Shoulder adhesive capsulitis in cancer patients undergoing positron emission tomography - computed tomography and the association with shoulder pain
Daichi Hayashi, Elaine Gould, Robert Shroyer, Eric van Staalduinen, Jie Yang, Musa Mufti, Mingqian Huang
Daichi Hayashi, Elaine Gould, Robert Shroyer, Eric van Staalduinen, Musa Mufti, Mingqian Huang,Department of Radiology, State University of New York at Stony Brook, Stony Brook, NY 11794, United States
Jie Yang, Department of Family, Population and Preventive Medicine, Stony Brook Medicine,Stony Brook, NY 11794, United States
Abstract BACKGROUND Adhesive capsulitis is a relatively common condition that can develop in cancer patients during treatment. Positron emission tomography - computed tomography (PET-CT) is routinely performed as a follow-up study in cancer patients after therapy. Being aware of PET-CT findings to suggest shoulder adhesive capsulitis may help to alert clinicians for the diagnosis of unsuspected shoulder capsulitis.AIM To assess the association of shoulder adhesive capsulitis with cancer/therapy type and symptoms in cancer patients undergoing PET-CT.METHODS Our prospective study received Institutional Review Board approval. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients, who answered a questionnaire regarding shoulder pain/stiffness at the time of PET-CT study, between March 2015 and April 2019. Patients with advanced glenohumeral arthrosis, metastatic disease or other mass in the shoulder, or shoulder arthroplasty were excluded.Patterns of shoulder capsule 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake were noted.Standard Uptake Value (SUV)max and SUVmean values were measured at rotator interval (RI) and deltoid muscle in bilateral shoulders. Normalized SUV (SUV of RI/SUV of deltoid muscle) was also calculated. We assessed if SUV values are different between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients in both shoulders.Covariates were age, gender, and therapy type (surgery, chemotherapy, radiation). Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to compare unadjusted marginal differences for age, SUV measurements between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. Multiple linear regression models were used to examine the relationship between right or left shoulder SUV measurements and symptom status, after adjusting for covariates. Statistical significance level was set at P < 0.05.RESULTS Of 252 patients initially enrolled for the study (mean age 66 years, 67 symptomatic), shoulder PET-CT data were obtained in 200 patients (52 were excluded due to exclusion criteria above). The most common cancer types were lymphoma (n = 61), lung (n = 54) and breast (n = 53). No significant difference was noted between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients in terms of age, gender,proportion of patients who had surgical therapy and radiation therapy. A proportion of patients who received chemotherapy was higher in patients who were asymptomatic in the right shoulder compared to those symptomatic in the right shoulder (65% vs 48%, P = 0.012). No such difference was seen for the left shoulder. In both shoulders, SUVmax and SUVmean were higher in symptomatic shoulders than asymptomatic shoulders (Left SUVmax 2.0 vs 1.6, SUVmean 1.6 vs 1.3, both P < 0.002; Right SUVmax 2.2 vs 1.8, SUVmean 1.8 vs 1.5, both P < 0.01).For lung cancer patients, bilateral RI SUVmax and SUVmean values were higher in symptomatic shoulders than asymptomatic shoulders. For other cancer patients, symptomatic patients had higher left RI SUVmax/mean than asymptomatic patients after adjustment.CONCLUSION In symptomatic patients metabolic activities in RI were higher than asymptomatic patients. Adhesive capsulitis should be considered in cancer patients with shoulder symptoms and positive FDG uptake in RI.
