The influence of genetic polymorphisms in drug metabolism enzymes and transporters on the pharmacokinetics of different fluvastatin formulations
,Yimin Cui
a Department of Pharmacy, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
b State Key Laboratory of Drug Release Technology and Pharmacokinetics, Tianjin Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Tianjin 300193,China
c School of Pharmaceutical Science, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China
Keywords: Genetic polymorphisms SLCO1B1 Fluvastatin Immediate-release Extended-release
ABSTRACT The purpose of the present study was to investigate the impact of genetic polymorphism on fluvastatin pharmacokinetics.In addition,we compared the fluvastatin pharmacokinetics differences between extended-release (ER) 80 mg tablet and immediate-release (IR) 40 mg capsule in terms of drug metabolism enzyme and transporter genetic polymorphisms.In this open-label,randomized,two-period,two-treatment,crossover study (n=24),effects of ABCG2,SLCO1B1,ABCB1,CYP2C9 and CYP3A5 polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of fluvastatin were analyzed.The administration dosage for IR 40 mg and ER 80 mg were twice and once daily,respectively,for total 7 d.Blood samples for pharmacokinetic evaluation were taken on the 1st and 7th d.The lower exposure following ER was observed.For ER tablets,SLCO1B1 T521C genotype correlated with AUC 0-24 of repeat doses (P=0.010).SLCO1B1 T521C genotype had no statistically significant effect on AUC 0-24 of IR capsule of fluvastatin after single or repeated doses.In vitro study demonstrated that when the concentration of fluvastatin was low (< 1 μmol/l),the uptake of fluvastatin in the HEK293-OATP1B1 with SLCO1B1 521TT (K m=0.18 μmol/l) was faster than that with SLCO1B1 521CC (K m=0.49 μmol/l),On the other hand,when concentration reached to higher level (> 1 μmol/l),transport velocity of fluvastatin by HEK293-OATP1B1 with SLCO1B1 521TT (K m=11.4 μmol/l) and with SLCO1B1 521TCC (K m=15.1 μmol/l) tend to be the same.It suggests that the increased effect of SLCO1B1 T521C genotype on ER formulation of fluvastatin was mainly caused by lower blood concentrations.We recommend that formulation should be incorporated into future pharmacogenomics studies.?Corresponding authors.Department of Pharmacy,Peking University First Hospital,No.6,Dahongluochang Street,Xicheng District,Beijing 100034,China.Tel:+86 10 66110802
1.Introduction
Fluvastatin sodium is a potent synthetic competitive reversible inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase,which is the rate limiting enzyme for cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver [1].It is widely used to improve lipid profiles in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia.Fluvastatin treatment has been shown to reduce concentrations of total cholesterol,lowdensity lipoprotein (LDL) and triglycerides,and to increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels [2].Therefore,it exerts antiatherogenic effects and reduces the incidence of coronary heart disease [3,4].A widely applied fluvastatin regimen includes a 40 mg immediate-release (IR) capsule twice daily or an 80 mg extended-release (ER) tablet once daily.Both formulations have been reported to be effective in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia;however,the ER formulation is more potent than the IR formulation [5,6].
The treatment effects of statins could be influenced by pharmacogenetics.Genetic variations could alter the activity of cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes and transporter proteins [7,8],therefore result in pharmacokinetic differences.Significant Statistical differences have been shown in the pharmacokinetics of fluvastatin in subjects with different numbers ofCYP2C9?3alleles (P<0.0001,F-test) [9].Although it has been shown that the pharmacokinetics of fluvastatin was not altered bySLCO1B1(encoding OATP1B1) T521C polymorphism [10],a tendency of attenuated reduction in total cholesterol and LDL in subjects carrying one or more variant allele(s) ofSLCO1B1T521C polymorphism has been observed [11,12].In addition,it has been shown thatSLCO1B1contributed to inter-individual variability of fluvastatin pharmacodynamics [13].Therefore,the association ofSLCO1B1single nucleotide polymorphism(SNP) with pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of fluvastatin needs to be further clarified.
ER formulations enable the less frequent administration of drugs and reduce peak serum concentrations,thereby lowering the risk of adverse events.Since the genetic variations influencing pharmacokinetics are usually related to proteins involved in drug metabolism,which would be expected to be affected by peak concentrations of serum drugs,the influence of genotype on pharmacokinetics might be different in different formulations that modify drug exposure.However,there have been very few studies addressing this.Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium posted a series of gene/drug clinical practice guidelines,which emphasized the pharmacokinetics-genetic polymorphism relationship [14].These guidelines have a great influence on global clinical application.However,none of them mentioned the potential effects of the dosage form on the pharmacokinetics-genetic polymorphism relationship.
