The association between folic acid supplementation, maternal folate during pregnancy and intelligence development in infants: a prospective cohort study
Shokng Wng, Jie Wei, Di Wng, Li Hu, D Pn, Lingmeng Fu, Jin Yng, Guiju Sun,*
a Key Laboratory of Environmental Medicine and Engineering of Ministry of Education, and Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Southeast University,Nanjing, China
b Jurong Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital, Zhenjiang, China
ABSTRACT
Objective: The study aimed to explore the association between folic acid supplementation, maternal nutritional levels during pregnancy and intelligence development of infants. Method: This was a prospective cohort study, mothers and their offspring in Jurong Maternal and Child Health Hospital were followed up through pregnancy up to 1 year. The basic information of pregnant women was obtained through questionnaire survey, including pregnancy lifestyle, marital status, vitamin and mineral supplements during pregnancy.Blood samples of pregnant women were collected on admission, serum folate, vitamin B12 and homocysteine concentrations were determined. Maternal postpartum colostrum was collected and the concentrations of folate and vitamin B12 in colostrum were determined. Pregnant women (n = 478) and their corresponding infants were followed up and the Developmental Screen Test scores were recorded at 1,3,6,8 and 12 months of age.Results: Compared with the normal group, infants in the low serum folate group had a score of 0.12 points lower in the intellectual energy zone (95% CI: -0.23- -0.01, P = 0.04), and infants with the high homocysteine level scored 1.30 points lower than the lower-level group (95% CI: -2.52- -0.08, P = 0.04). In the colostrum low-vitamin B12 level group, infants scored 0.10 points lower (95% CI: -1.84- -0.02, P = 0.02) in the social adaptation zone compared to the normal group. Conclusion: In conclusion, folic acid supplementation in the pre-pregnancy supplementation group and the post-pregnancy supplementation group may be not associated with infant mental development. In addition, maternal folate and homocysteine may be related to the intellectual development of infants. The level of vitamin B12 in colostrum may be associated with infants’social adaptive capacity. This result may be caused by individual differences in folate and homocysteine metabolism in pregnant women.
Keywords:
Folic acid
Vitamin B12
Homocysteine
Intelligent development
1. Introduction
Pregnancy as a primary stage of life development for 1 000 days,has a crucial impact on infant development. During this period, the demand for nutrition increases, in order to maintain the metabolism of pregnant women and the growth and development of the fetus [1].Therefore, malnutrition can affect pregnancy outcomes and newborns health [2]. At the same time, pregnancy and early postnatal period are considered to be sensitive periods of brain development. The status of maternal micronutrients is essential for the optimal development of the fetal brain and may affect DNA methylation and cognitive abilities in infancy and early childhood. Severe deficiency can also lead to brain functional disorders [3] and neural tube defects (NTDs) [4].
As an important water-soluble nutrient, folic acid is mainly involved in the metabolism of non-essential amino acids, DNA synthesis, methylation reaction and other important metabolic processes, which are closely related to cell proliferation and differentiation [4-6]. Vitamin B12is one of the indispensable vitamins for human body. It plays an indispensable role in DNA synthesis and maintaining the stability of genome, and it is involved in methylation as a cofactor of methionine synthase [7]. Homocysteine (Hcy) is a sulfur-containing amino acid, which can be methylated to methionine by methionine synthase, converts 5-methyltetrahydrofolate into tetrahydrofolate [6-8].
Current studies have shown that folic acid and vitamin B12play important roles in regulating the metabolic process of Hcy. Folic acid supplementation may be useful in reducing Hcy level in high risk patients with Hcy [9,10]. Because of the closely interlinked metabolism of folic acid and vitamin B12, they could prevent NTDs together [11].Adequate vitamin B12levels during pregnancy are also associated with a reduced risk of NTDs, and there is evidence that maternal vitamin B12status is associated with offspring cognition [12,13].
