Apolipoprotein E polymorphism influences orthotopic liver transplantation outcomes in patients with hepatitis C virus-induced liver cirrhosis
Jose Carlos Rodrigues Nascimento, Lianna C Pereira, Juliana Magalhaes C Rego, Ronaldo P Dias, Paulo
Goberlainio B Silva, Silvio Alencar C Sobrinho, Gustavo R Coelho, Ivelise Regina C Brasil, Edmilson F Oliveira-Filho, James S Owen, Pierluigi Toniutto, Reinaldo B Oria
Abstract
Key Words: Apolipoprotein E; Polymorphism; Liver cirrhosis; Hepatitis C virus; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver transplantation
INTRODUCTION
The World Health Organization reported in 2015, that around 71 million people had chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection worldwide, with a global prevalence of 1% and that 399,000 died of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or cirrhosis[1].
HCV infection causes a chronic liver inflammatory condition leading to chronic hepatitis[2,3]. The evolution from acute to chronic hepatitis C occurs in up to 80% of cases when HCV infection lasts for more than six months. Without characteristic symptoms, HCV evolves slowly, for years, with approximately 20% of those chronically infected progressing to cirrhosis, and between 1% to 5% to HCC[4,5].
Human apolipoprotein E (protein: ApoE, gene: APOE) is a 34-KDa glycoprotein of 299 amino acids. ApoE is an important protein constituent of very-low-density lipoproteins (LDL), high-density lipoproteins, and chylomicrons in plasma, and a ligand for the LDL receptor[6]. ApoE is synthesized mainly in the liver (90%), but also in spleen, kidney, lungs, gonads, monocyte-macrophages, and in the nervous system[7,8].
The human APOE gene is polymorphic with three common APOE alleles on chromosome 19 (19q13), named E2, E3 and E4, giving six possible genotypes: E2/E2, E2/E3, E2/E4, E3/E3, E3/E4 and E4/E4[9]. These alleles form different ApoE isoforms due to amino acid substitutions at positions 112 and 158: E2 = Cys-112/Cys-158; E3 = Cys-112/Arg-158; and E4 = Arg-112/Arg-158[10].
Several studies have documented the association between ApoE isoforms and chronic illnesses such as Alzheimer's disease[11], atherosclerosis[12], herpes simplex virus infection[13]and early childhood diarrhea[12]. The ApoE4 allele has been recently associated with a high risk for severe coronavirus disease 2019 infection, independent of preexisting cardiovascular disease, type-2 diabetes and dementia[14]. In addition, the APOE3/3 genotype is implicated in fibrosis progression in HCV-infected patients, likely through mechanisms of competition for viral entry and replication[15].
Although some studies report that APOE4 exerts a protective effect in HCV-induced liver damage, no studies have investigated the role of APOE genotypes in modifying the natural history of HCV-induced liver injury in liver transplanted patients in a Brazilian setting. Our aim, therefore, was to establish whether APOE4 genotype recipients were associated with more benign HCV-related liver injuries compared to patients with other APOE genotypes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
This is a cohort study conducted at the University Hospital Walter Cantídio and the Fortaleza General Hospital (HGF). A total of 179 consecutive patients were enrolled from May 2017 to July 2019 for the collection of buccal cells and medical record data. Medical records from liver transplant recipients before May 2017 were also collected retrospectively and prospectively each year. Patients in the orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) queue, or liver transplanted from May 2017 onwards, had data collected prospectively and annually during the study period.
The study included 179 patients of both genders and aged 34-70 years, with HCVrelated end-stage liver disease, 105 of them complicated with HCC and 74 without HCC, in pre- and/or post-OLT. At enrolment, 143 known HCV-infected patients were on antiviral treatment, 126 with direct-acting antivirals and 17 treated with the combination of interferon & ribavirin or pegylated interferon & ribavirin; 36 patients had not received any treatment. The HCV status of all patients was confirmed by identification of serum HCV-RNA and HCV genotypes. Exclusion criteria were: patient refusal, coinfection with HBV or HIV, and HCC associated with metastases.
The study protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Federal University of Ceará, Protocol No 2.018.768 and the HGF, Protocol No 2.062.278. The research team explained the study protocol to all patients and clarified that failure to participate in the study would not cause discontinuation of care or medical treatment. Patients then read and signed the informed consent form. All protocols of this study were in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
APOE polymorphisms
Of 179 patients, oral cells for DNA extraction were obtained at single time points from 56 (31.3%) pre-OLT patients, and from 123 (68.7%) who underwent liver transplantation. Oral cell DNA was extracted using the Gentra Puregene system (Qiagen, MD, United States)[12].
APOE genotyping was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), through enhancement of a fluorescent signal (SYBR?Green) interspersed in the double strand of the amplified DNA[16]. The primers were combined in three PCR amplification mixtures according to Calero et al[16]in a Light Cycler?Nano (Roche) with a 32-well RT-PCR system.