After reviewing all pharmacogenetic studies concerning fluvastatin [9,10,15],we found that these studies were usually performed in signal dose settings with IR 40 mg fluvastatin formulation,whereas in the studies investigating the effect of genetic polymorphisms on fluvastatin efficacy,the treatment regimen included repeated doses of fluvastatin with either IR 40 mg or ER 80 mg formulation.There has been no study investigating the difference in the relationships of genetic polymorphisms with pharmacokinetics parameters under different treatment settings.With the extensive application of sustained-release dosage forms,it is important to clarify the effect of formulation on the pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamic-gene relationship.Therefore,the present study aimed to examine the pharmacokinetics of fluvastatin in two treatment settings under different formulations with the same total daily dose [16].The effects ofSLCO1B1T521C,G388A,CYP2C9?3,CYP3A5?3,ABCG2C421A,ABCB1G2677T/A and C3435T genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of fluvastatin,for both initial and repeated doses,were examined.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Material
The extended-release (ER) 80 mg tablets and immediaterelease (IR) 40 mg capsules were provided by Novartis Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.Phosphate buffer solution (PBS)was purchased from Beijing solarbio science &technology co.,ltd.Fluvastatin was bought from Sigma-Aldrich ?(Hongkong,China).The dulbecco’s modified eagle medium (DMEM),fetal bovine serum (FBS),the 100 ×mixture of penicillin and streptomycin (PS),0.25% trypin were all obtained from Gibco (USA).The cell lines HEK 293-Mock (carrying the blank plasmid),HEK293-OATP1B1 (withSLCO1B1521TT)and HEK293-OATP1B1(withSLCO1B1521CC) were friendly offered by State key laboratory of drug release technology and pharmacokinetics in Tianjin Pharmaceutical Research Institute New Drug Evaluation Company.
2.2.Study population
A total of 24 healthy Chinese subjects were recruited to participate in the present crossover study.The health status of participants was confirmed based on medical history,physical examination,vital signs (blood pressure,pulse rate and temperature),safety laboratory tests (blood chemistry,hematology and urine analysis),and 12-lead electrocardiogram.The subjects had not been taking any medicine for at least 4 weeks prior to initiation of the study.All subjects were briefed about the purpose,duration,and potential risks of the study.Written informed consent was obtained from each subject.The study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki and the study protocol was approved by the Ethical Review Board of Peking University First Hospital.
2.3.Study design
Subjects were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio into 2 groups to receive fluvastatin as either a 40 mg IR capsule twice daily(8:00 a.m.and 8:00 p.m.) or an 80 mg ER tablet once daily(8:00 a.m.) for 7 days.Following a washout period for a week,subjects were switched to the other treatment.During the study period,subjects were served the same meals.At day 1 and day 7 of each treatment period,all subjects fasted overnight (10 h) before administration of the first dose and were not allowed to eat until 2 h after the first dose.Each formulation was administered with 240 ml of water.During day 2 to day 6,breakfast was provided half an hour after administration of fluvastatin.Lunch and dinner were provided at 12:00 a.m.and 6:00 p.m.,respectively.
On day 1 and day 7,whole blood samples (3.5 ml) were collected by intravenous puncture or forearm catheter at 0,0.5,1,1.5,2,3,4,6,8,10,12,16 and 24 h after administration in the ER group,and at 0.25,0.5,1,2,4,6,8,12 (before the second dose),12.5,13,14,16,20 and 24 h in the IR group.At day 5 and day 6,blood samples of 3.5 ml were taken just before drug administration.Blood samples were collected in serum separation tubes at room temperature,stored away from direct sunlight and ultraviolet radiation,and then centrifuged at 4 °C and 1500 ×gfor 15 min.The separated serum samples were collected in 4-ml centrifuge tubes and stored at ?70 °C until assay.
2.4.Determination of serum fluvastatin concentration
The high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) was employed to detect serum fluvastatin.The analytical column was a Waters Xterra MS C18(50 mm ×2.1 mm;3.5 μm;Waters Technologies,Inc.).The mobile phase A was 0.1% acetic acid aqueous solution,and mobile phase B was 100% methanol.The injection volume was 10.0 μL.A linear gradient was ramped up from 35% to 100%of moble phase A in 5 min at the flow rate was 320 μl/min.The column temperature was maintained at 40 °C,and the mass spectrometer was used in the negative scan mode.Quantitation was accomplished by API4000 (AB Sciex Pte.Ltd.) and monitoring of the precursor-to-production pairsm/z410.2–348.2 for fluvastatin andm/z418.2–356.2 for the internal standard.The linear calibration range was 0.5–500 ng/ml.The five QC sample concentrations were 0.500,1.50,15.0,125 and 400 ng/ml.The inter-and intra-day precision (RSD) were<3.6% (less than 19.1% for lower limit of quantification),and accuracy was within 97.6%–112.8%.Absolute recovery rates were 90.3% ± 13.5%,94.3% ± 13.2%,and 106.5% ±14.5% for 1.50,125 and 400 ng/ml,respectively.No significant matrix effect was found.All samples were analyzed within established storage stability periods.
