How to manage inflammatory bowel disease during the COVID-19 pandemic: A guide for the practicing clinician
Jllio Maria Fonseca Chebli, Natalia Sousa Freitas Queiroz, Aderson Omar Mourao Cintra Damiao, Liliana Andrade Chebli, Marcia Henriques de Magalhaes Costa, Rogerio Serafim Parra
Abstract Managing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has been a challenge faced by clinicians and their patients, especially concerning whether to proceed with biologics and immunosuppressive agents in the background of a global outbreak of a highly contagious new coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, SARS-CoV-2). The knowledge about the impact of this virus on patients with IBD, although it is still scarce, is rapidly evolving. In particular, concerns surrounding medications’ impact for IBD on the risk of acquiring SARS-CoV-2 infection or developing COVID-19, and potentially exacerbate viral replication and the COVID-19 course, are a current thinking of both practicing clinicians and providers caring for patients with IBD. Managing patients with IBD infected with SARS-CoV-2 depends on both the clinical activity of the IBD and the occasional development and severity of COVID-19. In this review, we summarize the current data regarding gastrointestinal involvement by SARS-CoV-2 and pharmacologic and surgical management for IBD concerning this infection, and the COVID-19 impact on both the patient's psychological functioning and endoscopy services, and we concisely summarize the telemedicine roles during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Key Words: Inflammatory bowel disease; SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19; Crohn disease; Colitis ulcerative; Biological therapy
INTRODUCTION
Over the past year, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has evolved as a public health emergency of international concern. The epidemiological panorama is constantly evolving, and the data updated to January 12, 2021 have 191 countries involved, with more than 90947243 confirmed cases and 1947243 confirmed deaths globally[1]. The first opportunity to eradicate the virus over the long term and to protect specific patients from COVID-19 is by introducing severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccines[2]. Although efforts to implement mass vaccination programs are currently in place globally, high rates of COVID-19 infections and fatalities are still expected in the months ahead.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD), are chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract affecting millions of people worldwide[3]. Patients with IBD and other immunemediated diseases often require treatment with corticosteroids, immunomodulators (thiopurines, methotrexate), biologics, and Janus kinase inhibitors, which can increase the risk of infections[4-6]. However, until now, the incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with IBD and immunosuppressive therapy did not appear to differ from the general population[7]. Also, based on data from an international registry developed to collect information from patients with IBD from all over the world with confirmed COVID-19 and its outcomes, and the Surveillance Epidemiology of Coronavirus Under Research Exclusion for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (SECURE-IBD), the evolution of COVID-19 does not seem to be worse in patients with IBD[8].
Notwithstanding, most elective clinical activities involving IBD care were drastically decreased during the pandemic[9-11]. Moreover, as suggested by the most qualified international societies and organizations, outpatient visits, colonoscopies, and nonurgent surgery have been postponed to prevent patient contact with the hospital and to enable patients with IBD to maintain social isolation[12,13].
As the world is gradually attempting to normalize, IBD physicians must face new challenges in terms of both future uncertainty, given the lack of supply of COVID-19 vaccines worldwide, and the ability to reorganize clinical activities for patients with IBD to provide optimal care while avoiding new outbreaks. Facing this scenario, this review aims to critically analyze the evidence on the effect of medications commonly used to treat IBD, as well as the management of the disease in its different degrees of activity, including the setting of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
WHAT IS THE RISK OF SARS-CoV-2 INFECTION IN THE IBD POPULATION?
Data on the incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with IBD have been conflicting. Initial evidence suggested that patients with IBD had a lower risk of COVID-19 compared to the general population, as subsequent studies reported that no case of COVID-19 was diagnosed among patients with IBD followed in referral centers in China and Italy[14,15]. However, other studies assessing the risk of COVID-19 among patients with IBD reported incidence rates of 4.9 cases per 1000 patients with IBD in a Spanish cohort[16]and 2.5 cases per 1000 patients with IBD in France and Italy cohorts[17]. In a recent systematic review and meta-analysis by Aziz et al[7]comprising six studies that incorporated data from 9177 patients with IBD, the pooled incidence of COVID-19 in the IBD population was approximately 0.3%, which is greatly reassuring, as the incidence is on the lower side compared with the general population (0.2%-4.0%)[7]. Although there is limited evidence available, it seems that patients with IBD are not at greater risk of acquiring COVID-19, and SARS-CoV-2 infection does not seem to be more prevalent in patients with IBD than in the general population. However, this data must be interpreted with caution given that IBD patients might have better adherence to protection, social distancing and hygiene measures, which could explain the lower incidence in this population.
MANAGING IBD MEDICATIONS DURING THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC
Managing IBD medications during SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19
Managing IBD during the COVID-19 pandemic has been a challenge faced by clinicians and their patients, especially concerning whether to carry on with biologics and immunosuppressive agents in the background of a global outbreak of a highly SARS-CoV-2. The knowledge about the impact of this virus on patients with IBD, although it is still scarce, is rapidly evolving[18].
In particular, concerns surrounding medications’ impact for IBD on the risk of acquiring SARS-CoV-2 infection or developing COVID-19, and potentially exacerbate viral replication and the COVID-19 course, are a current thinking of both practicing clinicians and providers caring for patients with IBD. Confounding a systematic management strategy reveals that evidence-based data are scarce[19].
Providers caring for patients with IBD during the COVID-19 outbreak are opportune to reduce the burden of COVID-19 by assuming or sharing responsibility for multidisciplinary management of patients with IBD in this common clinical difficulty. The main goal that must be kept in mind is to treat active disease and maintain remission[20].
Fortunately, the worldwide management of patients with IBD during the COVID-19 pandemic presents considerable agreement. Indeed, gastroenterologists, both adult and pediatric, and colorectal surgeons were attending the practical recommendations/ guidance and consensus statements from several societies of gastroenterology, endoscopy, surgery, and from the International Organization for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IOIBD) with adaptations based on local regional characteristics[18]. For instance, an international survey on this issue showed that most gastroenterologists reduced clinic visits, restricted steroid use, and postponed elective endoscopic procedures and surgery. Also, if a patient was diagnosed with COVID-19, biologics and immunomodulators were mostly held[21].
Understanding the short- and long-term safety of drugs used in patients with IBD remains an important area of research, especially now in the middle of the COVID-19 pandemic. Preliminary evidence specified that except high-dose systemic steroids, using aminosalicylates, budesonide, antibiotics, rectal therapies, nutritional therapy, immunomodulators, and biologics, including anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents, anti-integrin, or anti-interleukin (IL)-12/23, were well tolerated without an increased risk of unfavorable evolution or duration of viral disease in patients with IBD that develop infection by SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19[8]. However, recent accumulating evidence from SECURE-IBD registry based on data on over 1400 patients with IBD suggests that compared with anti-TNF monotherapy, thiopurine monotherapy, combotherapy of thiopurines with anti-TNF agent, and, surprisingly, aminosalicylates were associated with significantly increased risk of severe COVID-19, although the association with latter will require further replication in other IBD populations[22]. The authors of this study hypothesized that the influence of combotherapy on increased COVID-19 severity appears to be guided by thiopurines, as the estimated impact for thiopurines monotherapy and combotherapy compared with anti-TNF monotherapy were similar[22]. Furthermore, this hypothesis followed previous observations that found a higher risk of viral infections in patients during treatment with thiopurines alone or in combotherapy with anti-TNF agents[4]. In line with the British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) statements[13], these researchers proposed the withdrawal of thiopurine while the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic in high-risk patients with IBD, for instance, those with older age or multiple comorbidities that are in stable remission on combotherapy with anti-TNF agent[22]. Also, in this international registry in progress, there are no significant differences between biological classes (anti-TNF, anti-IL12/23, and integrin antagonists) on the risk of developing severe COVID-19.
