micro-structure and macro-properties of PVDF films casted from dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) solvent is investigated. The results demonstrated that a low molecular weight (180 kg/mol) and a low evaporation temperature (50 ℃) favored the formation of polar γ-phase, while a high molecular weight (1 000 kg/mol) and a high evaporation temperature (125 ℃) made PVDF crystallize into α-phase. Compared with films casted at 50 ℃, films casted at 125 ℃ exhibited higher dielectric loss at a low electric field and less loss conductivity at a high electric field, which was due to their low degrees of crystallinity and fine evaporation of the solvent, respectively. PVDF with a molecular weight of 180 kg/mol casted at 125 ℃ exhibited the highest remnant polarization (0.062 C/m2) among all of the solution-processed films, being a result of high chain mobility resulted from the low molecular weight.
Key words: ferroelectric polymer; poly(vinylidene fluoride)(PVDF); solution casting; remnant polarization; dielectric constant
Introduction
Recently, as an important category of functional polymers, poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) based ferroelectric polymers have raised great academic and industrial interests, being mainly ascribed to their excellent electroactive properties such as dielectric, piezoelectric, and ferroelectric properties[1-4]. These properties enable them to be utilized in various applications, especially in dielectric capacitors for energy storage, pressure sensors and touch screens, non-volatile memories,etc.[5-8].
PVDF is a semi-crystalline polymer with at least four crystalline phases[9], arising from differently adopted chain conformations:α-phase with trans-gauche (TG) chain conformation (antiparallel packing of two adjacent chains),δ-phase with TG chain conformation (parallel packing of two adjacent chains),β-phase with all-trans (TTT) chain conformation, andγ-phase with mixed chain conformation of T3GT3G′. Among all of these phases,α-phase is non-polar because of the self-cancellation of dipole moment. When cooled from the melt, theα-plase usually forms and undergoes a phase transition toδ-phase at an applied electric field of 170 kV/mm, and further toβ-phase at 500 kV/mm[10-11]. Bothδ-phase andβ-phase are polar phases, and especiallyβ-phase has the highest dipole moment 7×10-30C·m perpendicular to the chain axis, and favourable piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties (piezoelectric coefficientd33: about 20-30 pC/N; spontaneous polarization: 0.13 C/m2)[9,12]. Treatingα-phase at a relatively high temperature (167-180 ℃) and high pressure (200 kPa) can transform the material toγ-phase[13].γ-phase can be also formed with the inclusions of specific fillers such as clays[14]or carbon materials[15]. Even thoughβ-phase exhibits the highest polarity, the transparency ofβ-PVDF is deteriorated on account of post-treatment[16], which makes the highly transparentγ-PVDF more attractive for practical applications. It was documented thatγ-phase could exhibit better dielectric energy storage properties compared toβ-phase because of the absence of early polarization saturation[17-18]. It was also reported that pureγ-phase could be formed when crystallized from the solvent[11]. However, there are controversies with respect to the formed crystalline phases using solution casting methods[19-20]. Herein, in order to clarify the crystalline structures of PVDF formed during solvent crystallization, PVDF with different molecular weightsMw(180, 534, and 1 000 kg/mol) is casted from dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) solvent at two different temperatures of 50 ℃ and 125 ℃. Through the characterization of structure, dielectric and ferroelectric properties, the crystallization features and ferroelectric properties of solution casting processed PVDF are analyzed.
1 Experiments
1.1 Materials
PVDF (molecular weight: 180 kg/mol and 534 kg/mol) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Limited Liability Company(Missouri, USA). PVDF (Solef?5130; molecular weight: 1 000-1 200 kg/mol) was purchased from Solvay (Brussels, Belgium). DMSO (anhydrous, ≥99.9% in mass fraction, Sigma-Aldrich, Missouri, USA) with a density of 1.10 g/cm3was used as casting solvent.