2.5.Analysis of CYP2C9 , SLCO1B1 , ABCB1 , and ABCG2 genotypes
DNA was extracted from peripheral whole blood samples of each subject using a DNA purification kit (Wizard,Promega,USA).Further,SLCO1B1G388A (rs4363657),ABCB1C3435T (rs1045642),CYP2C9?3(rs1057910) andCYP3A5?3(rs776746) alleles were detected using polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-restriction fragment length polymorphism,andSLCO1B1T521C (rs4149056),ABCG2C421A (rs2231137) andABCB1G2677T/A (rs2032582) alleles were evaluated using PCR sequencing.The primers and restriction enzymes that were used are listed in Table S1.All methods were verified by sequencing and all sequences were compared with the reference sequences in GenBank.
2.6.Pharmacokinetic evaluation
Pharmacokinetic analyses and simulations were conducted using WinNonlin Professional Edition,Version 3.1 (Pharsight Corp.,Mountain View,CA,USA).CmaxandTmaxwere directly estimated from the observed serum concentration-time data.AUC0-tandAUCt1-t2were calculated using the linear trapezoidal rule.Pharmacokinetic parameters determined after first dosing includedAUC0-t,AUCt1-t2Cmax,TmaxandT1/2,and after multiple dosing includedAUC0-t,AUCt1-t2Cmax,Tmax,T1/2,Cminand average concentration (Cav).
2.7.Statistical analyses
Allele and genotype frequencies for the variant SNPs were assessed for deviation from Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium using theχ2 test.The Mann–WhitneyU-test was applied to evaluate significant differences in pharmacokinetic parameters between genotypic group pairs.Data from three or more different genotypic groups were compared using the Kruskal–WallisH-test.Correlations between variables were examined using Pearson’s correlation analysis.Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS for Windows,version 22.0.AP-value ≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2.8.In vitro study
The lines cryopreserved in ?80 °C ultra-cold storage freezer were revived and after two time passages,the confluent cells were treated by 0.25% trypsin and the cell suspensions were diluted with culture medium (DMEM+10%FBS+PS) to the concentration of 2.0 ×105(cells/ml).The diluted suspension were injected into 24-well cell culture plates by 1 ml per well and thereafter,the plates were removed to the incubator with 5% CO2and 95% air humidity at the temperature of 37 °C.After 48 h culture,when cells were completely confluent,the plates with different cell lines were removed to water bath of 37 °C.The old medium was replaced by 1 ml PBS.After incubation for 10 min,the PBS was replaced by 0.5 ml PBS with different concentrations of fluvastatin.After incubated for 5 min,the fluvastatin solution was removed and all the cells were washed by cold PBS for three times to stop the uptake action.Thereafter,the cells were lysed by multigelation for three times,and then added 0.4 ml methyl alcohol with 50 mg/l simvastatin taken as interior label.After ultrasonic treatment for 10 min,the samples were centrifuged at 10 000 ×gfor 5 min and 0.1 ml supernatant was carried to analyze by LC-MS.
3.Results and discussion
3.1.In vivo pharmacokinetic study
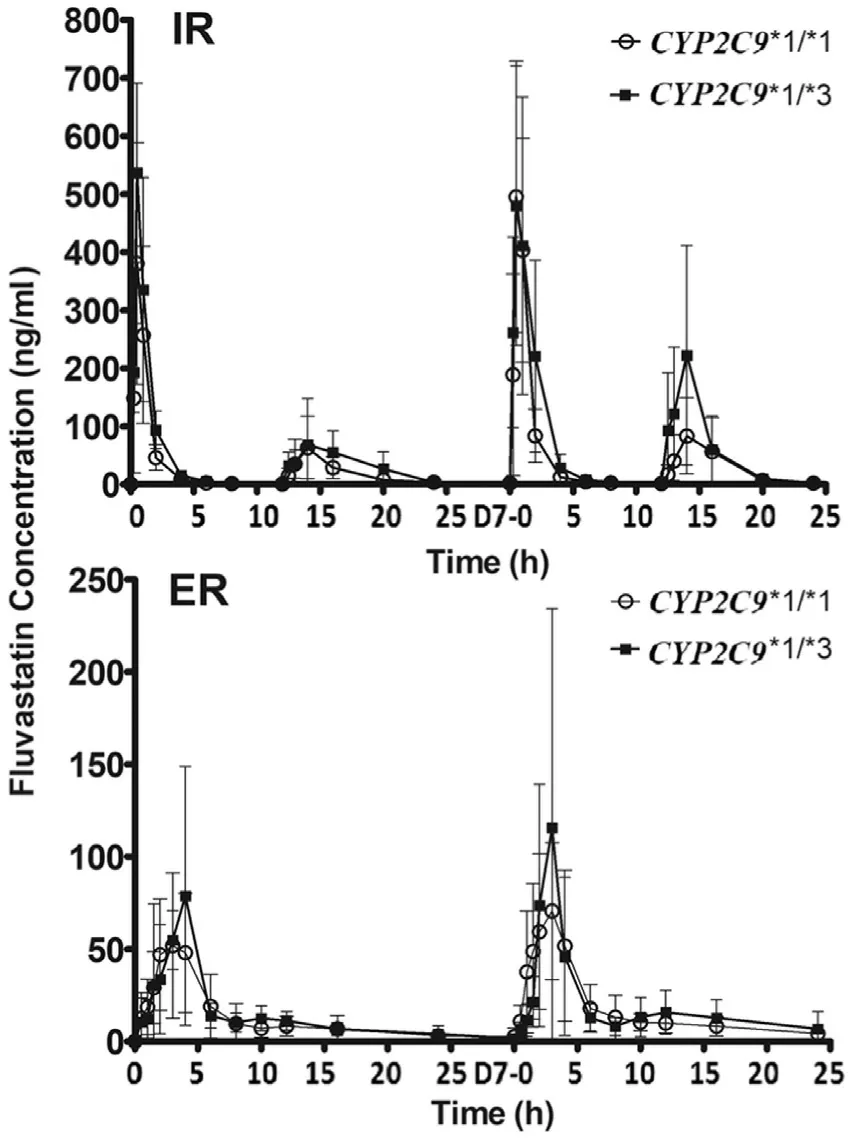
Fig.1–Mean serum concentrations of fluvastatinin different CYP2C9 ?3 genotypes after the administration of the first single dose and repeated doses.Values are represented as mean ±SD.