Key Words: Adhesive capsulitis; Positron emission tomography - computed tomography;Cancer; Shoulder; Pain; Imaging
INTRODUCTION
Adhesive capsulitis is a relatively common and potentially debilitating disorder of the shoulder joint, with most common onset in the 5to 6decades. Typical clinical presentation include shoulder pain, stiffness, and loss of range of motion, and can persist for extended periods of time if not adequately addressed clinically[1-4]. While adhesive capsulitis is a clinical diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is currently the most commonly used imaging tool for its diagnosis[5-7], however not all cancer patients undergo MRI of the shoulder unless there is specific clinical suspicion for adhesive capsulitis or other shoulder-specific pathology. Positron emission tomography - computed tomography (PET-CT) is a useful imaging modality for cancer diagnosis, particularly for the purpose of staging and follow-up of malignancy. PETCT is also useful in monitoring inflammatory disorders, and the shoulder joint can be hypermetabolic on PET-CT when there is active inflammation such as osteoarthritis,inflammatory and infectious arthritis, bursitis, rotator cuff injury, and adhesive capsulitis[8,9]. However, there has been relatively scant literature evidence on PET-CT findings specific to adhesive capsulitis. One study demonstrated radiotracer uptake in the joint capsule of the glenohumeral joint connecting the rotator interval, anterior joint capsule, and axillary recess is related to adhesive capsulitis[10]. Another study found secondary adhesive capsulitis (depicted by PET-CT) after modified radical mastectomy for breast cancer was common (9.6%) and differed in severity and the progression pattern depending on whether the range of motion in the shoulder was mildly or severely limited[11]. Given the fact that PET-CT imaging is routinely performed as a follow-up study in cancer patients after therapy, being aware of PETCT findings to suggest shoulder adhesive capsulitis may help to alert clinicians for the diagnosis of unsuspected shoulder capsulitis and avoid potential misdiagnosis of cancer progression, while simultaneously allowing for earlier initiation of appropriate therapy of capsulitis to potentially improve outcomes. Therefore, the aims of our study were to: (1) Evaluate the frequency of shoulder capsulitis in cancer patients undergoing PET-CT; (2) Determine if there is correlation between cancer type/treatment regimen and frequency of adhesive capsulitis; and (3) Evaluate if metabolic activities in the rotator interval (RI) are different between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data collection
Our prospective study received Institutional Review Board approval at our institution(Protocol# 2015-3396-R2). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.All participants (cancer patients) answered a questionnaire regarding shoulder pain or stiffness and its duration at the time of presentation to an imaging study at our institution (outpatient cancer center) between March 2015 and April 2019. Questions included: Do you have shoulder pain or stiffness (yes/no, if yes, which side); if yes,how long have you had shoulder pain? Have you noticed decreased range of motion in the affected shoulder (yes/no)? Is the symptom worse at any particular time of day?Do you have difficulty raising arms above your head or moving your arms behind back (yes/no)? Electronic medical chart review was performed to collect demographic information (age and gender) as well as details of cancer type and treatment regimen(type and date of surgery, type and date/duration of chemotherapy, and type and date/duration of radiation therapy). All eligible cancer patients who presented to our outpatient imaging center for PET-CT imaging within the recruitment period and were willing to participate in the study were included in our study. Patients with advanced glenohumeral arthrosis, metastatic disease or other mass lesion in the shoulder (all of which could give positive FDG uptake without adhesive capsulitis), or history of shoulder arthroplasty were excluded.
PET-CT image acquisition and interpretation
All patients fasted for at least 6 hours prior to thePET-CT scan. Blood glucose levels were measured before the injection of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) and were lower than 200 mg/dL in all patients. PET-CT was performed using a Siemens Biograph LSO(Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany). Whole-body CT from the basal skull to the thigh was performed with a continuous spiral technique on a 40-slice helical CT scanner (120 kV; 65 mAs, slice thickness of 4 mm) in the supine position with the arms down. Next, an emission scan was performed from head to thigh at 3 min per frame at 60 min after the intravenous injection of 0.14 mCi/kg of 18F-FDG. CT data were used for attenuation correction and PET images were reconstructed with a threedimensional (3D) ordered-subsets expectation maximization algorithm (20 subsets,two iterations). CT and PET scan data were accurately coregistered on a dedicated workstation.