In the critical period of 1 000 days in the early life, infant behaviour, intelligence and language development may continue to affect children’s language, social, academic and social adaptation,and will also bring burden and suffering to society and families [14].The worldwide recommendation of folic acid is at least 0.4 mg daily for all women of reproductive age, and 4-5 mg for high-risk women[5,15]. Previous study found that folate deficiency may be associated with neurobehavioral dysplasia and social affective disorders such as autism spectrum disorders [16].
Since 2009, China has been free to distribute folic acid to women in rural areas [17]. However, after a literature search, such researches are rarely studied in China, and the effect of folic acid supplementation have not been clearly concluded. Jurong City is a county-level city in Zhenjiang City, Jiangsu Province. It is located in southern Jiangsu and is an emerging city in the Yangtze River.The city covers an area of 1 385 km2, with a resident population of 623 600 at the end of 2013. In order to further improve women and children health in the city, Jurong City has provided subsidies for maternal hospital delivery since the launch of the special maternal and child health free program in 2009, and free folic acid to reduce the birth defect rate of new-borns. Although the economy in the Yangtze River Delta region is relatively developed and the population is highly recognized, there are still some pregnant women in rural areas who lack the awareness of folic acid supplementation, and most pregnant women begin to supplement folic acid after pregnancy.
Therefore, this study aimed to assess the associations of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy and folic acid levels in mothers and the intelligent development of infants, and provide evidence for nutrition counselling, infant health care and policy development during pregnancy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Study subjects
The study recruited 500 pregnant women in the Jurong City Maternal and Child Health Hospital within 10 months. The specific inclusion criteria are as follows: 1) breastfeeding after childbirth; 2) no folic acid supplementation or occasional folic acid supplementation during early pregnancy or second trimester; 3) living in Jurong City after childbirth. Exclusion criteria are as follows: 1)twin and multiple births; 2) long-term use of folic acid supplements;3) with NTDs, peripheral nervous system diseases; 4) cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases (including coronary heart disease,arteries atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, etc.); 5) suffering from dementia, depression, mental disorders, schizophrenia and other diseases, and have sufficient understanding and expression skills.Therefore, 478 pregnant women who met the criteria of the study were selected, and their physical examination data during pregnancy were collected. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Zhongda Hospital affiliated to Southeast University (Approval No. 2015ZDSYLL075.1.), and informed consent was signed in all the surveys. Based on the birth cohort study, infants were followed up at 1, 3, 6, 8, and 12 months of age to test their mental development.
2.2 Data collection and sample collection
When pregnant women were admitted to the hospital,questionnaires were used to collect their general information(including age, occupation, education level, per capita income and medical insurance), marriage birth history, folic acid supplementation during pregnancy, pregnancy test results. Investigation was carried out until production, pregnancy outcomes.
Before delivery, 5 mL of peripheral venous blood of each pregnant woman was collected and centrifuged at 3 000 r/min for 5 min, then the serum was obtained and stored in the refrigerator at 20 °C for later use. After delivery, the colostrum was collected by professional breast milk collection device, centrifuged at 3 000 r/min for 5 min, and the whey was obtained, frozen and transferred to -80 °C refrigerator.
Investigation of intelligent development monitoring within 1 year after birth of a new-born was followed up (according to the requirements of the baby’s physical examination, the intelligent development screening test was conducted at 1, 3, 6, 8, and 12 months of age).
2.3 Biochemical measurements
The concentrations of folic acid and vitamin B12in serum and breast milk were detected by chemiluminescence immunoassay using Beckman Coulter UniCelDxI 800 chemiluminescence analyser, the kit was provided by Beckman Coulter Co., Ltd., USA, and samples were processed and determined strictly according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Hcy was determined by circulating enzyme method using Cobas701 biochemical analyser. The kit was provided by Shanghai Desai Diagnostic System Co., Ltd., and the samples were processed and determined strictly according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.4 Infant intelligence development screening test
Follow-up for 1 year was carried out for the included infants, and the pregnant women were told to come to the hospital for physical examination at the age of 1, 3, 6, 8 and 12 months after the birth of the new borns. Intelligence development level of the infants at age from 0 to 6 months was evaluated by trained investigators using the Developmental Screening Test (DST). To provide an appropriate environment for assessing the intelligence development level of the infants, the test room was quiet, bright, comfortable and simple, and the indoor temperature was suitable. During the test, the doctor and the tested baby established a friendly atmosphere. In the test table, all items that babies were able to complete were rated as passing, and all items that they were not able to complete were rated as failing. Score was evaluated according to the scoring standard of this test. The average test time was approximately 15 min.
