Molecular isolation and identification of Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis in Didelphis virginiana from Hidalgo, Mexico
Nallely Rivero-Perez, Juan Ocampo-López, Benjamín Valladares-Carranza, Fabián R. Gómez de Anda,Francisco J. Pe?a Jiménez, Victor M. Martínez Juárez, Armando Peláez Acero, José I. Olave Leyva, Deyanira Ojeda-Ramírez, Adrian Zaragoza-Bastida?
1área Académica de Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia, Instituto de Ciencias Agropecuaria, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Hidalgo, Av.Universidad Km 1, Ex-Hda. de Aquetzalpa, C.P. 43600 Tulancingo, Hidalgo, México
2Centro de Investigación y Estudios Avanzados en Salud Animal, Facultad de Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México, Km 15.5 Carretera Panamericana Toluca-Atlacomulco, C.P. 50200 Toluca, Estado de México, México
3Centro Universitario del Sur/División de Ciencias de la Salud/Departamento de Ciencias Clínicas/Hospital Veterinario CUSUR Universidad de Guadalajara, Av. Enrique Arreola Silva No. 883, colonia centro C.P. 49000, Ciudad Guzmán, Jalisco, México
ABSTRACT Objective: To isolate and identify the exact species of the genus Mycobacterium from Didelphis (D.) virginiana, and the direct implications of this bacterium to public health and veterinary medicine.Methods: Thirty-one D. virginiana were captured and necropsied in Hidalgo, Mexico. Tissue samples were collected to culture mycobacteria present and examine individual specimens’histopathology. Mycobacterium identification was obtained through the application of amplification and sequencing of 16S rDNA techniques.Results: Three strains were isolated and identified as Mycobacterium(M.) avium subsp. hominissuis by utilizing M. avium complexspecific primers. Granulomatous lesions were observed in the subpleural zone (granuloma grade Ⅱ) and bronchial (granuloma grade Ⅰ) of the lungs of D. virginiana with positive isolation.Conclusions: Three strains of M. avium subsp. hominissuis, from lung tissue samples of D. virginiana were identified. This subspecies of M. avium has important implications in public health and veterinary medicine.
KEYWORDS:Didelphis virginiana; Mycobacterium avium complex; Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis; Public health
1. Introduction
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are frequently associated with water, soil, dust, feed, aerosol, plants, invertebrates, protozoa and animals. More than 150 species of NTM have been identified and approximately 50% of these are pathogenic for humans and animals(wildlife, livestock) and can be transmitted between them and the environment. NTM can cause a wide range of clinical diseases in humans and animals such as lymphadenitis, lung disease, skin infections, soft tissue infections and visceral or disseminated diseases[1-3].
Mycobacterium (M.) avium complex (MAC) is the most clinically significant NTM species in humans and animals. This complex includes four subspecies, i.e., M. avium subsp. avium, M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis, M. avium subsp. silvaticum, and M. avium subsp. hominissuis, each with specific pathogenic and host range characteristics[2-4].
In particular, M. avium subsp. hominissuis, is an opportunistic pathogen with zoonotic potential presented in soil and dust. Animals serve as reservoirs and potential threat for human infection, but the route and source of human infection remains unknown in most cases[4].
The opossum [Didelphis (D.) virginiana] is a marsupial found on the American continent and is well-adapted to anthropogenic activities,such as agriculture and livestock production[5]. This wild species can act as a reservoir for many zoonotic agents, e.g., Toxoplasma gondii,Trypanosoma cruzi, Rickettsia felis, and MAC[6-9].
It is important to mention that in this region of the country(Mexico), D. virginiana can be included in the peoples’ daily diet according to Acosta-Salinas et al.[5]. This represents a possible source of infection for the human population of the region, but it has not been confirmed.