Data and statistical analysis
Demographic, clinical and laboratory data were collected after thorough reviews of medical records during the preoperative period (179 patients) and after OLT with follow-up of the 144 transplanted patients over 10 years (Supplementary Figure 1). Data included serological markers such as anti-HCV antibodies to define the agent and quantitative HCV-RNA; severity markers of liver cirrhosis [models for end-stage liver disease (MELD)]; liver imaging (computed tomography, nuclear magnetic resonance, and ultrasonography) for identification of liver tumor and classification according to the Milan criteria[17]. Out of 144 patients who underwent OLT based on Milan classification, 24 (16.7%) were subjected to one or more sessions of chemoembolization to reduce tumor size before Milan criteria were reached.
Staging the degree of liver damage and hepatic fibrosis
Liver damage severity was categorized into different criteria. Less severe cases were identified by Milan scores (single nodule < 5 cm, or up to 3 nodules < 3 cm), METAVIR (≤ A2 and ≤ F2), and MELD < 25. Patients with more severe liver injury were scored according to the Milan expanded criteria of the University of San Francisco[18](1 nodule ≤ 6.5 cm; ≤ 3 nodules, each ≤ 4.5 cm with total diameter ≤ 8 cm), METAVIR score (A3 and ≥ F3), and MELD > 25. METAVIR scoring was categorized to assess liver inflammation/fibrosis severity (Supplementary Table 1).
Liver fibrosis was assessed by using aminotransferase-platelet ratio index (APRI) and fibrosis-4 (FIB4) scores. APRI = [AST (U/L)/35 (ULN, the upper limit of normal AST is estimated at 35)]/platelets count (109/L) × 100 and FIB4 = AST (U/L) × age (years)/[platelets count (109/L) × ALT1/2(U/L)]. The cut-off points of severity are: for significant liver fibrosis (APRI ≥ 1.5, METAVIR F3-F4, and FIB4 ≥ 3.25) and for lowdegree fibrosis (APRI ≤ 0.5, METAVIR F0-F1, and FIB4 ≤ 1.45)[19].
Liver biopsy data were obtained from liver explants patients in pre-OLT and of post-OLT liver grafts. Liver biopsies were performed post-transplant in 91 of the 144 transplant recipients, who presented positive HCV viral load, or high risk of viral recurrence or rejection. All recipients had a minimum 1-year follow-up period post-OLT, and donated at least one liver biopsy more than 1 year after their OLT.
Data were analyzed with the SPSS statistical 22.0 software. For normality, D’Agostino and Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests were performed. The absolute and relative frequencies were calculated for the categorical variables and mean ± SD for the numerical variables. Fisher’s exact test or the Mann–Whitney test was used to compare frequencies or means, respectively, when appropriate. Multilinear regression and correlation analyses were performed to avoid other potential confounders. Either oneway or two-way ANOVA test followed by Bonferroni's or Kruskal-Wallis, and Dunn's test were used for multiple comparisons. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
A total of 179 patients (145 males, 34 females) were enrolled in this study with a median age of 61 (range = 34-70). All patients were diagnosed with HCV-induced chronic liver cirrhosis; 105 of them (58.6%) complicated with HCC.
Analysis of pre-OLT data in the overall population
Demographic and clinical data were collected from all patients only in pre-OLT. Their APOE allele stratification is reported in Table 1; no statistical difference was found in any comparisons.
The APOE allele frequency according to group, HCV viral load and liver inflammation by the METAVIR score are depicted in Table 2. The APOE allele frequencies were 67.3%, 17.1% and 15.6% for E3, E2 and E4, respectively. The most frequent genotype was E3/E3 (51.4%).
APOE allele frequencies were associated with liver inflammation based on METAVIR score, assessed in biopsies of liver explants from 89 patients and from 2 patients in pre-OLT. The degree of severe inflammation (A3F4, 0.0%) was significantly less frequent than in patients with minimal and moderate degree of inflammation (≤ A2F4, 16.2%) P = 0.048, in patients carrying the APOE4 allele when compared to non-APOE4. In addition, a significant difference was also found regarding METAVIR score (≤ A2F4, 64.4% vs A3F4, 0.0%; P = 0.043) and (A1F4, 57.4% vs A3F4, 0.0%; P = 0.024) in APOE4 patients compared to APOE3 carriers (Table 3). All patients with advanced liver inflammation (A3) were treated with antivirals only in the post-OLT period.