We evaluated the intensity of 18F-FDG accumulation as standardized uptake values(SUVs), defined as the tissue concentration divided by the activity injected per body weight. A region of interest was drawn in transaxial images showing FDG uptake within the RI and also low grade FDG uptake at the deltoid muscle. SUVs were measured at the RI and the deltoid muscle from attenuation-corrected axial images.Maximum SUV (SUVmax) at a pixel with the highest uptake of 18F-FDG within each region of interest (ROI) as well as the mean SUV (SUVmean) of each ROI were recorded in bilateral shoulders. Normalized SUV (SUV of RI/SUV of deltoid muscle)was also calculated. None of the ROIs included osseous structures or muscles other than deltoid to exclude the effect of the tracer uptake at the bone marrow and other muscles.
Patterns of shoulder capsule 18F-FDG uptake were recorded on PET-CT scan by two experienced board-certified musculoskeletal radiologists and a Musculoskeletal Radiology Fellow, blinded to clinical information. FDG uptake was considered positive and suggestive of adhesive capsulitis if there was hypermetabolism corresponding to the location of RI on fused PET-CT images.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using SAS9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC) to assess if SUV values are different between patients with and without symptoms in both shoulders. Covariates were age, gender, history of therapy (surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation). Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to compare unadjusted marginal differences for age, SUV measurements between patients with and without shoulder symptoms. Multiple linear regression models were used to examine the relationship between right or left shoulder SUV measurements and symptom status,after adjusting for cancer type, therapy status, gender and age. To enable meaningful statistical analyses, cancer types were classified into the following 5 categories; Breast,lung, lymphoma, “multiple” (= patients who had two or more cancers), and “other” (=includes the rest of patients with only one cancer that is other than breast cancer, lung cancer or lymphoma). Interaction of shoulder symptom status and cancer type was also included in the models to model the differences within each specific cancer types.Statistical significance level was set at< 0.05.