The objective of the present investigation was to isolate and identify species of the genus Mycobacterium and its potential implications for public health and veterinary medicine. This was achieved through examination of tissue samples obtained from D. virginiana captured in the State of Hidalgo, México.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study site and sampling
Tulancingo de Bravo is located in Hidalgo, Mexico (Coordinates:20°5′0″N 98°22′0″W), at a distance of 93 km from Mexico City (Figure 1). A total of 31 D. virginiana were captured in three representative zones of the municipality: A, characterized by agriculture and livestock; B, characterized by urban areas(including the city of Tulancingo), agriculture and livestock;and C, characterized by agriculture and livestock, all three zones have anthropogenic disturbance. The captures were made using Tomahawk? traps (12×24×42 inches, USA) following the methodology described by Abdala et al.[10]. Females with offspring were excluded from the study.
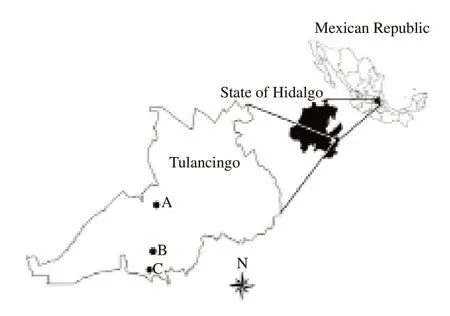
Figure 1. Capture zones and location of Tulancingo de Bravo in Hidalgo,Mexico.
2.2. Ethical approval
The procedures were approved by the Internal Ethics and Animal Care Committee of the Institute of Agricultural Sciences of the Autonomous University of the State of Hidalgo (No. CIECUAICAP/08/15) with a maximum sample size of 31 animals. The animals were trapped in accordance with the official norms for animal care (No. NOM-033-ZOO-1995), transportation of live animals (No. NOM-051-ZOO-1995), and wildlife protection (No.NOM-059-SEMARNAT-2010) established by the government of Mexico and with a scientific collecting permit issued by General Directorate of Wildlife of the Secretariat of Environment and Natural Resources of Mexico (Office N° SGPA/DGVS/003613/18).
2.3. Biological sample collection
Thirty-one animals were necropsied for macroscopic observations of lesions suggestive or characteristic of a mycobacterial infection.Lung, spleen, liver, and kidney samples were collected and divided into two sections, one used for bacteriology and another for histopathology.
2.4. Bacteriology
The samples (lung, spleen, liver, and kidney) used for bacteriological studies were preserved in a saturated solution of sodium borate. The samples were crushed using a mechanical homogenizer IKA? T18 (Madrid, Spain) and decontaminated using the N-acetyl-L-cysteine-NaOH technique[11].
The samples were seeded in duplicate in L?wenstein-Jensen (BD,220908, USA) and Stonebrink (BD, 220504, USA) media and reviewed periodically for 8 weeks. Bacterial growth was assessed by Ziehl-Neelsen staining for the identification of acid-fast bacilli.
2.5. Histopathology
For the histopathological analysis, the samples of lung, spleen,liver, and kidney were fixed by immersion in 3.8% formaldehyde in an aqueous phosphate-buffered solution for at least 24 hours and embedded in paraffin using an automated tissue processor Leica TP1020 (Nussloch, Germany). Then, the samples were cut using a microtome Leica 2125RT (Nussloch, Germany) into 4 μm thick sections and stained with hematoxylin and eosin and Ziehl-Neelsen acid fast stains[12].
2.6. Genus and species identification
Isolated strains with cocci or acid-fast bacilli were inoculated in liquid Middlebrook 7H9 medium (BD L007467) to obtain biomass,from which genetic material was extracted using the Wizard?Genomic kit Promega A1120 (Madison, USA) system according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The extracted genetic material was quantified using a NanoDrop Thermo Fisher Scientific 1000(Delaware, USA) and visualized on a 1% agarose gel.
Identification at the genus and species levels was performed through PCR-based amplification of the 16S rDNA gene using the primers 8f: AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG and 1492r:TACGGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT and reaction conditions described by Zaragoza et al.[13]. The amplified products were sequenced by Macrogen (Rockville, MD, USA). The sequences were aligned using the software BioEdit V7.2[14], and compared with sequences in the GenBank database using BLAST[15], and EzTaxon[16].