1.2 Preparation of PVDF films
Appropriate amounts of PVDF powders or pellets were dissolved into DMSO to obtain a solution with a weight concentration of 10%. The mixtures were magnetically stirred at 70 ℃ for 2 h to fully dissolve PVDF. The solution was then casted on a glass petri dish, which was then incubated in a vacuum oven at 50 ℃ and 125 ℃ for at least 24 h. The thickness of solution casted(SC) films was about 50-100 μm. A list of films produced in this work is presented in Table 1.
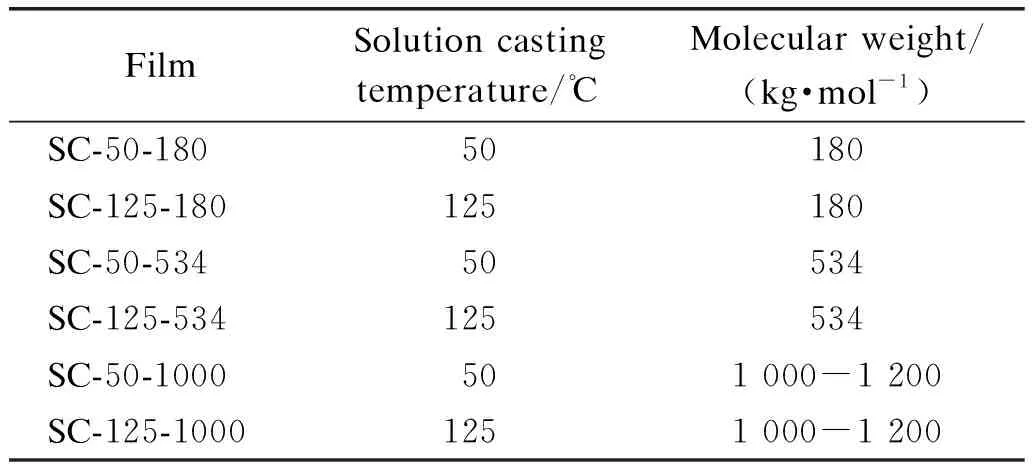
Table 1 Denoted names, preparation temperatures and molecular weights of produced films
1.3 Instruments
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (FEI Inspector-F, the Netherlands) was used to characterize the morphology of the film surface. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) (Tensor 27, Bruker Optik GmbH, Germany) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Cu/Kα(λ= 0.154 18 nm) and 2θrange of 5°-70° (X’Pert Pro, PANalytical, the Netherlands) were used to characterize the crystalline structure of PVDF films. The thermal analysis of PVDF films was conducted using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) (DSC 25, TA Instruments, Belgium) with a temperature range of 25-200 ℃ and a heating rate of 10 ℃/min. The frequency dependence of dielectric spectra under an applied voltage of 0.5 V was characterized using a Precision Impendence Analyzer (4294A, Agilent, USA) at room temperature with frequency ranging from 100 Hz to 100 MHz. The ferroelectric hysteresis loops were measured using a ferroelectric tester (National Physical Laboratory, UK) with a triangle waveform at room temperature and 10 Hz[21]. Gold was sputtered on both sides of films to serve as electrodes for electric measurement. The diameter of electrodes for dielectric and ferroelectric characterization was 5 mm and 2 mm, respectively.
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Morphology control of solution casted PVDF films
The morphology analysis was elucidated using SEM. Films crystallized at 50 ℃ were highly porous and contained some slackly aggregated beads except for samples with ultrahigh molecular weight (1 000-1 200 kg/mol) which displayed a homogenous and smooth morphology shown in Fig. 1(a). The formed beads are suggested to be crystals since PVDF is a semi-crystalline polymer. Films formed from solution at 125 ℃ clearly displayed the morphology of spherulites shown in Fig. 1(b), where large spherulites with a diameter of about 40-50 μm could be seen in samples with a low molecular weight (180 kg/mol), and slightly irregular and smaller spherulites (about 25 μm) were formed in samples with a moderately higher molecular weight (534 kg/mol). A different morphology, ring-banded spherulite with separated lamellae bundles[22], was obtained in films produced at 125 ℃ with ultrahigh molecular weight (1 000 kg/mol). More details about crystallization characteristics will be discussed in section 2.2.