A total of 24 healthy subjects were recruited and completed the study,which included 14 males and 10 females.The mean age was 27.5 years (range:21–42 years),the average height was 166.6 ±6.95 cm (range:155–177 cm),the mean weight was 60.8 ±5.15 kg (range:51.0–71.0 kg),and the mean body mass index was 21.9 ±1.25 kg/m2(range:19.5–23.9 kg/m2).ForCYP2C9?3 SNP,there were 19 subjects with?1/?1 and 5 subjects with?1/?3 genotype.ForSLCO1B1T521C SNP,there were 17 individuals with TT and 7 with TC genotype.Genotypes ofCYP2C9?3/?3 andSLCO1B1521CC were not observed in the subjects of the present study.Serum concentrations on day1 and day7 are illustrated for subjects with differentCYP2C9?3 andSLCO1B1T521C genotypes,respectively (Figs.1 and 2).Following single and multiple doses of IR formulation,the serum concentrations of fluvastatin after the second dosing were lower than that after the first time.The most likely explanation for this phenomenon is a reduced exposure due to the effect of food as the evening meal was provided to the subjects 2 h before the second daily dose.This is consistent with previous studies [17,18].
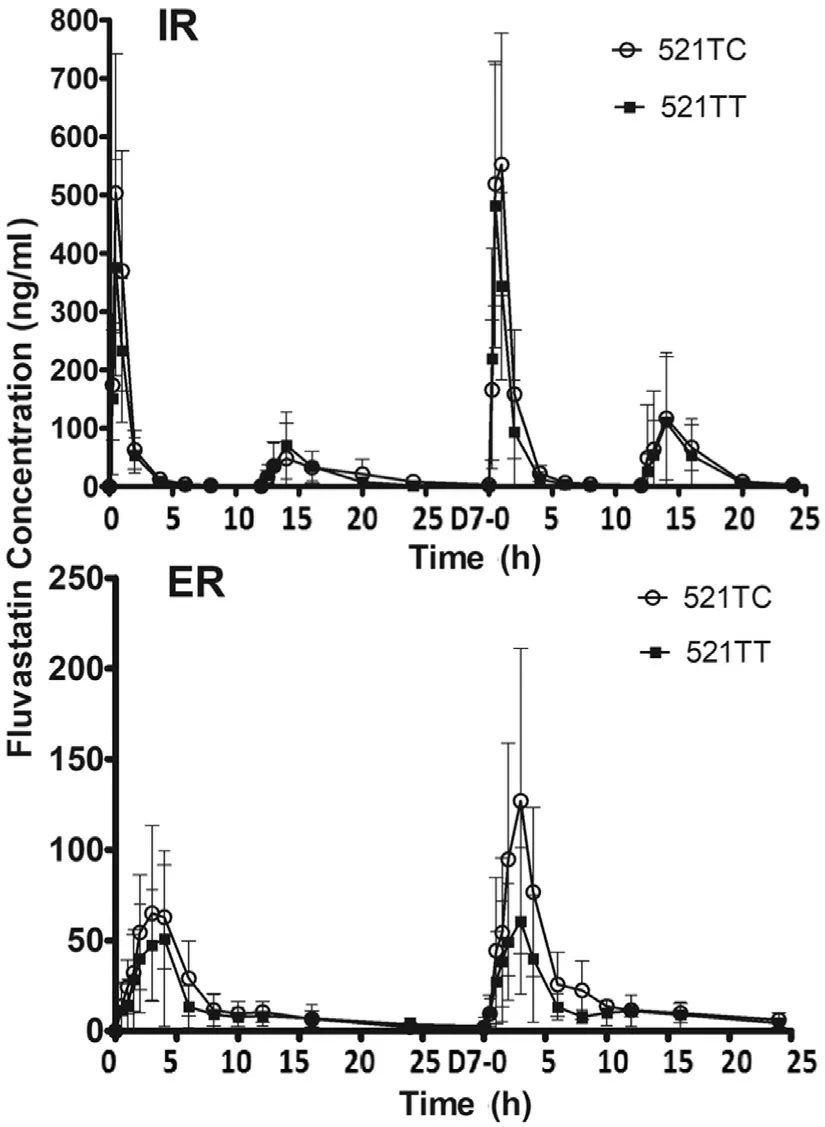
Fig.2–Mean serum concentrations of fluvastatin in different SLCO1B1 T521Cgenotypes after the administration of a first dose and repeated doses.Values are represented as mean ±SD.