A phylogenetic tree was constructed with the obtained sequences and reference strains from the M. tuberculosis complex (M.tuberculosis ATCC27294, M. caprae CIP105776T, M. bovis BCG CIP1173P2and M. canettii CIP140010059) and MAC (M. avium subsp. avium ATTC25291, M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis Strain5617, M. avium subsp. silvaticum ATCC49884and M. avium subsp. hominissuis E128)using the maximum parsimony method implemented in MEGA ver.7[17], the grouping stability was estimated using 1 000 bootstrap replicates.
2.7. Genetic identification at the subspecies level
To identify strains at the subspecies level, the methodology described by Shin et al.[18] was employed. Regions specific to MAC members were amplified, including a 484-base pair (bp)fragment of the 16S rDNA gene, 398 bp in the IS900 region, 753 bp in IS901, 608 bp in IS1311, and 296 bp in DT1. Escherichia coli ATCC35218 was used as the negative control, and M. avium subsp.paratuberculosis ATCC19698 was used as the positive control.
3. Results
Thirty-one D. virginiana were included in the study; 61.29%(19/31) were female and 38.71% (12/31) were male. Based on necropsy, lesions suggestive of mycobacterial infection were observed in three animals; however, all 31 samples were processed for both bacteriological and histopathological analyses.
Three strains with morphological properties (acid-fast bacilli)similar to those of the genus Mycobacterium were isolated from lung samples of the three animals with macroscopic lesions, of which two were females and only one was male, representing 9.68% (3/31) of animals in the study area and 27.27% (3/11) in zone B.
3.1. Identification at the genus and species levels
In a 16S rDNA gene sequence analysis, the three isolated strains showed a sequence similarity of 100% with the 16S rDNA of MAC members in two databases. In the phylogenetic tree, the isolated strains grouped with the MAC reference strains. Both analyses clearly indicated that the strains belonged to the MAC (Figure 2).
3.2. Identification at the subspecies level
Subspecies was determined through the following method. Two regions were amplified in the three isolated strains from the lung one with 484 bp (16S rRNAgen, common for all mycobacterial species) and the other with 608 bp (IS1311, common for members of MAC), (Table 1 and Figure 3). According with Shin et al. the only subspecies of the MAC that amplify these two regions is M. avium subsp. hominissuis.
3.3. Anatomopathology
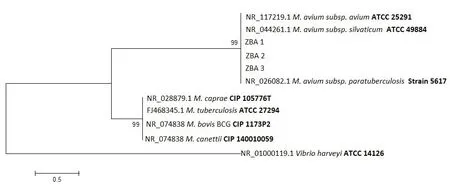
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rDNA gene sequences from the isolated and reference strains.
In a macroscopic analysis, lesions suggestive of mycobacterial infection were only observed in three animals (two female and a male). These lesions were observed in the lungs with nodular relief; they were whitish, circularly delimited, and multifocal,located mainly in the dorsal area of the caudal lobes with a bilateral distribution.
Lesions in a granular form with a dorsal distribution from the cranial to caudal lobes with marked anthracosis, were observed in the lungs. Additionally, in the male, a round heart was observed, with possible concentric cardiac hypertrophy and hydropic degeneration of the mediastinal fat.
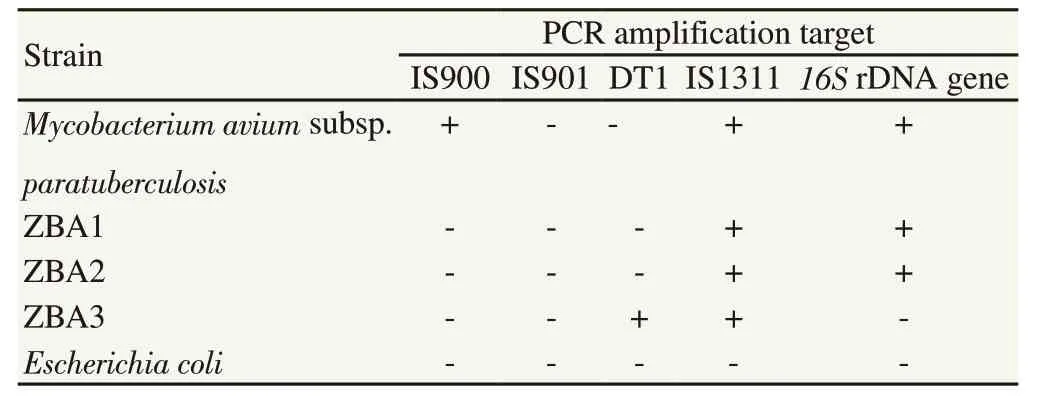
Table 1. Isolated strains used in the specificity test for multiplex PCR.