The test form consisted of a general case and a formal test part. The formal test consisted of three energy zones, namely the exercise energy zone, the social adaption energy zone and the intelligence energy zone. The test results were expressed in terms of developmental quotient (DQ) and mental index (MI). The DQ means the exercise, social adaptation, and intellectual primary scores.The MI means the original score of the intellectual energy zone.The results were divided into three categories based on DQ and MI:normal, suspicious, and abnormal. The standard is: DQ or MI < 70 is abnormal; 70-84 is suspicious; ≥ 85 is normal.
Denver Developmental Screening Test-II (DDST-II) is a formal developmental screening tool that can assess children from birth to age 6, but it is suspected of its limited specificity (43%) and the risk of over-referral [18]. The Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development (BSID III) is widely used at home and abroad to assess the cognitive, language and motor skills of infants aged 1-42 months[19]. However, BSID III was originally designed for American babies,some language projects in the first few months may not be suitable for cross-cultural applications [20].
The Developmental Screening Test for children under six (DST)was prepared by Liu [21] from the Pediatric Hospital of Shanghai Medical University, and is suitable for children aged 0-6. It is the first child development screening scale developed by Chinese children’s developmental behaviour experts based on Chinese children’s population and cultural background. DST has good reliability,moderate validity [21]. Considering the reliability, validity, and sensitivity of the above scales, DST was selected as the developmental screening test scale for this project.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The database was built using EpiData 3.1 software and data were double entered. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ±standard deviation, and categorical variables were expressed in frequency (%). The data analysis was performed using SPSS 18.0 and SAS 9.2 software. Statistical methods included χ2test, mixed effect linear model, analysis of variance, etc., withP< 0.05 considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1 Basic information of pregnant women
A total of 500 pregnant women were recruited in this study,whereas 478 pregnant women were finally included due to the exclusion criteria. According to whether the folic acid was added during pregnancy and the time of starting the supplement, the pregnant women were divided into the unsupplementation group,the pre-pregnancy supplementation group and the post-pregnancy supplementation group. Folic acid supplementation included folic acid supplementation alone, iron folic acid supplementation,and multivitamin supplementation with folic acid at doses of approximately 0.4, 0.2, and 0.8 mg/day, respectively.
There was no significant difference in age, education, type of medical care and lifestyle habits such as smoking, drinking and drinking tea during pregnancy among the three groups of pregnantwomen. The annual per capita income of the family in the postpregnancy supplementation group was statistically higher than that of the unsupplementation group and the pre-pregnancy supplementation group. Compared with the unsupplementation group and the postpregnancy supplementation group, pregnant women who started folic acid supplementation before pregnancy had a significantly lower percentage of haemoglobin below 110 g/L during pregnancy(P= 0.047) (Table 1).