Among patients with less severe liver disease (MELD ≤ 25), the degree of severeinflammation (A3F4, 0.0%) was significantly less frequent in APOE4 carriers when compared to non-APOE4 patients with minimal and moderate degree of inflammation (≤ A2F4, 15.7%, P = 0.046), and with minimal degree of inflammation (A1F4, 18.2%, P = 0.044). These results were also significant in APOE4 patients when compared to APOE3, as categorized by their METAVIR scores [≤ A2F4, 65.7% vs A3F4, 0.0% (P = 0.042) and A1F4, 61.4% vs A3F4, 0.0% (P = 0.040)] (Table 4).
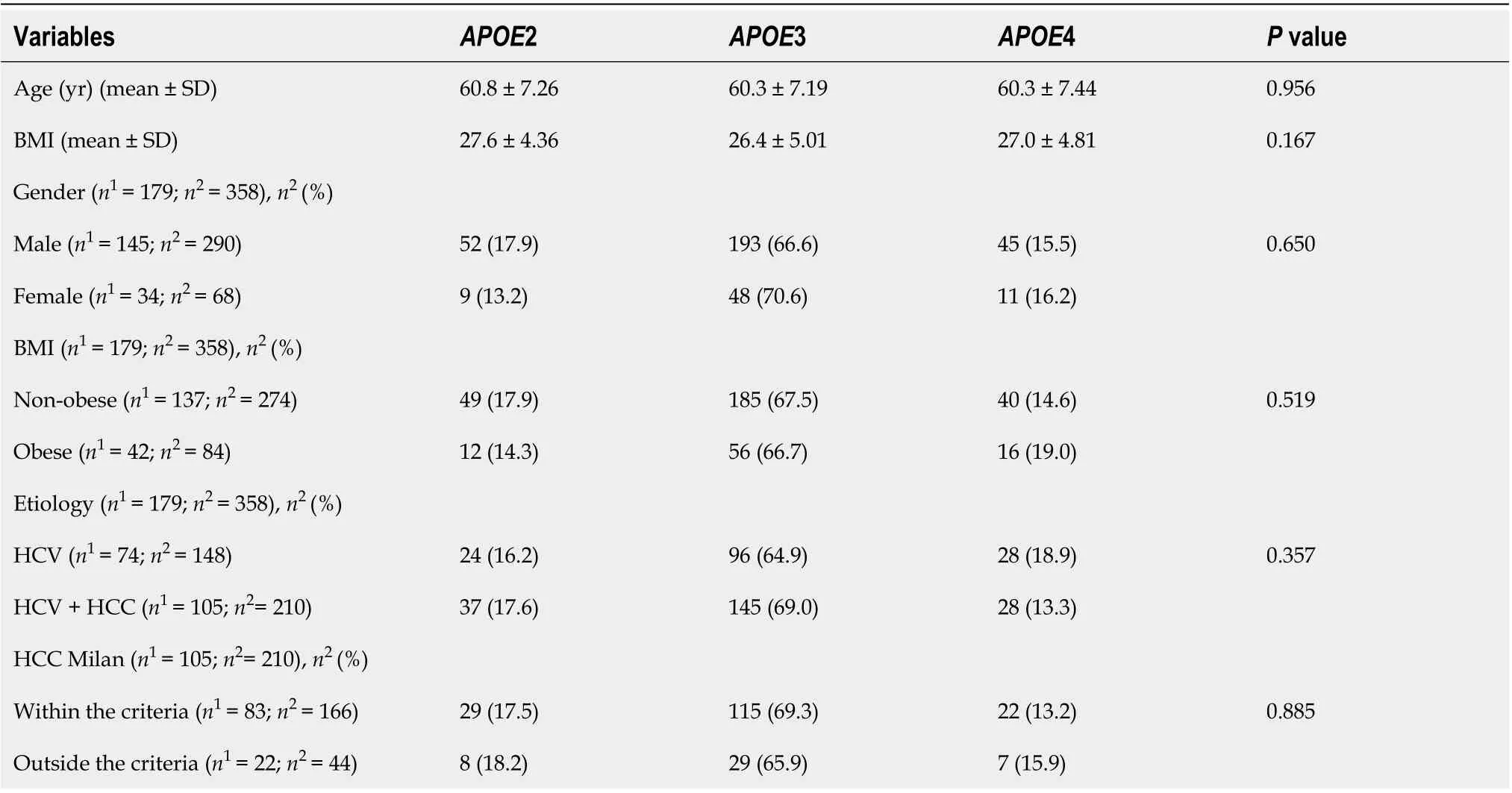
Table 1 Demographic and clinical profile of all candidate patients for liver transplant according to E2, E3 and E4 allele stratification

Table 2 Genotypic and allele distribution of apolipoprotein E according to group, hepatitis C virus serology/viral load and severity of liver inflammation by the METAVIR score of the total population
Logistic regression model predicting moderate and severe (A2A3) vs minimal (A1)degree of liver inflammation included as significant predictors male-gender (P = 0.032), and mean-BMI (P = 0.017). In the other analyses, there was no significance without adjustment or with adjustment for potential confounders (MELD, age and BMI) (Table 5).
