Chinese Expert Consensus on Early Prevention and Intervention of Sepsis
Zhong Wang, Xuezhong Yu, Yuguo Chen, Chuanzhu Lv, Xiaodong Zhao
Emergency Medicine Branch of China International Exchange and Promotion Association for Medicine and Healthcare
Chinese Society of Emergency Medicine, Chinese Medical Asssociation
China College of Emergency Phsicines, Chinese Medical Dcoctor Association
Emergency Medicine Committee of Chinese People's Liberation Army
ABSTRACT Sepsis is currently a major problem and challenge facing the medical community. With rapid development and progress of modern medicine, researchers have put more and more attention on sepsis; meanwhile, the morbidity and mortality of sepsis remains high despite great efforts from experts in various fields. According to updated guidelines, sepsis is de fined as life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection.Infection is the initial step of sepsis progression, and development from infection to sepsis is a complex pathophysiological process,including pathogen invasion, cytokine release, capillary leakage,microcirculation dysfunction, etc. which finally leads to organ metabolic disorders and functional failure. According to the latest recommended international guidelines of Sepsis 3.0, the presence of infection and SOFA score ≥ 2 are considered as the diagnostic criteria for sepsis, and the "rescue" measures mainly focus on reversal of organ dysfunction. However, despite nearly two decades of efforts, the "Save Sepsis Campaign" has not achieved satisfactory results. Emergency medicine is the frontier subject of acute and severe illness which treats patients with acute infections at the earliest. If at this stage, physicians can predict the possibility of sepsis progression from demographic characteristics, localize the pathogen and infection, detect the in flammatory storms by tests of cytokines and evaluate the severity of the infection with more effective clinical scoring system, and then take effective measures to prevent infection from developing into sepsis in high-risk patients,the morbidity and mortality of sepsis in patients with acute infection will be greatly reduced. Based on this situation, Chinese emergency medicine experts proposed the concept of "preventing and blocking"sepsis, and launched the nationwide "Preventing Sepsis Campaign in China (PSCC)" nationwide. The main concept is summarized as"three early and two reduces" which includes early detection, early diagnosis and early intervention during the "pre-symptomatic" and"peri-septic” stage in order to reduce the incidence of sepsis and it proposed a new approach for diagnosis and treatment of acute severe infection. This consensus is jointly advocated, discussed and written by four academic associations in the field of emergency medicine and five scholarly publishing organizations. More than 40 experts from fields of emergency medicine, critical care medicine,infectious diseases, pharmacy and laboratory medicine have participated in several rounds of deliberation and finally reached consensus on the criteria of identifying patients with acute infection,taking anti-infective treatments, screening of high-risk patients with sepsis, detection and treatment of in flammatory storm, protection of vascular endothelial cells and the regulation of coagulation function,as well as strategies of liquid support and organ function protection etc. The consensus summarizes the commonly used clinical diagnosis criteria and treatment measures of sepsis both in Western medicine and traditional Chinese medicine for clinicians in order to provide evidence for the diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
KEYWORDS: Sepsis; Preventing; Infection; Cytokines; Organ function
1. Introduction
Sepsis is a collection of symptoms linked to high fatality arising from a dysregulated response to an infection which leads to lifethreatening organ dysfunction[1]. Sepsis not only threatens human life, but also brings a huge economic burden on medical and health care system. A meta-analysis of studies on incidence and mortality of sepsis among the adults in 27 developed countries from 1979 to 2015 showed the incidence of sepsis was 288 per 100000 per year,while the 10-year incidence of the disease was 437 per 100000 per year and the mortality was 17%; the incidence of severe sepsis was 270 per 100000 per year and the mortality was 26%[2]. Few sepsis-related studies have included data from developing and less developed countries, where the incidence and mortality of sepsis is higher as shown in other reports[3].
Studies on incidence of sepsis mainly reported data of ICU patients.In 2020, a multi-center research showed the incidence of sepsis among ICU patients in 44 hospitals across the country was 20.6%[4].Similarly, mortality data of sepsis are mostly from ICU patients. In the above mentioned multi-center study, the mortality was 35.5%.For severe cases, the mortality was as high as 50% or above. The study also found there was no signi ficant difference in the mortality between patients who met the diagnostic criteria of Sepsis 3.0 and Sepsis 2.0[4]. In Australia and New Zealand, the hospital mortality rate for severe sepsis was 18.4%-35%[5]; while in the United States,the mortality rate for sepsis (de fined by ICD-9-CM) decreased from 27.8% in 1979 to 17.9% in 2000[6].
According to reports on sepsis, the fatality rate of sepsis in China is higher than that in developed countries. A population-based epidemiological survey of sepsis found that 1025997 people died of sepsis in 2015, accounting for 12.6% of the total hospital fatality cases[7]. Another single-center retrospective study of 759severe sepsis patients from 2006 to 2016 showed that the mortality rate was as high as 36.6%[8]. Although the correct and reasonable application of antibacterial drugs are the key measures of successful treatment and one of the main factors to reduce the mortality, other active auxiliary treatments, such as fluid resuscitation, immune conditioning, nutritional support and other measures also prevent sepsis from developing to severe sepsis or septic shock[9].
Considering its high incidence and mortality[4,10], the diagnosis and treatment of sepsis has been the study focus of emergency medicine, critical medicine, infectious diseases, as well as surgery since 2001. Experts have successively proposed versions 1.0, 2.0,and 3.0 of sepsis diagnosis, and have also proposed plans such as“save sepsis action”, “Early goal-directed therapy (EGDT)”, “cluster therapy” and other concepts like “restrictive ventilation”, “optimal PEEP”, “protective lung ventilation”etc. However the incidence and mortality of sepsis have not been signi ficantly reduced over the past two decades[10].
Based on the characteristics of emergency medicine, Chinese experts put forward Preventing Sepsis Campaign in China(PSCC) in May 2018. They advocated prevention, diagnosis, and intervention at earliest to decrease the morbidity and mortality of sepsis, and put forward the theory of pre-sepsis state as well as the principle of prevention before the onset and prevention from deterioration of sepsis. They highlighted preventing the onset and blocking the progression of sepsis as the key points, and suggested some breakthrough points including cutting off the intermediates during the development of infections into organ failure, controlling infection and in flammation, and regulating blood coagulation by endotheliocyte protective agents during peri-sepsis. Considering that patients with severe infections usually visit the emergency department firstly, it is important and feasible to start with prevention measures in the emergency department, which could help effective early goal-directed therapy (EGDT). In January 2017,WHO also proposed integrated intervention of prevention, diagnosis,and treatment. Moreover, all participants agreed on improving the prevention and treatment of sepsis at the regular meeting of WHO on 26 May 2017[11]. Flow chart of sepsis prevention and control in Emergency Department was shown in Figure 1.
2. Diagnosis of acute infectious diseases
As the commonest diseases in the emergency department,infectious diseases are preconditions to sepsis. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment is the first step to prevent its early intervention.However, for physicians in the emergency department, it is very difficult to con firm the occurrence of infections due to the diversity of symptoms.
Acute infections occur in a short time (<72 h) and are caused by in flammatory changes of tissues or organs[12], which are attributed to pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria, viruses, funguses,mycoplasma or chlamydia, parasites,etc. The clinical symptoms consist of general and local symptoms.