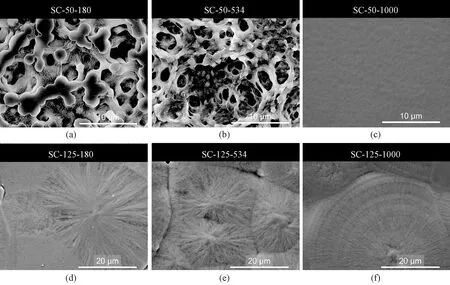
Fig. 1 SEM images for the surface of SC PVDF films with different molecular weights at different casting temperatures: (a) 50 ℃ with Mw of 180 kg/mol; (b) 50 ℃ with Mw of 534 kg/mol; (c) 50 ℃ with Mw of 1 000 kg/mol; (d) 125 ℃ with Mw of 180 kg/mol; (e) 125 ℃ with Mw of 534 kg/mol; (f) 125 ℃ with Mw of 1 000 kg/mol
2.2 Crystallization features of SC PVDF films
2.2.1Determinationofcrystallinephase
The crystalline structure of PVDF films was determined using FTIR shown in Fig. 2(a) and XRD shown in Fig. 2(b). FTIR shows characteristic bands for different phases[23-24].α-phase: 612, 766, 975, and 1 212 cm-1;β-phase: 840 cm-1and 1 270 cm-1;γ-phase: 812, 835, 840, and 1 234 cm-1. The sample with the highest molecular weight (1 000 kg/mol) casted at 125 ℃ (SC-125-1000) showed the invisible band at 835-840 cm-1, which suggested the almost pureα-phase crystallized in SC-125-1000 sample. The other films show the appearance of 835-840 cm-1, which demonstrates the possible existence of polarβ-phase andγ-phase. Bands at 1 270 cm-1(exclusive toβ-phase) and 1 234 cm-1(exclusive toγ-phase) were used to resolve the crystalline characterization. The absence of 1 270 cm-1band (β-) and the presence of 1 234 cm-1(γ-) highlighted the fact that the 835-840 cm-1band was only ascribed toγ-phase not to the combined contributions ofβ-phase andγ-phase, which suggested that PVDF did not form intoβ-phase when casted from DMSO solvent (dipole moment: 1.32×10-29C·m).