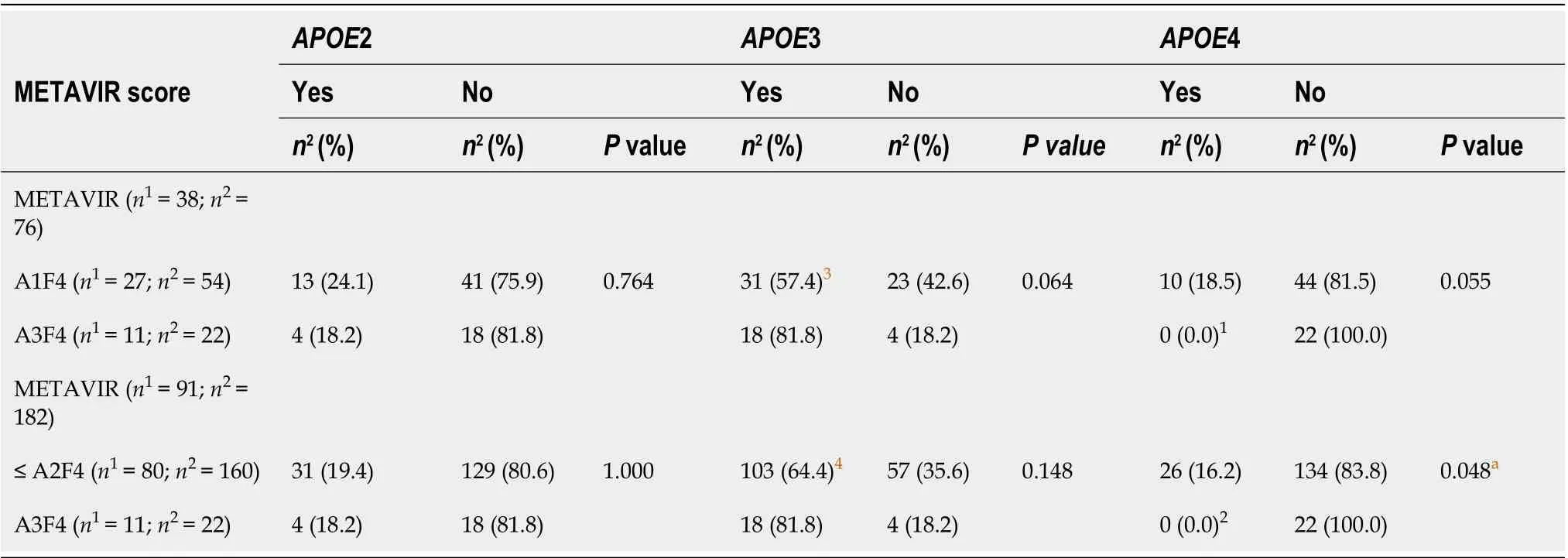
Table 3 METAVIR scores for liver inflammation in pre-orthotopic liver transplantation patients according to E2, E3 and E4 alleles stratification
Analysis of the post-OLT data
With respect to the fibrosis degree, using METAVIR scores, of liver grafts in 91 non-APOE4 patients undergoing OLT, the frequency of patients with a moderate degree of fibrosis (F2) was significantly higher in up to 1 year when compared to those between 1 and 5 years (P = 0.006) (Figure 1D). No other significant differences were found (Figure 1). Of note, patients who progressed to moderate (F2) fibrosis in the post-OLT follow-up were treated with antiviral therapy only in the post-OLT period.
In a 10-year follow-up post-OLT, based on non-invasive tests (APRI and FIB4) of the total transplanted population, a significant higher mean of the 1styear APRI score was found when compared to the 4thand 5thyears (P < 0.001), as well as between the 1styear FIB4 and the 5thyear scores (P < 0.001) (Figure 2A). APRI and FIB4 scores over the follow-up time did not significantly change regardless of the E2 and E4 alleles (Figure 2).
DISCUSSION
Increasing evidence associates APOE polymorphisms with progression of chronic liver disease[20,21]. Here, we evaluate the impact of ApoE genetic background in patients with HCV-induced liver cirrhosis, with or without HCC, transplanted or non-transplanted, and with positive or negative viral loads; in particular, in a Brazilian population and with a focus on the influence of E2, E3, and E4 alleles. We related E2, E3, and E4 carriers with the degree of liver inflammation, fibrosis and severity of the disease assessed by MELD scores, using liver biopsy and/or non-invasive indices, such as APRI and FIB4, and the METAVIR score. In addition, we also associated APOE alleles with co-morbidities and lipid blood levels.