RESULTS
252 patients were initially enrolled (143 women, 109 men, mean age 66 years, 67 symptomatic). Of these, two patients had right sided shoulder arthroplasty and one patient had left sided shoulder arthroplasty, and these affected shoulders were excluded from analyses. One patient had a large mass in the left proximal humerus,and was also excluded from analysis. Other patients who did not have PET-CT imaging of shoulders (patients who had brain PET-CT only, or bilateral shoulders being outside the field of view) or other applicable exclusion criteria described earlier were also excluded. In the end, there were 200 right shoulder PET-CT imaging, and 200 Left shoulder PET-CT imaging. Most common cancer types were lymphoma (=61), lung (= 54) and breast (= 53) (Table 1). No statistically significant difference was noted between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients in terms of age, gender,proportion of patients who had surgical therapy and radiation therapy. A proportion of patients who received chemotherapy was higher in patients who were asymptomatic in the right shoulder compared to those symptomatic in the right shoulder (65%48%,= 0.012). No such difference was seen for the left shoulder.
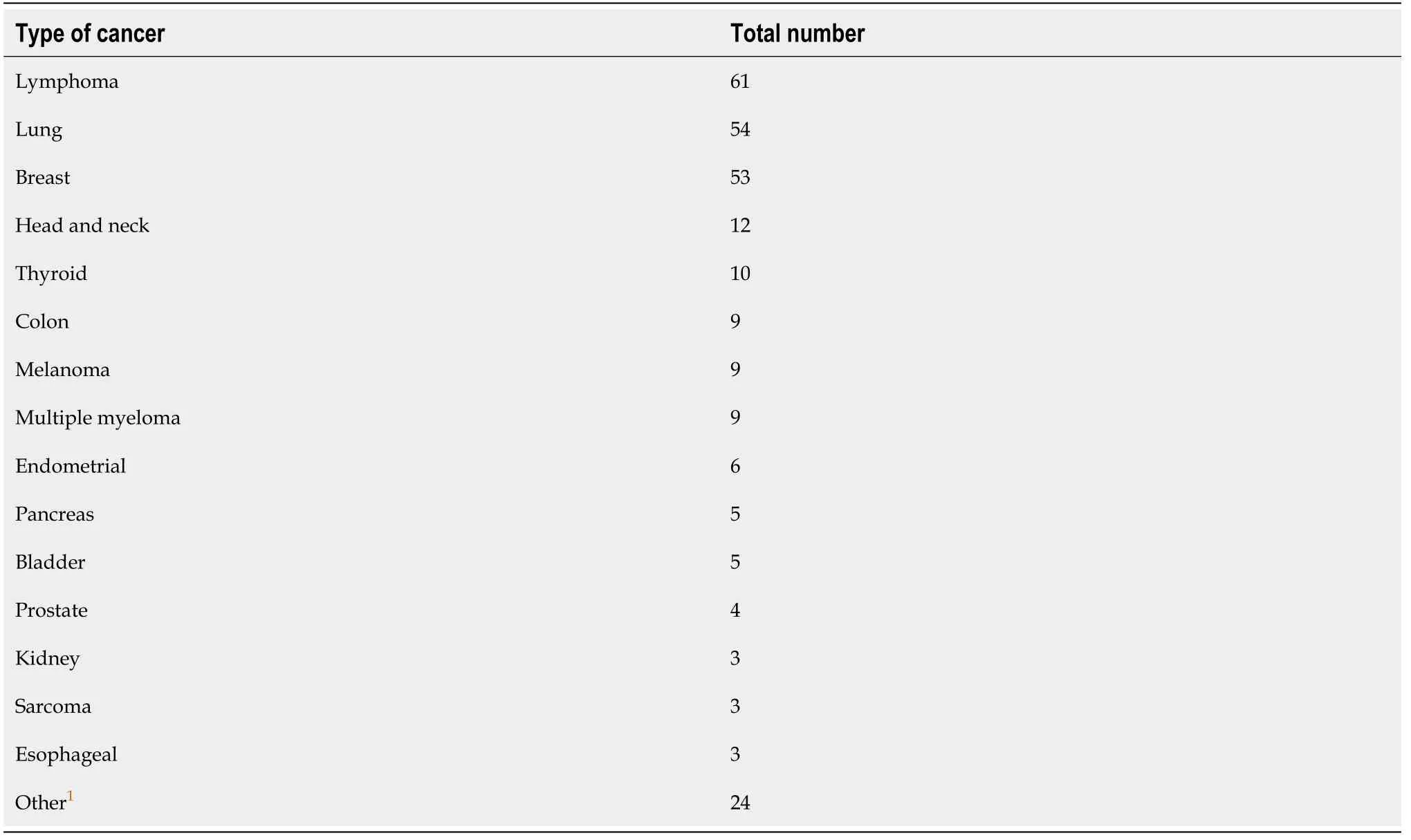
Table 1 The total number and types of cancers that were included in our patient population
In both shoulders, SUVmax and SUVmean were higher in symptomatic shoulders than asymptomatic shoulders (Left SUVmax 2.01.6, SUVmean 1.61.3, both<0.002; Right SUVmax 2.21.8, SUVmean 1.81.5, both< 0.01), as shown in Table 2. Based on the multiple linear regression models, for lung cancer patients,bilateral RI SUVmax and SUVmean values were higher in symptomatic shoulders than asymptomatic shoulders after adjustment (Table 3). Examples of symptomatic shoulders with abnormal capsular FDG uptake are shown in Figures 1 and 2. For other cancer patients, symptomatic patients had higher left rotator interval SUVmax and SUVmean than asymptomatic patients after adjustment.