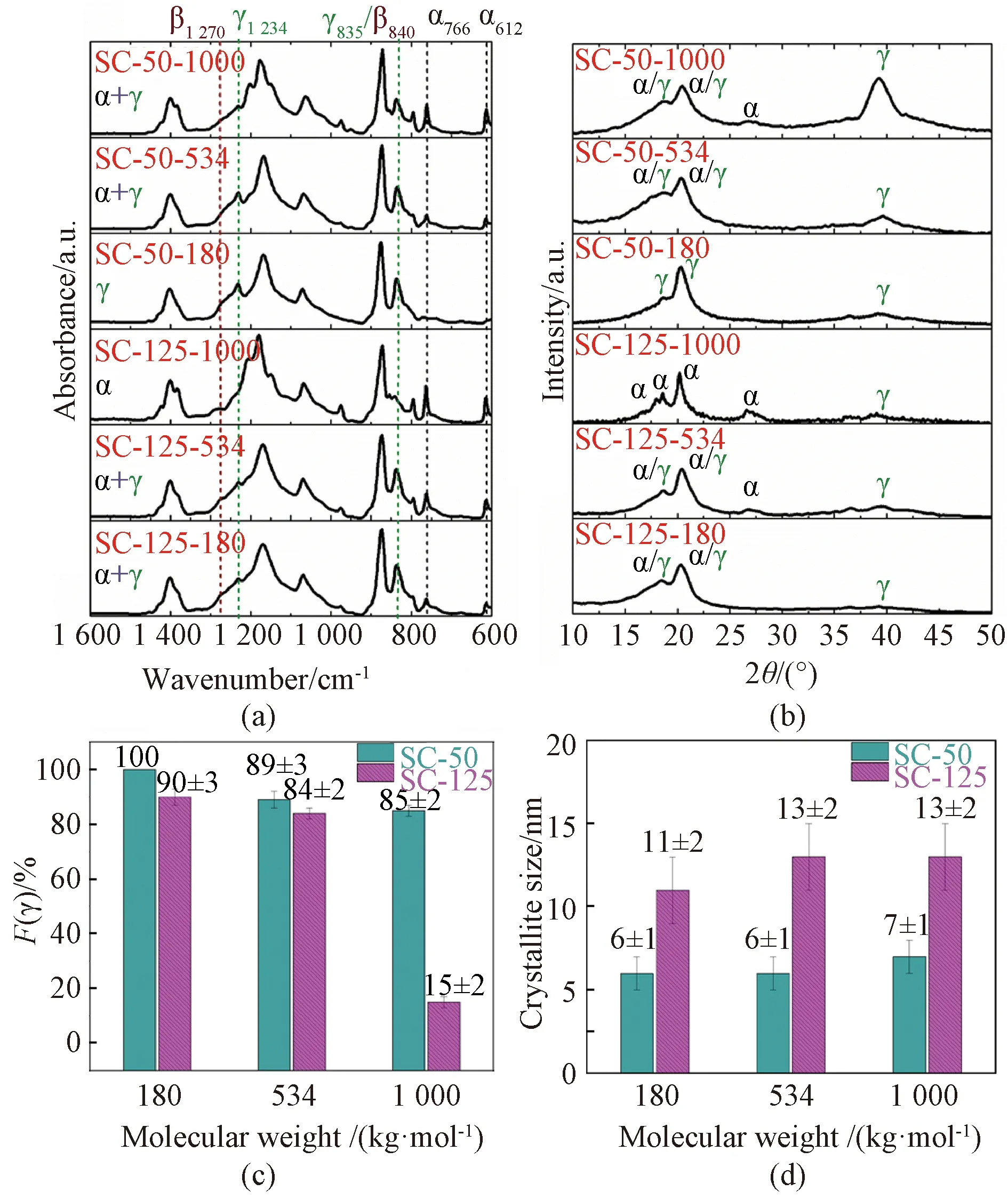
Fig. 2 Phase determination of SC PVDF films with different molecular weights at different casting temperatures: (a) FTIR; (b) XRD; (c) content of γ-phase of SC samples calculated from FTIR data; (d) average mean size of crystallites calculated from XRD data
The above results are consistent with the previous studies thatβ-phase only forms from the solvent with high dipole moment. For example, PVDF casted from hexamethylphosphoramide (HMPA) (dipole moment: 1.85×10-29C·m) can crystallize intoβ-phase regardless of casting temperatures ranging from 60-140 ℃[25]. PVDF with the lowest molecular weight (180 kg/mol) crystallized into the pureγ-phase when casted at a low temperature of 50 ℃ (SC-50-180), as concluded from the absence ofα-characteristic bands (766 cm-1and 612 cm-1). FTIR can also be used to determine the phase content of PVDF. The SC PVDF films only containedα-phase andγ-phase. Therefore, the content ofγ-phaseF(γ)[23]was calculated by
(1)
whereAαandAγare the absorbances at 766 cm-1and 835 cm-1, respectively;KαandKγare the corresponding absorbance coefficients, which are 0.365 μm-1and 0.150 μm-1, respectively. The calculated results are depicted in Fig. 2(c). It is clearly concluded that the low casting temperature and the low molecular weight favour the formation of polarγ-phase.