As expected, we found E3 the most common APOE allele (67.3%), though slightly lower than the expected 70%-80% seen in the general Brazilian population[22]and in other countries[15,23]The E2 allele frequency was 17.1%, higher than in the Brazilian general population[22]and even greater than the E4 allele (15.6%). This E2 frequency in our study population was also higher than that reported by Wozniak et al[24](7.7%).
Our liver biopsies from 89 liver explants and from 2 pre-OLT patients showed that cirrhotic E4 carriers were less likely to present with severe inflammation. These results were also evident in patients with MELD score ≤ 25. All these patients with severehepatic inflammation were treated with antivirals only post-OLT. In agreement, others identified a protective role of APOE4 against severe HCV-related liver damage, when comparing to patients with mild liver disease[24], while another study found that APOE4 allele was under-represented in 996 patients chronically infected with HCV[23]. Other researchers have also noted a higher frequency of the E4 allele among patients with chronic non-cirrhotic hepatitis C, suggesting that the E4 allele is protective against severe HCV infection[25]However, somewhat inconsistent with these findings a 2003 report by Mueller et al[26]was unable to associate the E4 allele in chronic HCVinfected patients with a strong antiviral treatment response, although a later study by Price et al[27]found an association of the E2 and E4 alleles with reduced likelihood of chronic infection in HCV patients.
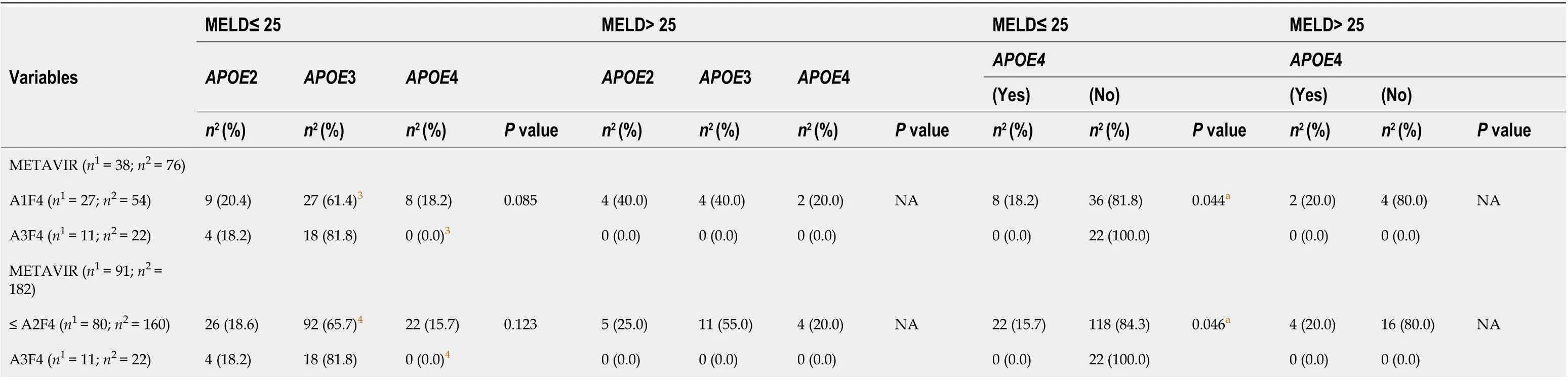
Table 4 Association of the models for end-stage liver disease score and variables in pre-orthotopic liver transplantation patients according to E2, E3 and E4 allele stratification
In 2012, Ahn et al[20]suggested that high ApoE serum levels in patients with liver cirrhosis may be due to liver inflammation. ApoE is known to modulate immune function by inhibiting CD4 and CD8 lymphocyte proliferation, reducing lymphocytederived production of IL-2, a key cytokine in regulating lymphocyte differentiation[28]. We speculate that a reduction in ApoE plasma levels, which is recognized for APOE4 carriers[6], could be protective to support OLT and to reduce over-inflammation and fibrosis caused by chronic HCV infection.