The blood concentration time curve of 521TC was always above 521TT after repeated dosing of ER fluvastatin.Pharmacokinetic parameters of fluvastatin in the study are summarized in Tables 1 and 2 .TheCYP2C9?3 genotypes were significantly associated with theAUC0-24after the first dose of IR (P=0.043).AUC0-24values after repeated doses for 7 d also showed an increase inCYP2C9?3 carriers;however,the differences were not statistically significant (Table 1).SLCO1B1T521C genotype significantly influenced theAUC0-24for repeated doses in the ER regimen (P=0.010),whereas no significant correlation was observed for the first and repeated doses in the IR regimen (Table 2).To further clarify the effect ofCYP2C9?3 andSLCO1B1T521C,we performed a combined analysis of the two genes.Fig.3 shows the comparison of the fluvastatinAUC0-24among four differentCYP2C9/SLCO1B1genotype groups.The results did not show any significant correlations between pharmacokinetic parameters with other genotypes,includingSLCO1B1G388A,ABCG2A421C,ABCB1G2677T/A,ABCB1C3435T,andCYP3A5?3 (Table S2).Both these treatments were generally well tolerated by the healthy subjects in the present study.
To the best of our knowledge,this is the first study to investigate the relationship between genetic polymorphism and pharmacokinetics of ER fluvastatin and repeated doses of IR fluvastatin.The findings of the present study indicated that with ER formulation,the effect ofCYP2C9?3 on pharmacokinetics was less significant and the influence ofSLCO1B1T521C was more significant than those with IR formulation.TheSLCO1B1T521C was associated withAUC0-24,Cmax,andCavafter the repeated doses of ER formulation.In addition,Cminafter the repeated doses of IR formulation were influenced bySLCO1B1T521C.Conversely,theCYP2C9?3 genotype was significantly correlated with theAUC0-24andAUC0-12after the first dose of the IR formulation,but not with those in the ER formulation settings.
To date,there are only three studies that have reported the effects of genetic polymorphisms on fluvastatin pharmacokinetics,and all of these studies administering fluvastatin IR 40 mg in a single dose [10,15].Niemi et al.[10]recruited specificSLCO1B1T521C genotype volunteers to investigate the effect of the genotype on fluvastatin pharmacokinetics after a single dose and found no difference between the genotypes.SpecificCYP2C9genotype volunteers were investigated in another study,in a treatment setting with fluvastatin at IR 40 mg for 15 days,whereCYP2C9?3 genotypes showed significant influence onAUC[9].However,in the study,the blood samples for pharmacokinetic evaluation were only taken after the first dose on day 1.Based on our results and those from previous studies,we concluded that fluvastatin pharmacokinetics after the first dose of IR 40 mg were correlated withCYP2C9?3 genotypes,but not withSLCO1B1T521C.