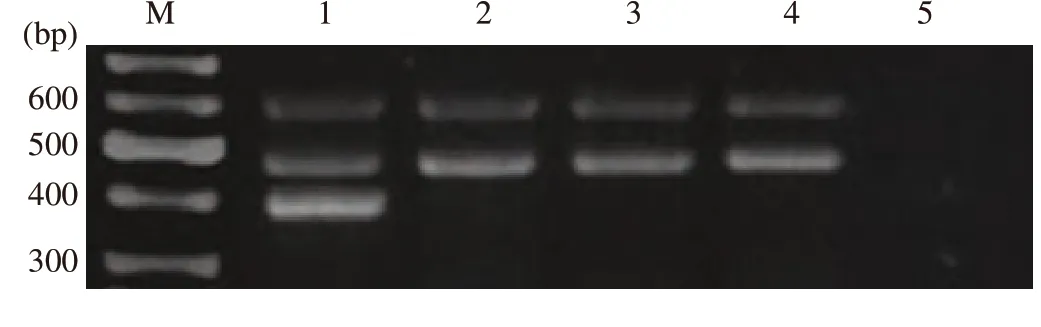
Figure 3. Representative gel of multiplex PCR products. Lane M, molecular size marker; lane 1, Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis ATCC 19698; lane 2, strain ZBA1; lane 3, strain AZB2; lane 4, strain AZB3; and lane 5, Escherichia coli ATCC 35218.
3.4. Histopathology
The lung samples of the three animals (two female and one male)with macroscopic lesions showed a slight but consistent thickening of the alveolar wall and the bronchial mucosa. However, the most significant finding in the three specimens was the presence of granulomatous lesions localized under a slightly thickened pleura with collagen tissue (Figure 4A) and focally on the surface of the organ, particularly in the cranial and middle lobes of both lungs or well, associated with some bronchi walls (Figure 4B).
These granulomatous lesions (subpleural and bronchi associated)were classified as grade II lesion according to criteria mentioned by Palmer et al.[19], because were observed a significant number of epithelioid cells and lymphocytes surrounded by a thin capsule connective tissue, without necrotic areas. Acid-fast bacilli, were not observed in the histological samples examined.
4. Discussion
The increasing interaction between domestic animals, sylvatic animals and humans has aided in the increase of emerging diseases in the world. Nontuberculous mycobacteria can cause a wide range of clinical diseases in humans and animals. The most common of these bacteria, associated with pulmonary disease, is the MAC[1].Moreover, this complex is ubiquitous in soil, water, and domestic and wild animals[20], further enhancing potential transmission as human population increases and interaction with these is heightened.According to research carried out by Witmer et al.[21], D. virginiana,is a susceptible specie infected by different etiological agents,including subspecies of MAC. This information coincides with the results obtained in the current study, in which 3 strains with characteristics of MAC were isolated.
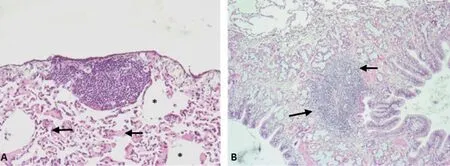
Figure 4. Representative lesions observed in the lungs of three specimens of Didelphis virginiana with isolated of Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis(Stain method: H-E). A. Grade Ⅱ subpleural granuloma. 100×. Note the fibrosis of the adjacent lung tissue (arrows) and atelectasis (*). B. Grade Ⅱgranuloma associated with the wall of a bronchus and adjacent alveolar tissue. 100×.