Contrary to FTIR, XRD can only be used to qualitatively analyze the crystalline structure of PVDF, sinceα-phase,β-phase andγ-phase show diffraction peaks at very close position (about 20.0°-21.0°), 20.0° (110) for pureα-phase, 20.7° (110)/(200) for pureβ-phase, and 20.4° (110)/(101) for pureγ-phase[11].
All of the films show diffraction peaks at 20.0°-20.4° with no appearance of a peak at 20.7°, being consistent with FTIR data that DMSO SC PVDF films does not crystallize intoβ-phase. In addition to 20.0° (110),α-PVDF also exhibits peaks at 17.8°, 18.4° and 26.6°, which corresponds to the diffraction of (100), (020), and (021). Similarly,γ-PVDF shows diffraction peaks at 18.5° and 39.0° which are ascribed to the crystal planes of (020) and (211). The peak at 26.6° (021) is exclusive toα-phase. Samples with a higher content ofα-phase (weight ratio >15%) for example PVDF with the highest molecular weight (1 000 kg/mol) and the one with a moderate molecular weight casted at a high temperature (534 kg/mol at 125 ℃) clearly displayed peaks at 26.6°. The average size of crystalliteτwas evaluated using the diffraction at 2θ≈20° and Scherrer equation, which was shown as
(2)
whereKis dimensionless shape factor and equals 0.89;γis the wavelength of X-ray and is 0.154 06 nm;Bis the full width at half maximum (FWHM);θis a Bragg angle that corresponds to diffraction of (110)αand (110)/(101)γ. The calculated values are described in Fig. 2(d), where films formed at a low temperature (50 ℃) show a smaller mean size of crystallites (about 6 nm), being half of the samples ( about 12 nm) casted at a high temperature (125 ℃).
2.2.2Thermalanalysis
The thermal properties of SC films were characterized using DSC (shown in Fig. 3). The degree of crystallinity was evaluated using the ratio between the experimental fusion enthalpy and the theoretical value for a fully crystalline PVDF (104.6 J/g)[26]. The melting temperatureTmof PVDF samples is in the range of 160-172 ℃, and for PVDF with the same molecular weight, theTmpeaks are at almost the same position. However, the degree of crystallinity varies with the solution casting temperature. Films formed at 50 ℃ exhibit higher degrees of crystallinity (about 55%) compared to samples formed at 125 ℃ (40%-45%).
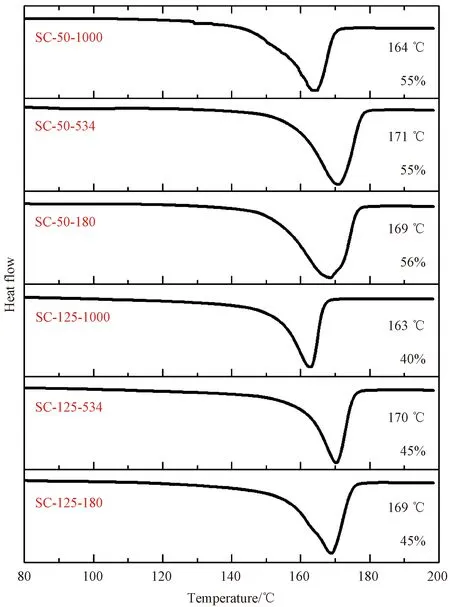
Fig. 3 DSC analysis of SC PVDF films with different molecular weights at different casting temperatures
2.2.3Discussionofcrystallizationfeatures
The formed crystalline phase of PVDF is under the combined influence of crystallization temperatures and molecular weights. The high polarity of DMSO at a low temperature of 50 ℃ enables strong interaction between PVDF and DMSO, which induces the rotation of C—F bonds around polymer chain backbones and the formation of polar phases. However, the polarity of DMSO decreased and the chain mobility of PVDF increased at a high temperature of 125 ℃, which hindered the interaction between PVDF and DMSO, leading to the formation ofα-phase with trans-gauche chain conformation. As a result, PVDF with a molecular weight of 180 kg/mol crystallized into pureγ-phase when casted at 50 ℃ shown in Fig. 2(c). With respect to the molecular weight, a high molecular weight corresponds to low chain mobility, which is similar to the effect of decreasing the crystallization temperature. Therefore, PVDF with a high molecular weight of 1 000 kg/mol tended to crystallize intoα-phase. Apart from the crystalline phase, the low casting temperature enhances the degree of crystallinity of processed PVDF films shown in Fig. 3. One possible reason could be that the crystallization time was extended at a low evaporation temperature[27], giving PVDF more time to crystallize. Moreover, a low casting temperature favours the process of nucleation but hinders the growth of crystallites, as a result, PVDF films casted at 50 ℃ have smaller crystallites compared to films produced at 125 ℃ because of the reduction of the nucleus and the obstruction of crystal growth.