2.1. Diagnosis based on general symptoms
2.1.1. Temperature change
Temperature change is the most important indicator for the diagnosis of infections. More than 90% of patients with infectious diseases have an acute fever. Some in firm or immunocompromised patients may not present with fever, some patients with severe infections may have hypothermia, and some patients may present with pseudo normal temperature due to antifebrile or physical cooling. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is an important intermediate during the development of sepsis and was an important diagnostic indicator. According to the diagnosis standard of SIRS, the temperature change is the top one indicator. Thus, acute infections should be taken into consideration for any patients with abnormal temperatures.
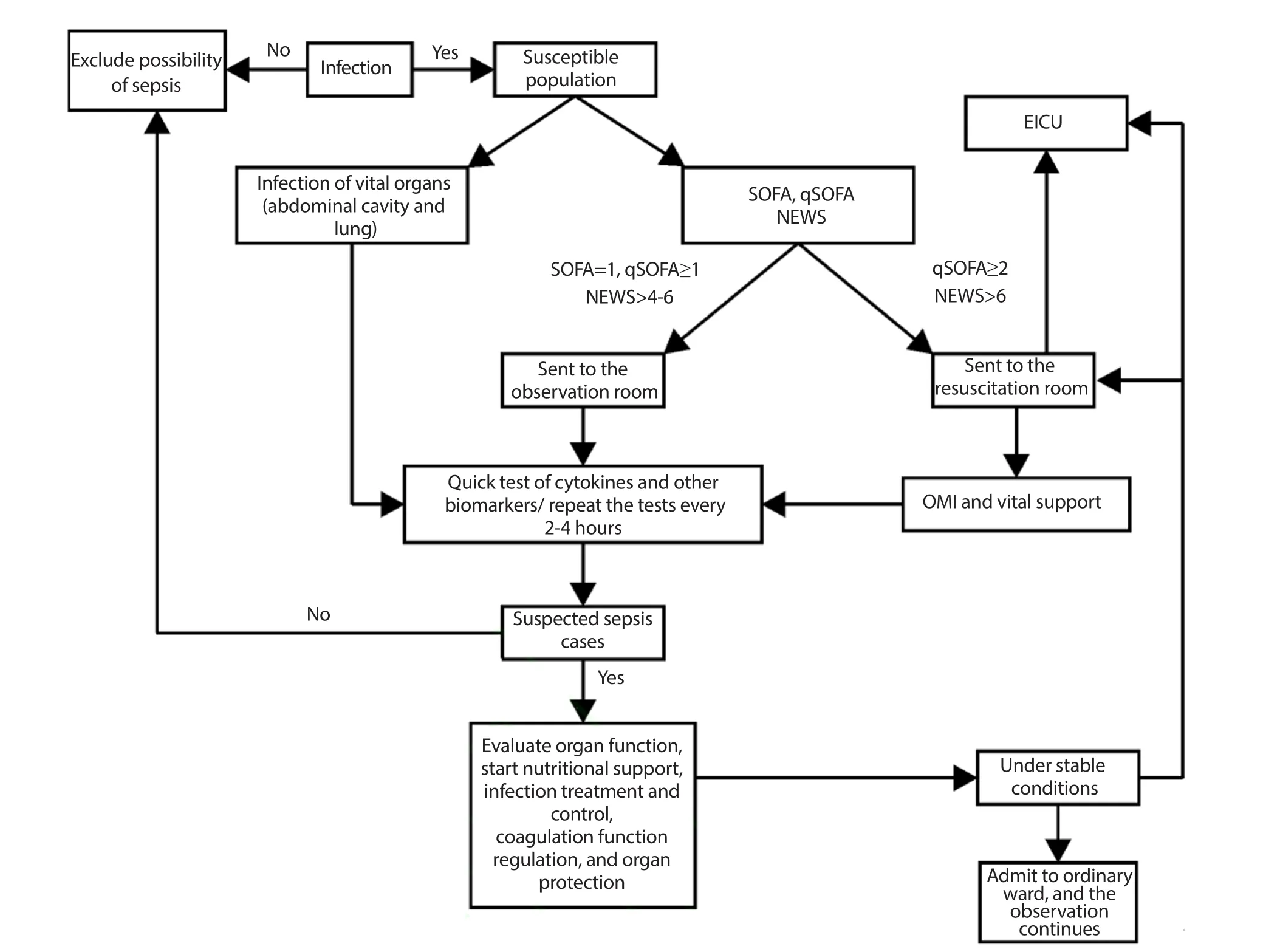
Figure 1. The flowchart of sepsis prevention and control in Emergency Department.
2.1.2. Leukocyte change
Leukocytes change in peripheral blood is the second characteristic change of acute infections and could help to differentiate various infections. Increased leukocyte count is one of the most speci fic changes of acute bacterial infections. Increased neutrophil or obvious shift to left could appear during classi fication detection, which is supportive of acute bacterial infections. Decreased leukocyte could occur during virus infections and some special infections.
2.2. Biochemical markers of infections
Biochemical markers are indicators useful for infection detections in recent years. They could help identify the occurrence of infections and possible pathogens. At present, the common biochemical markers include serum C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin(PCT), interleukin-6 (IL-6), serum amyloid protein A (SAA), and heparin-binding protein (HBP)[13].
2.2.1. CRP
CRP is one of acute-phase reactive proteins and could be increased rapidly by most infections. It is usually increased 2 h after infection and reaches the peak 24-48 h later. CRP level increases signi ficantly during bacterial infections, but stays normal or increases slightly during virus infections. Therefore, it is usually used as a reference to differentiate bacterial and virus infections. However, the critical value for the diagnosis of bacterial infections is unclear. Some researchers suggest 40 mg/L, while some consider >20 mg/L as the borderline value. The half-life period of CRP is 18 hours and the level will decrease rapidly 1-2 d after controling of the infection.
2.2.2. PCT
PCT is a glycoprotein without hormonal activity and is positively associated with the severity of bacterial infections. The level of 0.1-0.25 ng/mL is considered as the indicator of little possibility of infections, 0.25-0.5 ng/mL as medium possibility, and >0.5 ng/mL as great possibility[14]. Thus 0.5 ng/mL is suggested as the critical value by the majority of experts. PCT increases rapidly 2-4 h after infection and reach a peak 12-48 h later. With high speci ficity, PCT is the recommended indicator in many guidelines and consensus at home and abroad. The diagnosis and treatment scheme of COVID-19in 2020 points out that most patients show normal PCT levels, which indicates that PCT is generally not elevated during virus infections and could be used as a speci fic marker of bacterial infections.
2.2.3. IL-6
IL-6 is a multiple-effect cytokine induced by IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor-α. It is a multi-functional glycoprotein and consists of 212 amino acids. As the key mediator of in flammatory cytokines,it has core regulatory function during inflammatory reactions.The level is obviously increased during bacterial infections and is positively correlated with levels of HBP, SAA,etc. With consistency with the degree of infection, it is a common indicator to evaluate and detect the infections[15]. Moreover, IL-6 has great significance in judging the severity of sepsis. It is reported that serum IL-6 levels of sepsis patients were signi ficantly higher than the non-sepsis patients;while the levels were also signi ficantly higher in patients with septic shock compared with non-septic shock patients[16].