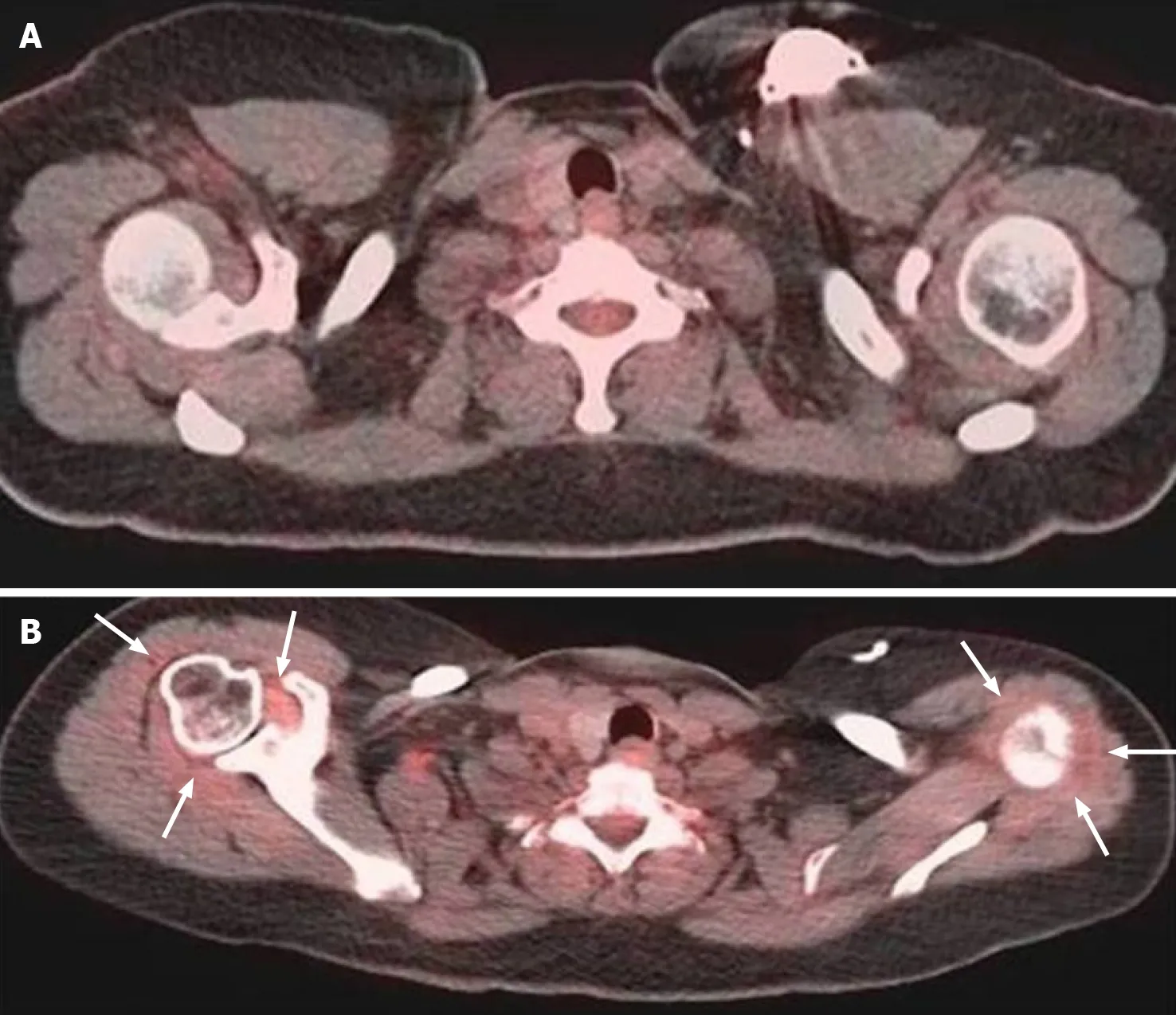
Figure 1 Fifty-two years old patient with lung cancer. A: Initial pre-therapy Positron emission tomography - computed tomography showed no significant capsular 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake; B: After the patient was treated with chemotherapy for his lung cancer, the patient developed bilateral shoulder pain with bilateral capsular FDG uptake.

Figure 2 Fifty-six years old patient with lung cancer. Fused Positron emission tomography (PET) - computed tomography (A) and (C) maximum intensity projection (MIP) PET images demonstrate mild diffuse non-specific bilateral shoulder capsular FDG uptake at initial pre-therapy imaging (arrows, better seen on MIP images); B and D: After diagnosis of lung cancer and treatment, the patient developed right shoulder pain and more focal capsular uptake in the right shoulder capsule in the region of rotator interval (arrows).