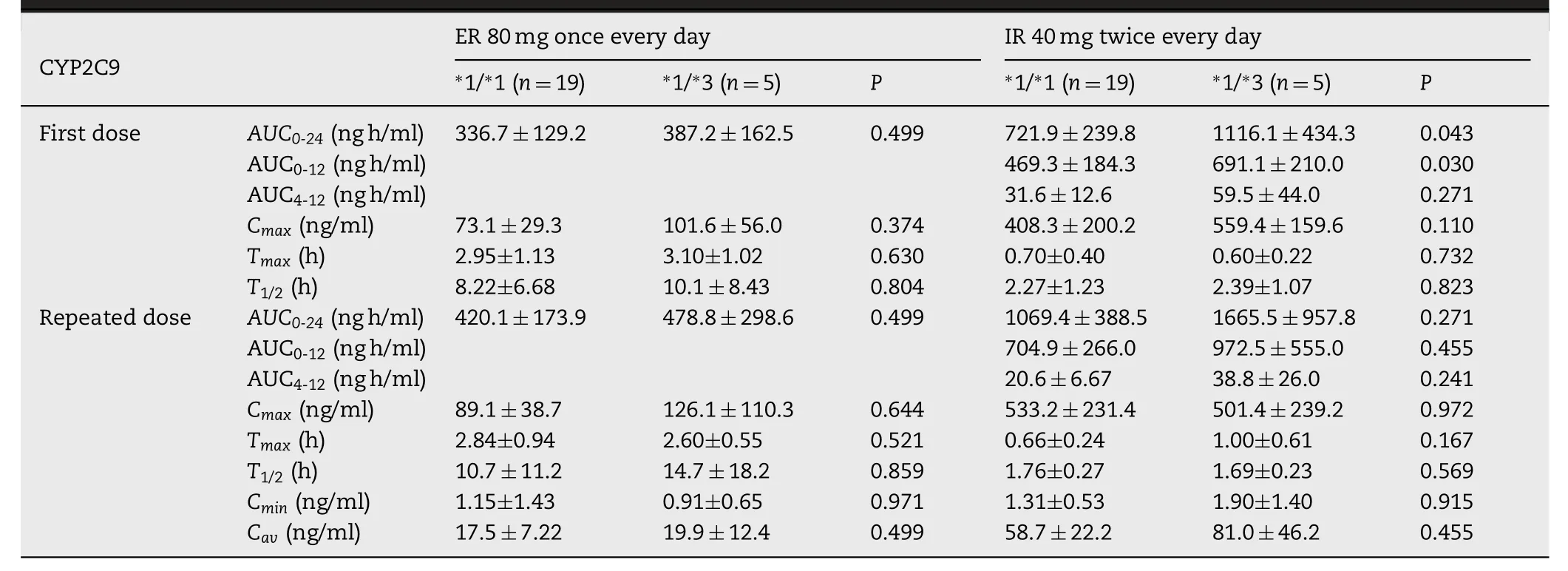
Table 1–Summary of pharmacokinetic parameters of fluvastatin after the first and subsequent dosing subjects with CYP2C 9 ?1/ ?1and CYP2C9 ?1/ ?3 genotypes.
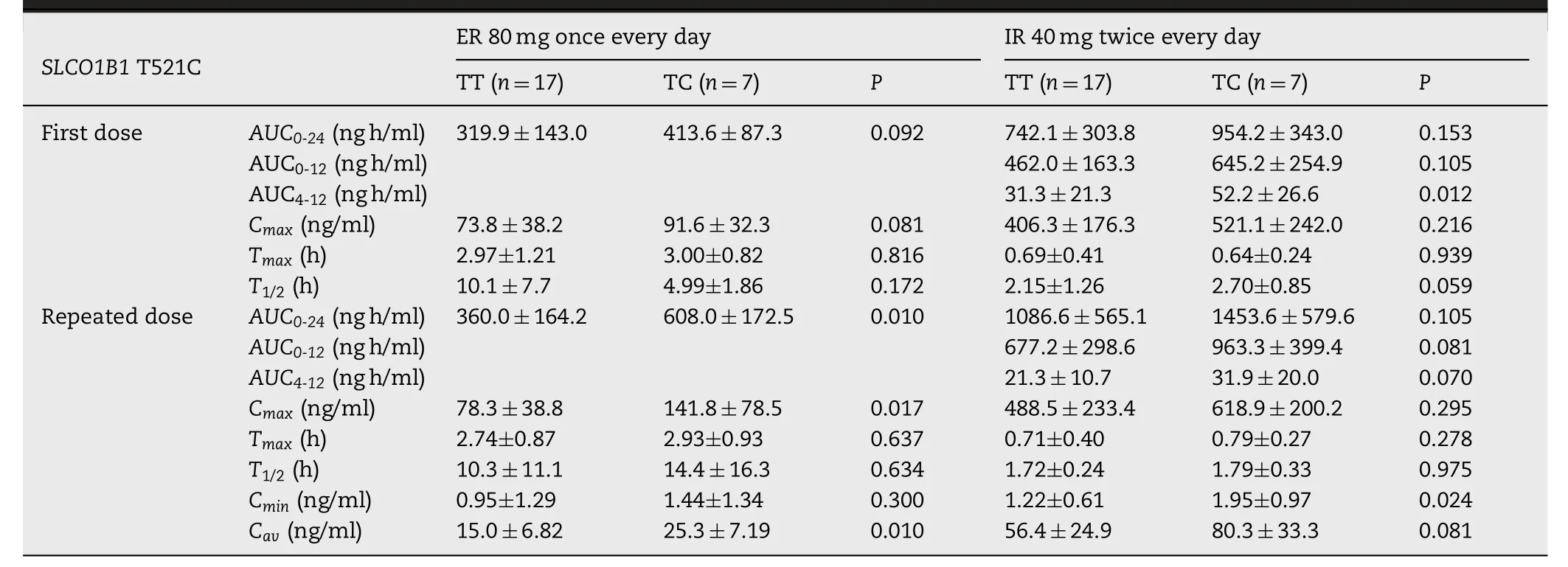
Table 2–Summary of pharmacokinetic parameters of fluvastatin after the first and subsequent dosing subjects with SLCO1B1 T521C TT and TC genotypes.