2.2.4. SAA
SAA is a sensitive acute-phase reactive protein. The stimuli such as bacteria, viruses,etc.induce the body to produce a series of cytokines, then stimulate hepatic cells to synthesize and secrete plenty of SAA, which enters into blood and is 10-1000 times higher than normal level in 5-6 h. SAA is not influenced by gender or age and is usually used in combination with CRP to differentiate bacterial and virus infections. The simultaneously increased levels of SAA and CRP indicate possible bacterial infections; while the increased levels of SAA and normal CRP indicate virus infections.The half-life period of SAA is about 50 min. It restores quickly after the elimination of antigens. Thus, it could be used as a sensitive indicator of the control of infections and in flammations.
2.2.5. HBP
HBP is a protein molecule released from the neutrophils activated by organism. Studies have shown that sepsis patients’ HBP signi ficantly increased when the IL-6 level was normal or slightly elevated, and HBP shows higher accuracy on diagnosing of sepsis than other cytokines[17,18], and it is especially valuable in the early and rapid diagnosis of severe bacterial infections. As an acute phase protein, HBP is an effective biomarker for evaluating disease severity in patients with sepsis, which plays more significant roles in the early diagnosis and monitoring curative effect of patients with septic shock.
2.3. Confirming infection by local symptoms and signs
Some patients, especially the elderly or those with compromised immune systems, may lack a systemic response to infection. For such patients, the characteristic signs of infection site and symptoms can help us con firm or suspect the possibility of infection, such as clear cough, cough with phlegm indicates respiratory tract infection,acute consciousness changes or headache indicates central nervous system infection, urinary frequency, urgent urination, painful urination and lumbago indicate urinary system infection, abdominal pain or diarrhea with purulent bloody stool indicates abdominal cavity or the digestive tract infections,etc.
2.4. The confirmation of acute and suspected infections
Based on the above research results and clinical experience, the presence of acute infection can be considered if the following symptoms occur: (1) acute fever (within 72 h) or hypothermia;(2)total white blood cells count increases or decreases; (3) CRP and IL-6 increase; (4) PCT, SAA and HBP increase; (5) there is a con firmed or suspected site of infection.
Confirmed infection:any two items in (1-3) + (4) with de finite results, could help determine the types of pathogen, or + (5) with de finite symptoms could help determine the site of infection.
Suspected infection:any one item in (1-3) + (4) without de finite result, or + (5) with suspected site of infection.
3. Screening of high-risk population of sepsis
3.1. Sepsis susceptible population
More and more studies indicate that sepsis is associated with speci fic genes in the body. In recent years, studies have con firmed that there are significant differences in the expression of sepsis biomarker genes in patients with acute infection, sepsis and septic shock and put forward a useful indicator for the screening of sepsis[19]. As a biomarker of sepsis, the sensitivity and speci ficity of gene detection were higher than that of PCT, which indicates that the occurrence of sepsis is related to the body constitution and also reveals that we may be able to develop a rapid detection method for sepsis biomarker gene in infected patients in the future.
In addition, age, underlying diseases, malnutrition,immunode ficiency and some other factors are also considered to be significant for occurring sepsis. In 2007, a multicenter study results showed that the risk factors for the incidence of severe sepsis and in-hospital mortality include age, malignant tumor and other chronic complications[20]. The Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHEⅡscore), Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), respiratory dysfunction and cardiovascular dysfunction score are crucial factors as well in assessing sepsis and its mortality[21]. The results of another multicenter prospective observational cohort study in 2014 showed APACHEⅡand SOFA scores, bloodstream infection and cancer history were signi ficantly associated with mortality[22]. In 2016, an analysis of one-year mortality in sepsis patients showed that age, acute renal failure,fungal infection, anion gap and pulmonary infection were the predictors of one-year mortality[23].
3.2. Potential pathogenic types and common infection sites of sepsis
According to the study on the infectious pathogens causing sepsis, the proportions of various infectious pathogens in sepsis are different[24,25], with bacteria still accounting for the largest proportion, followed by viruses. Domestic epidemiological studies suggest that more than half of patients with sepsis are infected with G-bacteria[23]. Zhouet al.[22] present that the infection rate of gramnegative (G -) bacteria can reach 62.5%, while gram-positive (G +)bacteria only account for 14.5%. However, more studies believe that the most common pathogenic bacteria causing sepsis are G +bacteria[26,27].The incidence of fungal sepsis has increased in the past 10 years, but it is still lower than that of bacterial sepsis[25,28].This difference may be due to the lack of large-scale epidemiological studies, and etiology in different regions and ICU differs as well.It may also be related to the changes in the etiology types caused by the usage of antimicrobial drug[29].Various viral infections are also important causes of sepsis. Both globally prevalent COVID- 19 in 2020 and SARS-CoV-2 lead to multiple organs disfunction syndrome (MODS) through generating cytokines and interfering with RAS system[30].
The research on the site of infection causing sepsis is also one of the research focus. A multicenter study in 2007 showed that the abdomen was the most common site of infection for sepsis (72.3%),followed by the lungs (52.8%)[20].The results of a multicentre prospective study in 2014 showed that pulmonary infection was the most common cause of sepsis, accounting for more than 50% of all sepsis patients, followed by abdominal infection and urinary tract infection[22]. A study found that the fatality rate of sepsis caused by unknown infection site, gastrointestinal tract or lung infection was between 50% and 55%, compared with only 30% for sepsis caused
by urinary tract infection[31]. Similar results were reported in a retrospective multicenter cohort study of nearly 8000 patients with septic shock, with the highest case fatality rate (78%) in patients with sepsis due to intestinal ischemia and the lowest case fatality rate(26%) in patients with sepsis due to urinary tract obstruction[32].
In summary, the risk factors for sepsis in patients with acute infection include: (1) advanced age and malnutrition; (2) abdominal,pulmonary and urinary tract infections; (3) malignant tumor,immunosuppression, respiratory dysfunction, cardiovascular dysfunction and other basic diseases. High attention should be paid to this high-risk group in emergency department through the observation of clinical manifestations, screening of biomarkers and early prevention.
4. Diagnosis and clinical suspicion of sepsis
4.1. Diagnosis of sepsis and Sequential (Sepsis-related)Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score
Sepsis 3.0 de fined that patients with infection and total SOFA score≥ 2 points can be diagnosed with sepsis. Sepsis 3.0 included the de finition and clinical diagnostic criteria of sepsis.
The SOFA score is a scoring system for the prognosis of patients through evaluation of degree of major organ damages, and is usually used in ICU[33]. It is suggested that the SOFA score is applied 24 h after admission to ICU and every 48 h afterwards. Therefore, it is named as “Sequential Organ Failure Assessment”. This score is more suitable to be used for inpatients because of its requirement of various clinical data and sequential assessment, but has certain limitation to early and rapid diagnosis in the emergency department.The mean value and maximum value of the SOFA score can predict the mortality of sepsis patients. If the score is increased by 30%, the mortality will reach at least 50%[34]. However, the SOFA score is of little signi ficance for predicting the incidence of sepsis. Below is the calculation method of the SOFA score (Table 1)[33,35].
