Comparison of point and two-dimensional shear wave elastography of the spleen in healthy subjects
Friederike Nowotny, Julian Schmidberger, Patrycja Schlingeloff, Andreas Binzberger, Wolfgang Kratzer
Friederike Nowotny, Julian Schmidberger, Patrycja Schlingeloff, Andreas Binzberger, Wolfgang Kratzer, Department of Internal Medicine I, University Hospital Ulm, Ulm 89081, Germany
Abstract BACKGROUND Few systematic comparative studies of the different methods of physical elastography of the spleen are currently available.AIM To compare point shear wave and two-dimensional elastography of the spleen considering the anatomical location (upper, hilar, and lower pole).METHODS As part of a prospective clinical study, healthy volunteers were examined for splenic elasticity using four different ultrasound devices between May 2015 and April 2017. The devices used for point shear wave elastography were from Siemens (S 3000) and Philips (Epiq 7), and those used for two-dimensional shear wave elastography were from GE (Logiq E9) and Toshiba (Aplio 500). In addition,two different software versions (5.0 and 6.0) were evaluated for the Toshiba ultrasound device (Aplio 500). The study consisted of three arms: A, B, and C.RESULTS In study arm A, 200 subjects were evaluated (78 males and 122 females, mean age 27.9 ± 8.1 years). In study arm B, 113 subjects were evaluated (38 men and 75 women, mean age 26.0 ± 6.3 years). In study arm C, 44 subjects were enrolled. A significant correlation of the shear wave velocities at the upper third of the spleen(r = 0.33088, P < 0.0001) was demonstrated only for the Philips Epiq 7 device compared to the Siemens Acuson S 3000. In comparisons of the other ultrasound devices (GE, Siemens, Toshiba), no comparable results could be obtained for any anatomical position of the spleen. The influencing factors age, gender, and body mass index did not show a clear correlation with the measured shear wave velocities.CONCLUSION The absolute values of the shear wave elastography measurements of the spleen and the two different elastography methods are not comparable between different manufacturers or models.
Key Words: Ultrasonography; Elastography; Spleen; Healthy subjects; Acoustic radiation force impulse; Two-dimensional shear-wave elastography; Point shear wave elastography
INTRODUCTION
Ultrasound shear wave elastography is gaining importance in diagnostics for a variety of diseases[1-4]. In recent years, several ultrasound-based elastography techniques have been developed for non-invasive quantitative assessment of tissue elasticity,primarily liver stiffness[5]. The first method in this field was transient elastography(TE) by FibroScan. A newer generation of elastography techniques that do not require mechanical pulses to generate shear waves, but instead use high-intensity ultrasound waves, is summarized as acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography.Compared to TE, ARFI techniques are more precise and allow more valid measurements, even in patients with high body mass index (BMI) or ascites[6].
Currently, there are two different techniques that work on the basis of this principle,both of which can be generally summarized under the term shear wave elastography:point shear wave elastography (pSWE) and two-dimensional shear wave elastography(2D-SWE)[5]. Different manufacturers have increasingly integrated p-SWE and 2DSWE techniques into their ultrasound scanners. In a meta-analysis, the pSWE and 2DSWE techniques showed significantly better results than FibroScan with respect to the rate of unreliable measurements in healthy subjects and in patients with chronic liver disease[6]. However, some of the study populations examined in the comparative studies were small and, often, only two different ultrasound devices from different manufacturers were compared[7-9]. Recent studies with larger samples have shown good agreement between the p-SWE and 2D-SWE techniques for different manufacturers, with slightly lower shear wave velocities for 2D-SWE depending on the software version used[10-12]. Furthermore, various factors, such as fasting time,breathing, and BMI, can substantially affect the measurement of shear wave velocities and, therefore, must be taken into account when interpreting the results[5]. A recent meta-analysis of 2D-SWE reconfirmed the higher reliability of the method compared to the other ultrasound elastography methods as demonstrated in various studies[6].
In recent years, the measurement of splenic stiffness has increasingly become the focus of scientific investigations, especially for prognostic assessment of esophageal varices and as a marker of portal hypertension[13-15]. In a recent meta-analysis, Song[16] demonstrated a good correlation between splenic stiffness and blood pressure measured by hepatic venous pressure gradient. The current recommendations of the European Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology (EFSUMB)note obvious methodological limitations for transient splenic ultrasonography,especially in patients with high BMI, the detection of ascites and pulmonary or colonic gas overlays, and in patients with a splenic diameter < 4 cm. The successful application of TE in measuring splenic elasticity has been reported to be approximately 70%[15]. With few studies currently available on 2D-SWE, the technology has been viewed critically in the assessment of splenic stiffness[15,17]. For p-SWE, recent studies report sensitivity of up to 97% for the measurement of splenic stiffness, but spleen size, adiposity, and abdominal wall thickness seem to affect reproducibility in p-SWE[15,18-21]. In addition to the above parameters, the anatomical position for measurement in splenic elastography seems to influence the results. To date, most elastography studies on the spleen have performed measurements at undefined anatomic positions or different splenic poles[22-26].