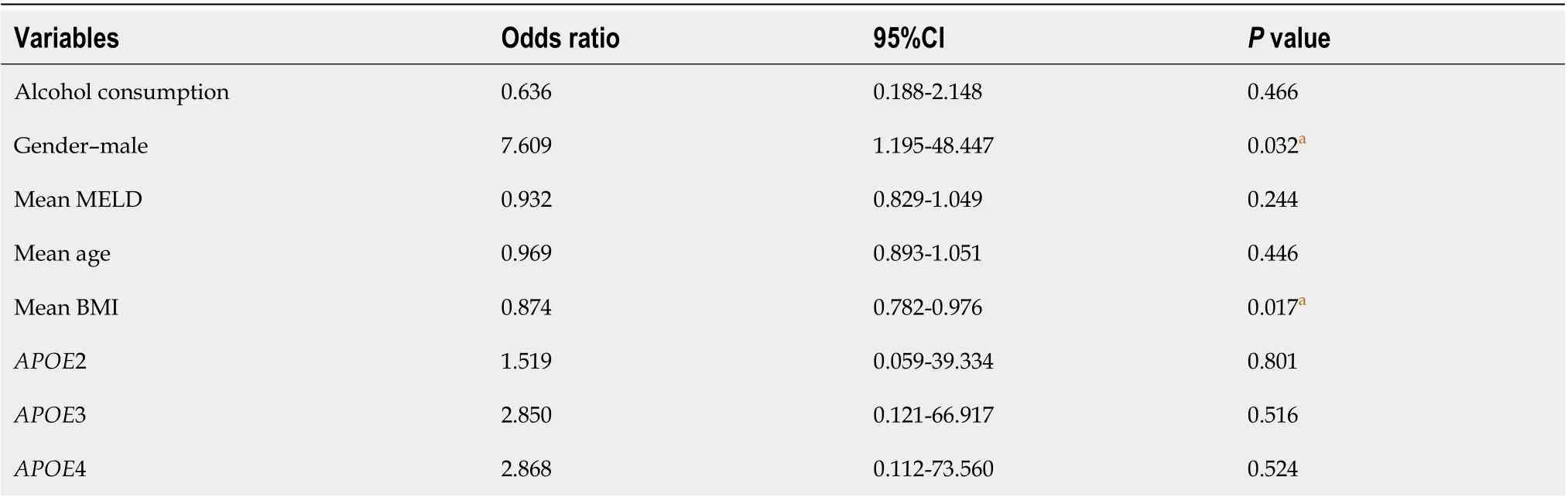
Table 5 Logistic regression model predicting moderate and severe (A2A3) degree of liver inflammation
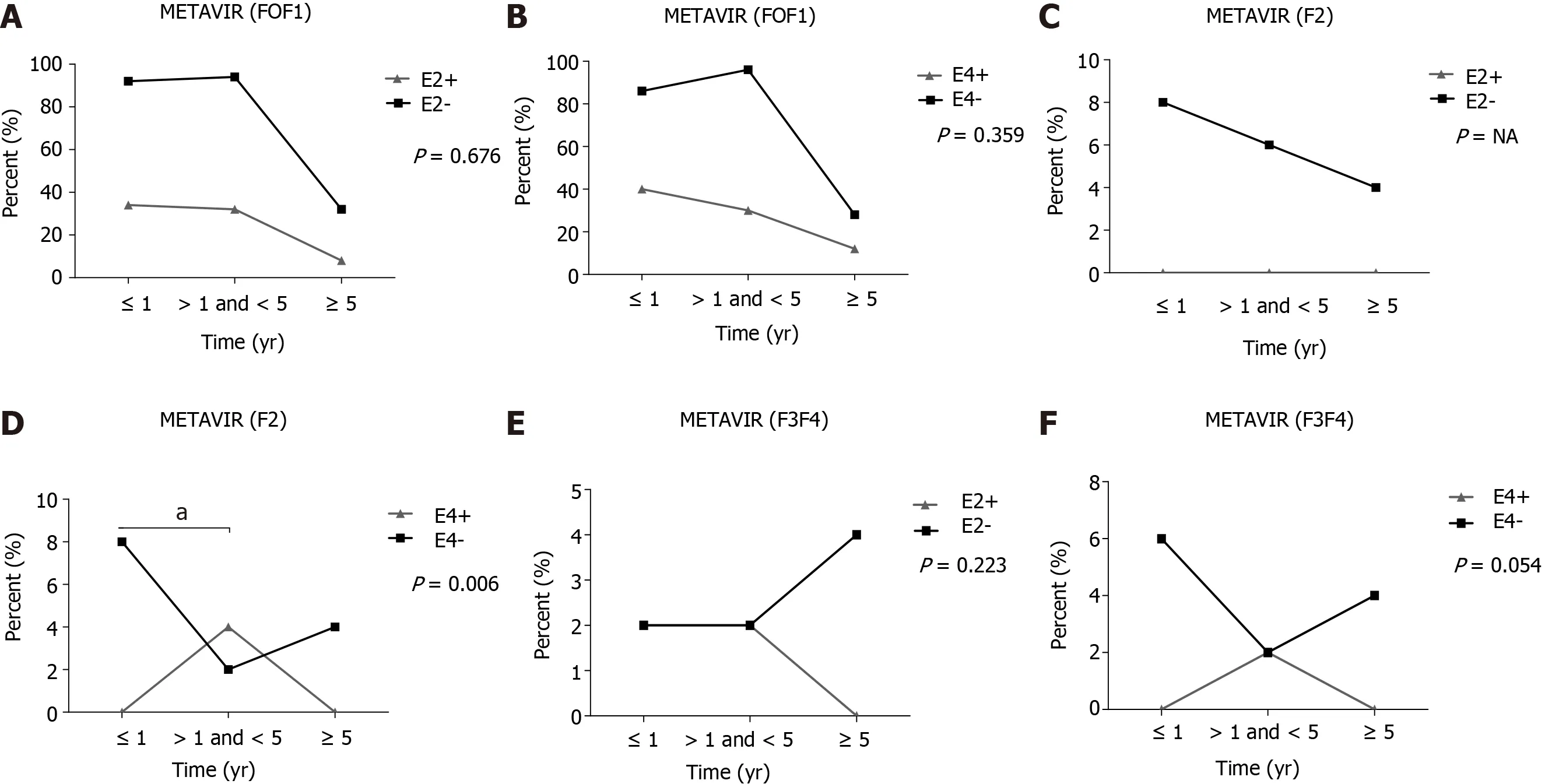
Figure 1 Follow-up of liver fibrosis in liver transplanted patients in the presence or absence of the E2 and E4 allele. A: METAVIR (F0F1) in the presence or absence of the E2 allele; B: METAVIR (F0F1) in the presence or absence of the E4 allele; C: METAVIR (F2) in the presence or absence of the E2 allele; D: METAVIR (F2) in the presence or absence of the E4 allele; E: METAVIR (F3F4) in the presence or absence of the E2 allele; F: METAVIR (F3F4) in the presence or absence of the E4 allele. aP < 0.01. E2- and E4-: Absence of the respective alleles; E2+ and E4+: Presence of the respective alleles. Fisher chi-square test; F: Degree of fibrosis; NA: Not applicable.
In the follow-up of our 144 liver transplanted patients, we identified the E4 allele as protective against the progression of liver fibrosis in 91 (63.2%) recipients. This protection of APOE4 against severe HCV-related liver fibrosis agrees with an early report[24]. Other investigators also showed a benefit of the APOE4 allele against fibrosis progression in liver transplanted patients diagnosed with HCV recurrence. Additionally, it is reported that liver transplanted patients carrying at least one E4 allele may present with reduced graft fibrosis progression during HCV recurrence. Indeed, ApoE polymorphism can be an important tool to monitor fibrosis progression in patients with hepatitis C and normal values of alanine aminotransferase, as there may be competition mechanisms for viral entry and replication in cells[15].
ApoE is a component of several lipoprotein classes and important for lipid transport. ApoE isoforms have several effects on lipoprotein entry into cells, and this mechanism might explain our results, supporting previous investigations in which ApoE4 protects against HCV infection[29,30].
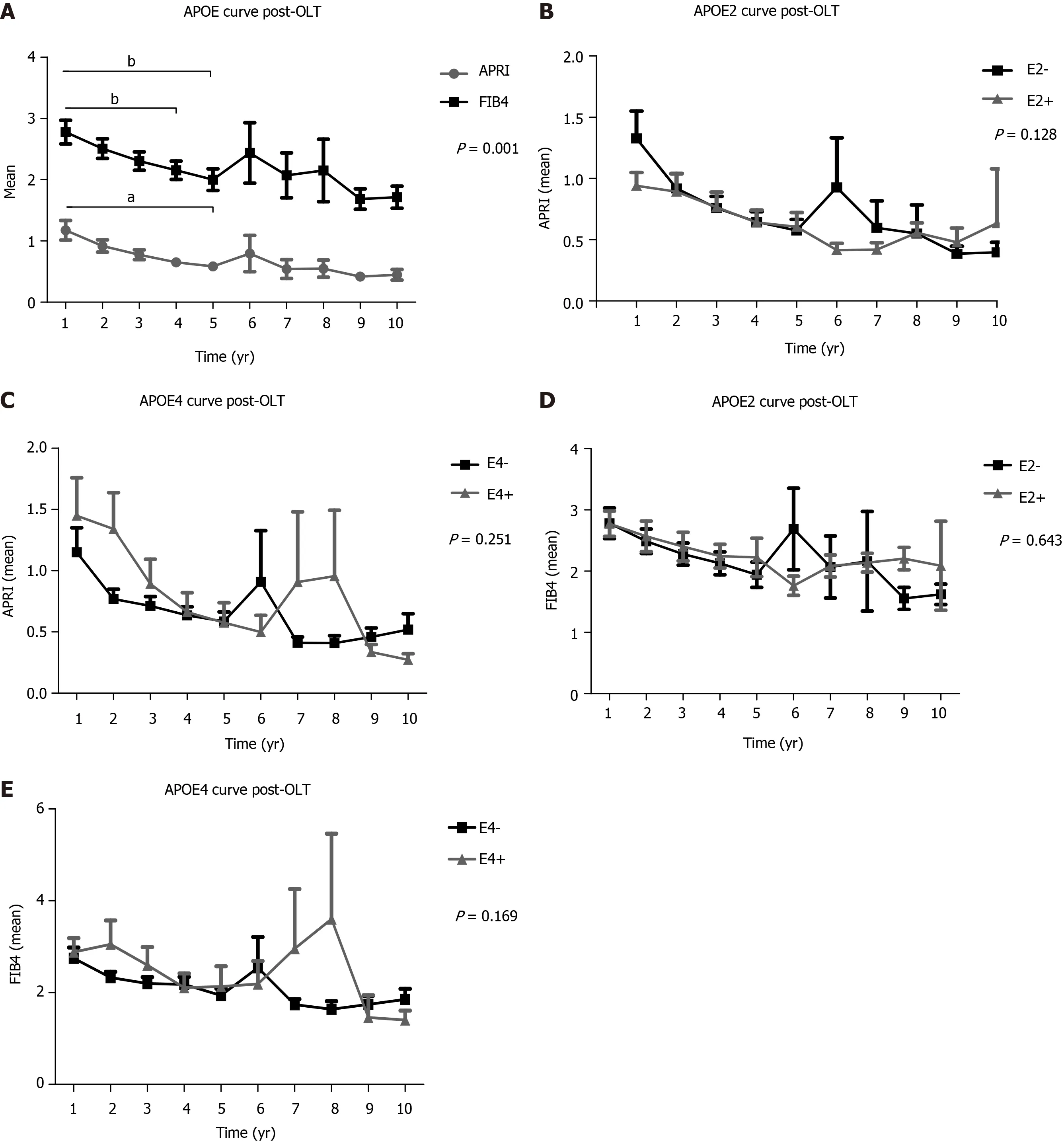