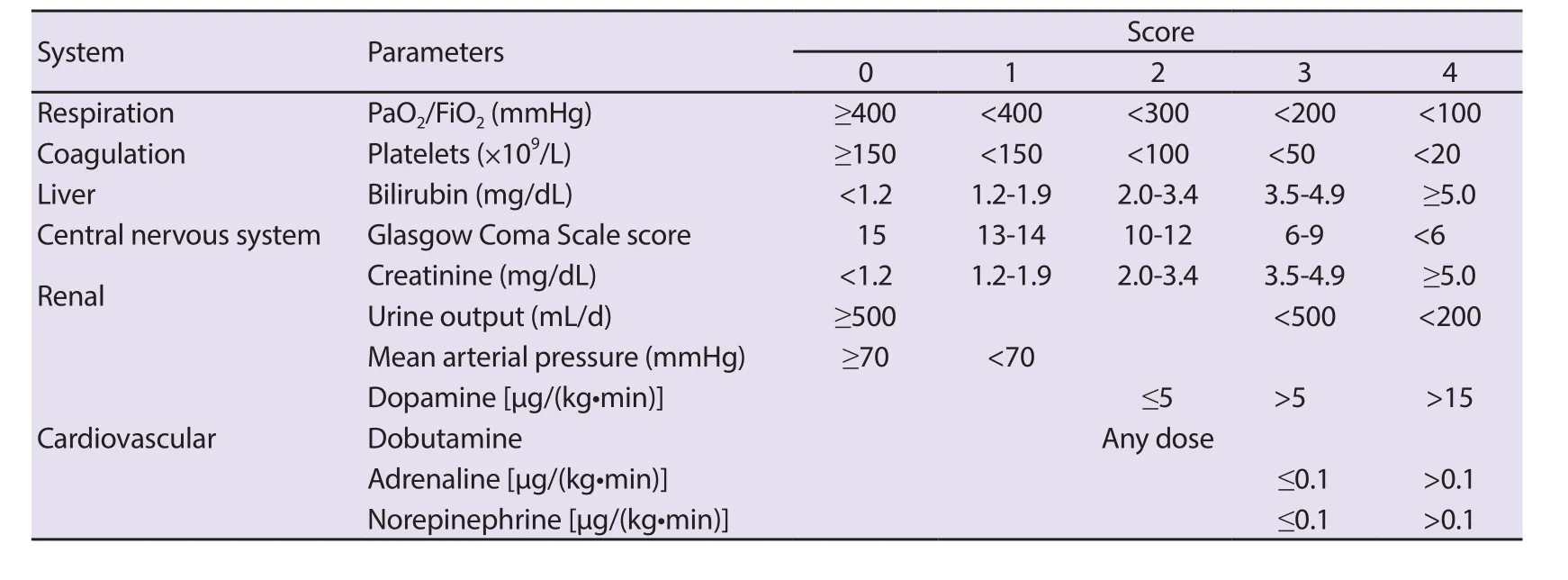
Table 1. Calculation method of the SOFA score.
4.2. Suspected sepsis in emergency department
According to the diagnostic criteria of Sepsis 3.0, organ dysfunction is considered as an important indicator of sepsis.However, manifestations such as insufficient effective circulating blood volume and severe inflammation may appear in infected patients in the emergency department before the occurrence of organ dysfunction. Such manifestations can be diagnosed as “Pre-sepsis stage” or “Suspected sepsis”, which is of great importance to PSCC.Emergency phsicians usually make empirical diagnosis based on clinical data, and screen patients who may develop sepsis according to the disease score.
4.2.1. The quickSOFA (qSOFA) score
The qSOFA score is a useful screening tool for the suspected sepsis recommended by Sepsis 3.0 (Table 2)[1]. The analysis shows that,the higher the qSOFA score, the higher the risk of death, but the prediction validity varies signi ficantly among the cases. In a study of patients with suspected infection, the predictive validity of qSOFA for in-hospital mortality is similar to the SOFA score: in total score< 2, the mortality is 3%; in total score ≥ 2, the mortality reaches 24%and 18%, respectively[36]. However, some studies have questioned the sensitivity and speci ficity of the qSOFA score. In 2018, a meta analysis that included 38 studies revealed that, the qSOFA had a lower sensitivity (88%vs.61%) but higher speci ficity (26%vs.72%)for predicting the mortality in patients with sepsis in comparison with the SIRS score[37]. Compared with non-ICU patients, the qSOFA had a higher sensitivity for ICU patients (51%vs.87%)with a lower speci ficity (80%vs.33%). Other retrospective studies on emergency patients found that the qSOFA score had certain limitation, one of which reported that the qSOFA was less useful than the Systemic In flammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) score in identifying sepsis[38]. In addition, another report demonstrated its low value for predicting 28-day mortality[39].
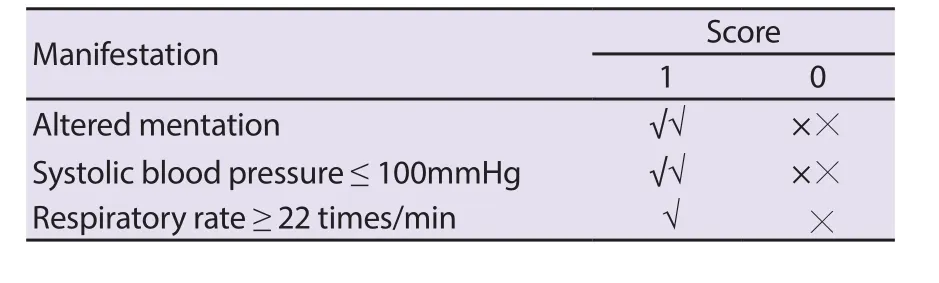
Table 2. The qSOFA score.
4.2.2. National Early Warning Score (NEWS)
The early scoring systems such as the Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS), NEWS and SIRS score are more effective than qSOFA in terms of the prediction of death of non-ICU patients and ICU transfer[40,41].
In clinical work of the emergency department, the most important indicators reflecting changes in the condition are not changes in breathing, consciousness, and blood pressure, but changes in heart rate (pulse). The Early Warning Score (EWS), MEWS and NEWS[42] developed by UK experts (Table 3) are a useful tool for rapid evaluation and grading of the severity of the disease which are recognized in the field of emergency medicine. The evaluation indexes supplemented with correction of oxygen inhalation measures, which are available in the emergency department of and the hospital, make the judgment of the condition more accurate,especially for patients with changes in cardiopulmonary function.The advantages of early warning scoring in assessment of the condition of emergency patients are fully con firmed in a previous study where the effectiveness of the improved early warning scoring system for the prognosis of elderly shock patients was evaluated[43].Hence, the NEWS is more comprehensive than the qSOFA in evaluating the critical condition of patients.
4.2.3. Diagnostic criteria for suspected sepsis in Emergency Department
Patient’s clinical manifestations include: (1) Patients with infection or suspected with infection; (2) qSOFA ≥ 2 points; (3) SOFA = 1 point; (4) NEWS: 4-6 points.
In addition to the first manifestation, patients who have any other manifestations can be diagnosed as “suspected sepsis”.