Interestingly, some anecdotal reports have shown improvement in pulmonary symptoms and multisystem inflammatory syndrome related to COVID-19 in patients with active IBD treated with infliximab[23,24]. However, whether anti-TNF alpha therapy or other anti-inflammatory agents may protect against cytokine release syndrome in patients with COVID-19 will require further investigation[25]. Moreover, as advances in IBD therapy broaden the therapeutic arsenal, it will be necessary to maintain investigations using collaborative multi-center registries for evaluating the possible impact of novel agents, such as Janus kinase inhibitors, IL-23 antagonists, and others, on SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19. It should be highlighted that as the knowledge regarding SARS-CoV-2 progresses, it is likely that IBD-specific recommendations in the COVID-19 setting also undergo substantial changes[26].
Managing patients with IBD infected with SARS-CoV-2 depends on both the clinical activity of the IBD and the occasional development and severity of COVID-19[12,27]. For practical purposes, we will present current recommendations for managing drugs for IBD concerning the SARS-CoV-2 infectious status into distinct clinical scenarios: (1) The patient attending outpatient clinic with IBD in remission in the setting of the asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection or confirmed or suspected COVID-19; (2) The patient with active IBD undergoing outpatient follow-up in the setting of the asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection or confirmed or suspected COVID-19; and (3) The patient with IBD hospitalized with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19.
Management of patient attending outpatient clinic with IBD in remission in the setting of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection or confirmed or suspected COVID-19 without systemic hyperinflammation syndrome
As the COVID-19 pandemic expands, an increasing number of tests for SARS-CoV-2 are being conducted, including asymptomatic contacts of COVID-19 index cases. Thus, the situation in which an individual tests positive for the virus but remains asymptomatic will be more and more frequent.
The IOIBD recommends for quiescent patients with IBD with asymptomatic SARSCoV-2 infection — quick withdrawal of prednisone or de-escalating to < 20 mg/d or switch to budesonide or budesonide MMX (Multi Matrix System) when appropriate[12]. Immunomodulators such as thiopurines, methotrexate, and tofacitinib (or other Janus kinase inhibitors) should be temporarily held for 2 wk while monitoring for the appearance of COVID-19 symptoms[12]. Similarly, biologic administration, including anti-TNF drugs, vedolizumab, and ustekinumab, should be postponed for 2 wk if the dose is due, even recognizing that the half-lives of these biologics are relatively long, so that immunosuppressive effects of these drugs will persist for a few additional weeks despite the withdrawal of these agents[26]. Conversely, nonimmune-based anti-inflammatory therapies such as aminosalicylates, antibiotics, budesonide, or rectal therapy may be continued[22,26]. However, for patients with IBD who have had the closest contact with an individual with proven or suspected COVID-19, it is suggested that they isolate themselves and follow local recommendations from health managers. In this situation, European Crohn and Colitis Organization (ECCO) experts recommend that it is unnecessary to hold biologics or immunomodulators based on exposure only[20].
For patient attending outpatient clinic with quiescent IBD but with confirmed or suspected COVID-19, the approach to drug management is like that adopted for patients with asymptomatic infection by SARS-CoV-2. The American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) and IOIBD experts suggest that budesonide, aminosalycilates, antibiotics, and topical therapy may be maintained while systemic corticosteroids (prednisone) should be avoided and withdraw speedily, if possible. Likewise, it is recommended to hold immunomodulators, Janus kinase inhibitors, and biologics until after disappearance of symptoms, usually for 2 wk during the acute disease[12,26].
Management of patient with active IBD undergoing outpatient follow-up in the setting of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection or confirmed or suspected COVID-19 without systemic hyperinflammation syndrome
Currently, in the COVID-19 era, if a patient with IBD presents an apparent flare, it is important to always question the presence of concomitant symptoms suggestive of COVID-19, such as fever, cough, anosmia, or dyspnea, because GI symptoms including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain have been reported in 2%-33% of patients on initial presentation of COVID-19[28]. Moreover, in a few cases, these digestive symptoms may be the only clinical features of COVID-19[29]. This context is a clinical challenge, compounded by the frequent finding of remarkably elevated serum inflammatory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19.
When a patient with IBD presents diarrhea, it is doubtful whether this is secondary to a disease flare or COVID-19, a wait-and-see approach for the next 5-7 d is a reasonable strategy[27], once the diarrhea due to COVID-19 is mostly mild and selflimited, usually with an average duration of 5 d (range, 1 d to 14 d ) and a mean frequency of four bowel movements per day[30]. Also, follow-up using interval assessment of fecal calprotectin (FC) may be useful, as FC levels are typically both transiently raised and mildly elevated in patients with diarrhea caused by COVID-19[31]. In contrast, in active IBD, sustained and substantial elevation of FC is commonly seen. In any case, in the current era of COVID-19, the joint expert consensus from ECCO recommends that all patients with a suspected IBD flare be tested to exclude COVID-19 preferably with oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal swabs reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assays when the first symptoms emerge[20].
In cases where, after initial assessment, diagnostic doubts remain, computed tomography (CT) scans of the chest, abdominal cross-sectional imaging methods, and, more restrictively, ileocolonoscopy assessment can allow the real cause of diarrhea to be established[20]. Another question that remains unknown is whether SARS-CoV-2 can cause a flare of or de novo IBD[19]. Moreover, in patients with apparently active IBD (especially colonic IBD), it is important to be aware to exclude enteric superinfections, mainly due to Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile) and cytomegalovirus (CMV), assess adherence to therapy, and perform therapeutic drug monitoring of biologics[27].
If GI symptoms (including diarrhea) are not caused by COVID-19 and other causes for IBD flare are excluded, such as enteric superinfection, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory use, and non-adherence to therapy, the drug management for IBD will depend on the equilibrium between the severities of the IBD flare and those of the COVID-19[18-20]. For a flare of mild severity in outpatients with asymptomatic infection by SARS-CoV-2 or with mild to moderate COVID-19 without systemic hyperinflammation syndrome (SHS), it is recommended tapering off prednisone or its equivalent for < 20 mg/d with complete weaning where possible, balancing with the potential for possible adrenal insufficiency in the setting of chronic corticosteroid therapy[12,26,27]. Another option that can be considered in patients using systemic steroids is converting to oral budesonide or budesonide MMX on adequate dosing, provided the patient is in the appropriate clinical setting (e.g., mildly to moderately active ileocecal CD or UC, respectively). Further, it is suggested stopping or avoiding commencing immunomodulators, tofacitinib (or other Janus kinase inhibitors), and biologics for at least 2 wk during viral illness, while budesonide, aminosalycilates, antibiotics, and topical therapy may be initiated or maintained if needed[26,27].