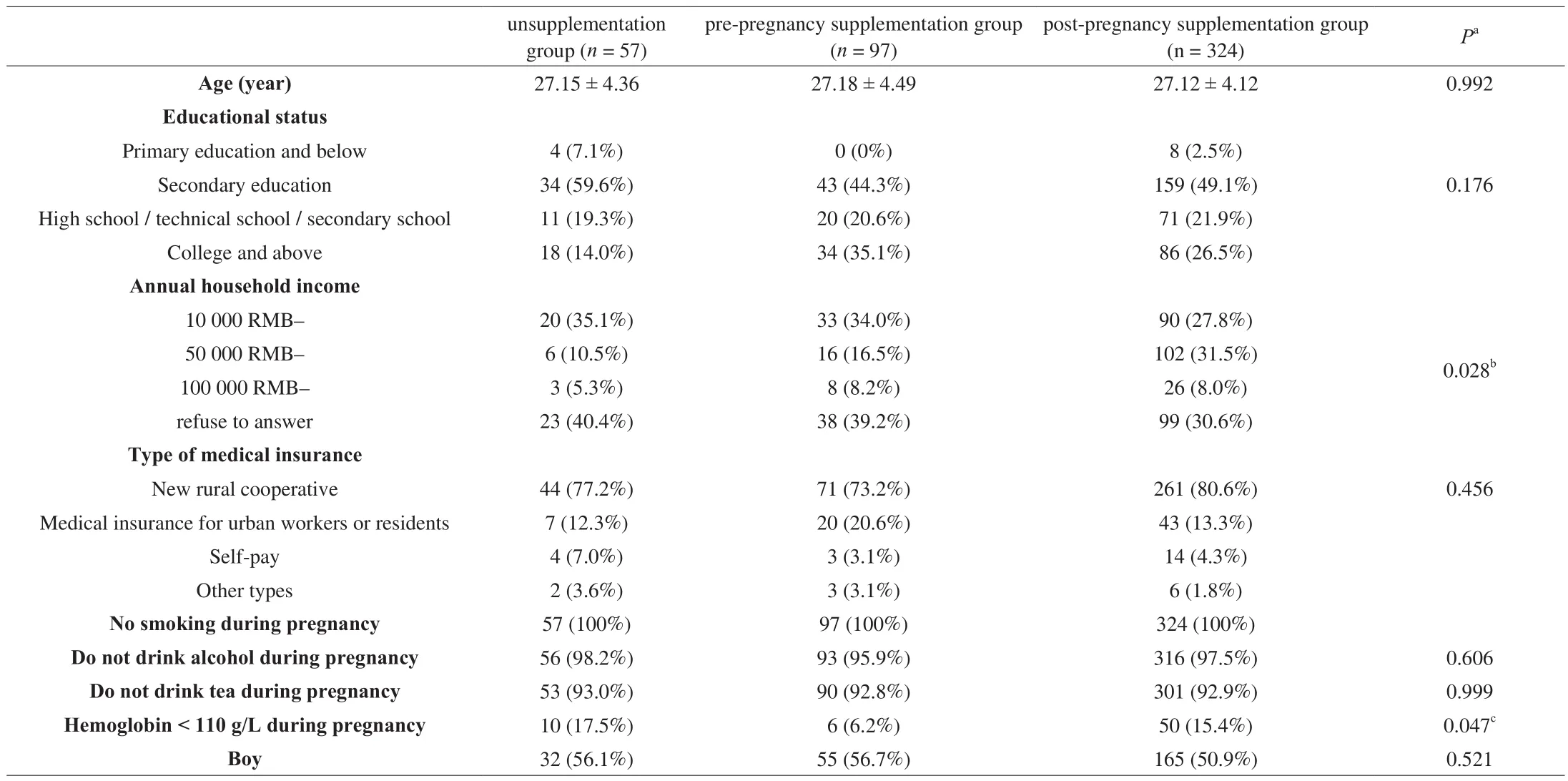
Table 1Basic information of pregnant women (n = 478).
The time when the folic acid supplement ends can be classified into the end of the first trimester, the end of the second trimester and the end of the third trimester. There were 143 pregnant women who completed the supplement in the first trimester, accounting for 33.89%;164 patients completed the supplement in the second trimester,accounting for 38.86%; 98 patients completed the supplement in the third trimester, accounting for 23.22%; and 17 pregnant women could not accurately recall the time when the supplement was completed.There was no statistical difference in the time distribution of the end of supplementation between the post-pregnancy supplement group and the pre-pregnancy supplement group (P> 0.05) (Table 2).

Table 2Time distribution of pregnant women ending supplementation n (%).
3.2 Mental development of infants at 1-12 months of age
With the increase of age, the infant scores increased gradually in exercise, social adaptation and intelligence energy region, but at 1, 6,8-month-old, the DQ and the MI are higher (Table 3).