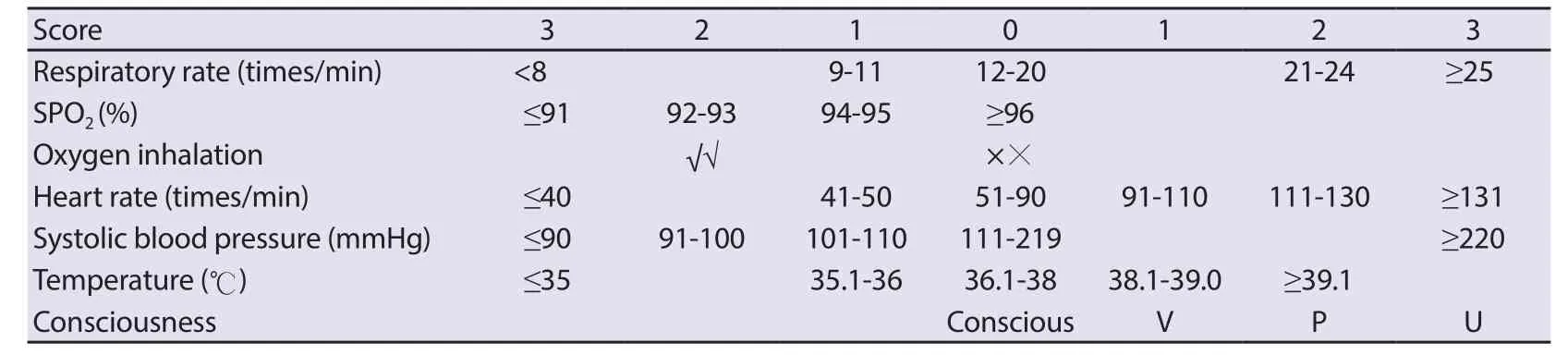
Table 3. The National Early Warning Score (NEWS).
5. Prevention of sepsis
5.1. Identification of patients at high risk for sepsis
Population at high risk for sepsis, namely being susceptible to sepsis, include those with speci fic genes, having infected sites with high incidence of sepsis or with pathogen infection. For the elderly,malnutrition or patients with basic diseases or immunocompromise,the infected site and possible pathogens should be identi fied as soon as possible. Patients with severe pulmonary abdominal and urinary system infections should be screened for cytokines in a timely manner. Any infected patients should be promptly evaluated for suspected sepsis. Those with SOFA = 1 point, qSOFA ≥ 2 points or NEWS of 4-6 points should receive timely treatment for preventing sepsis and the score should be done every two hours for their condition.
5.2. Infection control
5.2.1. Detection of pathogenic microorganism
The pathogens that cause acute infection are bacteria, viruses,fungi, mycoplasma or chlamydia, parasites,etc. However, pathogens leading to sepsis are mainly bacteria, viruses and fungi. Hence,identifying pathogens as soon as possible and adopting targeted antimicrobial therapy are the key to treat infectious diseases. Since traditional microbial culture is time-consuming and has a narrow coverage, a rapid detection system of etiology is quite needed for the acute infection. For common pathogens such as bacteria and viruses, the existing rapid detection methods are: detection ofStreptococcus pneumoniaeantigen in urine, detection ofLegionella pneumonophilaantigen in urine, detection of GXpertClostridium difficile, and multiple pathogen detection platforms such as FilmArray/Roche Cobas/Luminex; Fungal fluorescence staining,detection ofPneumocystis yersinensisby Gomori’s methenamine silver staining, detection ofCryptococcus neoformansantigen, G test,GM test,aspergillusIgG, IgE and other fungal detection methods;Detection of antigen and nucleic acid, Realtime-PCR detection of various viruses, and other virus detection methods. Currently, the second-generation sequencing technology has been increasingly mature and applied in clinic. It covers thousands of pathogens so as to avoid missing detection to the greatest extent and has become a powerful method for etiological diagnosis[44].

Table 4. Common infections and antibiotic selection[34].
5.2.2. Anti-infection treatment
Viruses, bacteria, fungi,etc.are likely to cause sepsis, and sepsis caused by bacteria and viruses is still more common in clinic.Actually, at present there is no specific effective treatment for viral infection, which is usually controlled by immune regulation or traditional Chinese medicine. In bacterial infections, infection control is not only an important measure to prevent sepsis, but also a crucial method to prevent death from infection. Therefore,when selecting antibiotics for treatment, priority should be given to the antibiotics that cover suspected pathogens and have higher concentrations at the possible infection site. In addition, patient’s age, immune status, anaphylactic reaction,etc.should be also taken into consideration. During anti-infection treatment in the emergency department, we need to consider pathogen coverage and infection control, and try to avoid the drug-resistant bacteria caused by the overuse of antibiotics. Therefore, antibiotic selection should be based on rapid pathogen detection, infection site and high incidence of pathogenic bacteria. The recommendations for clinical anti-infection treatment are given inThe Sanford guideline to antimicrobial therapy 2018[45] (Table 4). Furthermore, anti-infection treatment should be timely; anti-infection treatment should be started within 1 h after diagnosis for severe infection, and antibiotics should be used within 4 h after diagnosis for mild infection, and also it is recommended to collect pathogenic specimens before the use of antibiotics.
5.2.3. Removal of the focus of infection
It is difficult for antibiotic therapy alone to effectively treat traumatic infection, pyogenic cholecystitis, abdominal with a de finite infectious site infection, urinary obstruction complicated with infection,etc. So, antibiotic therapy must be used in combined with localized treatment of infection sites including drainage,debridement and surgical resection. In addition, taking timely intervention is a crucial step to prevent sepsis.
5.3. Detection and blocking of cytokine storms
The local in flammatory response caused by infection can promote the replacement of damaged tissue with new tissue and weaken the damage that has occurred. However, when excessive in flammatory response occurs, it may cause SIRS and lead to sepsis. Therefore,timely detection of cytokine storms and appropriate regulation of in flammatory response are of great signi ficance for preventing sepsis and are the core of the prevention of sepsis.
5.3.1. Cytokine screening and SIRS determination
Cytokine screening should be performed in high-risk patients with sepsis and patients with suspected systemic in flammation, to determine the status of SIRS. At present, it is not clear what factors trigger and promote cytokine storms. But, it is known that many cytokines are involved in the response to sepsis. Numerous studies suggest the factors mainly involved in SIRS and compensatory antiinflammatory response syndrome are: TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-12,MIF, sCD74 and HMGB-1[46,47], and anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL -4, IL-10, IL-35, IL-37, TGF-β, IL-13,etc[48]. Evidence suggests that in flammatory regulation should be initiated when proinflammatory factors are significantly elevated or when an in flammatory response is out of balance. Therefore, for those at a high risk of infection of sepsis, regular cytokine monitoring (repeat every 2-4 h) should be conducted to detect and find the patients with suspected sepsis as early as possible. The expert team has organized the research and development of detection method for sepsis screening, which will be applied in the clinical practice of PSCC. At present, the cytokine commonly detected in hospitals is IL-6. As a cytokine of interleukin, IL-6 mainly stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of cells involved in the immune response and plays an important role in the body’s anti-infection immune response. When the in flammatory response occurs, the serum concentration of IL-6 increases earlier than other biomarkers. Also, PCT and CRP are induced after an increase of IL-6 concentration.