To the best of our knowledge, no comparative studies are currently available on different elastography methods (, pSWE, 2D-SWE) for sonoelastographic measurement of splenic stiffness taking into account the anatomical location of the measurement in healthy volunteers. The aim of the present study was to compare 2DSWE to p-SWE in healthy volunteers taking into account whether the measurement is performed in the upper, middle, or lower third of the spleen.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study process
The study consisted of three arms: A, B, and C (Figure 1). Arm A tested four ultrasound devices: the Siemens Acuson S3000, Toshiba Aplio 500 (software version 5.0), Philips Epiq 7, and GE Logiq E9. We chose the Siemens S3000 ultrasound scanner as the reference device because the largest number of studies exist for this ultrasound scanner or its predecessor, the Siemens S2000[27-29]. The Siemens S3000 and Philips Epiq 7 devices use p-SWE technology, and the Aplio 500 Toshiba and GE Logiq E9 devices use 2D-SWE technology. Study arm A showed that the Toshiba Aplio 500 device (software version 5.0) generated strongly deviating results compared to the other ultrasound devices tested. Due to the divergent results between Toshiba Aplio 500 (version 5.0) and the other tested devices, especially the reference device, the Toshiba Aplio 500 was tested using software version 6.0 against the Siemens Acuson S3000 in study arm B. In study arm C, the results of study arms A and B were compared to investigate the differences between the two different software versions of the Toshiba Aplio 500. Study arm A was conducted from May 2015 to September 2015 and study arm B from November 2016 to April 2017.
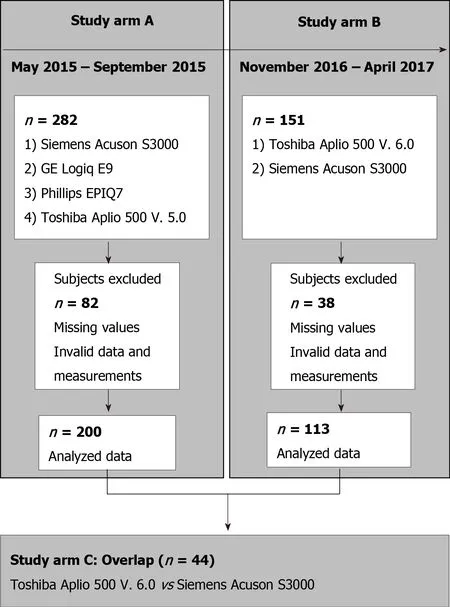
Figure 1 Flow chart of study arm inclusion and exclusion.
Subjects
Initially, 282 subjects were included in study arm A. Due to incomplete measurements and invalid data and measurements, the data sets of 200 subjects could be evaluated.In study arm B, 151 subjects were initially recruited, but because of missing or incomplete data 113 subjects could be analyzed. The characteristics of the subjects in study arms A and B are given in Table 1. Study arm C included 44 subjects. The same study protocol applied to both study arms. Only subjects who met the inclusion criteria and provided informed written consent to participate in the study were recruited. The study had a positive vote from the local ethics committee (No. 415/15)and was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki[30]. The inclusion criteria in the study were age ≥ 18 years; no history of hepatopathies (viral hepatides, hemacromatosis, autoimmune hepatitis, toxic hepatides, Wilson's disease)or