Table 2 Standard uptake value measurements of right and left shoulders in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients
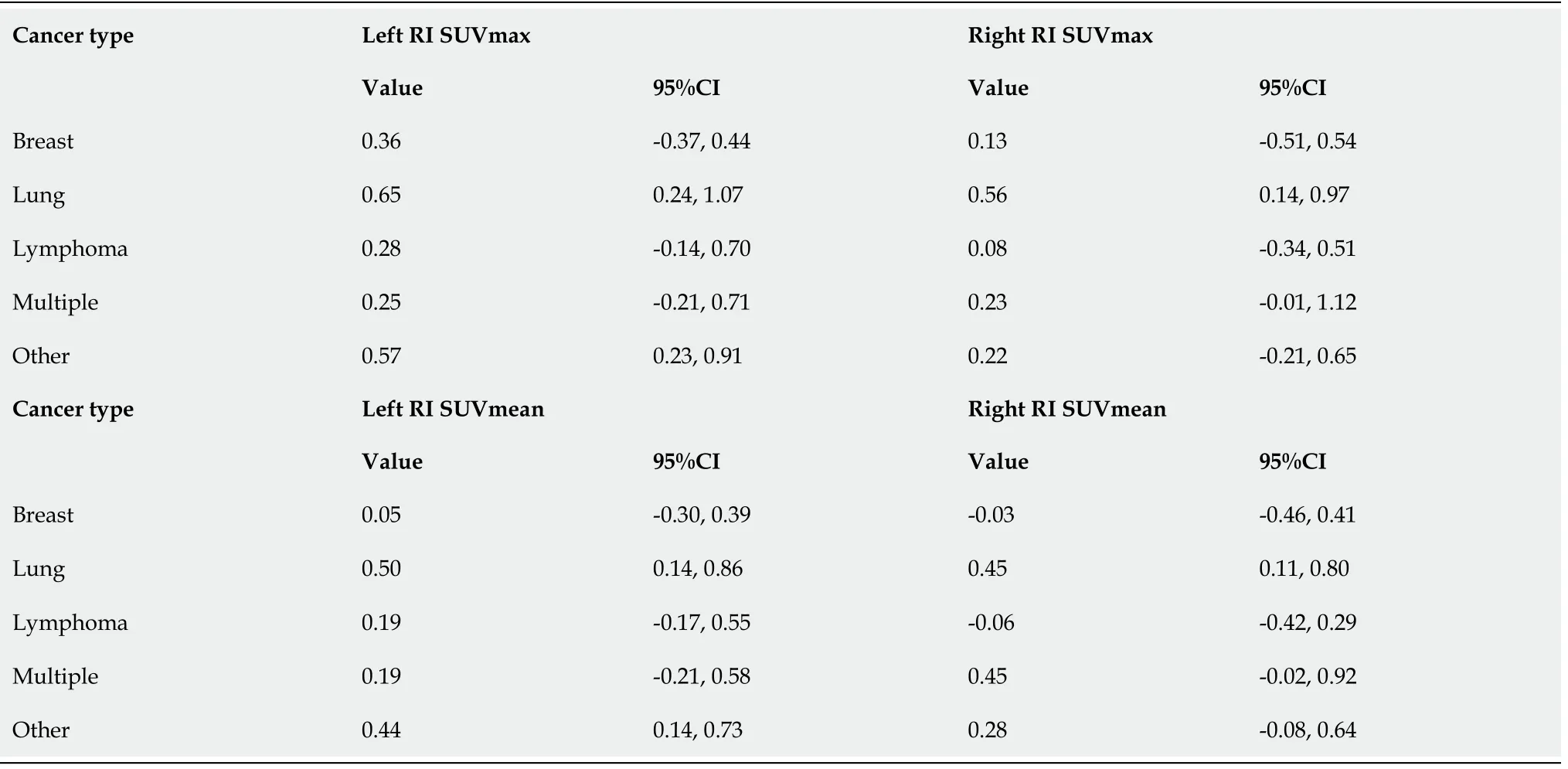
Table 3 Multiple linear regression analyses showing association between right or left shoulder standard uptake value measurements and symptom status after adjusting for covariates, stratified by cancer type
DISCUSSION
Adhesive capsulitis is a relatively common condition that can develop and perhaps,can predate, diagnosis of cancer in patients undergoing treatment[12], and can beincidentally identified on PET-CT imaging, or other imaging such as ultrasound and MRI[13]. In symptomatic patients, metabolic activities in the RI were higher than asymptomatic patients. The presence of adhesive capsulitis may explain shoulder pain or stiffness in cancer patients, which can be incidentally diagnosed on PET-CT. In general population, it has been shown that risk factors for adhesive capsulitis include age 40 years or older, female gender, immobility or reduced mobility of the shoulder(due to pathologies such as stroke, fracture, recovery from surgery, and rotator cuff injury), and underlying systemic diseases such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and Parkinson’s disease[14]. In our study sample, demographic characteristics, treatment regimen, and cancer type did not appear to be an independent risk factor.