5.3.2. Inflammation regulation
When the level of cytokine is significantly increased, or the in flammation disorders are detected in the infected patients, the in flammation should be regulated as soon as possible to restore the in flammatory response in a stable and balanced state.
5.3.2.1. Glucocorticoids
Most studies recommend that glucocorticoids can be used in the treatment of septic shock[49,50], while there is no evidence that glucocorticoids can reduce the mortality of patient with sepsis who did not show sustained shock and has a low risk of death. However,there are studies suggesting that glucocorticoids can be given at a certain dose in the early stage to inhibit the secretion and release of inflammatory cytokines. Clinical trials have evidenced that glucocorticoids can regulate the immunity of patients with sepsis,restore their in flammatory response and prevent organ failure[51],which was included in theGuidelines for emergency treatment of sepsis/septic shock in China (2018)[52]. What is important now is the timing to use the hormone when SIRS-related detection methods are unavailable.
5.3.2.2. Nonhormonal anti-inflammatory drugs
The literature has shown that ulinastatin serves in regulating cytokines[53]. Ulinastatin is a glycoprotein that can inhibit the activity of various proteolytic enzymes and it is also a protease inhibitor that can inhibit trypsin and other enzymes. It has a stable lysosomal membrane, which is able to inhibit the release of lysosomal enzymes,to suppress the myocardial inhibitory factor (MDF), to scavenge oxygen free radicals and to inhibit the release of cytokine. In the early stage of cytokine elevation, the use of low-dose ulinastatin can regulate cytokines. When the cytokine is out of control, proin flammatory cells and anti-in flammatory cytokines would be out of balance, causing organ dysfunction. The use of high-dose ulinastatin can signi ficantly decrease the patients’ sepsis-related indicators.
5.3.2.3. Chinese medicinal formulations
The traditional Chinese medicine advocates a harmonious balance state of the body in order to treat both symptoms and internal causes of the disease. At present, many studies have proved that certain traditional Chinese medicinal substance or formula can prevent sepsis and improve the prognosis of sepsis patients by regulating in flammation and immune response, inhibiting platelet aggregation, and improving microcirculation.The Diagnosis and treatment protocol for novel coronavirus pneumonia (trial version 7)released by the China’s National Health Commission, has included the traditional Chinese medicine treatment as one of the important treatment methods, and recommended the use of Chinese herbal medicines and Chinese patent medicines according to degrees of severity. Specific prescriptions of Chinese patent medicines that have relatively clear efficacy, such as Reduning, Xuebijing and Shenfu injections, were recommended in the treatment of severe and critical cases. Although the active ingredients and mechanism of action of many Chinese patent medicines have not been de fined,the overall efficacy of Chinese medicine has been clinically proven.Reduning injection has a certain effect on viruses inhibiting and anti-bacteria in the treatment of sepsis. By binding antagonism endotoxin and toll-like receptors, it can inhibit the NF-κB receptor and MAPK signaling pathway and regulate the expression of cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, TNFα, IL-10, IL-13, ICAM-1,ET-1,etc, further affecting the biological function of regulatory T cells and improving the permeability of capillaries and pulmonary vessels[4]. It can also reduce neutrophil and lymphocyte exudation and antagonize the in flammatory response and regulate immune disorders[54-56]. Such drugs neither affect the anti-bacteria effect of antibiotics, nor lead to the spread of infection. Clinical practice has shown that Reduning injection with an appropriate dose at an appropriate time can shorten the treatment time of the disease and the relief time for symptoms, and reduce the probability of organ failure when the disease is getting worse, thus effectively prevent the occurrence of sepsis and disease progression[57]. Xuebijing injection has the effects of invigorating blood circulation for removing blood stasis, relieving meridian, and expelling toxin through inhibiting proinflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17,inhibiting expression of high-mobility group B1 (HMGB1) protein in late in flammatory cytokines, inhibiting the activation of the TLR4-NF-κB pathway[58- 63], thus achieving an anti-in flammatory result.There is evidence that combined with Western medicine treatment,Xuebijing injection can reduce the occurrence of sepsis, improve the patients’ condition and clinical outcomes[64]. A randomized controlled clinical study of patients with pneumonia complicated with sepsis showed that Xuebijing injection reduced the case fatality rate by 8.8% in 28 d, the pneumonia was severe PSI risk rating improvement by 14.4%, the length of mechanical ventilation was reduced by 5.5 d and the length in the ICU was reduced by 4 d. The study. The results was published in the international Critical Care Medicine journal (CCM) [65].
5.3.2.4. Inflammatory mediator and specific antibodies
At present, many researches have been devoted to investigating TNF-α, IL-1 antibodies and anti-endotoxin lipopolysaccharide(LPS) antibodies; these antibodies can relieve symptoms of sepsis by inducing proin flammatory cytokine inactivation[66]. In addition,studies have found that pentoxifylline can inhibit the activation of monocytes-macrophages and neutrophils, thereby inhibiting the secretion of IL-1 and TNF-α[67]. However, the clinical effect of these methods and the new antagonist drugs still need to be further studied before they can be applied in the clinic.
5.3.3. Regulation of the immunity system
Recent studies reported that inflammatory response always combined with immunosuppression in the sepsis, rather than that a pro-inflammatory response followed by an anti-inflammatory response as previously described[68]. Many studies have shown that the innate immunity and adaptive immunity are suppressed during sepsis, which can be found from the decrease of mature granulocytes and mature ratio, the “endotoxin tolerance” of mononuclear-macrophages, and reduction of dendritic cells and lymphocyte,etc[69]. Therefore, timely regulation of the immunity system is one of the important methods to prevent sepsis. Current preventive methods including regulating the innate immune response through granulocyte-macrophage colony factor and interferon γ,and regulating the adaptive immune function by using thymosin 1 and interleukin 7,etc[70]. However, the timing, dosage, and speci fic drugs of the immunomodulator are not yet clear. Whether it is for the prevention of sepsis or the clinical effect of the treatment of sepsis needs further study.
5.4. Vascular protection and regulation of coagulation
Vascular endothelial injury and microthrombosis lead to decreased perfusion of tissue cells, causing disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), which are considered to be the direct causes of organ dysfunction. The mechanisms that cause DIC include upregulation of procoagulant substances, downregulation of anticoagulant substances, and impaired fibrinolysis mechanism.Therefore, timely monitoring of coagulation related indicators is essential to prevent the occurrence of sepsis, especially platelet count. In addition, plasma D-dimer (D-dimer) is also a commonly used clinical reference index for coagulation function, re flecting the activation state of coagulation function[71].

Table 5. Stages of disseminated intravascular coagulation and their manifestations.
The clinical manifestations varies in different stages of DIC,including bleeding, organ dysfunction, shock, and microvascular disease hemolysis (Table 5). In the PSCC Campaign, the expert panel believes that We should focus on hypercoagulation in the early stage and give timely treatment.