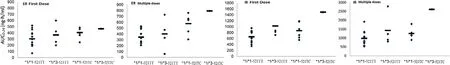
Fig.3–Comparison of AUC 0-24 of fluvastatin among four different C YP2C9 ?3/SLC O1B1 T521C genotype groups.─,mean value of AUC 0-24 .
In conflict with previous pharmacokinetic studies [9,10,15],invitrostudies have demonstrated the affinity of fluvastatin to OATP1B1 transporter as being 1.4–3.5 μmol/l [17,18].What is more,the influence ofSLCO1B1genotype on pharmacodynamics after repeated doses of IR or ER fluvastatin has been reported previously.Meyer et al.[11],conducted a cohort study that evaluated the influence ofSLCO1B1on the therapeutic efficacy of fluvastatin in dyslipidemia patients during the 5-year follow-up.They pointed out that subject carrier 521TT received a higher dose (65.1 ±5.6 mg) thanSLCO1B1521TC and CC carriers (40.9 ±7.6 mg),without demonstrating any other significant effects.In this study,the authors did not specify the fluvastatin formulation.But according to the dose they presented,it seems they used IR.Another cohort study provided evidence thatSLCO1B1521T was not associated with total cholesterol and LDL in patients treated with fluvastatin IR 20 mg per day [12]On the other hand,Couvert et al.[13]found that there was a tendency of attenuated reduction in total cholesterol (P=0.06)and LDL (P=0.17) that lowered the response in subjects carrying one or more variant allele(s) ofSLCO1B1T521C polymorphism in elderly hypercholesterolemic patients receiving ER 80 mg fluvastatin therapy after 2 months follow-up.These authors also demonstrated that C463A(Pro155Thr) ofSLCO1B1was significantly associated with a superior response to fluvastatin therapy (P<0.001).Table 3 lists all previous studies that have reported the influence ofCYP2C9orSLCO1B1genetic polymorphisms on fluvastatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics[9–11,13,15,19–21].Our study provided evidence thatSLCO1B1521C was associated with an increased in fluvastatin exposure.As shown in Fig.2,the blood concentration time curve of 521TC is always above 521TT after repeated doses of ER fluvastatin.Therefore,the conflict of previous pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies could be explained by attributed to the fluvastatin formulation.
To further clarify the effect ofCYP2C9?3 andSLCO1B1T521C,we undertook a combined analysis of the two genes.After the first and repeated doses of ER (Fig.3),the mean value ofAUC0-24in the four groups were?1/?1–521TT<?1/?3–521TT<?1/?1–521TC<?1/?3–521TC,and after repeated doses the subjects harboring bothCYP2C9?1/?3 andSLCO1B1521TC had the highestAUC0-24.However,after the first and repeated doses of IR the mean values ofAUC0-24were?1/?3–521TT>?1/?1–521TC.This reversal suggests that the weight of the two genes might have changed.CYP2C9?3 might has greater influence on the IR fluvastatin exposure,whereasSLCO1B1T521C was more important for ER.
3.3.Hypothesis
The difference of pharmacokinetics between fluvastatin IR 40 mg twice every day and ER 80 mg once every day were reported in detail in previous studies [22,23].The pharmacokinetics profile of IR and ER fluvastatin in previous studies was consistent with the present study.The systemic exposure to fluvastatin following the same total dose over 24 h period was about 2–3 fold lower when subjects received ER compared with IR following single and multiple doses.The lower exposure following the ER could be due to the efficient first pass uptake of the drug as a result of slower and sustained drug release [23].The average concentration was much lower in ER than IR at each time point.Therefore,we speculated that the influence of genotype on different formulation of fluvastatin was mainly caused by different blood concentrations.
If this hypothesis is correct,then when the serum concentration was decreased at 4 h after the first IR dose,AUC4-12should be influenced bySLCO1B1T521C.We found that after administration of the first dose of IR,the mean values ofAUC4-12ofSLCO1B1521TT carriers andSLCO1B1521TC carriers were 31.3 ±21.3 and 52.2 ±26.6 ng h/ml,respectively (P=0.012).Therefore,the significant association betweenAUC4-12andSLCO1B1T521C supported our hypothesis.Base on the hypothesis we designedinvitrostudy to detect the characteristics of OATP1B1 withSLCO1B1521TT and OATP1B1 withSLCO1B1521CC at high and low concentrations.
3.4.In vitro study
The uptake-concentration curve of fluvastatin in HEK293-OATP1B1 (carryingSLCO1B1521TT;the following is presented as OATP1B1-521TT) and HEK293-OATP1B1 (carringSLCO1B1521CC;The following is presented as OATP1B1-521CC) were shown in Fig.S1.Results showed that the transport velocity in OATP1B1-521TT was significantly faster than that in OATP1B1-521CC.Results of diagraph analysis through Eaddie–Hofstee method (Figs.S2A and S2B) suggested that the uptake proceed of fluvastatin in OATP1B1-521TT and OATP1B1-521CC were biphasic kinetics,in which the kinetic profile does not follow saturation kinetics and has two distinct phases.At lower substrate concentrations (<0.3 μmol/l) the kinetic profile exhibits curvature similar to a hyperbolic profile,however,as the substrate reaches higher concentrations (<0.3 μmol/l),the profile increases linearly (instead of becoming asymptotic)with no evidence of saturation as shown in Fig.S2.