The approach for a IBD flare-up moderate to severe in patients attending outpatient clinic with COVID-19 without SHS may include continuation of current biological therapy for IBD with optimization to rescue a state of remission or starting a new biological agent if needed, preferably in monotherapy and with subcutaneous biologics to reduce the risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in infusion units[20,27].
In this clinical context, if glucocorticosteroids are considered essential, the dose of prednisone (or its equivalent) should be ≤ 40 mg/d limiting the duration of use, if practicable[26]. Also, it is advised to stop if in use or avoid commencing immunomodulators or tofacitinib. If COVID-19 is progressive with significant pulmonary involvement and hospitalization, consultation with infectious diseases experts for possible COVID-19 treatment with antiviral or experimental anticytokine therapy may be interesting[19,20,27]. In Tables 1-3, we present an approach for managing IBD medications in patients attending outpatient clinic who are infected with SARS-CoV-2 with or without COVID-19.
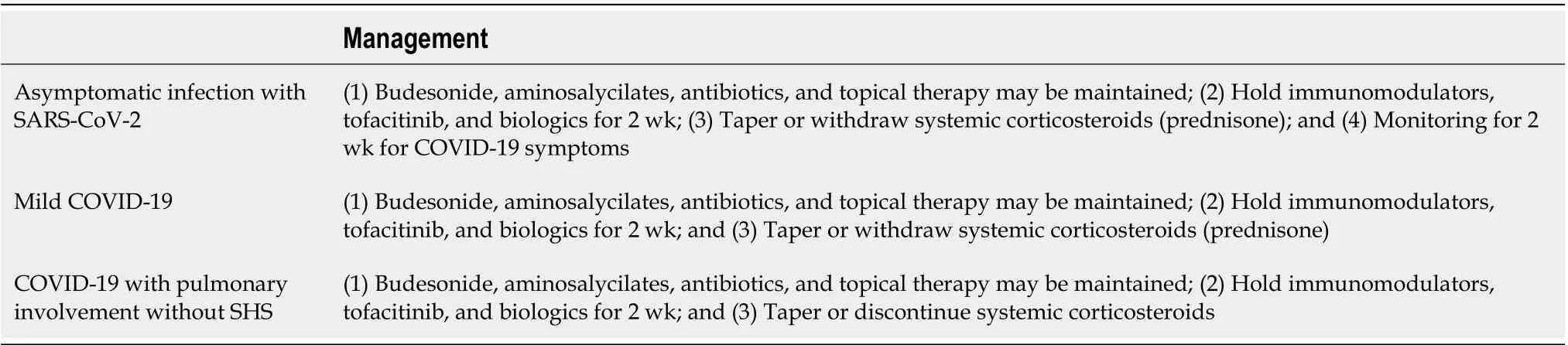
Table 1 Management of patients attending outpatient clinic with quiescent inflammatory bowel disease in the scenario of asymptomatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection or confirmed or suspected coronavirus disease 2019[12,20,26,27]
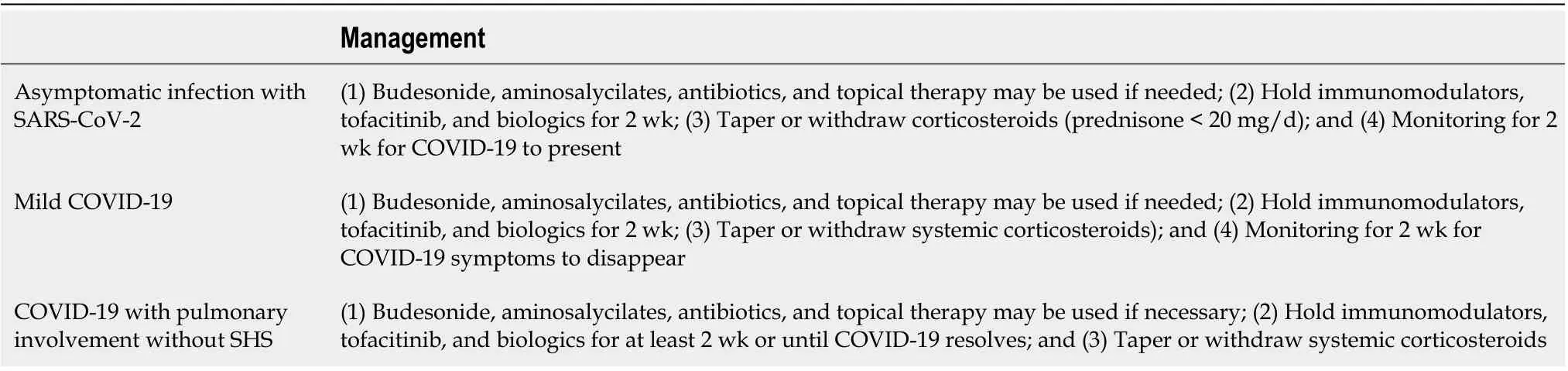
Table 2 Management of patients attending outpatient clinic with mildly active inflammatory bowel disease in the scenario of the asymptomatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection or confirmed or suspected coronavirus disease 2019[12,20,26,27]

Table 3 Management of patients attending outpatient clinic with moderately to severely active inflammatory bowel disease in the scenario of asymptomatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection or confirmed or suspected coronavirus disease 2019[12,20,26,27]
Management of patients with IBD hospitalized with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19
Although the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has substantially impacted the management of IBD, with unprecedented restriction of hospitalizations, many patients with IBD will still be hospitalized in the COVID-19 era either because of severely active or complicated IBD, or because they were infected with SARS-CoV-2 and developed progressive or severe COVID-19 with SHS requiring supplemental oxygen or ventilator support, use of vasopressors, or present evidence of end organ damage[19,26]. In fact, hospitalization should be restricted to life-threatening circumstances or complications[20].
For patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19, the priority is life support, while IBD therapy is likely to have less priority. Nonetheless, when possible, therapy for COVID-19 should consider the underlying IBD[12,27]. Ideally, treatment decisions should be personalized and decision-making should include a multidisciplinary approach, involving teams of experts on both conditions. This way, consultation with pulmonary medicine and infectious disease experts is crucial, with discussion involving the possibilities of COVID-19 treatment with experimental antiviral drugs or anticytokine therapy trials, and staying aware of potential interaction with IBD medications[32]. If IBD is mildly active, budesonide, aminosalycilates, and rectal therapies may be initiated while reducing or holding prednisone. Also, stopping biologics, immunomodulators, and tofacitinib throughout the duration of the COVID-19 is appropriate[18,19,26]. For moderately-to-severely active IBD, the limited use of intravenous corticosteroids for IBD is acceptable, if necessary. Topical therapy may be ordered if deemed adequate, while immunomodulators, tofacitinib, or biologics that failed for IBD should be stopped[18,19,27]. Other therapies for IBD should only be used if definitely required. Intravenous cyclosporine may be a reasonable option for severe UC, based on limited evidence of its benefit against coronavirus[26,27].