other chronic diseases, such as diabetes or arterial hypertension; fasting period ≥ 3 h before ultrasound examination; BMI < 30 kg/m2 and > 18 kg/m2; normal findings on previous abdominal ultrasonography, specifically normal echogenicity, texture, and size of the liver (≤ 16 cm) and normal echogenicity and size of the spleen (up to 14 cm length allowed); and alcohol consumption < 40 g/d in men and < 20 g/d in women.
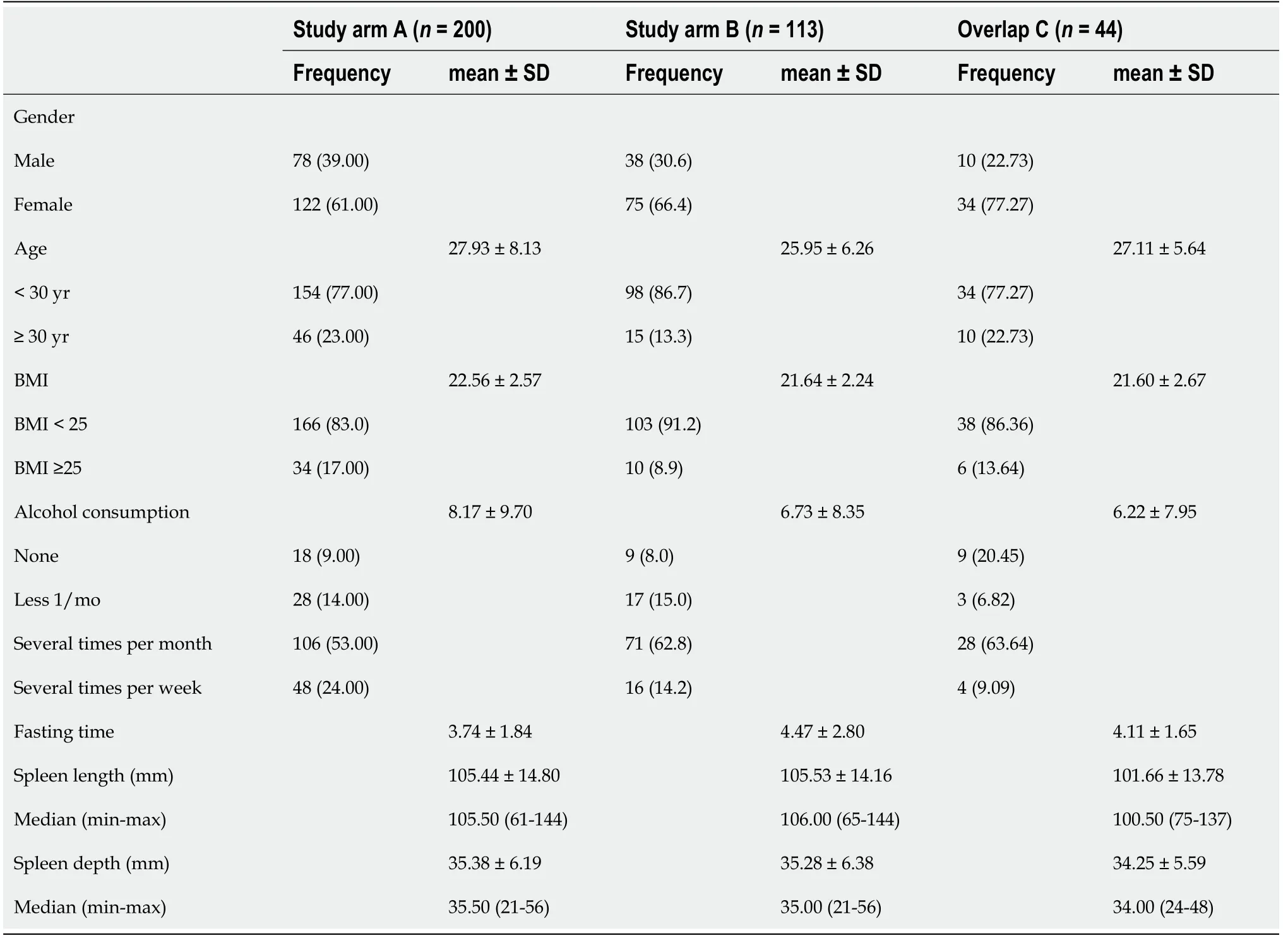
Table 1 Characteristics of subjects included in study arms A and B and their overlap, n (%)
Ultrasound and elastography examinations of the spleen
Before elastography, standardized abdominal ultrasonography of the liver and spleen in B-mode was performed in each subject to document the liver size, echogenicity, and parenchymal structure and the spleen size, shape, and parenchymal and vascular status. Subjects with pathological findings on focused abdominal ultrasonography were excluded from the study. One subject at a time was examined by one investigator using all devices. Study arm A had 6 investigators and study arm B had 2 investigators; an experienced supervisor (> 5000 examinations/year) was available in case ofunclear findings. Splenic elastography was performed in all subjects in the supine position with the left arm maximally abducted and in expiration. Care was taken to place the transducer at right angles to the splenic capsule as much as possible. Shear wave velocity measurements were obtained in meters per second at each of three anatomic positions: the upper, middle, and lower thirds of the spleen (Figure 2). Five valid measurements were obtained per anatomic position using the Philips Epiq 7 and Siemens Acuson S3000 to calculate a median and mean value. A total of 15 measurements per spleen were performed using p-SWE. Elastographic studies on the Toshiba Aplio 500, GE Logiq E9, and Siemens Acuson S3000 were performed with convex transducers (6C1HD, 1.5-5.5 MHz) and on the Philips Epiq 7 with one transducer (5C1 HD, 1-5 MHz). The preset region of interest (ROI) was 10 mm × 5 mm for Siemens. The ROI for the other manufacturers was set to 10 mm × 10 mm. As the quality of the generated shear waves can be visualized with the Toshiba Aplio 500 and GE Logiq E9, the investigator could directly assess the reliability of the measurement;therefore, with these devices only one measurement was made per measurement site(three measurements per spleen). The measurements were considered reliable as soon as the shear waves could be displayed in parallel in the defined ROI. If this was not the case, the measurement was repeated until the required quality was achieved. If this was not successful, the subject was excluded from the study (Figure 1).