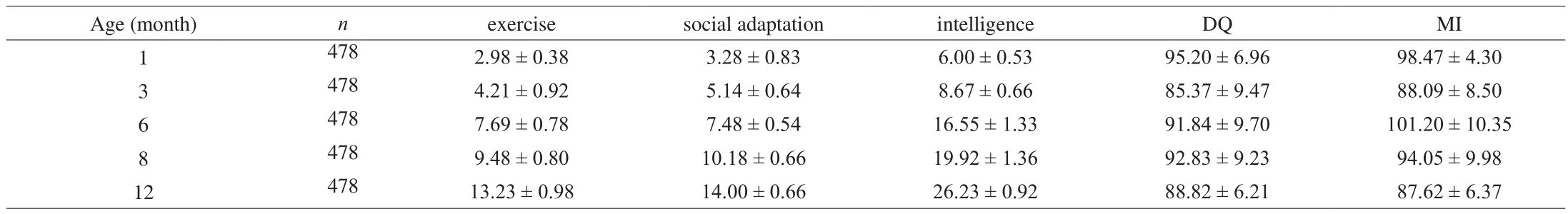
Table 3DST test scores according to age in infants.
3.3 Effect of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy on infants’ intelligent development
A screening test was conducted on the corresponding infants of the recruited pregnant women, a mixed-effect linear model was used to analyse the results of exercise, social adaption, intelligence scores,DQ and MI (Table 4).
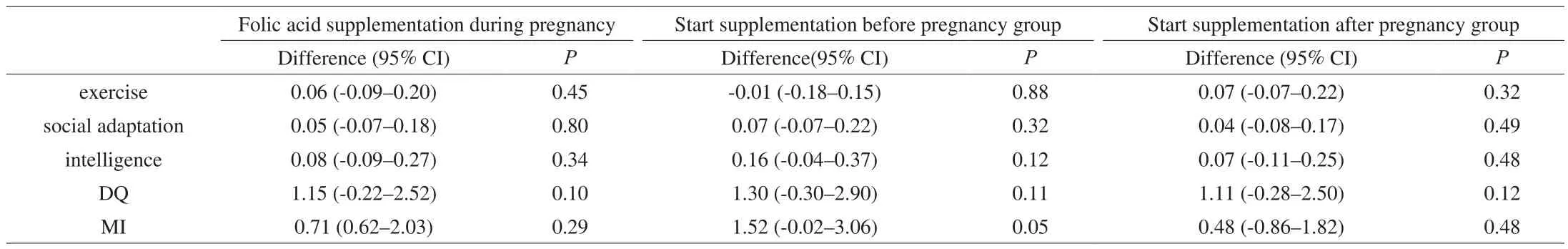
Table 4Comparison of intellectual development between infants who unsupplemented, received folic acid supplementation before pregnancy and after pregnancy.
Table 4 shows the difference in the scores of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy (including pre-pregnancy supplementation group and post-pregnancy supplementation group)compared with the unsupplemented group, as well as the difference in the scores of folic acid supplementation during the pre-pregnancy supplement group and the post-pregnancy supplement group compared with the non-supplemented group. No association between folic acid supplementation during pregnancy and different timing of supplementation and infants’ intellectual development was found.
3.4 The effect of prenatal serum folic acid, vitamin B12 and Hcy levels on infants’ intelligence development
Pregnant women were divided into normal group and low serum folic acid group according to the prenatal serum folic acid concentration. Pregnant women with serum folate concentration less than 7 nmol/L had low folate levels. Vitamin B12levels below 150 pmol/L are recognized as low vitamin B12group. The high homocysteine group is defined as a serum homocysteine concentration greater than 7 μmol/L. The mixed effect linear model was used to analyse the effect of serum indicators on infant intelligence development (Table 5).

Table 5The association between prenatal serum index and infants’ mental development.