Interestingly, in a recent trial involving patients without IBD hospitalized with COVID-19, patients were randomized to therapy with oral or intravenous dexamethasone at a dose of 6 mg once daily for up to 10 d or until discharge, whichever was sooner, or to receive usual care only[33]. The group treated with dexamethasone presented significantly lower 28-d mortality in patients receiving either oxygen alone or with invasive mechanical ventilation (23.3% and 29.3% vs 26.2% and 41.4% with usual care, respectively). Importantly, the same benefit was not found in subjects receiving no respiratory support[33]. Whether other glucocorticoids like methylprednisolone or hydrocortisone on equivalent doses might also be effective in this setting is unknown and will require future studies. From the perspective of pharmacological effects and on the immune system, there is nothing specific about dexamethasone that other steroids do not offer as well, and so other glucocorticosteroids could in theory be used if dexamethasone is unavailable[34]. If this hypothesis is confirmed in prospective studies, this important therapeutic strategy can help us clarify our approach for suitably managing the challenging and lifethreatening scenario of a patient hospitalized that concomitantly presents with a severe flare of IBD and moderate-to-severe COVID-19, where intravenous methylprednisolone or hydrocortisone could be one of the first-line therapies for both conditions.
However, for patients hospitalized due to severe flare of UC and who also have asymptomatic infection with SARS-CoV-2 or mild-moderate COVID-19, priority must be given to address issues pertinent to severe exacerbation of IBD, and usually a standard approach directed to the care of hospitalized patients with IBD should be followed[26,35]. In this clinical setting, expert opinions of the AGA recommend limiting intravenous steroids to three days and then transitioning to infliximab or cyclosporine[20]. Evaluating enteric superinfections, especially those caused by C. difficile or CMV, using fecal toxin A/B enzyme immunoassay and/or PCR for detecting toxins A and B genes or for detecting CMV DNA by quantitative PCR should be a routine practice for these patients[27]. In contrast, when CMV superinfection remains suspected despite the results of non-invasive tests, urgent colonoscopy should be reserved for patients in whom the procedure may change or target a specific therapy[12,19,20]; also, colorectal surgery expert consultation in the first days of hospitalization of the patient should also be a standard practice in this context[35]. Foremost, a recent ‘RAND appropriateness panel’ adapted from the BSG guidelines for managing acute severe UC recommended that regarding the COVID-19 pandemic, prophylactic anticoagulation post-discharge is ordered for patients hospitalized with acute severe colitis that had a positive SARS-CoV-2 testing due to the predisposition to develop thromboembolic complications in both conditions[36]. Indeed, the British Thoracic Society proposes that it is a reasonable approach to consider extended venous thromboembolism prophylaxis on discharge with low molecular weight heparin or direct oral anticoagulant during four weeks in high-risk patients with COVID-19[37]. Table 4 depicts the suggested approach for managing patients with IBD hospitalized with severe COVID-19.
When to restart biological and other immunosuppressive agents in patients with IBD infected with SARS-CoV-2 with or without COVID-19
Considering that patient safety should be a priority in the context of still limited but rapidly expanding knowledge regarding the management of IBD during the COVID-19 pandemic, most consensus statements and expert opinions recommend temporarily holding biologics and other immunosuppressant drugs in patients with IBD with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection or in the presence of symptoms suggestive of COVID-19 until a patient recovers[38]. However, if used prolongedly, this practice can lead some patients to both lose the effectiveness of their therapy and present an IBD flare[39]. Therefore, guidance on when to restart IBD medications in this setting is very welcome.

Table 4 Management of patient with inflammatory bowel disease hospitalized with severe coronavirus disease 2019[12,19,20,26,27]
Although the timing for treatment restart is nonconsensual, currently, for decision making, the IOIBD expert panel recommends preferably for most patients a symptoms-based strategy due to the lack of accuracy of current molecular tests available for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection, and also because of the clinical significance still unclear of the prolonged persistence of viral RNA detected by these tests in individuals that had COVID-19[38].
In asymptomatic patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, some experts advise waiting at least 10 d from the first positive COVID-19 test for restarting immunosuppressive drugs as long as there is no development of symptoms suggestive of COVID-19 in this time interval[12,38]. In patients with COVID-19, the timing of resumed biologics or other immunosuppressants should be guided by the balance between the severity of both viral disease and IBD[38]. Thus, based on updated guidelines from the IOIBD, using a symptom-based strategy, it is recommended to wait at least 10 d since the appearance of the first symptoms of COVID and at least 3 d since recovery, defined as resolution of fever and significant improvement in respiratory symptoms, to re-start these medications[38]. Having two consecutive negative PCR tests in swab specimens, collected at least 24 h apart, is no longer required when this strategy is embraced[38,40]. In severe COVID-19, a longer time frame for re-initiating immunosuppressant may be necessary according to the personalized clinical strategy, if possible awaiting full patient recovery[41]. However, when doctors require a test-based strategy to decide about restarting IBD medications, in addition to the patient having clinically recovered based on the described parameters of the symptom-based strategy, he must have two consecutive negative nasopharyngeal swabs COVID-19 molecular assays collected at least 24 h apart[38].
MONITORING IBD TREATMENT DURING THE PANDEMIC
The outbreak of the COVID-19 infection forced government authorities to impose several restrictions, including lockdown[42]. Hospitals were then forced to rapidly restructure their activities to accommodate this critical and emergent situation. Institutional rearrangements have challenged IBD units worldwide, forcing them to adapt and generate specific approaches to maintain appropriate IBD care[10]. Referral IBD centers and Gastroenterology/IBD Societies published their guidance, helping clinicians tackle this troublesome situation[10,12,13,19,26,42-47]. In common, they advised remote monitoring, drug home delivery whenever possible, infusion unit restrictions, and patient education concerning protective measures (Table 5). Although necessary, all these measures and restrictions may negatively impact patients with IBD. A recent survey among 225 patients with IBD from a referral center showed depressive moodas the most prevalent social impact (80.2%), followed by anxiety/fear of death (58.2%), insomnia (51.4%), daily activity impairment (48%), sexual dysfunction (46.2%), and productivity impairment (40%)[11]. These health repercussions in patients with IBD are essential, and healthcare professionals should be aware of them when talking remotely with the patients.