Diagnostic utility of PET-CT for diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder has been infrequently documented in the literature, some are related to cancer patients[11,14,15] but others are not[10,16,17]. A retrospective analysis of patients with clinically diagnosed adhesive capsulitis showed increased FDG uptake in the RI or inferior glenohumeral joint capsule conferred a moderate increase in the likelihood of adhesive capsulitis[16]. In this study, of the 123 patients, 9 patients had clinical diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis, while 15 patients had FDG uptake in the RI or inferior joint capsule, with the sensitivity and specificity of PET for detection of capsulitis being 56%and 87%, respectively. PET-CT had a positive likelihood ratio for adhesive capsulitis was 6.3 (95%CI: 2.8-14.6)[16].
In a prospective study with 35 middle aged patients with unilateral idiopathic shoulder adhesive capsulitis, correlation between FDG PET-CT depicted metabolic pattern at the four ROIs (RI, anterior joint capsule, axillary recess, and posterior joint capsule) and clinical parameters (pain, functional scores, and passive range of motion)was evaluated[17]. Mean SUVmax values for the four ROIs of the affected shoulder were significantly higher than those of the unaffected shoulder. More specifically, the anterior-inferior capsular portion, including RI and axillary recess, was found to be the main pathologic site of idiopathic adhesive capsulitis and revealed significant correlations between the limited range of motion (both elevational and rotational) and increased FDG uptake in these locations[17].
While the above two studies did show PET-CT can be useful for imaging diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis, they were not directly related to cancer patients, which are actually the primary research interest in our study. A retrospective study including 230 breast cancer patients demonstrated FDG-PET is useful in evaluating adhesive capsulitis after breast cancer treatment[11]. Twenty two patients had clinically identified adhesive capsulitis and were categorized into 2 groups: With severely limited and mildly limited range of motion in the shoulder joint. SUVs of the shoulder joint capsule were significantly higher in patients with severely limited range of motion compared with those with mildly limited range of motion[11].
Although potentially useful for detection of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder,interpretation of FDG PET-CT requires caution because a focus of increased metabolic activity can mimic a metastatic lesion in lung cancer patients due to non-specific nature of the positive PET finding and limited anatomical resolution of PET itself as well as potential misregistration of FDG avid focus onto CT images at the time of PETCT fusion[15]. This is an important point to note, as our study showed the lung cancer was associated with higher SUVs in symptomatic shoulders bilaterally. It is thus important to confirm a suspicion for adhesive capsulitis (raised by PET-CT finding) by dedicated MRI of the shoulder, so as not to mistakenly diagnose a metastasis and potentially altering staging of the cancer and thus management plan.
Interestingly, one large scale study including prospectively collected 2572 incident cancers among 29098 adhesive capsulitis patients showed adhesive capsulitis might be an early predictor for a subsequent cancer[14]. Investigators followed these patients for development of cancer, and found 6-month cumulative incidence of any cancer was 0.70% (standardized incidence ratio [SIR] of 1.38, 95%CI: 1.19-1.58), and risk increases were highest for lung cancer (SIR: 2.19, 95%CI: 1.48-3.13). The findings of our study are in line with this study, in that lung cancer was the only cancer type that showed statistically significant association of higher SUV in symptomatic shoulders. It is unknown why such association was not demonstrated in other types of cancers,despite the fact that there were similar numbers of lymphoma and breast cancer patients in our study. All other types of cancers were likely too small in number to be able to show statistically meaningful association.