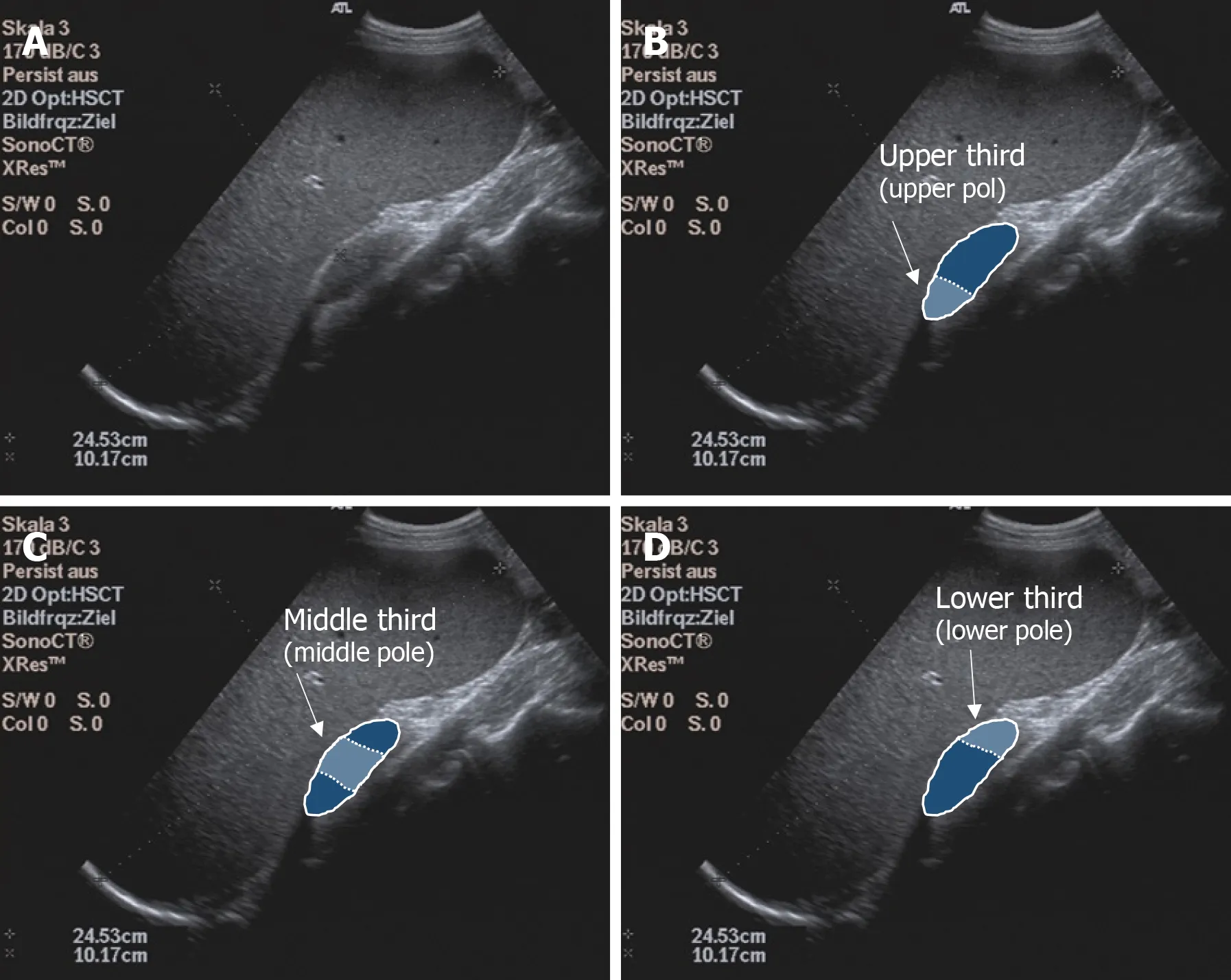
Figure 2 Illustration of the examination of the spleen. A: B-Mode Ultrasound image of the spleen; B: Upper spleen pole; C: Middle spleen pole; and D:Lower spleen pole.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SAS Version 9.4 software (SAS Institute,Cary, North Carolina, United States). Normal distribution was tested with the Shapiro-Wilk test. Differences were determined using the non-parametric Wilcoxon rank sum test. Potential confounding variables, such as age and BMI, were taken into account with partial correlation analyses. The inter-observer reliability (ICC) was used to determine the reliability of the agreement of measurements between the examiners.All tests were two-sided.< 0.05 was considered significant according to the specified α = 0.05, with a probability of error of 5%.
Biostatistics
The statistical methods of this study were reviewed by Dr. Julian Schmidberger, MPH,Ph.D., from the Department of Internal Medicine I, University Hospital Ulm, Albert-Einstein-Allee 2389081 Ulm, Germany.
RESULTS
Ultrasound device comparison depending on the anatomical measurement position in study arm A
In our study the ICC was 0.83 (95%-KI 0.74-0.89), being comparable to similar studies[31,32]. The comparison between the Siemens Acuson S3000 and GE Logiq E9,taking into account age, BMI, and gender, showed no correlation of the collected measurements at any of the three anatomical measurement positions (Tables 2 and 3).Comparison of the Philips Epiq 7 with the Siemens Acuson S3000 demonstrated a significant correlation of the shear wave velocity of the two devices as a function of age, BMI, and gender at the upper third of the spleen (= 0.33088,< 0.0001). We found no correlation of the measurements at the lower or middle third of the spleen(Table 4). Examination of the splenic elastography by the Toshiba Aplio 500 compared to the Siemens Acuson S3000 revealed no correlation of the measured results at any of the three anatomical positions (Table 4). With overall poor correlations between the measurements by the different ultrasound devices, higher agreement was found between devices using identical shear wave technology, especially p-SWE.