Compared with the normal level group, the infants with low serum folate levels score reduce by 0.12 points (95% CI -0.23--0.01) in the intelligence energy zone, and the MI decreased by 0.80 points (95% CI -1.56--0.03). The effect of prenatal serum vitamin B12concentration on infant intelligence development was not observed.Compared with the normal level group, The MI score of the high homocysteine group was reduced by 1.30 points (95% CI -2.25- -0.08).
3.5 Effects of folic acid and vitamin B12 levels in colostrum on infants’ intelligent development
Since the concentration of folic acid in colostrum is about 10 times that of serum folic acid, a pregnant woman with a folic acid concentration of less than 70 nmol/L in colostrum is defined as a colostrum low folate level group. The concentration of vitamin B12in colostrum is comparable to the serum concentration, so low colostrum vitamin B12group means less than 150 pmol/L. The scores of infants in the normal concentration group were compared (Table 6).

Table 6The association between colostrum and infant intellectual development.
Compared with the normal group, the society energy region score of infants’ colostrum in low vitamin B12group reduced by 0.10(95% CI -1.84- -0.02), but the association between vitamin B12in colostrum, and DQ and MI was not found.
4. Discussion
4.1 Folic acid supplements
Among 478 pregnant women, the proportion of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy was about 88.08%, and 11.92% of pregnant women did not take supplementary folic acid during pregnancy. As an important water-soluble vitamin, folic acid can reduce the incidence of fetal NTDs [22-26], as well as reduce the level of Hcy in pregnant women to reduce the incidence of related adverse pregnancy outcomes [2,27-29]. According to research [30-32],vitamin B12and folic acid play key roles in one-carbon metabolism and influence each other. Inadequate intake of folic acid during pregnancy can interfere with the early development and function of the brain, leading to neurochemical or neurometabolic changes.These changes are expressed by limiting myelination and synaptic connections and changes in tissue levels of neurotransmitters, which further affect the brain structural and functional development.
Therefore, standard supplementation of folic acid during pregnancy is of great significance. However, it has been reported that in many countries including Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom,the United States, Pakistan, New Zealand, Italy and Germany, less than 50% of pregnant women use folic acid supplements [33-38],and women with lower education are less likely to take folic acid supplements than women with higher education [34,39]. Therefore,pregnant women should consume more food rich in folic acid or take folic acid supplements according to their own conditions.
4.2 Serum folic acid and Hcy
The results of the study did not find the association between folic acid supplementation during pregnancy and infant intelligence development. However, compared with normal serum folate and Hcy levels, low folate levels and high Hcy levels may affect the infant’s mental development. The infants in the colostrum low vitamin B12group had low scores in the social adaptive energy zone, but no association between colostrum vitamin B12concentration and the total scores DQ and MI was found.
At present, many researchers are studying on improving the nutritional status in early life, in order to promote the development of physique and intelligence. Because folic acid plays an important role in the proliferation of neurons and glial cells and the synthesis of neurotransmitters, in recent years, the relationship between the levels of folate, vitamin B12and homocysteine during pregnancy and the cognitive development level of offspring has become a hot spot.
In a cohort study on birth defects in Jiangsu, Liu et al. [40] found that oral folic acid dose over 0.4 mg/day in the first two months of pregnancy can significantly improve offspring MI score. Prospective pre-birth cohort study in Massachusetts indicates that higher levels of folate intake in early pregnancy are associated with higher intelligence scores in 3-year-old children [41]. A Northern Ireland study by Henry[17] suggested that there may be a link between the beneficial effects of folic acid on brain development and subsequent psychological factors in children’s development. A large Norwegian (n = 38 945) mother-child cohort study found that compared with the non-supplemented group,folic acid supplementation alone or supplements containing folic acid in the first trimester can reduce the risk of severe language development retardation of the offspring at 3 years of age [42].
However, research in recent years has found that excessive folic acid supplementation during pregnancy also has hazards and hidden dangers. Skórka et al. [43,44] evaluated the evidence on whether folic acid supplementation during pregnancy and early life affects children’s intellectual development. The results showed that supplement does not affect the intellectual development of infants with an average age of 11 months and the development quotient of 2- and 6-year-old children.