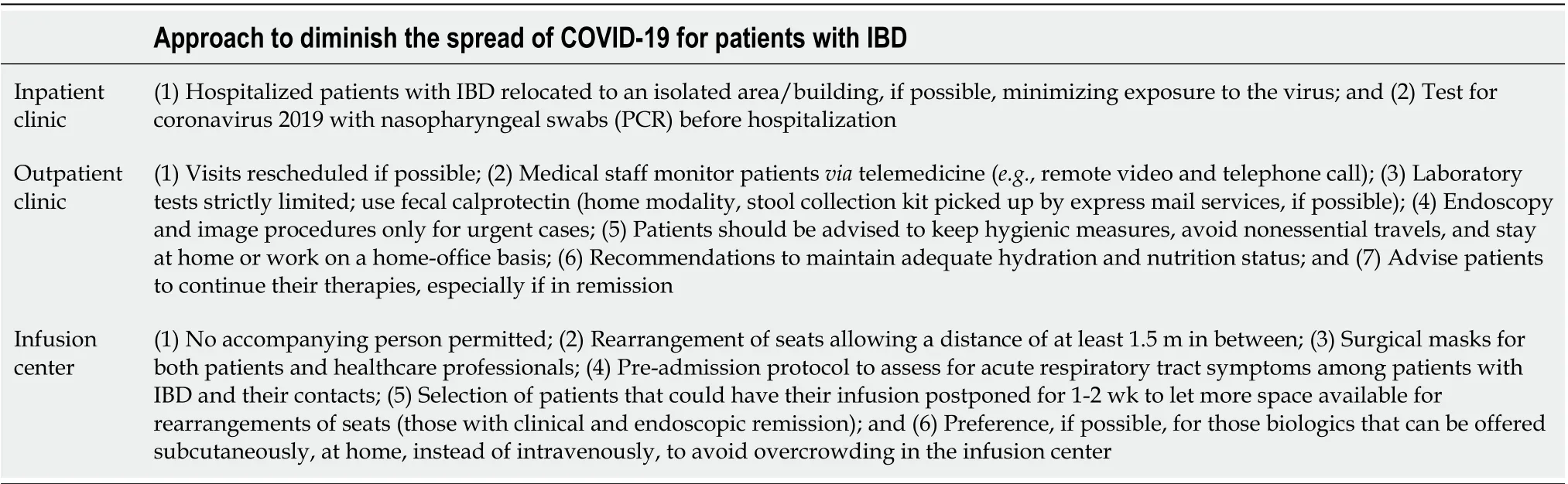
Table 5 Approach to diminish the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 for patients with inflammatory bowel disease[10]
A common feature in the various IBD units is that telemedicine has replaced followup visits[48]. Although not the ideal way to follow these patients, that was the best way to do it now. Some authors prefer to term these remote visits video office or telephone office visits[44]. They avoid the term “virtual,” which could mistakenly connote that the visits were not “real”[44]. In general, patients found those remote visits worthwhile, but no doubt, this was exhausting for the healthcare professionals that ended up with the well-described “zoom-fatigue”[44]; consequently, the personal visits were reduced by 30%-40%[10,42-44]; for comparison, endoscopic procedures were reduced by 90%-95%[10,42-44]and were indicated in selected cases[42,44,49,50]. Image procedures were also largely deferred and only indicated in cases of intestinal obstruction or suspected abscess[44]. There has been a lack of information on the impact of remote monitoring of patients with IBD during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. In a single-center cross-sectional Italian study with 1083 patients with IBD, telemonitoring of patients by phone or videoconference was compared with clinical evaluation in person (control group)[48]. Despite fewer relapses in the control group, there were no statistically significant differences between the groups regarding the quality of life measured by the IBDQ-32 questionnaire[48]. Thus, the possibility of contacting the IBD staff through remote monitoring, although not ideal, partially contributes to maintaining the quality-of-life parameter.
FC has been a valuable tool during this pandemic[27]. Many centers have relied on commercial labs to send an overnight home stool collection kit for FC that can be picked up by express mail services, avoiding the patient from leaving home[44]. A home FC test (IBDoc) was compared with a laboratory test (Quantum Blue?calprotectin test, BüHLMANN, Sch?nenbuch, Switzerland) and the correlation between both tests was good (r = 0.776, P < 0.0001)[51]. Using 250 μg/g as the cutoff, the agreement between the home and laboratory tests was 80%[51]. Diarrhea can be one of the manifestations of COVID-19 or an IBD flare[27]. FC can be particularly useful to differentiate these situations since FC is usually only mildly elevated in patients with COVID-19 with diarrhea, whereas in patients with IBD and active disease, significant and sustained elevation may occur[27].
ENDOSCOPY IN PATIENTS WITH IBD IN THE COVID-19 ERA
Endoscopy is not only one fundamental pillar for diagnosing IBD but also plays an important role in its management, treatment, and colorectal cancer (CRC)/dysplasia surveillance. Differential diagnosis concerning other etiologies and between UC and CD as well as full evaluation of disease extension, activity, response to treatment, and even some therapeutic approaches are some endoscopic indications in a patient with IBD. Ileocolonoscopy, flexible proctosigmoidoscopy, and esophagogastroduodenoscopy are the most commonly used endoscopic methods, but enteroscopy and videocapsule endoscopy also play a role in IBD management[52,53]. The overcrowded healthcare system worldwide by the COVID-19 pandemic and the need to control the spread of infection required restructuring primary care and hospital activities, including endoscopy units[43,54].
Risk of infection during endoscopy
Regardless of being more contagious than the other coronavirus (SARS-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus), SARS-CoV-2 has similar ways of infection and complications[55], with aerosolized droplets produced by coughing, sneezing, or breathing as the main route of infection. SARS-CoV-2 infects the GI epithelium, and its RNA can be detected in stool samples, sometimes in high concentrations, even in patients without GI symptoms, lightening the possibility of fecal–oral transmission[55]. Although this route of transmission is controversial, some papers proved the presence of live virus in fecal specimens and even a positive PCR in material collected from the surface of the toilet and sink used by infected patients, thereby corroborating this route of transmission[56].
Both upper and lower GI endoscopies should be considered as aerosol-generating procedures. Upper GI endoscopy can generate respiratory droplets by coughing or gagging induced mainly during endoscopic insertion and lower GI endoscopy by passing flatus or pathogen-containing stools[57]. Therefore, endoscopy can be considered a high-risk procedure for SARS-COV-2 transmission for both patients and healthcare professionals, being reasonable to ration the endoscopic resources.
Indications of endoscopy during COVID-19 pandemic
To minimize the exposure and risk of infection, different Societies of Gastroenterology and Endoscopy worldwide (American Gastroenterological Association[58], BSG[13], European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy and European Society of Gastroenterology and Endoscopy Nurses and Associates[59], Asian Pacific Society for Digestive Endoscopy[60], and Brazilian Society of Digestive Endoscopy[61]) agreed to postpone all the endoscopic procedures during the pandemic period, except for the emergency ones and on a case-by-case basis, some urgent ones. The emergency and urgent endoscopic procedures can be resumed and divided into the following three categories: Emergent, urgent, and elective (Table 6)[62]. The restriction in the indications for GI endoscopy aimed not only to reduce the risk of patients and healthcare professional infection but also to save personal protective equipment (PPE) and other medical supplies[57].
Endoscopy, especially ileocolonoscopy, plays a fundamental role in the diagnosis and management of IBD, ruling out some other diagnoses and providing important information about the extension and activity of the disease, response to treatment, and even a therapeutic approach to stenosis and other complications. During the COVID-19 pandemic, these indications for patients with IBD were reviewed and based on expert opinions, the IOIBD[63]and French Society of Digestive Endoscopy (SFED) recommendations[64], the advice was again to postpone all endoscopic procedures that were not urgent and extremely necessary. However, sometimes, this emergent/urgent indication for endoscopy in patients with IBD is slightly unclear. Thus, next we are going to discuss some possible scenarios[57]:
Confirm IBD diagnosis:In highly suspected cases with moderate-to-severe symptoms and grounded by positive biomarkers and cross-sectional imaging findings (bowel ultrasonography or magnetic resonance enterography) of IBD, lower GI endoscopy (proctosigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy) with biopsies is still indicated[57]. Depending on the clinical situation and the presence of rectal symptoms, proctosigmoidoscopy might be preferable to full colonoscopy, as the former is faster and can be done without sedation (no need for companion) or oral bowel preparation[63]. Cases with mild symptoms can have their endoscopy postponed[57,63,64]. If an isolated small bowel disease is the hypothesis, after negative cross-sectional imaging and in the absence of obstructive symptoms, videocapsule endoscopy should be preferred to enteroscopy for its lower risk[64].