Influence of age, sex, and BMI on shear wave velocities in the spleen in study arm A
For the Siemens Acuson S3000 (p-SWE), GE Logiq E9 (2D-SWE), and Philips Epiq 7 (p-SWE), no significant correlation was detected between age and splenic elasticity. For the Toshiba Aplio 500 (version 5.0; 2D-SWE), we found a significant correlation at the lower and middle third of the spleen (< 0.05). A correlation was also found between gender and spleen elasticity for the Siemens Acuson S3000 at all anatomical positions (< 0.05). For the Toshiba Aplio 500 (software version 5.0), an influence of gender was determined for the anatomical location (upper and lower third;< 0.05). For the GE Logiq E9, there was a significant correlation with gender at the upper third of the spleen (< 0.05). For the Philips Epiq 7, no significant correlation with gender was detected at any position. A significant correlation with BMI was demonstrated for the Toshiba Aplio 500 (version 5.0) at the lower third of the spleen (< 0.05) and for the GE Logiq E9 at the middle third of the spleen (< 0.05). No correlation between BMI and changed shear wave velocities at the spleen were detected for the Siemens and Philips devices.
Ultrasound device comparison depending on the anatomical measurement position in study arm B
In study arm B, the Siemens device was compared against a newer software version(6.0) of the Toshiba Aplio 500 device. Using the mean values an controlling for age,BMI, and gender, a significant correlation of the shear wave velocities of the two devices was shown for the upper and lower thirds of the spleen (Tables 2 and 4,Figure 3).
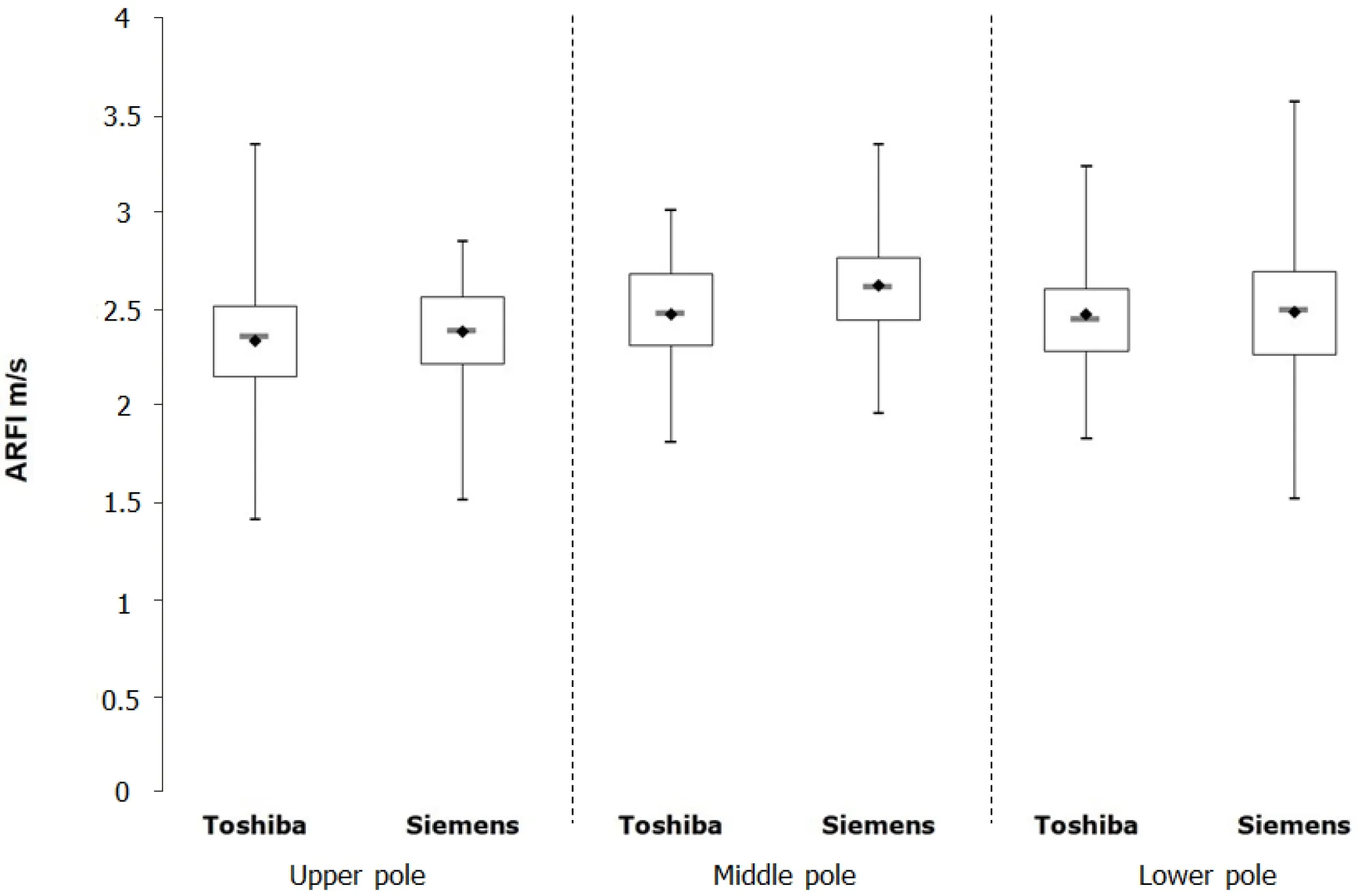
Figure 3 Boxplot diagram illustrating the measurements on the Toshiba Aplio 400 version 6.0 and Siemens devices for the different splenic sections. ARFI: Acoustic radiation force impulse.