Macroscopic analysis lesions, suggestive of mycobacterial infection were observed in three D. virginiana but these lesions had been reported in other parasitic and bacterial infection. Lopez-Crespo et al.[22] described that in the lung of D. virginiana naturally infected with the nematode Didelphostrongylus hayesi, an endogenous lipid pneumonia, characterized by pale yellow bilateral plates 1-5 mm in diameter, presented in the subpleural region and within the lung parenchyma. These nodular lesions were randomly distributed,but they were observed more frequently in the dorsal region of the caudal lobes[22]. Diegel et al.[23] described similar lesions, (irregular lesions of 4.0 mm diameter, within the parenchyma of the caudaldorsal right lung lobe), in the same species but in experimental infection by Mycobacterium bovis[23].
The main histologic lesion observed in the current study was a grade Ⅱ granuloma, without the presence of acid-fast bacilli.Granuloma type is dependent of the species of Mycobacterium, host susceptibility, presence or lack of acid fast bacilli, and the form of entry[23,24].
Three strains with similar morphologies to those of Mycobacterium spp., representing 9.68% (3/31) of the positive individuals within the entire study site, and 27.27% (3/11) only in zone B information are consistent with results obtained by García et al.[24], who isolated Nontuberculous mycobacteria from five D. virginiana which represented 27.78% (5/18) positivity in the state of Colima, Mexico.Notably, the sampling area for that study was greater.
The comparison of sequences obtained from 16S rDNA of the isolated strains and phylogenetic tree, allowed us to establish isolated strains belonging to MAC, with 100% similarity. However,the identification at subspecies level was not possible. To obtain those results required the amplification of specific fragments for MAC, according to the methodology described by Shin et al.[18].The isolated strains amplified two of five regions. According to these results the strain was identified as M. avium subsp. hominissuis. In Mexico, the species M. szulgai, M. terrae, M. asiaticum and M. gastri have been isolated from opossum samples[24], however, these were not identified in the current study.
In the present study, M. avium subsp. hominissuis was isolated from agricultural areas and urban settlements, including the city of Tulancingo (Zone B). This is relevant because the subspecies is an important opportunistic pathogen for humans and animals and therefore it is likely that they are infected by this mycobacteria(Alvarez et al.)[25].
D. virginiana is susceptible to infection by M. avium subsp.hominissuis and could contribute to its spread, however, further studies are required to determine if it can act as a reservoir.According with the definition of Hydon et al.[26], who established a reservoir as one or more epidemiologically connected populations or environments in which the pathogen can be permanently maintained and from which infection is transmitted to the defined target population. Studies to determine the zoonotic potential of M. avium subsp. hominissuis, among humans and wildlife are also necessary.Three strains of M. avium subsp. hominissuis, from lung tissue samples of D virginiana, were isolated and identified during this study. This subspecies of MAC has important implications in public health and veterinary medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dra. Sawako Hori-Oshima for providing the strain of M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial assistance from the Secretary of Research of Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Hidalgo (UAEH) through the project “Epidemiological surveillance of the genus Mycobacterium in the species Didelphis virginiana (Tlacuache) of the valley of Tulancingo Hidalgo” with number UAEH/DI/ICAp/MVZ/6.
Authors’ contributions
A.Z.B. and N.R.P. developed the concepts, definition of intellectual content, F.R.G.A., F.J.P.J and J.I.O.L. field sampling, B.V.C. and J.O.L. histopathological analysis, A.Z.B., N.R.P. and V.M.M.J isolation and identification of mycobacteria, A.Z.B. and N.R.P. wrote the paper, A.P.A. and D.O.R. contributed to the final version of the manuscript.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2020年3期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2020年3期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Dose prediction of lopinavir/ritonavir for 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)infection based on mathematic modeling
- Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) update: What we know and what is unknown
- Imported cases of 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections in Thailand:Mathematical modelling of the outbreak
- Blastocystis incidence, spontaneous clearance, persistence and risk factors in a rural community in Thailand: A prospective cohort study
- Etiologies of tropical acute febrile illness in West Pahang, Malaysia: A prospective observational study
- Mapping the high burden areas of cholera in Nepal for potential use of oral cholera vaccine: An analysis of data from publications and routine surveillance systems