Monitoring IBD treatment:Disease activity monitoring, if possible as mentioned before, should be made by checking patient report outcomes (PROs) and noninvasive tests such as FC, C-reactive protein (CRP), or even cross-sectional imaging[64,65].
Acute severe UC:This is an emergency condition with a high morbimortality. A patient who fulfills the criteria of a stool frequency (≥ 6 per day), with bloody stools, heart rate above 90 bpm, temperature exceeding 37.8 °C, hemoglobin levels below 105g/L, and high CRP levels (> 30 mg/L) needs to be hospitalized and undergo investigation to rule out infections other than IBD activity, especially COVID-19, C. difficile, and CMV[66,67]. Symptoms such as fever, cough, dysosmia, dysgeusia, and fatigue need to be questioned, and a PCR for SARS-COV-2 asked. If negative, analysis of stool samples should be performed looking for C. difficile and parasitological infection and, in this setting, it is advised to perform flexible proctosigmoidoscopy with biopsies to exclude CMV infection[57,63,64].

Table 6 Category of endoscopic procedures[13,62]
Postoperative recurrence assessment:Endoscopy plays an important role in the postoperative management of both CD and UC patients. In CD, mainly in cases of ileocecal resection, since endoscopic inflammation precedes biological and clinical activity, ileocolonoscopic findings allow us to tailor therapy. In UC patients, postoperative endoscopy is mainly indicated for pouchitis and surveillance of this segment for dysplasia. However, when we consider the risks and benefits of the procedure during this pandemic period, endoscopy to check postoperative recurrence and dysplasia could be delayed, and for inflammation, patients should be followed noninvasively[63,64,68].
Surveillance colonoscopies:It is known that patients with IBD have twice more risk of CRC than the general population, justifying the importance of its screening and surveillance. Based on ECCO guidelines, surveillance colonoscopy is indicated for all patients with UC, except if the disease is restricted to the rectum eight years after the beginning of the symptoms. Patients with colonic CD with more than 1/3 of the colon affected should follow the same protocol. If primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is present, surveillance is recommended to start immediately when the diagnosis is confirmed and continues yearly. The interval between colonoscopies will depend on the risk factors and the results obtained in the index exam[66]. However, for all the risks listed above, the recommendation is to postpone the colonoscopy in patients without alarming signs. With the extension of the pandemic period, this recommendation needs to be reviewed, and probably the patients will be stratified by risk factors for CRC, as with PSC or previous dysplastic lesions, and will be rescheduled as priorities for endoscopic examination[57,64].
Partial GI obstruction:Patients with IBD are at higher risk of some complications, such as benign or malignant strictures. In cases of a new colonic stricture, a colonoscopy is indicated to exclude malignancy, and if this hypothesis is confirmed, a stent or balloon dilatation might be needed if surgery could not be performed. In CD patients with a known short stricture (< 4 cm) with recurrent obstructive symptoms (nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and abdominal pain), endoscopic dilatation is a therapeutic option to avoid future admission to the emergency room, overloaded during COVID-19 pandemic[57,68].
Upper GI endoscopy:The indications for upper GI endoscopy in patients with IBD during this pandemic period are restricted to acute GI bleeding or dilatation of upper GI strictures[64].
Worsening cholangitis and jaundice in patients with IBD and PSC with a dominant bile duct stricture:Acute cholangitis in a patient with PSC is an emergency, and if there is a dominant bile duct stricture detected on a magnetic resonance cholangiography, an urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) will access the stricture to exclude cholangiocarcinoma and may decompress the bile duct[57].
Endoscopy in industry-sponsored clinical trials:Most of the recruitment of new patients and screening visits for clinical trials have been discontinued during this pandemic period, but the status of monitoring colonoscopies for participants already recruited should be discussed with trial sponsors and research ethics committees. A case-by-case discussion might be necessary, as for some patients, the investigational product is the only therapeutic option to avoid surgery and/or corticosteroids. Trial visits should occur virtually whenever possible[57,64].
In summary, endoscopy in patients with IBD during the COVID-19 pandemic should be restricted for the indications listed in Table 7.
Safety measures for protection against COVID-19 infection
Aiming to mitigate the risk of the spread of infection from possible COVID-19 patients, reduce the risk of cross-infection, and preserve resources and PPE, some measures are recommended by different GI endoscopy societies[62,69]. The safety recommendations can be targeted to the unit structure, patient safety, healthcare professional safety, and equipment/endoscopy room care.
Unit structure[57,70]:Limit the number of patients scheduled; Consider at least a onehour interval between exams; Select the indications of endoscopy and postpone the others; Remote pre-exam evaluation with a questionnaire about COVID-19 symptoms and contact; Inform the need to wear a mask; Apply social distancing rules in the waiting room; Avoid physical contact; Limit the waiting room time and number of people; Reassure that just exams with sedation or anesthesia require a companion; Relatives and caregivers are forbidden from entering the hospital or endoscopy unit unless required; Medical and nursing students are restricted in the endoscopy units during pandemic crises; Allow only essential staff with proper PPE inside the endoscopic unit; Keep doors closed; Provide information about hand hygiene; Followup call one week after endoscopy: As symptoms of COVID-19 can occur after infection, patients undergoing endoscopy could develop symptoms after the procedure if they have contracted the SARS-CoV-2 infection at the community level just before endoscopy. It is a way to verify whether the protective measures at the unit are working[64].
Patient safety[64]:Check again for COVID-19 symptoms (fever > 37.5 °C; cough, dysgeusia, dysosmia, and dyspnea) or contact at admission; Access body temperature; Provide the patient alcoholic solution to clean hands; Before entering the endoscopy room, the patient is asked to dress a cotton gown, a hairnet, and a surgical mask; Nasal swabs are not a routine recommendation, as they are not generally available or validated.
Healthcare professionals’ safety[64,70,71]:AGA and the SFED recommend the use of filtering face piece (FFP) respiratory class 2 or 3 (FFP2 or FFP3) instead of surgical masks to protect Healthcare professionals (HCPs) during upper and lower GI procedures, regardless of the COVID-19 status of the patient. The suggestion for mask changing depends on regional recommendations; Limit the number of endoscopy personnel and operational endoscopy rooms; Endoscopy work teams should comprise a consultant endoscopist, a highly trained endoscopy nurse, and, if possible, a consultant anesthesiologist; HCPs should be checked for COVID-19 symptoms and having their body temperature accessed; HCPs should wear FFP2 mask during the entire time at endoscopy unit as SARS-CoV-2 remained viable in aerosols for at least 3 h; HCPs should be trained in dressing and undressing the PPE, and hand washing is mandatory before both phases; HCPs must remove contact lenses and dress: Hairnet, a long water-resistant gown with back closure, an FFP2 mask, goggles for eye protection, and over-sleeve gloves over the gown. Over the other layers, a single-use gown and another pair of gloves; HCPs should change the disposable gown and the second gloves in each procedure; Hand washing is mandatory before and after every interaction with patient and other HCPs; Conscious sedation remains the most feasible option and can be provided and managed even if the patient is wearing a mask.