Influence of age, sex, and BMI on shear wave velocities in the spleen in study arm B
In study arm B, no correlation was found between the measured heavy-wave velocities and gender or BMI for both devices tested. In addition, no correlation could be demonstrated for age and shear wave velocity with the Siemens device. Only for the Toshiba Aplio 500 (version 6.0) did we find a significant correlation between age and the measured shear wave velocities, but only for the lower third of the spleen (<0.05).
Study arm C
With the help of the subgroup of 44 subjects, we compared the measurements made with the two software versions of the Toshiba Aplio 500 (Tables 1 and 3). All shear wave values obtained with the version 6.0 were significantly lower than those obtained with version 5.0 (< 0.0001). The mean values differed by 33.0% in the upper third (3.46 m/s2.32 m/s), by 14.0% in the middle third (2.94 m/s2.53 m/s), and by 25.4% in the lower third (3.38 m/s2.52 m/s).
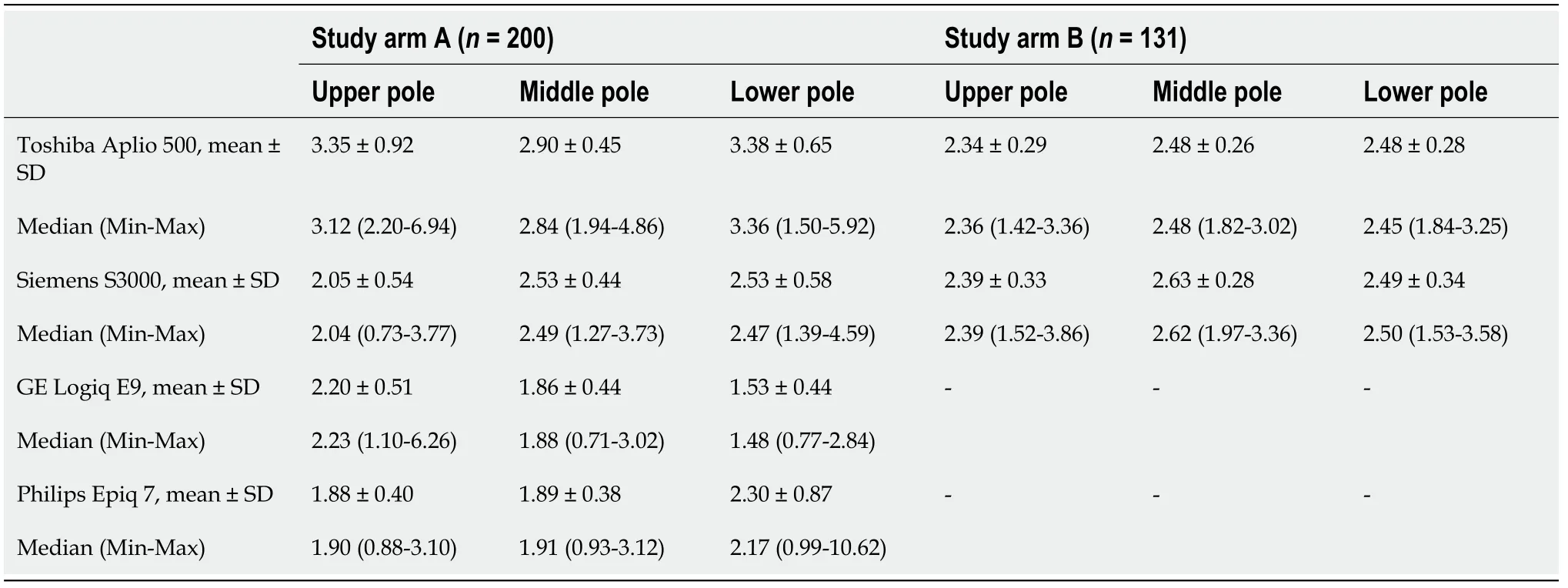
Table 2 Location and dispersion measures of shear wave velocity at the spleen measured with the Toshiba Aplio 500 version 5.0 and version 6.0, Siemens S3000, GE Logiq E9, and Philips Epiq 7 devices, n (%)