It was easy to speculate that fluvastatin may either binding in multiple productive orientations within the enzyme active site,or there are two substrate molecules bound within the enzyme active site.In this case,one of the binding orientations results in a lowKmandVmaxcomponent(OATP1B1-521TT,Km=0.18 μmol/l,Vmax=4.01 pmol/mg/min;OATP1B1-521CC,Km=0.49 μmol/l,Vmax=5.28 pmol/mg/min)as shown in Figs.S3A and S4A,while the other binding orientation produces the highKmandVmaxcomponent(OATP1B1-521TT,Km=11.4 μmol/l,Vmax=95.3 pmol/mg/min;OATP1B1-521CC,Km=15.1 μmol/l,Vmax=100.9 pmol/mg/min)as shown in Figs.S3B and S4B.
Results also suggested that for OATP1B1-521TT the concentration ofVmaxinward was about 0.36 μmol/l(148.0 ng/ml,2 km),while for OATP1B1-521CC concentration ofVmaxinward was about 0.98 μmol/l (402.8 ng/ml,2 km),when the transport of fluvastatin under the first kinetic phase (low concentrations).As the uptake of fluvastatin in OATP1B1-521TT was faster than OATP1B1-521CC,accumulation and elimination of fluvastatin in the liver ofSLCO1B1521TT carriers would be higher compared toSLCO1B1521CC carriers,which may lead to significantly lower blood concentration inSLCO1B1521TT compared toSLCO1B1521CC carriers.On the other hand,when concentration reached to a higher level (>1 μmol/l),the transport velocity of fluvastatin by OATP1B1-521TT and OATP1B1-521CC tend to be the same(2Km-OATP1B1TT<1 μmol/l<2 Km-OATP1B1CC).It means that there was probably no significant difference on the accumulation and elimination of fluvastatin in liver betweenSLCO1B1521TT andSLCO1B1521CC carriers.The results ofin vitrostudy were consistent with theinvivopharmacokinetic study.
OATP1B1 is important not only in the elimination of statins but also in their entry to the intracellular site of action in hepatocytes.Accordingly,low uptake capacity of OATP1B1 at high fluvastatin concentration might decrease the cholesterol-lowering effect of statins,resulting in increased plasma statin concentrations and the risk of muscle toxicity[7].Interestingly,it can explain the phenomenon that the ER formulation is more potent than the IR formulation[5,6].Further research should explore the influence ofSLCO1B1genotype on fluvastatin-induced muscle toxicity and hepatoxicity.At the same time,it is very interesting to investigate the different performance of OATP1B1 at high and low concentrations of other statins.
The limited sample size and absence of rare genotypesinvivostudy such asCYP2C9?3/?3 homozygous andSLCO1B1521CC subjects make our results preliminary in nature.According to the data of 1000 Genomes Project (http://www.1000genomes.org/),the frequencies ofCYP2C9?3/?3 andSLCO1B1521CC in East Asian population are 2% and 0.2%.It means if we want include oneCYP2C9?3/?3 orSLCO1B1521CC carriers,we need to expand our sample size to ≥50 or ≥500.It is hard to carry out in the present study.On the other hand,it means the result of our study could represent>98% of EAS population.In furtherinvivostudy,researchers could include subjects with specific genotype,such as 521CC,521TC and 521TT to verify the results of this study.
4.Conclusion
In conclusion,the present study provides evidence to challenge previous opinion that the T521C (p.Val174Ala)genetic polymorphism ofSLCO1B1(encoding OATP1B1)has no significant effect on fluvastatin pharmacokinetics[7,16,20].The conflict of previous pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies can be attributed to the fluvastatin formulation,and the main reason is probably the different profile of concentration time.Further studies should explore the influence of theSLCO1B1genotype on fluvastatininduced muscle toxicity and hepatoxicity,especially for ER formulation.In addition,we recommend that formulation should be incorporated into future pharmacogenomics studies.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (No.2016YFC0904900),National Natural Science Foundation (No.81673509 and No.81573504)of China,Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality(No.7171012) and National Science and Technology Major Projects for“Major New Drugs Innovation and Development”of China (No.2017ZX09304028 and No.2017ZX09101001).
Declarations Competing of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2019.06.002 .
 Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2020年2期
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2020年2期
- Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Special topic:Emerging role of transporters in drug interaction and delivery
- Organic anion transporters also mediate the drug–drug interaction between imipenem and cilastatin
- Chronic exposure to excess iron promotes EMT and cancer via p53 loss in pancreatic cancer
- Research and development of drug delivery systems based on drug transporter and nano-formulation
- Glutamine transporters as pharmacological targets:From function to drug design
- Amino acid transporters:Emerging roles in drug delivery for tumor-targeting therapy