Equipment/endoscopy room[62,64,72]:Negative-pressure room to prevent generated aerosols from diffusing outside the room is recommended mainly in COVID-19 confirmed or highly suspected cases; Disinfection and decontamination by neutral detergent and virucidal disinfectant using 0.05% sodium hypochlorite or 70% ethanol on surfaces and devices are effective in clearing the virus; All used endoscopes must undergo standardized reprocessing and disinfection; All used accessories must be disposed of; Beds must be cleaned with specific disinfection products and bed sheets changed for each patient.
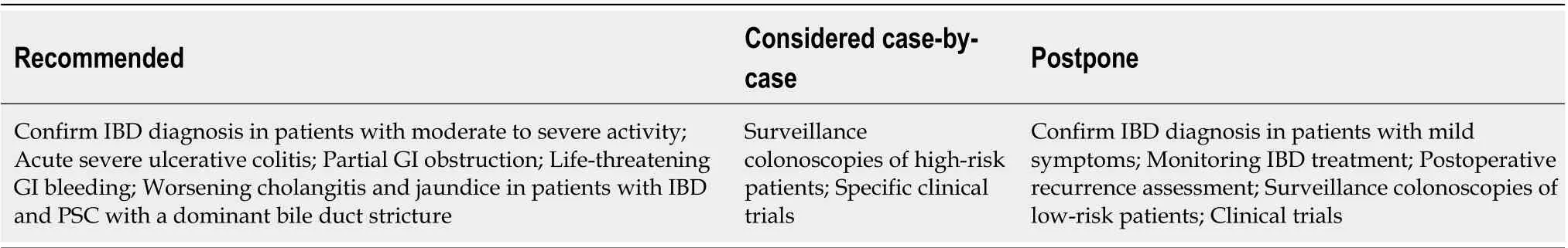
Table 7 Indications for gastrointestinal endoscopy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic[57,63,64]
Endoscopy post-pandemic phase
When the COVID-19 pandemic ends, endoscopy units must face a dammed demand list with the impossibility of returning to a regular agenda, as the interval between the exams will need to remain longer to prevent new outbreaks. A stratification of priorities will be necessary[73]. Some algorithms based on available point-of-care tests considering epidemiological regional data and an accurate clinical risk assessment are being proposed to stratify the patients[74]. Whatever method is used to prioritize endoscopy, it is important to maintain close contact with patients with IBD by phone or e-mail to monitor for specific symptoms. Planning carefully the post-pandemic phase is primordial, and a case-by-case analysis with reassessments of patients’ conditions by both clinician and endoscopist will be demanded, and telemedicine might be a useful tool to help this conversation[73].
SURGICAL INTERVENTIONS IN PATIENTS WITH IBD AND COVID-19
Despite significant advances in the medical management of IBD in recent years, many patients will require surgery. The most common indications for CD surgery include stenosis, fistulae, and abscesses[75]. In UC, the most common indications are acute severe colitis refractory to medical therapy and chronic refractory UC. Other indications of surgery in UC are dysplasia and CRC[76]. Many of these situations are elective or semi-elective surgeries that can be postponed for a few days or weeks in some patients with confirmed COVID-19. However, emergencies, such as perforation, acute severe colitis, and uncontrolled hemorrhage, may occur, and the surgery in these cases cannot be postponed and must be treated promptly. At the peak of the pandemic, one of the collateral effects was that elective surgeries were canceled or temporarily suspended[77]. Elective surgeries in IBD cannot be delayed too long when they are strictly indicated, mainly due to increased morbidity given the patient’s weakened condition (e.g., steroids and malnutrition)[78]. It is not recommended to delay surgical treatment for these patients with IBD, regardless of their COVID-19 status.
Conducting emergency surgeries during a pandemic such as COVID-19 is challenging for IBD surgeons and the entire hospital infrastructure[79,80]. The information available on COVID-19 and the possibility of contamination through aerosols and droplets lead to the need for modifications to perform surgery with success, reducing the risk of contaminating hospital facilities and protecting health teams and patients[79]. It is pivotal to protect all surgical teams (e.g., masks, glasses, face shields, and surgical caps) to avoid contagion with COVID-19 when they perform surgery in patients with IBD with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 and protect the patient to prevent him from contracting COVID-19.
There is a concern among surgeons with minimally invasive techniques (e.g., laparoscopy, and robotic surgery) due to a possible risk of viral transmission of the COVID-19 with the creation of pneumoperitoneum[81]. However, minimally invasive surgery (MIS), including laparoscopic surgery, is feasible and safe in IBD and has many advantages, such as reduced length of hospital stay, less pain, reduced trauma, less impact on respiratory movements, reduction of morbidity, and faster postoperative recovery[82].
There is little evidence of viral transmission through laparoscopic or open approaches. As shown by Somashekhar et al[79], the risk of infection by COVID-19 for the healthcare team during MIS (laparoscopic or robotic) is considered low. Therefore, in IBD, we should not postpone surgery, even if considered “elective,” due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, the care that must be followed by the surgical, nursing, and anesthesia teams must be standardized at the referred hospital and replicated to other health services referenced in the surgical treatment of IBD.
Precautions to avoid contamination of the surgical team are described in several studies published during the pandemic and include care with airway management during the anesthetic procedure and specific care during laparoscopy[79,81,83-85]. There seems to be a consensus in the literature that intubation and extubation are high-risk healthcare professionals’ procedures and that the maximum amount of PPE is needed. However, there is little evidence of the real risk of contamination by healthcare professionals during laparoscopy itself, nor of operating room (OR) pressure, surgical smoke, tissue extraction, or CO2deflation[83]. If surgery is considered necessary, the surgeon must minimize the risk of exposure to the virus, involving a minimum number of health professionals and shortening the occupation of the ORs. As said, there are no absolute contraindications to MIS; however, appropriate PPE for the OR team and smoke evacuation/filtration systems are unanimously recommended[85].
If there is a lack of safety measures to allow safe laparoscopy, open surgery should be considered[84]. Nevertheless, previous studies have shown that bacterial and viral aerosols can be detected in both open and laparoscopic surgical operations[86]; then, a surgical aspirator/smoke evacuation device should also be used in open procedures. Electrical instruments and energy devices should be used at the lowest energy level to preclude excessive aerosol and smoke production[87].
There are some tips and tricks to make MIS safer during the COVID-19 pandemic, such as avoid creating a leak for smoke evacuation, use a closed suction system; use leak-free trocars such as balloon trocars, aspirate the entire pneumoperitoneum before retrieving the surgical specimen at the end of a procedure before removing the trocars, or before conversion to open surgery[84]. Hospitals must prepare specific internal protocols and arrange adequate training of the involved personnel[88].