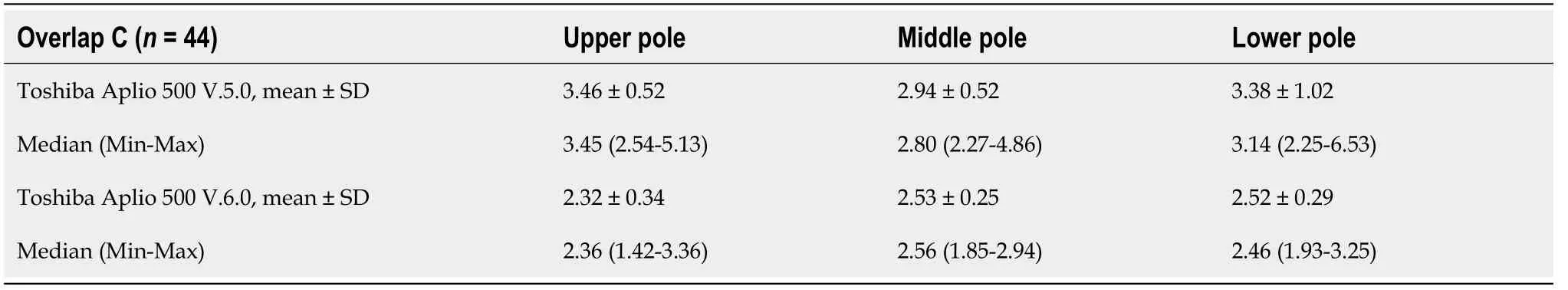
Table 3 Position and stress measurements of shear wave velocities measured with the Toshiba Aplio 500 version 5.0 and version 6.0
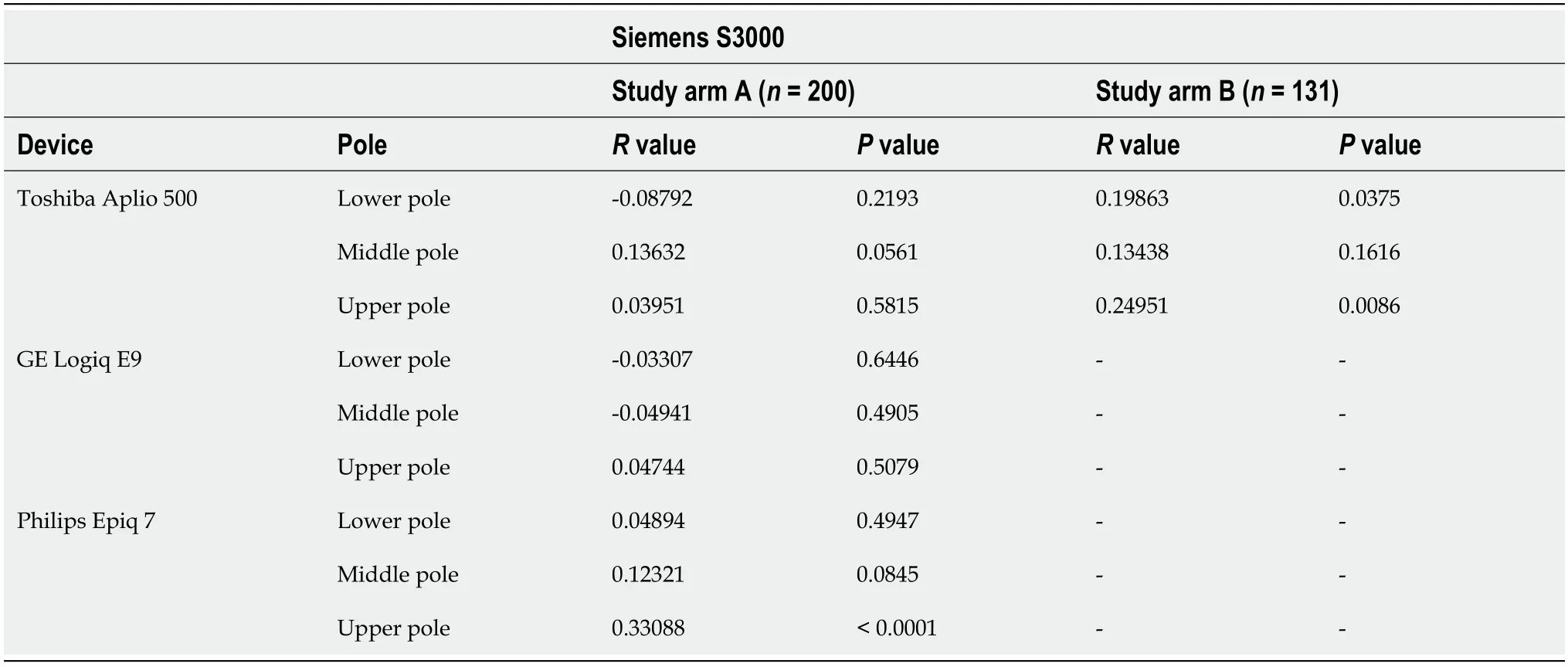
Table 4 Correlation of the heavy wave velocities of the Toshiba Aplio 500 version 5.0 and version 6.0, GE Logiq E9, and Philips Epiq 7 devices with the Siemens S3000
DISCUSSION
This study is the first to compare four ARFI-based ultrasound elastography methods,two pSWE techniques and two 2D-SWE techniques, from different manufacturers in healthy volunteers taking into account the anatomical location of the measurement of the spleen. Our results show that the anatomical position must be taken into account for splenic elastography. The best results were obtained with the lower pole of the spleen. Furthermore, when interpreting the results using different elastography techniques, attention must be paid to possible limitations in device compatibility. The absolute values of the shear wave elastography measurements of the spleen are not transferable between different manufacturers or models.