Figure 2 Follow-up using non-invasive methods (aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis 4) of liver transplant patients in the presence or absence of the E2 and E4 alleles. A: Post-orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) apolipoprotein E gene (APOE) curve for mean aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI) and fibrosis 4 (FIB4); B: Post-OLT curve considering the presence or absence of APOE2 for mean APRI; C: Post-OLT curve considering the presence or absence of APOE4 for mean APRI; D: Post-OLT curve considering the presence or absence of APOE2 for mean FIB4; E: Post-OLT curve considering the presence or absence of APOE4 for mean FIB4. Two-way ANOVA, results are shown in mean ± SEM. aP < 0.01. bP < 0.01. E2- and E4-: Absence of the respective alleles; E2+ and E4+: Presence of the respective alleles. APOE: Apolipoprotein E gene; OLT: Orthotopic liver transplantation; APRI: Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index; FIB4: Fibrosis 4.
In the follow-up of liver fibrosis progression evaluated between 1 to 10 years post-OLT of our transplanted population, the average score of APRI and FIB4, tended to decrease significantly over the years, implying liver graft survival without progression to fibrosis. Thus, non-invasive methods are now widely used in clinical practice to stage the degree of fibrosis[31,32].
Our findings suggest that APOE4 can be important tool in the medical management of patients following inflammation and liver fibrosis, since the carriage of APOE4 may select patients with a more benign clinical course of liver disease. Of note, patients with a degree of severe inflammation and moderate degree of fibrosis (F2) were cured for HCV only in the post-OLT period.
This study has some limitations: Data from liver transplanted patients were obtained retrospectively from medical records; no data from liver graft donors, including APOE genotypes, were collected. The sample size, may have been insufficient to draw strong, robust conclusions. Isoform studies have previously shown that transplanted donor livers supply > 90% of plasma ApoE[10]. The remainder is synthesized by circulating macrophages and immune cells, or by tissues such as kidney, adipose and muscle, and hence retains the phenotype of the recipient. However, to date, there are no reports of how each source, hepatic ApoE or circulating non-liver ApoE, particularly that of macrophages, might affect the inflammation and fibrosis status of the transplanted liver.
CONCLUSION
Our results indicate that APOE4 genotype may protect against HCV-induced severe hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in pre- and post-OLT patients. Additionally, the APOE2 allele was over-represented in these patients, suggesting that E2 carriers have increased risk and worse outcomes following HCV infection. Further studies are needed to better understand how ApoE levels via liver and extrahepatic derived sources, and biochemical activities, are affected by donor and recipient genetic backgrounds after liver transplantation.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors deeply thank patients and family members for agreeing to participate in this study and also staff and technicians from study hospitals for their support.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2021年11期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2021年11期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Fatigue in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in Eastern China
- Long-term follow-up of cumulative incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus patients without antiviral therapy
- Prospective single-blinded single-center randomized controlled trial of Prep Kit-C and Moviprep: Does underlying inflammatory bowel disease impact tolerability and efficacy?
- Study on the characteristics of intestinal motility of constipation in patients with Parkinson's disease
- Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric tube cancer: A multicenter retrospective study
- How to manage inflammatory bowel disease during the COVID-19 pandemic: A guide for the practicing clinician