2.3 Dielectric and ferroelectric properties
The frequency dependence of dielectric spectra is shown in Fig. 4. All of the films exhibit similar values(about 12±2) of dielectric constants at 100 Hz, and display relaxation loss peaks above 100 kHz which is related to the dipolar relaxation of polymer chains in amorphous regions[28]. SC-50-1000 shows the lowest dielectric constant, being ascribed to the low mobility of polymer chains due to the ultrahigh molecular weight, which discourages the response of dipoles to applied external voltage. It is clearly suggested that the relaxation peaks of films casted at 125 ℃ show higher values of loss compared to films casted at 50 ℃. The dielectric response at low voltage (0.5 V) mainly arises from dipoles in the amorphous region. A high loss relaxation peak can be linked to a low degree of crystallinity, which is consistent with DSC results suggesting that films casted at 125 ℃ exhibit low degrees of crystallinity.
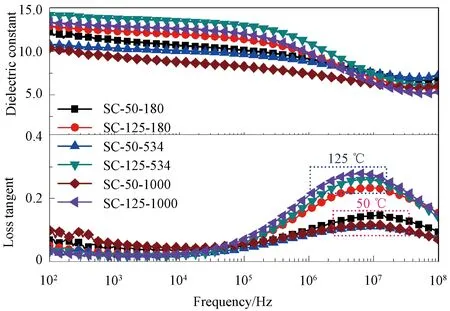
Fig. 4 Frequency dependence of dielectric properties of SC PVDF films with different molecular weights at different casting temperatures
The ferroelectric properties of current-electric field (I-E) and displacement-electric field (D-E) loops of SC PVDF films are shown in Fig. 5. PVDF with a low molecular weight of 180 kg/mol displayed an obvious ferroelectric switching feature with switching current peaks at an electric field of 70-80 kV/mm. However, PVDF with a high molecular weight (534 kg/mol and 1 000 kg/mol) exhibited high loss conductivity corresponding to large slopes of I-E loops, and did not show apparent switching current peaks especially for PVDF casted at 50 ℃. The high loss conductivity can be attributed to the residual solvent caused by a low evaporation temperature. A high molecular weight contributes to low chain mobility that could be the reason for less obvious peaks of switching current, since the ferroelectric switching of PVDF is accomplished by the collaborative long-range rotation of polymer chains, and low chain mobility hinders the rotation of polymer chains[29]. Especially for PVDF with 180 kg/mol, films casted at 125 ℃ showed the highest remnant polarization (0.062 C/m2), being a result of a high fraction of polarγ-phase (about 90%) and well evaporation of DMSO solvent.