5.4.1. Anticoagulant therapy
The inflammation with sepsis destroys the coagulation system,depletes endogenous anticoagulant factors, and inhibits fibrinolytic activity, which causes thrombosis, finally resulting in tissue hypoxia and organ damage. While in flammatory factors and in flammatory cells destroy the physiological anticoagulation mechanism, they also increase the release of tissue factors, which activates exogenous coagulation factors and worsens the inflammatory response.The entire process has been circulating, leading to the continued consumption and the final failure of anticoagulant substances, which eventually leads to abnormalities in the coagulation mechanism,which can seriously develop into multiple organ failure and cause death. Taking appropriate anticoagulant treatment for infected patients is one of the measures to prevent microthrombosis and sepsis. The drugs used clinically are mainly unfractionated heparin and low molecular weight heparin.
5.4.1.1. Unfractionated heparin
As effective anticoagulant drug, the application and dosage of Unfractionated heparin vary according to the clinical type and stage of DIC. Timely heparin treatment can improve the perfusion of surrounding tissues and has a tendency to reduce the case fatality rate, but it may also increase the risk of severe bleeding, therefore it is not recommended in a routine medication for sepsis complicated by DIC. What is matter is that how to detect the early hypercoagulable state. Only when patients in the hypercoagulable period have increased thrombin and thrombosis in their microcirculation, heparin anticoagulation therapy can achieve satisfactory results.
5.4.1.2. Low molecular weight heparin
As an anticoagulant drug depolymerized from ordinary heparin,Low molecular weight heparin can quickly exert antithrombotic effects after administration, and studies have shown that it can also signi ficantly improves hemodynamics[72], with high bioavailability and low bleeding risk as well as the characteristics of immune activity and longer half-life period. In addition, the use of lowmolecular-weight heparin for the treatment of infected patients with sepsis may inhibit abnormal coagulation function, reduce the abnormal loss of platelets, prevent oxygen free radical damage, and have a signi ficant effect on the improvement of microcirculation.While inhibiting the activation of the pathological coagulation system, low molecular weight heparin can also effectively reduce the occurrence of severe bleeding[73].
5.4.2. Alternative treatment
Alternative treatment depends on whether there is bleeding or a very high risk of bleeding due to a reduction in certain blood components.If the patient has the following conditions, an alternative treatment using blood products can be considered.
5.4.2.1. Blood platelet
For active bleeding, PLT needs to reach 50 × 109/L or more. Other indications for platelet importation include:
(1) PLT < 10 × 109/L without obvious signs of bleeding
(2) PLT < 20 × 109/L with high risk of bleeding
5.4.2.2. Coagulation factors
(1) When there is no bleeding or invasive operation plan, it is not recommended to use fresh frozen plasma to correct coagulation abnormalities.
(2) With prothrombin time (PT) or activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) prolonged longer than 1.5 times, or fibrinogen (FIB)less than 1.5 g/L, fresh frozen plasma of 15-30 mL/kg can be intravenously injected.
(3) Clotting factor concentrates can be used when the bleeding of DIC patients is caused by fluid overload. The plasma FIB of patients with DIC should be maintained at least 1.0-1.5 g/L.
5.5. Circulation capacity support
One of the important means of “curing sepsis” is fluid resuscitation.The premise of “resuscitation” is a clear decrease in effective circulating blood volume or shock. PSCC aims to prevent and stop the occurrence of sepsis early, so the focus of this consensus is before shock. Early endothelial cell damage and capillary leakage can cause invisible capacity shortage by when we need to identify and give liquid supplement support as soon as possible and the sooner the support time is, the better the effect will be, as the effective supplementation of liquid can not only ensure tissue perfusion, but also prevent blood hypercoagulability and microthrombosis. Early goal-directed (EGDT) fluid support should be started in the early stage of sepsis, and the qSOFA and NEWS scores should be reduced as soon as possible.
Although the ProCESS study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2014 and the ARESE study’s clinical application of traditional EGDT methods yielded negative results, it is believed that whether EGDT showed no advantages over a 60-day in-hospital mortality or secondary endpoints including long-term mortality and organ support[74-76]. The expert group believes that this loss of EGDT advantage is not a conceptual error, but because of the patient’s choice, timing, and goal setting. In the emergency department, patients can receive treatment much earlier than the ICU. Therefore, the opinions of experts believe that early positive liquid support is still one of the important treatment strategies for the emergency department to prevent sepsis.
Most studies believe that when choosing the type of fluid replacement, theoretically, the primary selection would be the crystal fluid, especially the crystal fluid that is similar to the factors that affect the internal environment such as the ionic composition,acidity, and charge of the extracellular fluid. Some experts believe that due to the small molecular weight of the crystal solution, it is easy to leak through the capillaries to the interstitial space, so it is not the first choice[77,78]. The clinical standard of the amount of fluid replacement is based on maintaining the stability of the whole circulation (heart rate, average arterial pressure and central venous pressure in the normal range) and normal lactate in arterial blood.
5.6. Protection of organ function
5.6.1. Increasing prevention awareness
It is a continuous process from infection to sepsis, and then from early stage of sepsis to organ dysfunction, eventually to multiple organ failure[79]. Emergency physicians need to accurately understand the MODS process caused by sepsis, investigate high-risk patients as early as possible, determine the degree of infection, detect and control in flammatory storms, provide respiratory and circulatory support, and protect the organ function as early as possible. For patients with signs of MODS, measures should be taken as soon as possible to avoid further aggravation of organ dysfunction and to avoid more organs damaged.
5.6.2. Improving the comprehensive awareness
Various organs of body interacted under a normal physiological status and its unction in a stable state. On one hand, when there is incomplete organ function, the balance of the body will be broken. If this imbalance failed to be timely adjusted, the damage to the organs will be further exacerbated, bringing the gradual failure of other organs. On the other hand, any intervention during the treatment may break the original balance and cause a series of subsequent organ damage. Therefore, in the process of diagnosis and treatment of patients, the “holistic health” and “prevention of disease progression should be emphasized, which should not only support injured organs, but also protect the normal organs and maintain the balance of organ functions. In the treatment, while supporting the organs, it should take into account the primary disease, in flammatory response and other aspects of treatment, and strive to make the body reach a new steady state as soon as possible.
5.6.3. Dynamic evaluation
Comprehensive and dynamic diagnosis of the functions of organs plays a vital role in early detection of organ impairments and he therapeutic effects of MODS. We should pay more attention to the changes in clinical parameters, for example, patients’ vital signs,urine volume, peripheral circulation, and skin mucous membrane,etc. Besides, other non-invasive or invasive surveillance methods are required. Respiratory and circulatory monitoring is a primary part of the diagnosis and treatment of emergency service, and surveillance of infection and inflammation factors of the suspected-sepsis patients should be attached same importance. In clinical, dynamic surveillance of NEWS scores, SOFA scores, and MODS severity scores can offer various monitoring indexes and views to prevent SIRS and MODS, and consequently prevent sepsis.
5.6.4. Early intervention
The core of early intervention of sepsis, is to reduce the negative effects of excessive response on the organs. Considering that, we should take full advantage of traditional Chinese medicine. From aspect of traditional Chinese medicine, sepsis has other names, for instance, externally contracted heat disease, collapse syndrome,blood syndrome, sudden dyspnea, “Shenhun” (unconsciousness),organ-exhaustion syndrome,etc. The pathogenesis of sepsis re flects the de ficiency of “Zhengqi” (anti-pathogenic energy), following by“Waixie” (exogenous pathogens) turning into heat after the invasion of the body, and then consuming “qi” and injuring “yin” (loss of energy). The energy is restrained, and the exogenous pathogens are deep inside the body, so that the circulation of blood and “qi”is blocked, resulting in heat toxin, blood stasis, sputum-induced stagnation of collateral channels, consequently the injury of organs.The concept of early intervention coincides with the theory of“treatment before disease attack” proposed inThe Inner Canon of Huangdi. As for the treatment of the disease, four treatments are applied to four different syndromes, heat-clearing and detoxicating remedy for the treatment of virus-induced heat; “Tongli Gongxia”herbs for blockage of “Fuqi”; Activating blood for blood stasis syndromes; supporting and consolidating body resistance for acute de ficiency syndrome.