Valera-Gran et al. [45] indicated that when the dosage of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy exceeds 1 mg/day, the neurocognitive development level of children at the age of 4 or 5 will be reduced. At the same time, a study showed that the nutritional status of folic acid in mothers in the second half of pregnancy had no effect on the neurodevelopment of 5-year-olds [46].
The survey found that compared with the normal level group,maternal prenatal serum low folate levels or high homocysteine levels may have an impact on infants’ mental development, possibly because some women have anaemia, and pregnant anaemia can affects the intellectual development of offspring [47]. Second, low folate levels lead to elevated homocysteine concentrations, while high concentrations of homocysteine impair cognitive ability [48-50]. Studies in the Indian population have found that, compared with lower levels of folic acid,higher folate concentrations during pregnancy predict better cognitive development in children [51]. Gross et al. [52] have confirmed that pregnant women with megaloblastic anaemia due to folic acid deficiency have adverse effects of neurodevelopmental delay.
4.3 Vitamin B12 in colostrum
Our study found that the scores of infants group with low vitamin B12in colostrum decreased by 0.10 in the social energy area, but vitamin B12in colostrum was not associated with DQ scores and MI.Vitamin B12plays an important role in brain development [53]. Strand et al. [32] assessed serum B12levels and cognitive ability of infants from 12 months to 18 months, and reported that vitamin B12status was related to cognitive ability. A study by Garcia et al. [54] reported that vitamin B12deficiency in the diet of pregnant women in the first trimester was negatively correlated with children’s intellectual development.
However, the study examined the link between the vitamin B12status of pregnant women and the cognitive function of future generations and found inconsistencies.
Studies in India have shown that there is no correlation between mother’s vitamin B12concentration and the cognitive function of 9-month-old infants [55] and 9-10 year-old children [51]. Among Canadian nutritionally rich women, the status of maternal vitamin B12has nothing to do with children’s cognitive ability [56]. Therefore, the impact of colostrum vitamin B12levels on social energy areas may be due to individual differences.
4.4 Innovation and limitations
In our study, the levels of folic acid and vitamin B12in postpartum colostrum were detected and combined with infant scores for statistical analysis, which has not been studied yet. At the same time, this study also assessed whether there is a causal relationship between maternal folic acid supplementation and the cognitive ability of future generations.
Regarding the limitations, we only analysed the scores of infants at 1, 3, 6, 8, and 12 months. In the next study, we can further analyse the association between folic acid supplementation during pregnancy and the intelligent development of infants aged 2-5 years. At the same time, animal and cell experiments can be carried out to further analyse the mechanism of folic acid, vitamin B12, homocysteine on the nervous system.
5. Conclusion
In summary, small doses of folic acid (0.2-0.8 mg/day) before and after pregnancy may be not related to infant intelligence development.This result may be caused by individual differences in folate and Hcy metabolism in pregnant women. The concentration of prenatal folic acid and homocysteine in pregnant women and the concentration of vitamin B12in colostrum may be associated with infants’ intelligent development.
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Nutrition Research Foundation of Chinese Nutrition Society ---Research Fund of Feihe Physical Nutrition and Health (Grant No: CNS-Feihe2018B01), and Nanjing medical science and technology development fund (Grant No:YKK19127).
- 食品科學(xué)與人類健康(英文)的其它文章
- Internal connections between dietary intake and gut microbiota homeostasis in disease progression of ulcerative colitis: a review
- Predominant yeasts in Chinese Dong fermented pork (Nanx Wudl) and their aroma-producing properties in fermented sausage condition
- Isolation and identification of fungi found in contaminated fermented milk and antifungal activity of vanillin
- Investigation of physicochemical, microbiological and sensorial properties for organic and conventional retail chicken meat
- Preparation and physicochemical/antimicrobial characteristics of asparagus cellulose films containing quercetin
- Simultaneous determination of 74 pesticide residues in Panax notoginseng by QuEChERS coupled with gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry