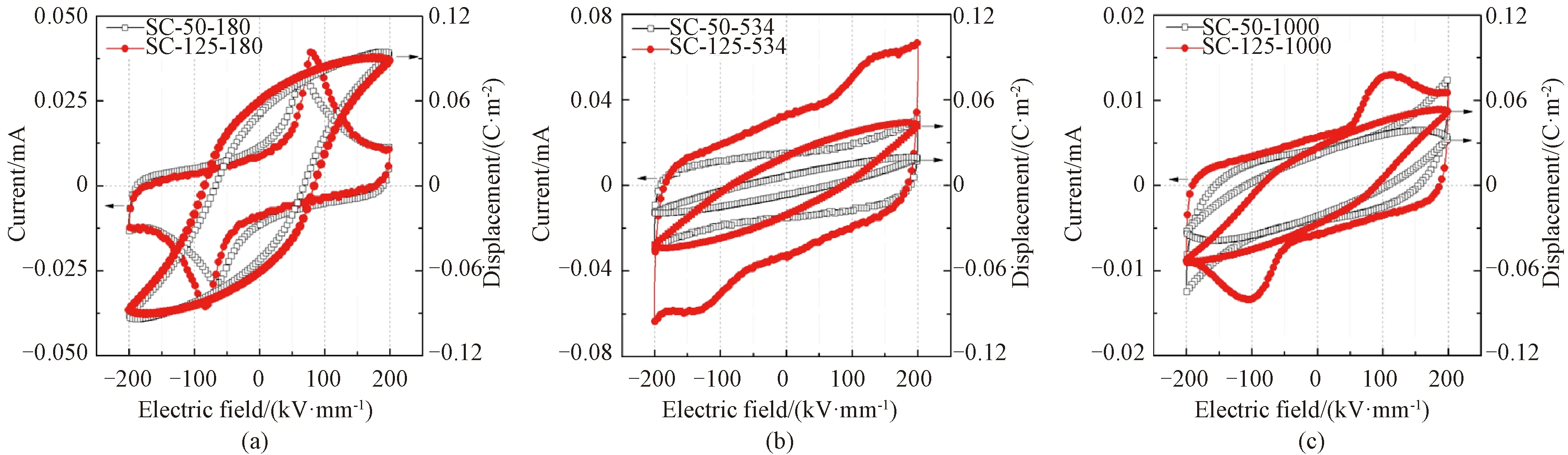
Fig. 5 Ferroelectric properties of PVDF films with different molecular weight solution casted at 50 ℃ and 125 ℃: (a) 180 kg/mol; (b) 534 kg/mol; (c) 1 000 kg/mol
3 Conclusions
The crystallization characteristics of PVDF casted from DMSO solvent were studied in this work, where the crystalline phase, crystallinity and average crystallite size are influenced by the molecular weight and the evaporation temperature of the solvent. A low molecular weight (180 kg/mol) and a low evaporation temperature (50 ℃) favour the formation of polarγ-phase, while PVDF with a high molecular weight (1 000 kg/mol) casted at a high temperature (125 ℃) predominantly crystallized intoα-phase. Films casted at 125 ℃ exhibited high dielectric loss, being a result of a low degree of crystallinity. On the contrary, films casted at a high temperature showed less conductivity loss at 200 kV/mm, which was ascribed to the fine evaporation of the solvent. Moreover, high chain mobility resulted from a low molecular weight allowed PVDF to display obvious ferroelectric switching. As a result, PVDF with 180 kg/mol casted at 125 ℃ exhibited the highest remnant polarization (0.062 C/m2) among all of the solution-processed films.
 Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2022年1期
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2022年1期
- Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Sentiment Lexicon Construction Based on Improved Left-Right Entropy Algorithm
- Expert Knowledge-Based Apparel Recommendation Question and Answer System
- Global Existence and Decay of Solution to Parabolic-Parabolic Keller-Segel Model in Rd
- Theoretical Calculation and Analysis of Muffler Based on Multilayer Sound Absorbing Material
- Preparation of Polyaniline/Cellulose Nanofiber Aerogel for Efficient Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution
- Consensus for High-Order Linear Multi-Agent Systems with Unknown but Bounded Measurement Noises