Although we attempted to correlate development of capsulitis and potential relationship with different therapy options, no statistically significant association of capsulitis with surgical therapy or radiation therapy was demonstrated. In the right shoulder, a higher proportion of asymptomatic patients received chemotherapy compared to symptomatic patients, but the same was not applicable to the left shoulder. This is likely an incidental finding, as the laterality of the capsulitis is unlikely to be affected by chemotherapy which is a systemic therapy and should not localize to one side of the shoulder.
Limitations of our study include a lack of clinical diagnosis of capsulitis based on clinical examination performed by non-radiologists, and our diagnosis of capsulitis is purely based on PET-CT finding and patient-reported symptoms. We do not know for sure if those patients with positive PET findings actually had clinical exam findings(such as pain and limited range of motion) consistent with adhesive capsulitis. Data collection was performedinternal electronic medical record review only. We did not have access to medical records of patients who were managed by physicians outside our institutional network. Lastly, there was no follow-up PET-CT data to assess for resolution of the adhesive capsulitis by imaging.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, our study showed metabolic activities in RI were higher in symptomatic patients than asymptomatic patients. Although appearance and relationship of capsulitis with malignancy is not fully understood, adhesive capsulitis should be considered in cancer patients with shoulder pain or stiffness and positive FDG uptake in RI, as it may allow for therapy in earlier stages of disease to improve outcomes.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder is a relatively common condition that can develop and possibly predate diagnosis of cancer in patients undergoing treatment. The presence of adhesive capsulitis may explain the presence of shoulder pain or stiffness in cancer patients, which can be incidentally diagnosed on Positron emission tomography - computed tomography (PET-CT).
Research motivation
Since PET-CT imaging is routinely performed as a follow-up study in cancer patients after therapy, being aware of PET-CT findings to suggest shoulder adhesive capsulitis may help to alert clinicians for the diagnosis of unsuspected shoulder capsulitis and avoid potential misdiagnosis of cancer progression.
Research objectives
To: (1) Evaluate the frequency of shoulder capsulitis in cancer patients undergoing PET-CT; (2) Determine if there is correlation between cancer type/treatment regimen and frequency of adhesive capsulitis; (3) Evaluate if metabolic activities in the rotator interval are different between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. We assessed if Standard Uptake Values (SUVs) are different between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients in both shoulders.
Research methods
In this prospective study, patients answered a questionnaire regarding shoulder pain/stiffness at the time of PET-CT study, between March 2015 and April 2019.Patterns of shoulder capsule 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake were noted.SUVmax and SUVmean values were measured at the rotator interval (RI) and deltoid muscle in bilateral shoulders. Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to compare unadjusted marginal differences for age, SUV measurements between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. Multiple linear regression models were used to examine the relationship between right or left shoulder SUV measurements and symptom status, after adjusting for covariates.
Research results
200 right shoulders and 200 Left shoulders were included in our study. No significant difference was noted between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients in terms of age, gender, proportion of patients who had surgical therapy and radiation therapy. In both shoulders, SUVmax and SUVmean were higher in symptomatic shoulders than asymptomatic shoulders (Left SUVmax 2.0 vs 1.6, SUVmean 1.6 vs 1.3, both P < 0.002;Right SUVmax 2.2 vs 1.8, SUVmean 1.8 vs 1.5, both P < 0.01). For lung cancer patients,bilateral RI SUVmax and SUVmean values were higher in symptomatic shoulders than asymptomatic shoulders.
R esearch conclusions
In symptomatic patients metabolic activities in the RI were higher than asymptomatic patients. Adhesive capsulitis should be considered in cancer patients with shoulder pain or stiffness and positive FDG uptake in the RI, as it may allow for therapy in earlier stages of disease to improve outcomes.
Research perspectives
Future studies may endeavor to perform radiomics research (texture analysis) on the PET-CT images.