If possible, postpone elective surgery and consider screening every surgical patient for COVID-19 either by RT-PCR swab or CT scan of the thorax[89]. In emergent (< 24 h) surgeries, such as perianal abscess, bowel perforation, toxic megacolon, the surgery must be done without any delay, and all patients must be treated as if they were COVID-19-positive. All surgical teams must strictly follow all rules related to infection against COVID-19. The same rules apply to patients under urgent (< 72 h) situations, such as bowel obstruction (without ischemia). Elective (up to 4 wk to 3 mo) surgeries must have an individualized approach. Seton replacements, “J” pouch confection, can be postponed up to three months. However, colectomy in patients with chronic refractory UC or dysplasia and CRC in UC should be referred to surgery, preferably before this period, so that there will be no worsening of the primary clinical condition.
It is important to emphasize that all known or suspected COVID-19-positive patients requiring surgical intervention must be treated as positive until proven otherwise to minimize infection spread[88]. Besides, whenever possible, dedicate specific OR to patients with COVID-19[83]. Create negative pressure ORs because they are considered ideal; yet, most ORs work at positive pressure, and their use is therefore permitted. An air exchange rate of ≥ 25 cycles/h is considered sufficient to effectively reduce the OR’s viral load. Only essential staff members should be admitted into the OR, limiting in/out traffic, and doors should be kept closed. Use level III PPE during intubation and extubation. Use proper filters and closed systems for CO2desufflation and do not perform transanal surgery[83].
There are some critical considerations for transanal surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic[90]. Several lines of evidence have supported the possible fecal-oral transmission of the COVID-19[91,92]. It is important to emphasize that positive pressure transanal surgery, such as transanal MIS and transanal endoscopic microsurgery, are aerosol-generating procedures. Hence, it is appropriate to perform routine preoperative fecal testing for SARS-CoV-2, in addition to nasopharyngeal screening, in patients undergoing transanal surgery under positive pressure. For patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection, conventional open and robotic approaches may be safer alternatives when surgery cannot be postponed.
MENTAL HEALTH AND EDUCATIONAL INITIATIVES
It has been recognized that the pandemic will greatly increase the incidence of severe psychological problems, such as mood disorders, anxiety disorders, or posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), as a consequence of isolation, human losses, and financial hardships[93]. For patients with IBD, psychological distress is already a common feature, with studies suggesting that active disease is strongly related to comorbid anxiety and depression[94]. A recent cross-sectional survey exploring the emotional state, perception, and concerns of Saudi patients with IBD during the pandemic found a diagnosis of anxiety in 48.4% of surveyed patients. In this context, patients with IBD require greater attention, and clinical or cognitive behavioral treatment should be offered to all patients who exhibit psychological distress.
Provided that patients with IBD are experiencing substantial changes to the routine management of their conditions during the pandemic, it seems highly critical to assess patients’ perceptions and viewpoints. In the earlier phase of the pandemic, the Federation of Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis Associations (EFCCA) conducted an anonymous online survey to investigate the concerns, fears, and behaviors of patients with IBD. Based on responses from 3815 participants from 51 countries worldwide, it was shown that about half of respondents reported receiving COVID-19 information or specific recommendations from doctors to prevent infection. However, most patients (60%) would have preferred to receive more recommendations regarding COVID-19 from their physicians[95]. These results emphasized the urgent need for better communication between physicians and patients and for clear and specific recommendations for people with chronic conditions in these unprecedented times. In this context, educational initiatives involving patient associations might play a crucial role in allowing dissemination of the correct messages regarding patient management. Also, patient compliance with healthcare providers’ guidelines could be achievable by enhanced collaboration, and long-term, trusted partnerships could also be established.
VACCINATION
The recent availability of vaccines to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection has raised concerns regarding the safety and efficacy of immunization in patients with IBD. Until now, there has been international agreement among the main international IBD expert groups that the risks of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with IBD are anticipated to be very low, and it is strongly recommended that patients with IBD should be given a COVID-19 vaccine once it is widely available[2,96-98]. All coronavirus vaccines, which are licensed or in the final stages of testing, are considered suitable for patients on biologics, steroids, and immunosuppressants, as they are not live vaccines. These include the mRNA (Pfizer, Moderna), the non-replicating adenovirus vector (Oxford), and the inactivated SARS-CoV-2 (Coronavac) vaccines. Analogous to other vaccines used for many years, such as influenza and pneumonia vaccines, there is no indication of worsening IBD symptoms or flares following vaccination, and immunization appears improbable to affect IBD activity[99]. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines have also been tested in tens of thousands of patients with safety profiles analogous to other vaccines commonly used in patients with IBD, such as the flu vaccine.
For patients under immunosuppressive treatments, it is anticipated that the vaccine may be slightly less effective, as other studies have shown that immunosuppressant medications may induce some reduction in antibody formation and lower immune response with other common vaccines. For instance, it has been demonstrated that the serologic conversion rate to influenza vaccine is lower in immunosuppressed patients with IBD[99,100]and that the immune response to pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination is reduced in patients with CD by combining TNF-blockers and immunomodulators[101]. Conversely, treatment with newer biologics, such as ustekinumab or vedolizumab, does not seem to decrease responses to flu vaccine[102,103]. We still do not know which IBD treatments, if any, will reduce the effectiveness of the coronavirus vaccine; however, it is important to emphasize that even if the COVID-19 vaccine works slightly less well in immunosuppressed patients, it will still offer greater protection than not having the vaccine.
It is not advisable that patients should stop their treatments to get vaccinated, as it can induce an exacerbation, putting patients at a greater risk of serious complications of COVID-19. Also, patients should avoid receiving their vaccine on the same day of an infusion/subcutaneous dose of biologic, just in the exceptional circumstance that the patient develops a reaction or adverse effect. It would be important to identify which one (vaccine or biologic) has caused it.
CONCLUSION
In this review, we presented a guide for the practicing clinician for managing IBD during the COVID-19 pandemic. We also reviewed the risk of infection during endoscopy, highlighting the restricted conditions where we still should indicate GI endoscopy in patients with IBD and the recommendations of the most important endoscopy societies for a safer procedure. All known or suspected COVID-19-positive patients requiring surgical intervention must be treated as positive until proven otherwise to minimize infection spread. It is not advisable that patients should stop their treatments to get vaccinated, as it can induce an exacerbation, putting patients at a greater risk of serious complications of COVID-19. In this time of an unprecedented pandemic, where knowledge about COVID-19 rapidly expands, we suggest that clinicians caring for patients with IBD should periodically check for updates in the SECURE-IBD registry and Gastroenterology Societies statements and guidelines to update knowledge about SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in patients with IBD for better information and follow the approach to manage medications in IBD in this challenging context.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2021年11期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2021年11期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Fatigue in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in Eastern China
- Long-term follow-up of cumulative incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus patients without antiviral therapy
- Prospective single-blinded single-center randomized controlled trial of Prep Kit-C and Moviprep: Does underlying inflammatory bowel disease impact tolerability and efficacy?
- Apolipoprotein E polymorphism influences orthotopic liver transplantation outcomes in patients with hepatitis C virus-induced liver cirrhosis
- Study on the characteristics of intestinal motility of constipation in patients with Parkinson's disease
- Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric tube cancer: A multicenter retrospective study