In previous studies of the spleen, the measurements were performed at undefined areas or different splenic poles (upper, middle, lower third)[22-26]. Giuffrè[33]preferably investigated the lower pole, Albayrak[21] performed shear wave elastography of the middle third of the spleen, and Karlas[34] performed measurements in an insufficiently defined area between the middle and lower thirds of the spleen. Our results show that the lower third of the spleen is the best anatomical measurement position due to good visibility, as shown by other research groups[26,35-37]. Our results also confirm the recommendations of the EFSUMB to perform elastography on the lower third of the spleen[16]. The upper third does not seem to be suitable for measurements because its anatomical position often makes it difficult or impossible to see by inspiration, as it is partly overlapped by the lung or intestinal segments and located far away from the transducer. Our results confirm that readings should not be assumed to be transferable from one anatomic region of the spleen to another. Whether this is due to the tissue itself or to the examination conditions, such as poor visibility of the upper third, is currently not clear. A previous study reported that the measurement differences between devices and investigators can be up to 15%[38]. In a recent study patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection show a good agreement of p-SWE and 2D-SWE in patients with F2-F4 fibrosis[39].Since only healthy subjects were examined in our collective, these results cannot simply be transferred to the situation in patients with chronic hepatitis C and to the spleen[39]. In addition, our results show that without considering the anatomic site of measurement for splenic elastography, reliable measurement results cannot be obtained, regardless of the method used. Again, our results confirm the recommendations of medical societies that the absolute shear wave values are not comparable between different systems and manufacturers[5].
We could not demonstrate any correlation between age and the measured shear wave velocities. This finding is in accordance with the results of recent publications that could not demonstrate any influence of age on the measured shear wave velocities regardless of the shear wave elastography technique used[20,21,33,40,41]. However, an age-related correlation was previously demonstrated in children and adolescents younger than 18 years[42,43]. Independent of the shear wave technique, our study showed a contradictory picture regarding the influence of gender on the measured heavy wave velocities. For both the Siemens device (p-SWE) and the GE device (2DSWE), gender-specific shear wave velocities were detected. This was not possible for the Philips device (p-SWE). Most of the available studies could not prove any genderspecific influence on the shear wave velocities[21,35,42,44]. A study of healthy children and adolescents concluded that gender influences elastography at the spleen[43]. The influence of BMI on spleen shear wave velocity was not clear according to other research groups[21,33,44]. The influence of abdominal wall thickness on shear wave velocities has not yet been clarified[17,19,20,26] and this parameter was not assessed in our study. Future studies investigating BMI and abdominal wall thickness as influencing factors seem to be necessary.
A limitation of our study is that the defined exclusion criteria were only inquired about anamnestically, and advanced or still undiagnosed diseases could only be excluded by abdominal ultrasonography. Here, in contrast to other studies, no laboratory parameters were determined[22,24]. Also no information on unsuccessful mesaurements was collected during the study. However, due to the predominantly healthy young and slim probands, a low number of unsuccessful measurements can be assumed[45]. Histological examination could not be performed either, as this was ethically unacceptable in young healthy subjects. Compared to current studies and recommendations regarding liver elastography, the low number of measurements in our study is a major limitation. At each position, one measurement was performed with 2D-SWE and five measurements with pSWE. The EFSUMB currently recommends three to five measurements for 2D-SWE in order to obtain good measurements[40]. Karlas[34] also recommend between eight and ten measurements for pSWE of the spleen in order to obtain the most accurate shear wave velocities.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the absolute values of the shear wave elastography measurements of the spleen and the two different elastography methods are not comparable between different manufacturers or models. Further studies are needed to confirm the present study results.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Measurement of shear wave velocity in the spleen has been increasingly used in prognostic assessment of esophageal varices and as a marker of portal hypertension.Few systematic comparative studies of the different methods of physical elastography of the spleen are currently available.
Research motivation
Currently, whether the different elastography methods and shear wave measurements with different ultrasonic devices provide comparable results have not been clarified.
Research objectives
The objective of the study was to compare point shear wave and two-dimensional elastography of the spleen considering the anatomical location (upper, hilar, and lower pole).
Research methods
As part of a prospective clinical study, healthy volunteers were examined for splenic elasticity using four different ultrasound devices between May 2015 and April 2017.The devices used for point shear wave elastography were from Siemens (S 3000) and Philips (Epiq 7), and those used for two-dimensional shear wave elastography were from GE (Logiq E9) and Toshiba (Aplio 500). In addition, two different software versions (5.0 and 6.0) were evaluated for the Toshiba ultrasound device (Aplio 500).The study consisted of three arms: A, B, and C.
Research results
In study arm A, 200 subjects were evaluated (78 males and 122 females, mean age 27.9± 8.1 years). In study arm B, 113 subjects were evaluated (38 men and 75 women, mean age 26.0 ± 6.3 years). In study arm C, 44 subjects were enrolled. A significant correlation of the shear wave velocities at the upper third of the spleen (r = 0.33088, P< 0.0001) was demonstrated only for the Philips Epiq 7 device compared to the Siemens Acuson S 3000. In comparisons of the other ultrasound devices (GE, Siemens,Toshiba), no comparable results could be obtained for any anatomical position of the spleen. The influencing factors age, gender, and body mass index did not show a clear correlation with the measured shear wave velocities.
Research conclusions
The absolute values of the shear wave elastography measurements of the spleen and the two different elastography methods are not comparable between different manufacturers or models.
Research perspectives
However, absolute values of splenic shear wave elastography measurements are not transferable between manufacturers or models.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Members of the Elastography Study Group: Hadeel Gamal El-Deen Abd El-Moniem,Gr?ter Tilmann, Hesse Julian, Klimesch Benjamin, Maa? Marie, Schall Katrin.