5.6.4.1. Selecting treatments for different syndromes
(1) Heat toxin syndrome: The symptoms include prolonged high fever, restlessness, unconsciousness, nausea and vomiting, crimson tongue, rapid pulse,etc. The frequently-used traditional Chinese medicines include Retoxonin injection, Qingkailing injection,Xingnaojing injection, Angong Niuhuang Wan,etc[80].
(2) Blockage of “Fuqi”: Similar to the symptoms of intestinal obstruction in Western medicine, symptoms of “Fuqi” include ventosity, vomiting, rare defecation or fart, decline or disappear of bowel sound,etc. One of the initial factors of sepsis, according to some studies, is the transmission of bacteria stemmed from bowel dysfunction[81,82]. Early recovery of bowel function is of great importance for the prevention of sepsis. As one of the prescriptions,Dachengqi decoction can markedly decrease the mortality of MODS patients, reduce in flammatory mediators, inhibit the in flammatory response, regulate immune function, and has antibacterial properties[83].
(3) Blood stasis: The symptoms include high fever,unconsciousness, extreme pain without fixed location which generally aggravates at night, tumor, bleeding, dark purple tongue with ecchymosis, deep and late pulse signs,etc. Herbs including Honghua, Chishao, Chuanxiong, Dangui, Danshen and Xuefu Zhuyu decoction are commonly used traditional Chinese medicines
for the treatment of the sepsis categorized as blood stasis. As for the Chinese patent medicine, compound Danshen injection and Xubijing injection are the representatives[84,85].
(4) Acute deficiency syndromes: The symptoms, similar to that of shock in Western medicine, include unconsciousness and restlessness, flushed face, enophthalmos, skin folds, fever and anxiety, thirst, less urine, red and dry tongue, thready and rapid pulses,etc. In clinical, Shengmai injection[86] or Shenmai injection is commonly used to strengthen “qi”, nourish “yin”. As one of the deficiency syndromes, “Yangtuo” syndrome is presented as cold sweet, cold limbs, confusion, red face and purple lips, uncontrolled urine and sluggish hands, pale purple tongue, weak pulse signs. For the treatment, Shenfu injection is commonly used in clinic to supply“Qi” and strengthen “Yang”. “Yin-yang Jutuo” syndrome, severe de ficiency syndromes with signs of acute disease presenting with hidrosis, mental exhaustion, breathlessness, uroclepsia, less saliva,week pulse sign or powerless pulse sign,etc. Shengmai injection,Shenmai injection, and Shenfu injection can be used in combination for the treatment.
5.6.4.2. Single herb for the treatment
(1)Rheum officinale. Rhubarb can promote gastrointestinal motility,protect intestinal mucosa, stimulate the expulsion of endotoxin,reduce bacterial and toxin translocation, and have anti-in flammatory and bacteriostatic effects. It has a significant preventive and therapeutic effect on MODS, and can improve the survival rate of MODS involving more than 4 organs[87,88].
(2)Salvia miltiorrhiza. The water-soluble components ofSalvia miltiorrhizahave good antithrombotic and circulatory effects, so as to reduce the damage of organ function.In-vitroexperiments showed thatSalvia miltiorrhizahad antagonistic effects on lipopolysaccharide(LPS), and its protective effect on lung might be through inhibiting or reducing the expression of TNF-α and other cytokines in blood and lung tissues to decline the acute in flammatory response in the lungs[89].
(3)Panax ginseng. Experimental studies have con firmed[90] that the various active ingredients of ginseng have little effect on the direct destruction of endotoxin structure, but it has a strong antagonistic and protective effect on fever, leukocyte sudden decline, shock and death caused by endotoxin.
6. Conclusion
Initiated with infection, sepsis causes organ dysfunction sequentially through cytokine storm, capillary endothelial injury,capillary leakage, microthrombus formation and tissue perfusion decline. The medical staff has reaped abundant experience in organ function protection and replacement over many years practice, but the treatment efficacy is still unsatisfactory. There is limited we can do the block the progression from infection to sepsis. The reasons lie in the complicated pathophysiology and the limited knowledge on the prevention methods of sepsis. As a clinical specialty with earliest contact with patients, emergency medicine has the features and advantages of early diagnosis, risk classification, reasonable transfer, and proper treatment. Through the early intervention on the pathophysiological progression, we can prevent sepsis and reduce the incidence. Besides, proper diagnosis and treatment can decline the mortality of sepsis. But we have proposed this treatment concept without a long time, so we are still confronted with many difficulties raised by MODS, for instance, the complexity of infectious disease,the complexity of susceptible populations, the complexity of cytokine storms in initiation and development,etc. Considering that,joint efforts should be made by the medical staff and researchers to prevent sepsis. With a good start, we believe the steadfast development of PSCC will obtain satisfactory achievements, and bene fit the medical sector, society and our people.
Appendix: List of consensus members
Yu Cao, Yanfen Chai, Yangong Chao, Biao Chen, Fang Chen,Feng Chen, Yuguo Chen, Wei Cui, Shimin Dong, Bangjiang Fang,Xiaotong Han, Xiaojun He, Yinping Li, Zhaofen Lin, Xiaoran Liu, Zhongqiu Lu, Chuanzhu Lv, Yuefeng Ma, Yuhong Mi, Shinan Nie, Qiao Pei, Chuanyun Qian, Lijie Qin, Deya Shang, Junli Si,Chaoyang Tong, Lijun Wang, Zhenjie Wang, Zhong Wang, Jie Wei,Feng Xu, Tie Xu, Yongming Yao, Xuezhong Yu, Hongke Zeng,Guoqiang Zhang, Hong Zhang, Jinsong Zhang, Xinchao Zhang,Mao Zhang, Min Zhao, Xiaodong Zhao, Zhigang Zhao, Bo Zheng,Huadong Zhu, Yimin Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no con flicts of interest.
Funding
This work was supported by CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2019-I2M-5-023).
Authors’ contributions
ZW, JW, HDZ, YC and the corresponding authors organized and drafted the consensus. Other members made comments and suggestions on the final version of this consensus.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2020年8期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2020年8期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- First COVID-19 related death in Pakistan in a patient with a travel history in Saudi Arabia
- COVID-19 pandemic in Rwanda: An overview of prevention strategies
- Using twitter and web news mining to predict COVID-19 outbreak
- Effectiveness of intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy with sulfadoxinepyrimethamine: An in silico pharmacological model
- Diagnostic performance of C-reactive protein level and its role as a potential biomarker of severe dengue in adults
- ATP gatekeeper of Plasmodium protein kinase may provide the opportunity to develop selective antimalarial drugs with multiple targets
